Biology Exam #2
4.8(4)
4.8(4)
Card Sorting
1/251
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
252 Terms
1
New cards
The cell membrane is composed of
phospholipid bilayer
2
New cards
phospholipids
-structural component of the membrane
-amphipathic
-selectively permeable
-amphipathic
-selectively permeable
3
New cards
Cell membranes are also composed of
proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, cholesterol
4
New cards
Proteins are the ___________________ components of of membranes.
functional
5
New cards
Transporters, receptors, enzymes, anchors
examples of functional proteins
6
New cards
Cholesterol in cell membranes
maintains an optimum fluidity of the membrane in animal cells
-prevents the membrane becoming too solid in cold temperatures or too fluid in high temperatures
-prevents the membrane becoming too solid in cold temperatures or too fluid in high temperatures
7
New cards
Glycosylation
process of attaching a carbohydrate chain to a protein or lipid
8
New cards
glycolipid
lipid with carbohydrate attached
9
New cards
glycoprotein
protein with carbohydrate attached
10
New cards
The carbohydrate chain in cell membranes
-provides a distinctive cellular marker
-helps protect proteins from damage
-helps protect proteins from damage
11
New cards
This type of model describes the cell membrane's structure
fluid-mosaic
12
New cards
The fluid mosaic model means that the cell membrane is
semi-flexible and a "tapestry" of several types of molecules
13
New cards
Since the cell membrane is semi-permeable, this allows the cell to maintain its internal conditions separate from the __________________
environment
14
New cards
Factors for molecules to cross membrane are
size, polarity, change
15
New cards
The membrane is MOST permeable to
small, hydrophobic molecules
16
New cards
The membrane is LEAST permeable to
large, hydrophilic, charged molecules.
17
New cards
Cells maintain
transmembrane gradients
18
New cards
chemical gradient
concentration of SOLUTE higher on one side than the other
19
New cards
electrochemical gradient
a chemical and electrical gradient (difference in electrical charges between the inside and outside of the cell)
20
New cards
Why is it important to maintain gradients?
-maintain water balance
-transmission of nerve impulses
-production of ATP
-transmission of nerve impulses
-production of ATP
21
New cards
Ways that molecules move across cell membrane include
passive transport and active transport
22
New cards
passive transport
molecules move from area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration
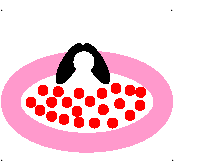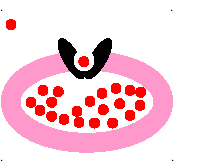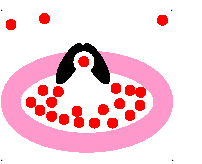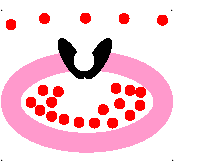
23
New cards
Passive transport requires NO ___________ and movement is DOWN a gradient.
energy
24
New cards
The 3 types of passive transport
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
25
New cards
simple diffusion
molecule passes across the membrane without help
26
New cards
facilitated diffusion
molecule passes across membrane with the help of membrane protein
27
New cards
osmosis
the net movement of a solvent (WATER) across a semi-permeable membrane into a solution with a higher solute concentration (SALT WATER)
28
New cards
_______________ molecules can NOT move across the membrane in osmosis.
solute
29
New cards
Osmosis _______________ the concentrations of solute on either side of the membrane
equalizes
30
New cards
Osmosis is responsible for
reabsorption of water in the kidneys
uptake of water by plant roots
dehydration resulting from cholera infection
uptake of water by plant roots
dehydration resulting from cholera infection
31
New cards
Tonicity
relative solute concentration of one solution compared to another
32
New cards
HYPOtonic solution
solution has LOWER solute concentration than other solution
33
New cards
Isotonic
EQUAL solute concentration in both solutions
net movement 0
net movement 0
34
New cards
HYPERtonic
HIGHER solute concentration than other solution
35
New cards
Water movement can make a cell _________ or _________ so cells must remain isotonic across the membrane
shrink, swell
36
New cards
crenation
shrinking of cell in a HYPERtonic solution
37
New cards
osmotic lysis
swelling and bursting of a cell in a hypotonic solution
38
New cards
osmosis in plants:
turgor pressure and plasmolysis
39
New cards
turgor pressure
pushes plasma membrane against cell wall and maintains shape and size; cell in a HYPOtonic solution
40
New cards
Plasmolysis
plants wilt because water leaves plant cells; cell in a HYPERtonic solution
41
New cards
active transport
molecule is transported from an area of LOW concentration to an area of HIGH concentration and requires ENERGY; moves AGAINST the gradient
42
New cards
Na+K+ ATPase- transmission of nerve impulses , H+/K+ ATPase- acidifies stomach juices required for digesting food.
active transport proteins
43
New cards
exocytosis
material inside cell is packages into vesicles and EXPORTED OUT of the cell; active transport
44
New cards
endocytosis
import of a molecule INTO cell through vesicle; active transport
45
New cards
cell communication AKA signal transduction
process of cells detecting and responding to signals in the extracellular environment
46
New cards
The 3 stage process of cell responsiveness
1. receptor activation 2. signal transductions 3. cellular response
47
New cards
receptor activation
receptor binds signaling molecule and becomes activated
48
New cards
signal transduction
signal gets transmitted through the cell; a series of proteins form a signal transduction pathway
49
New cards
cellular response
activity of target molecules is altered to change cell behavior
50
New cards
Target proteins:
1. enzyme-alter metabolism
2. structural proteins-alter cell shape or movement
3. transcription factor-alter gene expression
2. structural proteins-alter cell shape or movement
3. transcription factor-alter gene expression
51
New cards
True or false: some signaling proteins and receptors travel a short distance and bind receptors on a nearby target
True
52
New cards
neurotransmitters
signaling protein that travels a short distance
53
New cards
FSH
signaling molecules (called hormones) are released in the bloodstream and travel long distances to bind their receptors on target cells
54
New cards
protein kinase
enzyme that adds a phosphate to a target protein to switch them on or off
55
New cards
protein phosphatases
Enzymes that can rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins.
56
New cards
Adding/removing a phosphate group is a way to ________________ and ________________ alter protein activity
quickly, reversibly
57
New cards
second messenger
amplify signal throughout the cell
58
New cards
cyclic AMP
second messenger
59
New cards
cell communication steps
1. signaling molecule binds to receptor
2. signal is transmitted via a series of proteins in the cell
3. activity of target proteins is altered to bring about cellular response
2. signal is transmitted via a series of proteins in the cell
3. activity of target proteins is altered to bring about cellular response
60
New cards
target proteins
ultimately receive a message to alter cell activity
61
New cards
energy
the ability to do work
62
New cards
the two basic forms of energy
kinetic and potential
63
New cards
kinetic energy
associated with movement
64
New cards
potential energy
stored energy
65
New cards
chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds (form of potential energy)
66
New cards
chemical reaction
when one or more substances change into one or more new substances
REACTANTS to PRODUCTS
REACTANTS to PRODUCTS
67
New cards
True or False: In chemical reactions, existing chemical bonds are broken and new ones are formed
True
68
New cards
exergonic reaction
A chemical reaction that RELEASES energy
69
New cards
Gibbs free energy
the difference in energy stored in the chemical bonds of reactants and products
70
New cards
If the energy stored in products is less than the energy stored in the old bonds THEN
products have LESS energy than reactants
Reaction is exergonic
Reaction is spontaneous
Reaction is exergonic
Reaction is spontaneous
71
New cards
a NEGATIVE gibbs free energy indicates a
exergonic reaction
72
New cards
endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which energy is ABSORBED and REQUIRED for use of reaction
73
New cards
If the energy stored in the products is more than the reactants THEN
products have more energy than reactants
reaction is endergonic
reaction is NOT spontaneous
reaction is endergonic
reaction is NOT spontaneous
74
New cards
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
75
New cards
catabolic reactions
breakdown of molecules
used to RELEASE energy
recycle monomers (building blocks)
EXERGONIC bonds
used to RELEASE energy
recycle monomers (building blocks)
EXERGONIC bonds
76
New cards
anabolic reactions
build molecules and macromolecules
ENDERGONIC reactions
ENDERGONIC reactions
77
New cards
endergonic reactions
REQUIRE ENERGY
78
New cards
In exergonic reaction because products have less energy than reactants, there is a net _______________ of energy
release
79
New cards
In endergonic reactions because products have more energy than reactants, there is a net ______________ of energy
input
80
New cards
The energy source for many endergonic cellular reactions is
ATP
81
New cards
ATP is a product, what is it converted from?
ADP
82
New cards
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction; is not consumed and remains unchanged at the end of the reaction
83
New cards
enzymes
protein catlysts
84
New cards
ribozymes
RNA molecules that function as catalysts.
85
New cards
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started and to transition state
86
New cards
True or False: Activation energy is only needed for endergonic reactions
FALSE- it is needed for BOTH endergonic and exergonic reactions
87
New cards
transition state
intermediate state between reactants and products
88
New cards
common ways to OVERCOME activation energy
1. large amounts of heat
2. using enzymes to lower activation energy
2. using enzymes to lower activation energy
89
New cards
________________ lowers activation energy
enzymes
90
New cards
active site
location where chemical reaction occurs
91
New cards
substrates
reactants, that are first affected by enzyme, that bind to active site
92
New cards
enzyme-substrate complex
formed when enzyme and substrate bind
93
New cards
Products
molecules that are formed after the reaction
94
New cards
The steps of an enzyme catalyzed reaction are
1. substrates bind
2. enzyme undergoes conformational change that binds substrates more tightly
3. substrates are converted to products
4. products are released
2. enzyme undergoes conformational change that binds substrates more tightly
3. substrates are converted to products
4. products are released
95
New cards
induced fit model
explains conformational change an enzyme undergoes after binding substrate.
96
New cards
prosthetic group
small, non-protein helper molecule permanently attached to the enzyme
97
New cards
cofactor/coenzymes
non-protein helper molecules NOT permanently attached to the enzyme
98
New cards
Coenzymes are _______________ like vitamins, but cofactors are _____-_______________ like Sulphur phosphate
organic, non-organic
99
New cards
True or False: ALL chemical reactions in the body are catalyzed reactions
True
100
New cards
factors that affect the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions
substrate concentration, pH, temperature, and inhibitors