AP Computer Science A - Unit 1.9-1.15
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
argument
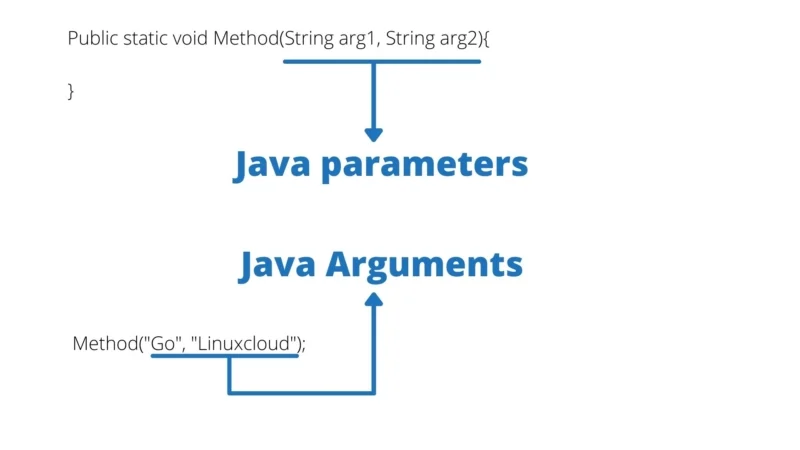
value that is passed into a method when the method is called
must be compatible in number and order with the types identified in the parameter list of the method signature.
method(9,10,11)
attribute/instance variable
data the object knows about itself.
turtle object knows the direction it is facing or its color.
Shape, Color, Height, Width, Direction, etc.
boolean equals(Object other)
returns true when the characters in the current string are the same as the ones in the other string. This method is inherited from the Object class, but is overridden which means that the String class has its own version of that method.
"Test string".equals("test string 1")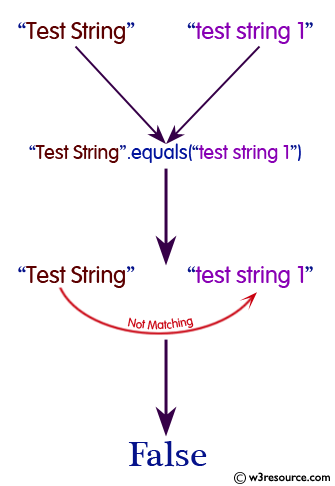
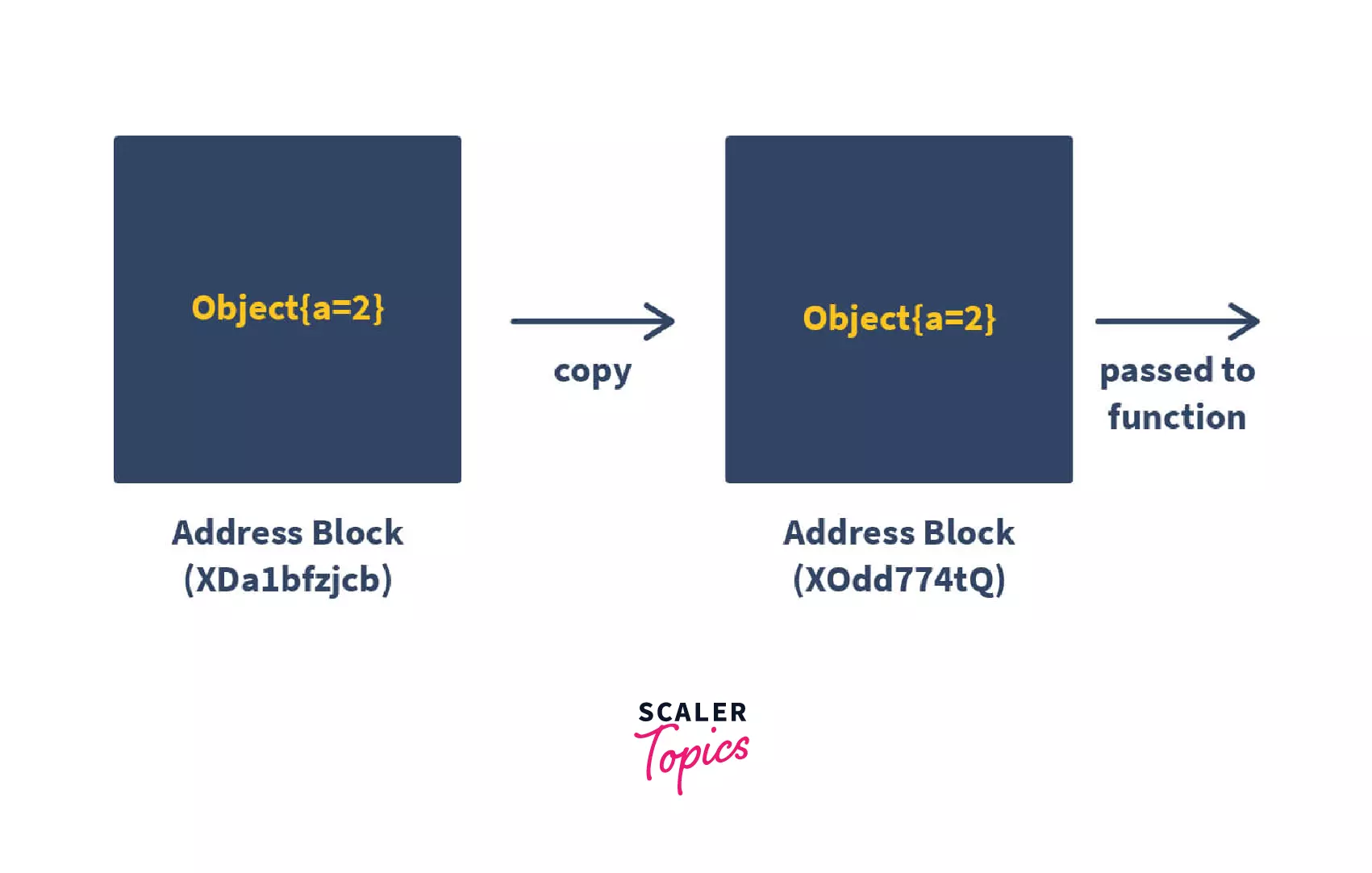
call by value
initializes the parameters with copies of the arguments.
Copying the value, not the actual variable
Refers to a location value, not the actual thing
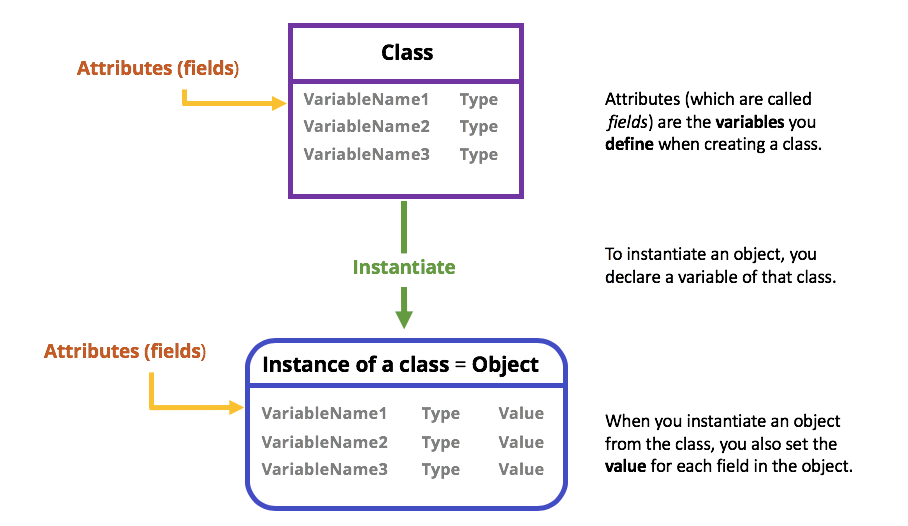
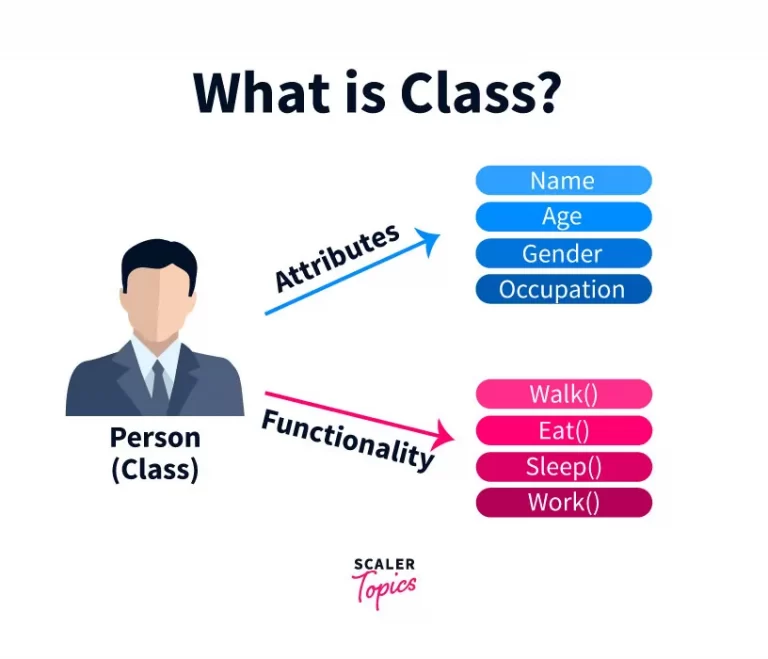
class
defines the attributes (data) and behaviors (methods) that all objects of that class will have
The objects are the specific instances of the class that have their own values for the attributes
Attributes: the data or properties that an object knows about itself
turtle object's color and size
Behaviors: things an object can do
turtle object's ability to play, jump, run, etc.
public class MyClass {
}
concatenation
Adding String(s) to each other to create a new string using the + or += operator
String name = "John";
int age = 25;System.out.println("My name is " + name + " and I am " + age + " years old.");String firstName = "John ";
String lastName = "Doe";
System.out.println(firstName.concat(lastName));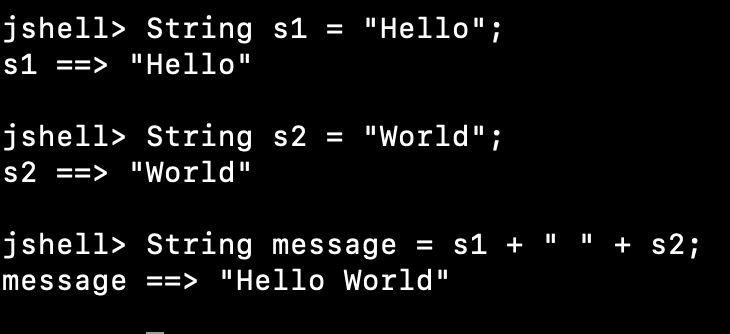
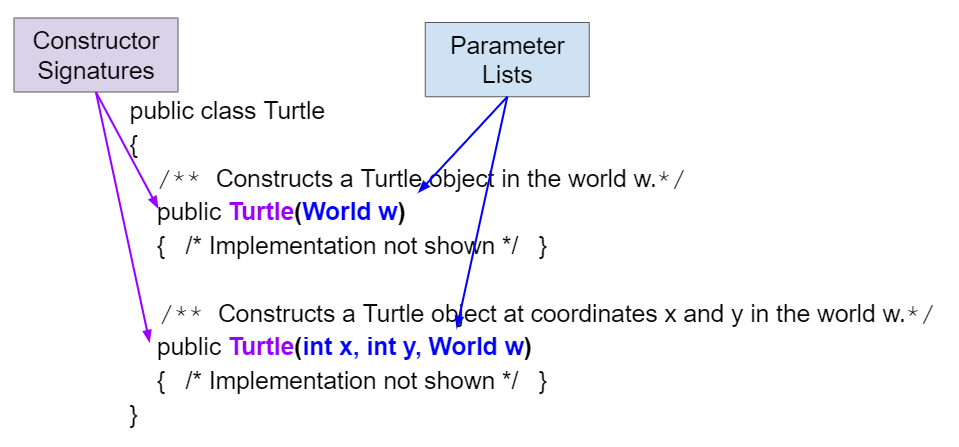
constructor signature
consists of the constructor's name, which is the same as the
class name, and the ordered list of parameter types.
World, width, height
World world1 = new World();
World world2 = new World(width,height);
constructors
Special methods used for the creation of an Object
Constructors have the same name as the class.
typically created using the keyword "new" followed by a call to one of the class's constructors
new ClassName()//Constructor here is ClassName
dot operator
access classes and objects
also known as separator or period used to separate a variable or method from a reference variable.
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();
objectName.fieldName; // Accesses the field 'fieldName' of 'objectName'
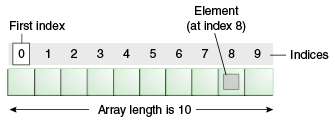
index
a number associated with a position in a string
Each character is at a position or index that starts with 0
The length of a string is the number of characters in it, including any spaces or special characters
int indexOf(String str)
method searches for the string str in the current string and returns the index of the beginning of str in the current string or -1 if it isn't found.
String s1 = "someone is a baby";int s2 = s1.indexOf("baby"); //will return 13int length()
method returns the number of characters in the string, including spaces and special characters like punctuation.
String s1 = "baby";int s2 = s1.length(); //will print 4intl compareTo(String other)
returns a negative value if the current string is less than the other string alphabetically, 0 if they have the same characters in the same order, and a positive value if the current string is greater than the other string alphabetically
before alphabetically = less than
negative = less than
0 = the same,
positive = greater than
String s1 = "baby";String s2 = "child";System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //will a negative numMath.abs method
takes a single argument, either a double or an int and returns a value of the same type which is the absolute value of the argument
The absolute value is the positive value of the number without its sign or its distance from 0
Math.abs(-4) = 4Math.pow
takes two argument, both doubles and returns a double which is the first argument raised to the power of the second argument.
Math.pow(2,3); //returns 8.0Math.random() method
used to generate a random number
int n = (int)(Math.random()*3)+3;multiplying by three: [0,1) -> [0,3)
adding by three: [0,3) -> [3,6) // last value isn't included
Math.sqrt method
takes one double argument and returns a positive double value which is the square root of the argument
Math.sqrt(9); //returns 3method
named block of code that only runs when it is called
method call
interrupts the sequential execution of statements, causing the program to first execute the statements in the method before continuing
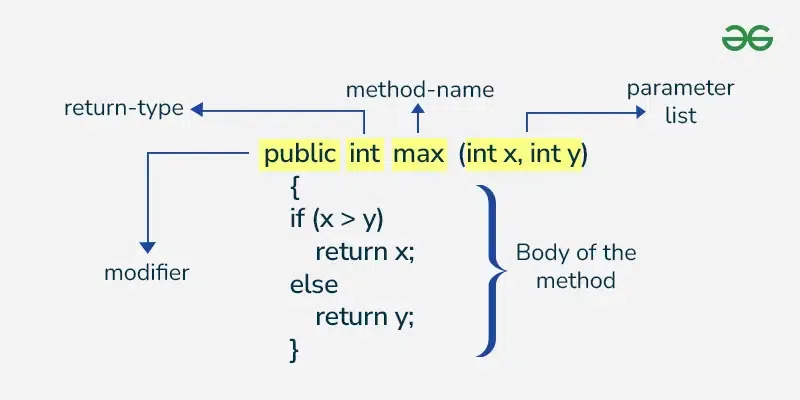
method signature
defines the method's name and the number and types of parameters it takes
A method signature for a method without parameters consists of the method name and an empty parameter list
println();
println("Hello World");
no-argument constructor
a constructor that doesn't take any passed-in values (arguments)
// Explicitly defined no-argument constructor
public MyClass() {
this.name = "Default Name";
this.age = 0;
System.out.println("No-argument constructor called.");
}
// Parameterized constructor
public MyClass(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;object
is a specific instance of a class with defined attributes
ClassName objectName = new ClassName(); // For a default constructor ClassName objectName = new ClassName(arguments); // For a parameterized constructor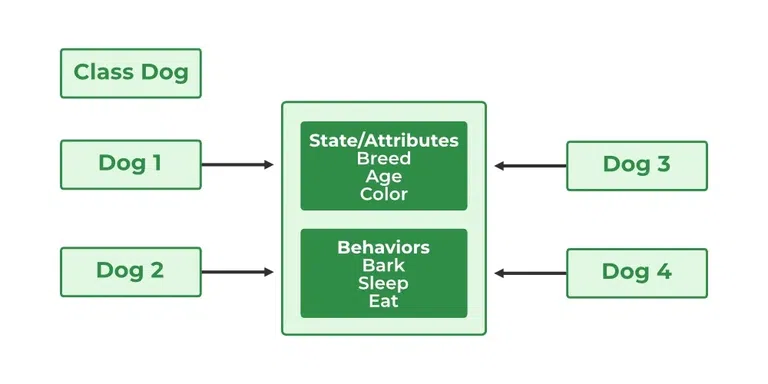
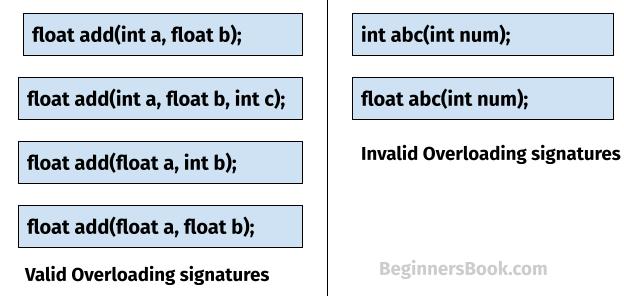
overloaded methods
multiple methods with the same name but different signatures.
Parameters have to be the same as what is called in the method
One method can share multiple parameters (int, double, boolean, etc)
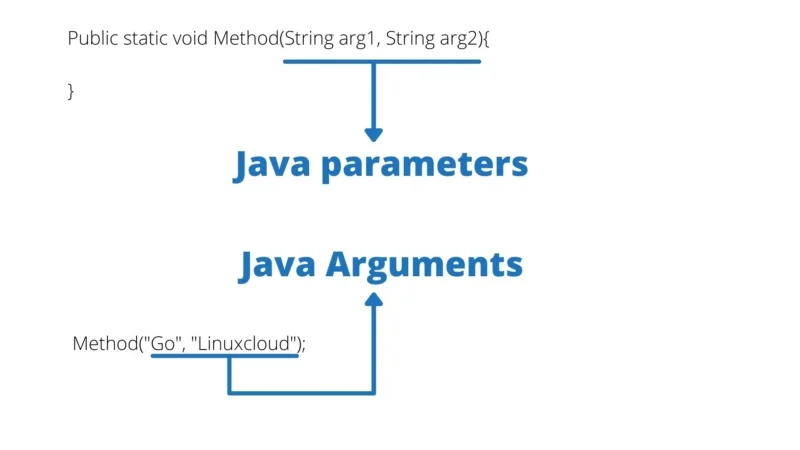
parameter
a variable declared in the header of a method or constructor
can be used inside the body of the method
allows values or arguments to be passed and used by a method or constructor
(int x, int y)
parameter list
in the header of a constructor, lists the types of the values that are passed and their variable names.

Procedural abstraction
allows a programmer to use a method by knowing what the method does even if they do not know how the method was written.
reference type
holds an object reference or null if there is no object
classes
Interfaces
Arrays
Enums
Signature
Defines a Method (method name + parameter)
Verse(String animal, String sound)triple(int n)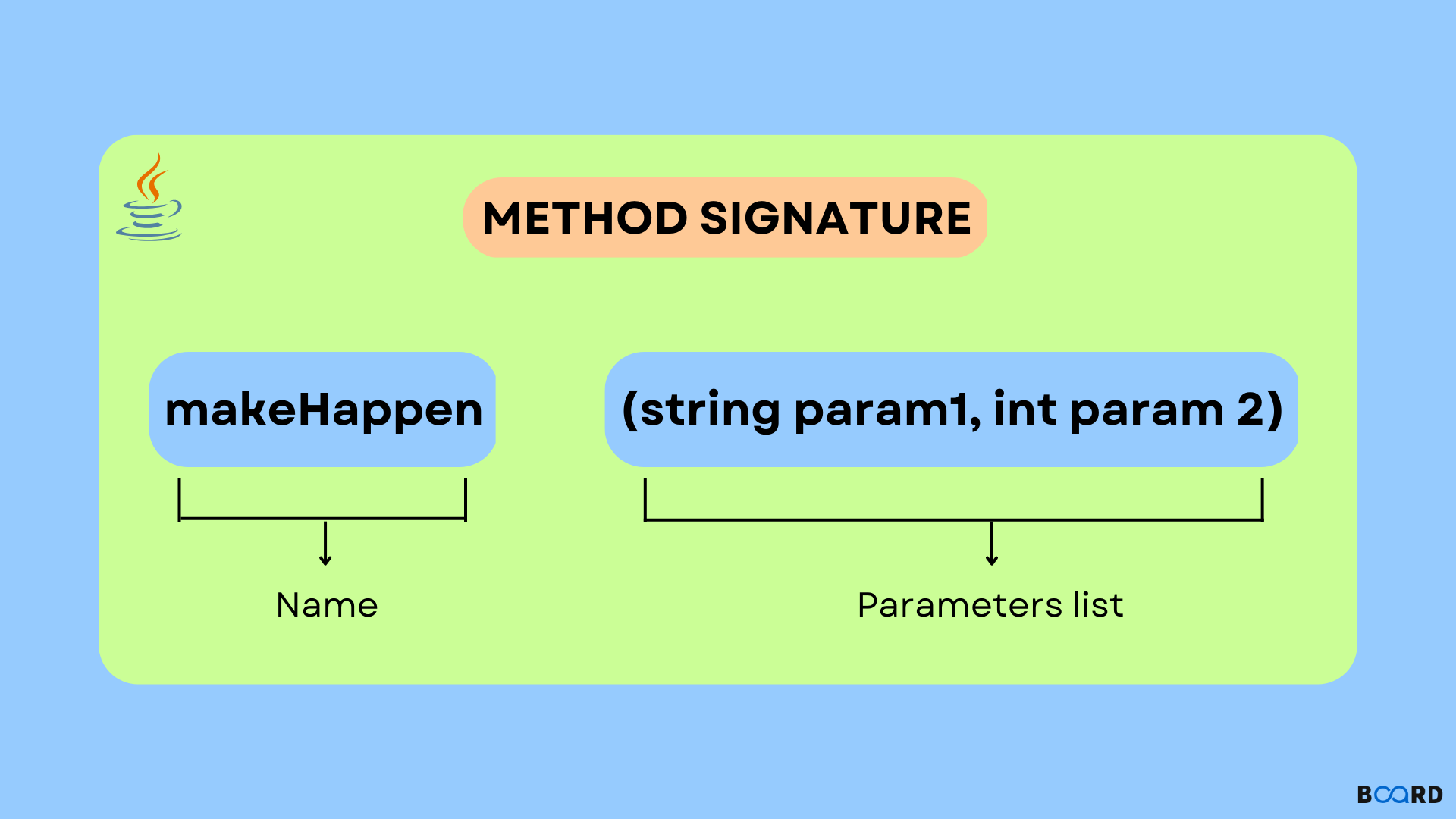
string literal
a set of characters enclosed in double quotes ("),
creates a String object.
String greeting = Hello;string object
use the new keyword followed by a space and then the class constructor and then in parentheses you can include values used to initialize the fields of the object
String greeting = new String("Hello");String substring(int from, int to)
method returns a new string with the characters in the current string starting with the character at the from index and ending at the character before the to index (if the to index is specified, and if not specified it will contain the rest of the string)
String s1 = "baby";String s2 = s1.substring(0,2); //will return bavariable
holds an object reference, which can be thought of as the of that object.
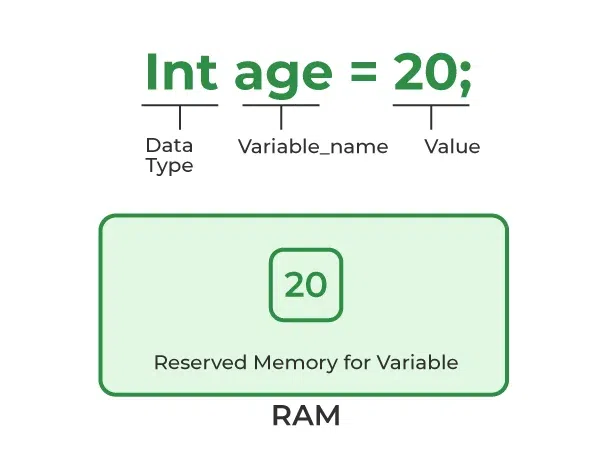
named storage location in memory used to hold a value