Glaciation and Glacial Landforms
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are alpine glaciers?
Glaciers that form in mountains and valleys
What are the different types of alpine glaciers
Valley
Piedmont
Icefield
Cirque
Tidewater
What are the types of glaciers?
Alpine glaciers
Ice Sheets (Continental glaciers)
Zone of Accumulation
Area where there is a build up of snow and ice
Equilibrium Line
Boundary between accumulation and ablation
Zone of Ablation
Area where melting and evaporation exceed accumulation (zone of wastage
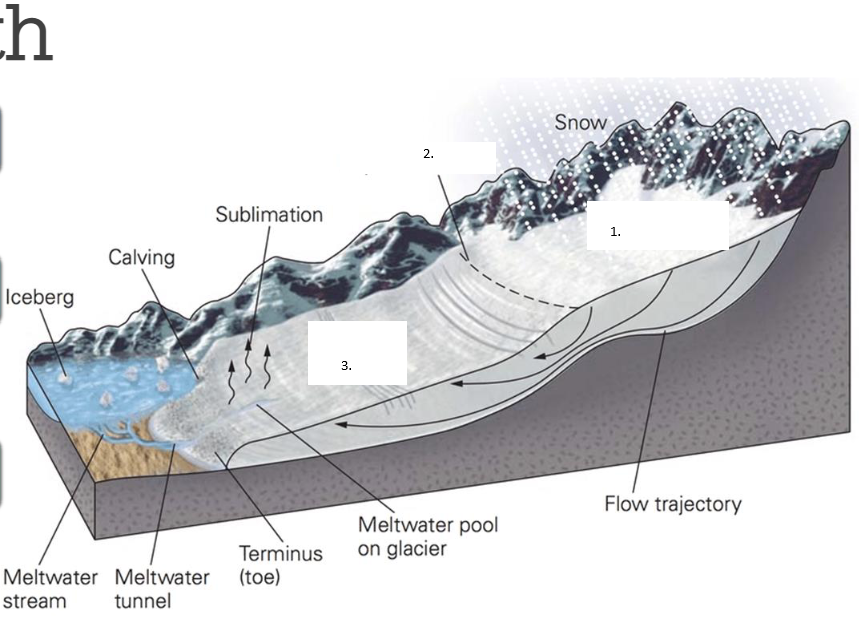
Label the areas
Zone of Accumulation
Equilibrium Line
Zone of Ablation
Describe the zone of fraction and where it occurs
Occurs on the upper portion of the glacier where ice behaves in a brittle matter
Describe the zone of flow and where it occurs
Occurs on the lower portion of the glacier where ice behaves as a plastic due to overlying mass
Internal Flow
Gradual melting and re-freezing of internal ice structure
Basal Slip
Movement of glacier over the meltwater at the base of the glacier
Causes of U shaped and V shaped valleys
Glaciers cause U-shaped valleys
Rivers cause V-shaped valleys
Glacial Drift
General term for materials (gravel, sand, silt, clay) deposited by glacial processes
Glacial Till
Unsorted and unstratified material deposited from glacial processes
What are the different types of moraines?
Lateral - sides
Medial - middle
Terminal - end
Cirque
A bowl shaped depression located at the head of the glacier, where snow accumulated, the underlying earth is slowly eroded away to create a cirque
What happens when a cirque metls?
A tarn lake is created
Crevasses
Are formed when the upper portion of a glacier cracks. Generally formed over sudden drops or changes in elevation.
Plucking
Eroded material gets “stuck” in the ice and moves along with the glacier suspended ice
Glacial Erratic
Larger pieces of plucked material that are left behind during glacial retreat
Striations
As glaciers advance pushing plucked rocks and debris forward the underlying bedrock becomes grooved and worn
Rafted Bedrock
Massive pieces of bedrock broken away from source material and relocated by glacial movement
Fluting
Surficial ridges formed parallel to the ice movement direction
Drumlin
hills of till sediment formed and elongated due to glacial movement
Hummocky Disintegration Moraine
Glacial drift deposited at the toe of a retreating glacier amongst blocks of melting ice resulting in knob and kettle topography
Moraine Plateau
Glaciolacustrine sediments are deposited resulting in large flat-topped area once the meltwater flows away
Linear Disintegration Ridge
Glacial till deposited in crevasses resulting in a net patter of narrow ridges following glacial retreat. Also known as crevasse filling
Glaciofluvial
Erosion or deposition caused by flowing meltwater, from melting glaciers, ice sheets, and ice caps
Esker
Long winding ridge of sand or gravel
Kame Delta
Steep side mound of sand and gravel deposited at the perimeter of a stagnant glacier
Kame terrace
Narrow steep sided ridge with a flat top
Outwash Plain
Fan shape deposit of sand and gravel spread out in front of a glacier by glacial runoff
Glaciolacustrine
Sediments deposited into lakes that have formed due to glacial runoff or where glacial meltwater ponds