Edexcel IGCSE Physics - Energy
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Define kinetic energy
The energy an object has as a result of its mass and speed
This means that any object in motion has kinetic energy
Define gravitational potential energy
The energy an object has due to its height in a gravitational field
This means: If an object is lifted up it will gain GPE. If it falls, it will lose GPE
Define elastic potential energy
The energy stored in any compressed or stretched object such as a spring, rubber band, etc.
Define electrostatic energy
Energy due to the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two charges
Define magnetic energy
Energy due to the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two magnets
Define chemical energy
Energy found in fuels, foods or batteries.
This energy is transferred during chemical reactions
Define nuclear energy
Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
Describe thermal energy
Energy a substance has due to its temperature
In what ways can energy be transferred?
The different energy transfer mechanisms are:
Heating
Electrical
Radiation
Mechanical
Remember HERM!
Describe the energy transfer for a falling object
gravitational potential energy ➝ kinetic energy
Describe the energy transfer for a battery powering a torch
chemical energy ➝ electrical energy ➝ light energy
Describe the energy transfer for a mass on a spring
elastic potential energy ➝ kinetic energy
What is the principle of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transferred from one store to another
Remember: this means that energy cannot be 'lost', it I just transferred into wasted energy
What are the energy changes in televisions?
Which transfers are useful and which transfers are wasted?
electrical energy ➝ light energy + sound energy + thermal energy
Light and sound energy are useful energy transfers whereas thermal energy (from the heating up of wires) is wasted
What are the energy changes in an electrical heater?
Which transfers are useful and which transfers are wasted?
Electrical energy ➝ thermal energy + sound energy + light energy
Thermal energy is useful, whereas sound and light are not
What are the energy changes in a gas cooker?
Which transfers are useful and which transfers are wasted?
chemical energy ➝ thermal energy + sound energy + light energy
Thermal energy is useful, whereas sound and light are not
What are the energy changes when someone is jumping on a trampoline?
elastic potential energy ➝ kinetic energy ➝ gravitational potential energy
There is also some energy transferred to the surroundings as heat and sound energy
Define efficiency
The ratio of the useful energy transferred by the device to the total energy supplied to the device
(This makes sense when you think of the equation!)
How can efficiency be calculated?
Exam tips:
Efficiency can be a ratio (between 0 and 1) or a percentage.
If the question asks for efficiency as a ratio, give your answer as a fraction or a decimal.
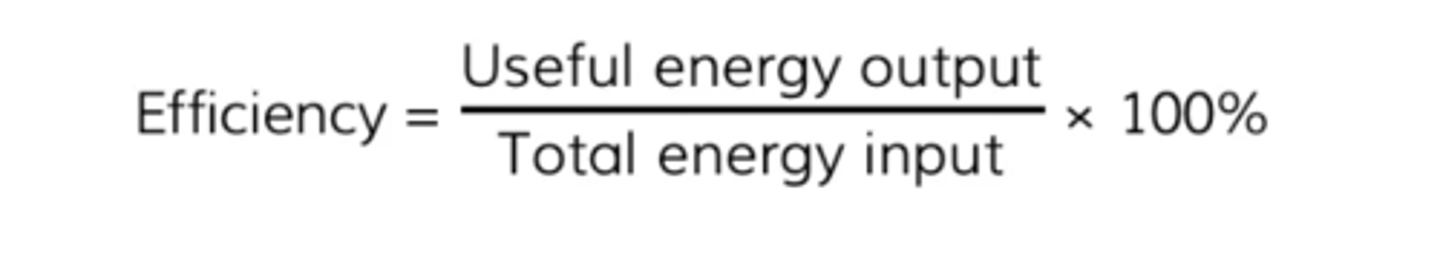
If a system has high efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is....
Useful
If a system has low efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is...
Wasted
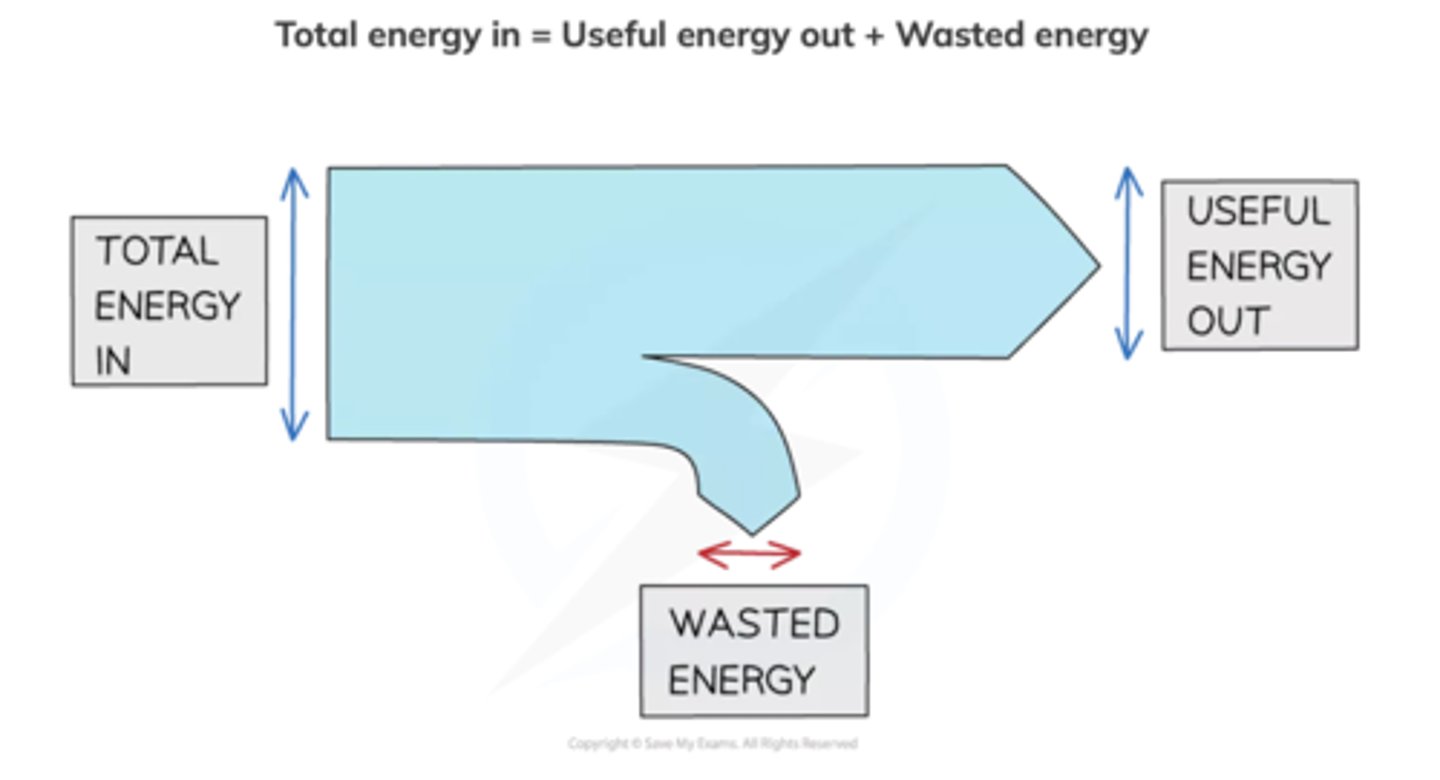
What are the diagrams that are used to represent energy transfers called?
Sankey diagrams
What do the arrows in a Sankey diagram represent?
The arrow pointing to the right represents useful energy output
The arrow pointing down represents wasted energy
(Remember that the width of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy going to each store)
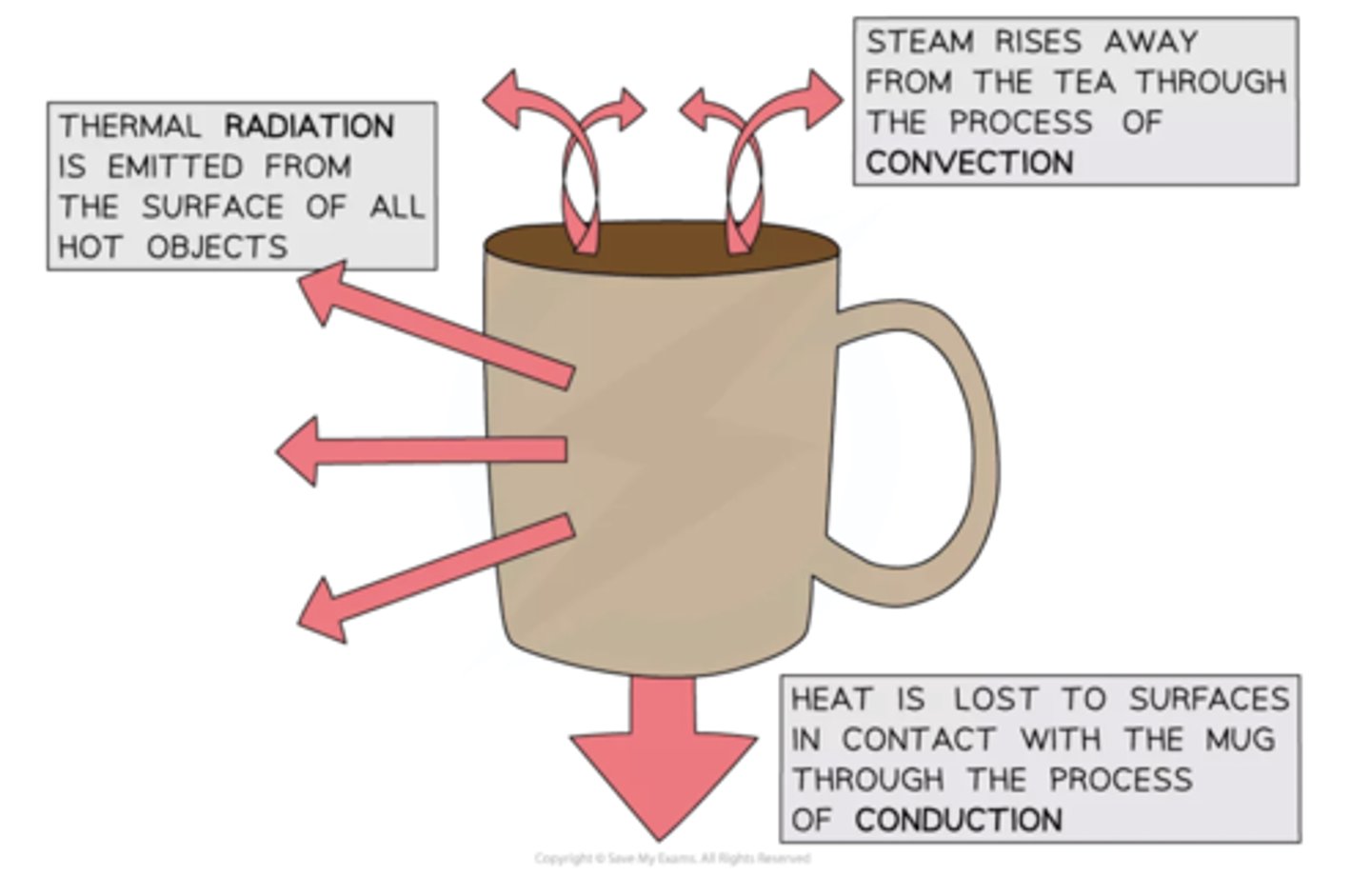
How is thermal energy transferred?
By conduction, convection or radiation
Remember that objects will always lose heat until they are in thermal equilibrium (same temperature) with their surroundings, e.g. a mug of hot tea will cool down until it reaches room temperature
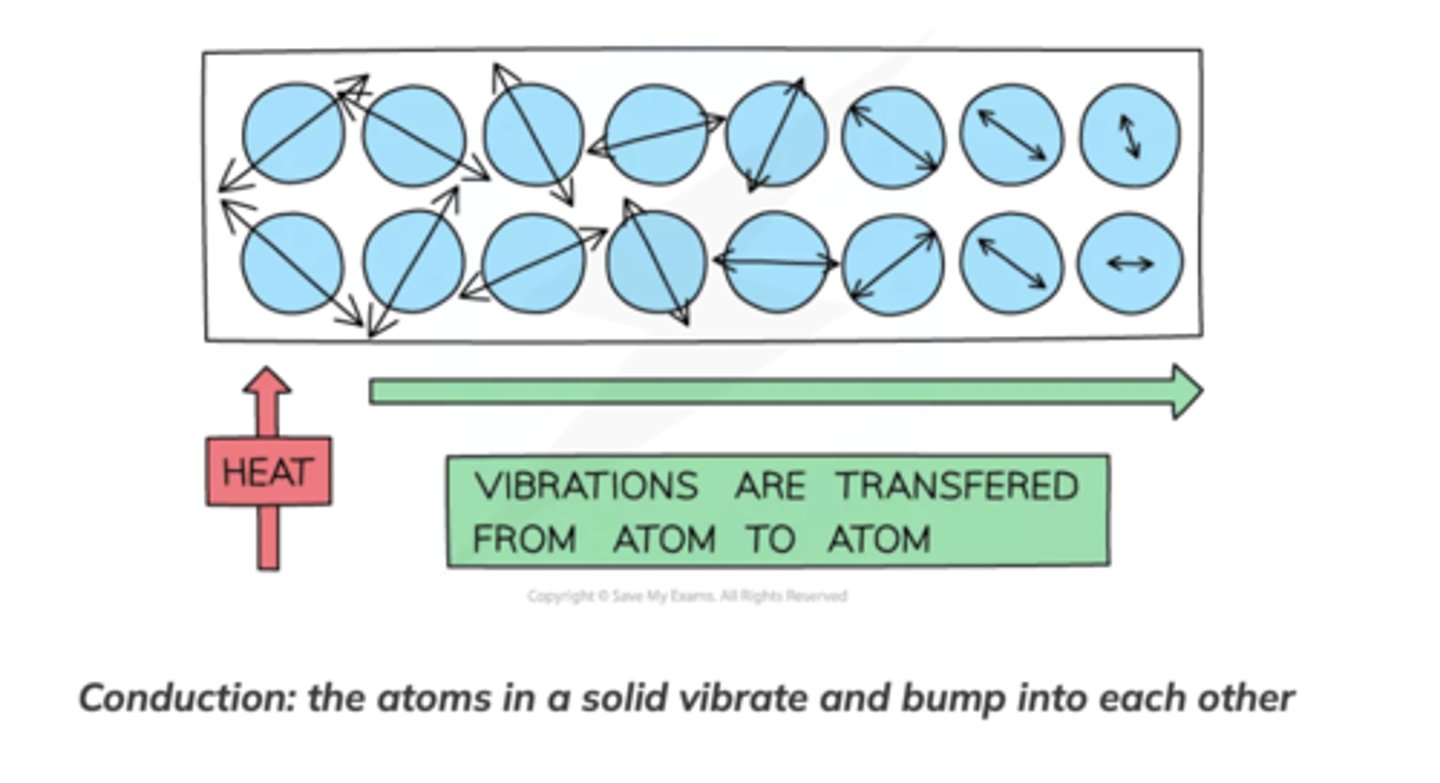
What is the main method of thermal energy transfer in solids?
How does it work?
Conduction
When a substance is heated, the atoms vibrate more. As they do so they bump into each other, transferring energy from atom to atom. Metals are especially good at conducting heat as the delocalised electrons can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material and hence transfer heat better
Poor conductors are called...
Insulators
What is the main way that heat travels through liquids and gases?
How does this work?
Convection (Remember convection CANNOT occur in solids)
When a fluid (a liquid or a gas) is heated: The molecules push each other apart, making the fluid expand. This makes the hot fluid less dense than the surroundings. The hot fluid rises, and the cooler (surrounding) fluid moves in to take its place. Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down againThe resulting motion is called a convection current
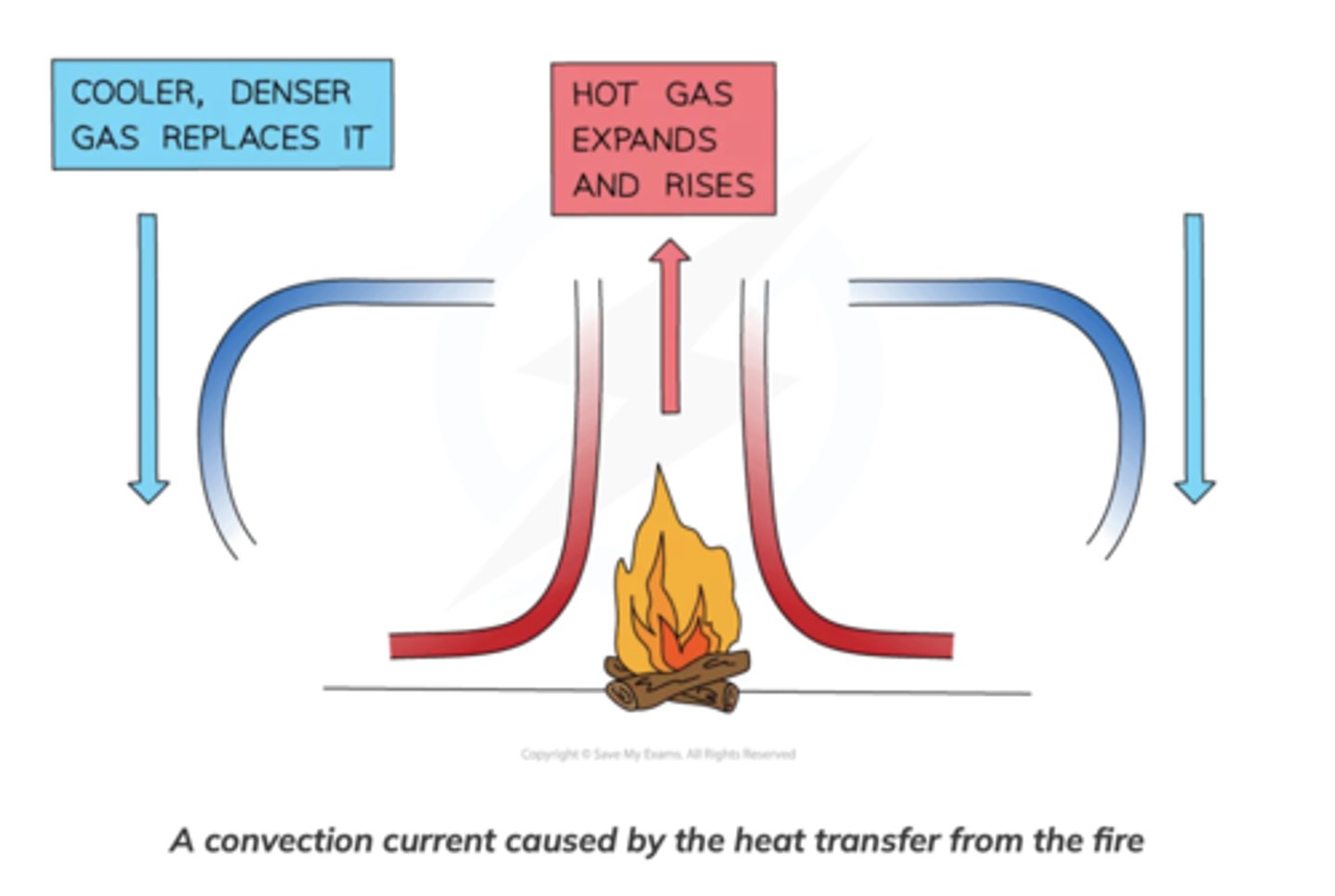
Thermal radiation is heat transfer by _______
Infrared
The hotter object, the more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time.
(Remember that all objects, no matter what temperature, emit a spectrum of thermal radiation)
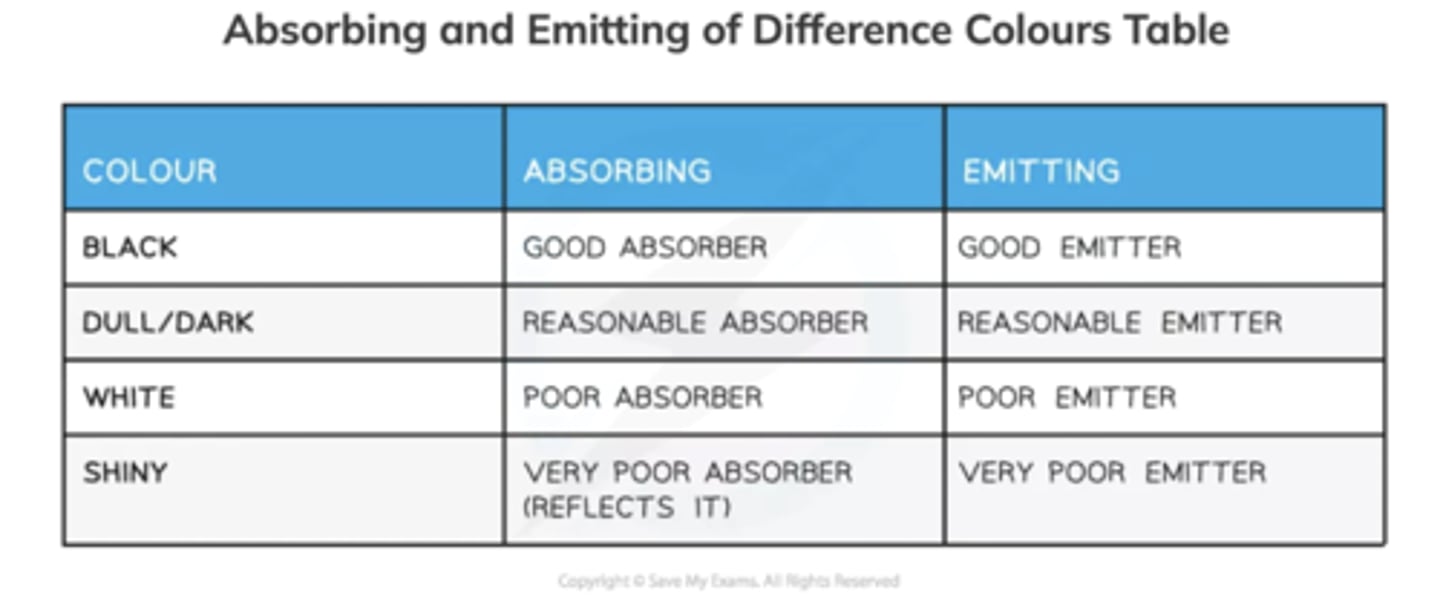
_______ objects are the best at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation
Black
Remember: Black things do not absorb heat (they absorb thermal radiation)
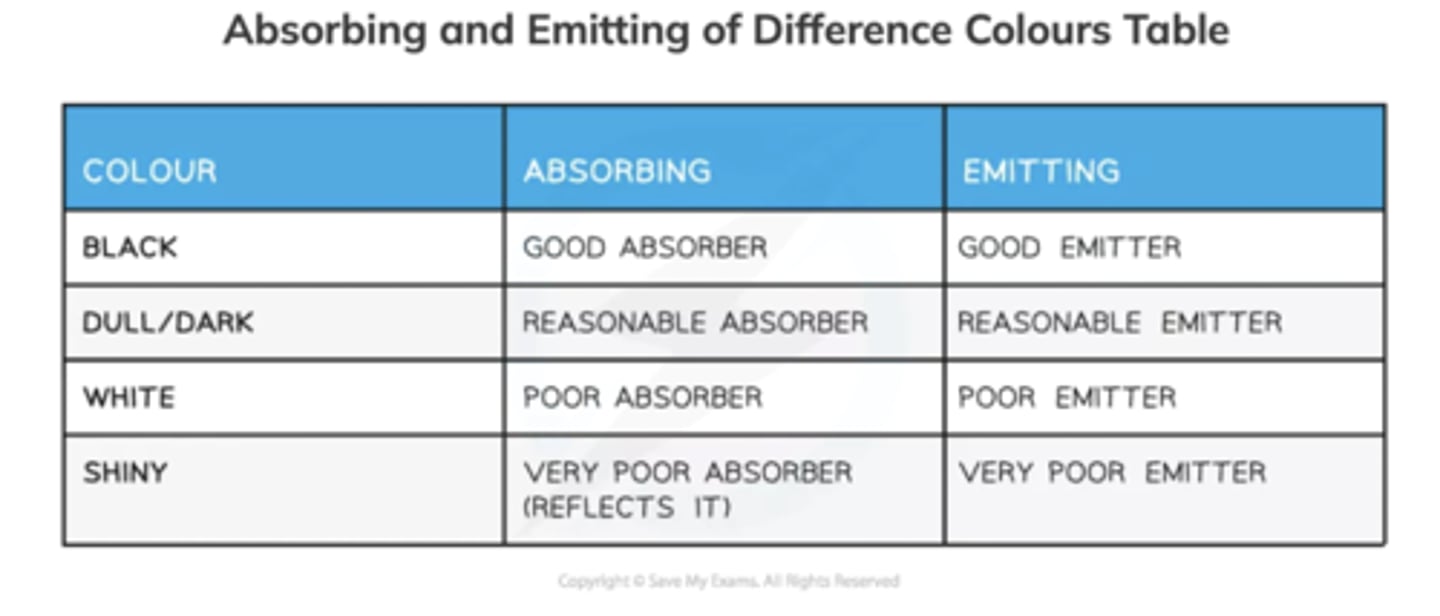
_______ objects are the worst at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation
Shiny
Remember: Shiny things do not reflect heat (they reflect thermal radiation)
What is the only way in which heat can travel through a vacuum? Why?
Radiation
Conduction and convection require particles to transfer heat!
What two factors does the effectiveness of insulation depend on?
How well the insulation conducts heat
How thick the insulation is
How does an insulator keep something warm?
The insulator contains trapped air, which is a poor conductor of heat.
Trapping the air also prevents it from transferring heat by convection.
This reduces the rate of heat loss from the object, meaning that it will stay warmer for longer
The amount of energy transferred (in joules) is equal to the ________ (also in joules)
Work done
Energy transferred (J) = Work done (J)
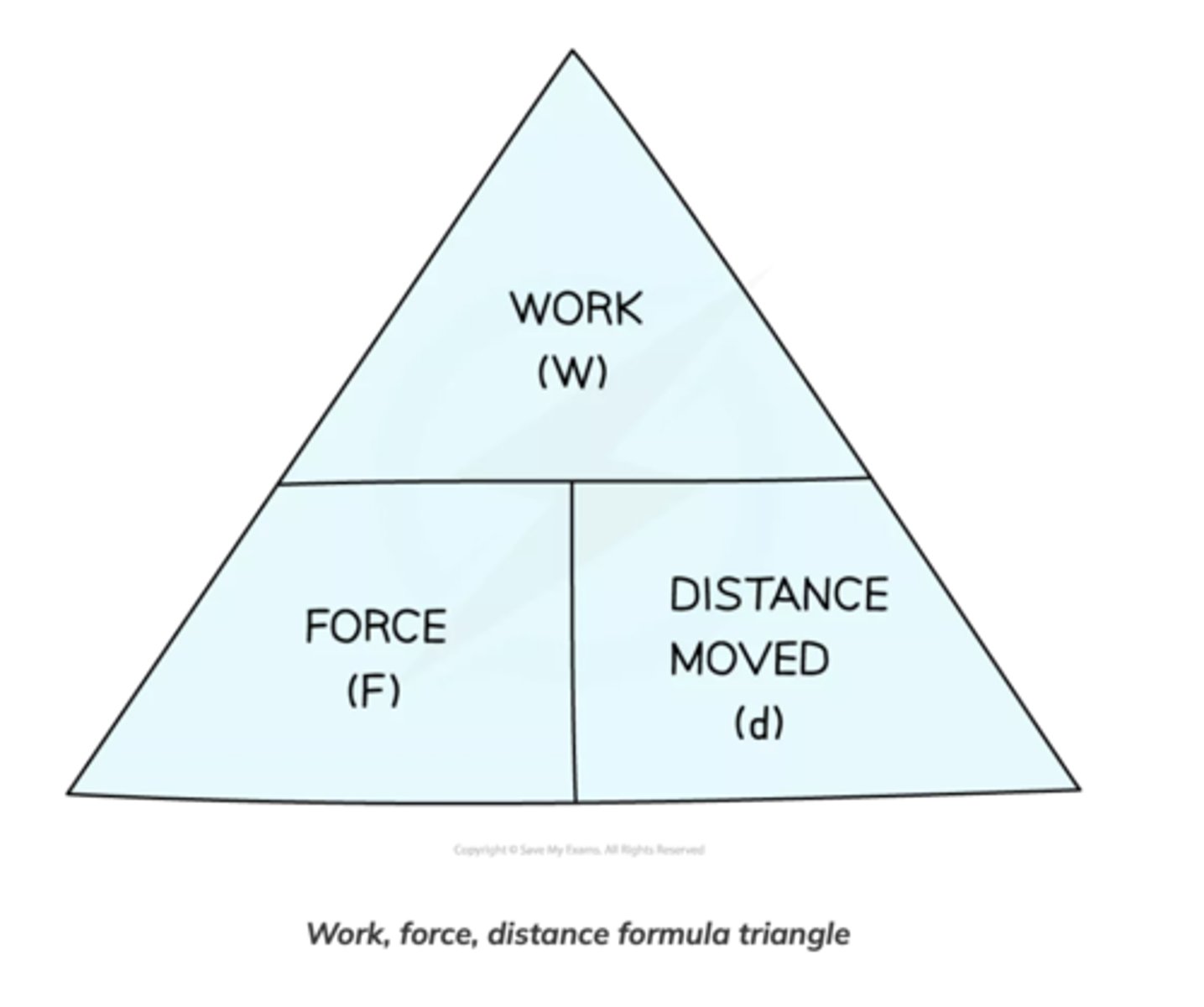
How can the amount of work done on an object by a force be calculated?
W = f × d
W= work done in Joules (J) or newton-metres (N m)
F = force in Newtons (N)
d = distance in metres (m)
How can the GPE of an object be calculated?
GPE = mgh
GPE = gravitational potential energy, in Joules (J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
g = gravitational field strength in Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
h = height in metres (m)
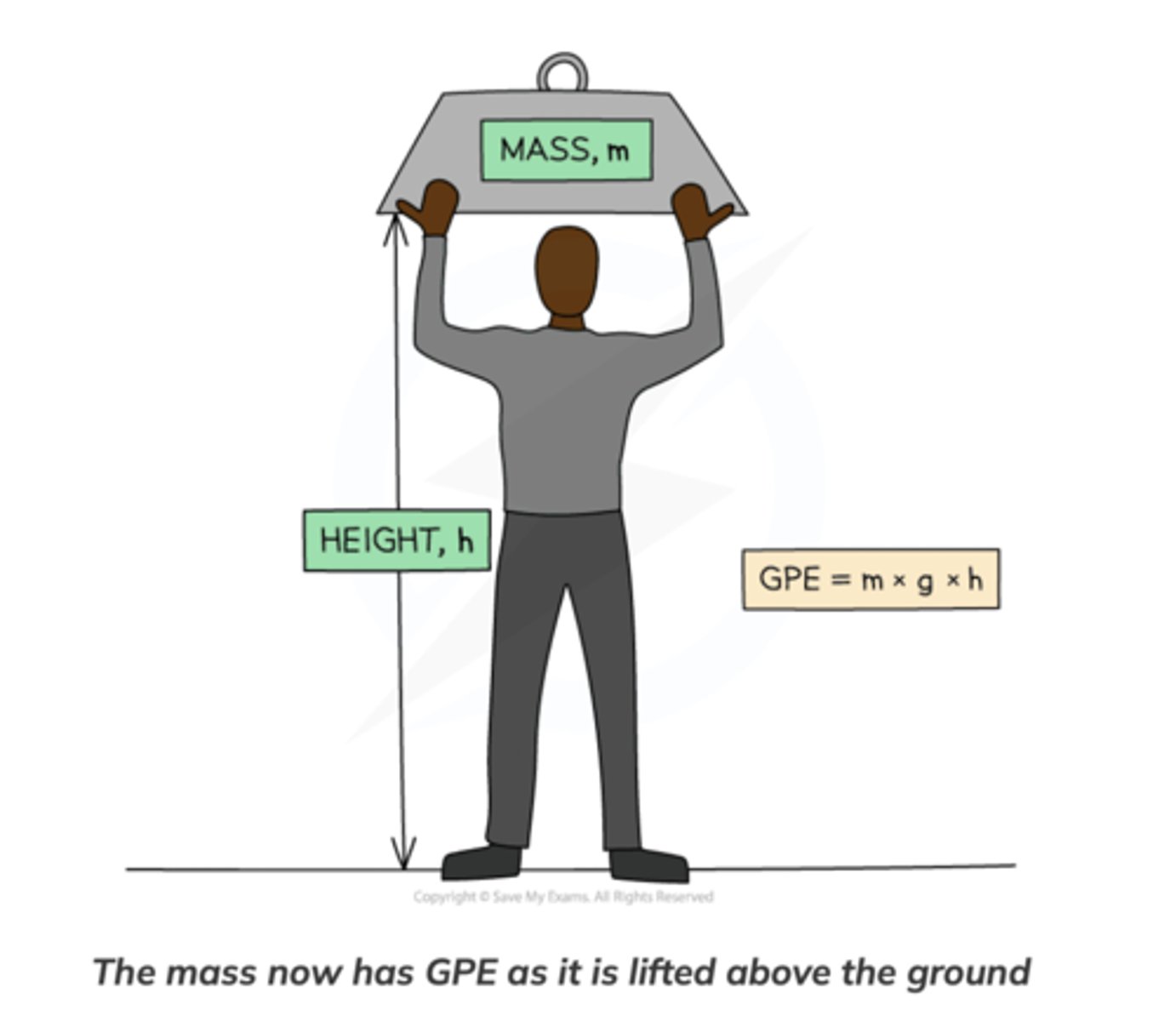
What is the gravitational field strength (g) on Earth?
Approximately 10 N/kg
Is the gravitational field strength on the surface of the moon greater than or less than on the earth?
Less than
So it would be easier to lift a mass on the Moon than on the Earth
Is the gravitational field strength on the surface of the gas giants (eg. Jupiter and Saturn) greater than or less than on the earth?
More than
So it would be harder to lift a mass on the gas giants than on the Earth
How can kinetic energy be calculated?
KE = ½ × m × v2
Where: KE = kinetic energy in Joules (J)m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
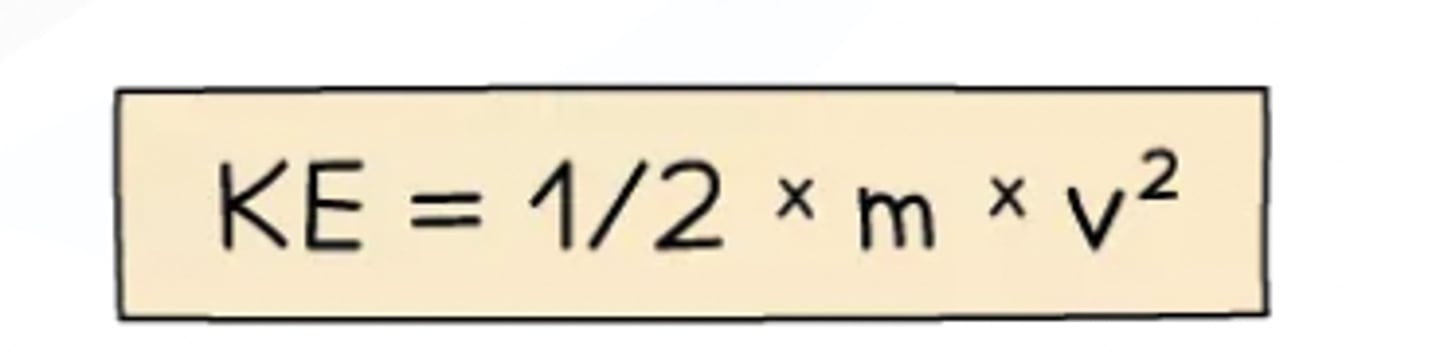
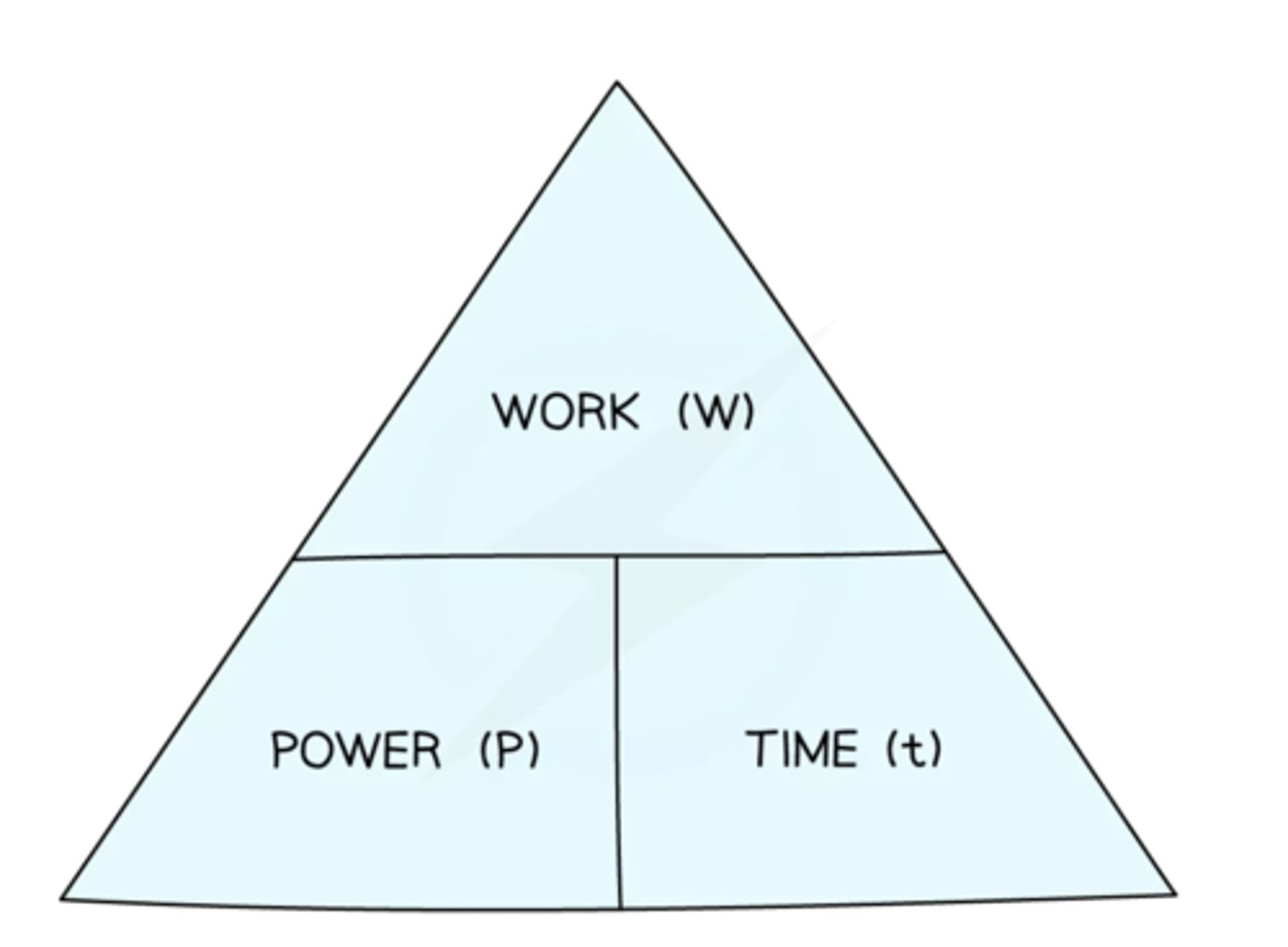
How is power defined?
Power is defined as the energy transferred per unit time or the work done per unit time
Exam tip: Think of power as “energy per second”
How is power calculated?
Energy or work done/time
E or W = The energy transferred, or work done, measured in joules (J)
t = time measured in seconds (s)
P = power measured in watts (W)
How is a renewable energy resource defined?
An energy source that is replenished at a faster rate than the rate at which it is being used
As a result of this, renewable energy resources cannot run out
Give examples of renewable energy resources
Solar energy
Wind
Bio-fuel
Hydroelectricity
Geothermal
Tidal
How are fossil fuels used as an energy resource?
Burning fossil fuels produces steam which can turn turbines
Describe the energy transfers that occur in fossil fuels when they are used as an energy resource
chemical energy → thermal energy → kinetic energy → electrical energy
How is nuclear energy used as an energy resource?
Nuclear fuel is reacted, producing heat which creates steam that can turn turbines
Describe the energy transfers that occur when nuclear energy is used as an energy resource
nuclear energy → thermal energy → kinetic energy → electrical energy
How are bio-fuels used as an energy resource?
Plant matter, ethanol or methane can be produced and then burned directly to generate energy
Describe the energy transfers that occur when bio-fuels are used as an energy resource
chemical energy → thermal energy → electrical energy
How is wind used as an energy resource?
Wind turbines can be used to produce electricity
Describe the energy transfers that occur when wind is used as an energy resource
kinetic energy → electrical energy
How is hydroelectric energy used as an energy resource?
Hydroelectric uses the GPE of water stored in reservoirs to turn turbines which generate electricity
Describe the energy transfers that occur when hydroelectricity is used as an energy resource
gravitational potential energy → kinetic energy → electrical energy
How is geothermal energy used as an energy resource?
Heat from underground can be used to create steam which spin turbines, producing electricity
Describe the energy transfers that occur when geothermal energy is used as an energy resource
thermal energy → kinetic energy → electrical energy
How is tidal energy used as an energy resource?
A dam is used to trap seawater at high tide, which can then be released through a turbine generating electricity
Describe the energy transfers that occur when tidal energy is used as an energy resource
kinetic energy → electrical energy
How is solar power used as an energy resource?
Solar cells convert light energy directly into electrical energy, or thermal radiation from the sun is used to warm water passing through black pipes
What is meant by a reliable energy resource?
A reliable energy resource is one that can produce energy at any time
Remember: Non-reliable resources can only produce energy some of the time (e.g. when it’s windy)
Advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels
Advantages
Reliable
Can produce large amounts of energy at fairly short notice
Disadvantages
Produces significant greenhouse gases and pollution
Advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy
Advantages
Reliable
Produces no greenhouse gases or pollution
A large amount of energy is produced from a small amount of fuel
Disadvantages
Produces dangerous radioactive waste that can take thousands of years to decay
Advantages and disadvantages of bio-fuels
Advantages
The CO2 produced while burning the fuel is balanced by the CO2 absorbed while producing it
Renewable
Disadvantages
Can take up a lot of land and consume resources that are needed for food production
Advantages and disadvantages of wind energy
Advantages
Renewable
Produces no greenhouse gases or pollution
Land can still be used for farming
Disadvantages
Not reliable - no wind = no electricity
Wind farms are noisy and may spoil the view for people living near them
Advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric energy
Advantages
Renewable
Reliable
Can produce a large amount of energy at short notice
Produces no pollution or greenhouse gases
Disadvantages
Hydroelectricity dams flood farmland, destroying important wildlife habitats and pushing people from their homes
Advantages and disadvantages of tidal energy
Advantages
Tides are very predictable and a large amount of energy can be produced at regular intervals
Disadvantages
Very few suitable locations. Can destroy the habitat of estuary species
Advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy
Advantages
Reliable
Renewable
Geothermal power stations are usually small
Disadvantages
Can result in the release of harmful gases from underground
Not many places are suitable
Advantages and disadvantages of solar energy
Advantages
Renewable
No greenhouse gases or pollution
Good for producing energy in remote places
Disadvantages
Not reliable - only work when sunny and do not work at night
Solar farms can use up lots of farmland
Expensive and inefficient