SCI112 Quest #1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is meant by "the environment"?
a sum of all the conditions surrounding us that influence life.
What is the difference between the terms "biotic" and "abiotic"?
Biotic: the living part of the earth
Abiotic: the nonliving part of the earth
What components make up an ecosystem?
The biotic & abiotic components
How are biological indicators used in environmental science?
Used to describe the current state of the environment.
What are the three forms of biological diversity?
Genetic diversity, species diversity, ecosystem diversity
Environmental scientists monitor natural systems for signs of _________.
Stress
What is the relationship between carbon dioxide and temperature?
Directly proportional
Another environmental indicator is ___________ depletion.
RESOURCE depletion
Sustainability
The practice of living on Earth in a way that allows humans to use resources without depriving future generations of those resources.
In order to live sustainably, environmental systems must not be damaged beyond their ability to ____________.
ability to RECOVER
What is one of the unique challenges of environmental science?
There is no "control" planet with which to compare the Earth. This means there is a lack of "baseline" data.
Ecological Footprint.
A measure of how much a person consumes, expressed in area of land.
A ________hypothesis is a statement that can be proved wrong.
NULL hypothesis
What is the first step of the scientific method?
Observations and questions
Define accuracy in measurements.
How close a measured value is to the actual or true value
Define precision in measurements.
How close the repeated measurements are to one another
What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
An atom is the basic building block of all matter. It is the smallest particle that can contain the chemical properties of an element. = smallest part of a matter
Molecules are particles containing more than one atom.
What is the pH difference between an acid and a base?
Acid: less than 7
Base: greater than 7
What value starts the pH scale and what value ends the pH scale?
Starts at 0, ends at 14
A water molecule has the unique property of ____________ due to its __________
COHESION OF THE MOLECULES
POLARITY
What are the four unique properties of water that support life?
Surface tension
Capillary action
Boiling and Freezing
Dissolving ability
A nucleus contains...
Protons & neutrons
Energy is the ability to do _____________.
WORK
First Law of Thermodynamics.
Just as matter can neither be created nor destroyed, energy is neither created nor destroyed.
It can only be converted from one form to another
Second Law of Thermodynamics
When energy is transformed, the quantity of energy remains the same, but its ability to do work diminishes
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
Why does ice float on water?
Because solid water (aka ice) is less dense than liquid water.
Greenhouse Gases
Naturally occurring atmosphere as that trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming
Global Warming
Global warming "refers to the recent and ongoing rise in global average temperatures near the Earth's surface. It is caused mostly by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere"
Climate Change
Climate change "refers to any significant change in the measures of climate lasting for an extended period of time...changes in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns" etc.
What are the Anthropogenic sources of CO2?
Coal
Oil
Natural gas
What is the evidence for climate change?
Global temperature rise
Glacial retreat and ice loss
Sea level rise
Extreme weather events
What is an ecosystem?
A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
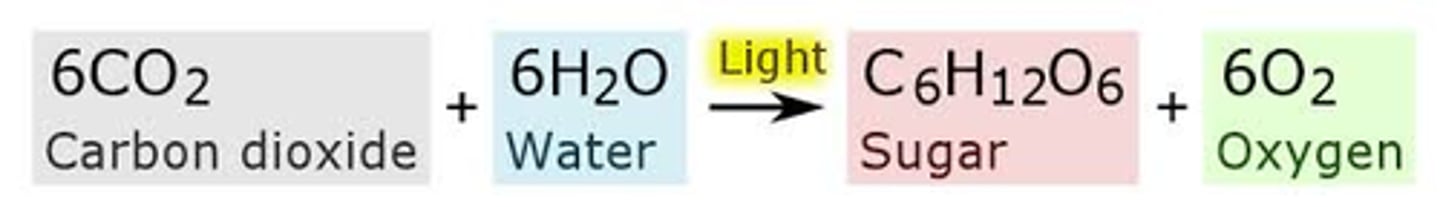
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
Solar energy + 6H2O +6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Primary Producer
aka Autotrophs
Produce usable energy through photosynthesis
Why are primary producers important in ecosystems?
Primary producers store energy in forms that make it available to other organisms that eat them, and are therefore essential to the flow of energy through the biosphere.
Give an example of a primary consumer.
Rabbits, zebra
What is a secondary consumer?
aka Heterotrophs
Obtain energy by consuming other organisms
Explain the distinction between an autotroph and a heterotroph.
Autotrophs are producers who prepare their own food.
Heterotrophs are consumers who depend on other sources for their food
Why is photosynthesis such an important process for ecosystems and the entire biosphere?
It provides energy for nearly all ecosystems. By transforming light energy into chemical energy, photosynthesis provides the energy used by organisms, whether those organisms are plants, grasshoppers, wolves, or fungi.
How efficiently is energy transferred between trophic levels in an ecosystem?
Only about 10% of energy is transferred, 90% is lost between each level
What are dominant elements (including macronutrients) in life forms?
The elements N, K, Mg, Ca, and S are termed macronutrients.
What are the 4 cycles we talked about?
Hydrologic Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
Carbon Cycle
Phosphorus Cycle
What is the difference between resistance and resilience in an ecosystem?
Resistance: A measure of how much a disturbance can affect the flows of energy and matter.
Resilience: The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance.
List the five main steps in Natural selection.
Individuals produce an excess of offspring
Not all offspring can survive
Individuals differ in their traits
Differences in traits can be passed on from parents to offspring
Differences in traits are associated with differences in the ability to survive and reproduce
List the four random processes involved in natural selection.
Mutations
Genetic drift
Bottleneck effect
Founders effect
What is a mutation? How does it affect evolution?
A random change in the genetic code
Effects evolution because they add to the genetic variation of a population
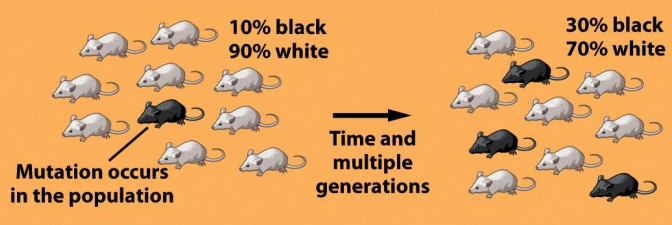
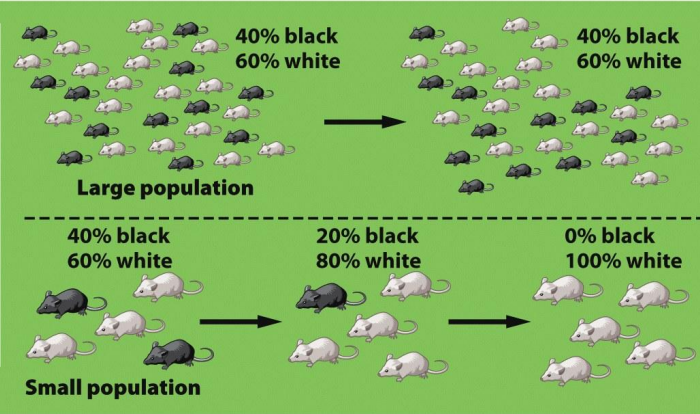
Genetic Drift
A random change in allele frequencies in a population over time, often due to chance events. This can lead to reduced genetic variation and can significantly impact the evolution of a population.
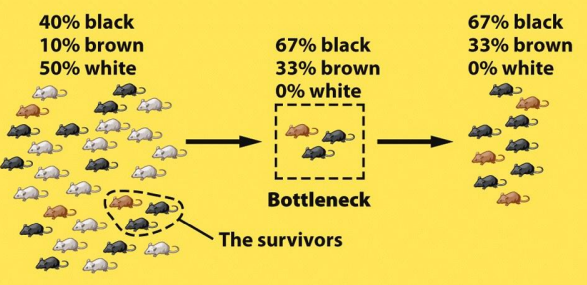
Bottleneck Effect
A sharp reduction in population size that results in a loss of genetic diversity due to environmental events or human activities.
Founders Effect
When a small group of individuals establishes a new population, there is a reduced genetic variability and potential differences in allele frequencies compared to the original population.
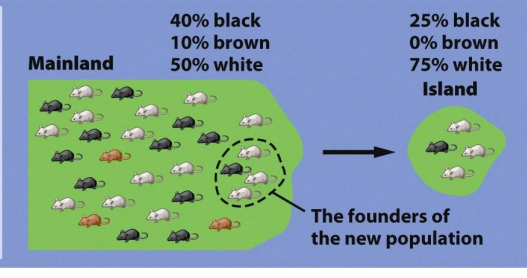
What factors determine the rate of evolution of a species?
The rate of environmental change
The amount of genetic variation in the species
The size of the population involved
How fast the species reproduces
Define a density dependent factor
Cause a population's growth rate to change (typically decrease) with increasing population density.
Define a density independent factor
affect growth rate independent of population density.
Ecosystem Diversity
Variety of ecosystems in a given region.
Species Diversity
The number of different species in a region or habitat
Genetic Diversity
The range of different inherited traits within a species
What is the difference between species richness and species evenness?
Species richness: The number of different species within a given area
Species evenness: Measurement of the abundance of species
What is the simplest and most common measure of biodiversity?
Simpson’s Diversity Index
What values represent low and high diversity in Simpson's diversity index?
Closer to 0 = low
Closer to 1 = high
What takes Simpson's diversity index into account?
Species richness and species evenness
Genetic drift states that a change in the genetic composition of a population over time happens as a result of __________ __________
Random mating
What factors determine the rate of evolution of a species?
Natural selection, mutation, genetic drift, gene flow
What are dominant elements (including macronutrients) in life forms?
The elements N, K, Mg, Ca, and S are termed macronutrients.
What are the 4 cycles we talked about?
Hydrologic Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
Carbon Cycle
Phosphorus Cycle
What is the difference between resistance and resilience in an ecosystem?
Resistance: A measure of how much a disturbance can affect the flows of energy and matter.
Resilience: The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance.
Humans live in what portion of the atmosphere?
Troposphere