
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
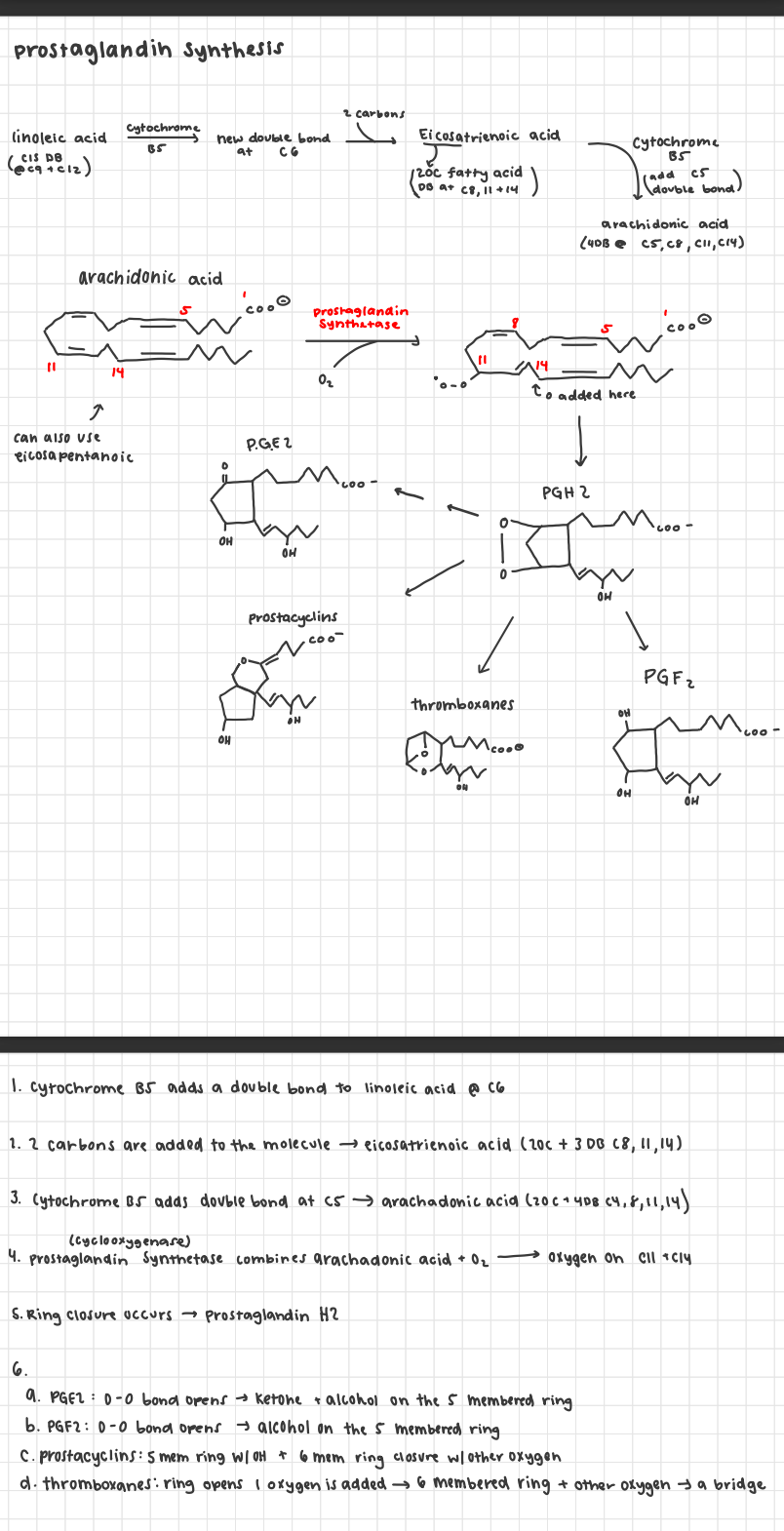
prostaglandins
derived from essential fatty acids which > arachadonic acid
hormone like properties
works on tissue its made in so not a hormone
increases cyclic AMP
affects platelet aggregation, muscle contraction, induce fever = inflammatory rxns
ASPRIN INHIBITS PROSTAGLANDINS
ASPRIN
INHIBITS PROSTAGLANDIN SYNTHESIS !!!!
taking too many > bleeding bc no blood clotting
cant add o2 to arachidonic acid bc cyclooxygenase is inhibited
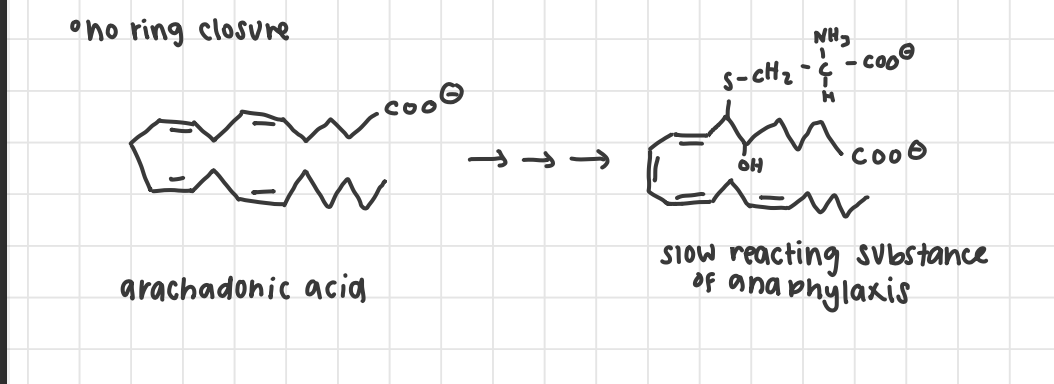
leukotrienes
made from essential fatty acids
add AA + o2 to arachadonic acid
NO RING CLOSURES
prostaglandin synthesis
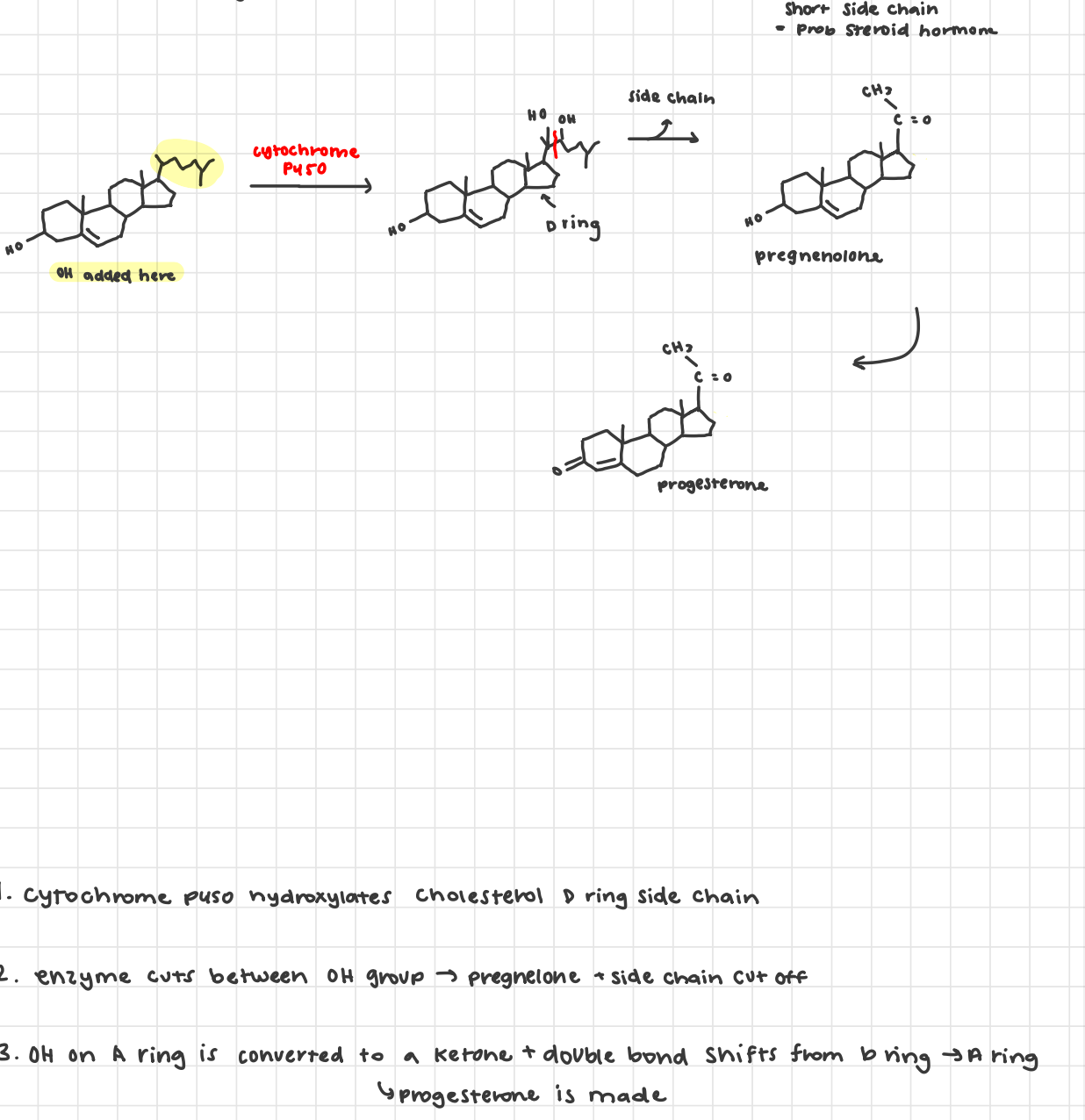
cholesterol
all carbons from acetyl COA
4 ring structure
mainly produced by liver but all cells can make it
reductase involved in cholesterol synthesis
converts 3 hydroxy 3 methyl glutaryl coa to mevalonic acid COMMITTED STEP
regulated by amt of dietary cholesterol and statin drugs
not allosteric
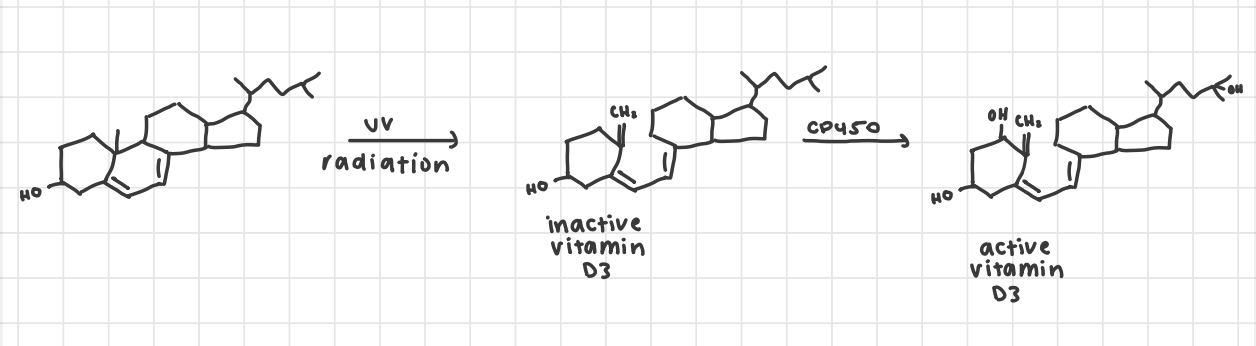
vitamin D activation
increases Ca2+ in blood + uptake from liver
regulated bone formation
intermediate reacts with UV > inactive vitamin D with open B ring > cytochrome p450 hydroxylates the ring > active vitamin D
SEE 21 + 22 for cholesterol synthesis (complex AF)
cholesterol uses
excretion
bile salts
to cell membrane
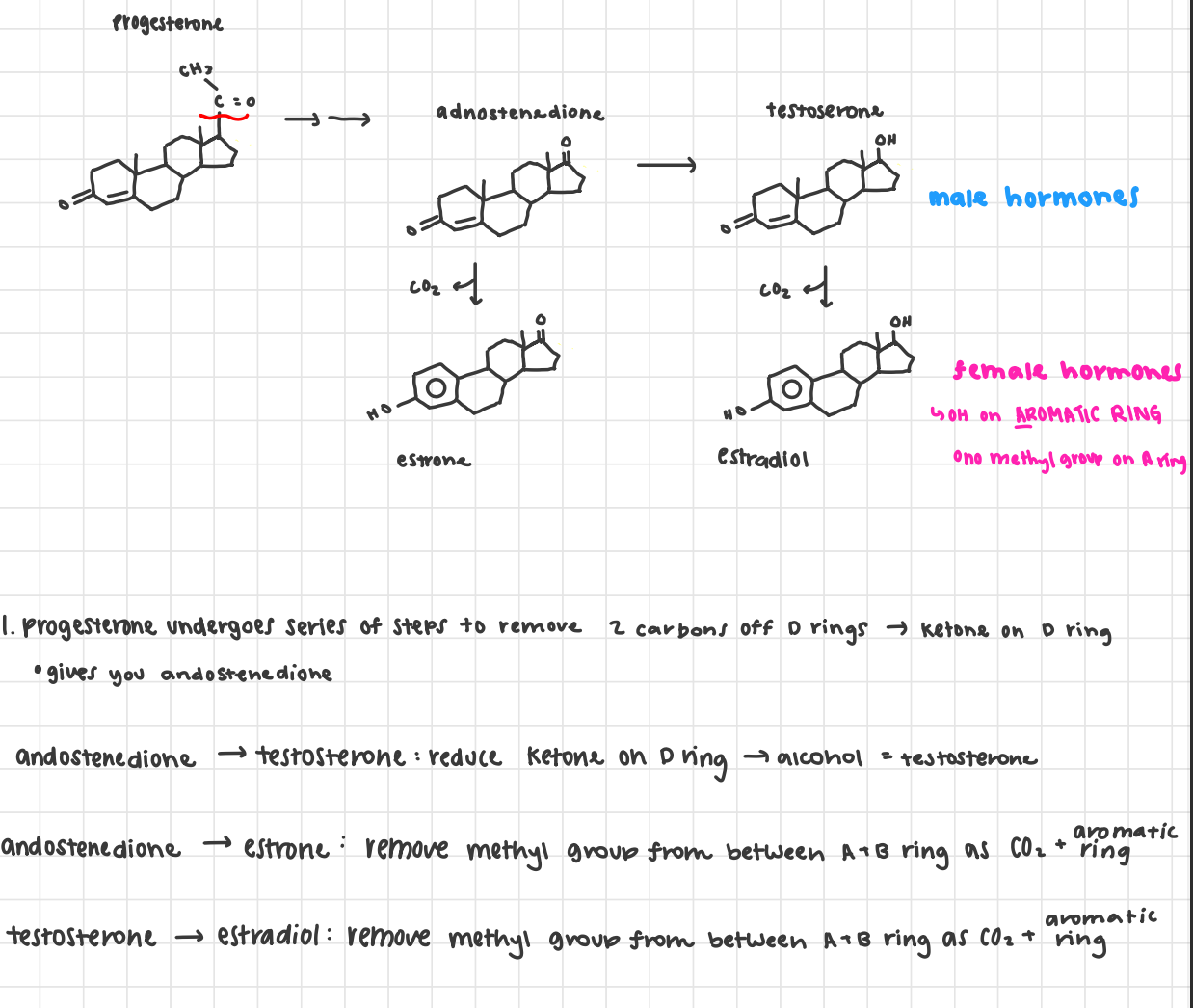
progestogens (glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids + sex hormones)
excretion
adds h+ to reduce double bond in b ring > single bond > intestines for excretion
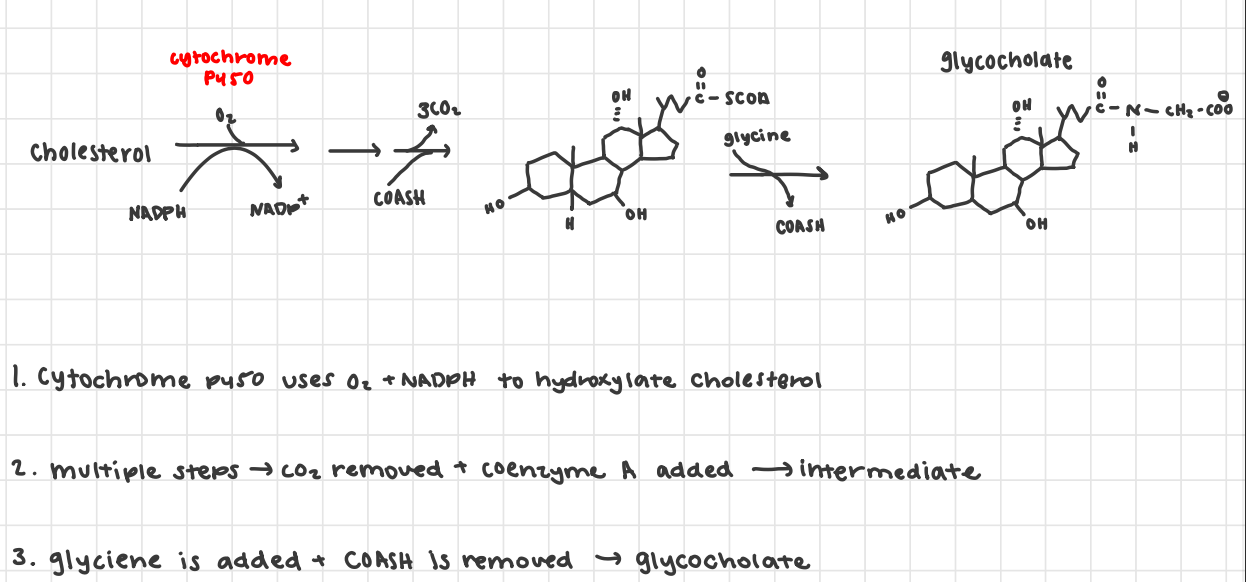
bile salts
made in liver
stored in gall bladder
secreted in intestines
emulsify dietary lipids act as detergent by adding OH to cholesterol > soluble lipids > intestine excretion
detergent
hydrophilic and hydrophobic region
steroid hormones/ progestrogens
derived from cholesterol + made in adrenal gland
produces progesterone
glucocortocoids + functions
adds oh to progesterone using cytochrome p450
made in adrenal gland
CHARACTERIZED BY OH GROUPS ON C RING AND D RING!
inc glucose-6-phosphatase activity > inc blood glucose
inc gluconeogenesis (pyr/lac > glucose) by inc enzyme conc
controls life span of fibroblasts (make collagen) + lymphocytes (immune)
role in AA + nucleotide metabolism
mineralocorticoid
stimulate ion absorption from blood and intestines
too many > too many ions > water in blood > high BP
BP medicine targets mineralocorticoids
characterized by aldehyde between C and D ring
sex hormones
made in ovaries and testes
21 hydroxylase
adds oh to side chain of progesterone > gluco + mineralocorticoids
deficiency: early puberty, issues w bone deficiency + mineral absorption
tx: injections