Pulmonology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is the trachea
windpipe
PET Scan of the lung
Positron Emission tomography
radioactive glucose is injeted adn images reveal metabolic activity in the lungs.
Ventilation perfusion ( VQ Scan)
records radioactivity in lung after intravenous injection of radioisotope and inhalation of a small amt of radioactive gas ( xenon)
What is the pleura, and two types
double-layered membrane surrounding each lung.
two types:
visceral ( inner layer of pleura closer to lung tissue)
parietal pleura ( outer layer of pleura lying closer to ribs and chest wall.
Atelectasis
collapsed lung ; incomplete expansion of a lung.
What are the two forms of atelectasis?
1) Bronchial obstruction
prevents air from reaching distal airways and alveoli collapse. ( caused mostly by blockage of a bronchus by mucus/ plug.
2) acumulation of fluids / blood or air within pleural cavity collapse lung.
can occur with pneumonia, fluid buildup in pleural cavity, pneumothorax
emphysema
cannot breath out properly→ lungs are hyper inflamed
pink puffer lips
strong association w/ cigarrete smoking.
blood vessels, and pulmonary artery pressure rises → right side of heart must work harder to pump blood. → right ventricular hypertrophy / right heart failure.
pneumothorax
air gets trapped in pleura making the lung collapse ( atelectasis)
when break in lung surface→ releases air into pleural space.
chronic bronchitis
inflammation of bronchi persisting over a long time.
type of COPD ( Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease )
Signs and symptoms:
excessive secretion of often infected mucus, productive cough ( wet cough) , obstruction of respiratory passaes.
Cystic Fibrosis
Inherited disorder
where exocrine glands result in thick mucinous secretions in respiratory tract that do not drain normally.
Diagnosed: newborn screenign blood test, sweat tess ,genetic testing.
What are the two types of COPD
1) chronic bronchitis
2) Emphysema
pneumonia
acute inflammation and infection of albeioli, which fill with pus or products of inflammatyr reaction.
pulmonary edema
fluid in air sacs and bronchioles
caused by inability of heart to pump blood ( congestive heart failure)
blood backs up in pulmonary blood vessels and fluid seeps out into the alveoli and bronchioles.
pulmonary embolism ( PE)
clot or other materials lodges in vessels of the lung
from DVT ( deep vein thrombosis)
Test: VQ scan ( Ventilation perfusion) gold star for Pulmonary embolism
next is CT angiography.
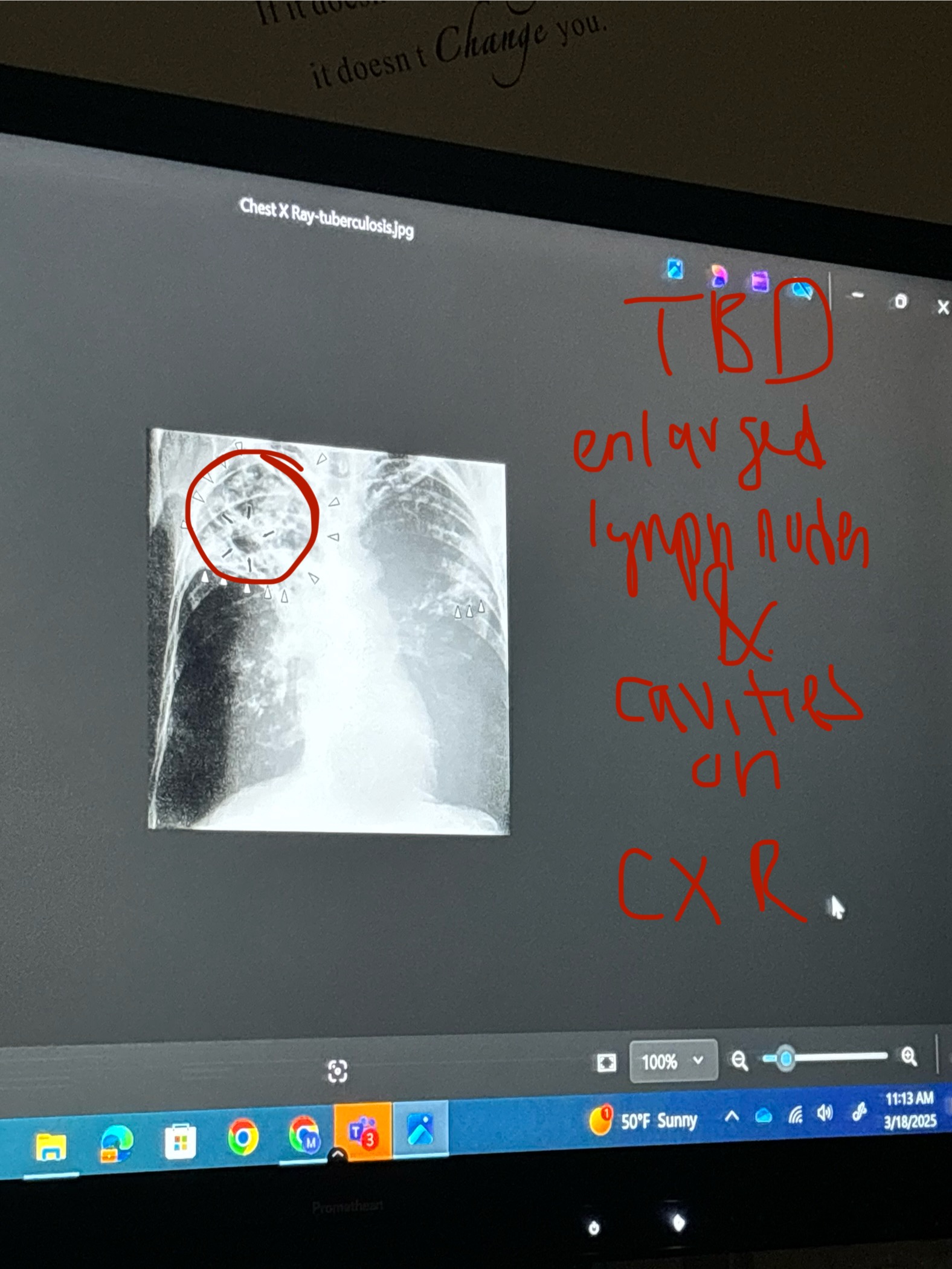
Tuberculosis
infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Signs and Symptoms:
cough, weight loss, night sweats, hemoptysis ( coughing up blood) , pleuritic pain.
Tests: sputum culture , PPD( Purified Protein Derivative) , Chest X ray.
Chest X Ray:
infiltrates ( areas of opacity)
cavitary lesions
swollen lymph nodes ( lumps on x-ray)
miliary pattern ( tiny dots scattered across lung fields)
What is the medical term for coughing up blood
Hemoptysis
What is sputum culture test
test the phlegm; et results back from 4-6 weeks
used as testing for TB
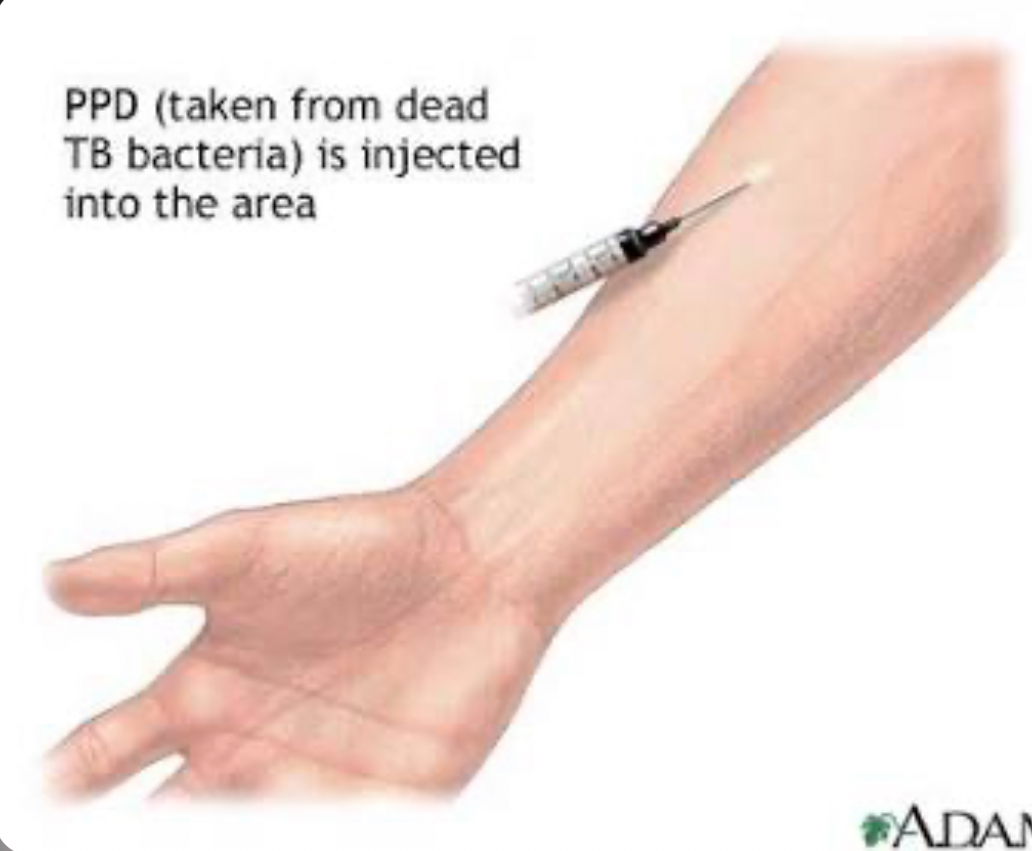
What is PPD ( Purified Protein Derivative )
used to detect TB infelction
injecting small amt of PPD under forearm skin ( a protein derived from TB bacteria)
if it swells / turns red, it indicates the patient has been infected with TB ( does NOT mean they have an active TB disease)
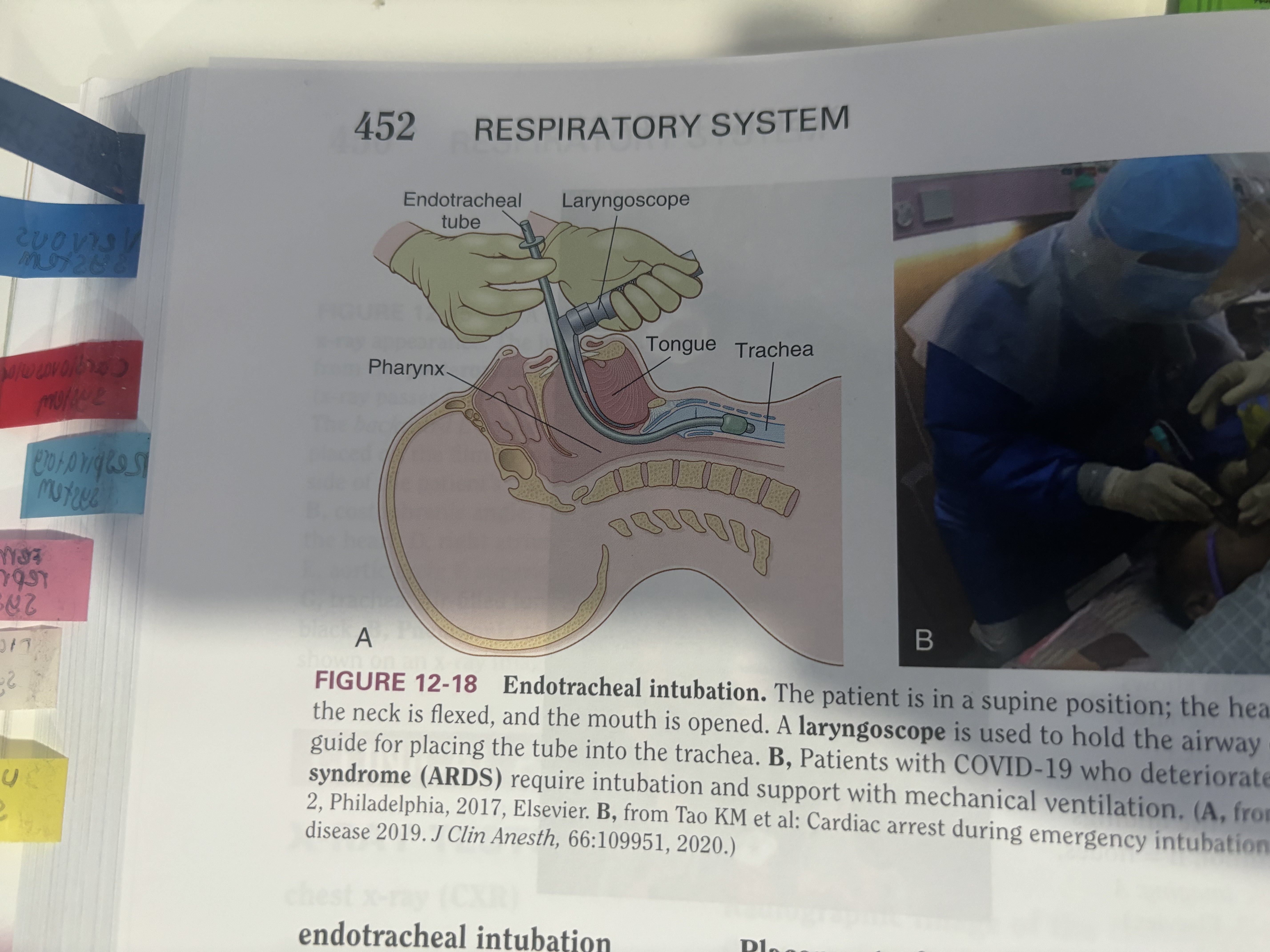
endotracheal intubation
placement of a tube through the mouth into pharynx, larynx and trachea to establish an airway.
What do white lines represent on X Rays
blood vessels.
asthma
respiratory condition; spasms of bronchi causing difficulty in breathing.
( airways narrowed, inflammed and produce extra mucus making it difficult to breath)
Test:
Spirometry ( type of Pulmonary function Test )
If no illness, CXR is normal.
every time someone has attack they do NOT need CXR.
if they are sick ( while attack) … check for pneumonia/ asthma or bronchitis.
What is tachypnea
fast breathing
What is term for difficulty breathing
dyspnea
apex of lung
top curvy part of lung.
How many lobes doe the lung have
5 lobes.
Right lung has 3 lobes ( upper , middle , lower)
left lung has 2 lobes ( upper and lower
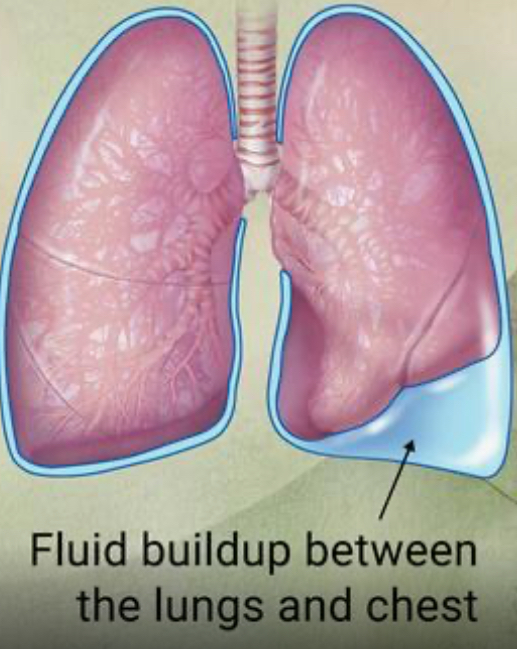
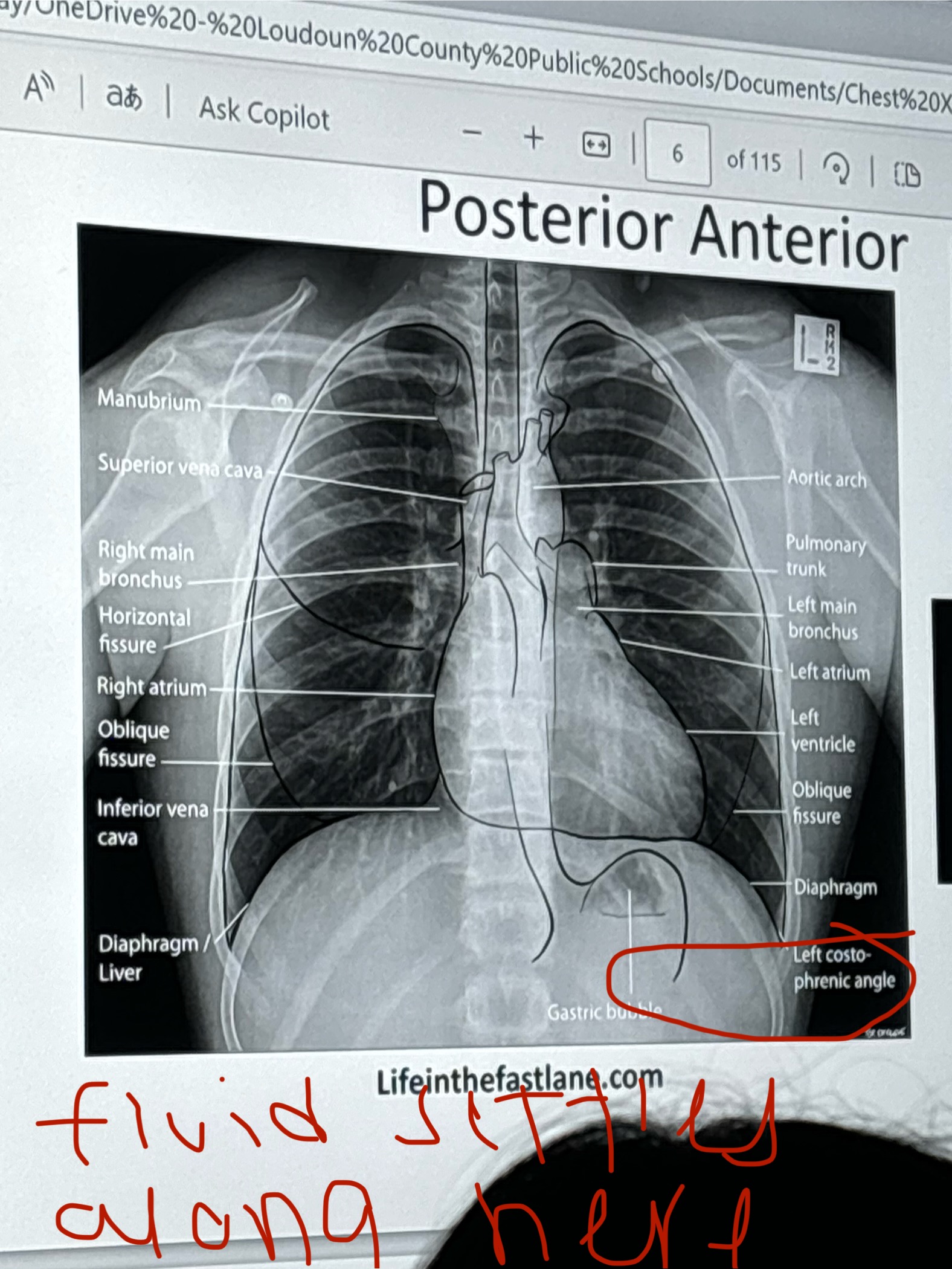
Pleural effusion
A buildup of fluid between the tissues that line the lungs and the chest
Fluid can accumulate around the lungs due to poor pumping by the heart or by inflammation.
what is treatment for pneumothorax
Treatment: chest tube.
Pleural Effusion X Ray
what is treatment for chronic bronchitis
Treatment:
variety of inhalers ( albuterol)
oxygen tanks
prednisone ( not every day)
treatment for asthma
Treatment:
albuterol ( inhaler)
prednisone ( steroid)