Chromosomes + cell division
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Genome
the entire DNA of an organism (the amount of DNA present in a diploid cell)
Modern molecular biology discovered that a big/small part of the genome consists of protein-coding genes
small
For example, in the human genome the genes coding for proteins only make up about 1.5% of the total DNA.
Diagram of our genetic makeup
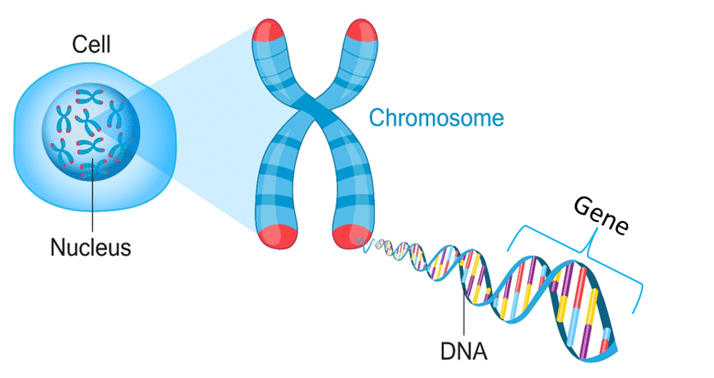
Chromosome
Threadlike structures of supercoiled DNA carrying genetic info in the form of genes
How many chromosomes do most human cells contain? What are pairs of matching chromosomes called?
46 chromosomes
Homologous pairs
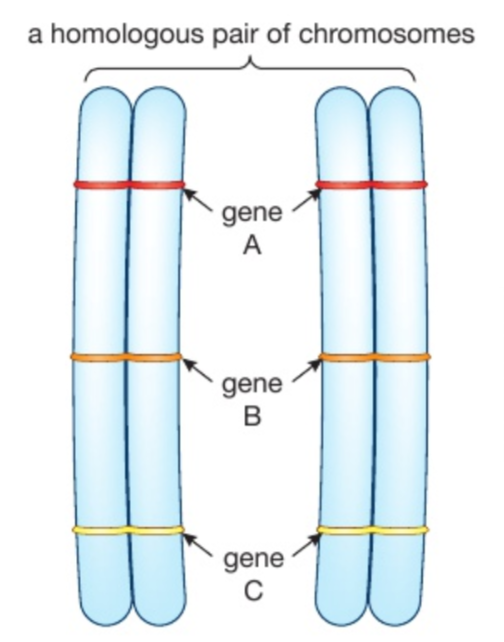
Remember that the total number of chromosomes in each species differs. Dogs have 78, humans 46 , rice plants 24
What is the only moment chromosomes are visible? Where can we find chromosomes?
During cell division
In the nucleus of each cell
What are the cells that do not have 46 chromosomes? Why and how many do they have?
Red blood cells have no nucleus and so have no chromosomes
Sex cells (called gametes) have half (23) because of meiosis
Key point
What are the sex chromosomes?
X and Y chromosomes
How are the chromosomes in a female and a male going to differ?
Each cell from a male has 22 pairs of chromosomes and 2 that do not form a pair -- X and Y chromosomes (46 total). Except the sperm
Each cell from a female has 23 matching pairs including a pair of X chromosomes (46 total). Except the egg cell
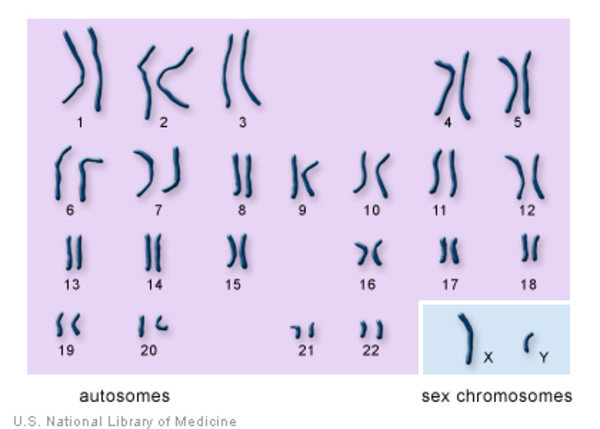
One of each of the 22 homologous pairs are shown, along with the X and Y sex chromosomes
How many chromosomes do human body cells have (somatic cells)? What name is given to these cells with these number of chromosomes?
46 in total (23 homologous pairs) — diploid
What cells are the exception to the number of chromosomes? How many do humans have? What is this called?
Gametes (sex cells)
23 chromosomes in total (one copy of each homologous chromosome)
This applies to most other organisms as well like dogs (diploid number of chromosomes is 78 whereas they have 39 haploid chromosomes)
What is mitosis?
A type of nuclear division that gives rise to two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell and are diploid cells
When does mitosis occur?
Growth: mitosis produces new cells
Repair: to replace damaged or dead cells
Need to know but is not on spec: replacing cells e.g skin cells and red blood cells
Asexual reproduction: mitosis produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
Cloning
All the cells in our bodies (except the gametes) are formed by mitosis from the ____. They all therefore contain the copies of all the chromosomes and genes of that
zygote
Describe the process of mitosis
Just before mitosis, each chromosome in the nucleus copies itself exactly (forms X shaped chromosomes called chromatids)
Chromatids line up along the centre of the cell where fibres (spindle) pull them apart
Two new nuclei form at the poles of the cell and the cell divides into two; each new cell has a copy of each of the chromosomes
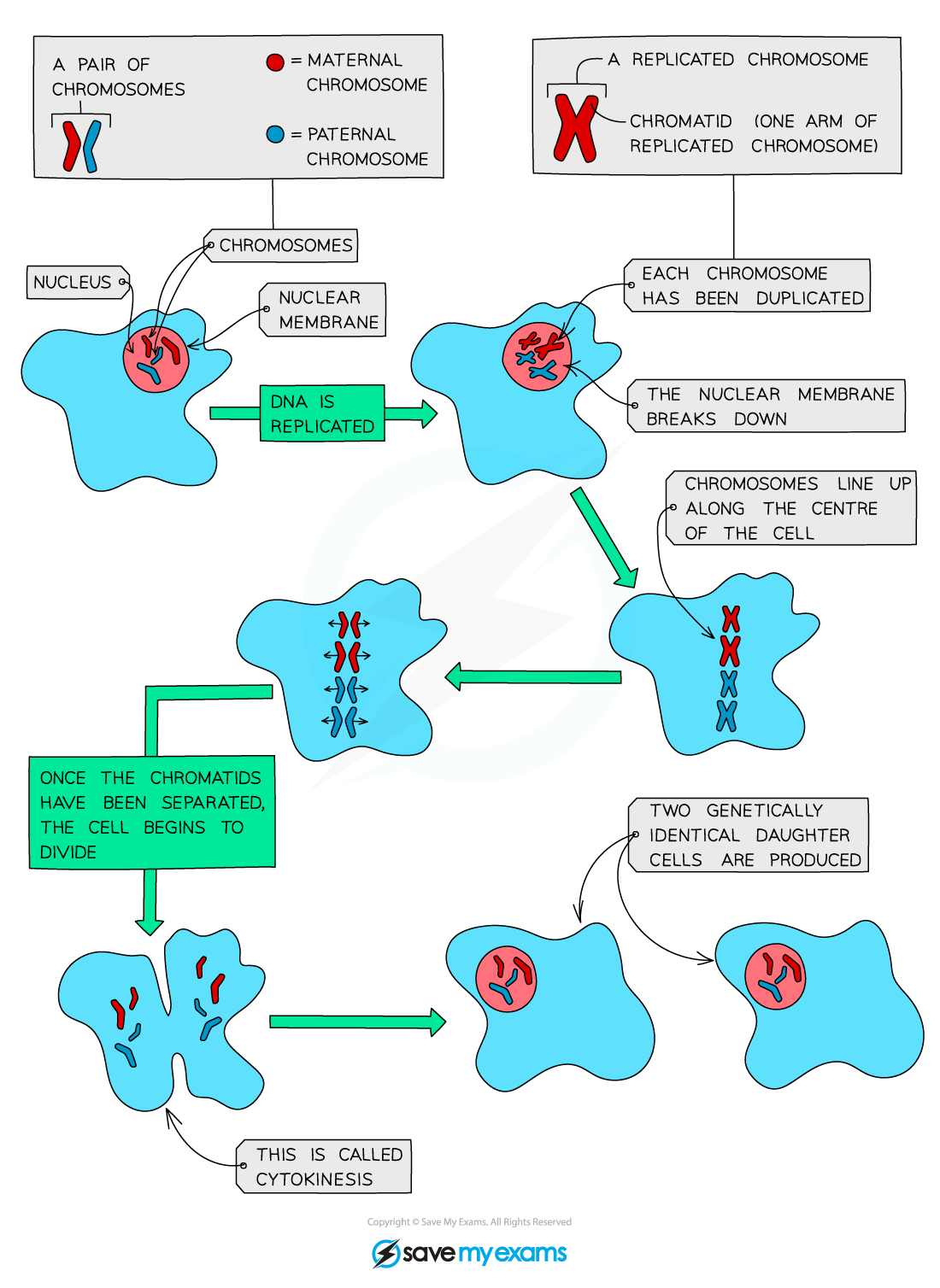
Why does each chromosome copies itself before the cell divides? What does this involve?
Each daughter cell will be able to receive a copy of each chromosome and be genetically identical to the parent cell. If not, both daughters cells won’t contain all the genes
This involves the DNA replicating and more proteins being added to the structure.
What is meiosis
It is a type of nuclear division that gives rise to 4 haploid daughter cells (these are the gametes) that are genetically different
Describe the process of meiosis
The parent cell must copy each chromosome so that there is enough genetic material to be shared between 4 daughter cells
First division:
chromosomes pair up in homologous pairs
Members of each homologous pair separated
Fibres pull them apart to form 2 nuclei with one chromosome pair
Second division:
chromosomes will line up along the centre of these (plural) cells, and cell fibres will pull the two chromatids of each chromosome apart forming 4 haploid gametes
It must divide twice so that each of the daughter cells receives just one chromosome from each homologous pair

Is there genetic variation in meiosis? How? Why is this good?
Yes. The gametes formed by meiosis don’t all have the same combinations of alleles. During the two cell divisions of meiosis, the chromosomes of each homologous pair are shared between the two daughter cells independently of each of the other homololous pairs. This allows for much possible genetic variation in the daughter cells.
If there is a change in the environment the best adapted offspring survive and passe on alleles for survival
Descriibe how cell division by meiosis is different from cell division by mitosis (4)
For meiosis
Produces 4 cells/has two cell divisions
Porduces haploid cells
Halves the chromosome number (ignore 23 chromosomes)
Produces genetic variation/cells not genetically identical
Produces gametes
Takes place in gonads/ovaries/testes/sex organs
What is a similarity between mitosis and meiosis?
Chromosomes make a copy before cell division begins