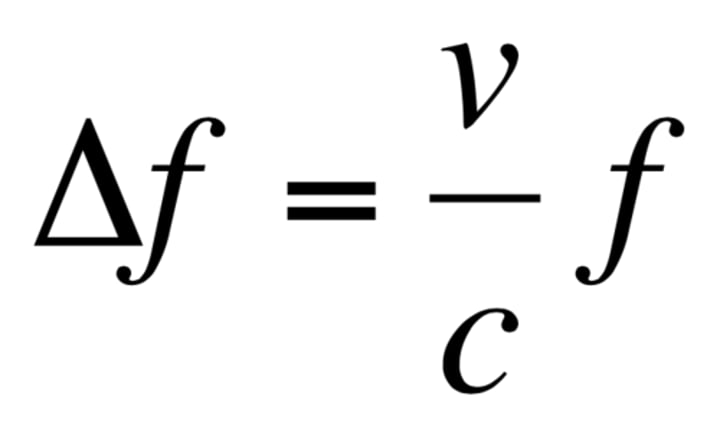IB Physics HL - Topic 9
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
displacement starting at equilibrium
x = x0sin(ωt) where ω is the angular frequency (2pi*f)
displacement starting at maximum
x = x0cos(ωt) where ω is the angular frequency (2pi*f)
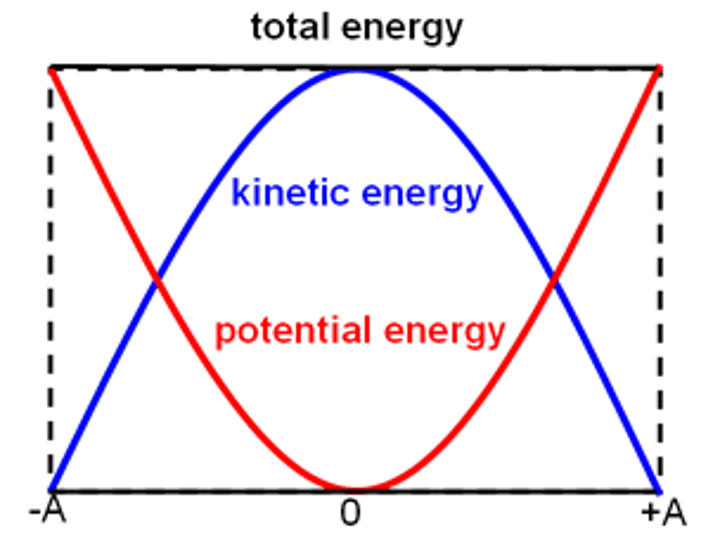
Energy changes in SHM
total energy is constant, KE is max at 0 displacement, PE is max at max and min displacement
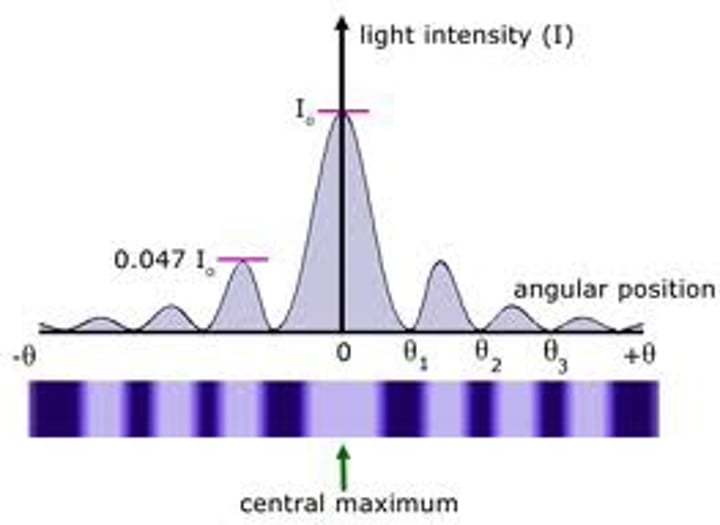
the angle of diffraction for first minimum in single slit diffraction
wavelength/widthof slit
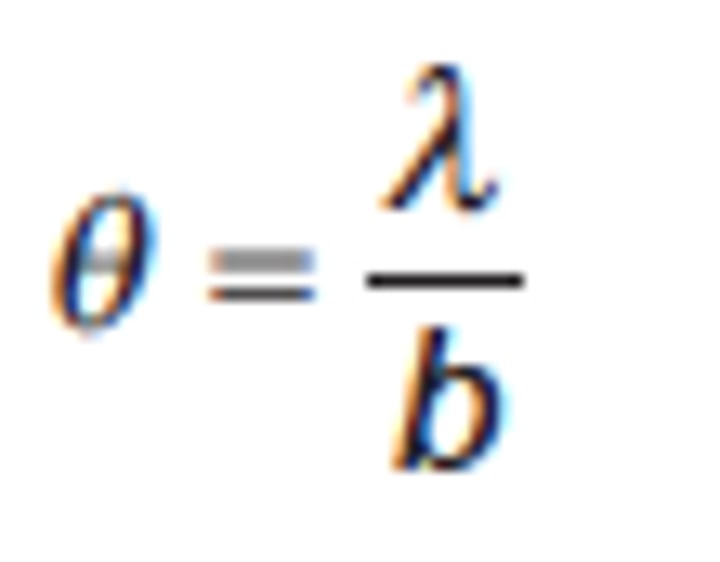
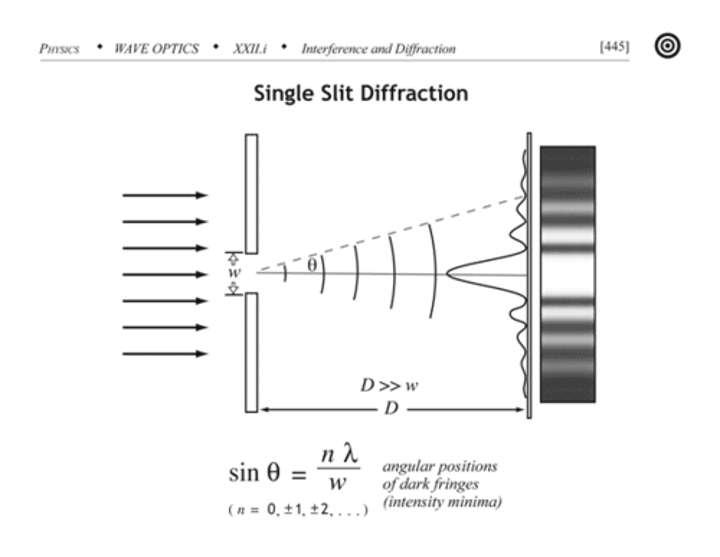
Single Slit Diffraction condition for a minimum
width*sin(θ) = mλ
Width of bright spot in Single-Slit Diffraction (y)
y = mλD/a
Young's double slit experiment
light is projected onto a screen with 2 small slits. The light waves diffracting through the 2 slits interfere with one another and produce a predictable pattern of alternating light and dark bands (maxima and minima) on the detector screen
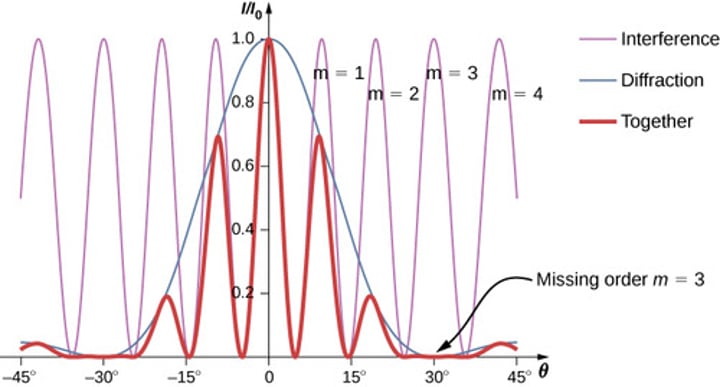
double slit diffraction maxima equation
distance between slits*sinθ = mλ
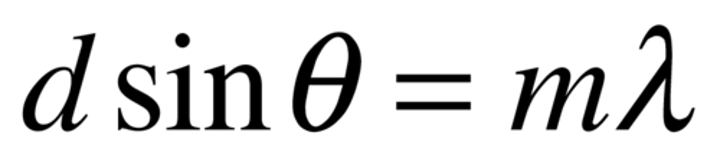
double-slit minima equation
distance between slits*sinθ = (m+1/2)λ
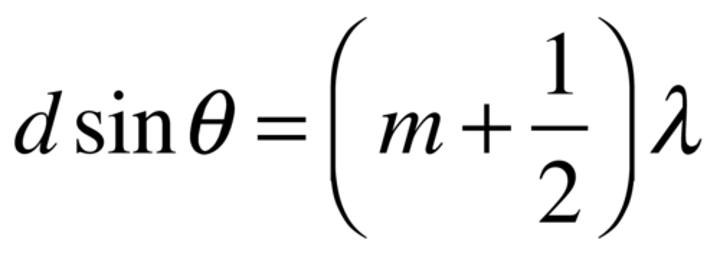
thin film interference
a phenomenon in which a spectrum of colors is produced due to the constructive and destructive interference of light waves reflected in a thin film
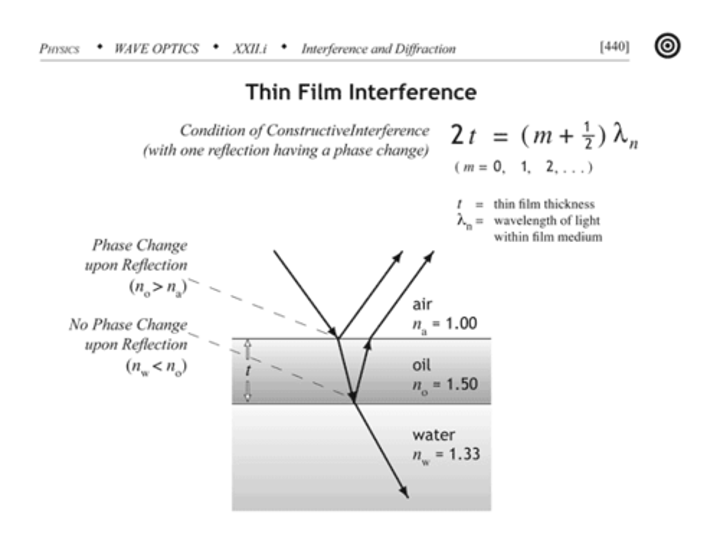
Thin-film interference phase shift
reflected waves have a 180 degree (1/2λ) phase shift when n2 > n1. reflected waves have no phase shift when n1 > n2
Multiple slit diffraction maxima equation
distance between slits*sinθ = mλ
thin film interference destructive interference equation
2dn = mλ

thin film interference constructive interference equation
2dn = (1/2 + m)λ where d = thickness of film, n = index of refraction in film, m = order, λ = wavelength of light
wave-particle duality
the concept that all matter and energy exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties
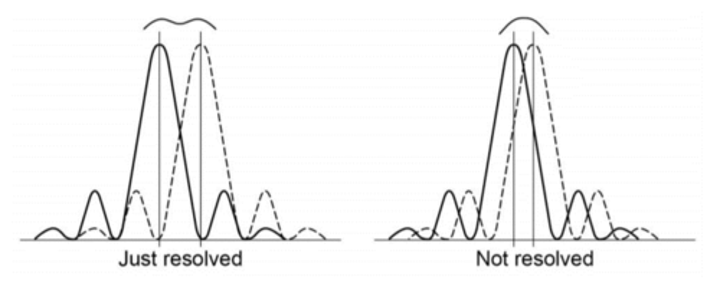
Resolution
the ability to distinguish two separate points
Larger aperture
more resolved
Raleigh criterion
when two points are just resolved, θ = 1.22λ/diameter of aperture
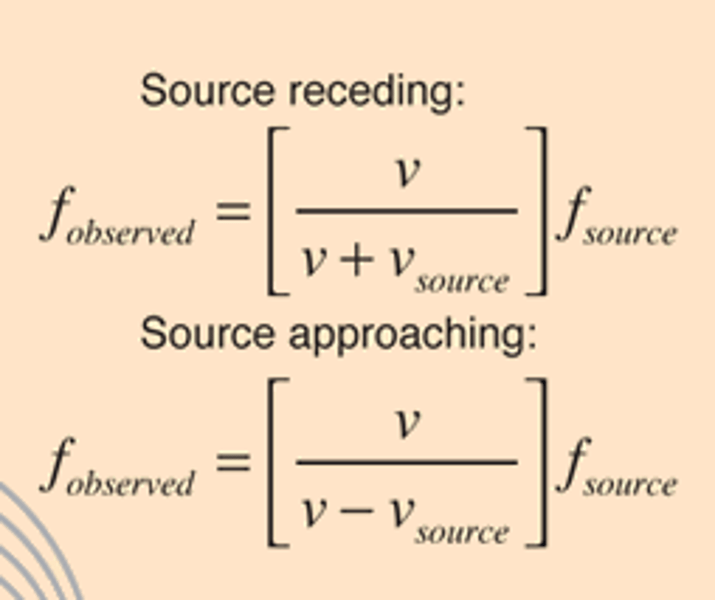
Source moving toward observer
subtraction in denominator
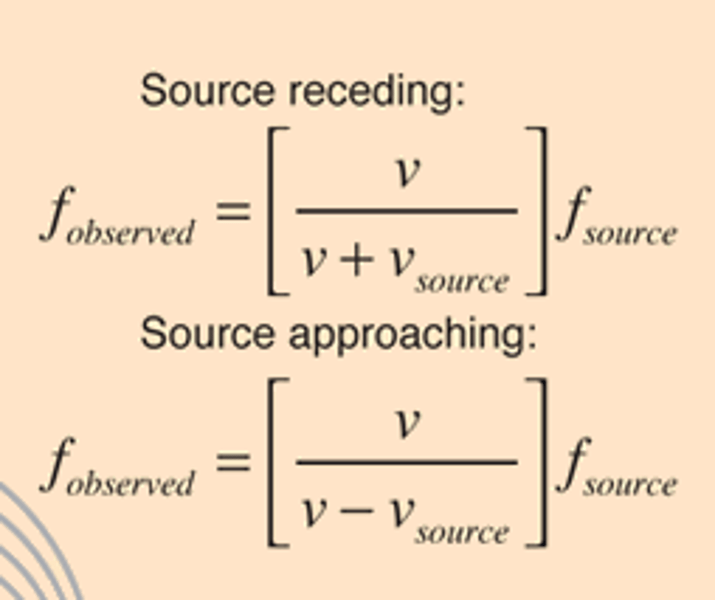
Source moving away from observer
addition in denominator
observer moving toward stationary source
addition in numerator
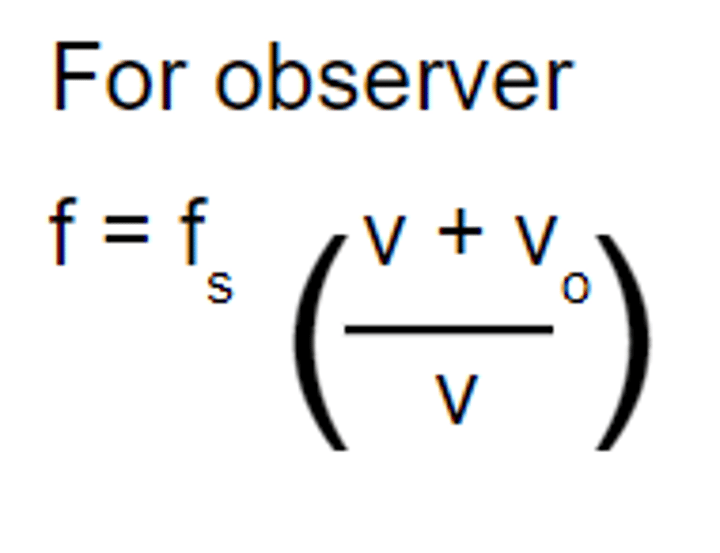
observer moving away from stationary source
subtraction in numerator
values in moving observer situation
velocity of wave changes, wavelength is constant, frequency changes
values in moving source situation
velocity of wave is constant, wavelength changes, frequency changes
doppler equation for electromagnetic waves
change in f / original f = v/c, should only be used when v is much smaller than the speed of light