Protein synthesis, RNA catalysis: ribozymes, ribosomes and riboswitches
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Translation machinery
mRNA
tRNAs
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Ribosomes
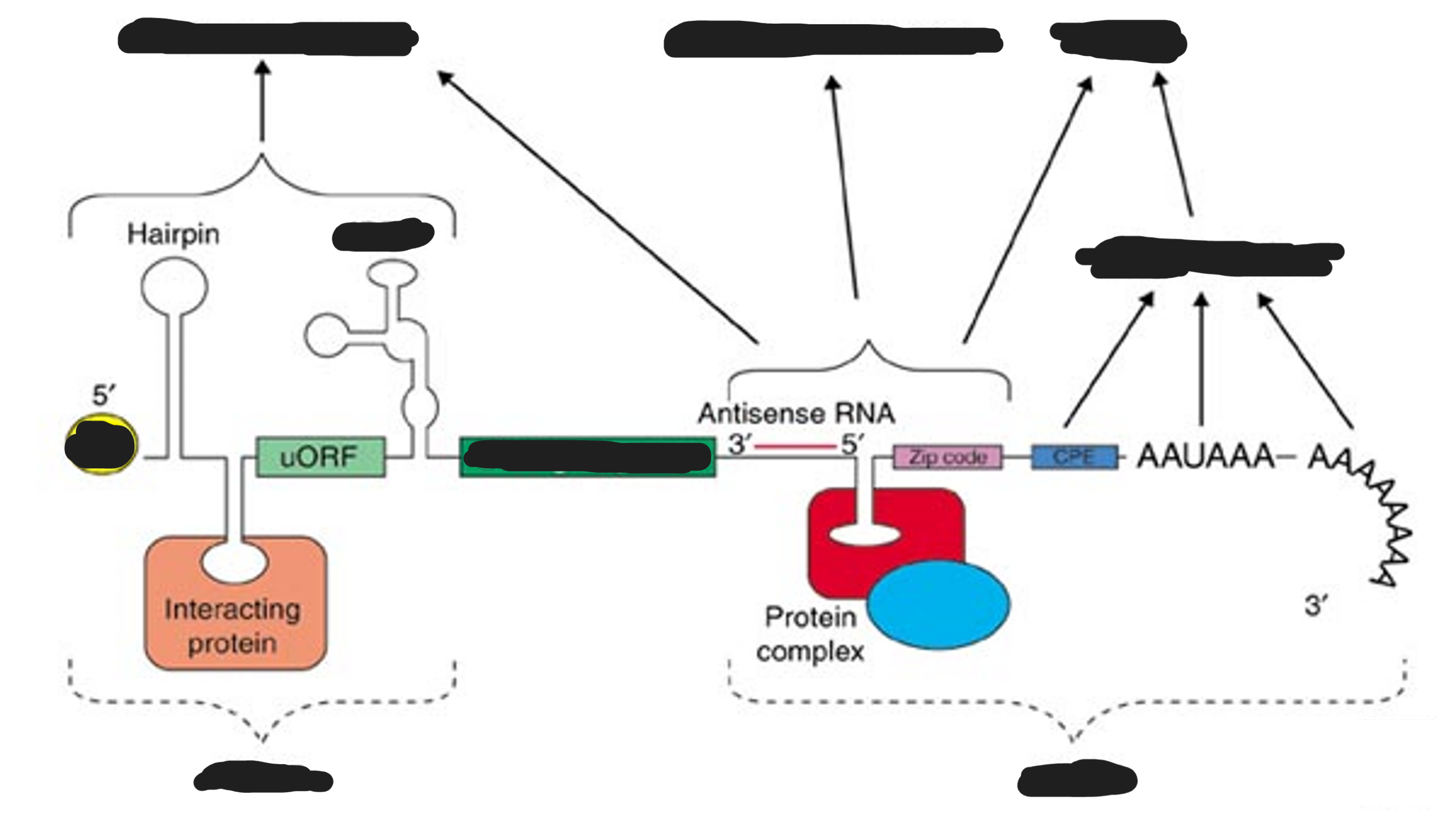
Eukaryotic mRNA structure
The generic structure of a eukaryotic mRNA, illustrating some post-transcriptional regulatory elements that affect gene expression. Abbreviations (from 5' to 3'):
UTR, untranslated region
m7G, 7-methyl-guanosine cap
uORF, upstream open reading frame
IRES, internal ribosome entry site
CPE, cytoplasmic polyadenylation element
AAUAAA, polyadenylation signal.
Start codon in eukaryotes
5’ to 3’: AUG
Stop codons
5’ to 3’
UAA (ochre)
UAG (amber)
UGA (opal)
Nonsense Mutation
A base substitution that generates a premature nonsense codon (stop codon) in the middle of an ORF
Frameshift Mutation
A base substitution that changes the reading frame - often leads to the generation of premature nonsense codons (stop codons).
Usually the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide pair.
wobble position
the third (closest to the 3’ end) nucleotide on the mRNA codon
Allows for redundancy in the genetic code
Missense Mutation
A base substitution that changes the coding capacity of a codon
Silent Mutation
A base substitution that does not change the coding capacity of a codon
(could affect things due to codon usage)
Nonsense suppression
Factors than suppress the effect of a nonsense mutation:
Mutational alterations of tRNAs (allowing them to bind to stop codon)
Mutational alterations of elongation or termination factors
Mutational alterations of ribosomal proteins
Action of some chemicals that alter ribosome decoding properties
3’ CCA tail of tRNA
Amino acid is attached to this
In prokaryotes CCA is transcribed
In eukaryotes, the CCA sequence is added during processing and therefore does not appear in the tRNA gene
Is important for the recognition of tRNA by enzymes critical in translation
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
an enzyme that catalyzes the esterfication of a specific amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an amino acyl-tRNA
How many aminoacyl tRNA synthetases are there for each amino acid
Only 1, despite the fact that there can be more than one tRNA and more than 1 anticodon for an amino acid.
Almost every individual has a unique fingerprint of ribosomal RNA gene repeats
Nucleolus
Actually a dense region of the nucleus where massive transcription of ribosomal RNA genes occurs
Its formed around specific genetic loci called nucleolar organizing regions (NORs)
Functions:
Primary function is to assemble ribosomes
Assembly of signal recognition particles
Modification of transfer RNAs
Sensing cellular stress
Ribosomal RNA genes are located at…
regions called nucleolar organizer regions
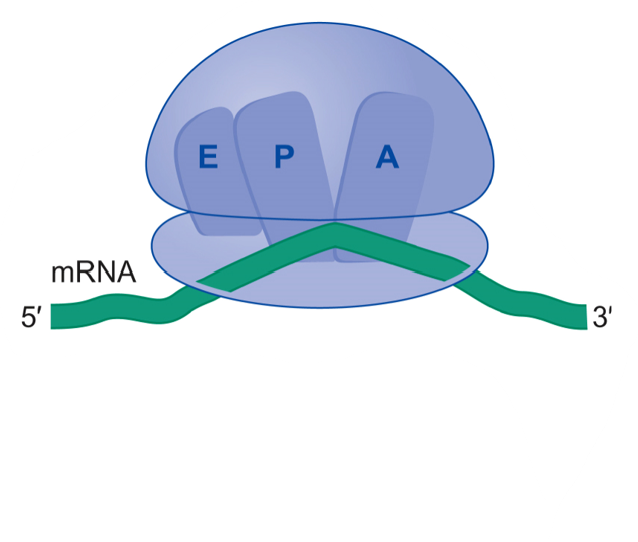
tRNA binding sites on ribosome
A: aa-tRNA binding site
P: peptidyl-tRNA binding site
E: exit site
What is the purpose of the 5’ cap in translation?
It’s where some translation initiation factors bind
Large ribosomal subunit only joins once tRNA for start codon has attached to mRNA with small ribosomal subunit.
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
A guanine-rich sequence of nucleotides upstream of the start codon AUG in prokaryotic mRNA. It pairs with a complementary sequence on the small ribosomal subunit that helps align the ribosome with the start codon.
There is no Shine-Dalgarno sequence in eukaryotic mRNA, but…
it is thought that some weak complementarities to 18S rRNA help to slow down the ribosome when it comes near AUG
Usually, eukaryotic ribosome begins translation when it…
recognizes the first AUG
What triggers the unbinding of translation initiation factors?
Correct base pairing between Met-tRNA and mRNA
Internal initiation of translation
Occurs at IRESs (Internal Ribosome Entry Sites)
Rare in eukaryotes but often encoded in viral mRNAs lacing a 5’ cap
They function like prokaryotic ribosome binding sites
They mediate the tight association of mRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit
Translation elongation factors are active if bound to
GTP
How do ribosomes select against incorrect aminoacyl t-RNAs
Additional hydrogen bonds form between the 2 A residues of the small ribosomal subunit and the minor groove of anticodon-codon pair, only when they are correctly base paired.
Correct base pairing allows EF-Tu (protein which escorts aa-tRNA to the A site) to interact with the factor-binding center inducing GTP hydrolysis and EF-Tu hydrolysis.
Only correctly base-paired aminoacyl0tRNAs remain associated with ribosome as they rotate into the correct position for peptide bond formation: tRNA accommodation.
New amino acids are attached to the —— terminus of the growing polypeptide chain.
C
Stop codons are recognized by __________ that__________.
proteins called release factors that activate hydrolysis of the polypeptide from the peptidyl-tRNA
Ribozyme
RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions
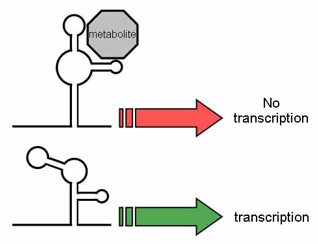
Riboswitches
They are found mostly in prokaryotes.
A part of an mRNA molecule that can directly bind a small target molecule, and whose binding of the target affects the gene’s activity
Selenocysteine
Added by a modification by a sequence after the stop codon