Chemistry Final - Unit 9 (Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
oxidation and reduction must occur _____
simultaneously
the total increase in oxidation numbers of the oxidized substance must equal the _______
decrease in oxidation numbers of the reduced substance
what is a free element?
an element in an redox reaction that is standing alone with a charge of 0
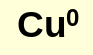
what is electrochemistry?
the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy
redox reactions also involve a transfer of _____
electrons
what did Michael Faraday discover?
that the water solutions called electrolytes conduct electricity
what is an electrolyte?
any substance which dissolved in water to form a solution that will conduct an electric current
what are solutions that cannot conduct electricity called?
non-electrolytes
solutions in which the solute is present entirely as ions are called ______
strong electrolytes
a solution in which there is a low concentration of dissolved ions is called a ____
weak electrolyte
dissociation is the separation of ions when an ____ compound dissolves
ionic
ionization is when a ______ substance dissolves into ions
covalent/molecular
water molecules pull ions apart due to its strong ______
covalent bonds
voltaic (galvanic) cells are _____
spontaneous
electrolytic cells are _____
non-spontaneous
what are electrochemical cells?
a system of electrodes and electrolytes where redox reactions occur
The E°cell of a voltaic/galvanic cell is ____
positive
The E°cell of an electrolytic cell is ____
negative
what is an electrode?
an electrical conductor (metal strip) used to establish contact with the electrolyte
what is an electrolyte?
a liquid, paste, or gel that serves to conduct charge bu moving ions in the cell
oxidation occurs at the ____
anode
reduction occurs at the ____
cathode
what is a half cell?
a single electrode immersed in a solution of its ions
what is a salt bridge?
a device placed between cells that maintains neutrality by allowing ions to migrate between cells
a salt bridge is used in _____
galvanic cells
what is an external circuit?
the part of the cell where charge is conducted as current of moving electrons
what is Standard Electrode Reduction Potential (E°)?
the measurement, in volts, of the tendency for a half reaction to occur as reduction
what is cell potential?
the measure of the diriving force, in volts, for an electrochemical reaction
in a voltaic/galvanic cell, the ____ is the negative electrode
anode
what is an example of a voltaic cell?
batteries
electrons flow from _____ to ____
anode to cathode
in an electrolytic cell, the anode is the ____ electrode
positive
equation for E°cell:
E°cathode - E°anode
examples of electrolytic cells:
electrolysis, electroplating