MECH2305 - Ceramics, Composites and polymers
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Why are dislocations difficult in ceramics
Slip is extremely difficult due to ionic/covalent bonds, which cause shattering upon enough force.
How to shape ceramics
Powder metallurgy (general ceramics)
Slip casting (Clay)
Glass methods
Slip casting process
Clay slurry poured into mould
Mould absorbs moisture from slip, forming solid clay.
After thickness is developed, excess is poured out.
Dried and sintered.
Allows for complex shapes.
Characteristics of glass
Microcracks over surface, causing breakage at low tensile stress
Removing cracks with acid greatly increases strength
Liquid at high temperatures
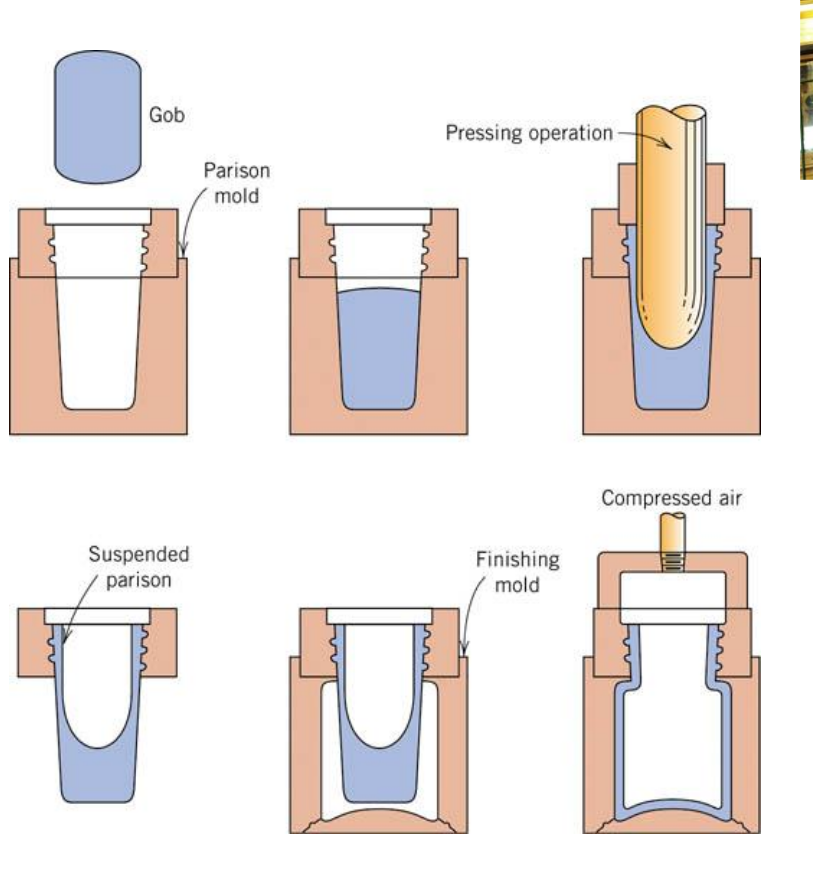
How to form glass bottles
Press glass glob into mould
Blown into final shape.
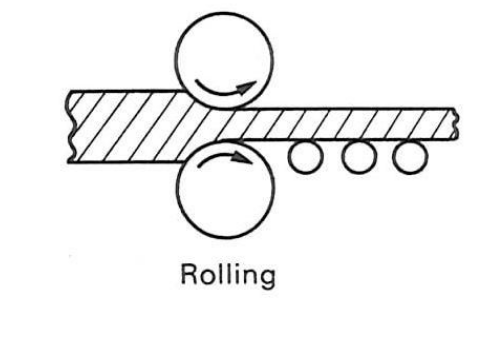
Rolled glass
Roll molten glass between two rollers so sheet is perfectly flat
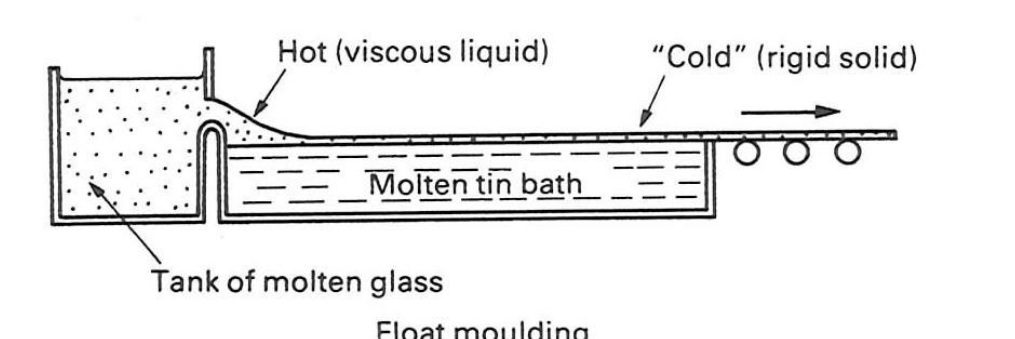
Float glass
Molten glass is floated off on bath of molten tin, creating very flat panes.
Laminated glass
Two or more layers are bonded by thin polymer layer
Tempered glass properties and process
Extremely strong, created through heating glass, cooling surface, forcing inside to go into compression
Polymers
Long molecules of repeating structures called monomers, extremely ductile, because long strands can simply decoil.
Thermoplastics
Polymers that can be heated and melted
Thermosets
Cross linked polymers cannot melt, heating simply causes burn
4 Polymer structures
a.) Linear polymer (straight line)
b.) Branched polymer (branches)
c.) Cross linked polymer
d.) Network polymer
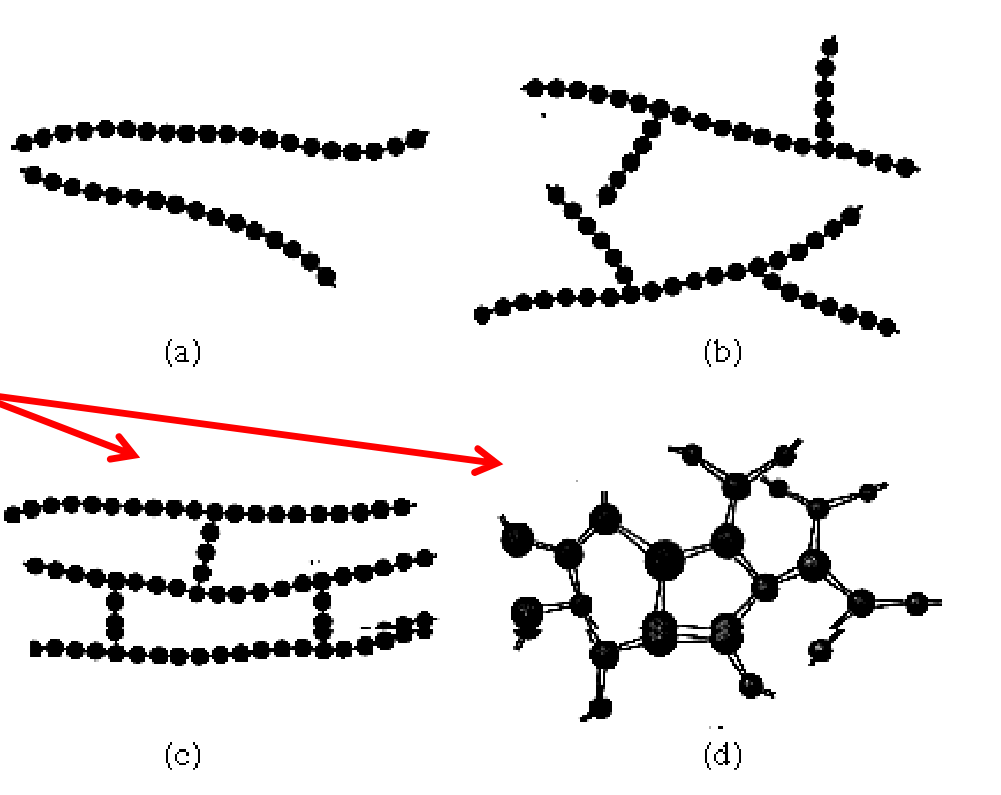
Polymer crystallinity
Long random intertwined polymer chains, increasing density, strength and hardness
Glass transition temperature
Temperature where sharp decrease in mobility
4 Ways to process polymers
Extrusion
Injection moulding
Blow moulding
Blown film
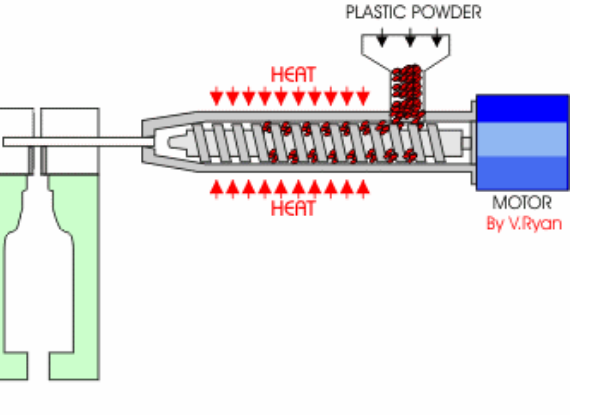
Injection moulding process
Molten material injected into mould under high pressure
Advantages of injection moulding
Fast and efficient
Forms complex shapes
Low waste
Disadvantages of injection moulding
High initial costs
Thin walls are dificult to mould
Long lead time (takes months to create)
Blow moulding
Gas is used to expand hot viscous polymer against steel die
Blow moulding advantages & disadvantages
Very good to create hollow parts
Seamless construction
Very limited wall thickness control
limited shapes can be made
Composites
Mixtures of two different materials to create a new one with different properties
Fibre reinforced composites
Contain fibres in a matrix, causing a lightweight strong material
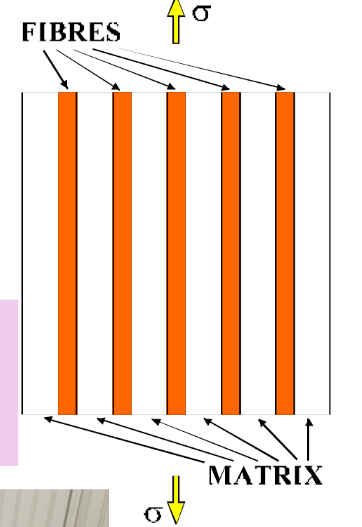
Fibre reinforced composite good and bad
Crack size is limited by change in material throughout matrix
Material is unfortunately highly anisotropic (i.e. directional)