BIODIVERSITY EVOLUTION
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
BIODIVERSITY
-Is the variety in:
species(species in diversity)
the genes they contain(genetic diversity)
ecosystems (ecological diversity)
ecosystem processes, such as energy flow and nutrient cycling (functional diversity)
OTHER TYPES OF DIVERSITY
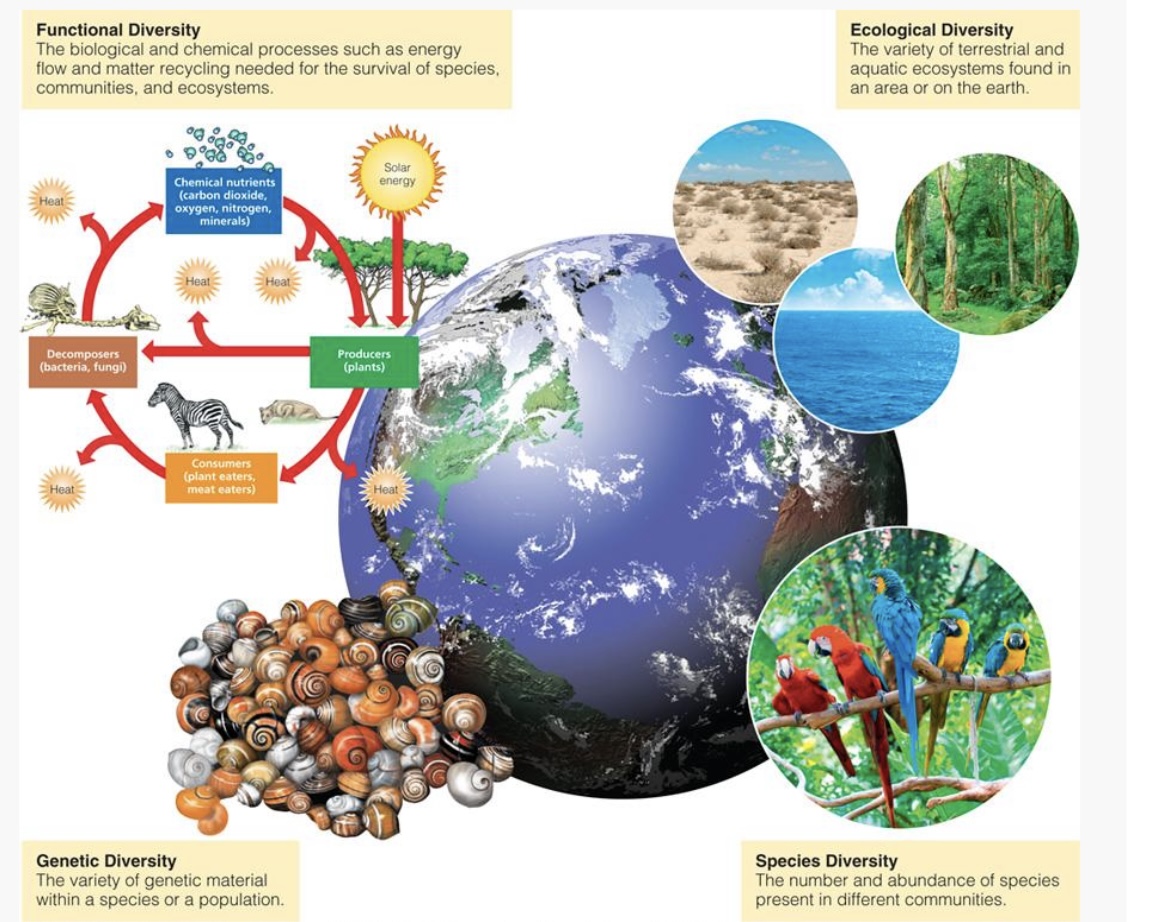
SPECIES
-Set of individuals that can mate and produce fertile offspring — every organism is a member of a certain species.
Competitive Service
-Desserts, grasslands, forests, mountains, oceans, lakes, rivers, and wetlands
4 IMPORTANT ROLES OF A SPECIES
Native
Nonnative
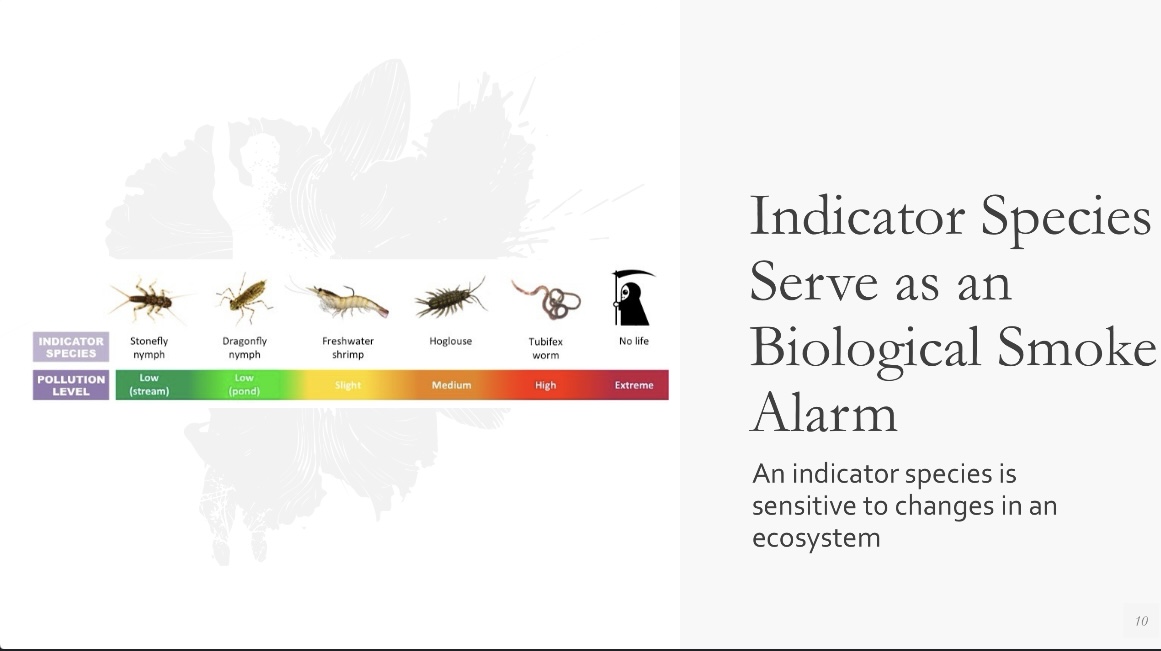
Indicator
Keystone
NATIVE SPECIES
-Live and thrive in a specific ecosystem.
NONNATIVE SPECIES
-Immigrate into, or are deliberately or accidentally introduced, into an ecosystem.
-Can threaten native species through competition for resources, reducing the number native species.
-Can spread rapidly if they find a favorable niche.
INDICATOR SPECIES SERVE AS AN BIOLOGICAL SMOKE ALARM
HOW DOES THE EARTH’S LIFE CHANGE OVER TIME?
Population evolution occurs through gene mutation
-explains how life on the earth changes over time due to changes in the genes pf populations.
-gives individuals genetic traits that enhance their ability to survive and produce offspring.
BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION BY NATURAL SELECTION EXPLAINS HOW LIFE CHANGES OVER TIME
Fossils reveal the history of life
Biological evolution
-the expression of genetic variation over time by succeeding generations (natural selection)
-through natural selection, species evolve over time from earlier ancestral ones.
-individuals with traits that increase their survivability are more likely to produce offspring and pass on these traits.
MUTATION ARE CHANGES IN GENETIC COMPOSITION (DNA)
-Some are random; others occur by exposure to radioactivity, ultraviolet radiation, and chemicals (mutagens).
-Genetic changes in reproductive cells are inherited by offspring(heritable traits).
COMMON MTYHS ABOUT EVOLUTION THROUGH NATURAL SELECTION
-“Survival of the fittest” means “survival of the strongest“.
-Evolution explains the origins of life
-Humans evolved from apes or monkeys
-Evolution by natural selection involves a grand plan of nature in which species are to be more perfectly adapted.
GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION
-Occurs when groups of the same population become physically isolated (by mountains, rivers, roads, or distance) from one another over time.
REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION
-Occurs when mutation and change by natural selection operate independently in the gene pool of geographically isolated populations.
WHAT FACTORS AFFECT BIODIVERSITY?
-As an environmental conditions change, biodiversity is determined by the balance between formation of new species and the extinction of existing species.
-Human activity has caused loss of biodiversity
by causing extinction of species
through degradation of habitats for development of new species.
HOW DO HUMANS AFFECT BIODIVERSITY?
-By contributing to the rise species through artificial selection
selectively breed or crossbreed between genetic variations of the same species.
-By using genetic engineering to quickly manipulate genes
alter segments of DNA for desired traits
transfer genes between different species that would not interbreed in nature.
EXTINCT ANIMALS
-Dinosaur
-Saber-toothed cat
-Dodo
-Tasmanian tiger
-Woolly mammoth
-Passenger pigeon
-Ground sloth
-Golden toad
BACKGROUND EXTINCTION
-Slower rate that existed before human population became significant.
MASS EXTINCTION
-Significant rise in extinction over background extinction rate.