Chapter 10: Aerobic Respiration
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, ETC, ATP synthesis, matrix, outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, matrix, cristae junction, cristae, intracristal space
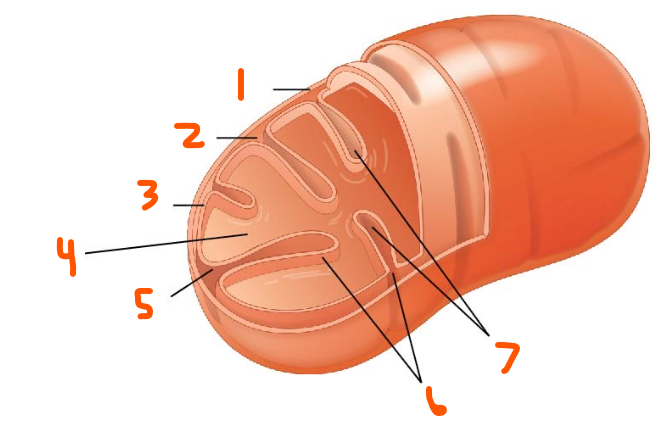
Mitochondria:
Where ___ ___, ___ ___ ___, ___, and ___ ___ are done
All happens in the ___
Structure:
___ ___
___ ___
___ ___
___
___ ___
___
___ ___
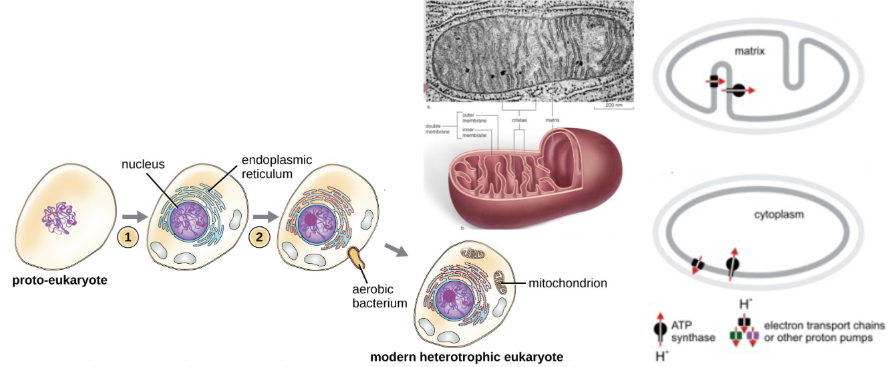
Lynn Margulis, G- bacteria, Hoffman, Avers
Endosymbiotic Theory:
Proposed by ___ ___
States that ___ ___ became mitochondria
Mitochondria Discovery:
By ___ and ___
38, NAD+, O2, 2, NAD+, lactate, ethanol
Respiration vs Fermentation:
Respiration:
Is the complete oxidation of glucose
Makes a max of ___ (#) ATP
___ is regenerated by e- transport
___ is the external e- acceptor
Fermentation:
Is the incomplete oxidation of glucose
Makes a max of ___ (#) ATP
___ is regenerated by pyruvate processing
Accumulates ___ and ___ wastes
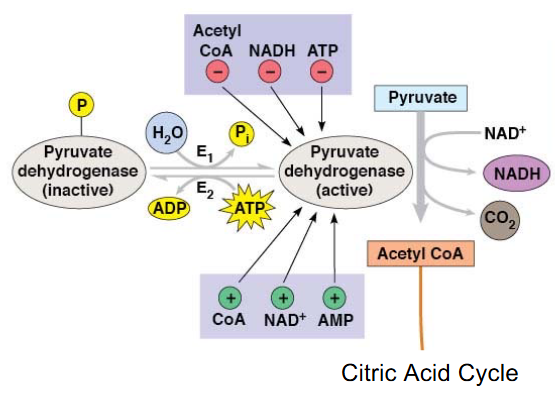
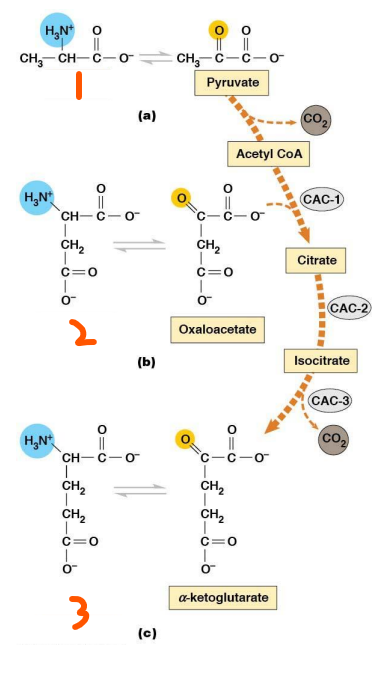
Acetyl CoA, CO2, NADH, pyruvate dehydrogenase, oxidative decarboxylation, phosphorylated, PDH kinase, ATP, dephosphorylated, PDH phosphatase, H2O
Pyruvate Processing:
Is the conversion of 2 pyruvate to 2 ___ and also makes 2 ___ and 2 ___ by the enzyme ___ ___ in a ___ ___ rxn
Enzyme is inactive when ___ by ___ ___ that requires ___ and active when ___ by ___ ___ with ___
Acetyl CoA, oxaloacetate, citrate, decarboxylation, 3, 4, oxidation, 3, 4, 6, 8, 5, oxaloacetate
TCA Overview:
Rxn 1 where ___ is added to ___ to make ___
___ rxns happen at rxn ___ and ___ to expel CO2
___ rxns happen at rxn ___, ___, ___, and ___ to make 3 NADH and 1 FADH2
ATP or GTP in animals is made at rxn ___ (#)
Finally, ___ is regenerated at rxn 8
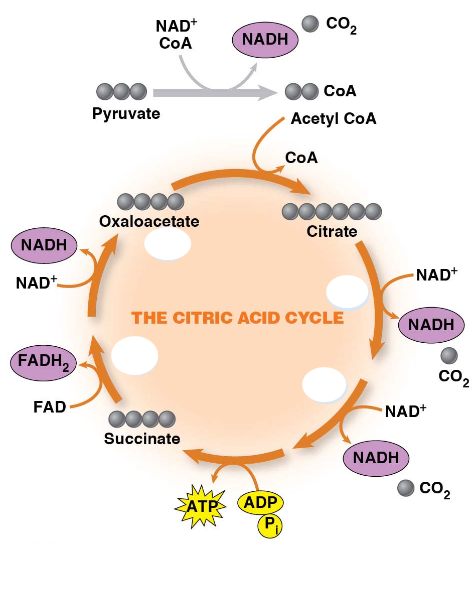
Citrate, isocitrate, a-ketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, succinate, fumarate, malate, oxaloacetate
TCA Intermediates:
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
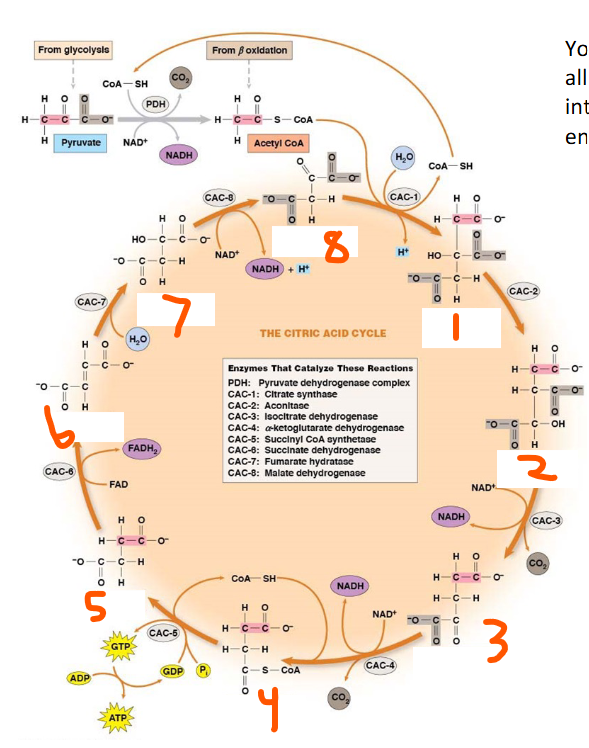
Citrate synthase, aconitase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinyl CoA synthetase, succinate dehydrogenase, fumarate hydratase, malate dehydrogenase
TCA Enzymes:
CAC-1: ___
CAC-2: ___
CAC-3: ___
CAC-4: ___
CAC-5: ___
CAC-6: ___
CAC-7: ___
CAC-8: ___
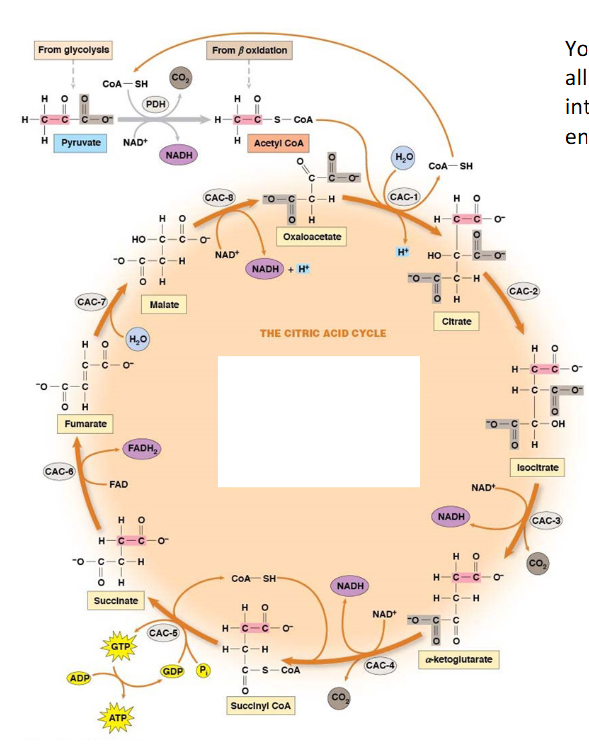
Review
TCA Allosteric Regulation:
idk
Acetyl CoA, NAD+, FAD, ADP, Pi, CO2, NADH, FADH2, CoA-SH, ATP
TCA Summary:
___ + 3 ___ + ___ + ___ + ___ → 2 ___ +3 ___ +___ + ___ + ___
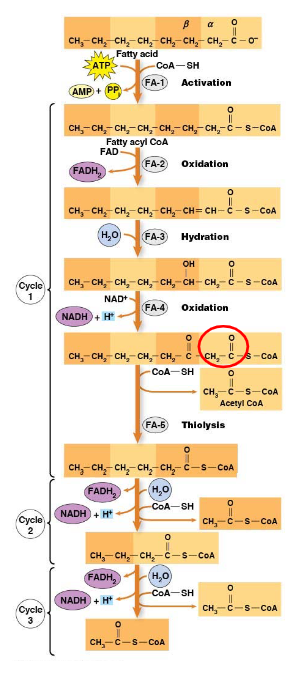
Glycerol, dihydroxyacetone phosphate, FA, CoA, fatty acyl CoA, beta-oxidation
Catabolism of Triacylglycerol:
Makes ___ that is then made to ___ ___
Also makes ___ that are linked to ___ to make ___ ___ ___ that are then degraded again by ___-___
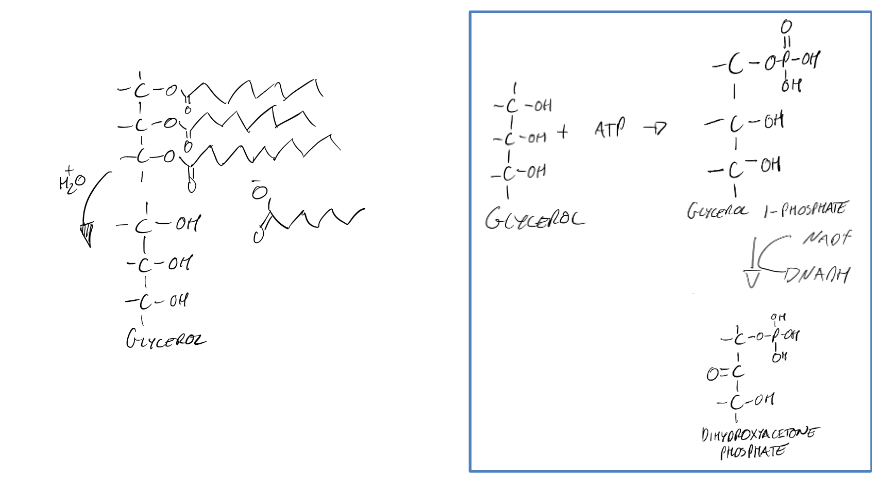
Mitochondria, peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, acetyl CoA, NADH, FADH2, 2 carbon, oxidation, hydration, reoxidation, thiolysis
Beta-Oxidation:
Happens in the ___ and ___
Plant subtypes of 2nd organelle are called ___
Makes ___, ___, and ___
1 cycle of beta-oxidation removes ___ (#) ___
4 Steps:
___
___
___
___
Alanine, aspartate, glutamate, TCA cycle
AA:
___ can be converted into pyruvate
___ can be converted into oxaloacetate
___ can be converted into a-ketoglutarate
These all can be fed into the ___ ___
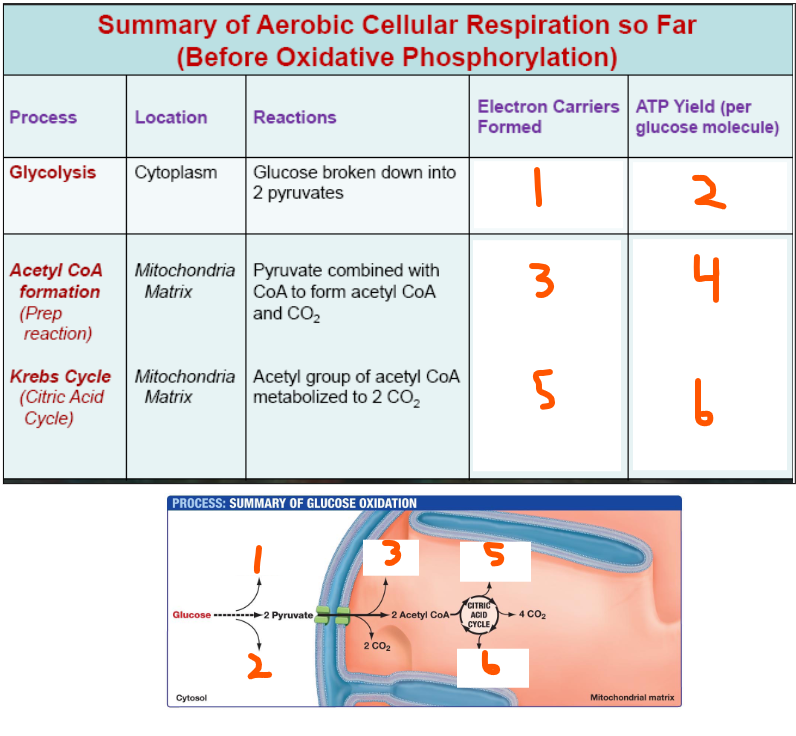
2 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 0 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
Summary of Aerobic Respiration - Oxidative Phosphorylation: (Assuming 2 of GA3P, Pyruvate, and Acetyl-CoA)
___ (#) ___
___ (#) ___
___ (#) ___
___ (#) ___
___ (#) ___ and ___ (#) ___
___ (#) ___
-52.4, -45.9
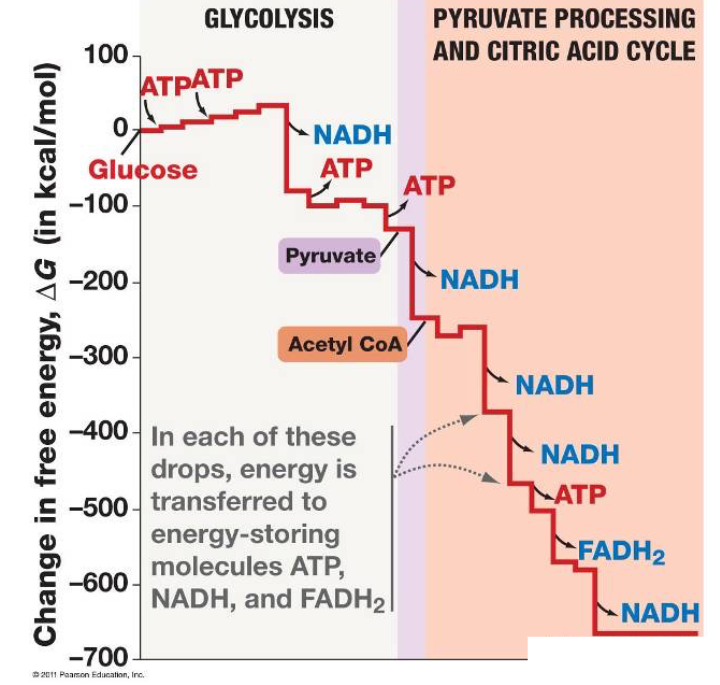
ETC Coenzyme Oxidation:
NADH + H+ + ½O2 → NAD+ + H2O
ΔG = ___ kcal/mol
FADH2 + ½O2 → FAD + H2O
ΔG = ___ kcal/mol
Flavoproteins, iron-sulfur proteins, cytochromes, copper cytochromes, coenzyme q, nonprotein, hydrophobic
5 Types of e- Carriers in Various ETCs:
___
___-___ ___
___
___ ___
___ ___
#5 is the only ___ type
All are ___
Oxidation, NADH, FADH2, high, low, H+ gradient
Redox in ETC:
___ rxn of ___ and ___ causes the molecules to go from a ___ energy state to a ___ energy state to fuel ___ ___
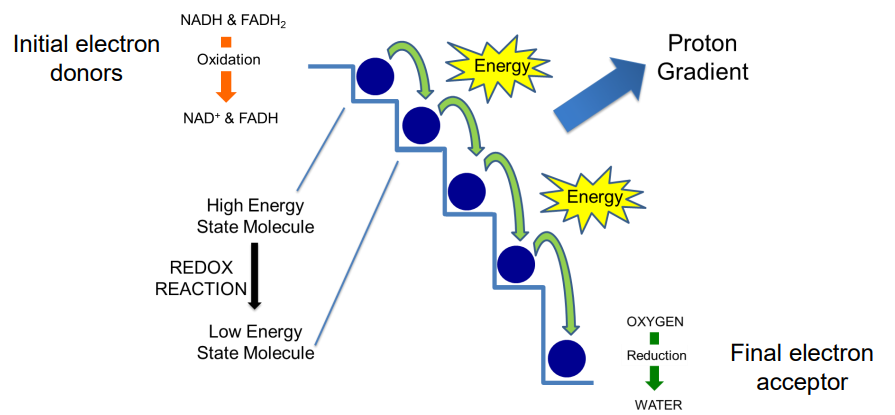
Standard reduction potential, V, e-, reduced, donor, oxidized, acceptor
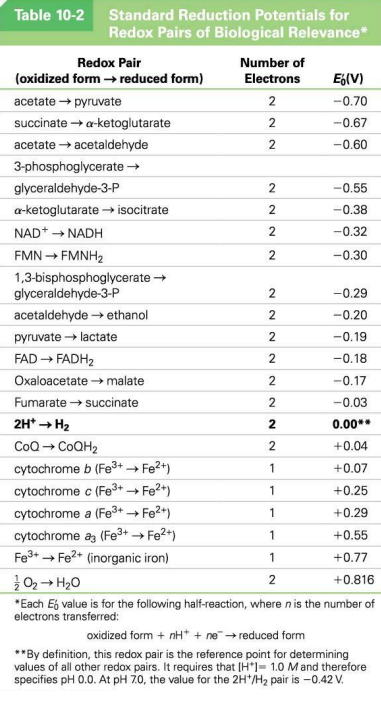
E’0:
Also called ___ ___ ___ measured in ___ and shows the affinity for ___
Redox pair with -E’0 means the ___ form is a good e- ___
Redox pair with +E’0 means the ___ form is a good e- ___
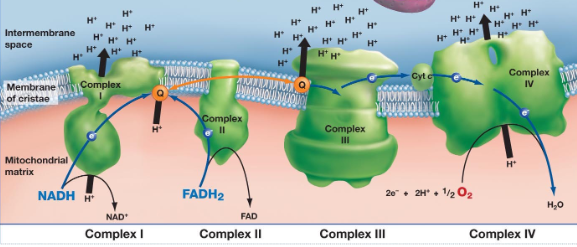
NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH dehydrogenase, succinate-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, succinate dehydrogenase, coenzyme Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase, cytochrome b/c, cytochrome c oxidase
Names of ETC Complexes:
Complex I: ___-___ ___ ___ or ___ ___
Complex II: ___-___ ___ ___ or ___ ___
Complex III: ___ ___-___ ___ ___ or ___ ___/___ complex
Complex IV: ___ ___ ___
NADH, flavin mononucleotide, Fe-S centers, coenzyme Q, succinate, flavin adenine dinucleotide, Fe-S centers, coenzyme Q, coenzyme Q, cytochrome b, Fe-S center, cytochrome c1, cytochrome c, cytochrome c, cytochrome a, cytochrome a3, Fe-Cu centers, O2
ETC Cofactors and e- Flow:
Complex I:
e- donor is ___ (1)
Cofactors: 1 ___ ___ (2) and 6-9 ___-___ ___ (3)
e- acceptor is ___ ___ (4)
Complex II:
e- donor is ___ (5)
Cofactors: 1 ___ ___ ___ (6) and 3 ___-___ ___ (7)
e- acceptor is ___ ___ (8)
Complex III:
e- donor is ___ ___ (9)
Cofactors: 2 ___ ___ (10), 1 ___-___ ___ (11), 1 ___ ___ (12)
e- acceptor is ___ (13)
Complex IV:
e- donor is ___ (13)
Cofactors: 1 ___ ___ (14), 1 ___ ___ (15), 2 ___-___ ___ (16)
e- acceptor is ___ (17)
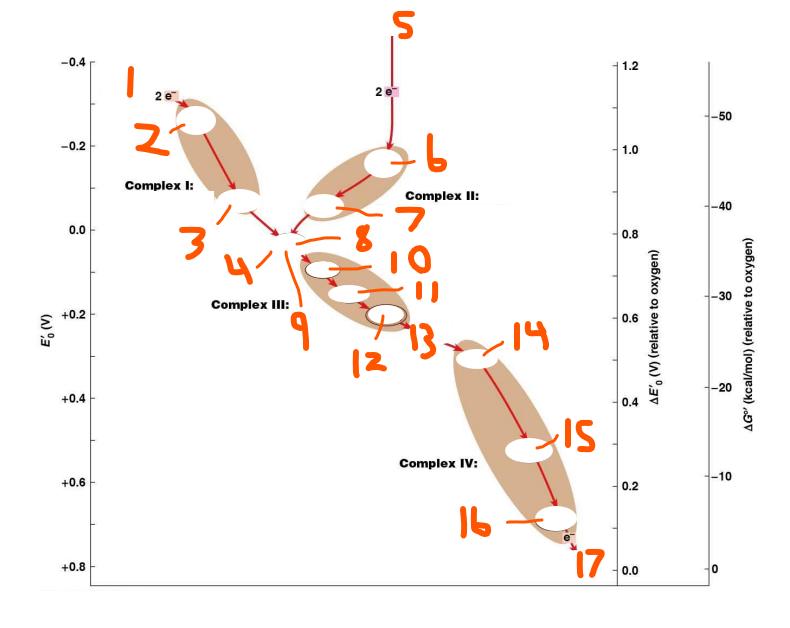
4, 0, 4, oxidation, coenzyme Q, 2
ETC H+ Transport:
Complex I: ___ (#) H+
Complex II: ___ (#) H+
Complex III: ___ (#) H+
Half from ___ rxn of ___ ___
Complex IV: ___ (#) H+
3, inner membrane, matrix, static, motor, 1 a, 2 b, 10 c, ionic, 1 delta, 3 alpha, 3 beta, 1 epsilon, gamma
ATP Synthase:
Takes ___ (#) H+ to make 1 ATP
Has a F0 component at the ___ ___ and F1 component at the ___
Each major component has ___ and ___ subcomponents
F0 static has ___ (#) ___ (1) subunit(s) that makes up the H+ channel and ___ (#) ___ (2) subunit(s) that links the other subunit to F1 component
F0 mobile has ___ (#) ___ (3) subunit(s) that make ___ bonds with subunit a and spin
F1 static has ___ (#) ___ (4) subunit(s) that anchor the catalytic site to the F0 b2 subunits and the catalytic hexagon of ___ (#) ___ and ___ (#) ___ (5)
F1 mobile has ___ (#) ___ (6) and ___ (7) subunits that anchor the F0 c subunits to the F1 catalytic site
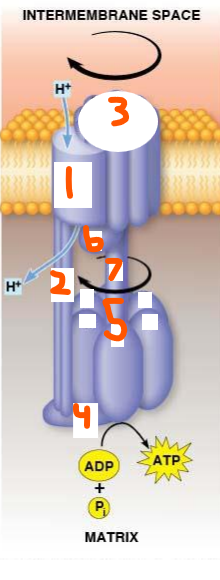
Beta, l, t, o, 120, gamma
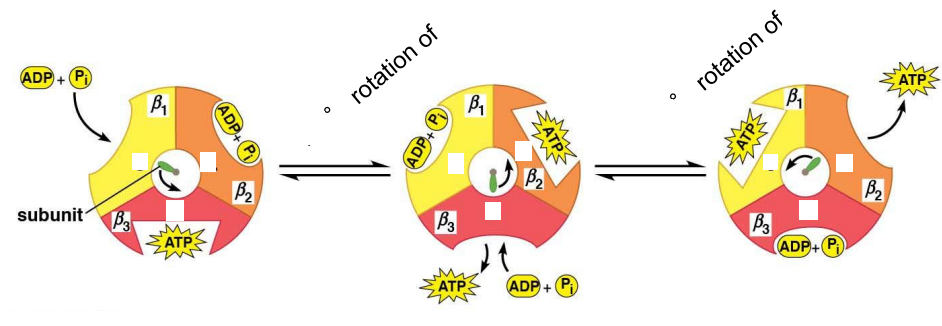
Binding Change Model for ATP Synthesis:
Shows how ___ subunits go through 3 different conformations
___ conformation where ADP and Pi are loosely bound
___ conformation where ADP and Pi are tightly bound to make ATP
___ conformation where it is open and has low affinity for substrates or products
Happens every ___° rotation of ___ subunit