Rocks
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Magma
Molten rock material beneath the Earth’s crust.
Lava
Molten materials that flow onto the Earth’s surface.
Lithosphere
The outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth.
Rocks
Naturally-formed aggregates of minerals that make up all of the Earth’s crust and the solid part of the mantle below (Lithosphere) - building blocks of landforms
How are rocks formed?
When minerals are compacted and consolidated or pressed together to form a firm, solid substance.
From cooling magma or lava
From compaction of layers of rock fragments eroded from other rocks or the hardened remains of plants and animals
From the great heat or pressure, changing the composition of the rock
Mineral
An inorganic solid with a crystalline structure and characteristic chemical composition
Igneous Rocks
Rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma/lava)
Intrusive igneous rocks
Rocks formed below earth’s surface
Extrusive rocks
Formed on earth’s surface
Acid igneous rocks
Igneous rocks of high silica content (light coloured)
Basic igneous rocks
Igneous rocks of high iron and magnesium content (dark coloured)
Examples of igneous rocks
Basalt, pumice, granite
Characteristics of igneous rocks
Coarse-grained for rocks of large crystals, vice versa
Not in layers
Do not have fossils
Hard and strong (more resistant)
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed from the compaction of layers of rock fragments eroded from other rocks or the hardened remains of plants and animals.
Weathered and eroded igneous, previous sedimentary and metamorphic rock materials (clastic)
Crystals of dissolved minerals (non-clastic)
Organic materials such as animal and plant remains (foliated)
Conglomerate
Sedimentary rock made up of consolidated gravels, with some mud or sand in between larger grains
Usually form from riverbed sediments
Large ‘cobbles’ are usually well-rounded, greater than 2 mm in diameter
Sandstone
Sedimentary rock made from small grains of the minerals quartz and feldspar
Form in layers
Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks formed from great heat and/or pressure beneath the Earth’s surface, changing the composition of the rock
Examples of metamorphic rocks
Marble, slate, quartzite
How to describe a rock?
Colour
Lustre (reflect light)
Layering
Crystal size
Hardness
Texture
Rock cycle
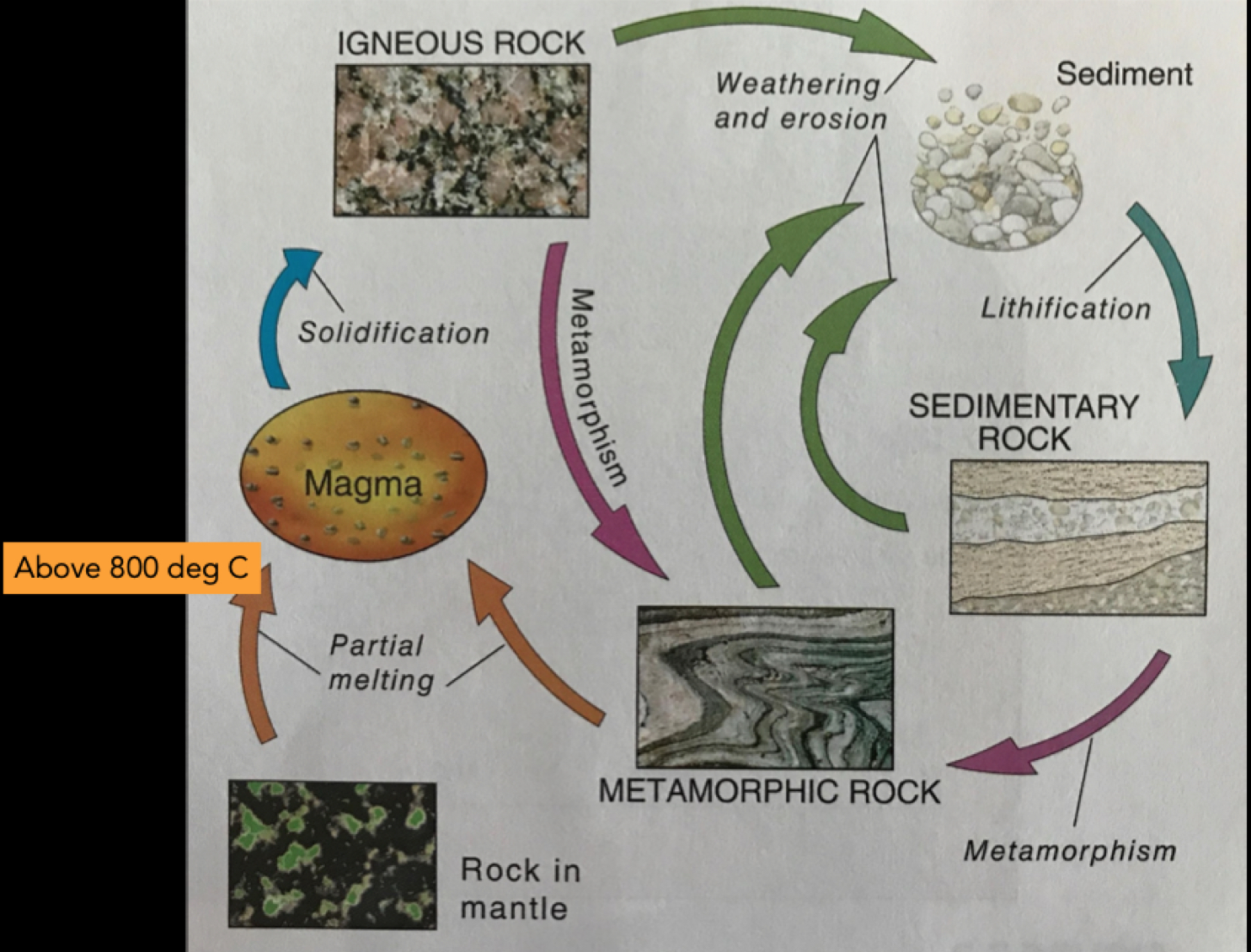
Weathering
The process that changes the physical and/or chemical character of rock at or near the Earth's surface.
Erosion
The picking up or physical removal of rock particles by agents such as water, wind, or ice.
Stratification
The layering that occurs in sedimentary rocks as they accumulate over time.