APHUG Unit 3 Migration FRQs
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
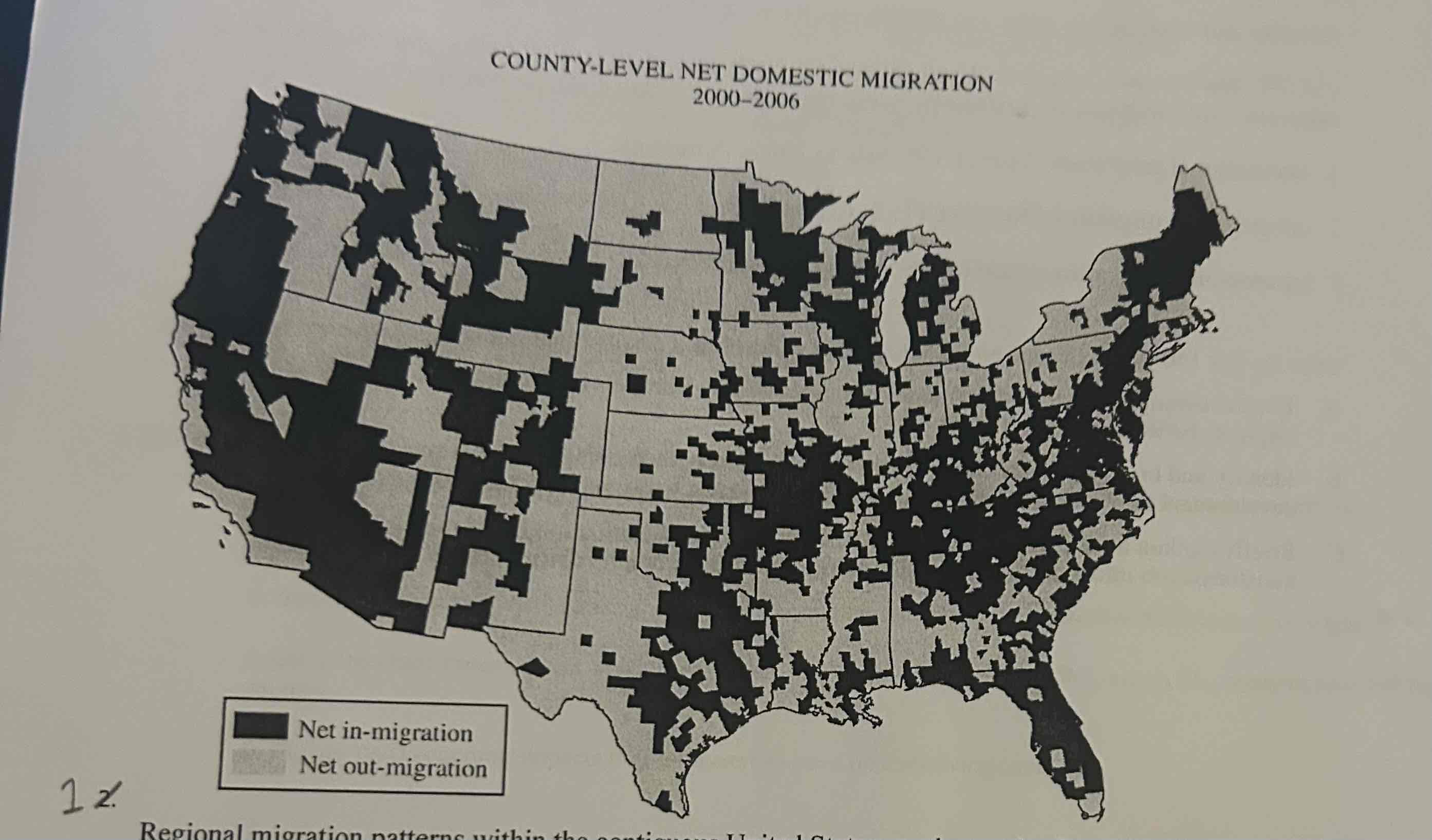
A. Identify two specific regions that have experienced net in-migration.
B. Identify two specific regions that have experienced net out-migration.
C. Explain the processes that contribute to the general patterns of migration within the United States shown on the map in terms of each of the following:
Economic structure
Friction of distance
Age structure of the population
A. Two regions that have experienced net in-migration are California and Florida.
B. Two regions that have experienced net out-migration are North Dakota and South Dakota.
C.
For economic structure, suburbanization has contributed greatly to the general patterns. Since many jobs arise in the suburbs, and most families would preferably raise their children in safe areas where the lifestyle isn’t busy and rushed like the city, school systems are good, and in homes with large backyards and areas to play in, people migrate from the city to the suburbs.
Friction of distance is not as influential in location decisions as people are more able to commute longer distances in less time due to improved transportation. Because of this, people may migrate to the suburbs or countryside regardless of where they work.
The age structure of the population changes as many young families migrate to suburbs in order to live in a nice area where their children can get a good education, play outside and live peacefully.
Identify and explain two push and pull factors for each of the following types of migration:
NOTE: you can use 2 push or 2 pull factors for each type of migration below, but they should be different classifications of push-pull factors (Economic, Cultural, Environmental))
International migration Europe OR Asia to North America).
Interregional migration (Northeast U.S. to Southeast U.S. OR Central America to Mexico).
Intraregional migration (rural to urban AND urban to Rural.
An economic push factor might be high unemployment rates or limited job opportunities in areas like Southern Europe and parts of Asia. Due to the high unemployment rates, migrants from those areas may immigrate to the United States in hopes of better job opportunities. An example of a cultural pull factor is that many migrants might immigrate to the United States because the US is thought of as a place where personal freedoms are valued greatly, the environment is diverse and inclusive and has more political stability. Emigrants from countries that do not have these things will likely want to migrate to the United States and escape their current situation.
An example of an economic push factor is the industrial decline in Northeast US. This has resulted in job losses which has pushed many residents of the Northeast to move to the Southeast, where there are more job opportunities. An example of an environmental pull factor is people from Northeast US migrating to the Southeast where the climate is more temperate and the oceans are warmer. This entices the residents of Northeast US as they may prefer warmer temperatures.
An economic pull factor is people moving from rural areas to urban areas because of job opportunities, more amenities, better hospitals, and more. This pull factors encourages residents of rural areas to migrate to the city and have more access to the cities amenities. An environmental push factor is that urban areas often have overcrowding, pollution, and high living costs which encourages residents to move out to rural areas for cleaner air, and a quieter lifestyle.
Over the last 150 years. Europe has changed from a source to a destination region for international migration.
A. Use the demographic transition model to explain briefly Europe's development as a source of international migrants between 1800 and 1920.
B.
Identify and briefly explain ONE factor other than demographic transition that was responsible for Europe's development as a source of migrants to the United States between 1800 and 1920.
C.
Briefly explain how THREE aspects of the demographic transition model account for Europe's transformation into a destination region for migrants from North Africa between 1960 and 2000.
A. Between 1800 and 1920, Europe transitioned into Stage 3. Since in stage 2, europe was experiencing high birth rates, and low deaths, resources were strained and jobs were scarce. When europe went to stage 3 declining death rates and high birth rates contributed to more strain and so migrants began migrating to new places like north america for resources.
Bz Another fsctor was political instability. A lot of uprisings were occurring in europe during 1800 - 1920, like wars and famines. Many irish and getman fled their countries to america seeking refuge.
C. stage 4, economic stability, slwoing population growth

4S. In recent years, the number of refugees has been increasing. However, most refugees come from just a few countries.
Define the term "refugee."
Discuss ONE political, ONE social, and ONE environmental reason why refugees flee their country of origin.
Using the chart shown, select a country of origin; then identify and explain ONE reason why refugees have left the country.
Explain TWO economic impacts that refugees can have on a receiving country.
A refugee is somebody who is forced to leave their home country.
religious persecution, fear for life during war, natural disaster
sudan; overrun with poverty and famine, so a refugee is liekly fleeing sudan due ton its lack of food, water, good education, and infrastructure.
two economic impacts are increased strain on resources and competition with locals for local jobs.