6.4 Heat Capacity & Calorimetry/ AP CHEM
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
heat capacity
energy required/ taken to raise the temp of an object by 1C
energy released when an object is reduced by 1C
diff substances have diff “heat capacity constants”, varied by structure, composition, amount (larger amount needs more heat)
specific heat capacity
depends on
type of substance (bond strength, molecular structure, etc)
grams
molar heat capacity
depends on
quantity
mole
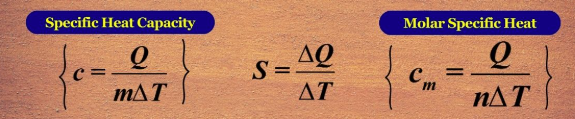
as Cp/cp goes up, more temp (q) can be absorbed; temp goes up by 1C
calorimetry
heat transfer technique
assumes no loss of heat to container
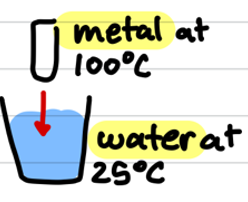
qmetal = -qH2O
qmetal (loosing heat)
-qH2O (gaining heat)
heat is transferred
temperature refers to
measure of average thermal energy of a system
heat refers to
energy transferred from a system to its surroundings / (surroundings to system)