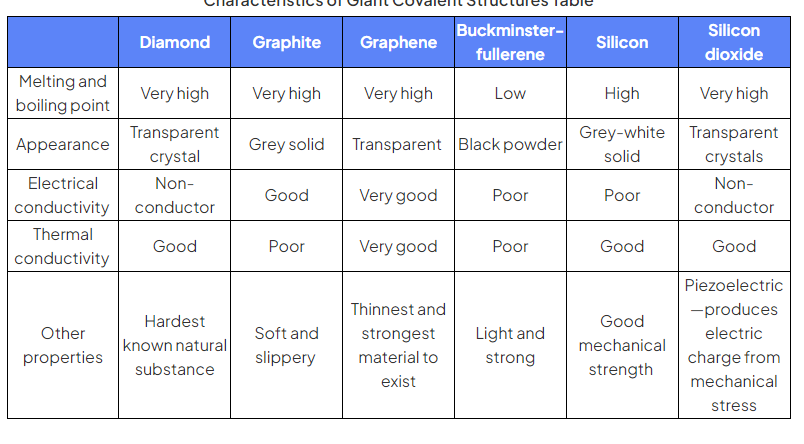
2.2.7 Giant Covalent Structures
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what are allotropes
different molecular arrangements of the same atom
what are the allotropes of carbon (4)
graphene
graphite
buckminster fullerene
diamond
what is a giant covalent network structure
3D structure where atoms are bonded covalently and indefinitely, forming a large lattice. No individual molecules.
describe the strucutre and bondign of diamond
each carbon atom covalently bonded to 4 other carbon atoms to form a tetrahedral structure with a bond angle of 109.5
describe the strucutre and bonding of grpahite
each carbon atom bonded to 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal layers with bond angles of 120, trigonal planar. layers are held together by weak intermoleucular forces
describe the structure and bonding of buckminster fullerene
contains 60 carbon atoms with each carbon atom bonding to 3 other c atoms. 4 electron delocalised so electrons can migrate through the strucutre
12 pentagons and 20 hexagons
describe the structure and bonding in graphene
single layer of carbon atoms (single layer of groahite) with each carbon atom bonded covalently to 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagons
describe the structure and bonding of silicon
tetrahedral arrangement like diamond and 109.5 bond angle, with each silicon atom covalentyl bonding to 4 other silicon atoms to form a giant lattice structure
descibe the structure of silicon (IV) dioxide (sand od silicon dioxide)
same structure of diamonds: gaint tetrahedral strucutre all bonded covalently with 109.5 bond angle
each silicon bonds to 4 oxygens and each oxygen bonds to 2 silicons
what is the empiricial formula of diamond
SiO2
dogianto covalent networks have high or low melting and boiling points and why
high because they have strong covalent bonds throughout which require lots of energy to overcome
is graphite soft or hard and why
soft becuse regular layers can slide over each other as a result of weak intermoleuclar forces
are diamond and silicon dioxide hard or soft and why
hard because difficult to break strong network of covalent bonds
why can graphite and graphene conduct electricity
have delocalised electrons between carbon layers as each c atom ony bonded to 3, not 4 so electron can carry a charge throught the structure
why do diamond and silicon dioxide not conduct electricity
all 4 electrons of every atom are part of covalent bond so no free electrons availible
table of properties