TCA Cycle
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Stage 1 of Cellular Respiration
oxidation of fuels to acetyl-CoA
generates ATP, NADH, FADH2
Stage 2 of Cellular Respiration
oxidation of acetyl groups to CO2 in the citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, Krebs cycle)
nearly universal pathway
generates NADH, FADH2, and one GTP
Stage 3 of Cellular Respiration
electron transfer chain and oxidative phosphorylation
generates the vast majority of ATP from catabolism
Coenzyme A (CoA-SH)
coenzyme A has a reactive thiol (–SH) group that is critical to its role as an acyl carrier
– the –SH group forms a thioester with acetate in acetyl-CoA
Pyruvate is converted into ____ by process of _______
(acetyl-coA) (oxidation)
pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex = highly ordered cluster of enzymes and cofactors that oxidizes pyruvate in the mitochondrial matrix to acetyl-CoA and CO2
– the series of chemical intermediates remain bound to the enzyme subunits
– regulation results in precisely regulated flux
PDH Complex (function, reactants, and products)
Catalyzes an Oxidative Decarboxylation
An irreversible oxidation process in which the carboxyl group is removed, forming CO2
Procuces CO2, NADH,
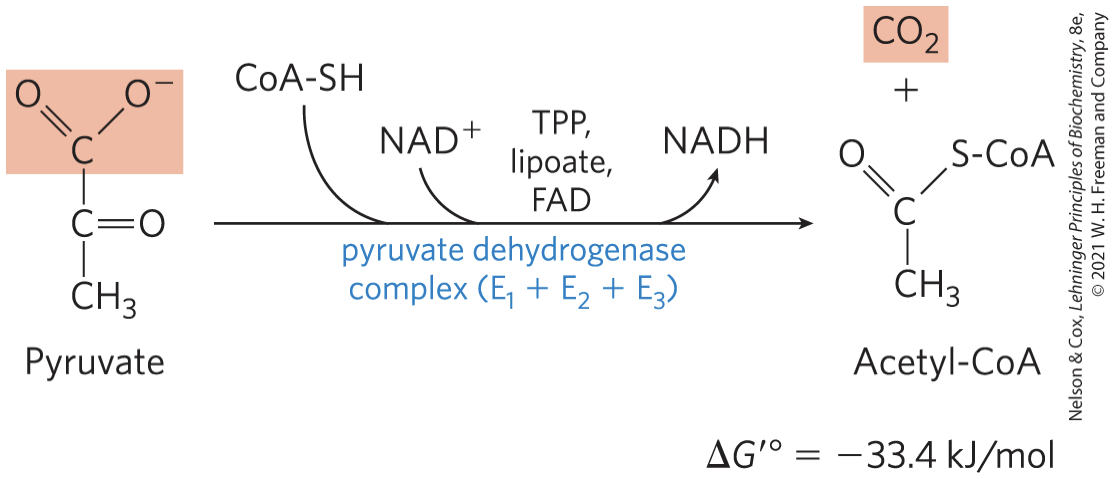
PDH Complex Employs Three Enzymes
and Five Coenzymes to Oxidize Pyruvate
three enzymes:
– pyruvate dehydrogenase, E1
– dihydrolipoyl transacetylase, E2
– dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, E3
• five coenzymes:
– thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
– lipoate
– coenzyme A (CoA, CoA-SH)
– flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
– nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
PDH Complex Channels its Intermediates through ______ (number) Reactions
Five
Chemical Logic of the Citric Acid Cycle
• each step of the cycle involves either:
– an energy-conserving oxidation
– placing functional groups in position to facilitate
oxidation or oxidative decarboxylation
The Citric Acid Cycle Has _____ Steps
Eight
Net products of TCA cycle
3 NADH, 1 FADH₂, 1 GTP (or ATP), and 2 CO₂
STEP 1 Formation of Citrate
citrate synthase catalyzes the condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate
– large, negative ∆G′° is needed because [oxaloacetate] is very low
![<p><strong>citrate synthase</strong> catalyzes the condensation of acetyl-CoA with <strong>oxaloacetate</strong> to form <strong>citrate</strong></p><p>– large, negative ∆G′° is needed because <strong>[oxaloacetate] is very low</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4f2c1e3b-929a-4b8e-8740-2e71bd6898eb.png)
STEP 2: Formation of Isocitrate
aconitase (aconitate hydratase) = catalyzes the reversible transformation of citrate to isocitrate through the intermediate cis- aconitate
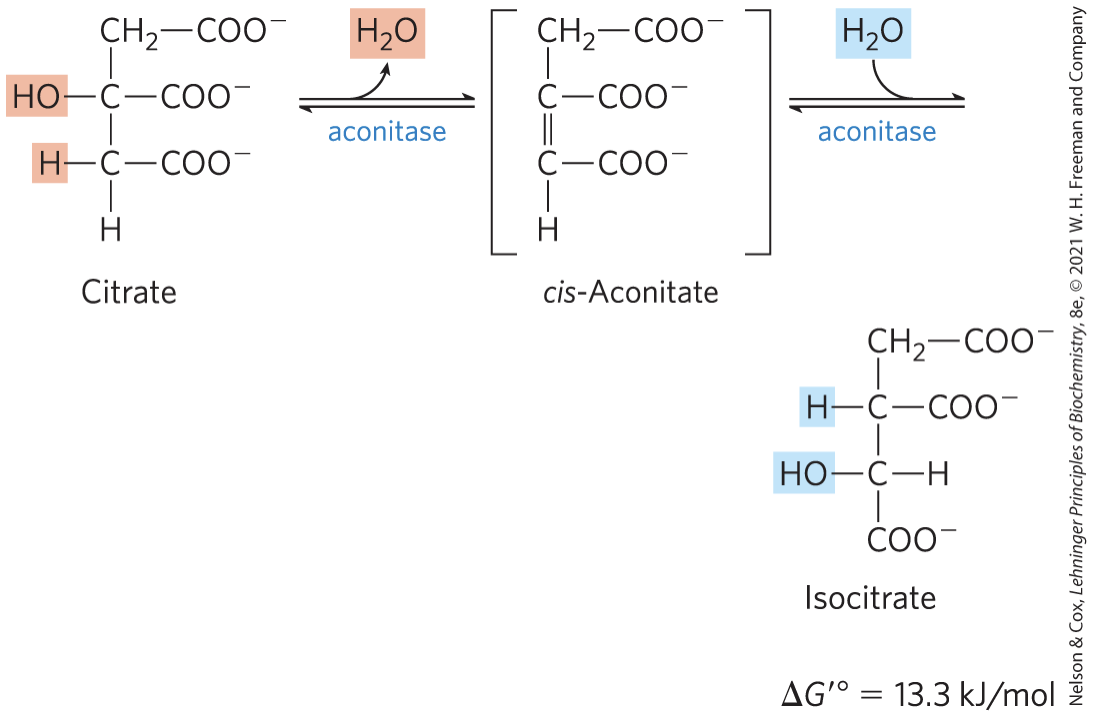
STEP 3: Oxidation of Isocitrate
isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidative
decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
– Mn2+ interacts with carbonyl group of the
oxalosuccinate and stabilizes transient enol
– specific isozymes for NADP+ (cytosolic and
mitochondrial) or NAD+ (mitochondrial)
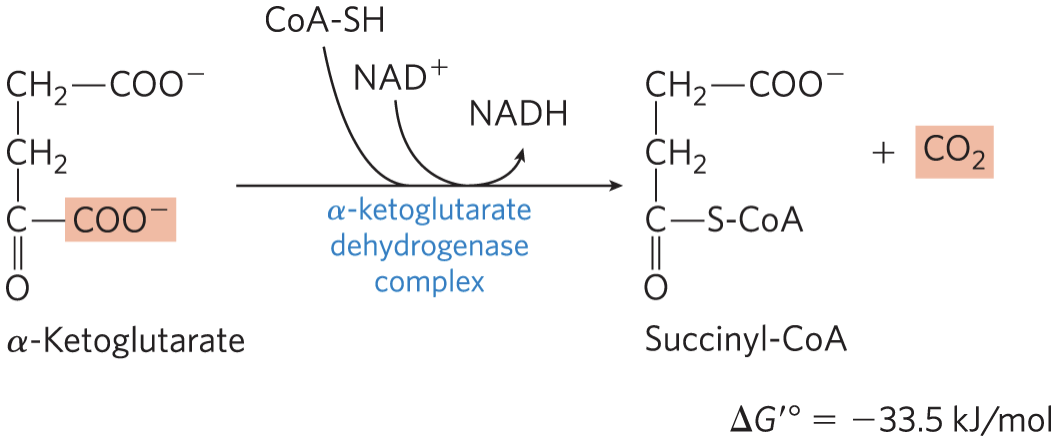
STEP 4: Oxidation of α-Ketoglutarate
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the
oxidative decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO2
– energy of oxidation is conserved in the thioester bond of succinyl-CoA
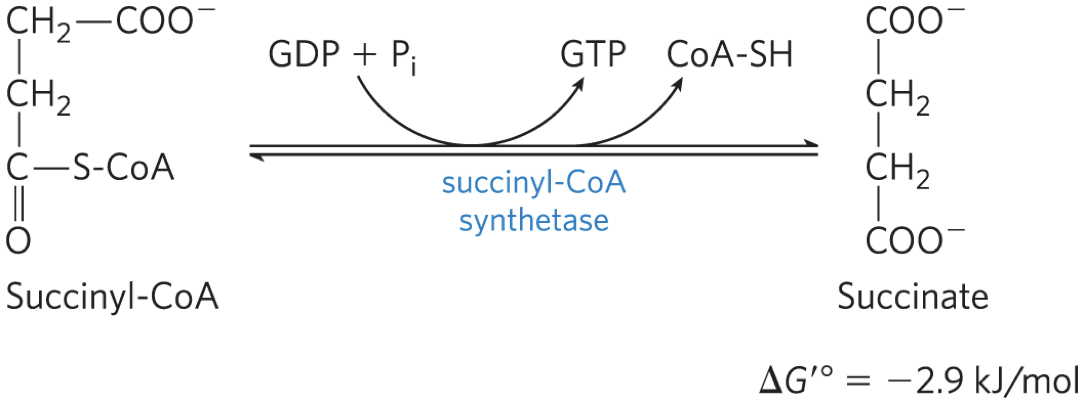
STEP 5: Conversion of Succinyl-CoA
succinyl-CoA synthetase (succinic thiokinase)
catalyzes the breakage of the thioester bond of succinyl-
CoA to form succinate
– energy released drives the synthesis of a
phosphoanhydride bond in either GTP or ATP (substrate
level phosphorylation)
STEP 6: Oxidation of Succinate
succinate dehydrogenase flavoprotein that catalyzes the
reversible oxidation of succinate to fumarate
– integral protein of the mitochondrial inner membrane in
eukaryotes
– contains three iron-sulfur clusters and covalently bound
FAD
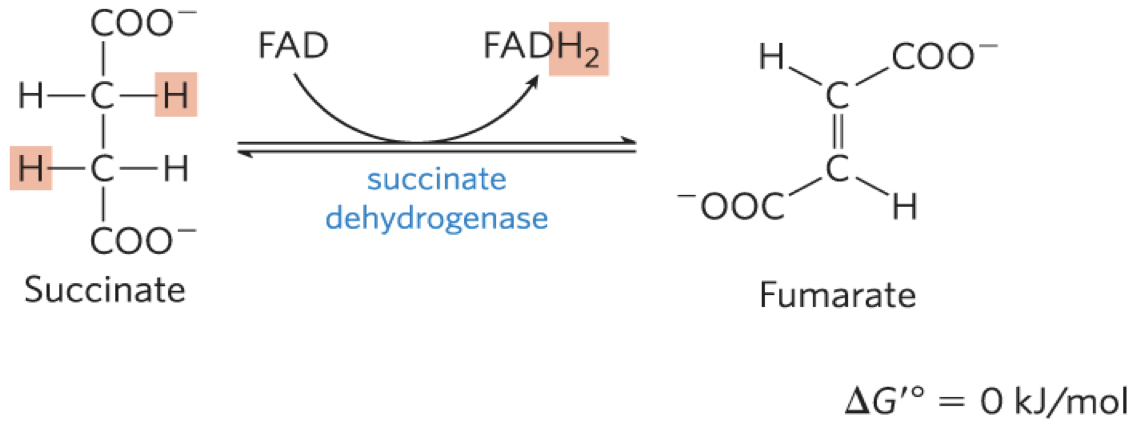
Step 7: Hydration of Fumarate
fumarase = catalyzes the reversible hydration of fumarate to L-malate
transition state is a carbanion
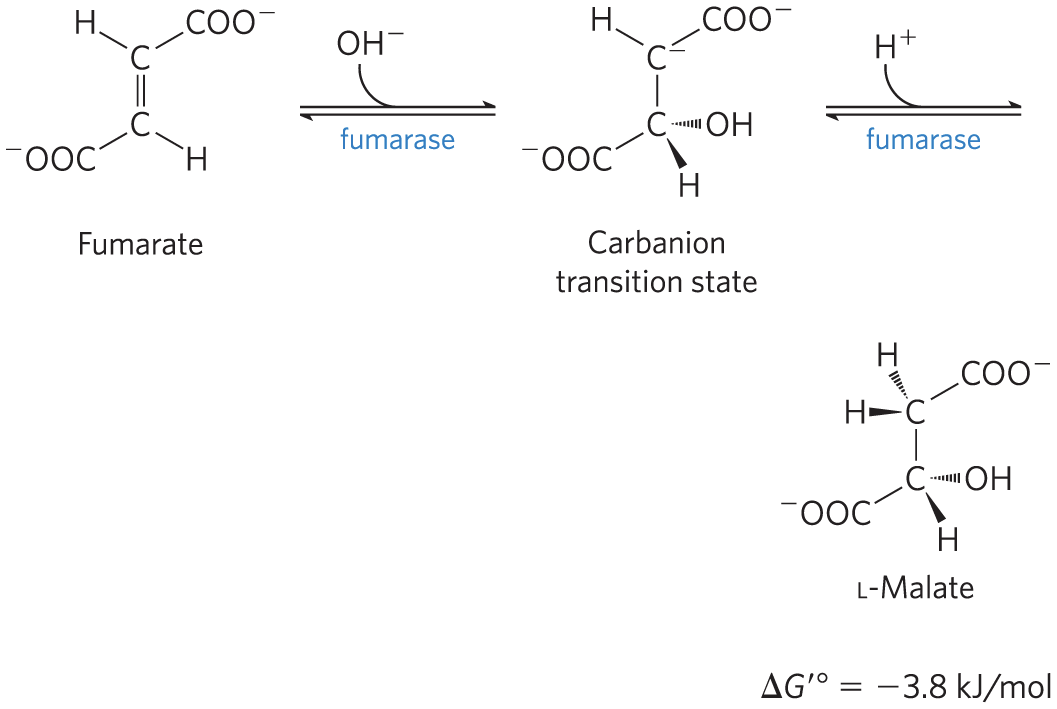
Step 8: Oxidation of Malate
L-malate dehydrogenase = catalyzes the oxidation of L-malate to oxaloacetate, coupled to the reduction of NAD+
low [oxaloacetate] pulls the reaction forward
regenerates oxaloacetate for citrate synthesis
![<p>L-malate dehydrogenase = catalyzes the oxidation of L-malate to <strong>oxaloacetate</strong>, coupled to the reduction of NAD+</p><p>low [oxaloacetate] pulls the reaction forward</p><p>regenerates oxaloacetate for citrate synthesis</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ae762ff6-2a00-4a37-b9e2-b9f32971db9c.png)
how much atp produced by nadh and fadh2
each NADH drives formation of ~2.5 ATP
each FADH2 drives formation of ~1.5 ATP
Citric Acid Cycle is (both)
amphibolic
anaplerotic reactions
chemical reactions that replenish intermediates
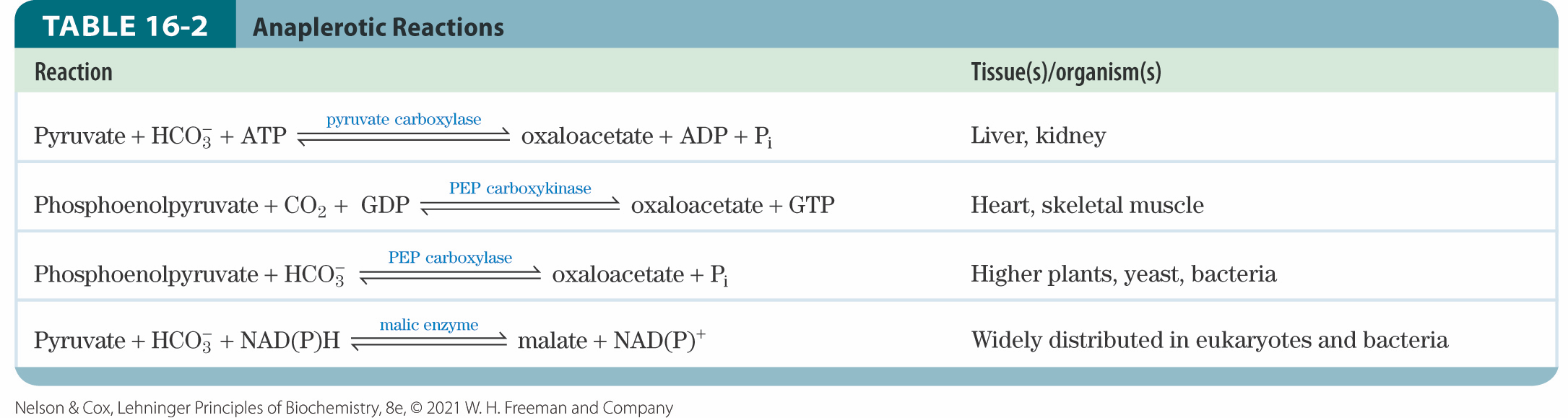
pyruvate carboxylase
catalyzes the reversible carboxylation of pyruvate by HCO3− to form oxaloacetate
most important anaplerotic reaction in mammalian liver, kidney, and brown adipose tissue
requires energy from ATP
allosterically activated by acetyl-CoA
Citric Acid Cycle Regulation points
PDH complex
citrate synthase
isocitrate dehydrogenase complex
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
PDH complex activity is turned off when
ample fatty acids and acetyl-CoA are available as fuel
[ATP]/[ADP] and [NADH]/[NAD+] ratios are high
PDH complex activity is turned on when
energy demands are high
the cell requires greater flux of acetyl-CoA into the citric acid cycle
PDH kinase
inhibits the PDH complex by phosphorylation
allosterically activated by products of the complex
inhibited by substrates of the complex
PDH phosphatase
reverses the inhibition by PDH kinase
Citric Acid Cycle regulation occurs at strongly exergonic steps catalyzed by
citrate synthase
isocitrate dehydrogenase complex
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
fluxes are affected by the concentrations of substrates and products
end products ATP and NADH are inhibitory
NAD+ and ADP are stimulatory
long-chain fatty acids are inhibitory