Scrotum and Prostate 6/16 exam
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
counter clockwise (first 6):
vas deferens, epididymal head, efferent ductules, rete testis (in mediastimun tesis), body of epididymus, tail of epididymus,
counter clockwise (last 7):
capsule (tunica albuginea), tunica vaginalis- visceral layer, cavity, parietal layer, seminiferous tubule, straight tubule
What is the reservoir for sperm?
Epididymis
Seminal fluid is produced by?
Prostate, Seminal Vesicles, and Cowper’s Glands
Location of Seminal Vesicles to the prostate gland
Superior and Posterior
The _____ zone of the prostate is the largest and most lateral zone
peripheral
Vascular Supply to the testicle waveforms are
low resistive vessels
Venous drainage in the testicle is via
the pampiniform plexus (veins in the spermatic cord)
RT drains into the IVC
LT drains into the LT renal vein.
veins and structures within the spermatic cord?
vas deferens, Rt/Lt testicular arteries, veins, lymph vessels
Mediastinum testes- location and sonographic appearance
runs through the length of the testicle. (middle)
appears as a hyperechoic line.
Rete testis location and sonographic appearance
tubules that connect the mediastinum to efferent ducts
seen as tiny tubules adjacent to epididymal head - usually only seen if dilated.
sm tubular structures seen near the mediastinum testes.NO COLOR DOPPLER- tubes not veins
Importance of using doppler
to rule out: torsion, varicoceles, orchitis
and in prostate- abnormal cells
epididymis is located
superiorly then courses posterolateral to the testis
sonographic appearance of epididymis
medium echogenicity; usually isoechoic to hypoechoic compared to the testis, echogenicity is courser.
Vas Deferens
connects the epididymis to seminal vesicles.
in the spermatic cord.
continuation of ductus epididymis. thicker and less convoluted. dilates at the terminal portion near the seminal vesicles
joins w/ duct of seminal vesicles to form ejaculatory ducts.
Tunica Vaginalis
lines the inner walls of the scrotum, covering each testis & epididymis.
consists of 2 layers the parietal and visceral
parietal lines the scrotal wall
visceral surrounds testis and epidid.
where do hydroceles, pyoceles, and hematoceles form?
in the layers of the Tunica Vaginalis
Pampiniform Plexus
drains the testicles
associated with varicoceles
Tunica Albuginea
dense fibrous tissue that completely covers the testis
transition zone
small area located on the lateral sides superior to the verumontanum near the center of the prostate
Cryptorchidism
undescended testicle, typically in newborns.
CF of cryptorchidism
asymptomatic, or a palpable mass in the pelvic/groin region
USF or cryptorchidism:
small, less echogenic, oval and homogeneous, mediastinum is not usually seen
risks of cryptorchidism
testicular cancer, torsion, infertility
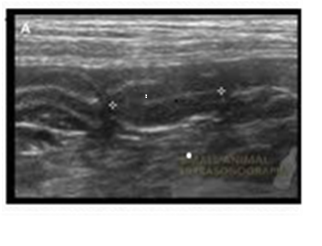
cryptorchidism
Epididymitis
infection/inflammation of the epididymis
most common cause of acute scrotal pain and tenderness
CF of epididymitis
scrotal pain/ possible discharge
fever and painful urination
severe infection
USF of epididymitis
enlarged, hypoechoic gland (decreased echogenicity)
increased vascularity on affected side.
reactive hydrocele
doppler waveforms show increased velocities with a low resistive waveform
body and tail not usually seen unless pathology is present
what structure connects the epididymis to the seminal vesicles?
Vas Deferens
Orchitis
infection that has spread to the testicle
can be focal or diffuse
CF of orchitis
fever, testicular pain on affected side.
increased WBCs
N & V
USF of orchitis:
decreased echogenicity & vascularity throughout entire testicle
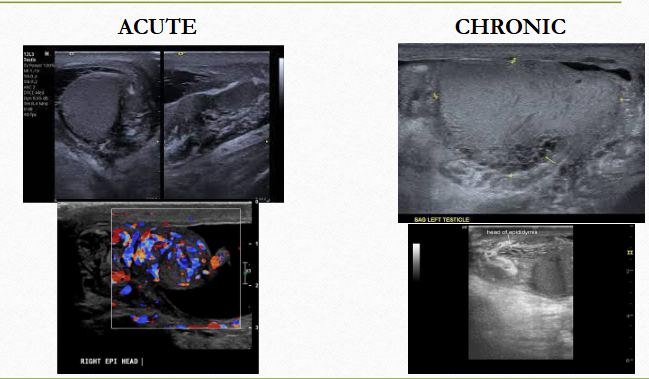
orchitis (chronic/ acute; diffuse/ focal)
infarction
tissue death due to lack of blood flow
CF of infarction
pain
USF infarction
hypoechoic wedge shaped area (may be round), decreased or complete abscence of doppler
hydrocele
found around the anterolateral aspect of the testes. collection of fluid between the two layers of the tunica vaginalis
may be congenital or acquired
idiopathic or secondary (infarction, inflammation, neoplasm trauma,
CF hydrocele
asymptomatic or scrotal enlargement
USF hydrocele
anechoic fluid in scrotal sac
may contain low level echoes, septations or debris
\complex may be due to infection
what can be confused with a complete infarction of the testis?
cannot be differentiated from testicular torsion
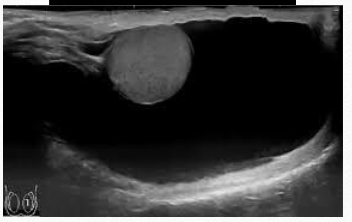
hydrocele
hematocele
fluid in the scrotal sac containing blood
usually due to trauma
CI for hematoceles
injury
USF hematocele
fluid may have mixed echogenicity, debris, may contain internal septations/ loculations
testicular torsion
most common cause of acute scrotal pain in adolescents
undescended are 10x more likely to be affected than normal testes
can be complete, incomplete, or intermittent
CF of testicular torsion
sudden onset of severe testicular pain
N&V
USF of testicular torsion
hypoechoic and enlarged after 4-6 hrs
decreased vascularity when compared to asymptomatic side
early stages: may appear normal
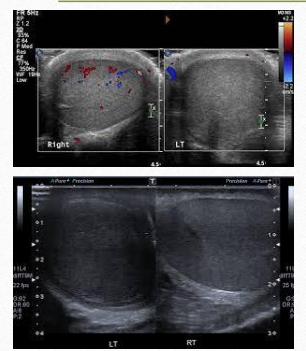
torsion
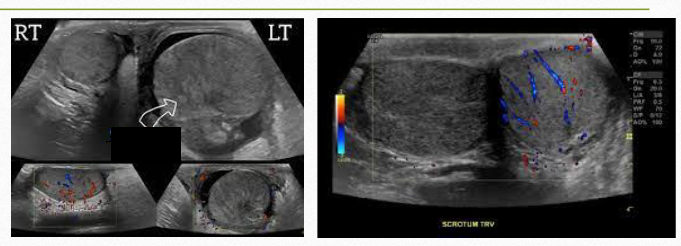
testicular torsion
what appears sonographically similar to an epididymal cyst?
spermatocele
Epididymal cyst:
small, clear cysts that contain serous fluid
can be found anywhere w/in the epididymis
Spermatocele:
cystic dilations of the efferent ducts of the epididymis
almost always located in the epididymal head.
sono appearance of spermatocele/ cyst
cyst: simple fluid filled structures, thin walls, post. enhancement.
spermato: simple cyst or multilocular cystic collection, containing internal echoes.
CF of spermatocele vs cyst:
palpable mass in upper region of scrotal sac unrelated to testicles.
usually painless
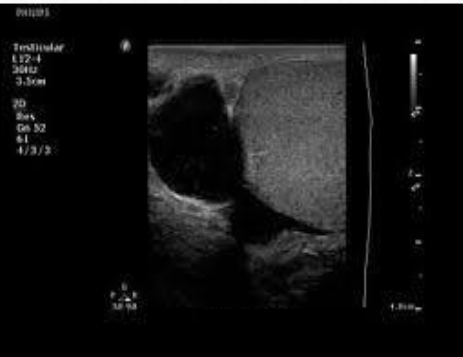
spermatocele/ cyst
testicular abscess
Usually, it is secondary to untreated infection, and will require surgical intervention/drainage
differential dx for testicular abscess:
complex hydrocele, cystic teratoma, Fournier’s Gangrene, Mass
CF testicular abscess
pain, fever, N & V
swelling and redness
^ WBCs
USF testicular abscess
round/oval mass w/ irregular shaggy borders, anechoic or mixed, with or without enhancement
may have “ring of fire” sign
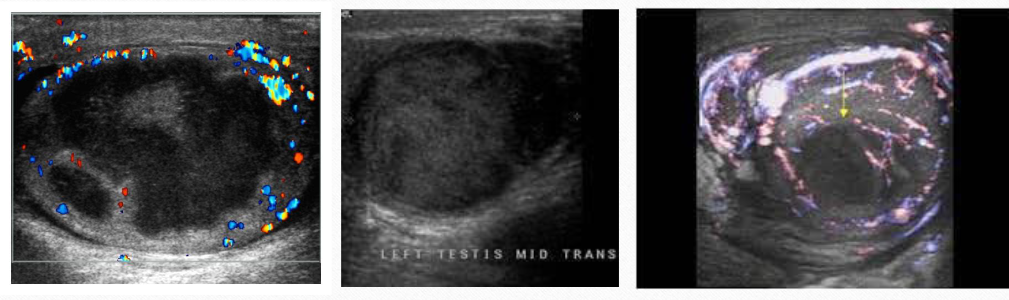
testicular abscess
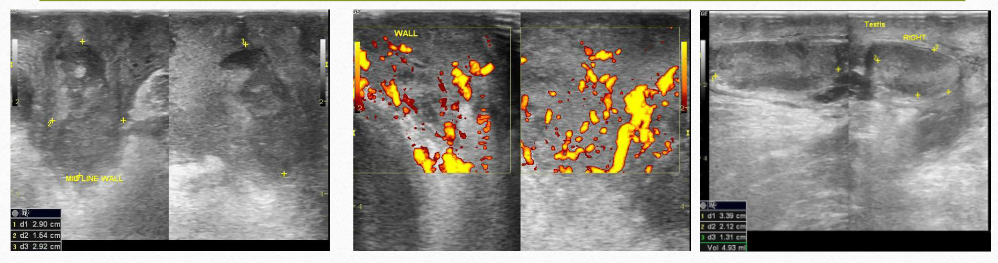
scrotal abscess
varicoceles:
abnormal dilation of the veins of the pampiniform plexus
usually caused by incompetent valves w/in spermatic vein
most common on left side due to angle of spermatic vein and left renal vein.
impaired fertility
Varicoceles CF
palpable tubular areas
infertility
Varicoceles USF
extratesticular fluid filled tubular structures
increased vascularity w/ val salva
measures > 2mm diameter
scan upright to increase visibility
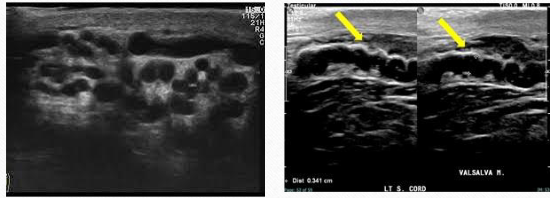
varicocele
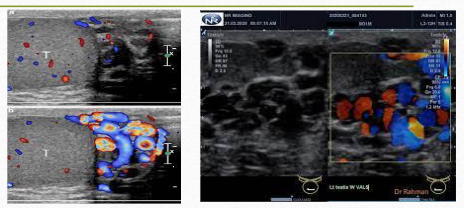
varicocele w/ vascularity shown
Dilated Rete Testis
dilated tubules, not vessels
USF of dilated rete testis
small tubular structures seen near the mediastinum testes.
No color/ doppler
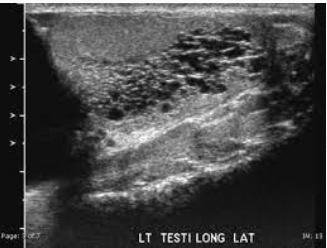
dilated rete testis
Scrotal Hernia
occurs when bowel, omentum, or other structures herniate into the scrotum
CF scrotal hernia
pain usually after a lifting injury
USF scrotal hernia
peristalsis from the bowel
bowel will appear both echogenic and anechoic
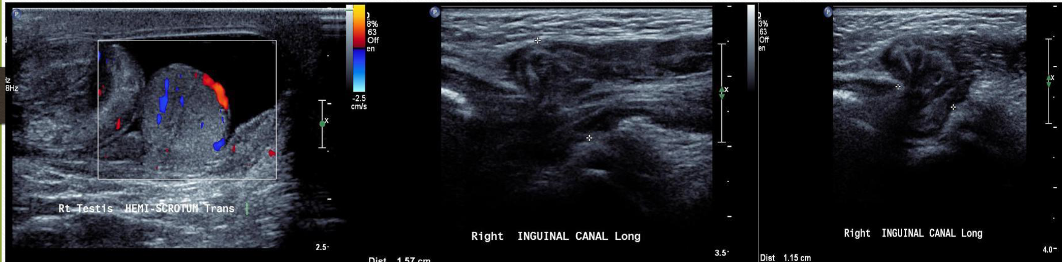
hernia
Germ cell tumor
highly malignant
most intratesticular masses are cancerous
extratesticular are mostly benign
types of germ cell tumors
seminoma, embryonal, teratocarcinoma
Labs with germ cell tumor
Elevated HCG, elevated AFP
Seminoma
most common type of germ cell tumor
ages 30-40
most favorable prognosis
seminoma USF
solid/homogeneous and hypoechoic with smooth well defined borders
embryonal cell tumor
second most common germ cell tumor
more aggressive than seminoma
yolk sac tumor is a form and most common in infants
USF embryonal cell tumor
heterogenous, hypoechoic, irregular borders, may contain calcifications
CF embryonal cell tumor
palpable mass
microlithiasis
uncommon condition characterized by tiny calcifications within the testis
usually bilateral
USF microlithiasis
multiple tiny echogenic foci throughout the testicle
with or without shadowing
“speckling”
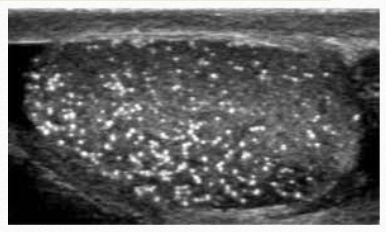
microlithiasis
lymphoma USF
enlarged testicles w/ diffuse or focal areas of decreased echogenicity
appears patchy
CF lymphoma
mass that may or may not be palpable
weight loss, anorexia, weakness
choriocarcinoma
less common
highly malignant
metastasizes rapidly
USF choriocarcinoma
complex, irregular borders,no calcifications
labs associated with choriocarcinoma
elevated HCG and AFP
teratoma
mostly benign in children
usually malignant in adults
second most common in infants and children
USF teratoma
Complex appearance and dense focal areas w/ shadowing
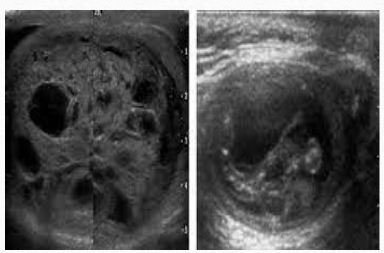
teratoma
BPH (benign prostatic hypertrophy)
common in older men
bladder outlet obstruction & increased resistance to urine flow
enlarged prostate constricts the urethra
occurs in the transition zone
bph usf
enlarged homogeneous prostate
transitional zone
prostattitis
acute: hypoechoic mass, may look cystic, thick walls, septations
chronic: heterogeneous with areas of increased echogenicity, enlarged venous plexus and seminal vesicles, may have thickened bladder neck
occurs in peripheral zone
CF prostatitis
acute: sudden fever, chills, voiding discomfort, pain in lower back, perineum, and rectum. increased vascularity
chronic: may be same as acute. may also have urinary frequency, dysuria, urgency and hematospermia
labs associated w/ prostate
PSA- prostate specific antigen
should be less than 10.
greater than 10 is suspicious
PSA density: divide PSA by volume of the gland
adenocarcinoma
most common malignant tumor of the prostate
located in the peripheral zone
elevated PSA and phosphatase
sono appearance: variable but usually seen as a hypoechoic area
the ejaculatory ducts descend inferiorly through the ______ portion of the gland and open into the _______ near the verumontanum
posterior, prostatic urethra
what structure lies anterior to the prostate?
Bladder