Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2 Study Guide
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
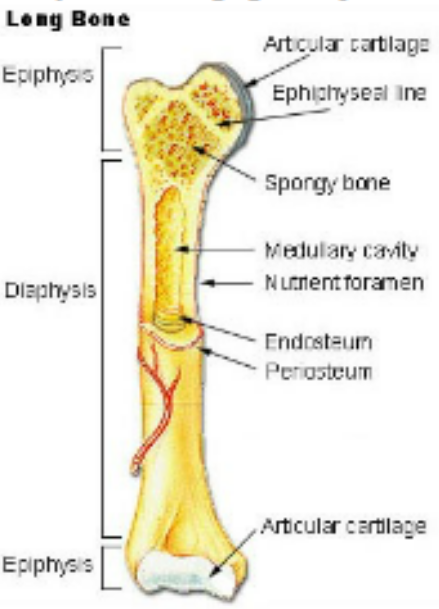
Long Bone Structure
Diaphysis: long shaft
central cavity: medullary cavity
yellow marrow- fatty
red marrow- blood production
endosteum: cavity lining continuouse with central canals of the osteons
periosteum: vascular surface covering
articular cartilage: surfaces of each epiphysis (hyaline)
Epiphysis: enlarged ends
Metaphysis: growth zones between the epiphysis and diaphysis, contains the epiphyseal disc (hyaline cartilage growth plates)
Bone Processes, Depressions, and Openings
foramen- opening for nerves and vessels
fossa- shallow depression, sockets
sulcus- grooves
fissure- narrow groove
sinus- cavity
condyle- rounded protuberance articulating with another bone
tuberosity- rough process that serves as an attachment for muscle
tubercle- small, rounded process
trochanter- large process
process- projection
head- area supported by a constricted neck
crest- narrow ridge
spine- sharp, slender process
sesamoid- rounded
general composition of axial skeleton
skull
hyoid
vertebral column
rib cage (12 pairs + sternum)
number of bones in the adult
206
general composition of appendicular skeleton
upper extremity
pectoral girdle
scapula
clavical
arm
humerus
radius
ulna
hand
carpals
metalcarpals
phalanges
lower extremity
pelvic girdle
os coxe; joint between anteriorly is the symphysis pubis
sacrum
leg
femur
tibia
fibula
patella
foot
tarsals
calcaneous
metatarsals
phalanges
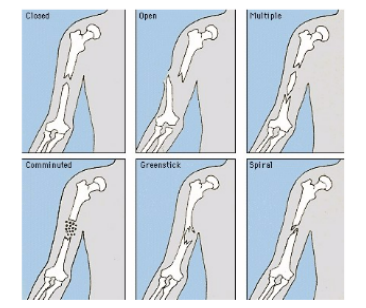
types of bone fractures
closed- simple fracture that do not penetrate skin
open- compound fracture that break through the skin
complete- broken clean through
transverse- right able to the long axis
oblique- angled to the long axis
spiral- from torional forces
incomplete- splintered, partial break, greenstick or linear
segmented- a single fragment
comminuted- 2 or more fragments
displaced- bone fragments out of alignment
compression- vertical compacted forces
compacted- portion of bone driven into the same bone
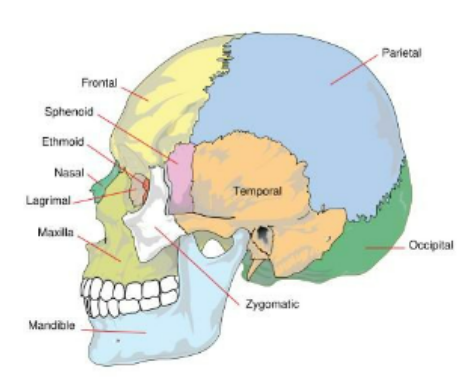
Skull Composition
Cranium- portion of the skull encasing the brain joined together by sutures
composed of…
frontal- anterior, forms the eyebrow ridges, bridge of nose, inferior eye orbits
supraorbital foramina- openings on the superior orbital ridge
two parietals- superior, meet at the midline at the sagittal suture, meet the frontal bone at the coronal suture
ridges- superior and inferior temporal line
occipital- posterior, inferior, joined to the parietals by the lambdoidal suture
occipital condyls- rest on fossa of the atlas, contains the hypoglossal canals
external occipital protuberance- prominent process on the median line
foramen magnum- surrounds the brain stem
two temporals- inferior to parietals, joined tothe parietals by the squamosal suture
mandibular fossa- depression for jaw articulatoin (mandibular condyl)
external acoustic meatus- opening for ear canal, posterior to mandibular fossa
processes
zygomatic- slender, articulates with the zygomatic bone meets at the zygomatic arch
styloid- spinelike, extends down from temporal bone, attachment for muscles of the pharynx, tongue
mastoid- rounded, inferior to the styloid, attachment of the sternocleidomastoideus of the neck
sphenoid- lateral to lateral; 2 greater wings (temple region), orbital surfaces (posterior eye orbits) and the pterygoid processes (ventral)
ethmoid- medial eye orbits, roof of the nasal cavity. contains the perpendicular plate medially, superior and middle nasal conchae
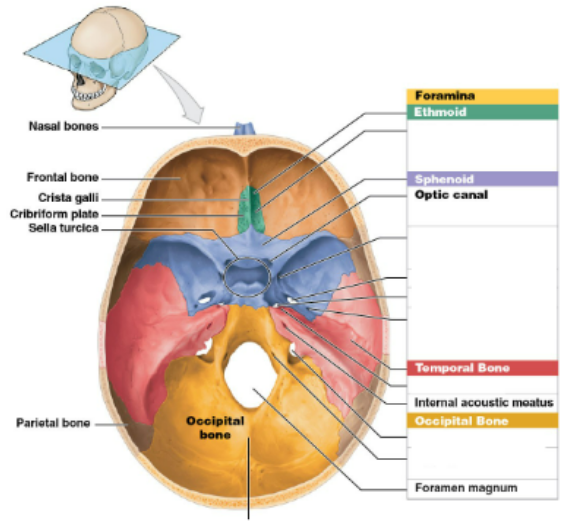
Floor of the Cranium
cranial fossae- 3 large depressions
anterior cranial fossa, formed by the orbital plates
posterior cranial fossa, deep, occipital bone depression
middle cranial fossa- sphenoid, temporal bone depression between the other two
ethmoid- perforated frontal portion is the cribform plate and crista galli (cock’s comb: upward projection)
sphenoid- hypophyseal fossa: depression holding the pituitary gland
sella turica (turkish saddle) is composed of hypophyseal fossa, dorsum sella (elevated ridge), and the spines of the clinoid process
temporals- 3 divisions
squamous portion, thin and flat
petrous portion, hardest portion of the skull, medially contains the internal acoustic meatus for the acoustic nerve
mastoid portion
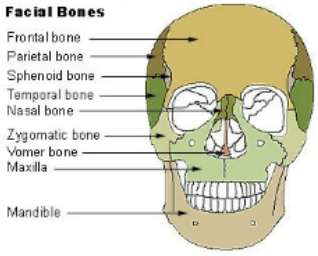
Parts of the Face- 13 fused bones
maxilla- upper jaw, 2 maxillary bones fused medially at the palatine suture
16 permanent teeth in a socket (alveolus) in the maxilla (alveolar process)
palatines- 2 fused together form the hard palate
zygomatics- cheek and inferior later eye orbit
nasals- thin, rectangular nasal bones
lacrimals- one in each orbit
vomer- unpaired, in the nasal cavity medial
inferior nasal conchae- curved bones attached to the nasal fossa
mandible- not fused
body, horizontal
rami- vertical (2)
symphysis- point of fusion along the midline
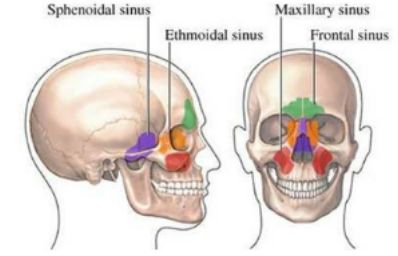
paranasal sinuses
frontal sinuses- above the eyes, forehead
maxillary
sphenoidal
ethmoid air cells
where are the sinuses located?
paranasal sinuses
frontal sinuses- above the eyes, forehead
maxillary
sphenoidal
ethmoid air cells
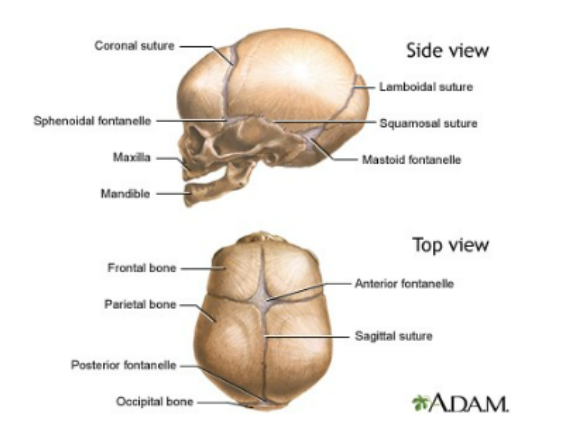
parts of the fetal skull
fontaonels: unossified membranous areas, ossification complete by 2 years old
anterior fontanel- median, frontal to parietal
posterior fontaonel- medial parietal to occipital
sphenoidal fontanel- behind eye orbit
mastoid fontanel- juncture between parietal, temporal, occipital
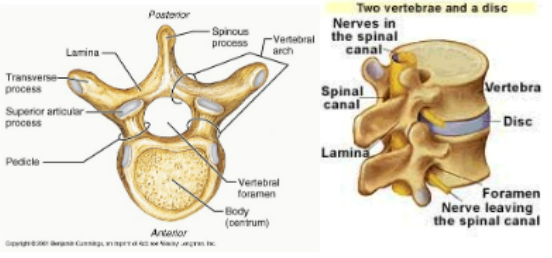
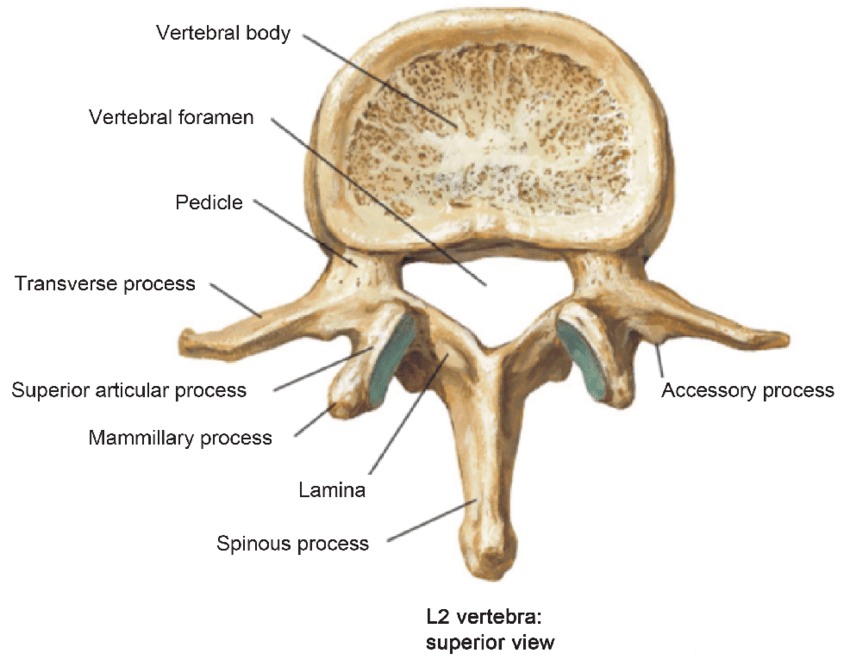
Parts of the Vertebra Column
Body- structural mass, load bearing, connected to the intervetebral discs (24 discs that cushion the joints)
transverse processes- connect and articulate with other vertebrae
superior articulating surface of the top vertebrae contacts the inferior articulating surface of the bottom vertebrae
spinal foramen- center opening containing the spinal cord
opening gets smaller superior to inferior spinal column
pedicles- bony arch around the spinal foramen; allow spinal nerves to exit the spinal cord
intervertebral foramen- opening for spinal nerves
laminae- two broad plates between te transverse processes
neural arch- 2 laminae+ 2 pedicles
parts of the cervical 7
atlas- first, accommodates a portion of the brain stem
small transverse foramen for artery and vein
axis- has odontoid process (dens: vertical protrusion) that provides a pivot for atlas rotation
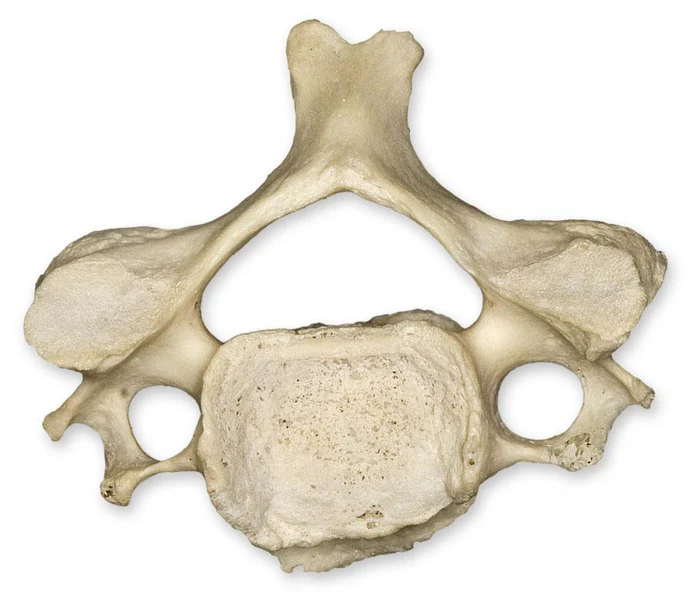
parts of thoracic 12 (one for each rib)
larger and thicker, all have articulate facets for the ribs
has costal facet
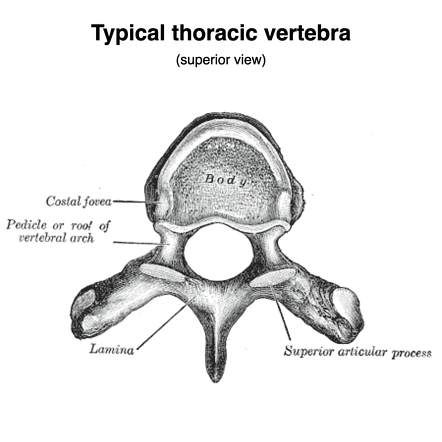
parts of the lumbar 5
large thick body to support weight and stress
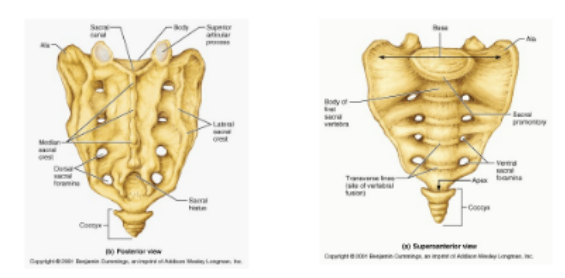
sacrum (5)
medial sacral crest
sacral hiatus- opening at the lower end of the sacral canal
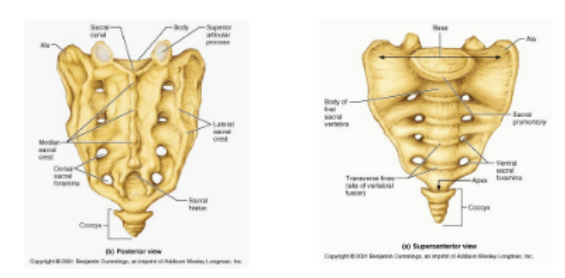
coccyx (4-5)
rudimentary vertebrae
triangular in shape
attached to sacrum by ligaments
name the spinal curvatures
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, pelvic
thorax + rib structure
Rib Structure
head- end that articulates with vertebrae
neck- flattened portion between head and tubercle
terbercle- articulating portions
body- flattened curved section
Sternum
manubrium (upper)
body (middle)
xiphoid process (lower)
Ribs 12 pairs
vertebrosternal ribs (true ribs) 7 pairs; attached to sternum
vertebrochondral ribs (upper 3 pairs of false ribs)
vertebral ribs (floating false ribs)
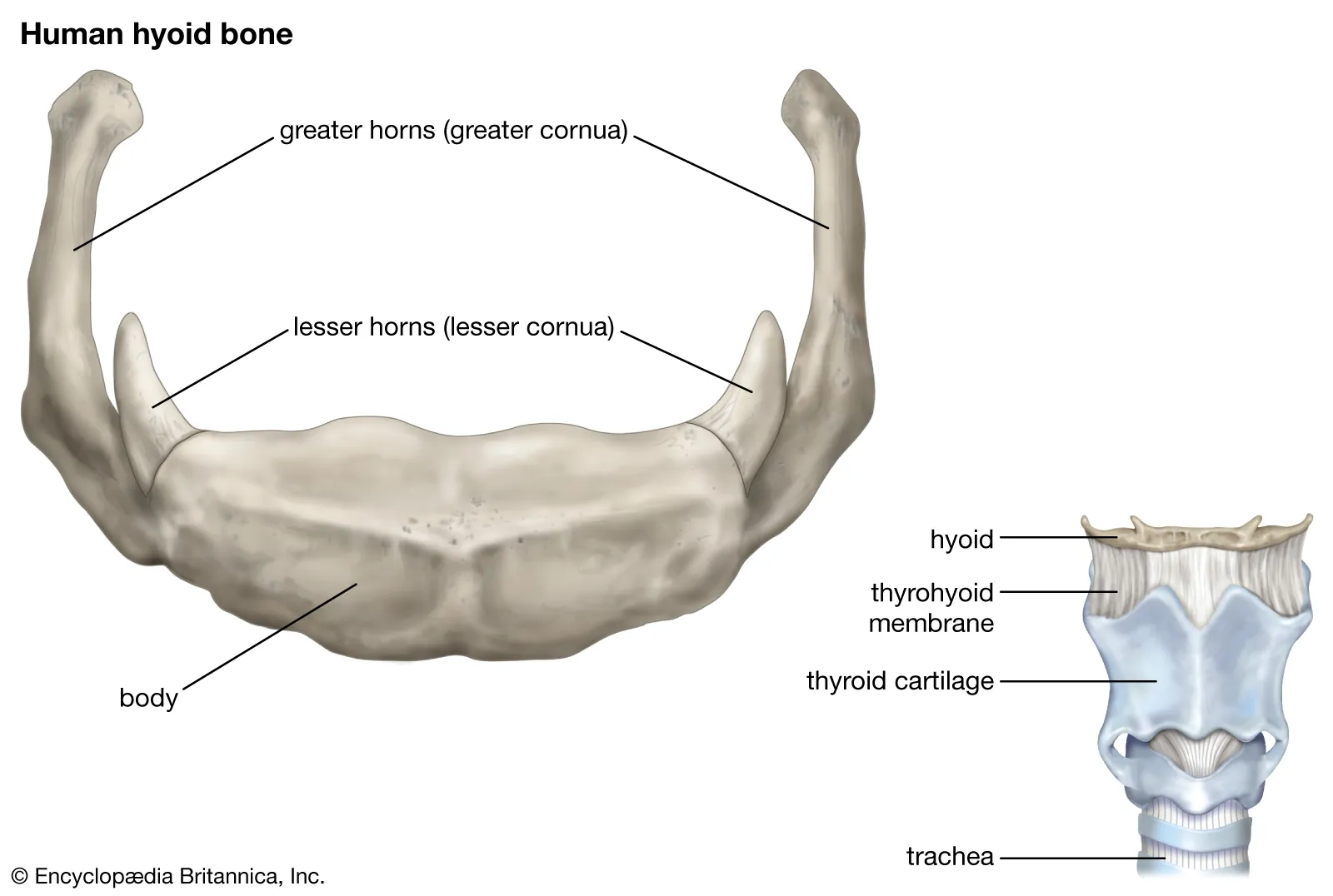
Hyoid bone segments
horseshoe, shaped bone, no articulation
body, central portion
lesser cornua (2) long arms, distal end terminates in a tubercle
greater cornua- (2) conical eminences
Upper Extremity
pectoral girdle: scapula + clavical
clavical- s shape, articulates with manubrium of the sternum medially and the scapula laterally
scapula- triangular flat bone of the shoulder
glenoid cavity- socket for humerus
scapular spine- ridge on posterior side dividing the superior (supraspinous fossa) from the inferior (infraspinous fossa)
subscapular fossa- anterior concave surface
scapular notch- on the superior margin, just medial to the coracoid process
3 margins
medial- vertebral margin
lateral- axillary margin
superior- superior margin
lateral process
acromion, attachment of clavical posteroirly
coracoid, anterior, smaller process, bent laterally
Upper Arm
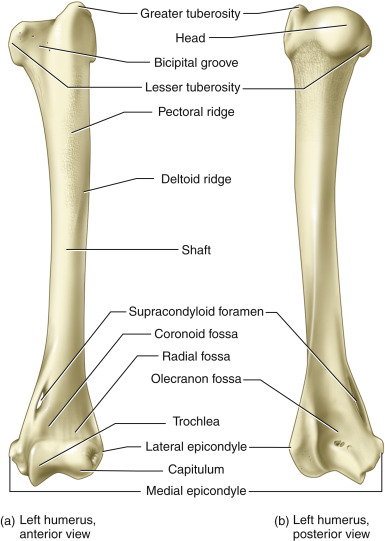
Humerus
head- proximal
neck- narrow section below the head
Tubercles
greater tubercle- lateral
lesser tubercle- medial
surgical neck- narrow section below the tubercles
tuberosity- deltoid tuberosity-rough area on diaphysis
distal areas
condyles
capitulum, lateral articulates with radius
trochlea, medial, articulates with ulna
fossa (depressions)
coronoid fossa, superior to the trochlea
olecranon fossa, posterior end
lower arm: radius
lateral
connected to thumb
head, articulates with capitulum of humerus
radial tuberosity, medial surface attaches to the biceps brachii flexor muscle
neck, area between the head and the radial tuberosity
styloid process, distal prominence that rotates with the wrist
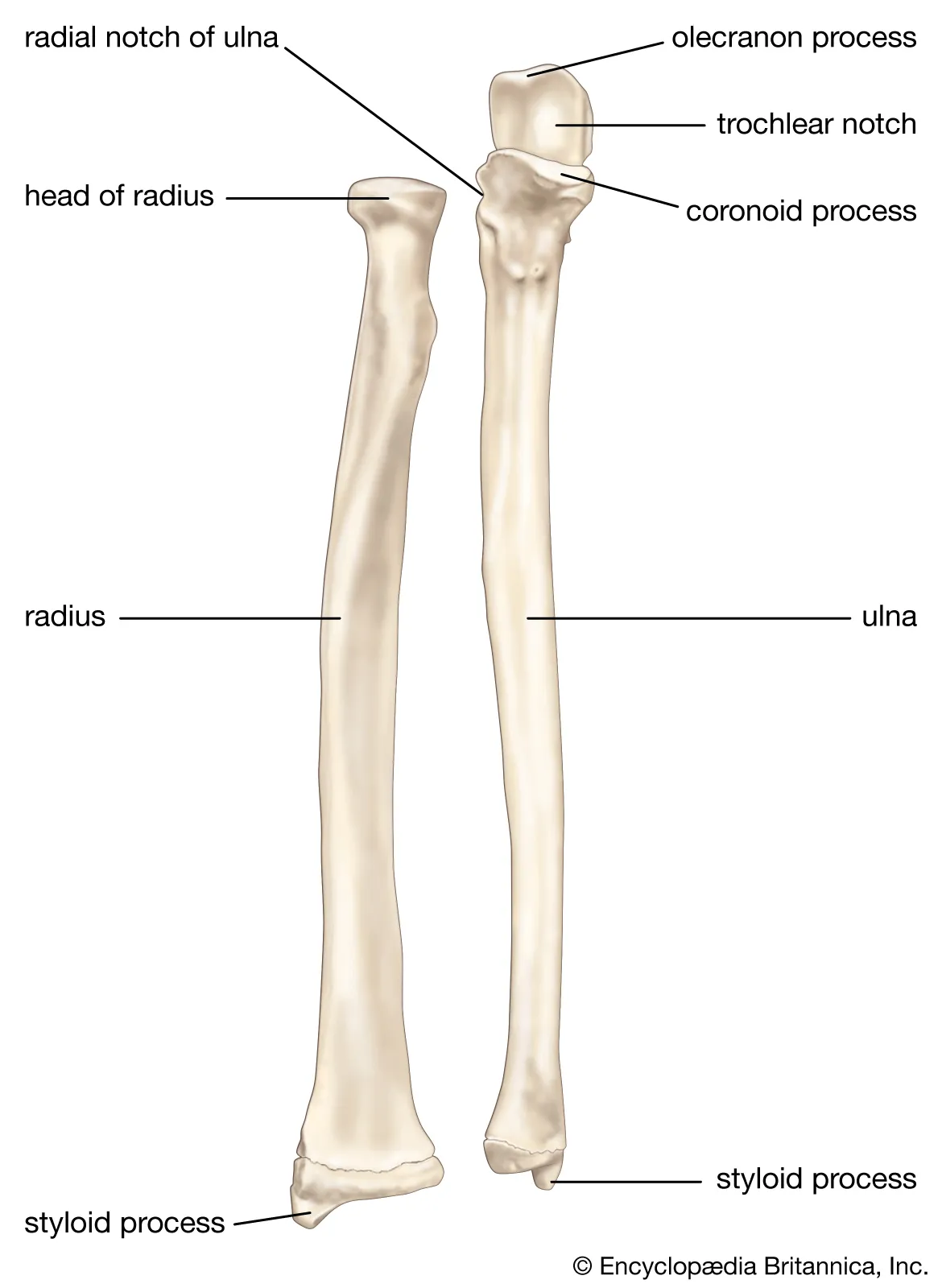
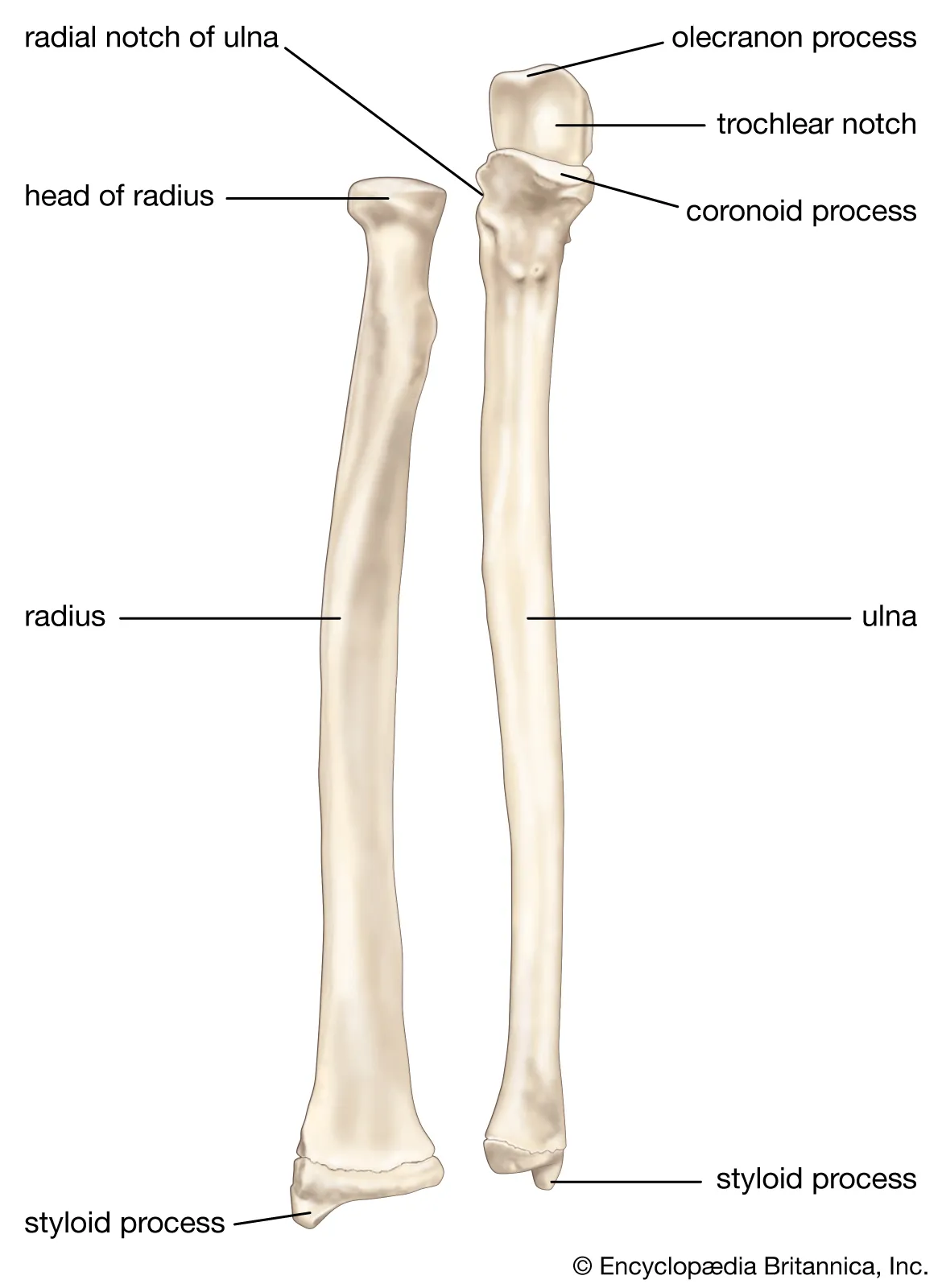
lower arm: ulna
medial
olecranon process, proximal end
semilunar notch- anterior depression
coronoid process, anterior process below the semilunar notch
radial notch- depression when ulna contacts the head of the radius
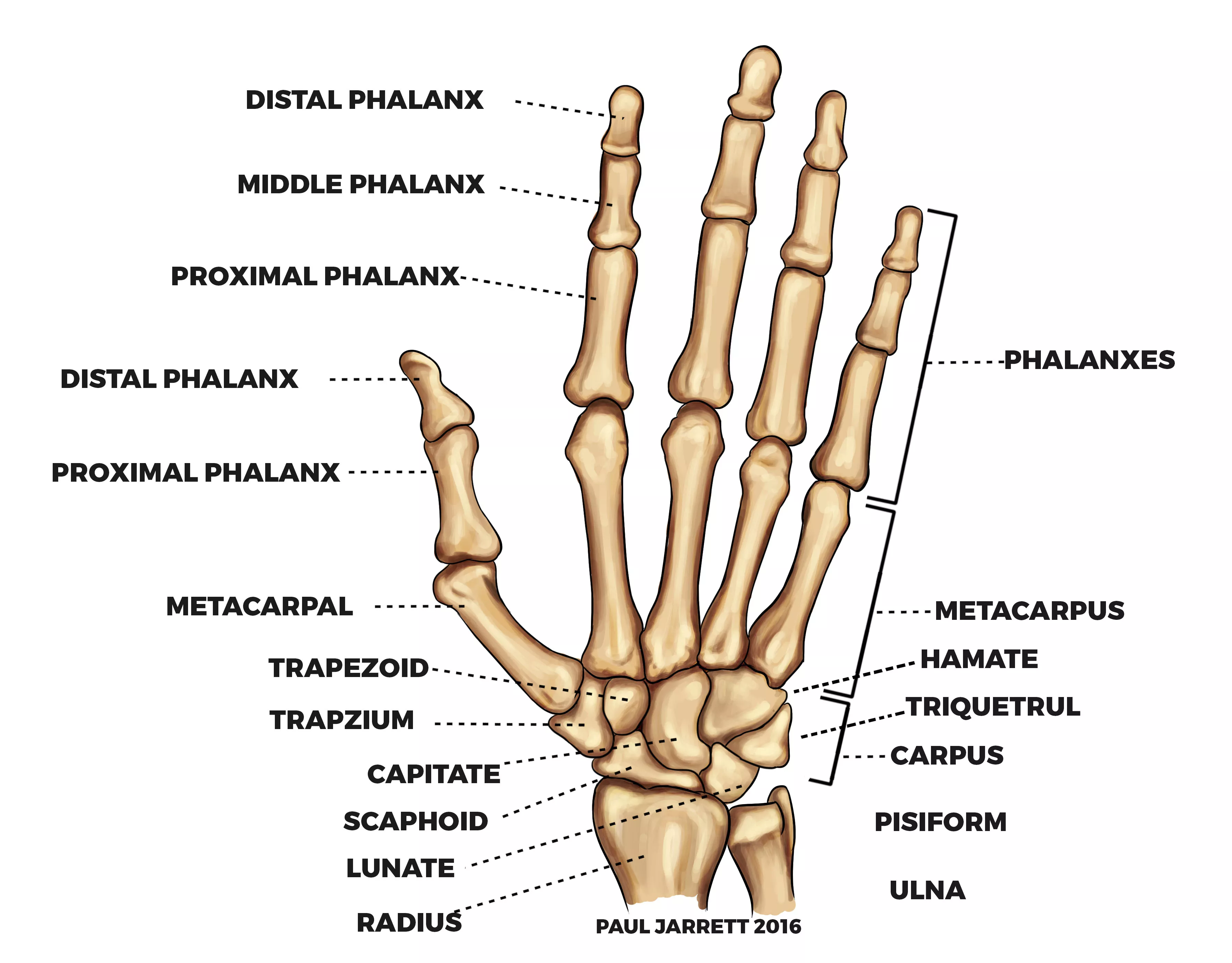
hand
carpals- wrist (8 bones)
metacarpals- palm (5 bones)
phalanges- fingers (3 each finger, 2 in the thumb)
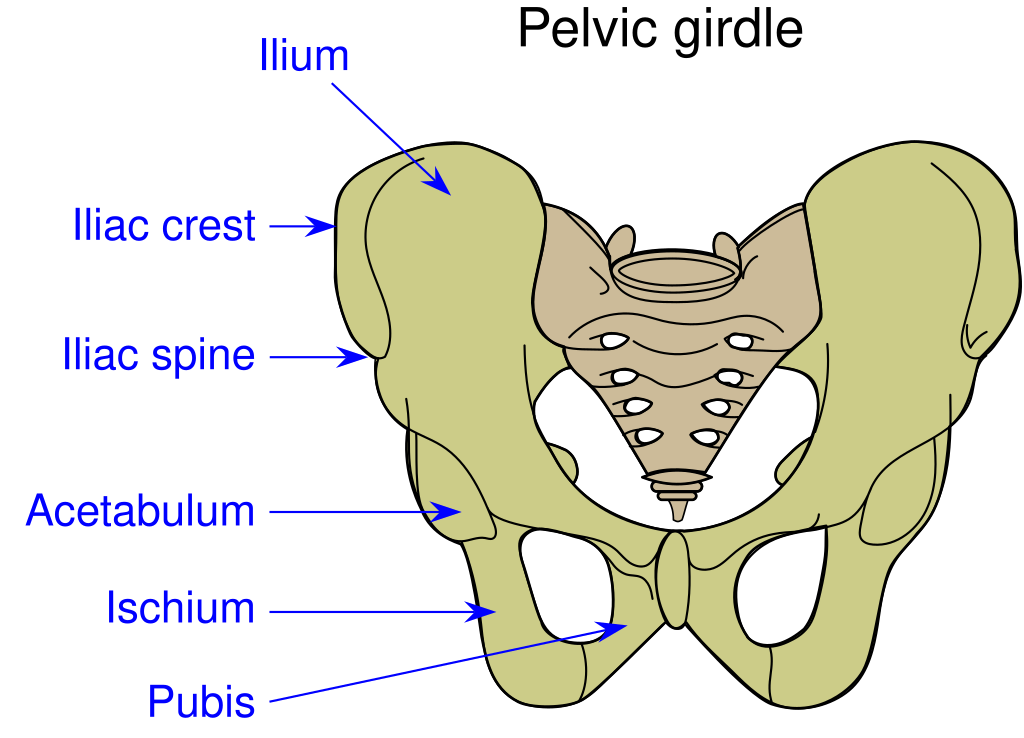
lower extremity: pelvic girdle
os coax: ilium, ischium, pubis- ossification is complete in the adult and the suture lines are not visible
front arch- os coax join at the symphysis pubis
articulates with sacrum and coccyx in back at the sacrum articulating surface
sacroiliac joint- between sacrum and ilium
iliac fossa- depresssion of the medial surface
acute line- ridge below iliac fossa
acetabulum- circular depression for femur
iliac crest- from the anterior superior spine to the posterior superior spine
ischium processes
ischial spine
ischial tuberosity- one sits on this
lesses sciatic notch- inferior to the ischial spine
greater ischial notch- superior to the ischial spine
obturator foramen- opening surrounded by ishium and pubis
pubis
upper leg: femur
proximal end
head- spherical
neck
trochanters
greater trochanter- large, lateral
lesser trochanter- small, medial
intertrochanteric line- ridge between trochanters anteriorly
intertrochanteric crest- ridge between trochanters posteriorly
distal end
lateral condyle
medial condyle
lower leg
tibia- larger
proximal end
medial condyle
lateral condyle
tibial tuberosity- below the condyles
distal end
medial malleolus- inner prominence of the ankle
anterior crest
fibula- smaller, lateral
proximal end
head- articulates with the tibia
neck
distal end- lateral malleolus, outer anklebone
anterior crest
foot
tarsus- 7 bones, calcaneous is the largest tarsal bone
metatarsal- instep, 5 elongated bones
phalanges- 3 in each toe, 2 in the great toe
Types of Joints
immovable- no mobility
synchondroses
held by cartilage (ex: metaphysix of long bones- growth plate)
sutures
irregular joints between flat bones, held by fibrous connective tissue continuous with the periosteum of the skull outisde and the dura mater inside
slightly movable
symphyses- interbertebral joints: pad of fibrocartilage, fibroelastic capsule
syndesmoses- held together by an interosseus ligament (fibula-tibia)
freely movable: synovial joints
bone ends covered with articular cartilage
fibrous articular capsule holds joints together
ligaments- outer
synovial membrane- inner; produceburs synovium
bursae- sacs of synovial tissue
types of freely movable joints
gliding- wrist, ankle
hinge- elbow, knee
condyloid- oval shaped bones, elliptical movement; wrist
saddle- covex bones + concave; thumb
pivot- roational around an axis; atlas + axis vertebrae
ball and socket- all directions; shoulder + hip
shoulder joint
articular cartilage on connecting surfaces
6-7 bursae
hip joint
enclosed in an articular capsule
3 accessory ligaments
iliofemoral- anterior
pubocapsular- medial
ischiocapsular- posterior
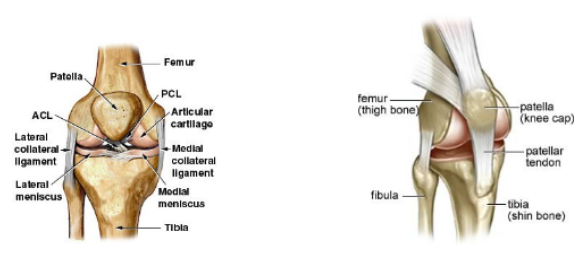
knee joint
most stressed joint of the body
semilunar cartilage (menisci) absorb stress; made of fibrocartilage, concave
lateral meniscus- lateral condyle of the femur + tibia
medial meniscusmedial condyle + tibia
connected by transverse ligament
ligaments
cruciates- form X on posterior surface
posterior cruciate
anterior cruciate
fibular collateral ligament- lateral
tibial collateral ligament- medial
oblique + arcuate popliteal- posterior
fibrous capsule- cover entire joint
patella- held by quadriceps tendon + patellar ligament
synovial membrane- lining
suprapatellar bursa- space between the synovial membrane + femur
gross anatomy
endomysium- thin layer of connective tissue separating each individual muscle fiber
fasciculi- bundle of muscle fibers
perimysium- covering of fibrous connective tisue surrounding each bundle (fasciculi)
epimysium- outer covering of coarse, connective tissue wrapping the entire muscle
deep fascia- surrounds the epimysium, covering the entire muscle and is continuous with tendons, ligaments and the periosteum
superficial fascia- connective tissue holding the deep fascia to the skin
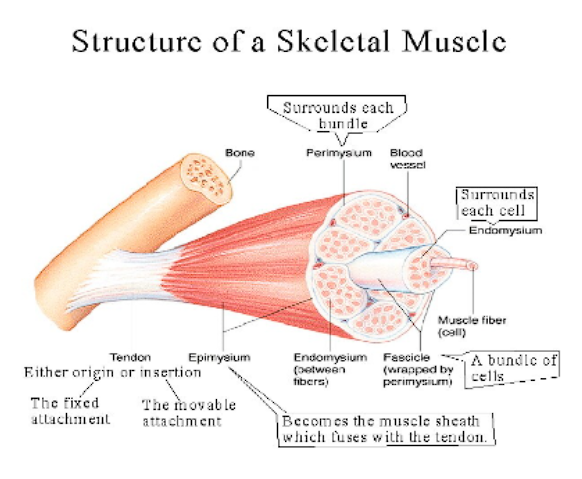
muscle attachment terms
origin- anchor; attached to immovable end
insertion- moving end
type of attachment
directly- attached to periosteum
tendon- band of white fibrous tissue; bone to muscle
aponeurosis- broad flat sheet of glistening pearly- white fibrous connective tissue; bone to bone or bone to muscle
microscopic structure
motor unit- bundle of muscle fibers controlled by a single neuromuscular junction
muscle fiber- individual muscle cell with thousand of myofibrils
sarcoplasm, intracellular fluid
sarcolemma, muscle cell membrane
t-tubules, connect sarcolemma to sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcoplasmic reticulum, specialized ER surrounding each myofibril
cisterns
calcium channels
myofibril, linear set of sarcomeres
sarcomere
thick filaments
myosin
thin filaments
f actin (strings of g-actin)
g-actin
tropomyosin (shields active site)
troponin (building site for calcium)
M line, connected to thick filaments and middle
Z line, connected to thin filaments and end of alphabet
Neuromuscular Junction
point at which a nerve fiber contacts a muscle fiber
usually at the fiber midpoint so that the impulse reaches both ends at the same time
structure contains…
synaptic gutters, invaginations of the sarcolemma
axon terminals, knob like branching terminals
axon terminal branch, each individual knob
synaptic cleft, gap
pre-synaptic membrane, axon end
post-synaptic membrane, muscle end
junctional folds, subneural clefts; infoldings of the sarcolemma on the post-synaptic side
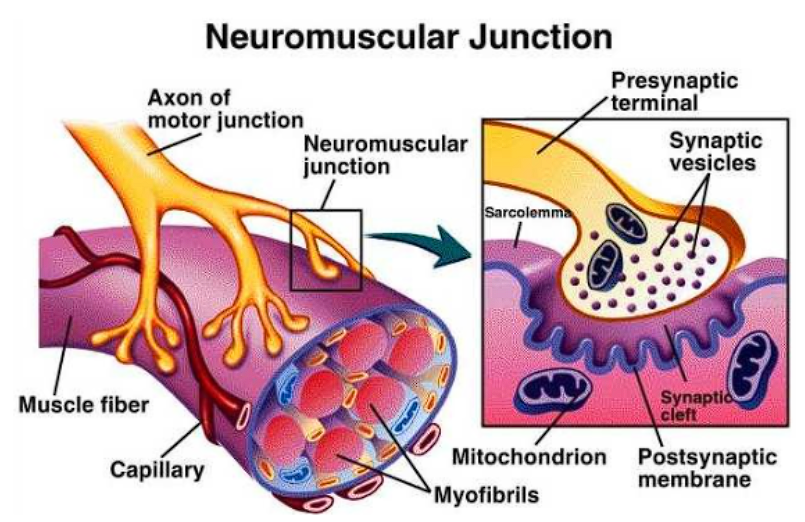
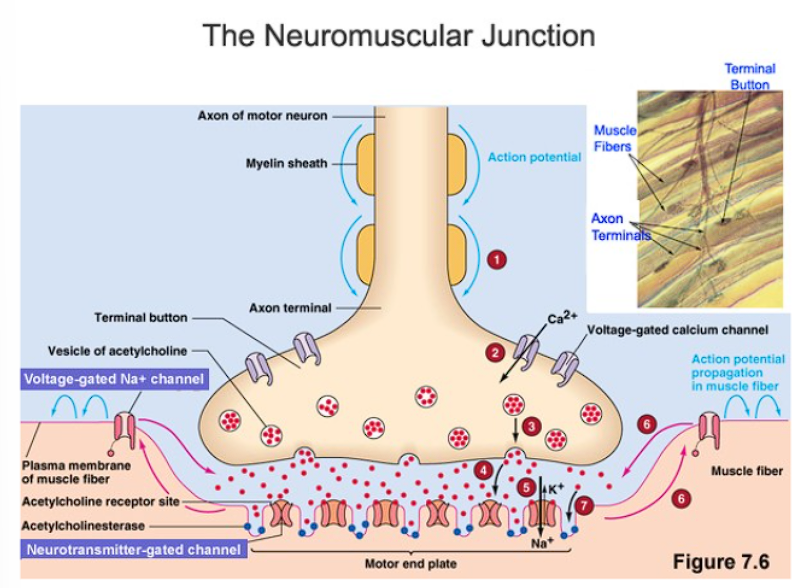
transmission across the synaptic cleft
depolarization: sodium gates open, sodium ions flow out
causes an action potential
repolarization: potassium gates open, potassium ions flow in
Impulse reaches synapse to open calcium gates, allowing calcium ions to flow into the axon at the axon terminals
Calcium releasesthe acetylcholine filled synaptic vesicles which diffuse to the membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the cleft
ACh diffuses out of the pre-synaptic membrane and binds to receptors on the post synaptic membrane
The action potential is again initiated on the sarcolemma
The action potential causes muscle-fiber shortening by releasing calcium
Calcium activates ATP release from mitochondria to supply the energy required for contraction
Inactivation is the result of acetylcholinesterase which breaks the neurotransmitter down into acetate and choline
Acetate and choline are reabsorbed by the presynaptic membrane and resynthesized into ACh by choline acetyltransferase
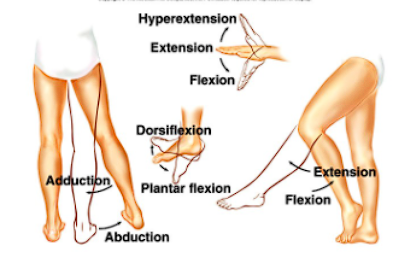
body movement
extension- increased angle of the joint
hyperextension- beyound normal posture
flexion- decreased angle of the joint
dorsiflexion: foot- flexed upward
plantar flexion: flexion of the toes, foot downward
abduction- away from median
adduction- towards the median
rotation- movement around the bone’s longitudinal axis without lateral displacement; rotation of the arm at the shoulder, or head
circumduction- circle movement at a freely movable joint
supination- turning the palm up
pronation- turning the palm down
inversion- applies to the foot; toward the median
eversion- applies to the foot; away from the median
sphincter; circular muscles; orbicularis oculi; orbicularis oris
muscle groupings
agonist- flexors, prime movers
antagonist- extensors, opposing muscle group
synergists- assist agonists
fixation muscles- hold structures in position
how many axial bones are there?
80
how many appendicular bones are there?
126
what are the cranial bones
frontal
suture coronal suture ( between parietal and frontal)
frontal sinuses
parietal (2)
sutures are
sagittal (between parietals)
lamboidal (between parietal and occipital)
squamous (between parietal and temporal)
occipital
occipital condyls
external occipital protuberance
foramen magnum
temporal (2)
squamous portion
mandibular fossa
zygomatic process
petrous portion
mastoid portion
external/internal auditory meatus
styloid process
mastoid process
sphenoid
greater wings
lesser wings
sella turica
optic canals
sphenoid sinus
ethmoid
perpendicular plate
cribform plate
crista galli
superior and medial nasal concha
sutures
coronal
saggital
lamboid
squamous
facial bones
maxilla (2 fused midially)
alveolar processes
alveolus (socket)
palatine (2 fused to form hard palate)
zygomatic (2)
zygomatic arch
nasal (2)
lacrimal (2)
vomer (1)
inferior nasal concha (2)
mandible
rami
condylar process (articulates in mandibular fossa)
coronoid process (more pointed)
angle
body
fetal skull
fontanelles
sphenoidal (anterior to the squamosal suture)
mastoid (lateral and posterior- at the end of the lamboidal suture)
anterior (at coronal suture)
posterior (at sagittal suture/ occipital bone junction)
associated bones
hyoid
greater horns
lesser horns
auditory ossicles
malleus
incus
stapes
parts of the vertebrae
body
transverse process
vertebral foramen
pedicles
lamine
spinous process
intervertebral foramina
vertebral canal
types of vertebrae
cervical (7)
atlas
transverse foramen
axis
dens
transverse foramen
thoracic (12, articulate with ribs)
costal facet
lumbar (5)
sacrum (5)
medial sacral crest
sacral hiatus
coccyx (4)
ribs
types
vertebrosternal ribs (true- 7 pair)
vertebrochondral ribs (false- 3 pair)
vertebral ribs (false-floating - pair)
costal cartilages
parts of a rib
head
neck
tubercle
shaft
sternum
manubrium
body
xiphoid process
What is part of the pectoral girdle?
clavical and scapula
What is part of the clavical
acromial end
sternal end
sternoclavicular joint
what is part of the scapula
coracoid process
acromion process
supraspinous fossa
infraspinous fossa
glenoid cavity
superior angle
inferior angle
subscapular fossa
scapular spine
what are the bones of the arm?
humerus, radius, and ulna
Parts of the Humerus
head
neck
greater tubercle
lesser tubercle
surgical neck
deltoid tuberosity
medial epicondyle
lateral epicondyle
capitulum
trochlea
olecranon fossa
Parts of the Radius
head
neck
radial tuberosity
styloid process
parts of the ulna
olcrannon process
trochlear notch
styloid process
parts of the hand
carpals (8) sam likes to push the toy car hard
proximal row (radial to ulnar)
scaphoid
lunate
triquetrum
pisiform
distal row
trapezium
trapezoid
capitate
hamate
metacarpals (5) make up most of the palm
phalanges (3 in each finger, 2 in the thumb)
parts of the pelvic girdle
coxal bones (2) created by fusion of
illium
illiac crest
greater siatic notch
pubis
pubic symphyses
pubic angle
ischium
ischial tuberosity
ischial spine
obturator foramen (pubis and ischium)
acetabulum- formed by all three
sacrum
sacro-iliac joint
coccyx
pelvic outlet
parts of the leg
femur
head
neck
greater trochanter
lesser trochanter
medial condyle
lateral condyle
patella
base
apex
tibia
tibial tuberosity
medial malleolus
medial condyle
lateral condyle
fibula
head
lateral malleolus
parts of the foot
tarsals (7)
talus
calcaneous (heel)
navicular (medial)
cuboid (lateral)
cuniforms (3 each foot- medial)
metatarsals (5)
phalanges (14, 3 in each toes, 2 in the big toe)
hallux (big toe)
fibrous
sutures of the skull
comphosis- teeth in alveolar sockets
syndesmosis- interosseous membranes
cartilagenous
symphyses
pubis symphysis
intervertebral discs
synchondrosis
between the manubrium and first rib
epiphyseal plate
synovial
hinge
pivot
ball and socket
planar
synarthrosis
sutures of the skull
gomphosis
synchondrosis
amphiarthrosis
syndesmosis: interosseous membrane
tibial-fibula
radius-ulna
diarthrosis
synovial joints
ball and socket
hinge
planar
pivot
structure list for synovial joints
articular capsule
articular cartilage
synovial membrane
joint cavity
synovial fluid
bursae
fat pads
structure of the knee joint
lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
medial collateral ligament (MCL)
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
medial meniscus
lateral meniscus
movement around joints
gliding
circumduction
rotation
flexion
lateral flexion
dorsiflexion
plantar flexion
extension
hyperextension
adduction
abduction
pronation
supination
opposition
retraction and protraction
depression and elevation