Lab 9: Brain and Special Senses
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
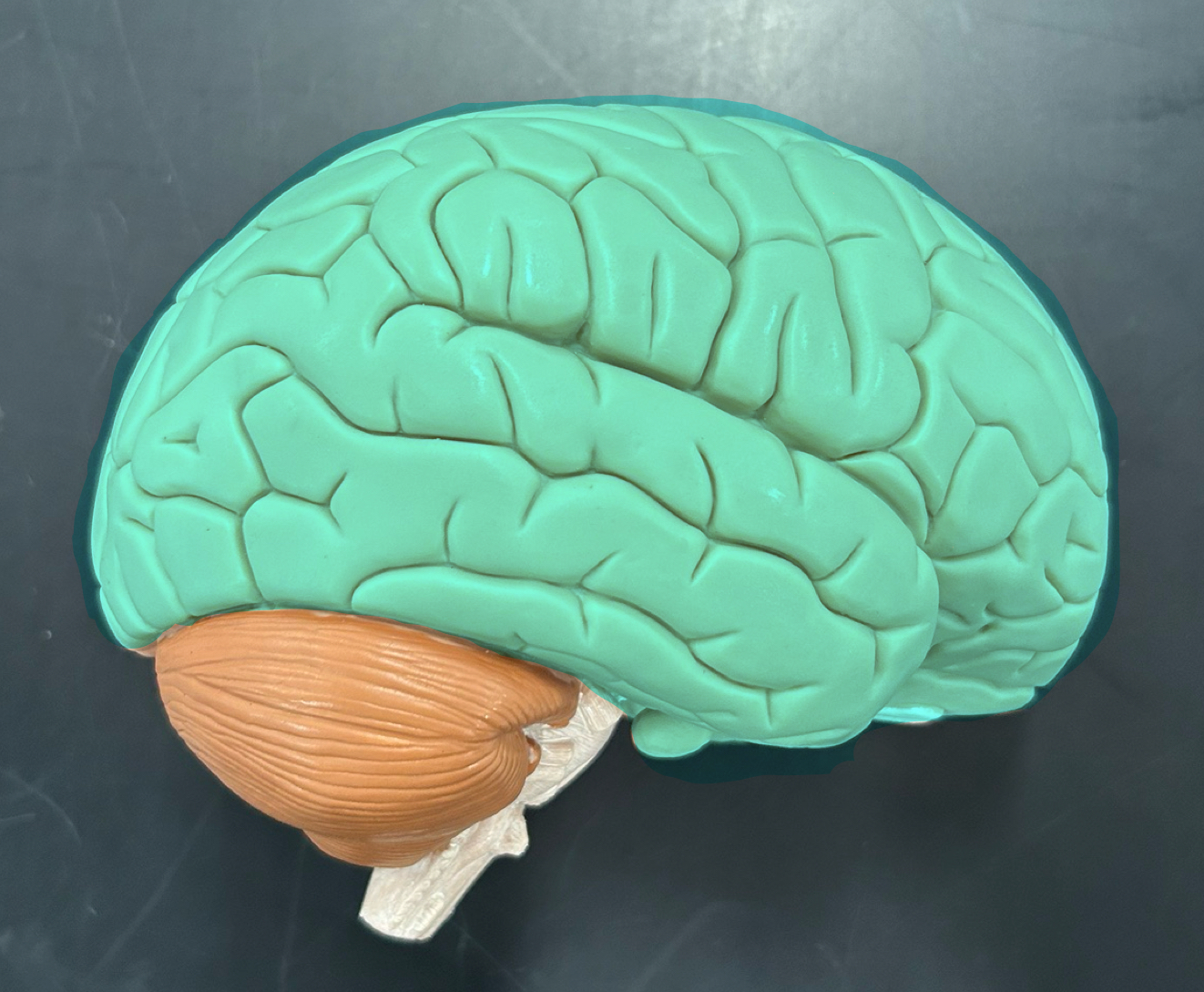
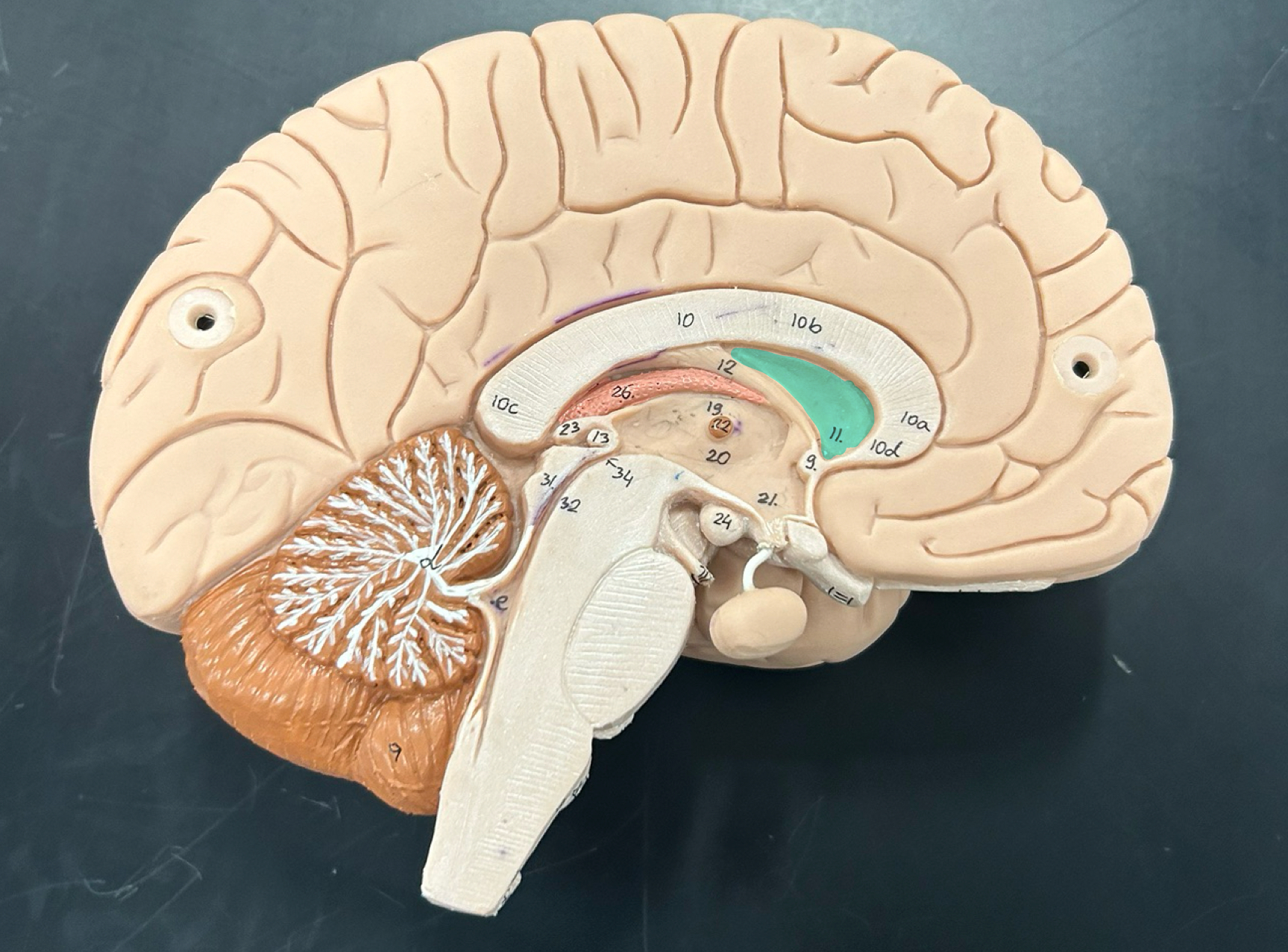
Cerebrum: Controls voluntary movements, sensory perception, reasoning, learning, emotions, and memory. It's the largest part of the brain.
*
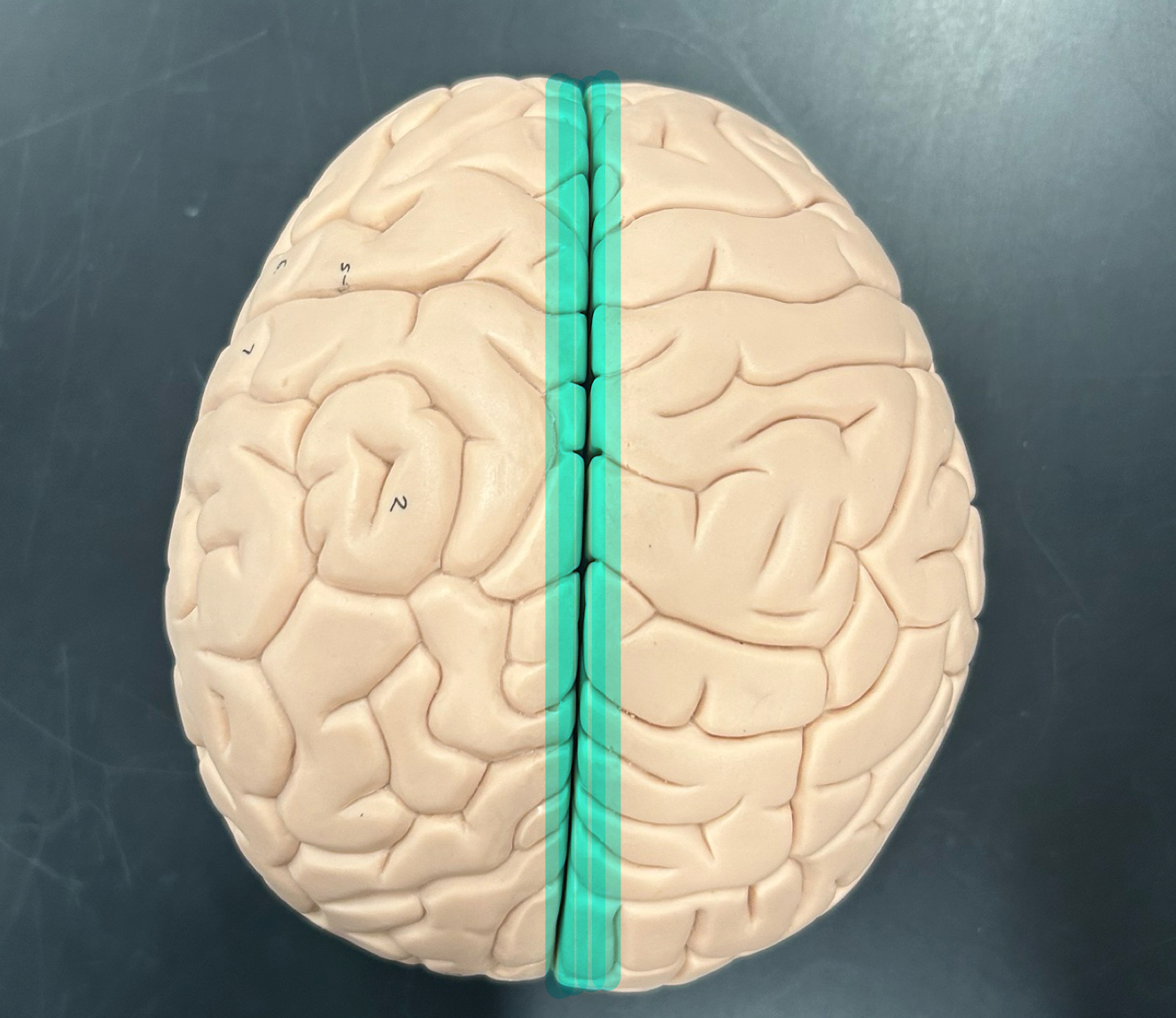
Longitudinal fissure
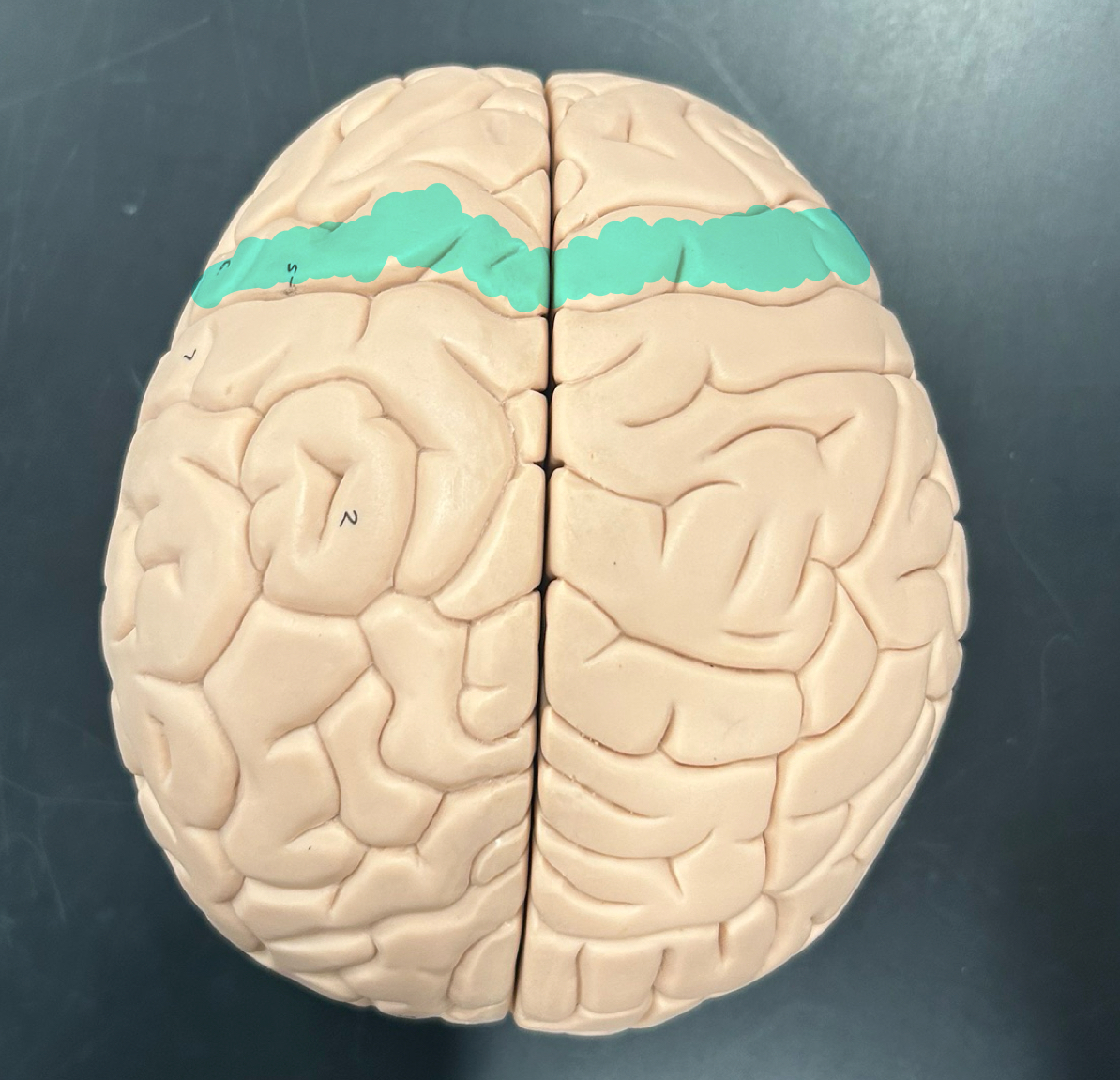
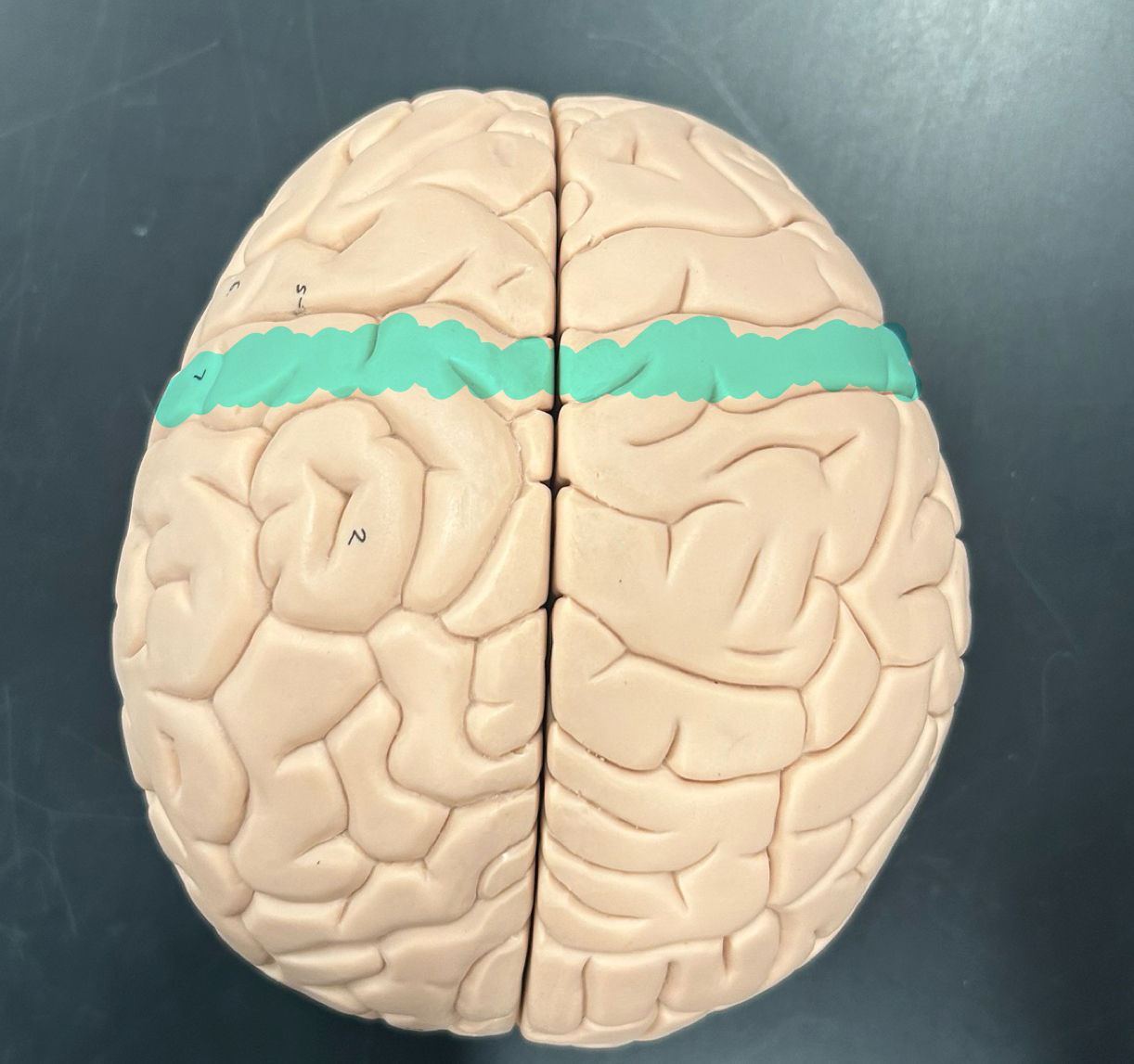
Central sulcus

Precentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
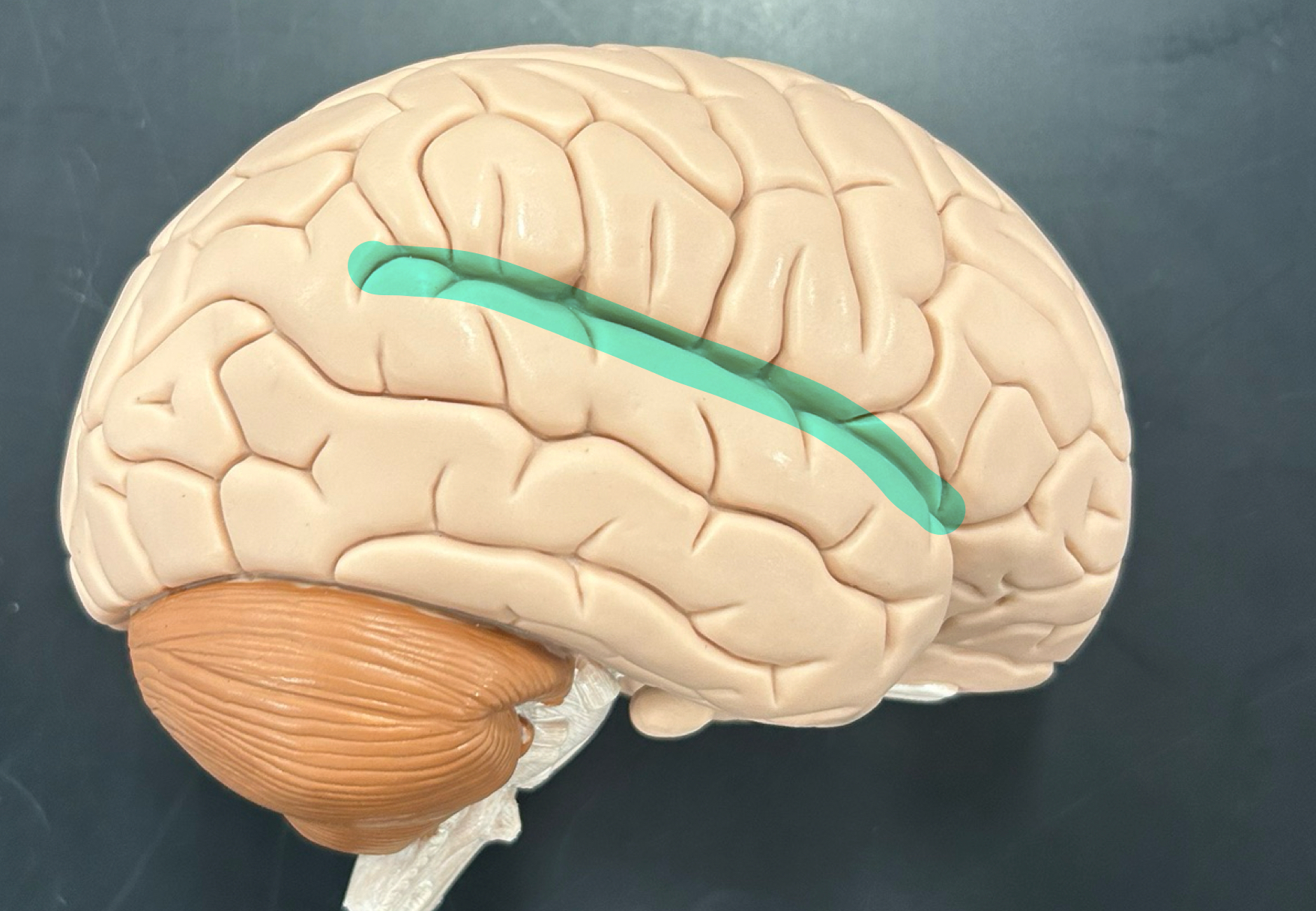
Lateral sulcus
Transverse cerebral fissure
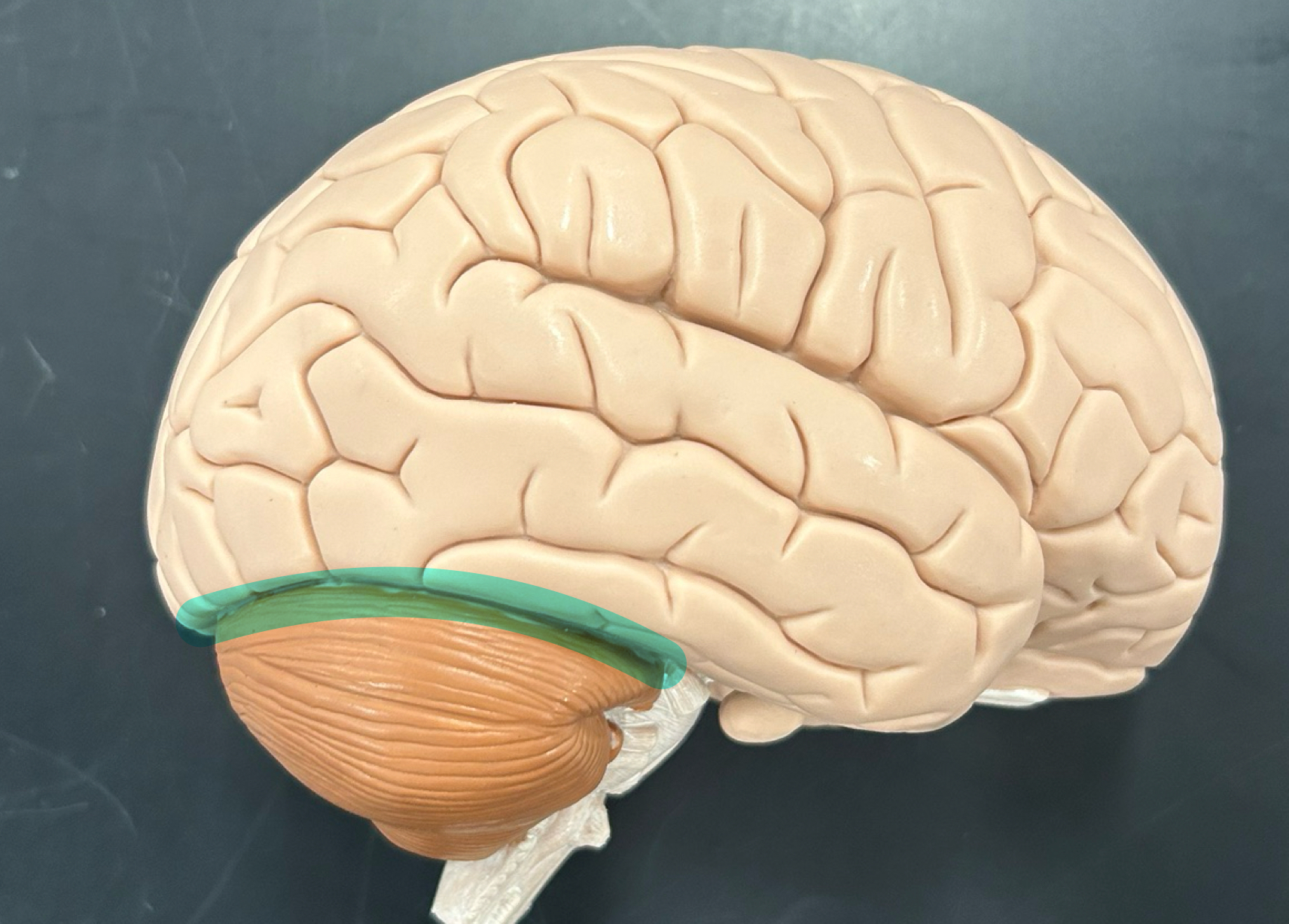
Cerebellum

Olfactory bulb: Processes smell information from the nose and sends it to the brain
*

olfactory tract

optic nerve

optic chiasma
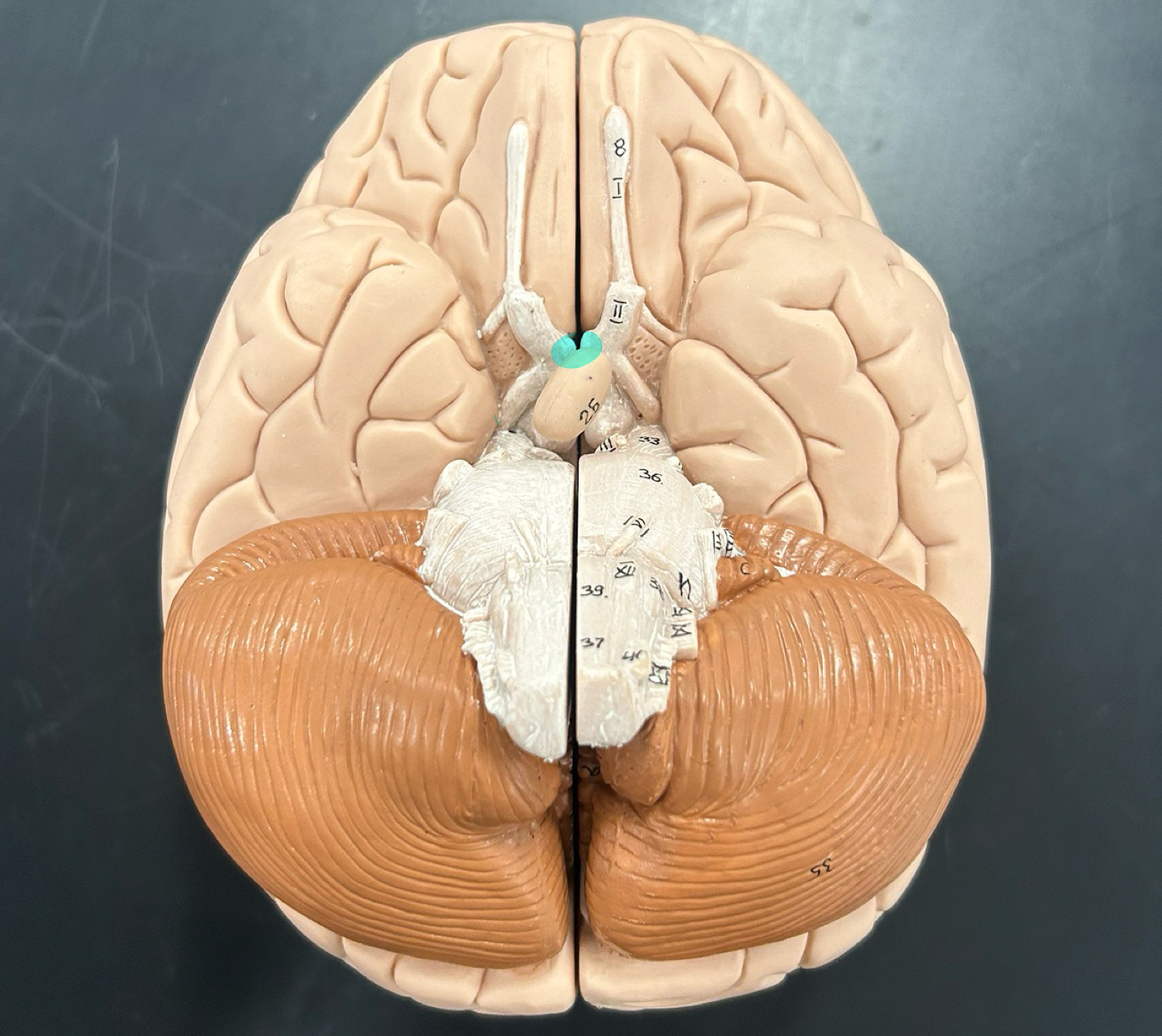
optic tract
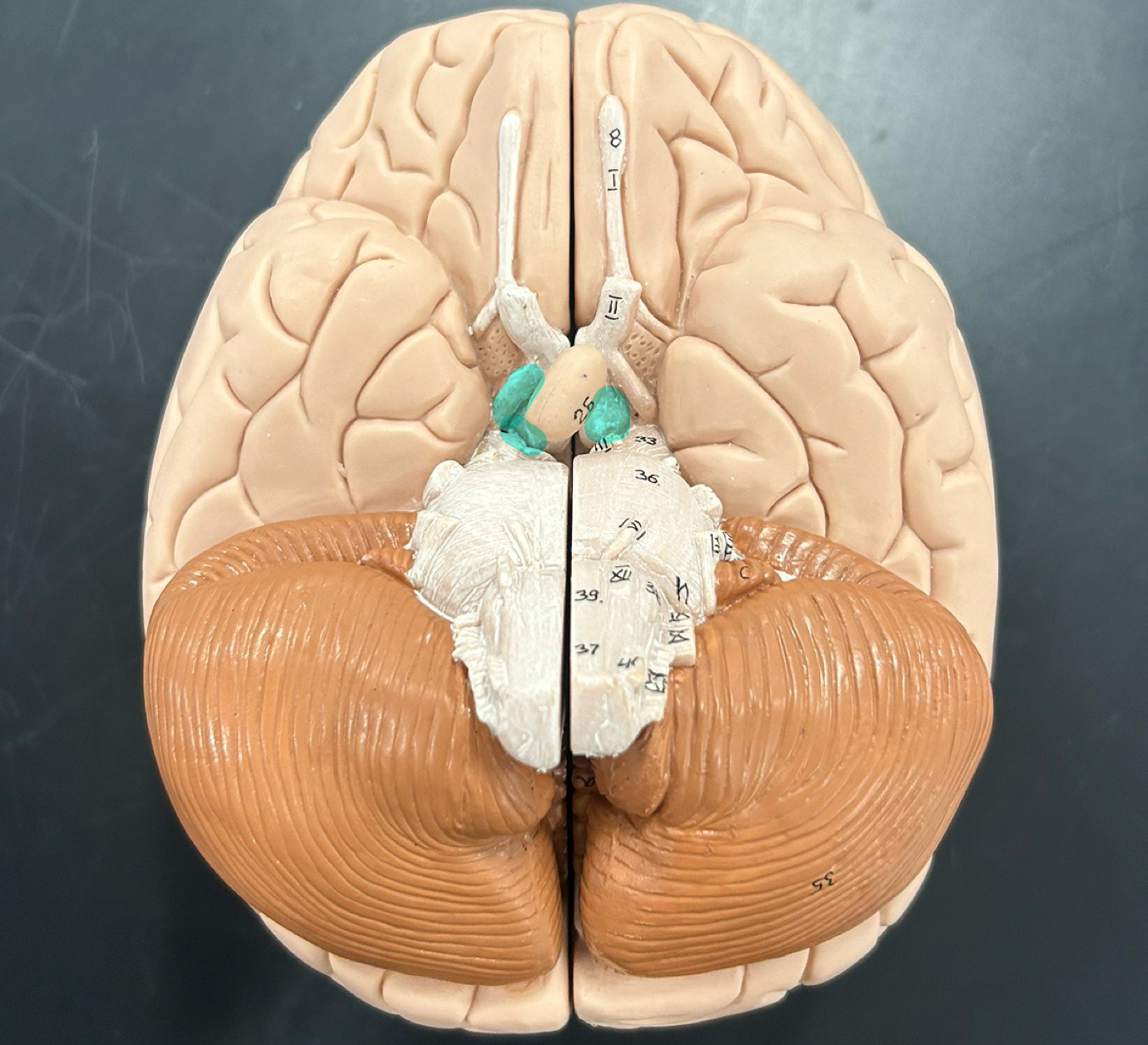
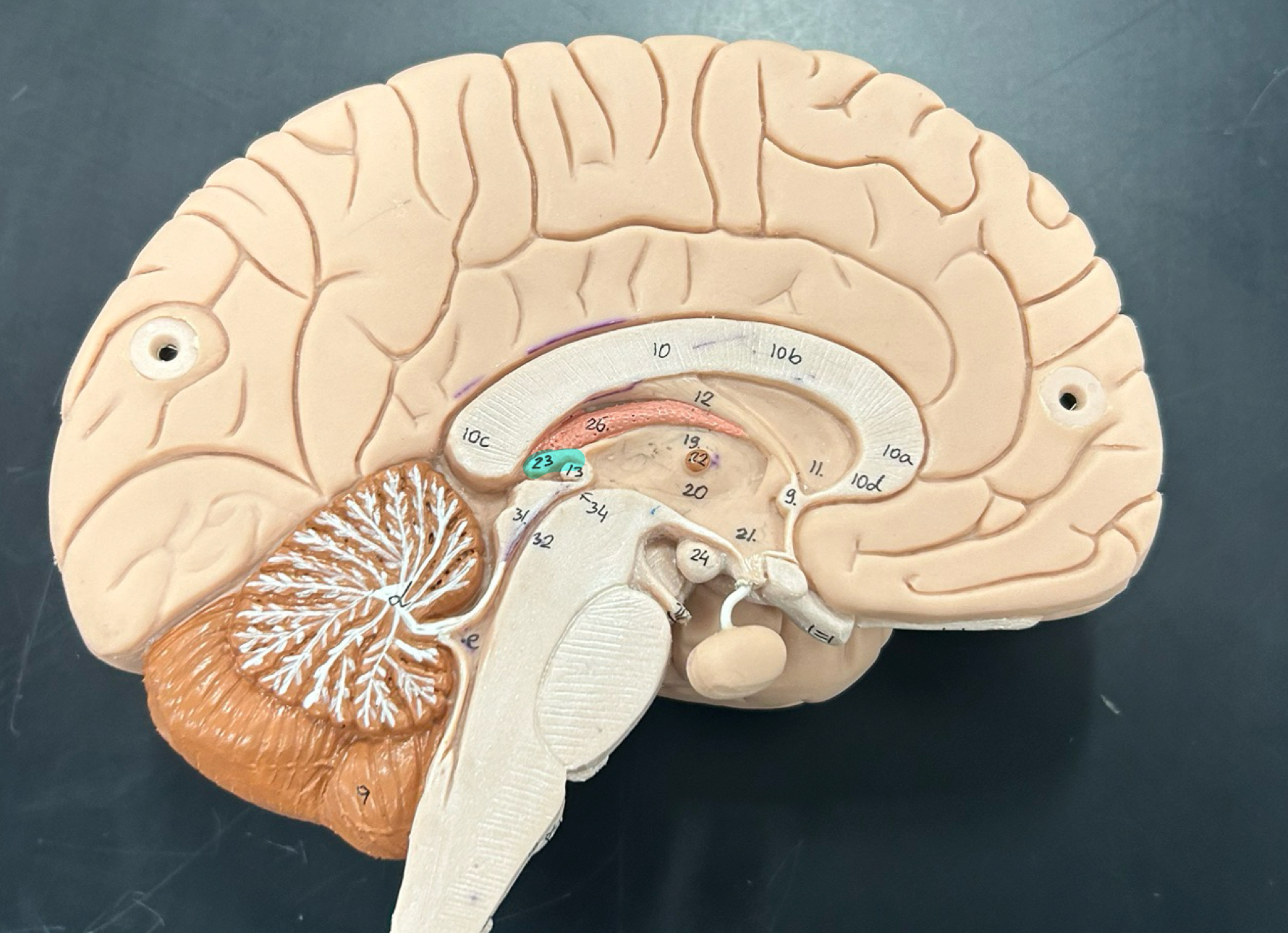
corpus callosum
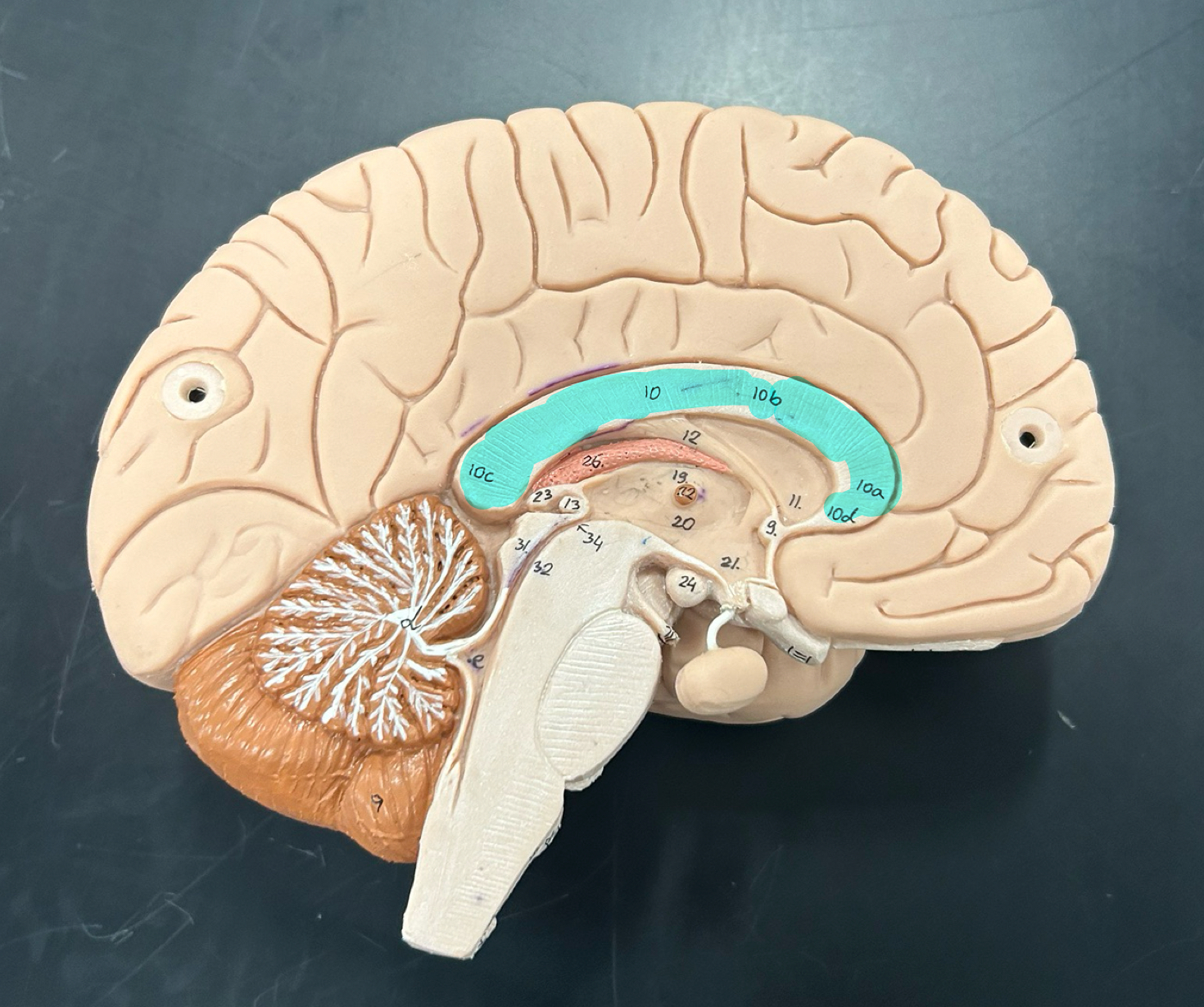
fornix
pons
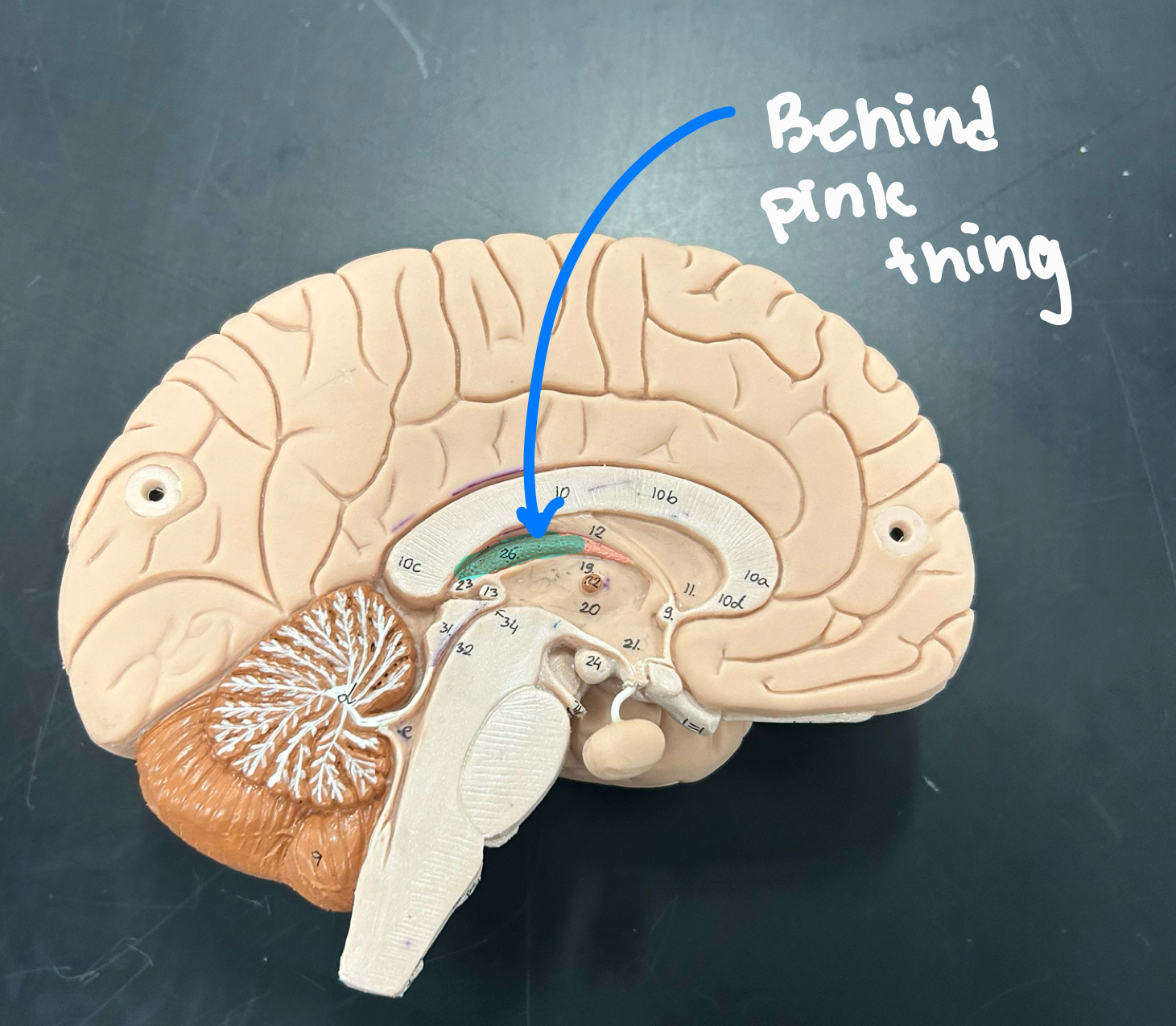
medulla oblongata: Controls vital functions like heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure. Also helps with reflexes like coughing and swallowing.
*
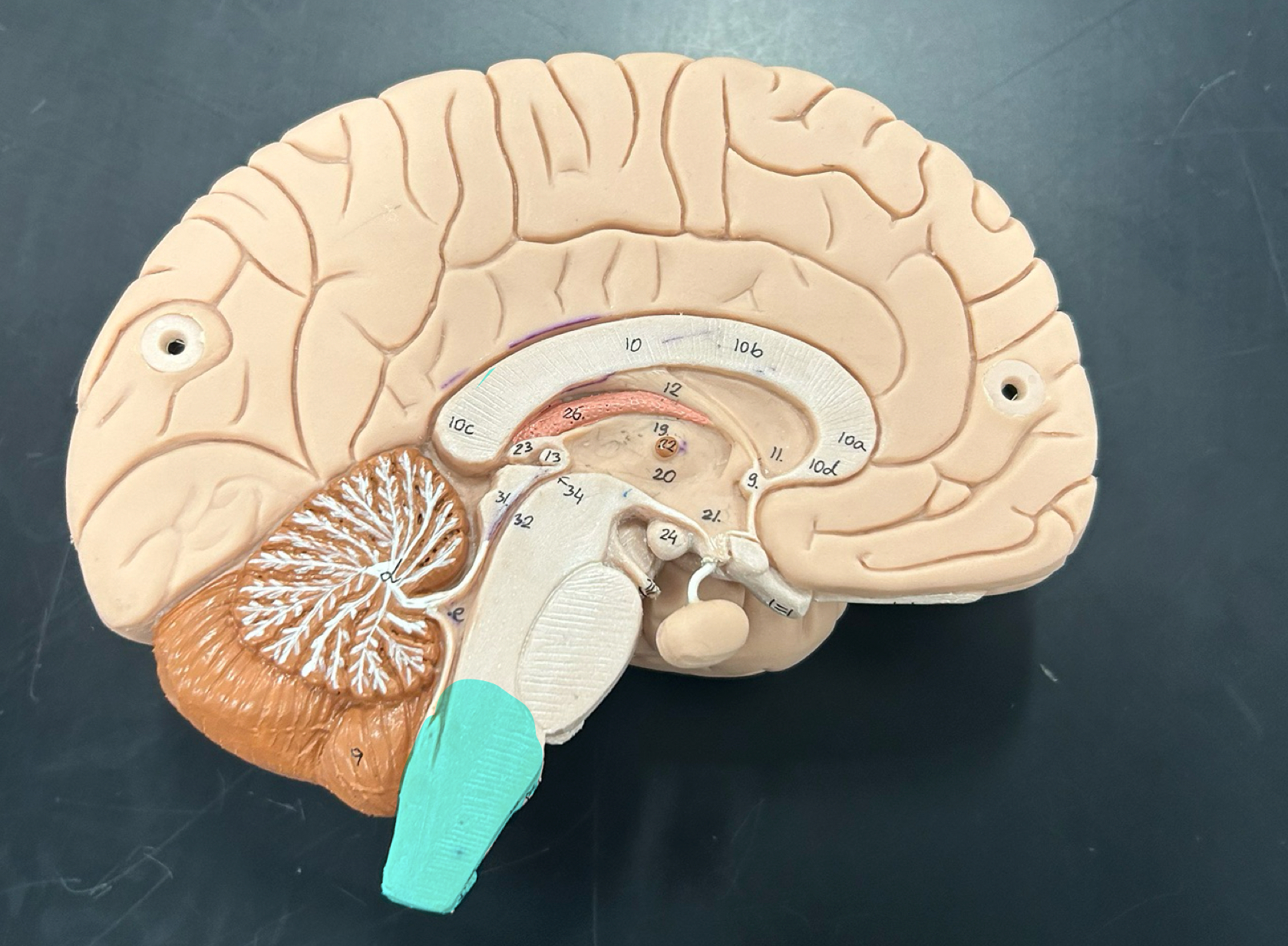
corpora quadrigemina
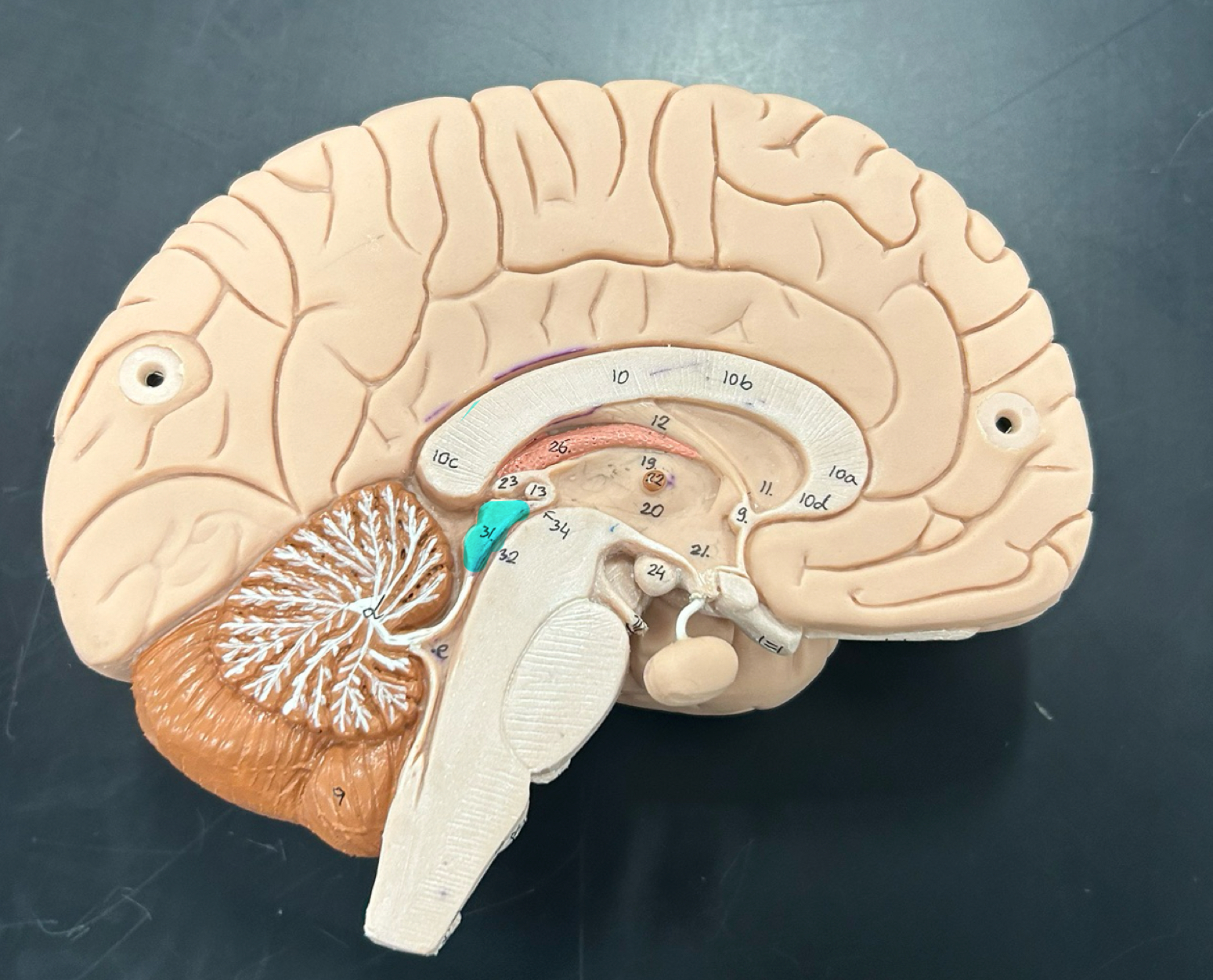
superior colliculi: Controls visual reflexes like tracking moving objects and coordinating eye movements
*
inferior colliculi: Processes auditory information and helps with reflexive responses to sound.
*
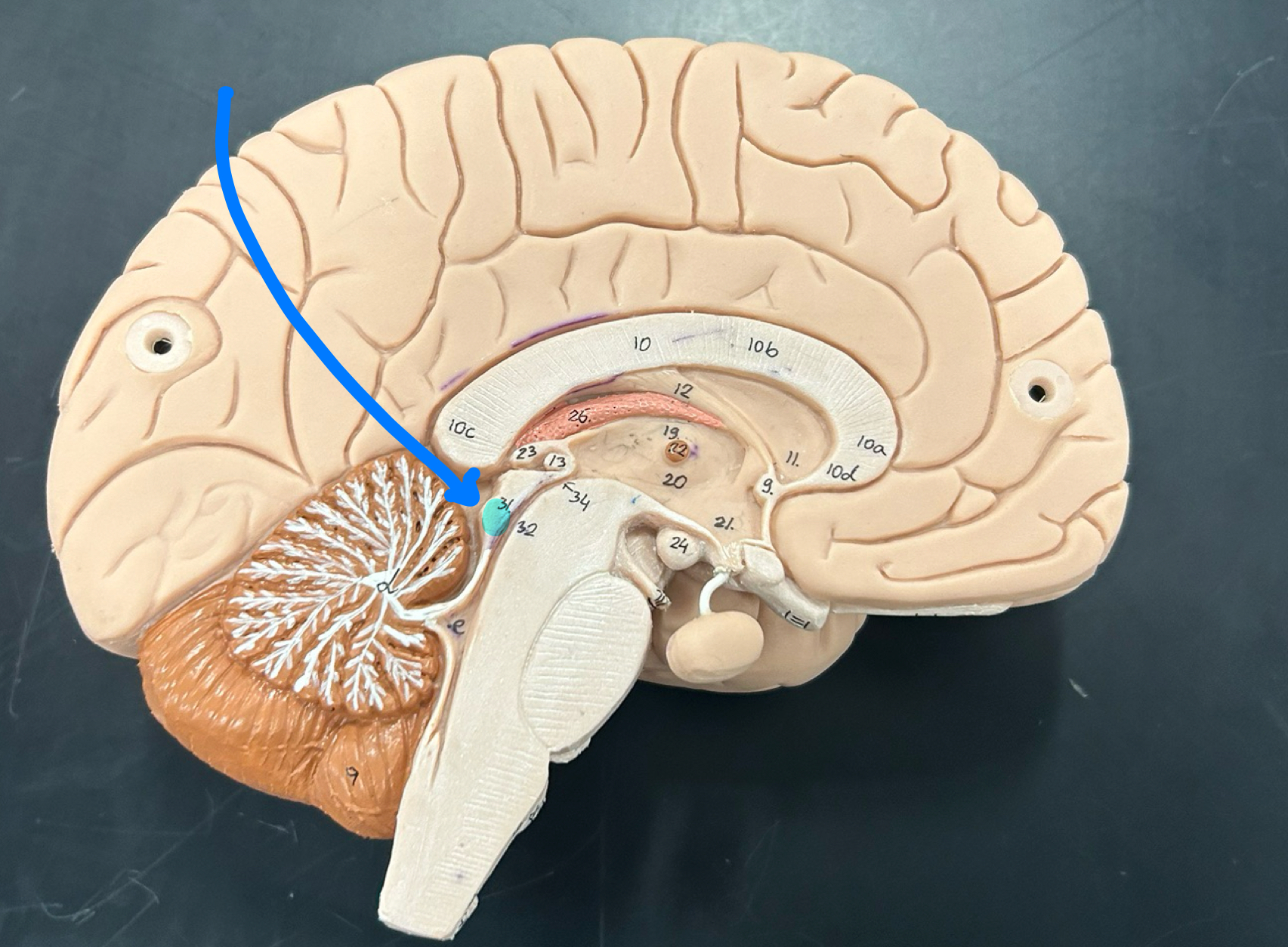
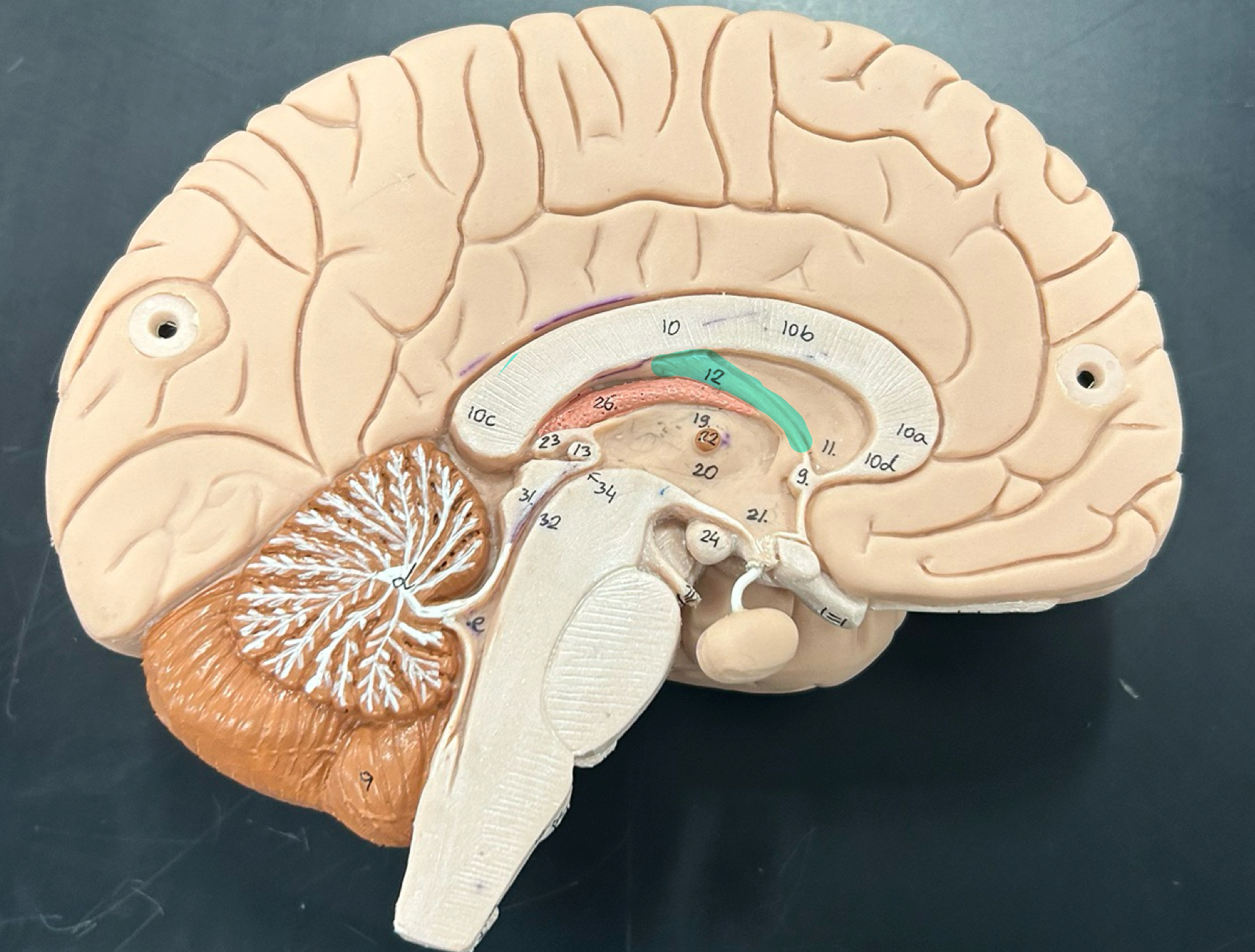
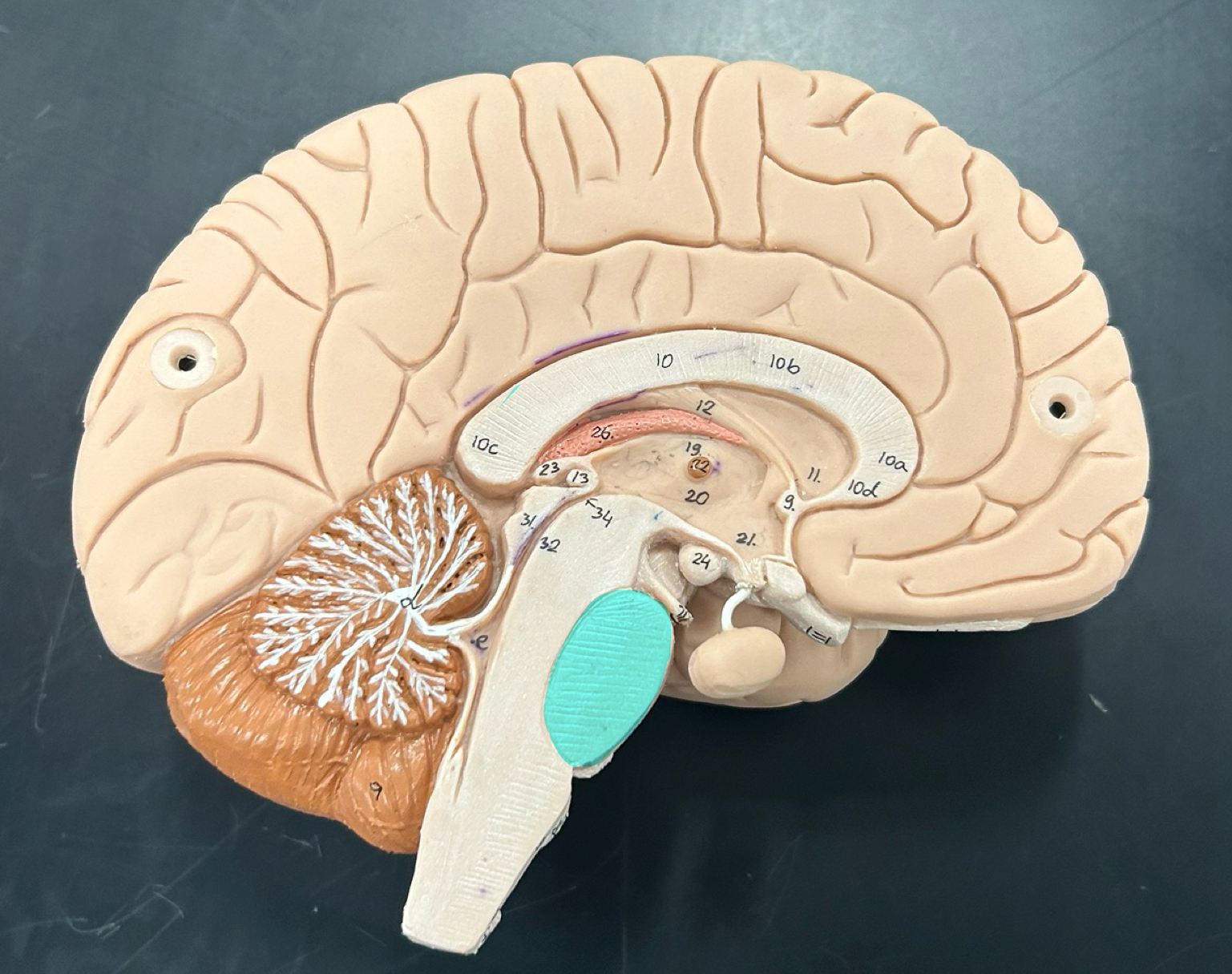
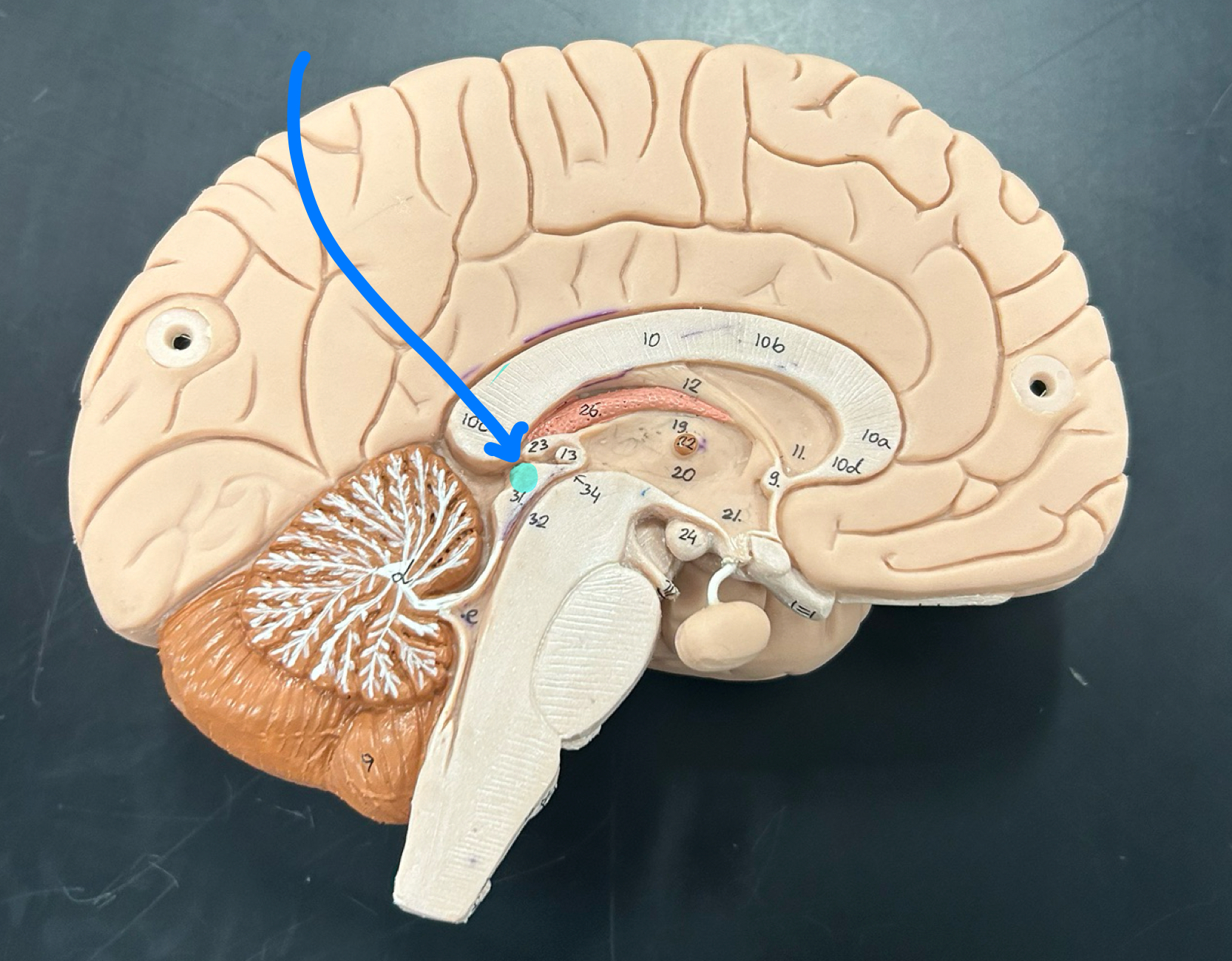
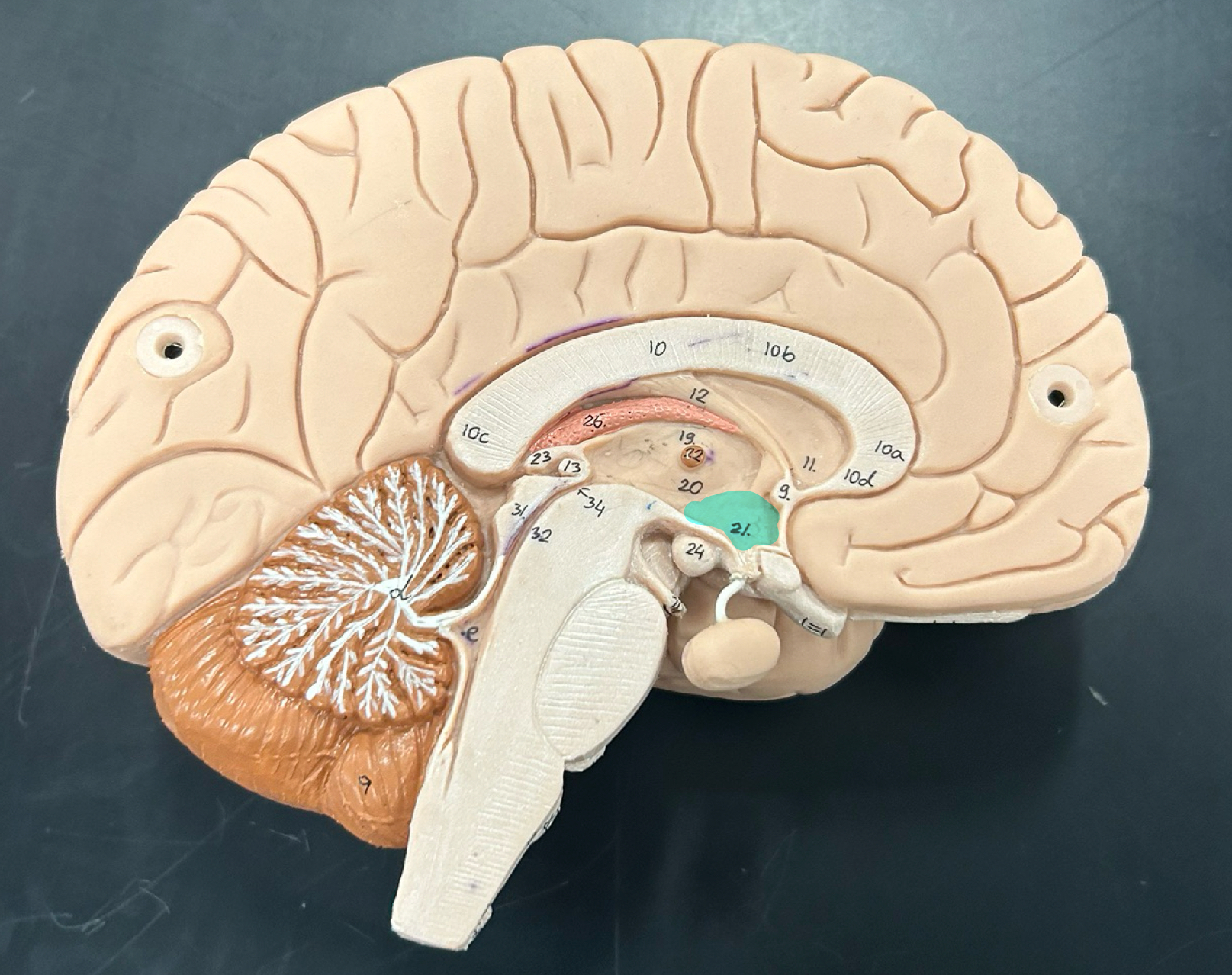
Mamillary body: Involved in memory processing, especially recollective memory; connects to the hippocampus
*

thalamus
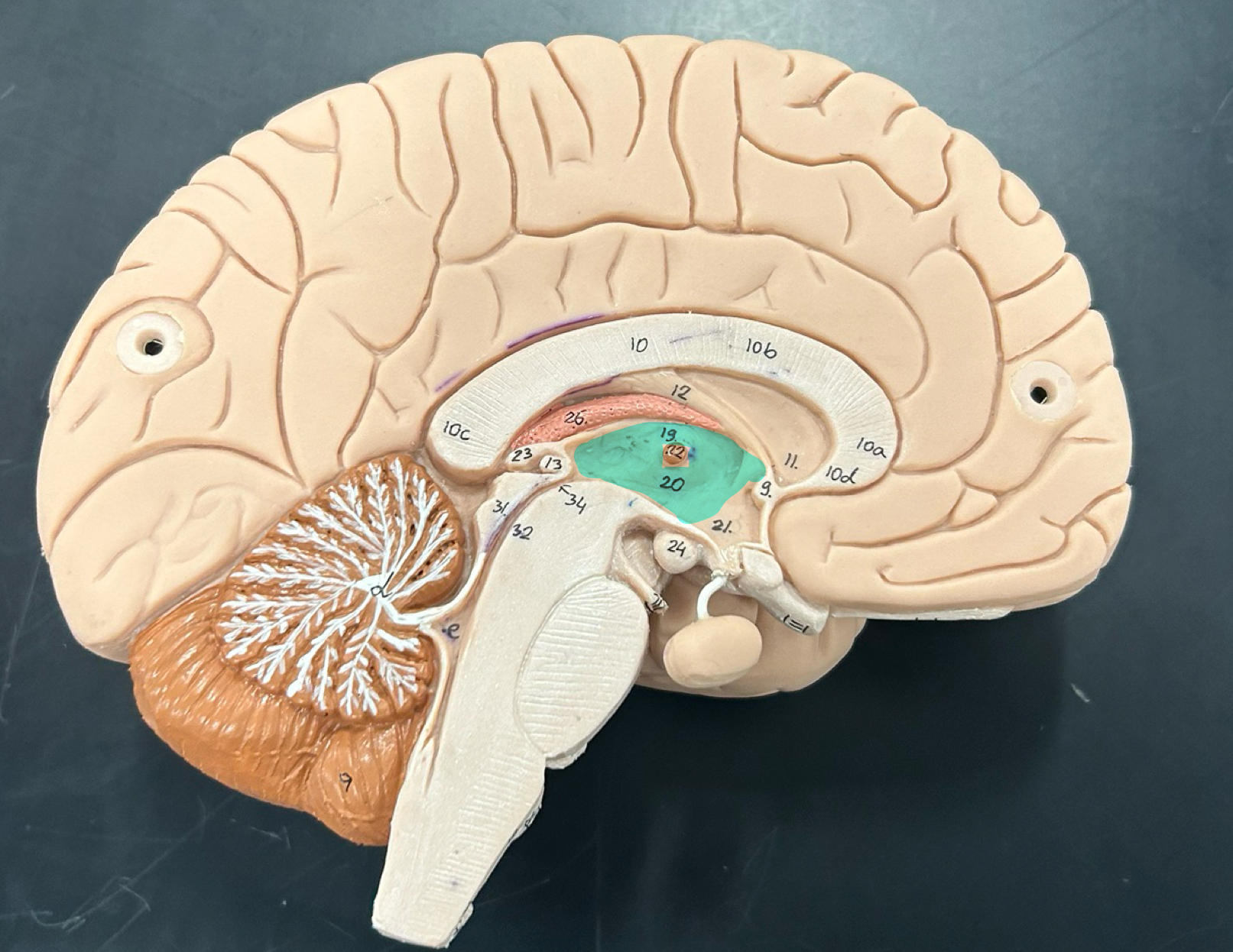
hypothalamus
pineal gland: Secretes melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythm)
*
choroid plexus: Produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions the brain and spinal cord
*
lateral ventricle
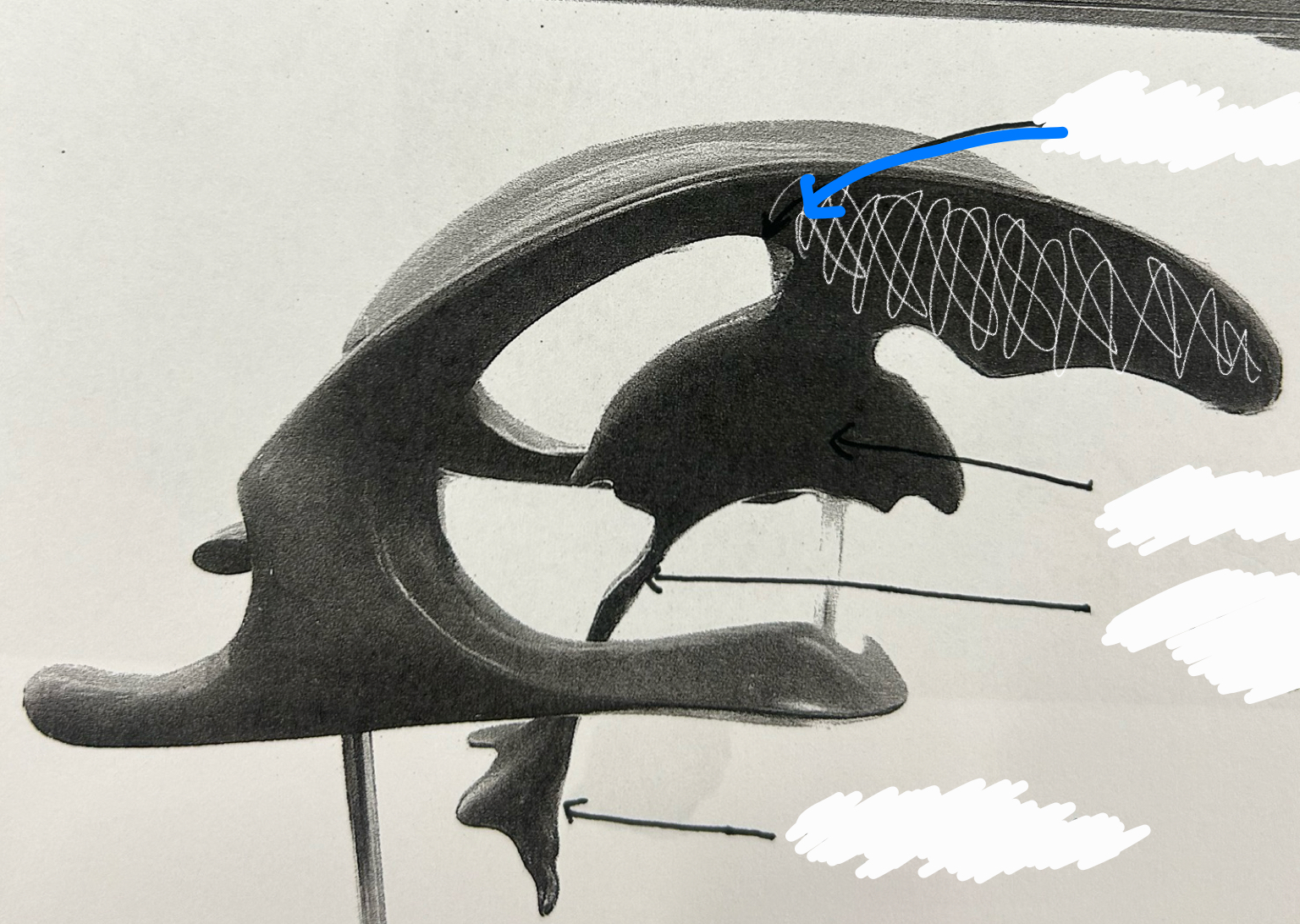
third ventricle
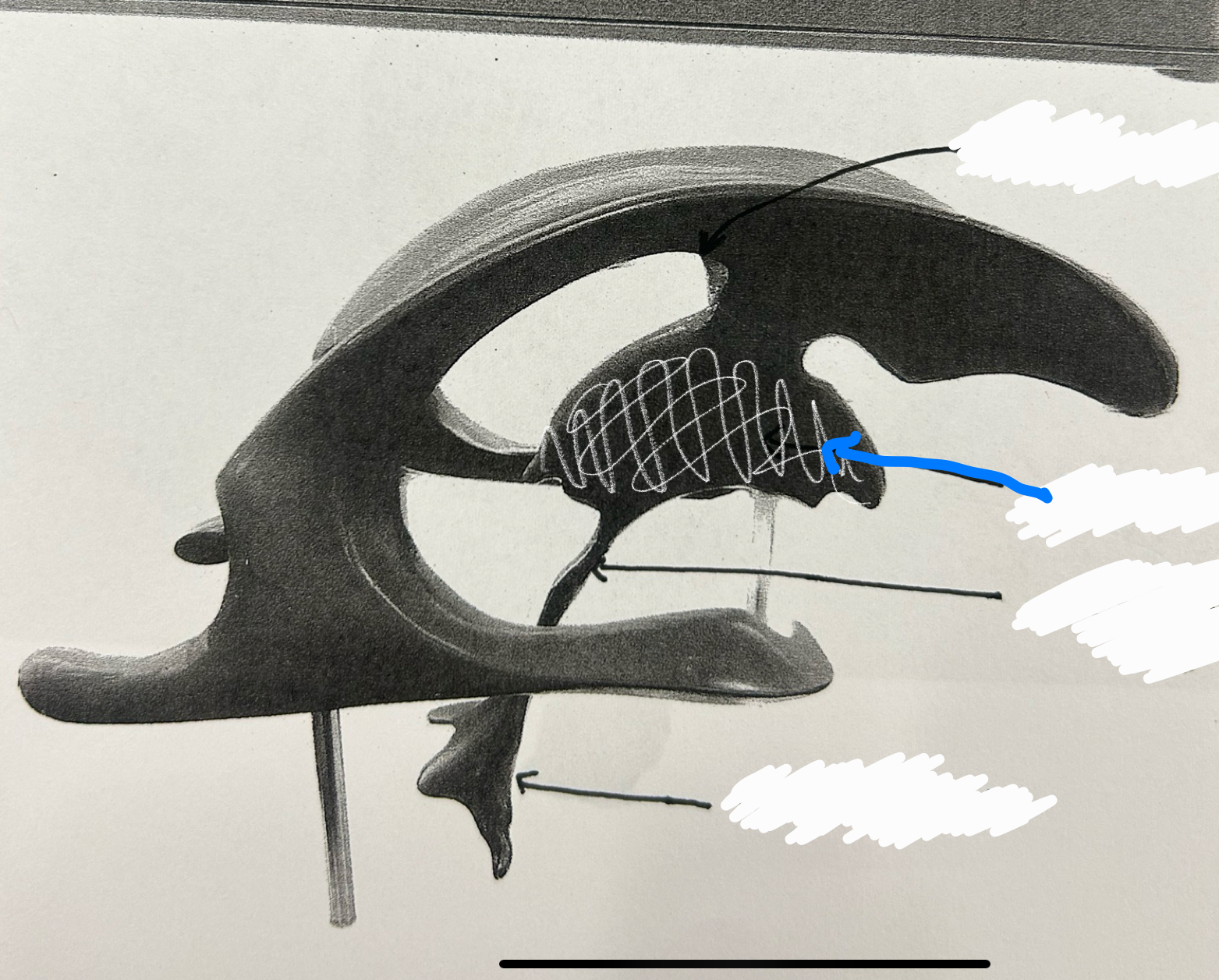
fourth ventricle
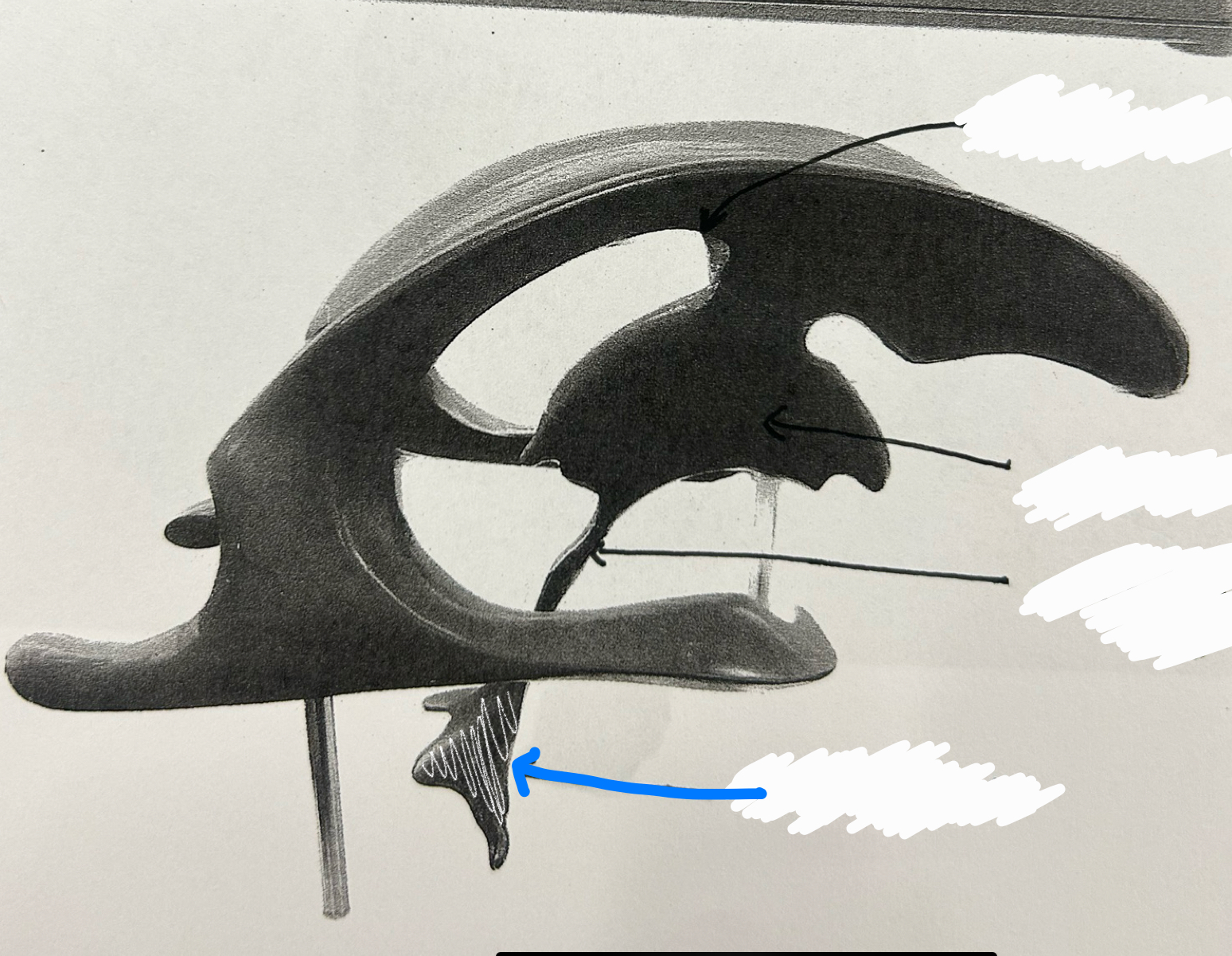

cerebral aqueduct
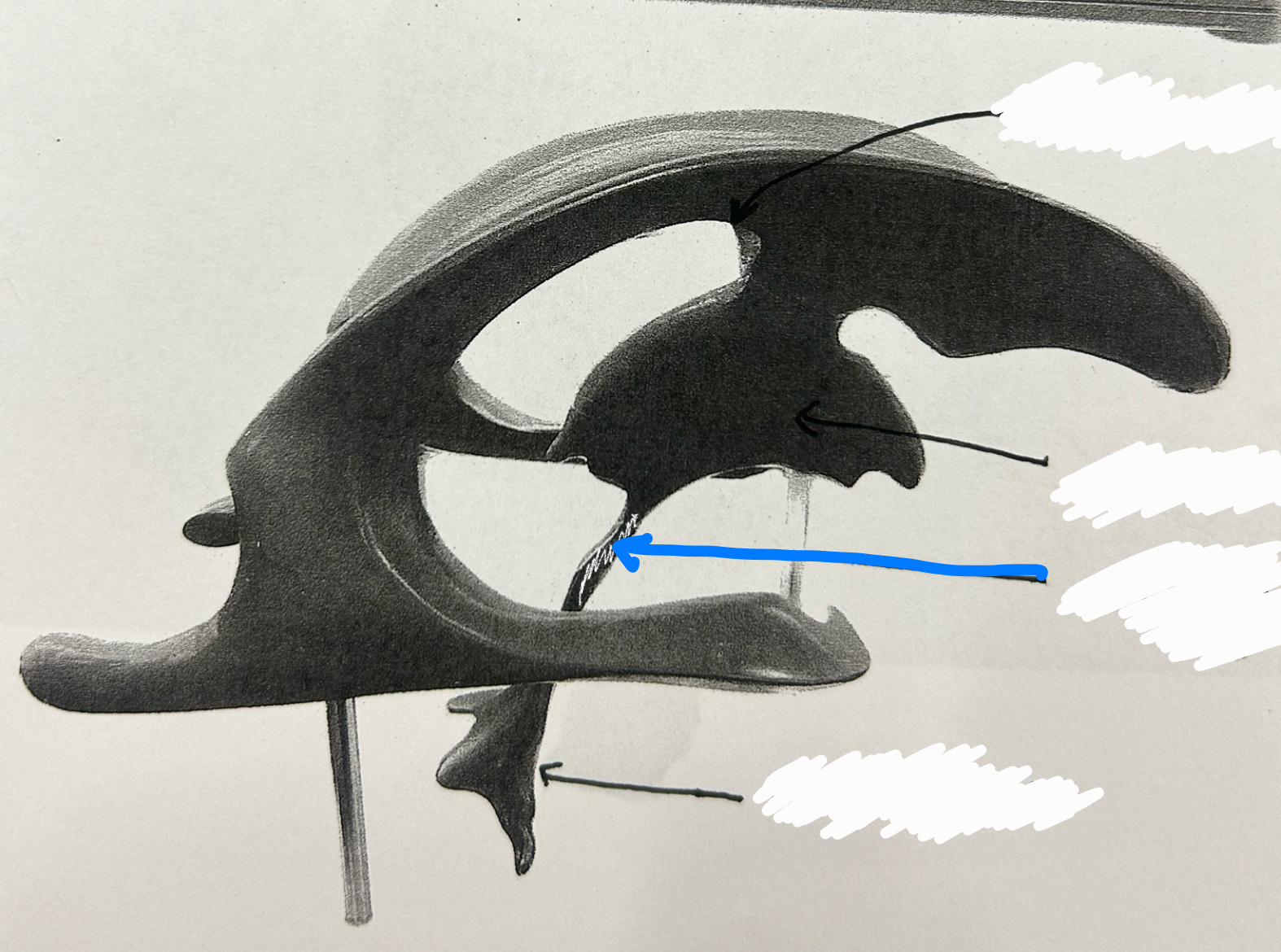
septum pellucidum
infundibulum

pituitary gland

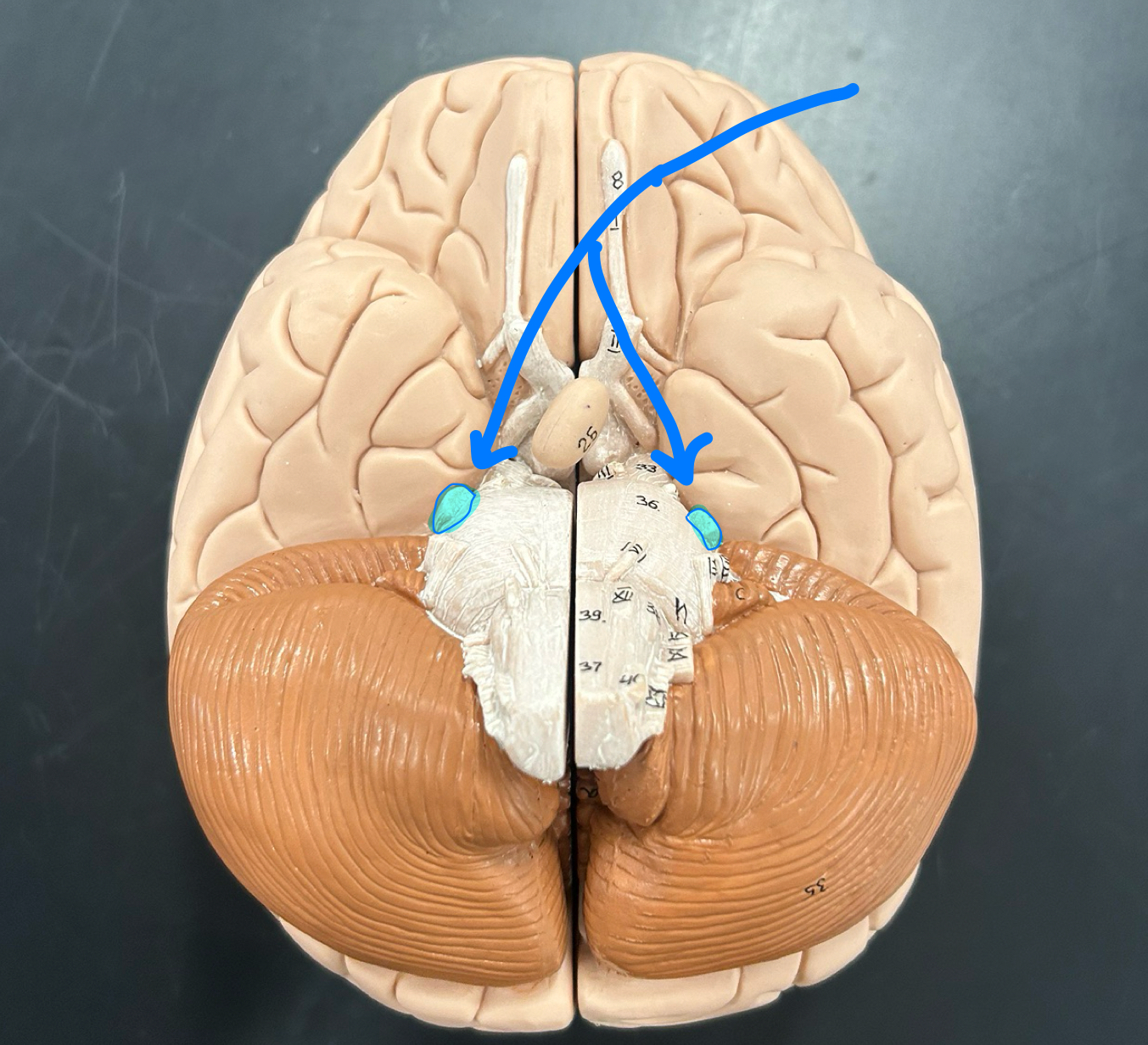
optic nerve (CNII)
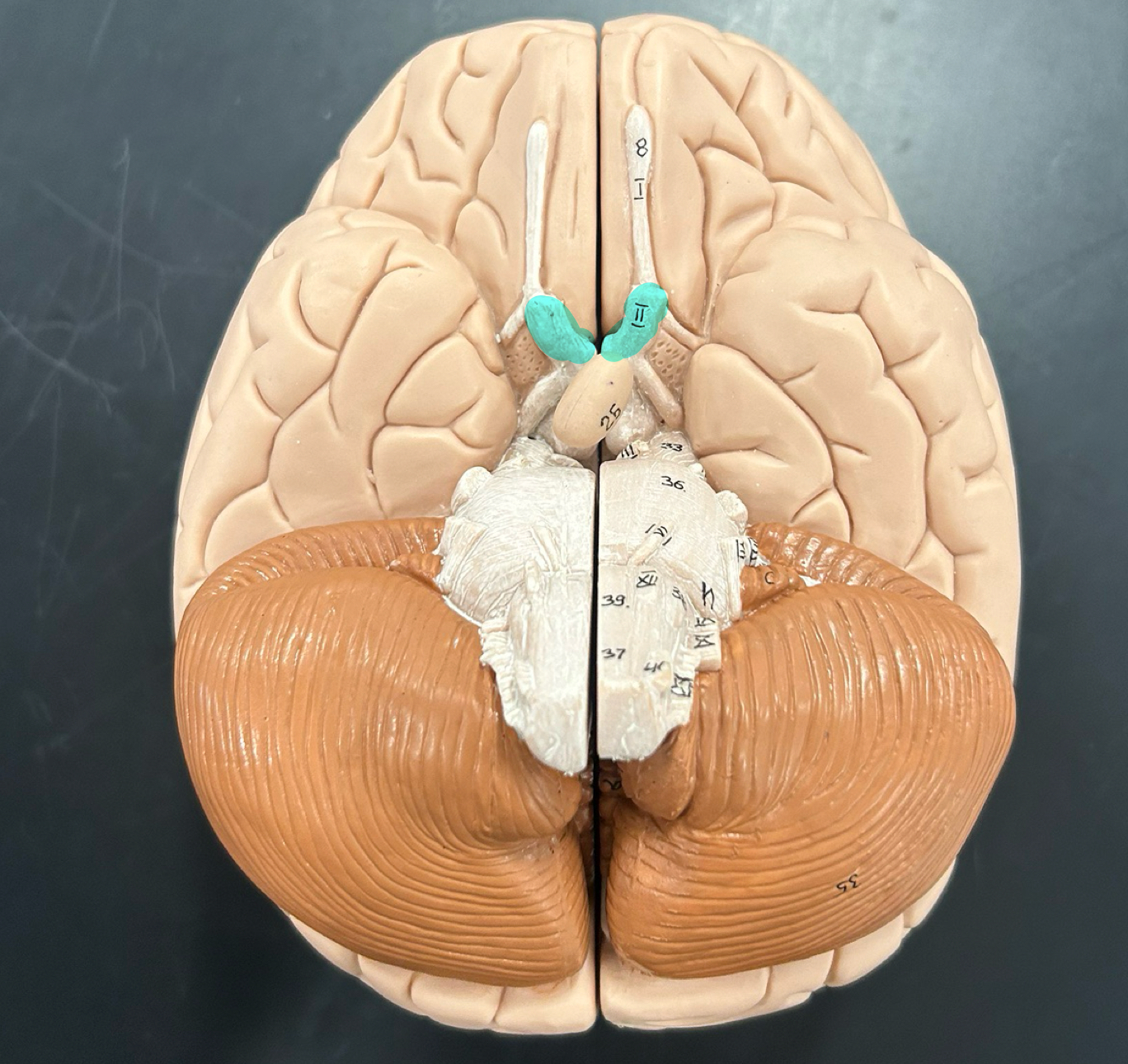
Ocularmotor nerve (CNV)
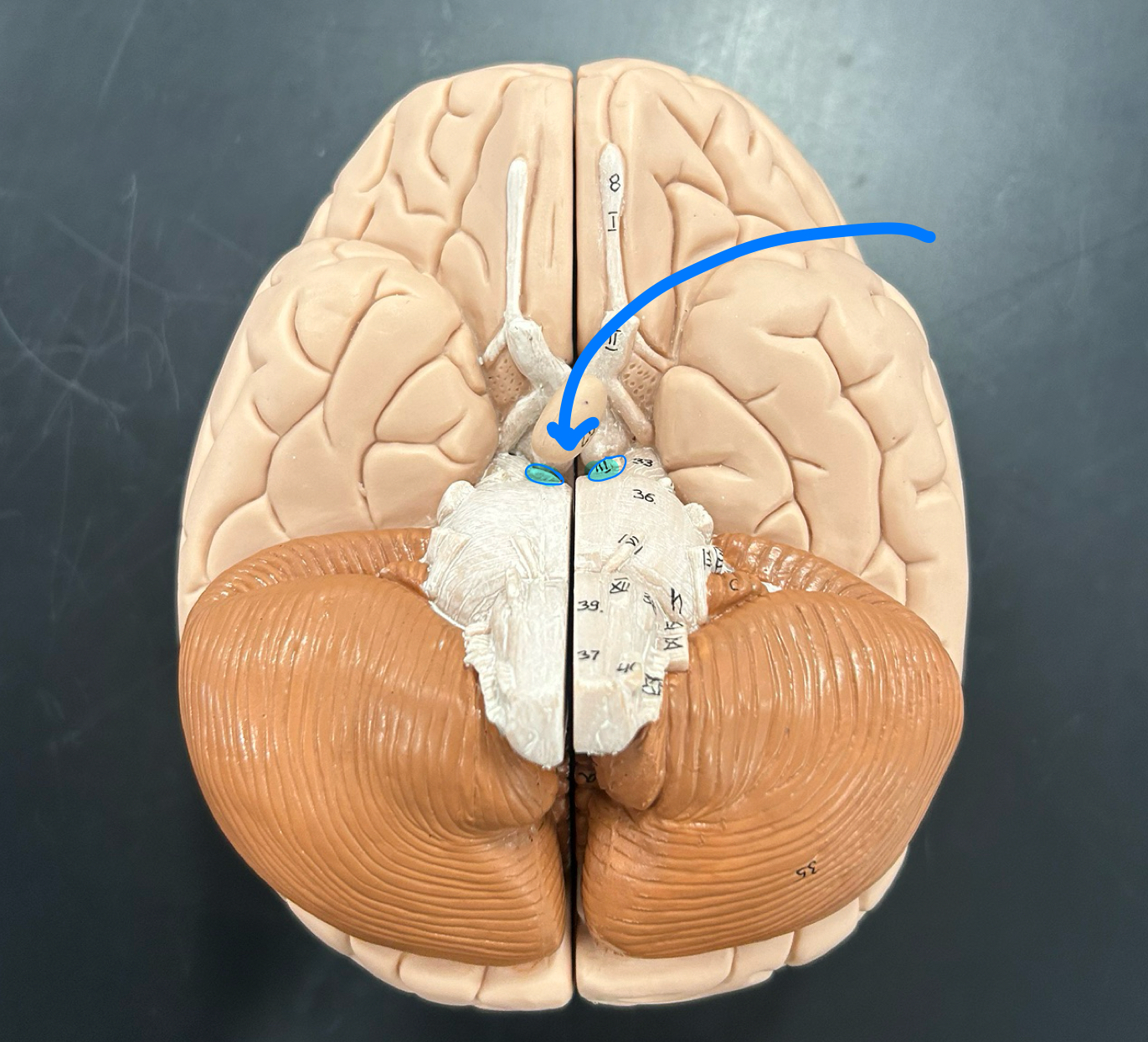
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
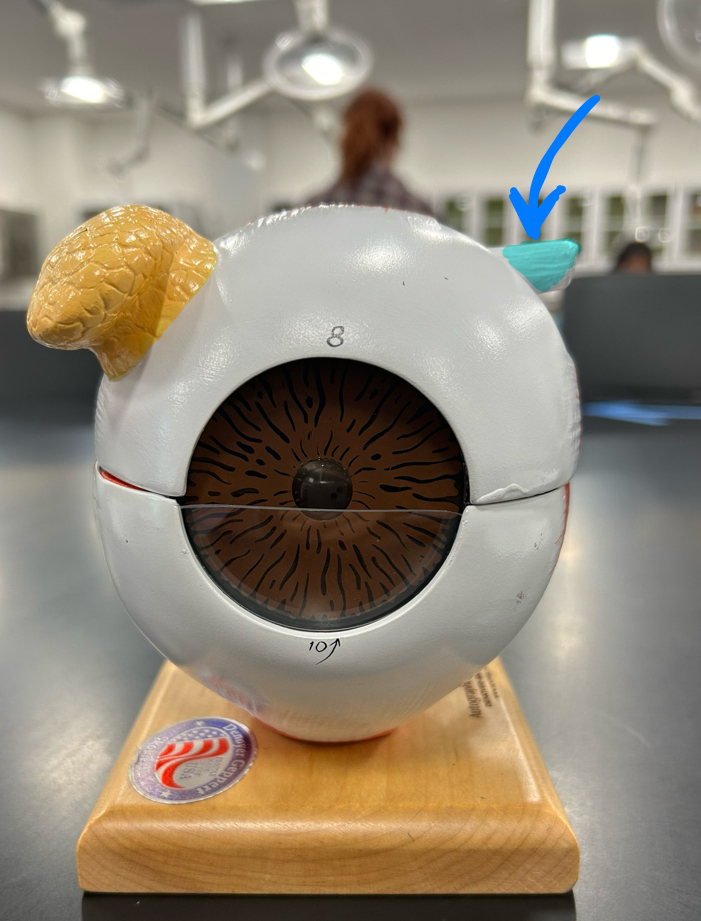
Sclera: Provides tough, protective outer layer of the eye and maintains its shape
*
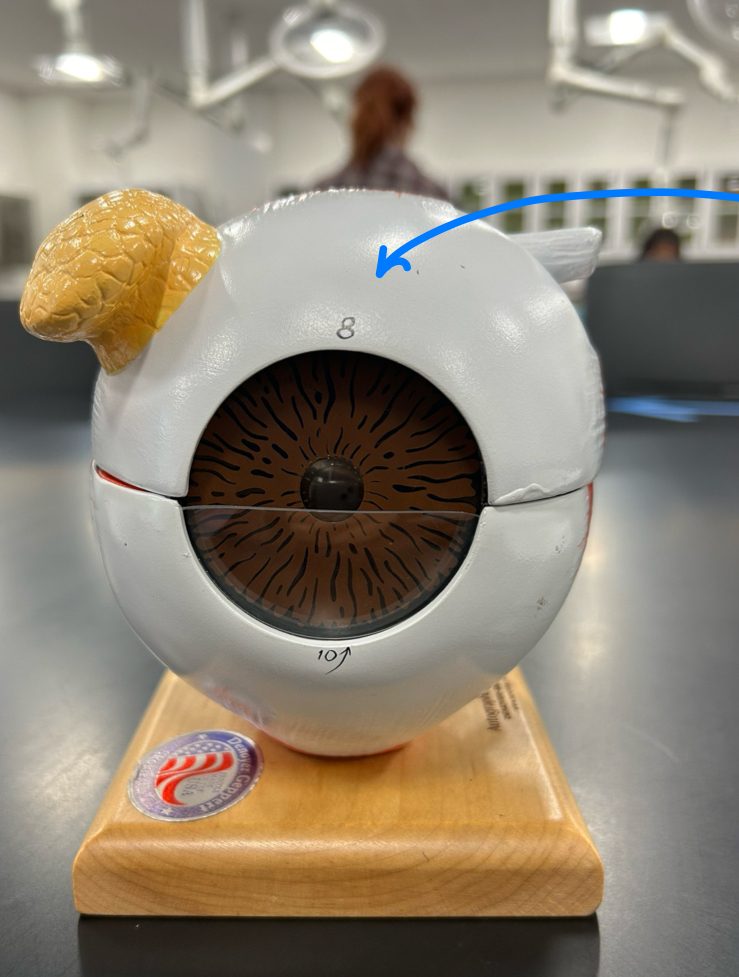

Cornea: Transparent front layer that helps focus light onto the retina for clear vision
*
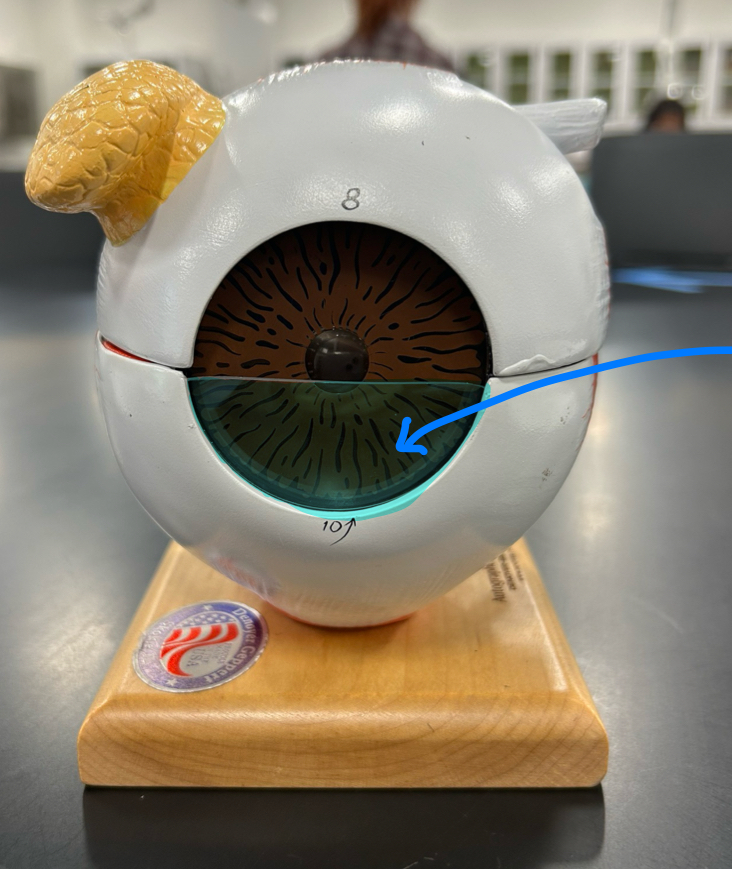
Choroid: Supplies blood and nutrients to the retina; contains pigment that absorbs excess light to prevent glare.
*
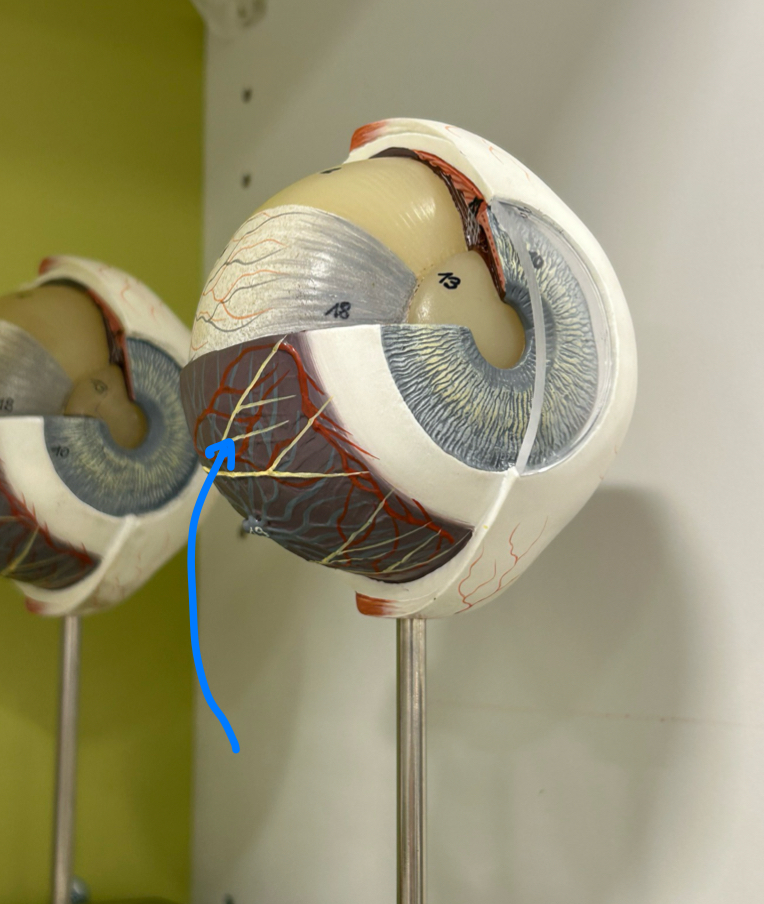
Retina: Contains photoreceptor cells that detect light and convert it into neural signals for vision
*

Iris

Pupil
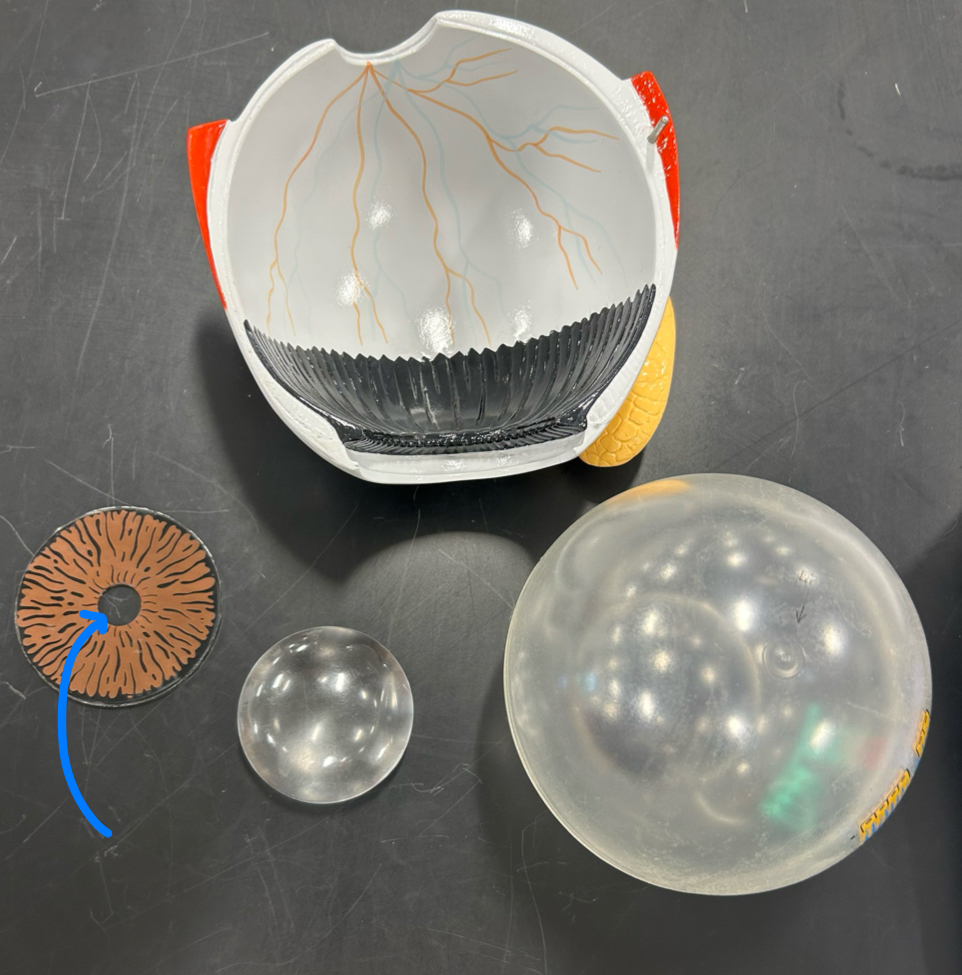

Optic nerve
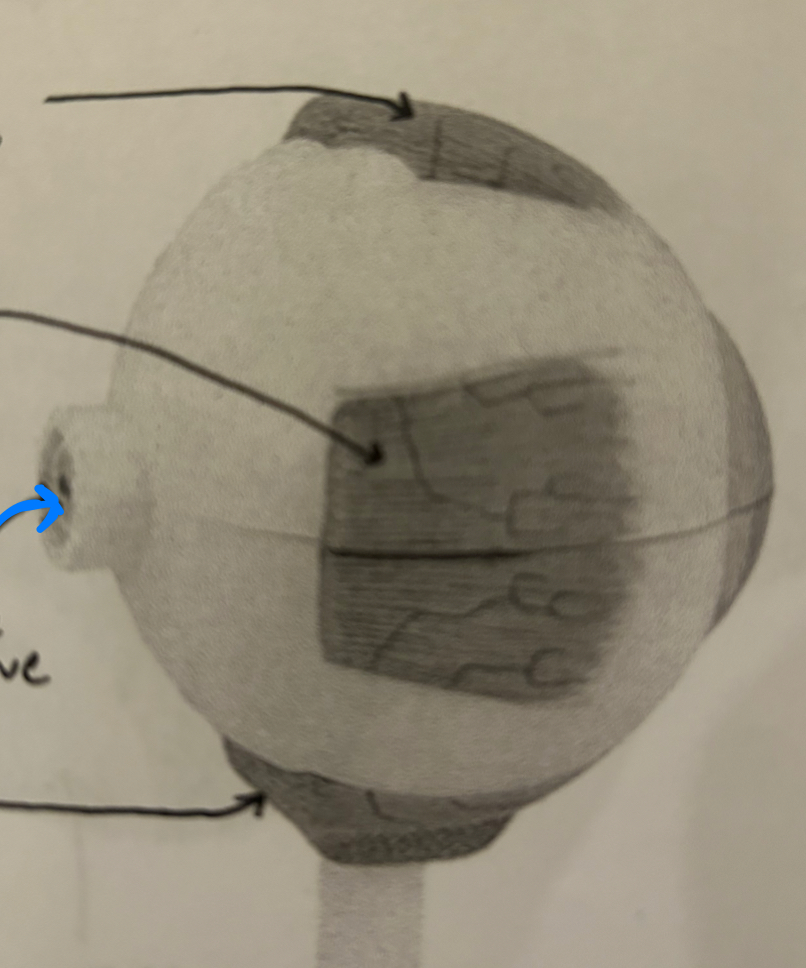
Fovea Centralis: Area of sharpest vision in the retina, packed with cones for detailed, color vision
*
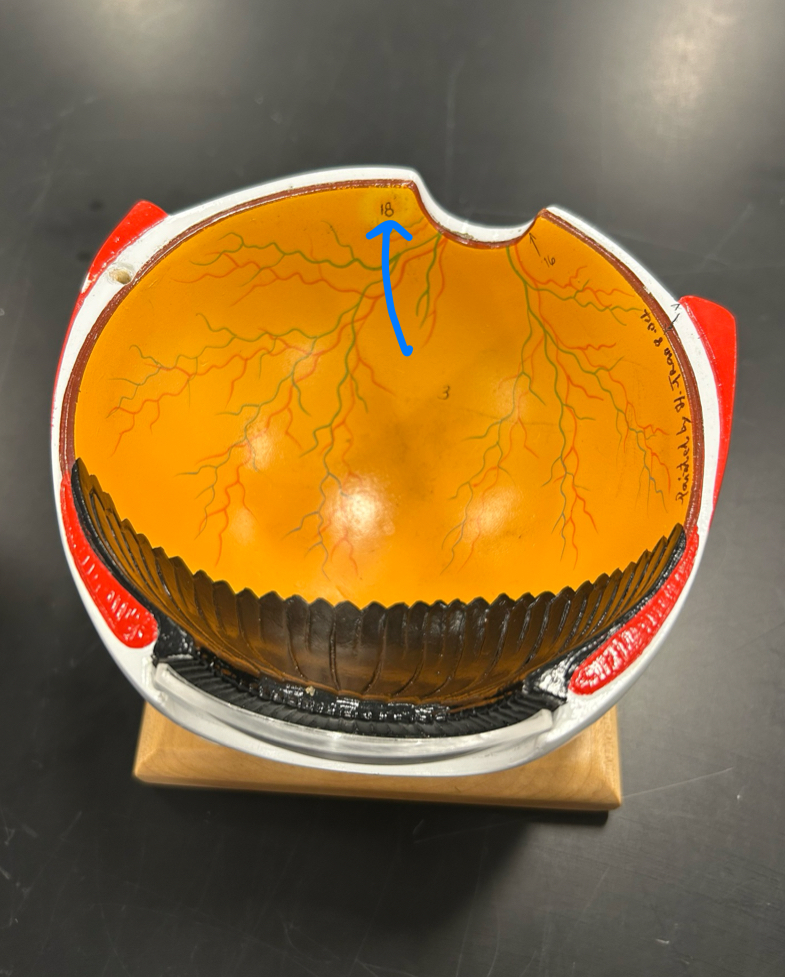

Ciliary body
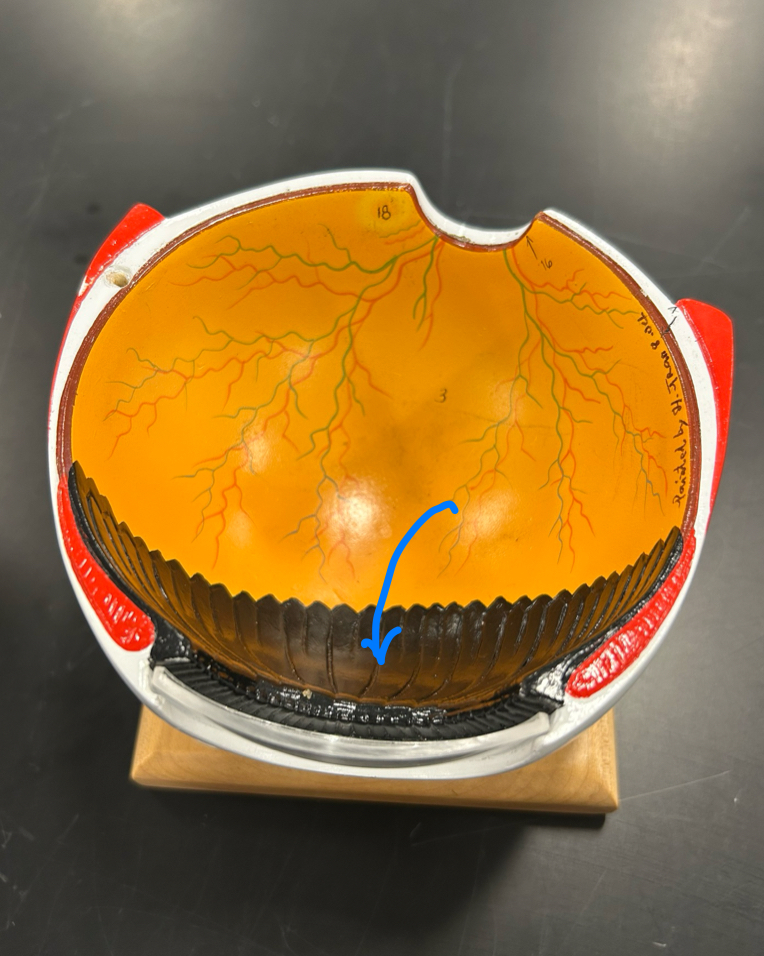

anterior segment
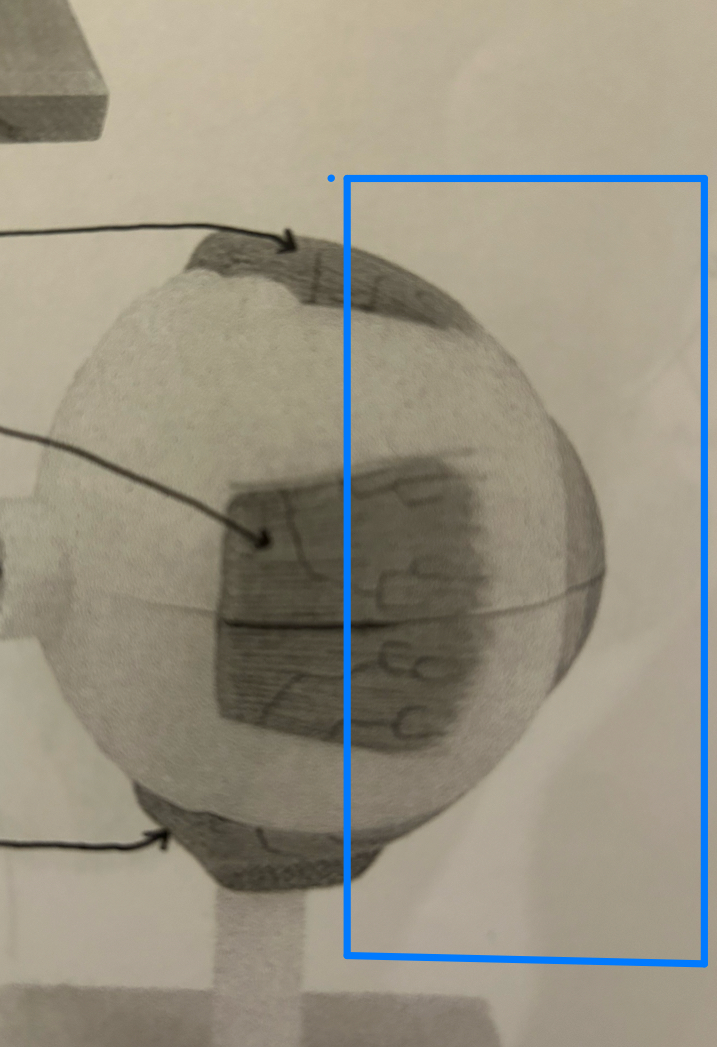
Posterior segment
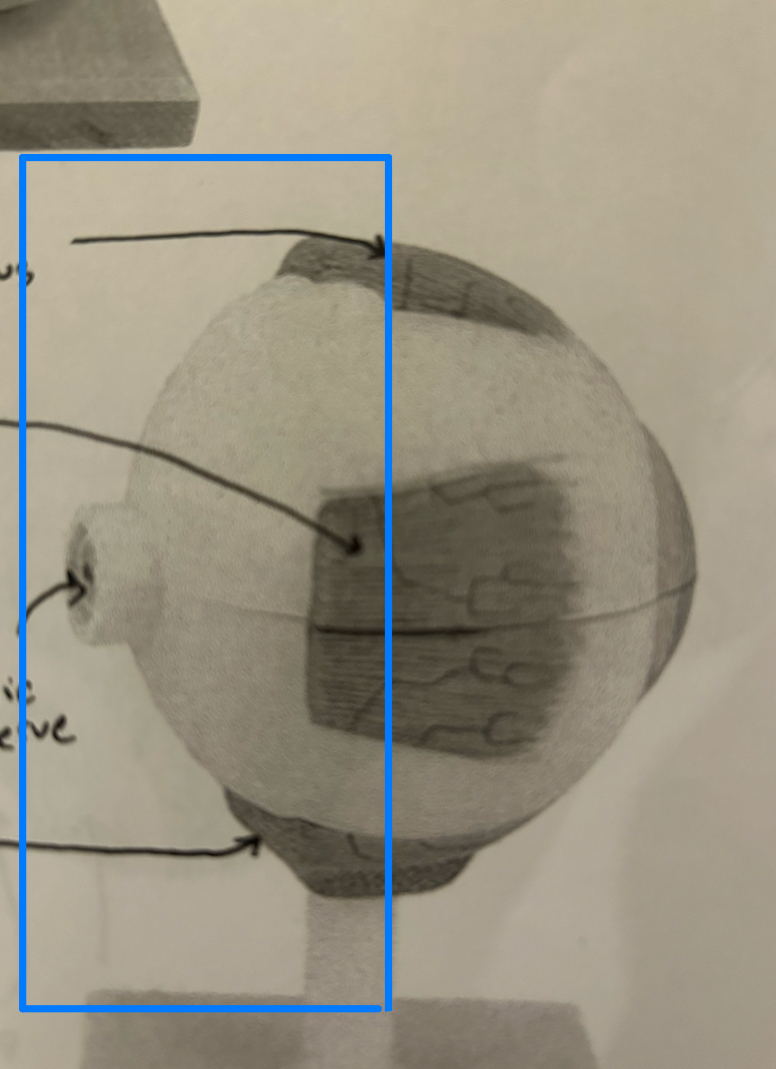
Lens: Focuses light rays onto the retina by changing shape to adjust for near or far vision
*
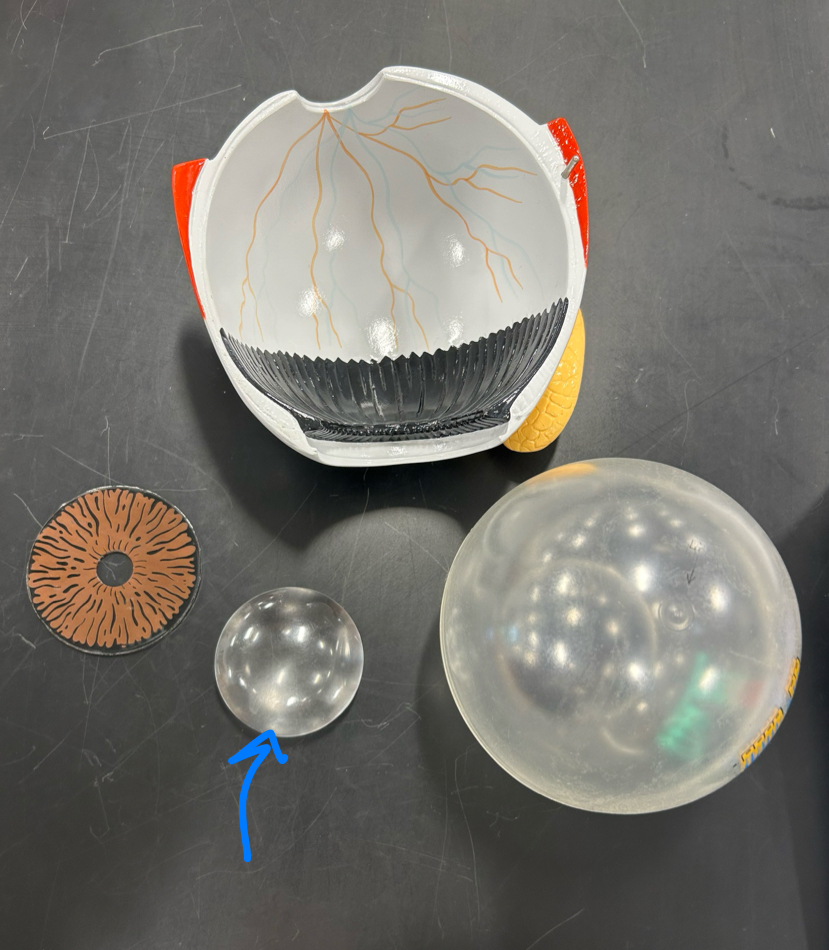

Lacrimal gland: Produces tears to lubricate and protect the surface of the eye
*
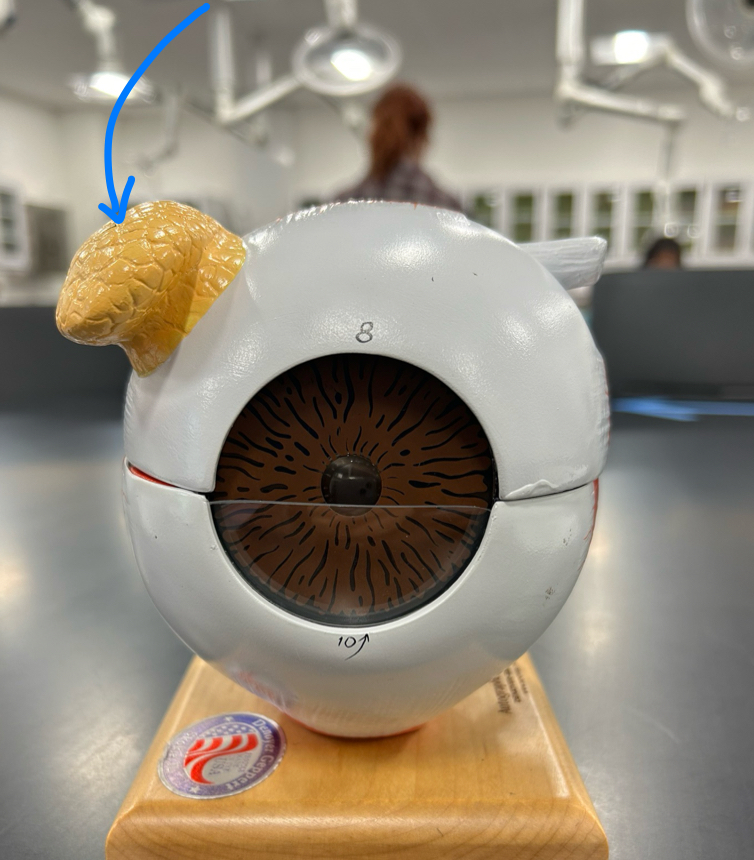

Lateral rectus
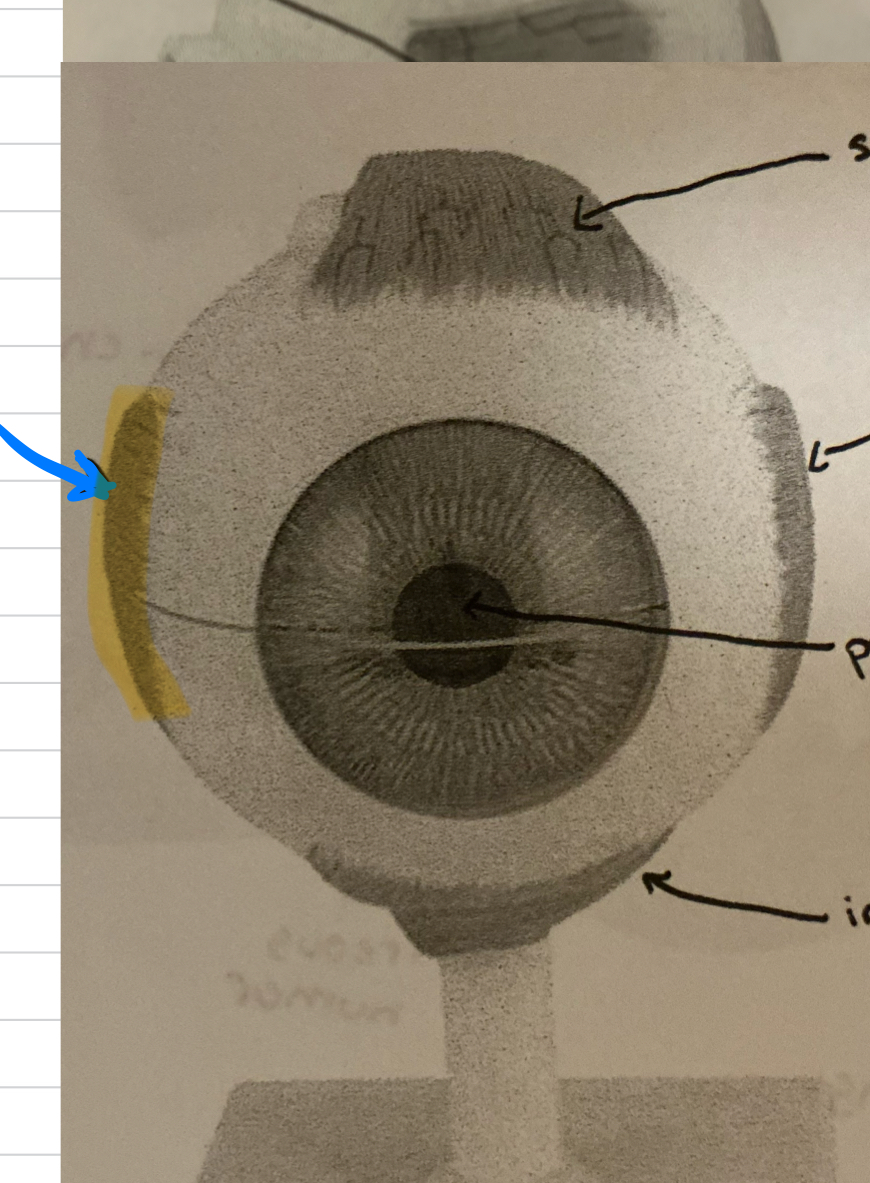
medial rectus
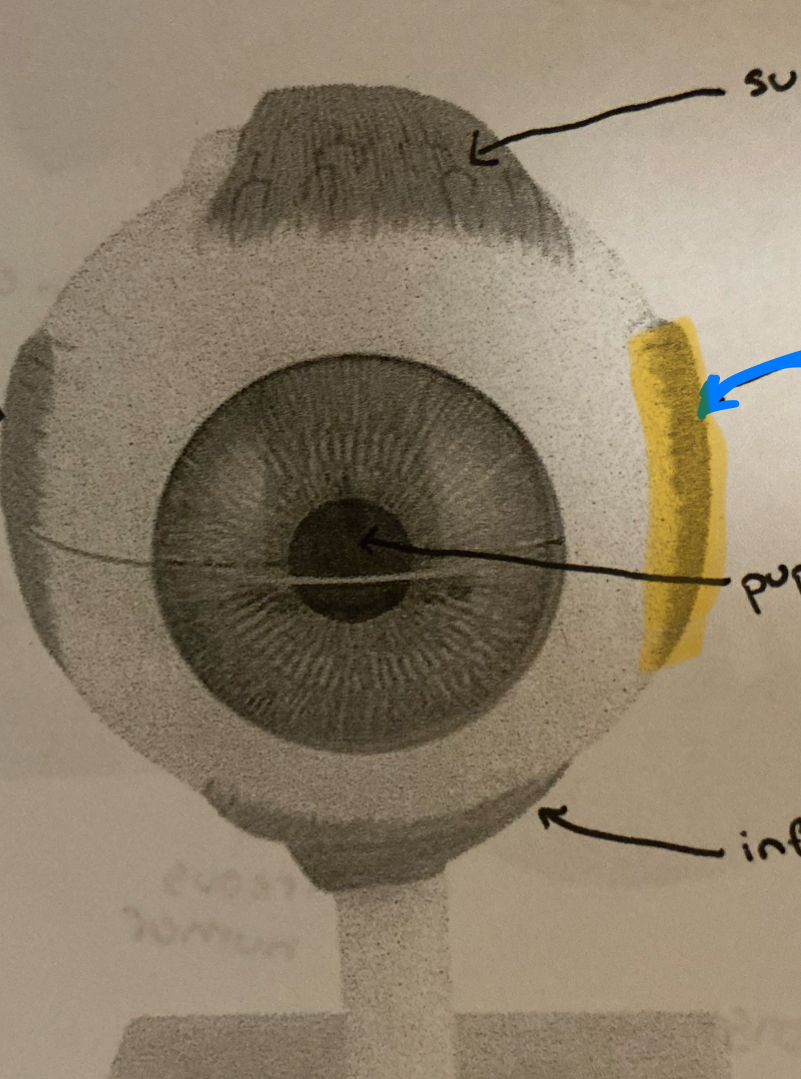
superior rectus
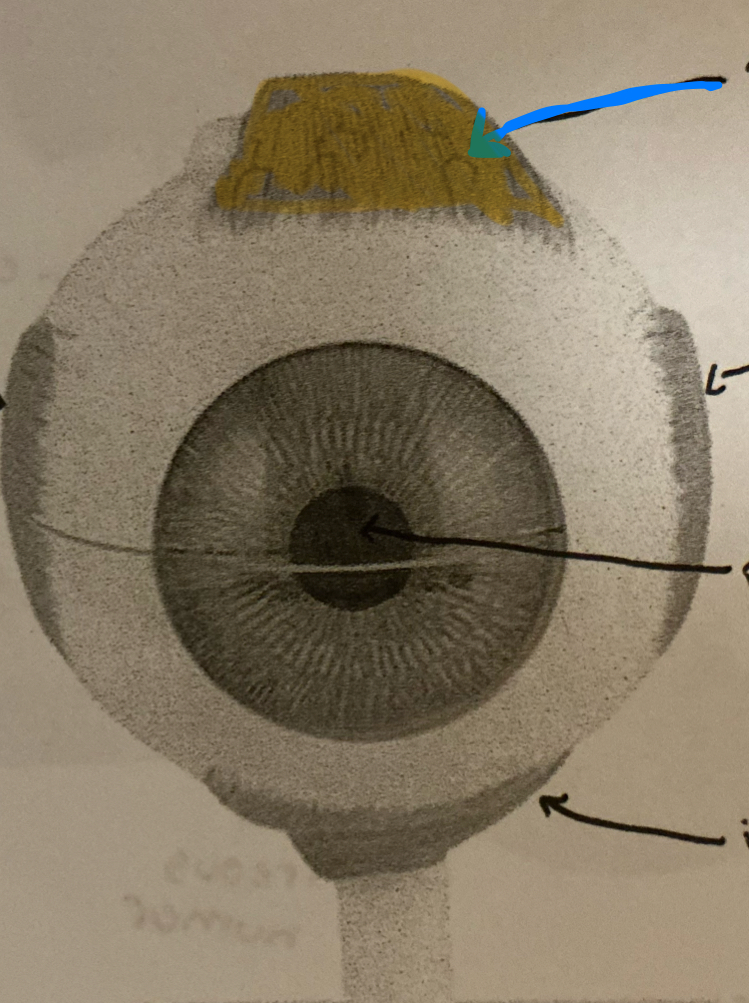
inferior rectus
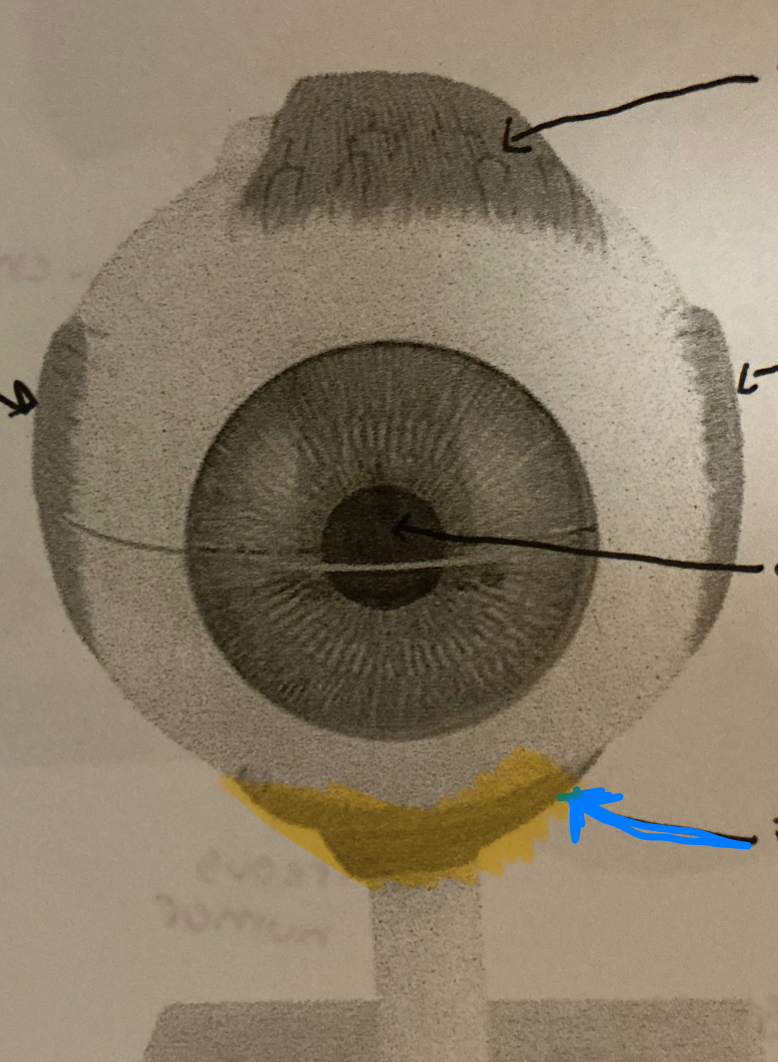
superior oblique
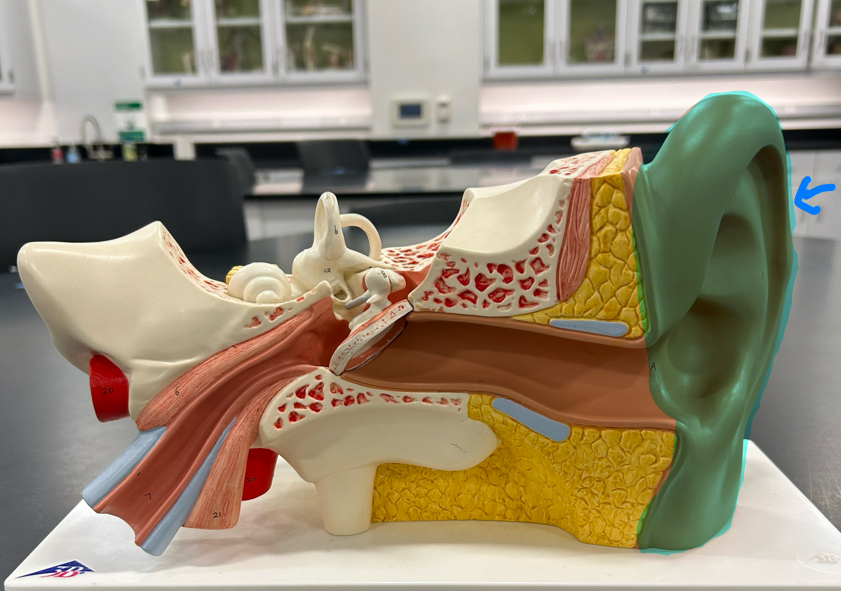
Auricle
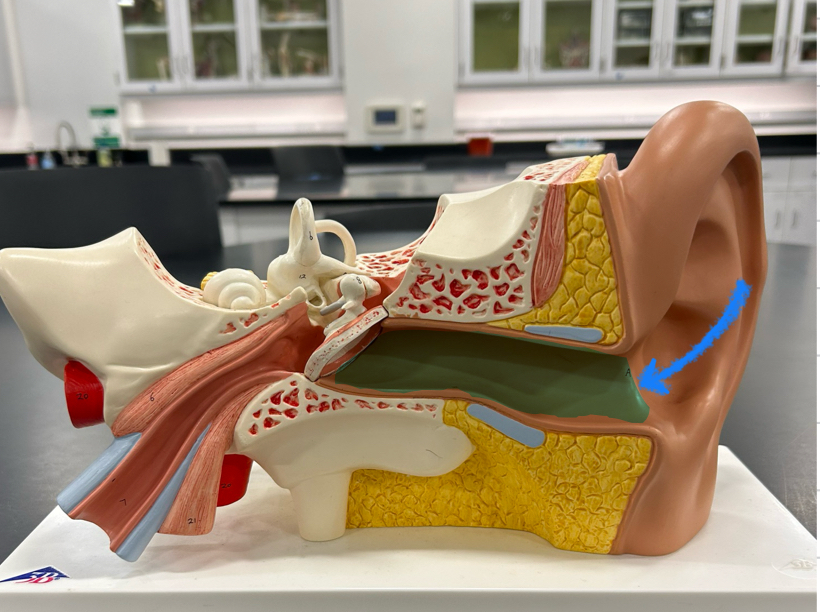
External acoustic meatus
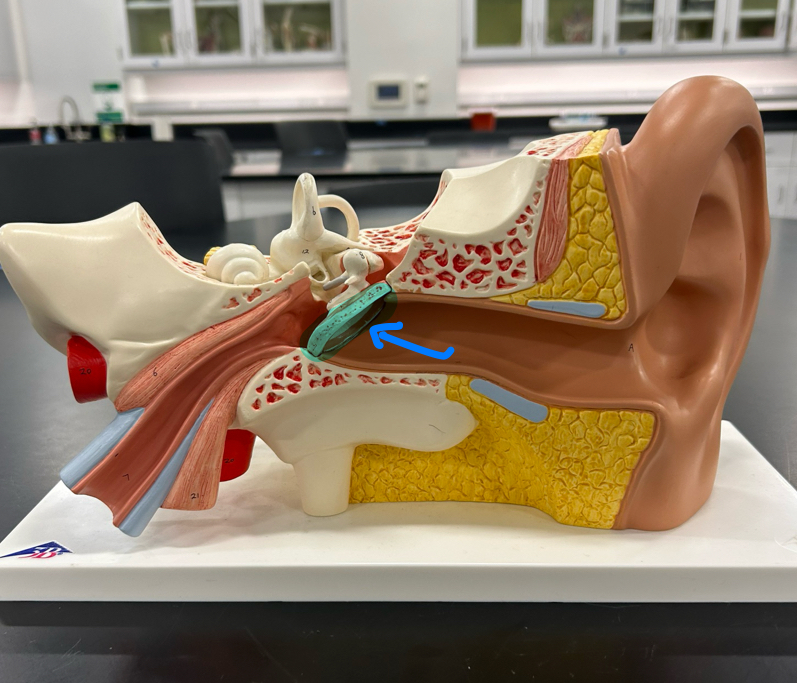
Tympanic membrane: Vibrates in response to sound waves and transmits these vibrations to the middle ear bones
*
Ossicles
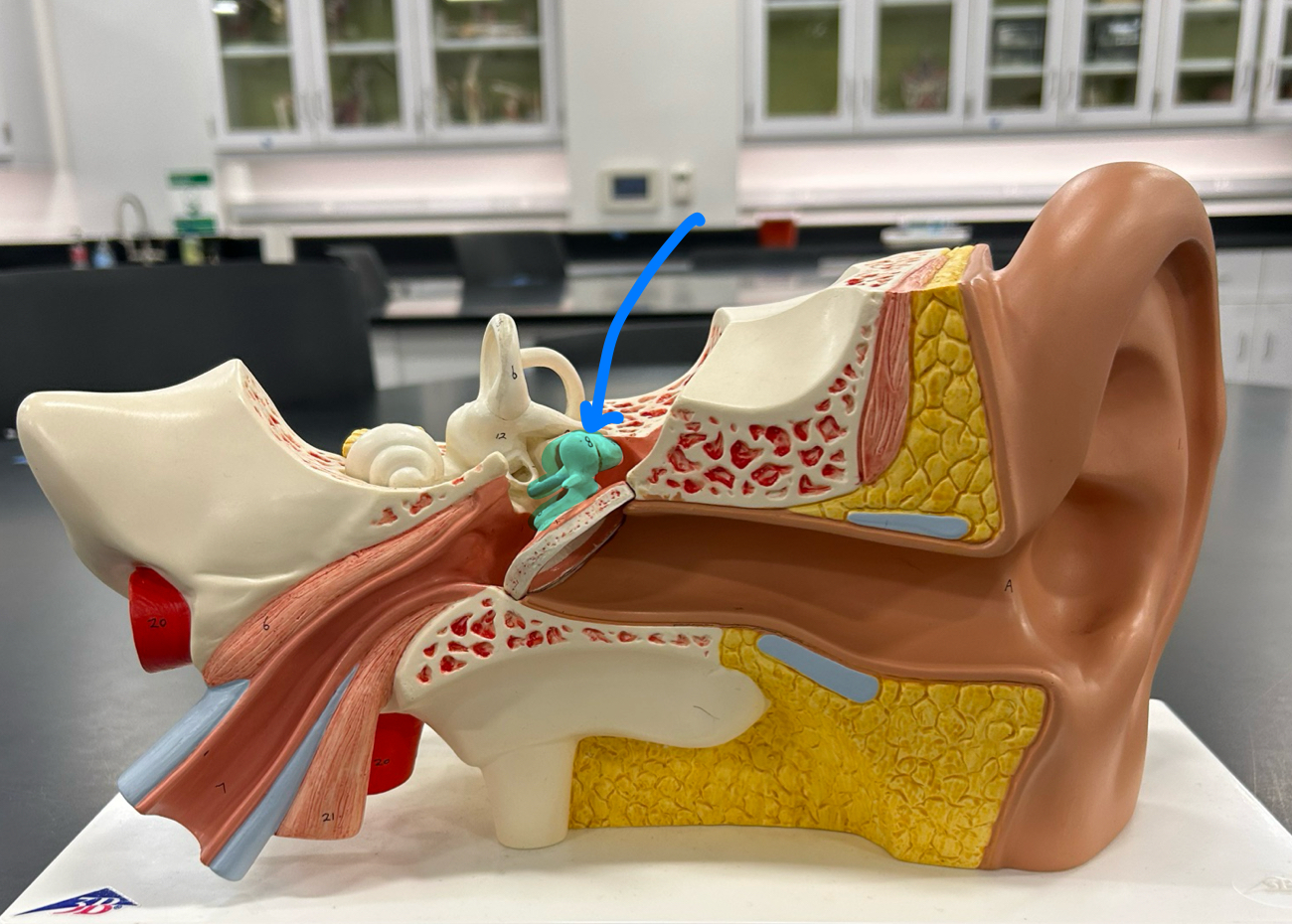
Malleus
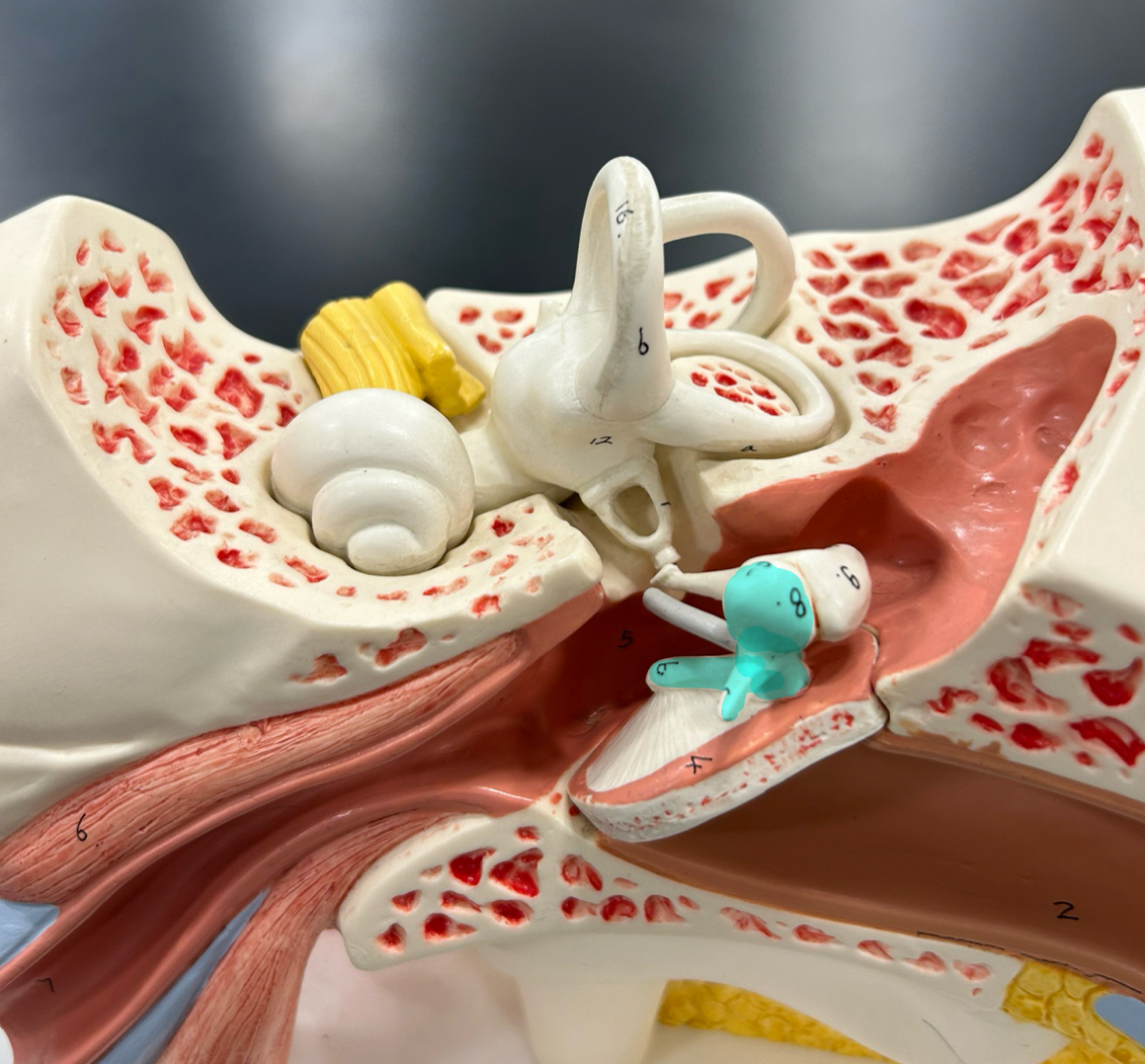
Incus
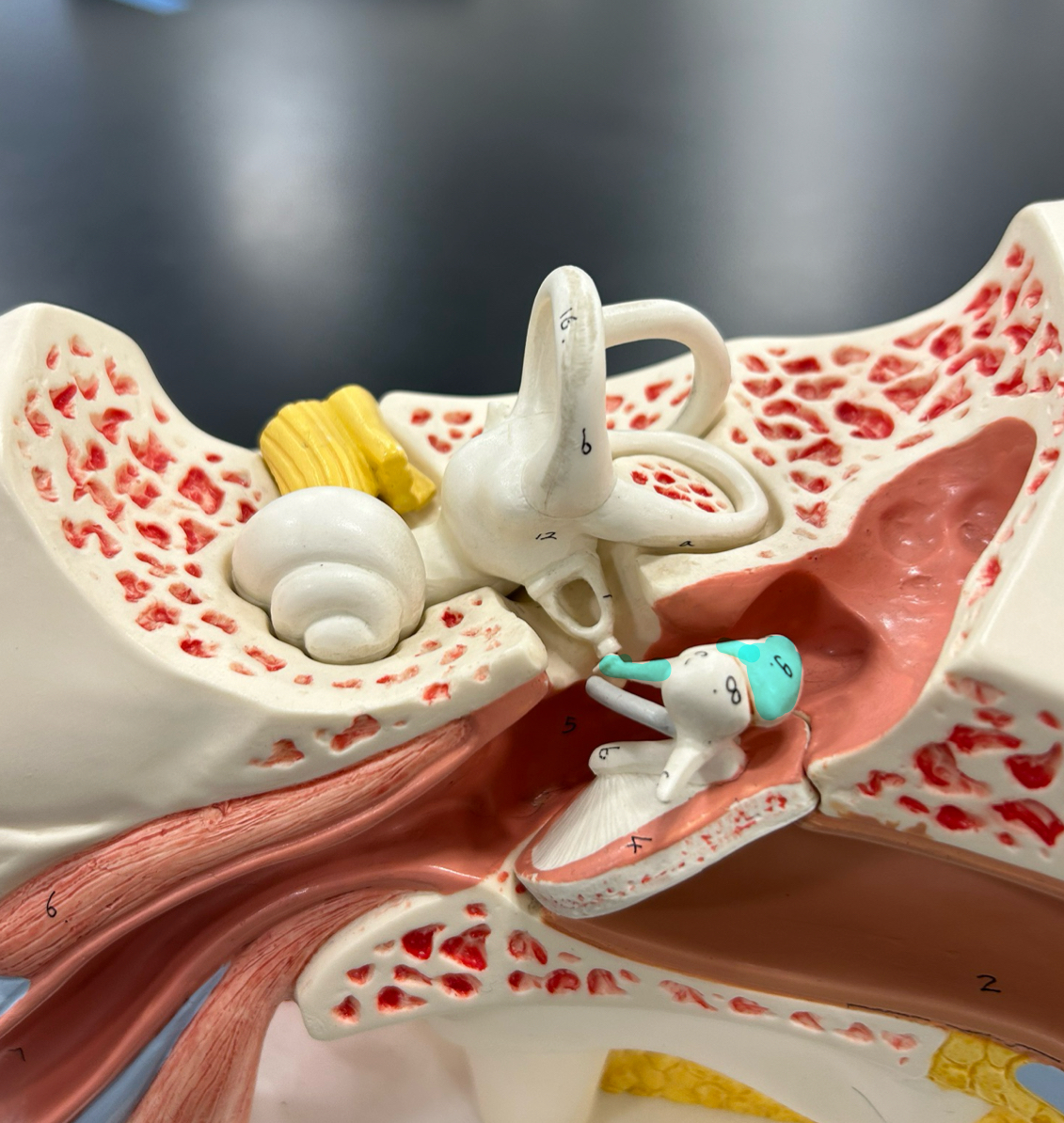
Stapes
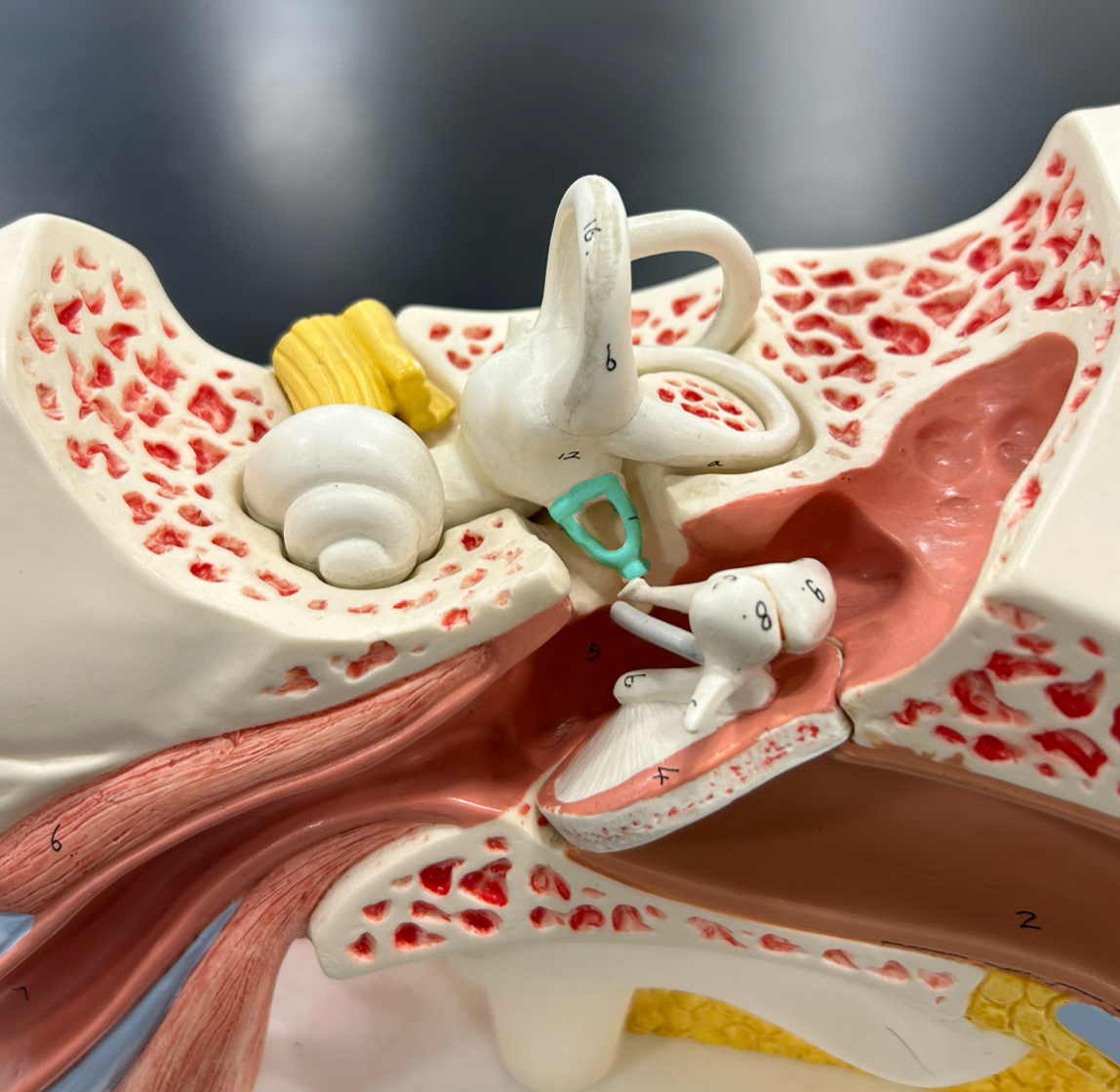
Auditory tube: Equalizes air pressure between the middle ear and the throat to maintain balance and proper hearing
*
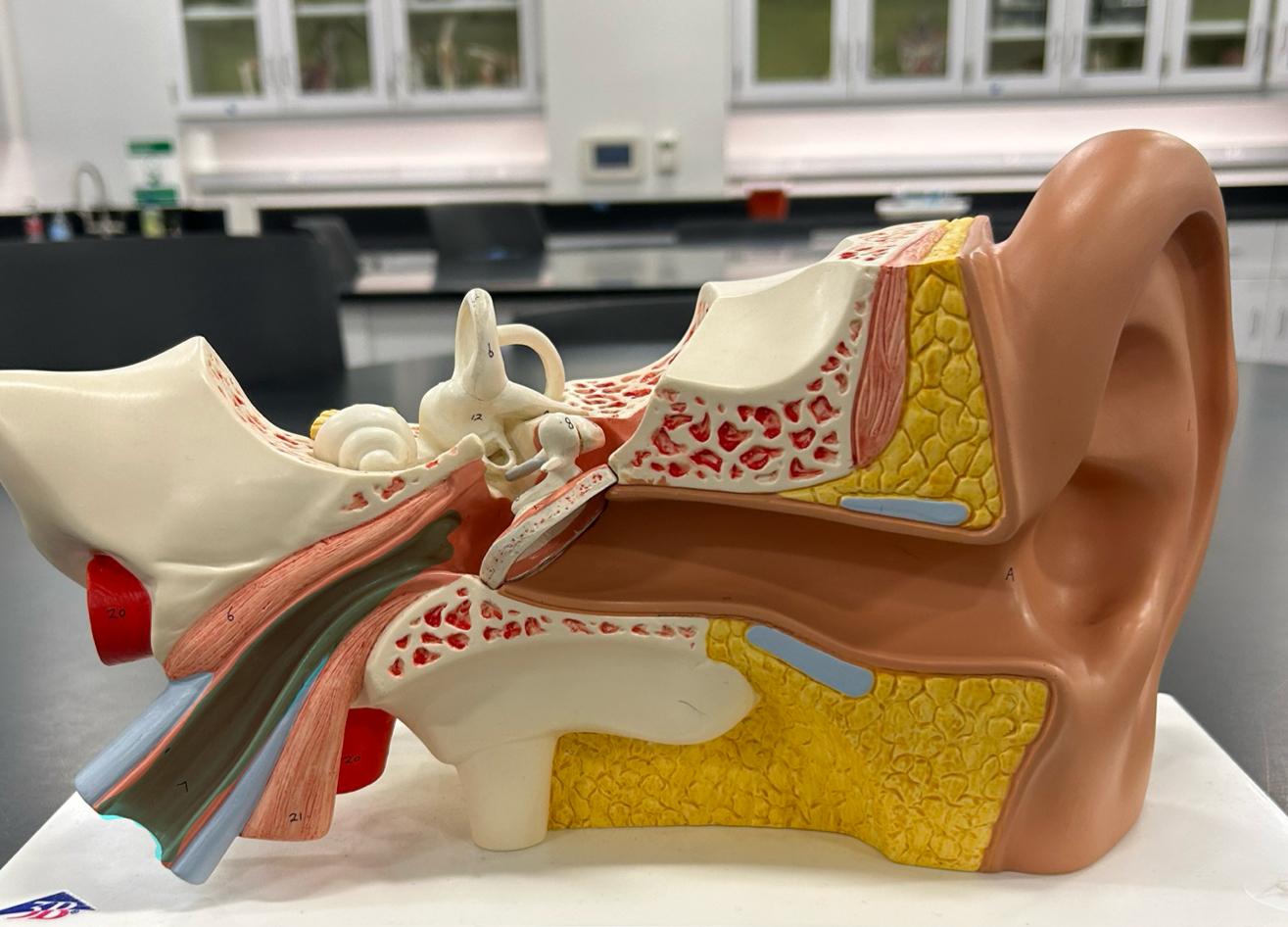
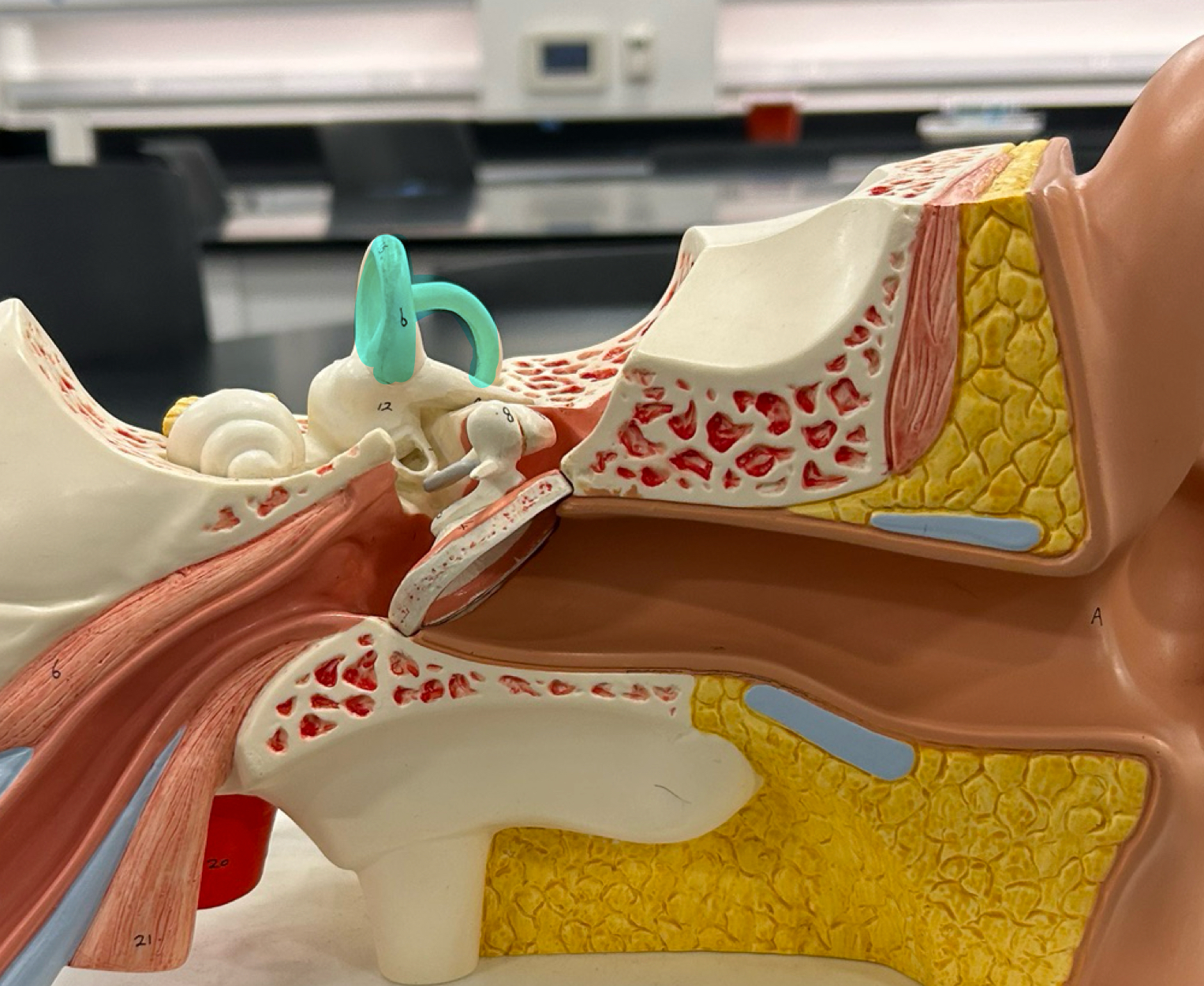
semicircular canals: Detect head rotation and help maintain balance and spatial orientation
*
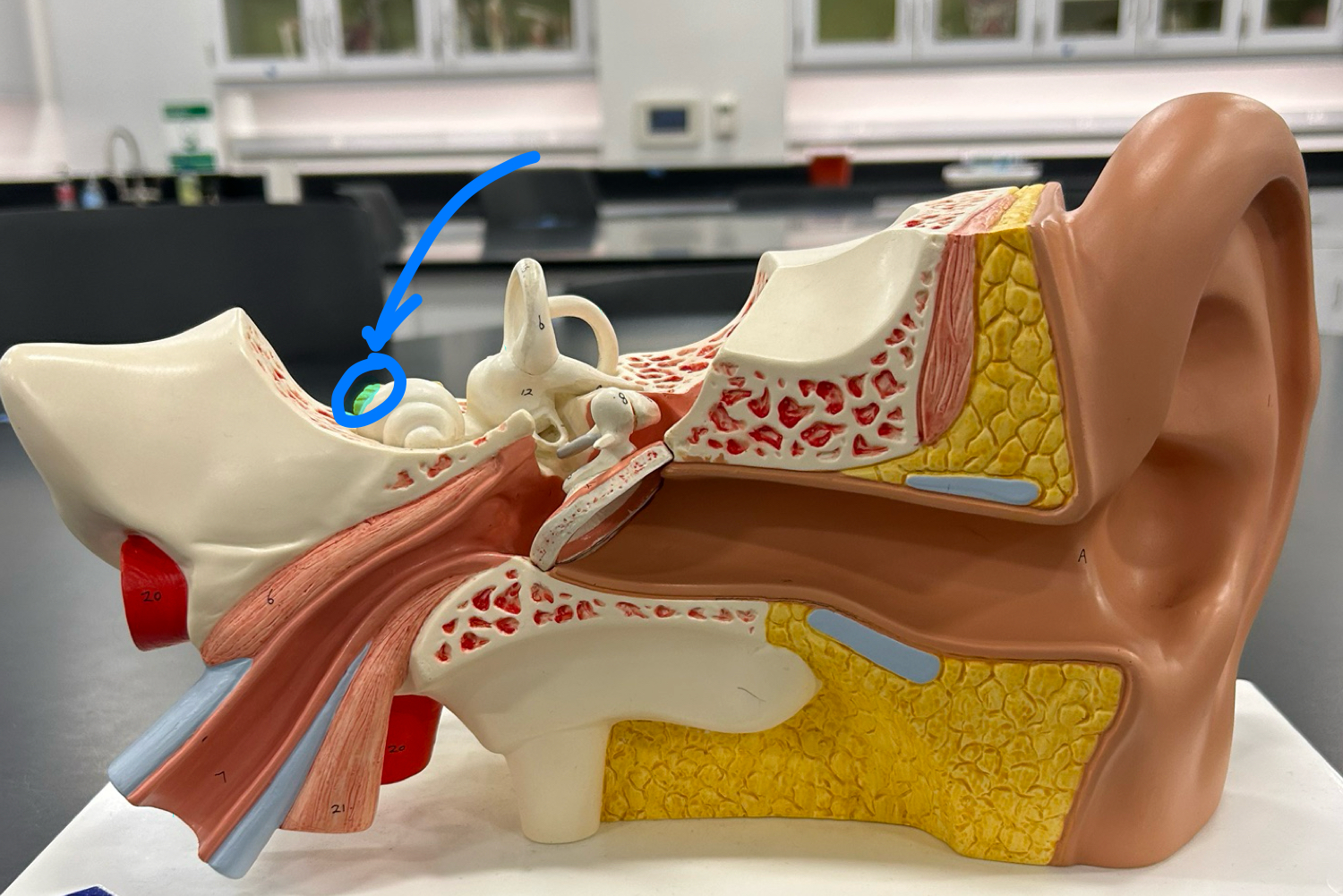
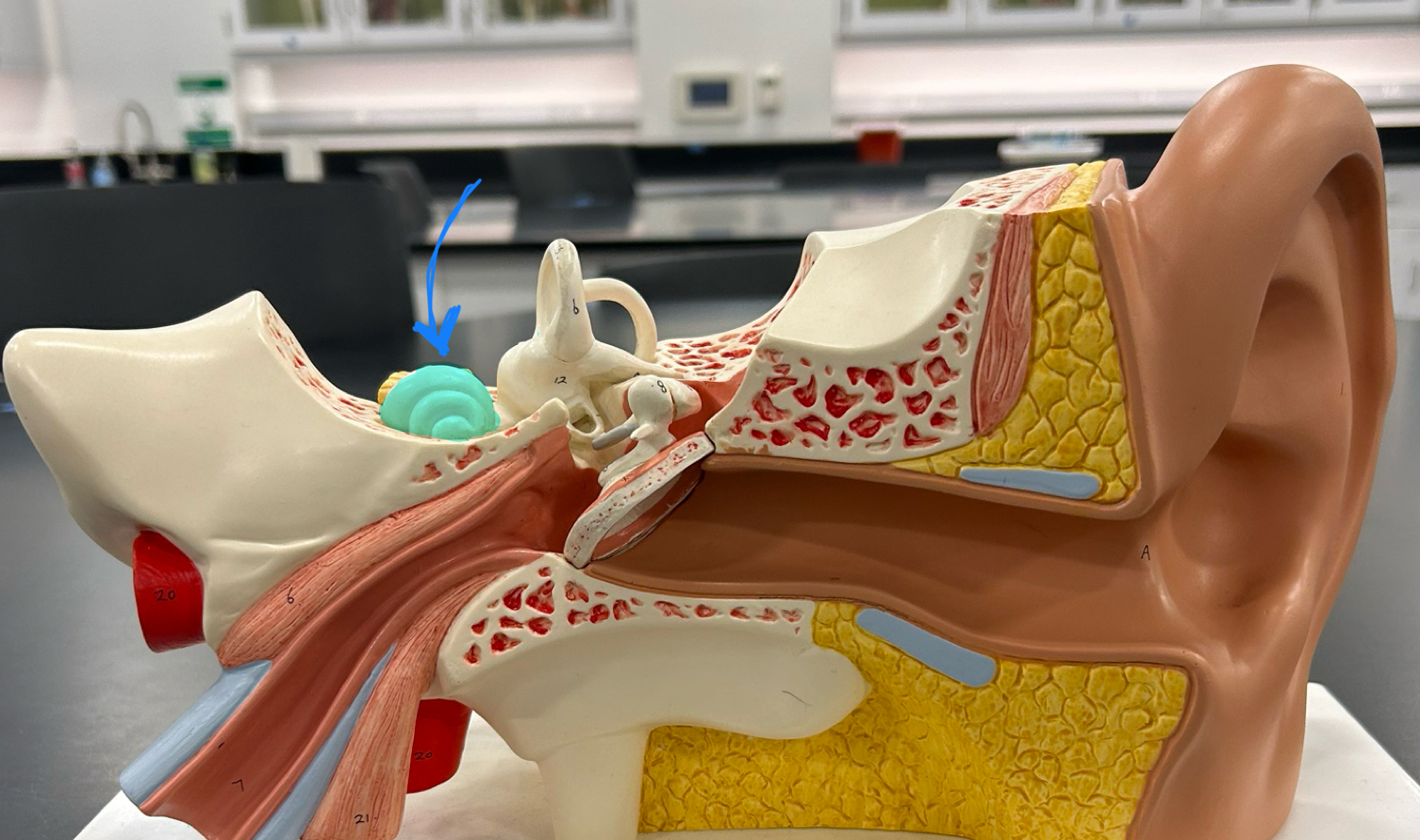
cochlea: Converts sound vibrations into nerve signals for hearing
*
Vestibulocochlear Nerve