NPTE studying
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Kellgren-Lawrence Grading System
A widely used classification system that grades the severity of osteoarthritis based on radiographic findings, ranging from normal joint appearance/possible osteophytes to severe joint space narrowing and the presence of bone deformities / osteophytes. grades 1-4. Pretty similar knee and hip
Meniscus Classes
Longitudinal - perpendicular to tibial plateau, common with ACL tear (divide central and peripheral)
Horizontal - parallel to tibial plateau (divides superior and inferior)
Radial - perpendicular to both tibial plateau and long axis (extends from free edge to periphery)
Meniscus tear - displaced
mostly longitudinal tears, when displaced called bucket handle tear
Soreness Rules for progressions
during warmup + continues: 2 day break, drop down 1 level
during warmup + goes away: stay at level
during warmup + goes away + comes back: 2 days off, drop down 1 level
non-muscle soreness day after lifting: 1 day off, do not advance
no soreness: advance 1 level per week
from Adams 2012 JOSPT with running progression of walk/jog
Well’s Criteria scoring
>= 3: >= 50% prevalence
1-2: 25%
<1: <=10%
Well’s Criteria DVT
+1: active cancer, paralysis / recent immob LE, recently bedridden >3 days / major surgery within 12 weeks, localized tenderness along the deep venous system, unilateral swelling of the entire leg, calf swelling >3 cm compared to the other leg, previously documented DVT, pitting edema symptomatic LE only, collateral non varicose superficial veins
-2: alternate diagnosis => likely DVT.
Ottawa Ankle Rules
Tenderness along: posterior/tip of medial / lateral malleoli, base of 5th MT, navicular
AND
Inability to WB 4 steps immediately AND in the ED/clinic
high Sensitivity, low Specificity → screen for x-rays
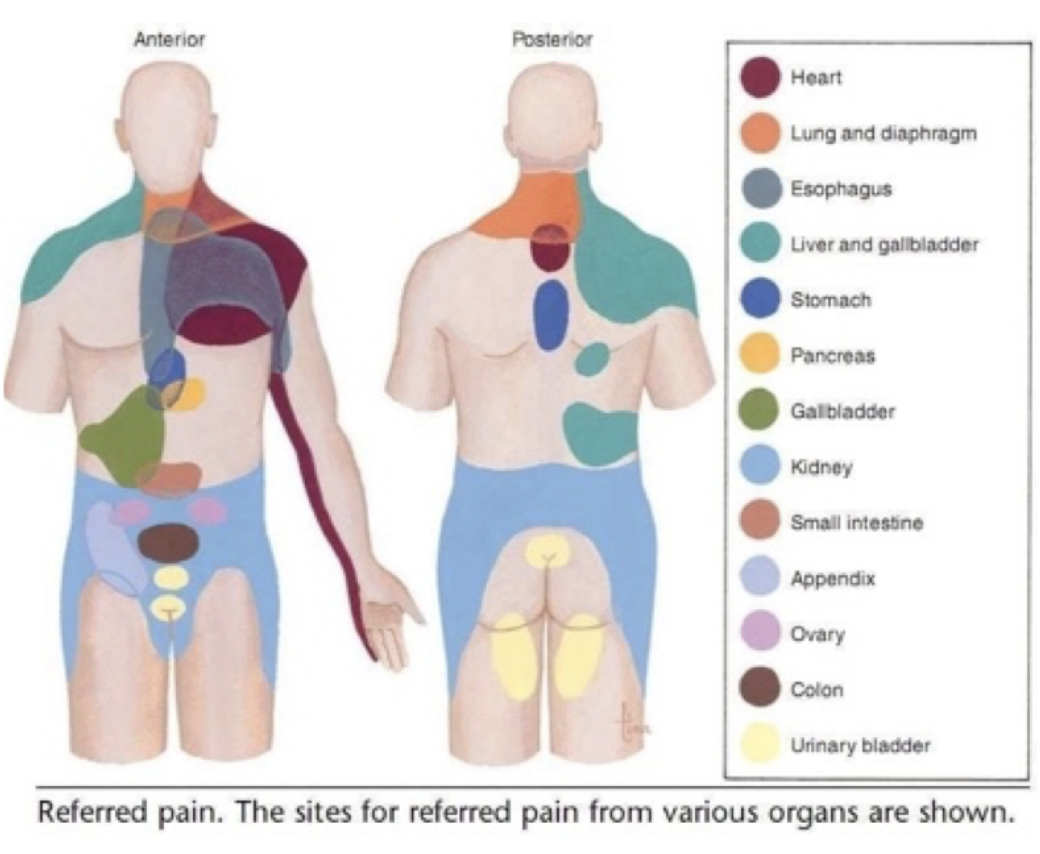
Referred Pain Map Visceral
Cranial Nerve location trick
CE MI PONS MEDU
Cerebrum: 1+2
Midbrain: 3 + 4
Pons: 5-8
Medulla: 9-12
CN 1
Olfactory
Sensory
identify odors
CN 2
Optic Nerve
Sensory
Test visual fields
CN 3
Oculomotor
Motor
Upward, Donward, Medial gaze
CN 4
Trochlear
Motor
Look down and in (SO4)
CN 5
Trigeminal
Both
Sensation of face, mm of mastication, corneal reflex, jaw reflex
CN 6
Abducens
Motor
Lateral Gaze (LR6)
CN 7
Facial
Both
mm facial expression, taste anterior 2/3 tongue, close eyes tight, smile, puff cheeks
CN 8
Vestibulocochlear
Sensory
Hearing, balance and coordination: finger to nose
CN 9
Glossopharyngeal
Both
Taste and sensation posterior 1/3 tongue, swallow, gag reflex (afferent)
CN 10
Vagus
Both
Gag reflex (efferent), say “ahh”, rise of uvula (or deviate away from side of lesion)
CN 11
Spinal Accessory
Motor
Resisted shoulder shrug
CN 12
Hypoglossal
Motor
tongue protrusion (deviates toward side of lesion)
Blood Pressure Categories
Normal: 120/80
Elevated: 120-129 AND /<80
Stage 1: 130-139 OR /80-90
Stage 2: >140 OR />90
HT crisis: >180 AND/OR />120 (prompt med change or emergency if signs of organ damage)
Heart Medications
Beta-1 Blockers: “cock block” epinephrines to increase HR → blunted HR response
Diuretics: decreased blood volume → decrease heart preload
Ace-1-inhibitors: reduces angiotensin 2 (incr. vessel constriction) → decrease after load (like vasodilat. Causes dry cough
Well’s Criteria for PE
+1.5: previous PE/DVT, HR > 100 bpm, Recent surgery / immobilization
+ 3: clinical signs DVT, alternative < likely PE
+ 1: Hemoptysis, Cancer treated within last 6 months.
0-1 = low, 2-6 = intermediate, >= 6: high
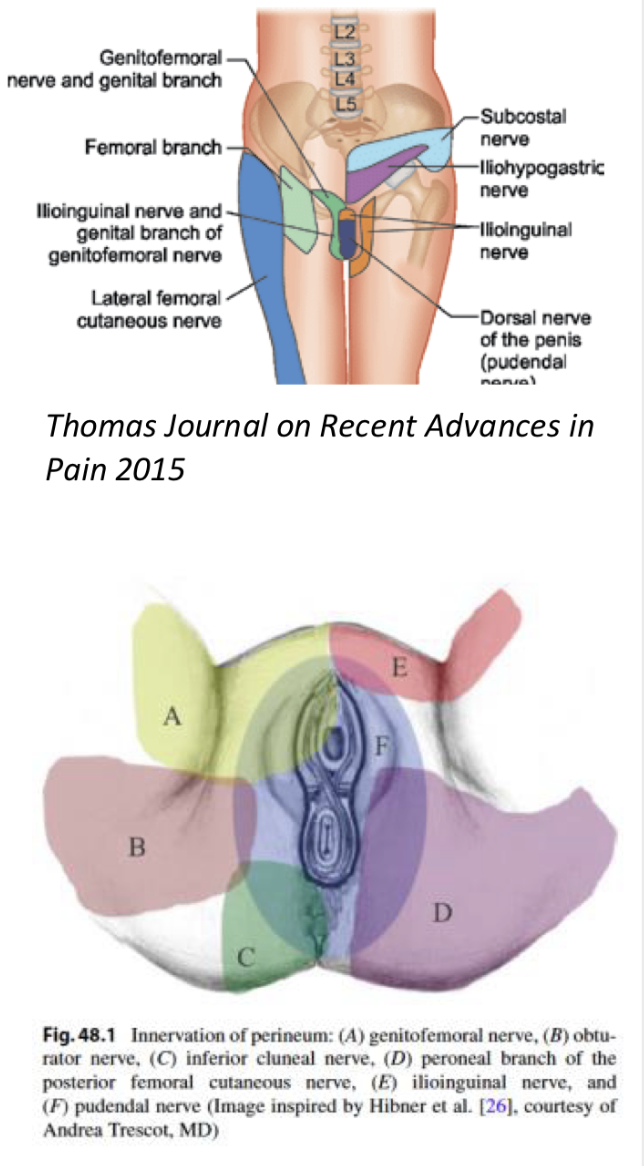
Gential area nerve Sensory Map
Trunk Rotation => SS or CL facet opening?
Lumbar = SS
Cervical = CL
Thoracic = CL
Two types of hearing loss
C.A.N.S.
Conductive: bone > air, Affected louder > unaffected
Sensorimotor: air > bone (normal), Unaffected louder > affected
Infant Reflexes and order of integration
0-3 mo.: rooting (touch cheek / mouth → turn and open mouth)
0-6 mo.: ATNR, TLR. asymmetrical tonic neck reflex (head turns → E SS, F CL), Tonic labyrinthine (Head extended → body E and stiffen. Head F → body flex)
1-2 mo.: Stand + Step
3-5/6: Moro (startle → bodily E then F), Gallant (spine curve toward side stroked)
4-7: UE grasp reflex
9-12: LE grasp reflex / Babinski
6-12: STNR. Symmetric tonic neck reflex (head F → arms F, legs E)
Pattern for abnormal infant reflexes
No reflexes early on: LMN
Reflexes not integrating too late: UMN
Obstructive vs. Restrictive
Obstructive diseases: CBABE (cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, asthma, bronchitis, emphysema). Only one that has increases with lung volumes (TV sometimes, FRC, RV, TLC)
Restrictive: only decreased lung measurements, maybe normal FEV1
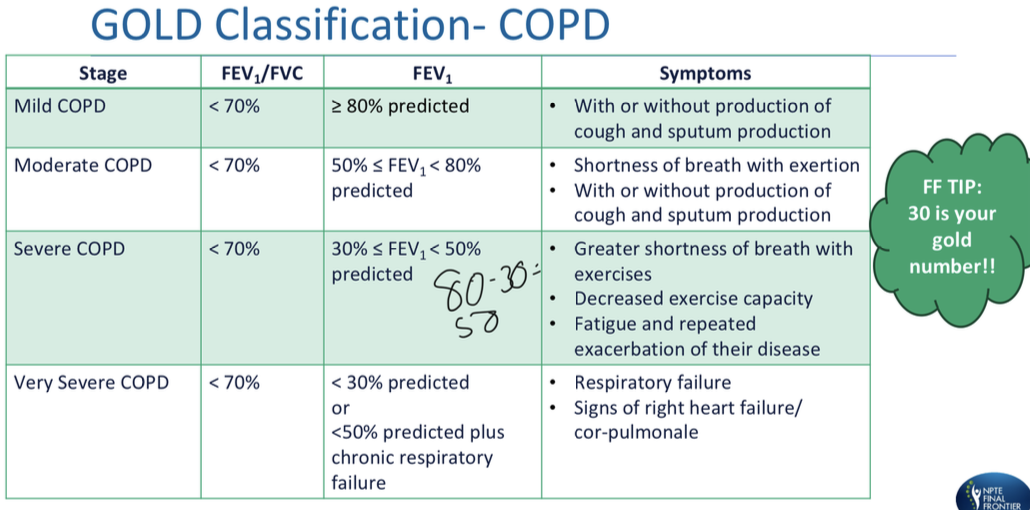
COPD - GOLD classification
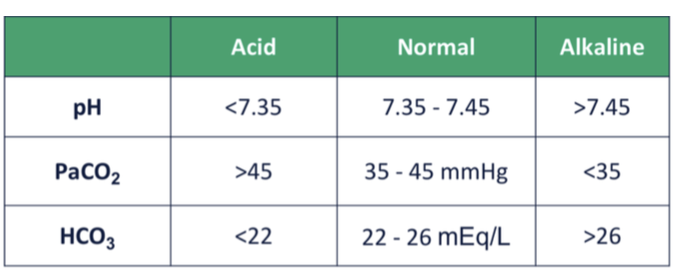
pH/PaCO2/HCO3
ROMs needed for gait
stance: swing
hip = 30 F -20 E: 30 F
knee = 0-40:0-60
ankle = 20 PF - 10 DF: 20 DF
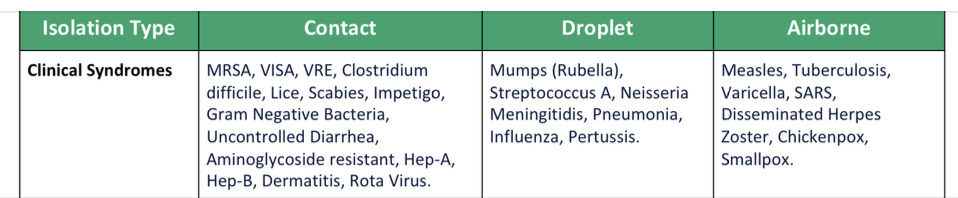
Isolation types for clinical syndromes
Wheelchair measurements
seat height: heel to political fold + 2 in
seat depth: buttock to popliteal - 2 in
seat width: hip widest point +1.5-2 in
back height: final seat to axilla - 4 in
armrest height: seat to olecranon + 1 in
axle: in line / just post to shoulder (FWD if bariatric, BCKW is BIL transfem)
Basics of 4 location of brain injuries - UMN
Structures: cortex, BS, SC
Tone: increased, spasticity = velocity dependent
Reflexes: Hyporeflexia and abnormal (clonus, babinski)
Sensation: Decreased
Involuntary Motions: mm spasms
Voluntary Movements: synergistic patterns
Basics of 4 location of brain injuries - LMN
Structures: peripheral n, n roots, cranial nerves
Tone: decreased
Reflexes: hyporeflexive / absent
Sensation: decreased
Involuntary Motions: denervation → fasiculations
Voluntary Movements: weak or absent
Basics of 4 location of brain injuries - Basal Ganglia
Structures: basal ganglia
Tone: increased, rigidity = not velocity dependent
Reflexes: decreased or normal
Sensation: normal
Involuntary Motions: resting tremors
Voluntary Movements: bradykinesia, akinesia
Basics of 4 location of brain injuries - Cerebellum
Structures: cerebellum
Tone: decreased / normal
Reflexes: decreased / normal
Sensation: normal
Involuntary Motions: none
Voluntary Movements: ataxia, intention tremor, dysdiadochokinesia (can’t rapid alternate movement), dysmetria (overshoot / undershoot), nystagmus
PD Staging
1: UL if present, minimal or absent
2: minimal BIL / midline. BALANCE NOT IMPAIRED
3: Impaired righting reflex, unsteady STS / turns. restricted, but can live independently and work (depends)
4: all symptoms present and severe. standing and walking only with assistance
5: confined to bed or wheelchair
Signs / Symptoms of MS
Lhermitte’s Sign: electric shock feeling with neck flexion (hair messy)
Uhthoff’s Phenomenon: heat intolerance (u hot)
Charcot’s Triad: cerebellar signs: scanning speech, intention tremor, nystagmus
Cranial N 2 involvement: decreased vision / pain, Marcus Gunn pupil (dilation with pupillary reflex)
ALS signs + symptoms
Motor Only, pain uncommon
UMN + LMN presentation (including bulbar): dysphagia, dysarthria, cognition changes, inappropriate affect, balance / weakness / coordination issues
Long thoracic n. impingement
C5-C7
scapular wingingggggg
pain distally when flexing extended arm
Lymphedema Grading Scale - CPG
0: subclinical, lymph impaired but no visible swelling, maybe subtle symptoms / tissue changes
1: early onset swelling visible → subsides with elevation. maybe pitting
2: consistent volume change, pitting present, elevation rarely changes, fibrosis present
3: Pitting absent, tissue is very fibrotic with skin changes (thickening, hyperpigmentation, increased folds, fat deposits, warty overgrowths)
Stroke basic: ACA
CL paresis and sensory loss LE
urinary incontinence
problems with imitation, bimanual tasks, apraxia
slowness, delay, motor inaction
CL grasp reflex, sucking reflex
ACA → ABCD → baby things
Stroke basics: L vs. R
L = language / dominant
Frontal lobe = Broca’s / expressive / non-fluent (use yes/no) ← superior branch MCA
parietal lobe = Wernicke’s / receptive / fluent (use visual) ← inferior branch MCA
global aphasia ← MCA stem
OLD: slow, cautious. distractible. always negative thoughts / difficulty pos.
R = visual / perceptive
NEGLECT, difficulty visual cues
Childish: quick, impulsive, safety risks. Rigidity of thought. Positive thoughts / difficulty negative (aka. poor deficit awareness)
both: homonymous hemianopsia
Stroke basics: MCA
CL paresis / sensory loss UE and face
L lesion: language impairments
R lesion: UL neglect (L neglect)
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia (R MCA → L eye half vision loss)
Stroke Basics - PCA
Peripheral territory: vision related. CL homonymous hemianopsia, visual agnosia - prosopagnosia (don’t understand vision, aka can’t recognize people / things. dyslexia without agraphia. color discrimination. memory deficits. topographical disorientation (bad at directions)
Deep territory: central issues: thalamic pain syndrome
Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery
Bell curve shape between y=spasticity, x = motor control
1: flaccidity, no AROM
2: Start minimal voluntary movement - in synergy, increase tone
3: voluntary control of movement synergy - spasticity / tone is peak
4: Movement outside of synergy, tone decreasing
5: increase complex movements, greater limb synergy IND
6: Individual joint movement, coordinated movement (hand + 1 finger ~ IJC)
7: normal function
UE spasticity vs. synergy pattern
Rest (spasticity)
-scapula retract / Down Rot, shoulder ADD/IR/depressed, elbow F, forearm pronated, wrist F/ADD, hand F, thumb ADD (chicken dance)
Active (Synergy)
-F: scapula retract / elevate, shoulder ABD / ER, elbow/ wrist/ finger F, forearm supinated
-E: scapula protract, shoulder ADD/IR, elbow E, forearm pronated, wrist / finger F
strong man pose
LE spasticity vs. Synergy pattern
Passive (spasticity)
- pelvis retracted / hiked, hip ADD / IR / E, knee E, Foot PF / INV / equinovarus / claw toes / toes curl. ballerina pose
Active (synergy)
-F: hip F / ABD / ER, knee F, ankle DF / INV, toe DF (figure 4)
E: hip E / ADD / IR, knee E, ankle PF / INV, toe PF (ballerina)
Ranchos Los Amigos TBI Scale “cheat”
1-3 “Response” → 4-6 “Confused” → 7-8 “appropriate”
1: no response / coma
2: general whole body, non purposeful responses
3: purposeful, follows simple commands but still inconsistent
interventions - positioning, PROM, education, respiratory
4: + agitated, no memory, make up stories, non-cooperative
5: + inappropriate, consistent w/ simple commands / a bit complex, some socializing
6: + appropriate, more carryover, more goal oriented actions
interventions - consistency / routine, closed options (not Y/N), simple environment
7: + automatic, does routine actions but robot-like / unsure why
8: + purposeful, more carryover / getting why and abstractions. Still impaired stress / emergency responses
interventions - re-entry to outside environments and focus on life adaptations
Cryotherapy physiological effects + parameters
store @ 25 degrees, apply 10-20, every 1-2 hours
increased: joint stiffness, pain threshold, mm activation (short term)
decreased: collagen extensibility, blood flow, capillary permeability, local metabolism, spasticity (long ice times), nerve conduction velocity
Heat physiological effects + parameters
store @ 158-167 degrees F, 20-30 min, 6-8 layers, heat peaks 5 min
increased: CO, vasodilation, HR, RR, metabolic rate
decreased: mm activity, BP, blood to internal organs and resting mm, SV
E-Stem parameters mm strengthening
Pulse frequency: 35-80 pps
pusle duration: small mm = 125-200 us. large = 200-350 us
amplitude: injured = >10% MVIC. uninjured = >= 50% MVIC
On:Off: 6-10: 50-120s (1:5 initially, can reduce off with time)
ramp time: > 2 sec
treatment time: 10-20 min for 10-20 reps
times / day: every 2-3 hours while awake
E-stim for muscle re-education
Pulse frequency: 35-50 pps
pusle duration: 125-200 us. large = 200-350 us
amplitude: sufficient for functional activity
On:Off depends on activity
ramp time: > 2 sec
treatment time: depends on functional act
times / day: NA
E-stim for muscle spasm reduction
Pulse frequency: 35-50 pps
pusle duration: 125-200 us. large = 200-350 us
amplitude: to visible contraction
On:Off: 2-5:2-5 (equal on:off)
ramp time: >1 sec
treatment time: 10-30 min
times / day: 2x/day
E-stim for edema reduction with mm pump
Pulse frequency: 35-50 pps
pusle duration: 125-200 us. large = 200-350 us
amplitude: to visible contraction
On:Off: 2-5:2-5 (equal on:off)
ramp time: > 1 sec
treatment time: 30 min
times / day: 2x/day
Increase patient comfort with e-stim
ramp time: increase
pulse duration: decrease
electrode size and quality: larger, stickier
pulse frequency: increase
on:off: increase off time
High Voltage Pulsed Galvanic Current for wound healing parameters
waveform: HVPV
polarity: negative if bad/infected wound, positive if proliferating wound
pulse frequency: ~100 pps
pulse duration: ~100 us
amplitude: for comfortable tingling feeling
treatment time: 45-60 minutes, at least 3-7 days/week
placement: around wound area, if in use saline soaked gauze
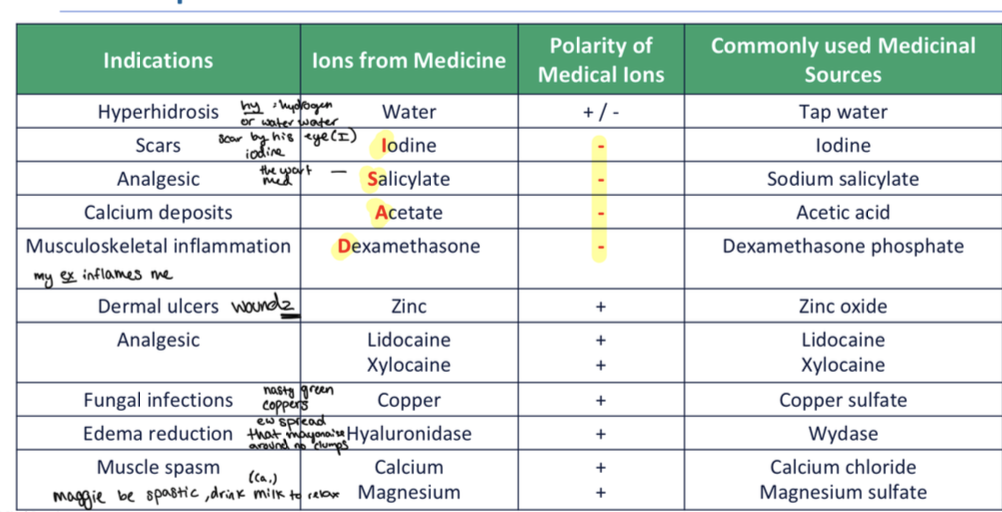
Iontophoresis
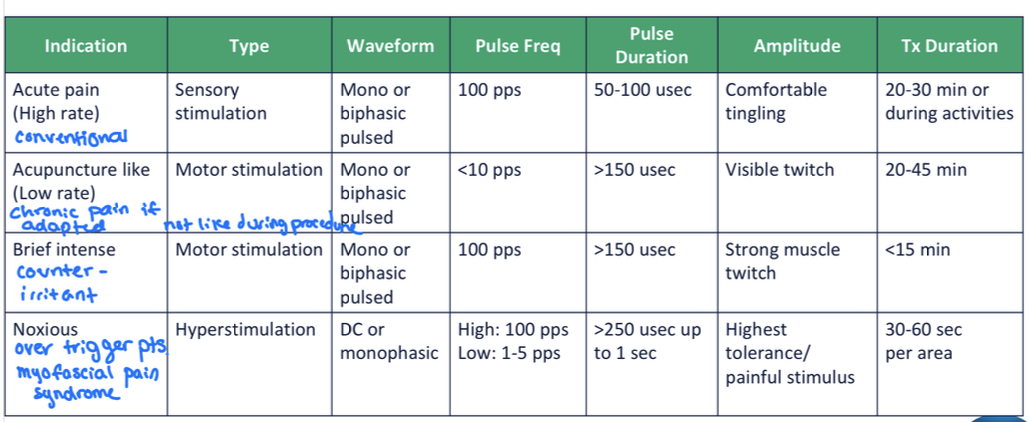
TENS chart
Ultrasound parameter flow chart
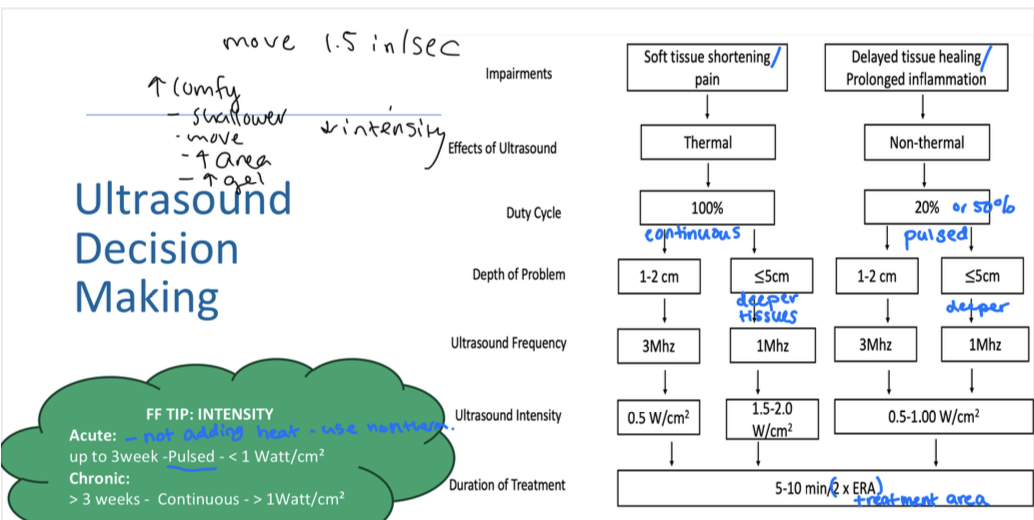
transducer head should 2-3x smaller than treatment area
EMG Biofeedback Parameters
Initial
relax / inhibit mm: low sensitivity, close electrode placement (quiet cuddles)
re-educate / facilitate mm / increase tone: high sensitivity, far apart electrodes
Later: reverse parameters as they make progress
Lumbar Traction parameters

Cervical traction parameters
Joint distraction: max = 20-29 lbs / 7% BW
disc protrusion / mm spasm / elongation: 11-15 lbs
Phases of motor learning
Cognitive: initial, what to do. Heavy thinking. Bimanual transfer, outcomes / results feedback after, closed environment early
Associative: knows what to do, learning how to do it. Can do more performance based feedback
Autonomous: experienced, working on automaticity
General: Feedback = less frequent, less precise, externally focused, terminal, some delay, self-initiated = increases learning. more often / during / not above increases performance.
Distributed = better learning, but massed early performance increase and can be good cognitive impairments. Random = improved retention. Variable = increased task transfer
Smith’s Fracture
distal radial fracture with volar displacement of bone (Mrs. smith gardens in the front yard)
Colle’s Fracture
Most common distal radial fracture, bone projects dorsally. = dinner fork deformity
-acusis
hearing
hyperacusis = over sensitive hearing, can be facial n damage
presbycusis = age related hearing loss
ankle eversion glide
lateral glide “I Love emails”
Supine to Sit test
SIJ dysfunction test (boo) → apparent leg length discrepancy
ALPS: anterior longer posterior shorter: supine position
LLE supine long → sitting short = L anterior rotated innominate
Short Form Health Survey
measures QOL
vs like DASH as symptoms / disability
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
symptoms: swelling / stiffness, change in color / temp of skin (warm), increased sensitivity to touch including clothing, loss of fine motor control, tremor / spasm. Burning type pain
heart blocks
AV communication issues
1 degree: prolonged PR interval
2 degree: increased PR interval, occasional dropped beats
3 degree: no AV communication, no relationship P waves and QRS = emergent referral
Waves and meaning
P-wave = SA node firing / atrial depolarization
QRS complex = ventricle depolarization
PR interval = conduction from atria to ventricle
T wave = ventricle repolarization
ST segment = ventricular contraction (elevated = STEMI, depressed = NSTEMI)
S3, S4 abnormal heart sounds
S3 = CHF
S4 = MI or HTN