IM COOKED T2
1/319
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
320 Terms
slow transforming viruses RNA causing neoplasia
feline leukemia virus
simian leukemia virus
bovine leukemia virus
avian leukosis virus
fast transforming virus RNA causing neoplasia
rous sarcoma virus
murine leukemia virus
feline sarcoma virus
DNA viruses causing neoplasia
hepadna- sqiurrels, woodchuck, duck- hepatocellular carcinoma
papilloma-rabbit, dog, horse- papilloma
herpes- chicken,guinea pigs, rabbit, monkey, frog- lymphosarcoma
Pox- rabbit, monkey- fibrosarcoma, histiocytoma
direct effects of tumors
necrosis
obstruction
direct compression
chronic inflammation
hemorrhage
penetration/perforation of a tissue barrier
pathological bone fractures
not seen on abdominal radiographs
pancreas
adrenal glands
ovaries
ureters
lymph nodes
canine small intestine proper sizing
not wider than 1.6x the L5 and/or
2x the width of a rib
feline small intestine proper sizing
no wider than 12mm or
2x the height of mid-body L2
vitamins are essential for what two things in the body
enzyme activity
structural components
minerals are essential for what two things in the body
coenzymes
regulators of metabolism
barrow
castrated male pig
wether
castrated male goat
steer
castrated male bovine
hog
mature pig of 120+ lbs
colt
male horse that is younger than 4 years old
hepatocellular adenoma
benign neoplasm of hepatocytes
described in young ruminants
single variably sized, brown masses
compress adjacent parenchyma
hepatocellular carcinoma
malignant neoplasma of hepatocytes
not common in all domestic species
reported in dogs, ruminants, especially sheep
described as massive (single mass), nodular, and diffuse
cholangiocellular adenoma
single, firm, discrete, white mass
mass comprises tubules with well differentiated cuboidal epithelium separated by minimal stroma
common in cats
cholangiocellular carcinoma
all species
large single mass or multiple masses
gray-tan unencapsulated masses
often metastatic to to other tissues
hepatic metastatic tumors
lymphoma (focal or diffuse)
hemangiosarcoma
melanoma
mammary carcinoma
transitional cell carcinoma
anal sac gland carcinoma
malignant melanoma→ multifocal variable sized black masses
mild to moderate elevation in ALT (disorders leading to 5x increase)
vs
marked elevation in ALT (stimulus leading to up to 10x increases)
5x: diabetes
±feline hyperthyroidism
2ndary to passive congestion and GI disease
anticonvulsant drugs
steroid drugs
phenobarbitol can induce liver dz
10: THT : toxic, hypoxic, trauma,
acute severe hepatic injury/ necrosis or cell death
when does AST increase
anticonvulsants
exercise (30% increase)
NO steroids increase AST
(Race horses is increased typically)
most common hepatic neoplasms
carcinoma
lymphoma
in cats any increase in ALP is significant because it indicates what two things and what is its half life
primary liver disease and hyperthyroidism
half life is short less than 8 hours
GGT can be used as an alternative to ALP in small animals
calcium and phosphorus excess causes what in large breed dogs
growth deformities
lameness, motility issues, pain
what is the rate limiting step in the synthesis of catecholamines in the adrenal medulla?
tyrosine hydroxylase
regulated via a negative feedback loop (rising level of cytoplasmic norepinephrine)
pheochromocytomas
catecholamine secreting tumors of chromaffin cells more frequent in dogs than cats
what are the three causes of Cushing’s Dz?, what is the most common tumor by what percent? species differences? dog /cat /horse
intake of steroids, pituitary tumor, adrenal tumor
pituitary tumor 80-90%
dog: primary (adrenal dependent) & pituitary dependent
cat: less common than in dogs
horses: PPID caused by a pituitary tumor
what are the adrenal gland tumors involved in addisons and cushings
cortical adenomas or adenocarcinomas: includes pheochromocytomas (medulla)
contralateral atrophy
*carcinomas are ofter large and involve the kidneys
Cushing’s CBC findings and Chemistry findings/ urinalysis
CBC:
Stress leukogram ( mature netrophilia, lymphopenia, eosinopenia, monocytosis)
Thrombocytosis (slightly increased)
Chem:
ALP increased
mild ALT increased
leads to vacuolar hepatopathy (glycogen)
increase in bile acids and cholestasis
hyperglycemia (cats may show insulin resistance bc of DM)
ELEVATED cholesterol/triglycerides
lipemia (due to altered lipid metabolism)
LOWERED UN associated with PU/PD
electrolytes: mild hypernatremia, hypokalemia
Urinalysis:
USG= dilute from PU/PD
proteinuria with albumin WNL (mild protein leakage)
UTIs are common without pyuria due to immunosuppression
what drugs interfere with assay for hyperadrenocorticism?
cortisol= 100%
prednisolone= 69%
Dexamethasone= 0.1%
Basal cortisol is helpful in the dx of what disease?
addisons it is helpful to rule out Addison (it will decrease)
NOT useful in hyperA because of pulsatile ACTH secretion resulting in variable cortisol levels throughout the day and may be affected via non-adrenal issues
testing for hyperA and hypoA what are the screen testings, the diagnostic tests, and differentiating tests?
Screening tests: UCCR (urine cortisol:creatinine ratio) (negatives rule out hyperA=low ratio is negative) (higher ratio is more likely cushings)
diagnostic test: LDDST (low dose dexamethasone supression test) and ACTH stim test
differentiating test: HDDST (high dose dexamethasone suppression test) (differentiates from PDH and ADH) and eACTH (endogenous ACTH) (differentiates PDH from ADH)
hyperA suppression tests
complete suppression at both 4 and 8 hours→ stressed animals may fail to suppress
pituitary dependent LDDST= lack of suppression at 8 hours, elevated endogenous ACTH levels, eACTH is high and ultrasound show bilaterally enlarged adrenals
adrenal dependent LDDST= lack of suppression at ANY time point, ONE enlarged adrenal gland with contralateral atrophy, eACTH levels suppressed (decreased for primary adrenal)
ACTH testing is used for these three things
dx of iatrogenic cushing’s, addison’s and monitors HAC tx:
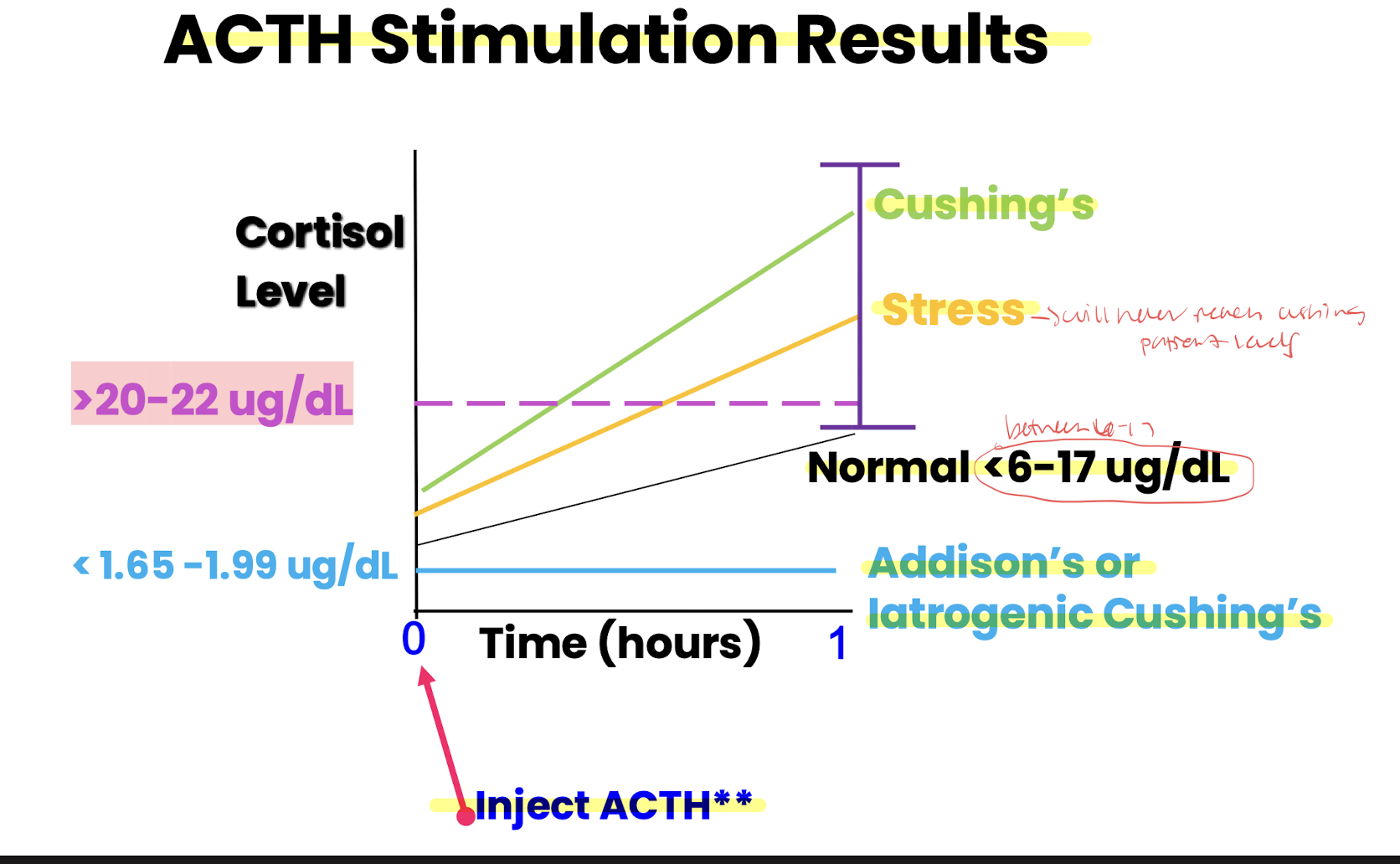
cushings= >20-22 ug/dL
addisons= <6-17 ug/dL
what type of tube should be used for eACTH?
Plastic because ACTH adheres to glass
Pituitary dependent hyperadrenocorticism High dose dex stim test
not used much since ultrasound and eACth measurements are less invasive and more precise alternatives for PDH vs ADH differentiation
HDDST= suppresses cortisol secretion in 75% of PDH cases and 25% of PDH cases show no suppression often linked to larger pituitary tumors
supression supports PDH dx while resistance can be either PDH or AT
what dx test is used most commonly to confirm PPID in horses? what is the relationship between PPID and EMS?
baseline plasma ACTH measurement and/or Thyrotropin releasing hormone stimulation test
relationship= horses with EMS are at increased risk of developing PPID as they age
primary vs secondary addisons
primary: caused by adrenal cortical destruction or insufficiency→ electrolyte disturbances and cortisol insufficiency (90-95%) causes: neoplasia (carcinoma), autoimmune, iatrogenic (over tx of drugs), surgical removal
secondary: caused by pituitary ACTH deficiency usually without electrolyte disturbances
Addisons dz CBC, CHEM, URINE
CBC:
mild non-regenerative anemia, lymohocytosis or esosinophilia (LACK of stress leukogram)
CHEM:
electrolytes: hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia (ADDISON NEEDS SALT, NO MORE BANANAS, HATES BLEACH); mild hypercalcemia linked to reduced corticosteroids and altered renal calcium handling
NA:K ratio <15:1 → <23:1= suspect addisons
elevated UN
URINE:
dilute urine
Pseudo Addisons is caused by what organism
trichuris vulpis (whipworms)
what are the three main players of Ca-P homeostasis
GI: ca absorption from diet via active mech, P mostly passive absorption
kidney: ca filtered both passive and active reabsorbed, P filtered actively reabsorbed or excreted bc often high in intake
bone: deposition and resorption of Ca-P salts→ calcium buffer system
the three hormones that are in control of plasma calcium and P and which one is the most powerful regulator of Ca-P
PTH and Vit D increases Ca in blood
calcitonin (activates Vit D3) decreases Ca in blood (peptide hormone produced in C cells in the thyroid gland stimulated by hypercalcemia, favors osteoblast formation/bone formation)
**PTH (peptide hormone) is the most powerful regulator of Ca-P which is secreted by chief cells within the Parathyroid gland and calcium sensing receptors on the cheif cells regulate PTH secretion
stimuli for release of PTH and what does PTH do?
low levels of ca and high levels of phosphorus
hypercalcemia inhibits the release of PTH
PTH stimulates bone= bone resorption which stimulates osteoclasts dissolving ca-p salts increasing them in blood;
kidneys= stimulates calcium reabsorption (ca-atpase pump) and phosphate excretion (inhibits via Na-dependent cotransporters) and activates Vit D to D hormone;
GI= D hormone stimulates Ca and P absorptions by stimulating calbindin (ca binding protein) (sodium phosphate cotransporter)
vitamin D/ D hormone and species differences
Vit D3 is animal derived and more effective; Vit D2 is plant derived and less effective
pro vit D3 is synthesized in the liver sent to the skin to get activated by the UVB turns into vit D3 back to the liver or kidney (with PTH stimuli) which gets turned into D hormone to be utilized in the gut to absorb Ca and P
dogs/ cats= dietary dependent
herbivores/reptiles/many birds/llamas/alpacas= UV-B dependent
PTHrP=
hypercalcemia of Malignancy tumors (anal sac tumors) release uncontrolled amounts of PTH-related protein which mimics the actions of PTH
mechanisms of hypercalcemia (4)
increased GI absorption
increased osteolysis
decreased renal excretion
protein binding
effects of hypercalcemia
kidneys: nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (PU/PD due to reduced response to ADH), renal damage, urinary tract infection
soft tissue: mineralization
muscle: decreased excitability
nervous system: coma, paresis. reduced neural excitability
heart: rare arrhythmias lead to ventricular fibrillation
PTHrP is most commonly secreted by which tumor types
Squamous cell carcinoma
anal sac adenoma
lymphoma
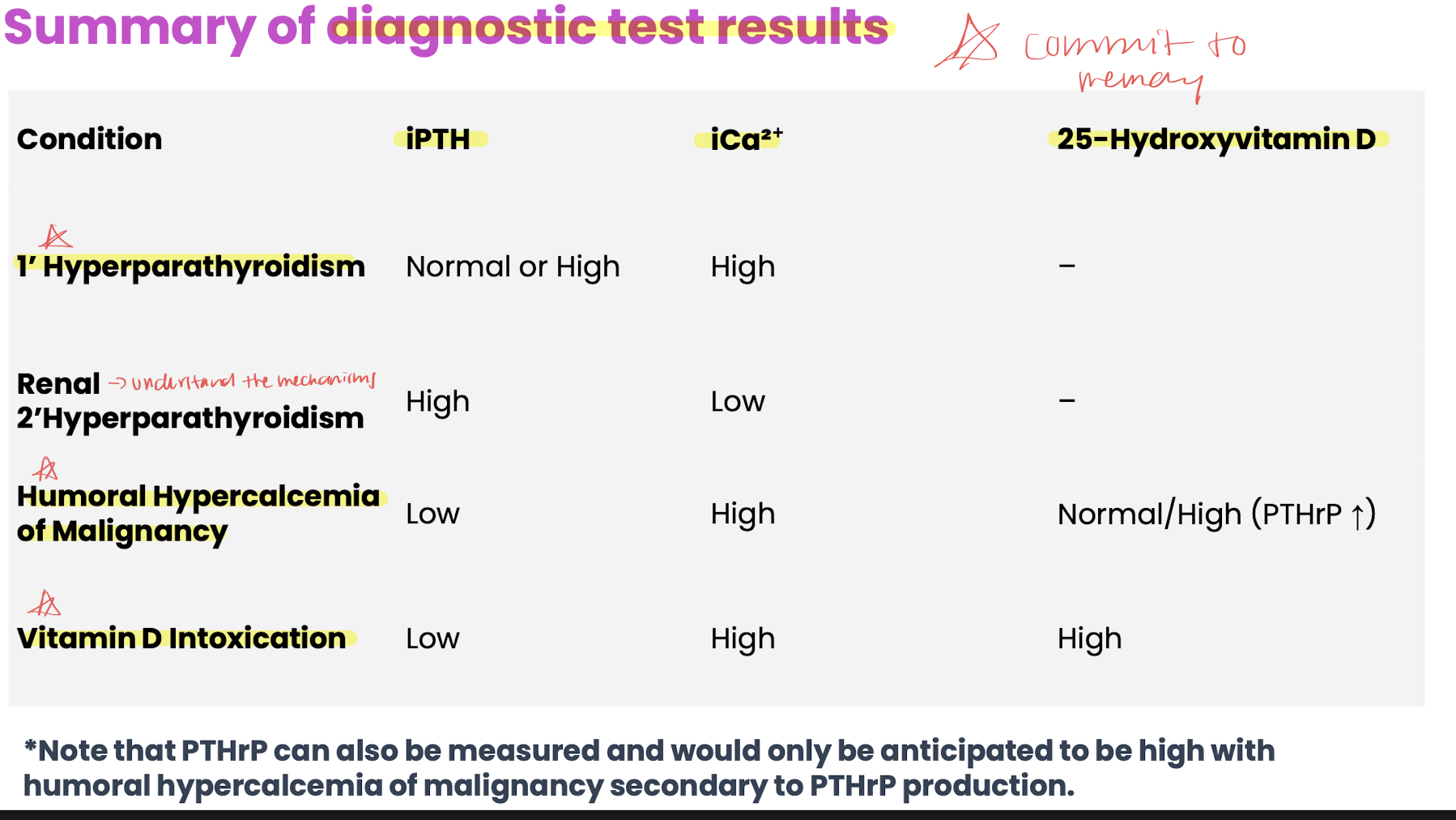
primary hyperparathyroidism, humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy
primary: PTH secreting tumors common in dogs→ signs: hypercalcemia, hypophospatemia, uroliths
humoral: most common cause in dogs (tcell lymphoma, apocrine glad adenocarcinoma)→ production of PTHrP
hyper D: sources rodenticides, dietary supplements, toxic plants
hypocalcemia mechanisms (5)
decreased absorption: GI dz, dietary imbalance
excessive losses: renal, GI, milk
PTH-related issues: hypoparathroidism, PTH resistance or pseudohypoparathroidism
protein binding: hypoalbuminemia lowers total ca but not free ionized calcium; total calcium may not correlate with ionized calcium
hypoalbuminemia: causes mild hypo-ca without clinical signs
other causes: toxicoses (oxalates, ethylene glycol), endocrine diseases (pancreatitis, cushings), sweat losses
hypoparathyroidism, nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism, renal secondary hyperparathyroidism
hypoparathroidism: low ca, low ipth, hyperphosphatemia
nutrional: imbalanced ca:p →osteolysis
renal: vit D deficiency (rickets), hyperphosphatemia
Growth hormone
(Somatotropin) peptide hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland controlled by the hypothalamic GH releasing hormone and GH inhibiting hormone
released in a pulsatile fashion with superimposed peaks caused by: hypoglycemia/starvation, ghrelin (hunger hormone), exercise, stress, trauma, sleep, progesterone
highest during adolescence and decline with age
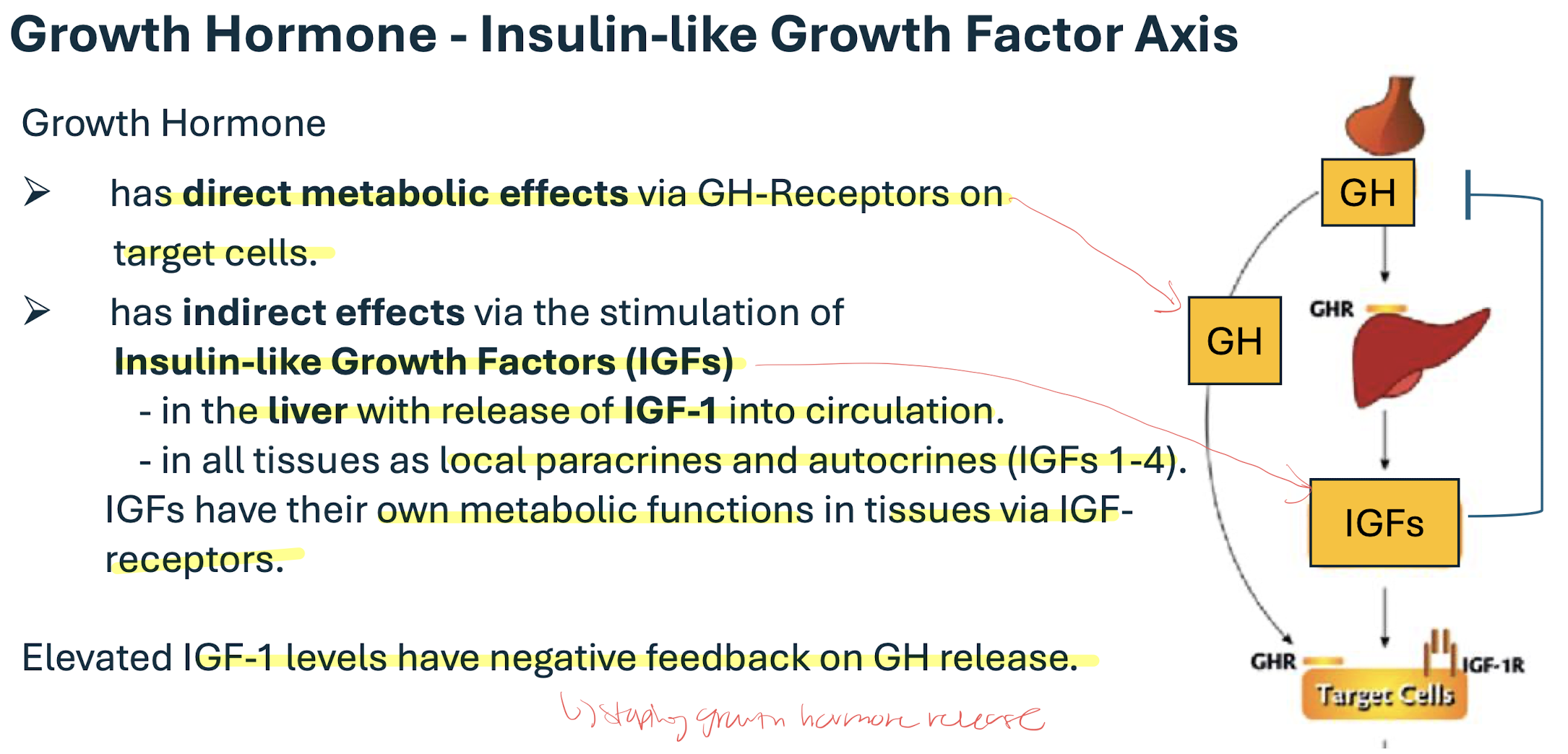
IGF-1 has a negative feedback on the GH release
low vs high energy status changes dominance between GH and IGF-1
low energy= LOW INSULIN→ GH dominant bc igf receptors are down-regulated in the liver = direct effects on tissues; simulates lipolysis, gluconeogenesis, insulin resistance (diabetics)
high energy= HIGH INSULIN→ IGF-1 dominant= indirect effects on tissues= stimulates protein anabolism affects all tissues most obvious in cartilage/ bones (stimulates bone length and width growth) and muscles (increases muscle mass)
juvenile onset panhypopituitarism (dwarfism) and acromegaly
panhypopituitarism= deficiency at birth low GH, TSH, FSH/LH, ACTH→ delayed growth, retained puppy coat, bilateral alopecia, delayed dentition, small sex organs, infertility
acromegaly= functional pituitary tumors secreting excess growth hormone→ joint problems, increased body weight, facial broadening, paw enlargement, prognathia with increased spacing in teeth, laryngeal hypertrophy, tongue enlargement, organomegaly (DIABETIC CATS)
hyperphosphatemia causes
intake: excess intake, hypervitaminosis D, decreased GI motility
physiologic: young animals
decreased excretion: reduced renal excretion, hypoparathyrodism
shifting: hemolysis, excess muscle damage
hyperthyroidism: 21% of cats show elevated phosphate
hypophosphatemia causes
decreased intake: starvation, malabsorption, vomiting, diarrhea, tube feeding
increased intake: renal losses, hyperparathyroidism, pseudohyperparathroidism, osmotic diuresis
shifting ICF: insulin therapy (rapid uptake into cells)
defective mobilization: post parturient states (milk fever, eclampsia)
ovaries are made up of two regions:
cortex→ follicular growth and corpora luteal location
medulla→ very irrigated and rich in nerve endings
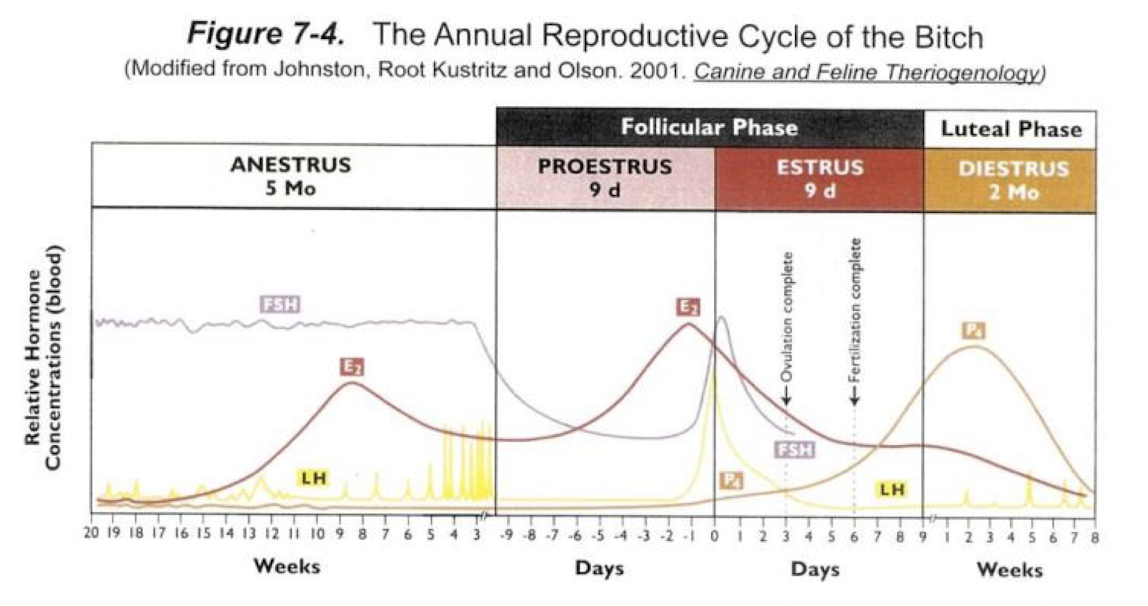
estrous cycle and the stages
cyclical pattern of ovarian activity that transitions from reproductive receptivity to non receptivity
PEMDA (protestus, estrus, metestrus, diestrus, anestrus) (Please excuse my dear aunt)
P: very short (non existent in queens) Active follicular growth and estrogen production follicular phase
E: sexual receptivity to the male (estrogen is very high and induce estrus); follicular phase
M: some species (mare, ruminants, sow) transitional phase between estrus and diestrus were the corpus lutea are developing
D: longest period of the cycle: presence of corpora letea and high levels of progesterone; luteal phase
A: reproductive quiescence
ovarian follicles
follicles contain the oocyte and develop from primordial or more mature, pre-ovulatory stages→ produce increasing amounts of estrogen
ovulation: local inflammatory process that results in the release of a mature oocyte (expect dogs release immature)
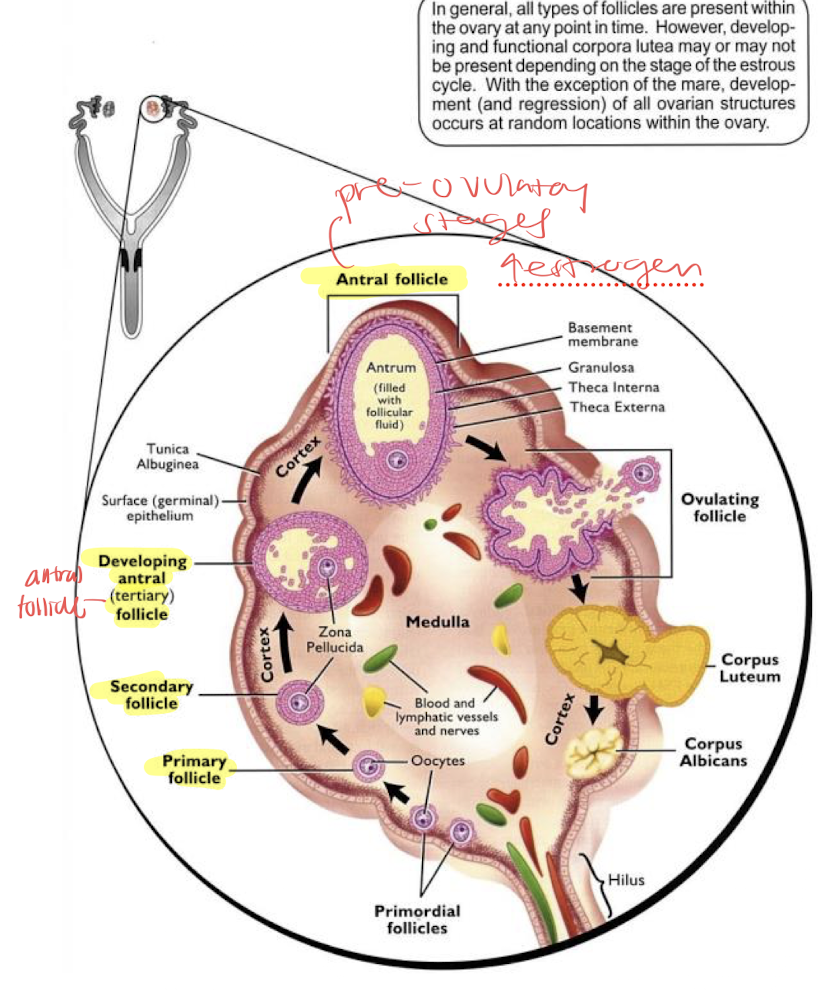
corpus luteum produces progesterone; some species can have multiple corpus luteum with multiple ovulations (bitch, queen ewe, sow)
folliculogenesis and oogenesis, and progesterone
depends on FSH and LH from the pituitary/ hypothalamus
oocyte matures inside the follicle
progesterone= has strong negative feedback on the hypothalamic pituitary axis during the luteal phase, high levels of P4 reduce GnRH and FSH/LH pulses and surges, inhibits estrus behavior
two cells of estrogen production
theca cells: stimulated by LH produce androstenedione (precursor to estrogen)
granulosa cells: stimulated by FSH convert androstenedione into estrogen (estradiol)
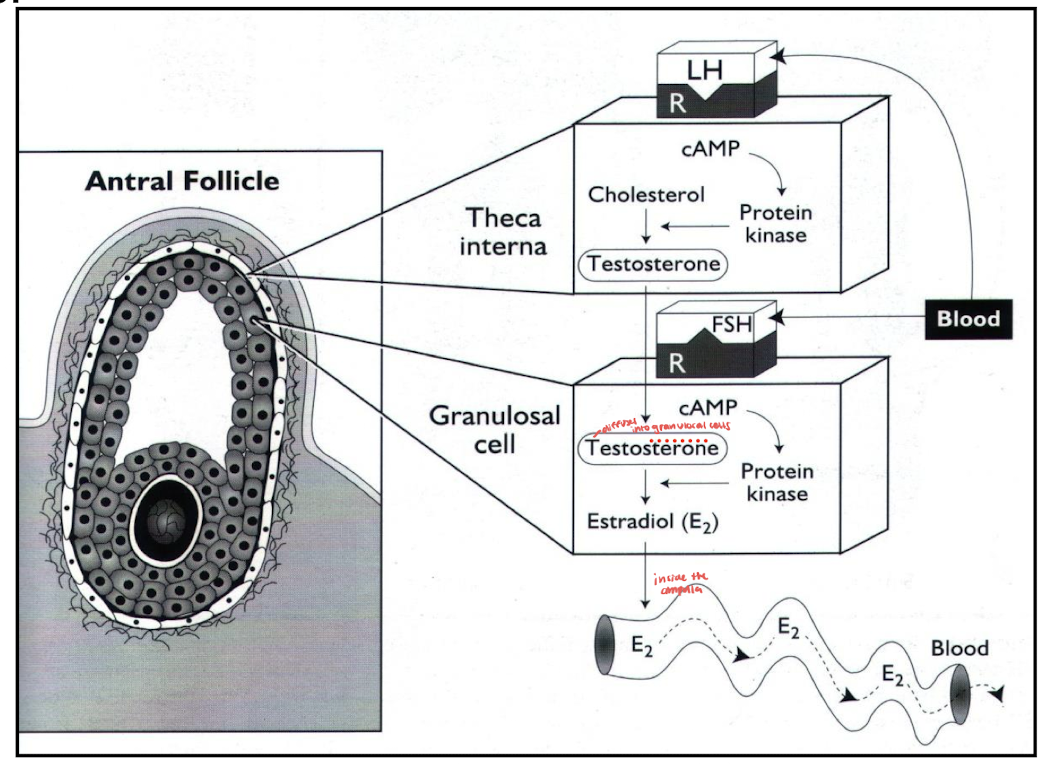
ovulation: spontaneous vs induced
high levels of estrogen stimulate brain centers (surge center) that induce sexual receptivity, mating posture, phonation and increased physical activity= very high levels of estrogen creates a strong positive feedback on the hypothalamic pituitary axis during estrus leading to a massive release of GnRH and surge of LH inducing ovulation
LH stimulates histamine, proteolytic enzymes, and prostaglandins, causing follicular swelling, pressure increase, and rupture releasing the oocyte= spontaneous ovulation
follicular wall collapse bleeding occurs then lutenization begins producing progesterone
lack of estrogen terminates estrous behavior
induced ovulation= (queens, rabbits, camels) vaginal mechanoreceptors in the wall of the vagina need to be stimulated by physical copulation with the male and once recptors are stimulated impulses sent to hypothalamus for GnRH and LH surge
luteinization
folliular granulosa and theca cells transform into luteal cells forming corpus luteum producing progesterone
LH is essential for CL development and is needed to keep the luteal phase viable
high progesterone levels suppress the surge center in the hypothalamus , reducing LH pulses, preventing further ovulation
progesterone main targets: uterus, mammary glands (prepares for pregnancy)
luteolysis
process whereby the corpus luteum undergoes regression and cell death
most species= induced physiologically by prostaglandin F2 alpha
cows, sows, mares= have active luteal destruction activated to end the cycle and start a new estrous cycle
end of diestrus= oxytocin initiates the PGF2a release from the ednometrium closer to diestrus the amplitude and frequency of PGF2a increases and inhibits progesterone synthesis and opens calcium channels leading to apoptosis
declining progeserone activates the HPaxis starting new cycle
pregnancy
to maintain pregnancy the corpus luteum must be sustained for pregnancy to continue meaning progesterone is crucial
in some species placenta takes over progesterone production in later stages of pregnancy
the embryo must prevent the release of endometrial PGF2alpha to avoid luteolysis
PGF2a triggers luteolysis which leads to CL degeneration and pregnancy loss
site of spermatogenesis, testis functions what plexus supplies the testies
seminiferous tubules (sperm production)→ straight→rete→efferent ductus→ epididymus head→ body→ tail → ductus deferenes
functions: gametogenic and testosterone production
pampiniform plexus: for temperature regulation and counter current exchange of testosterone (forms around the testicular artery)
epididymis is the site of what two things
fluid absorption and sperm maturation (final steps)
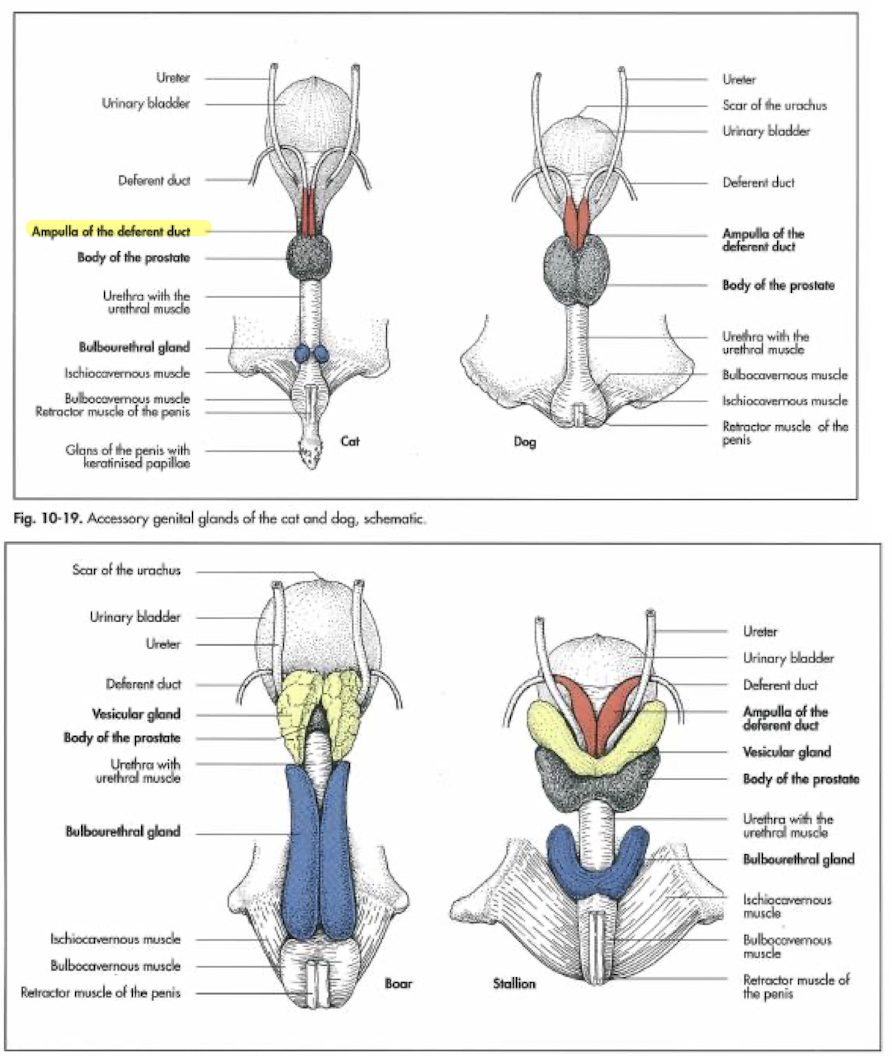
accessory sex organs
ampulla of the ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands; provide: optimal environment and nourishment for the spermatozoa
male hormone crucial nuclei in the brain
hormone production cycle is fully functional after puberty (reproductive competence)
fetal testosterone abolishes the males fetus’s surge center and males only remain with the tonic center
male fetus testosterone freely enters the brain it is transformed in estradiol which minimizes the function of the surge center
tonic center produces: GnRH
after puberty the hypothalamus starts to release GnRH in a pulsatile fashion every few hours which then induces pulse of LH and FSH release from the anterior pituitary gland →circulation (FSH has longer ½ life)
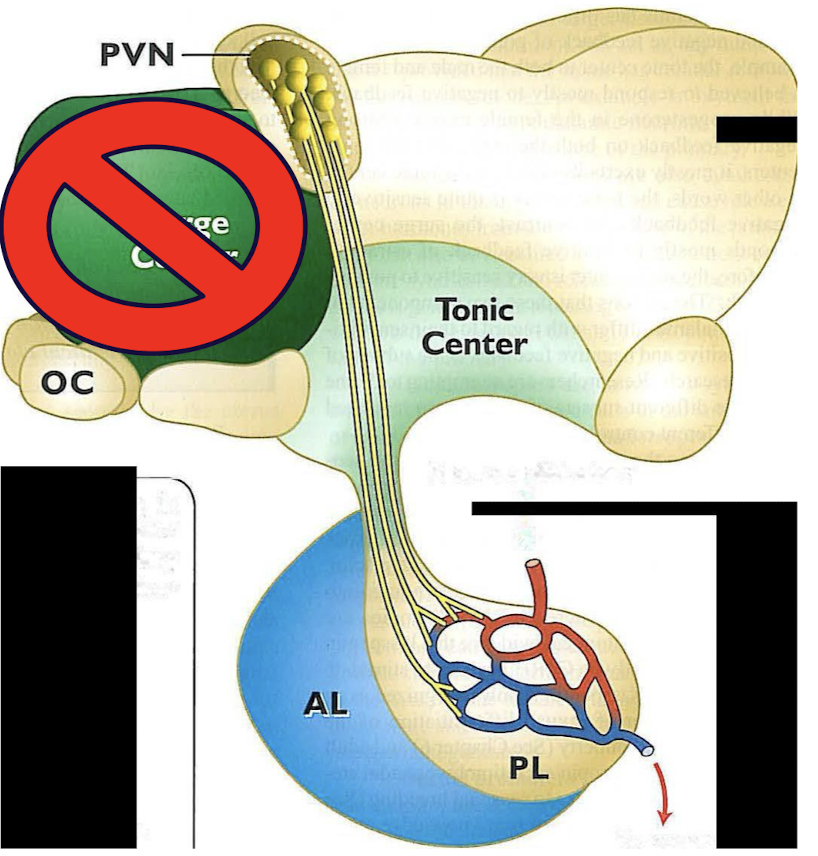
male hormones with testosterone and spermatogenesis production
testosterone: LH stimulates Leydig cells which produce testosterone
sperm: FSH stimulates the steroli cells which are responsible for spermatogenesis
*testosterone from leydig cells diffuse into the steroli cells where its converted into dihydrotestosterone and estradiol which is essential for spermatogenesis production
testosterone also released into circulation for metabolism and behavior and suppresses further release of GnRH
**FSH produces spermatogenic substances (androgen binding protein) maintains higher tubular testosterone concentration despite pulsatile release and INHIBIN (selectively inhibits FSH release)
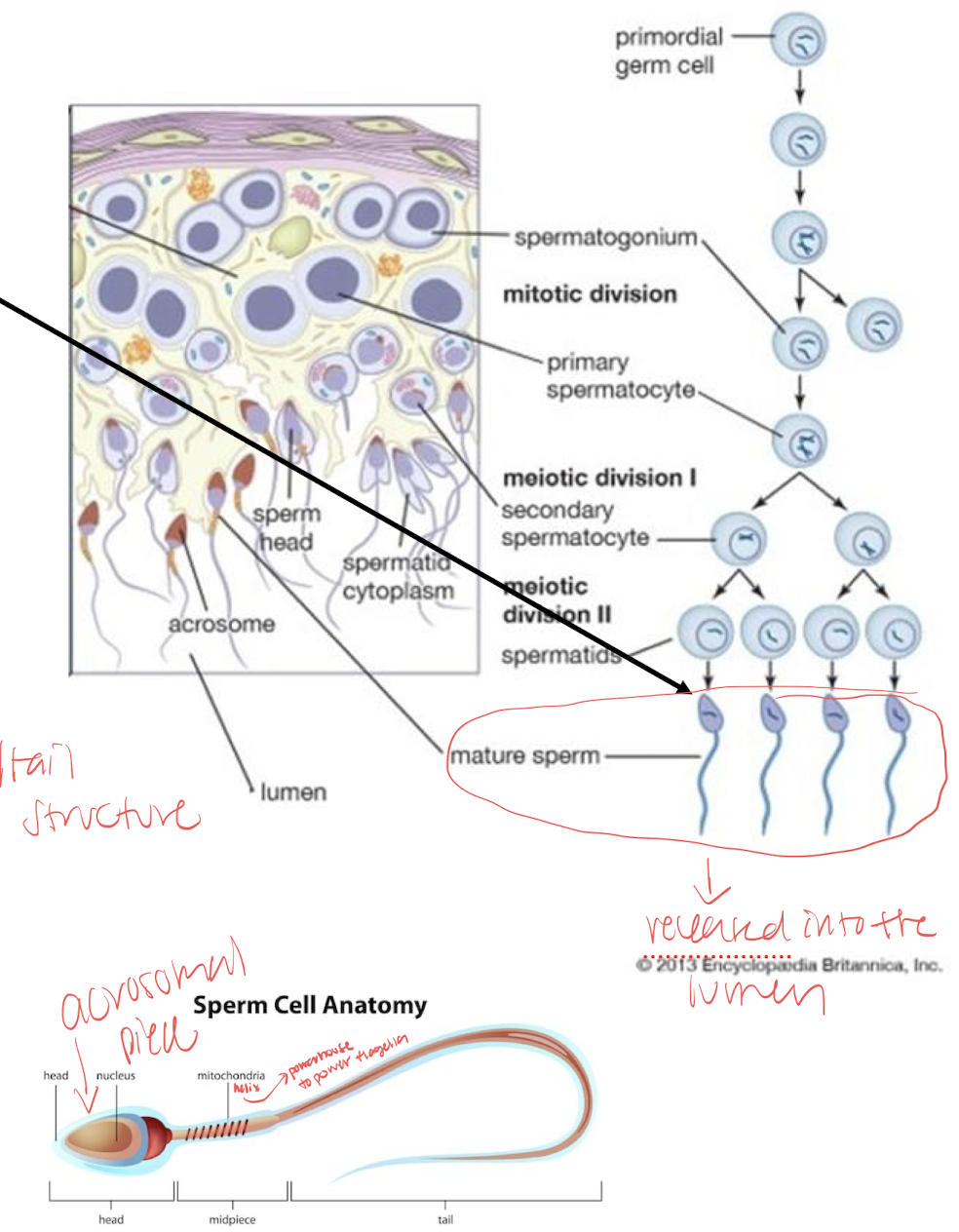
spermatogenesis
within the seminiferous tubules
requires 40-60 days for spermatogenesis; most immature are at the periphery of a seminiferous tubule near the basement membrane
divided into three phases mitosis, meiosis, differentiation
mitosis: proliferation phase; contains all mitotic divisions A-spermatogonia→B-spermatogonia→primary spermatocyte *stem cell renewal is important part here allows some sperm to revert to stem cells providing continual renewal which new spermatogonia can develop (loss of intercellular bridges)
meiosis: meiosis 1 ensures DNA diversity and crossing over, primary spermatocytes → secondary spermatocytes; meiotic phase produces haploid spermatids forming the secondary spermatocyte secondary spermatocytes→ spermatids
differentiation: evolvement stage (no more cell division) commonly called spermiogenesis: golgi phase, cap phase, acrosomal phase, maturation phase→ turns into fully differentiated spermatozoon containing head and flagellum including mid-piece(mitochondrial helix) and principle piece (tail)
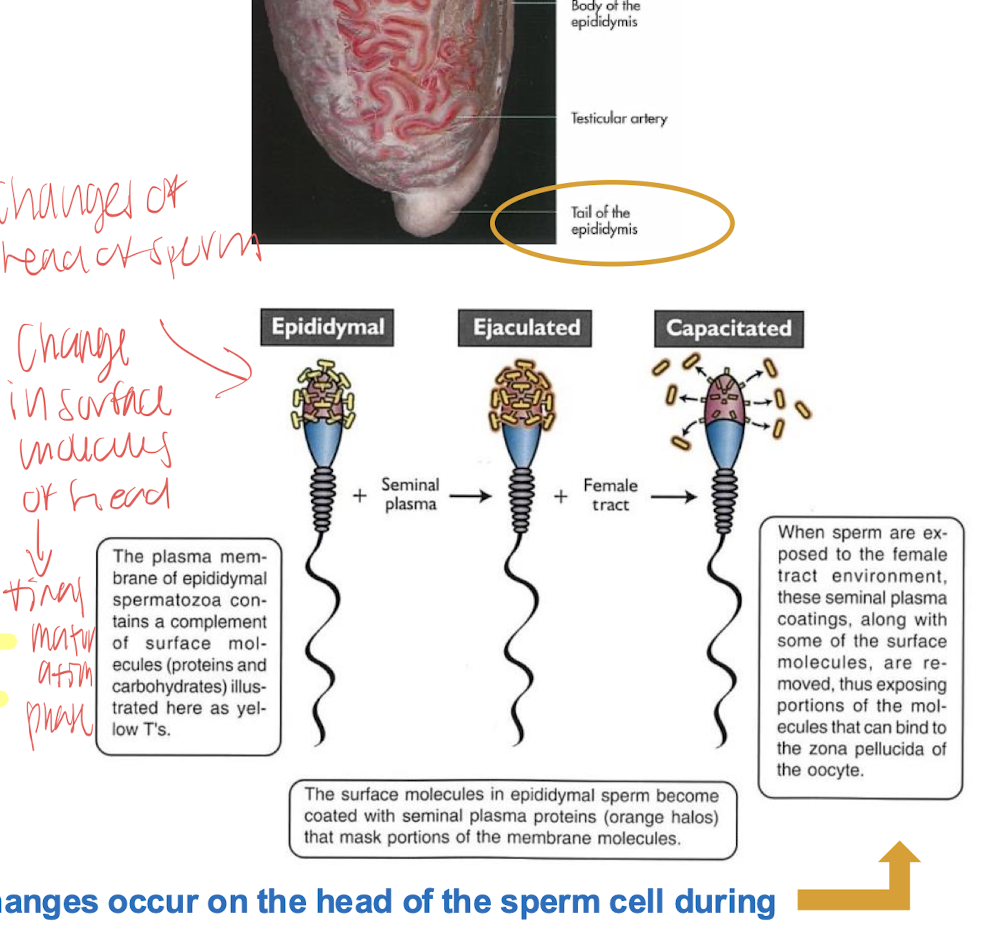
capacitation
in tail of epididymus, sperm require certain degree of maturity but in order to acquire maximum fertility the spermatozoa must spend time in the female reproductive tract
final functional enhancement of the flagellar activity (hyper activation) and acrosome reaction
capacitation is completed in the isthmus of the oviduct
all sperm are not capacitate at the same time
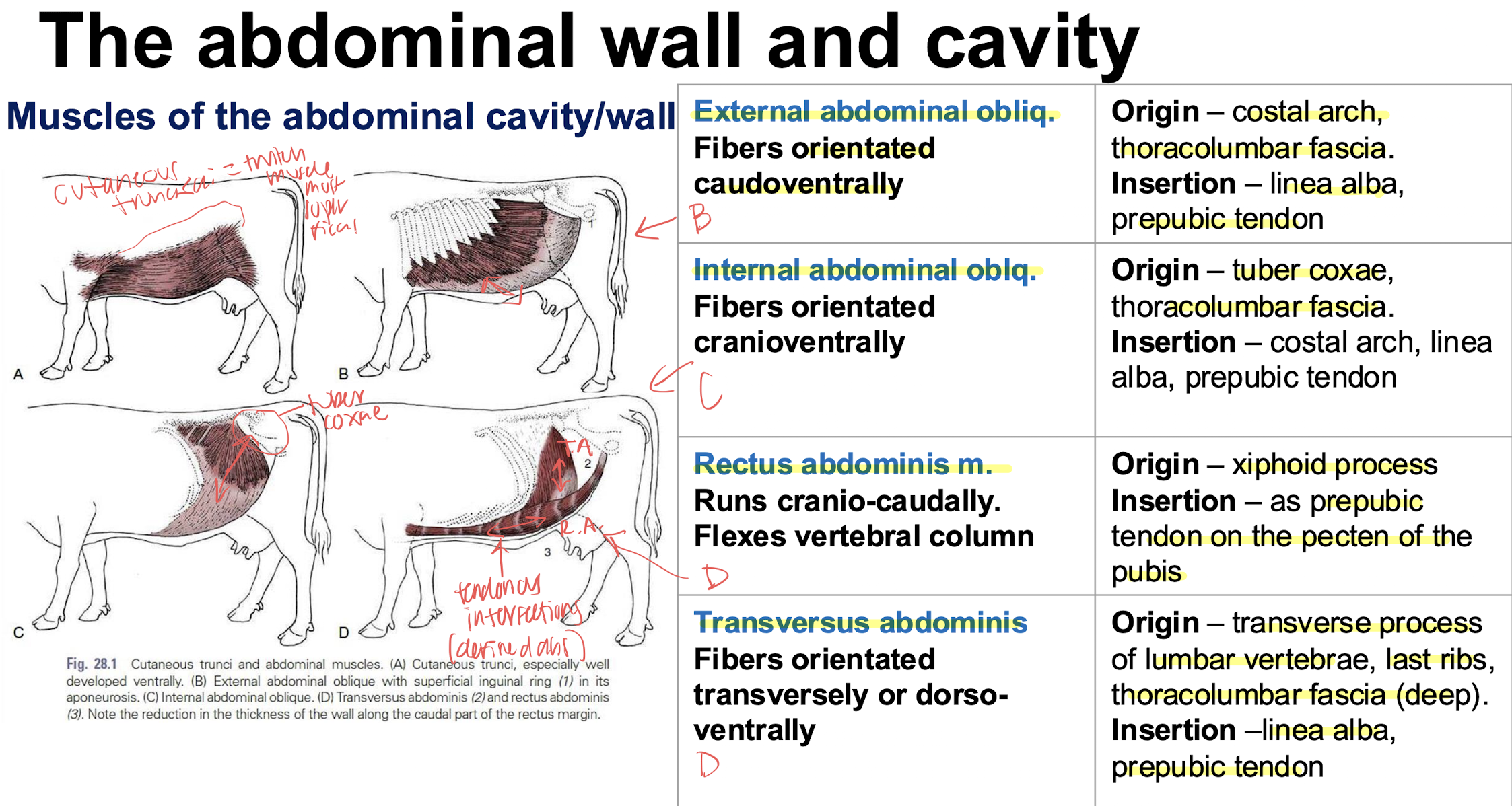
structures of the abdominal cavity/wall superficial to deep
skin→ subcutaneous connective tissue→ cutaneous trunci muscles→ external abdominal m→ internal abdominal m→rectus abdominis m→ transversalis facia→ parietal peritoneum
internal vs external rectus sheaths what muscles make them up
internal- transverse muscle (forms internal lamina of sheath of rectus abdominis)
external-external and internal abdominal oblique muscles forms external lamina of the sheath of the rectus abdominis
abdominal wall nerve supply
T13- costo-abdominal n
L1- cranial lliohypogastric n
L2- caudual lliohypogastric n
L3-llioinguinal n
L4-lateral cutaneous femoral n
farquharson method vs magda method of nerve blocks vs inverted L block
farquharson= proximal paravertebral nerve block
magda= distal paravertebral nerve black
inverted L= for obese or aggressive cows
boundaries of the pelvic cavity
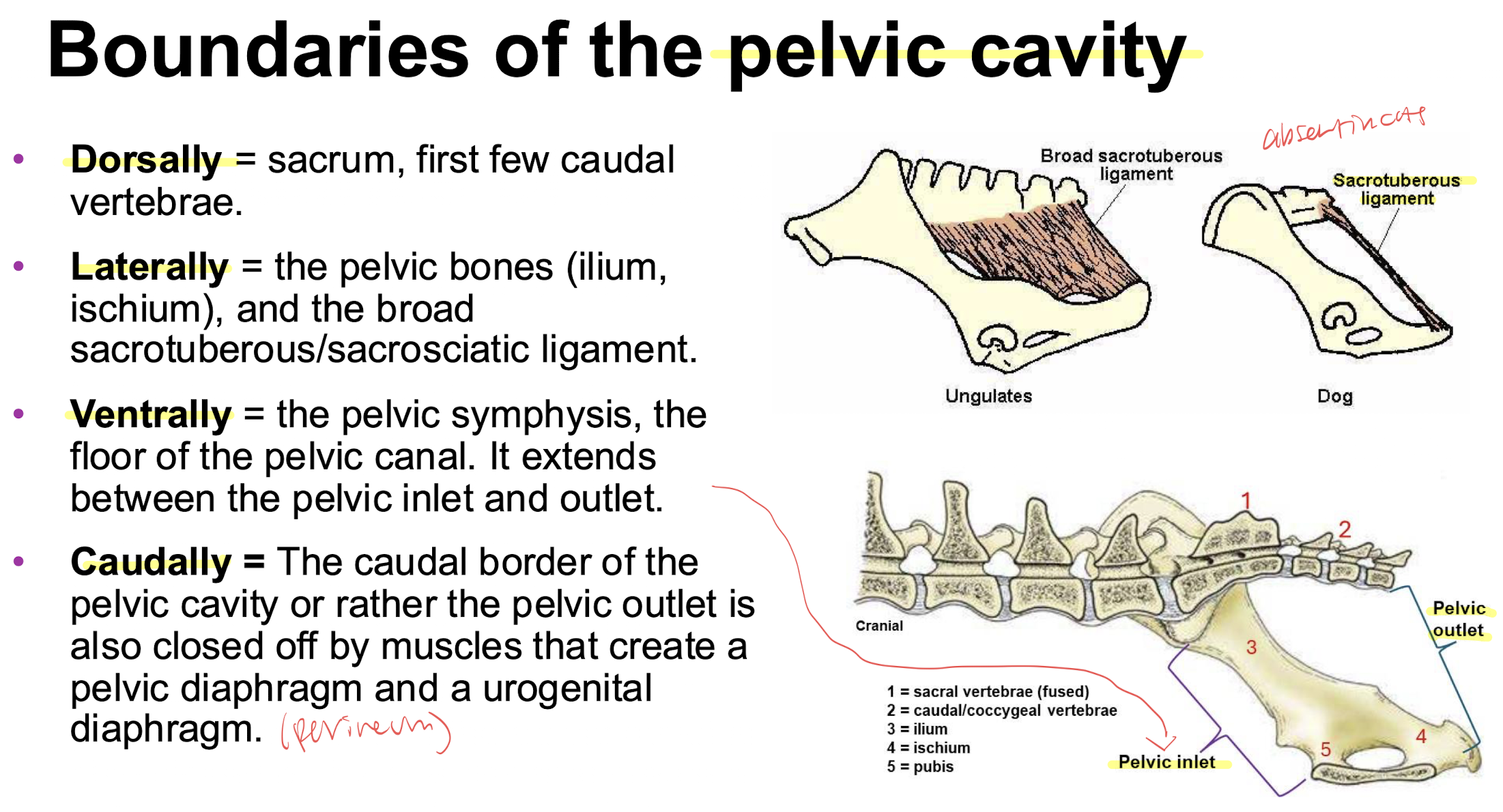
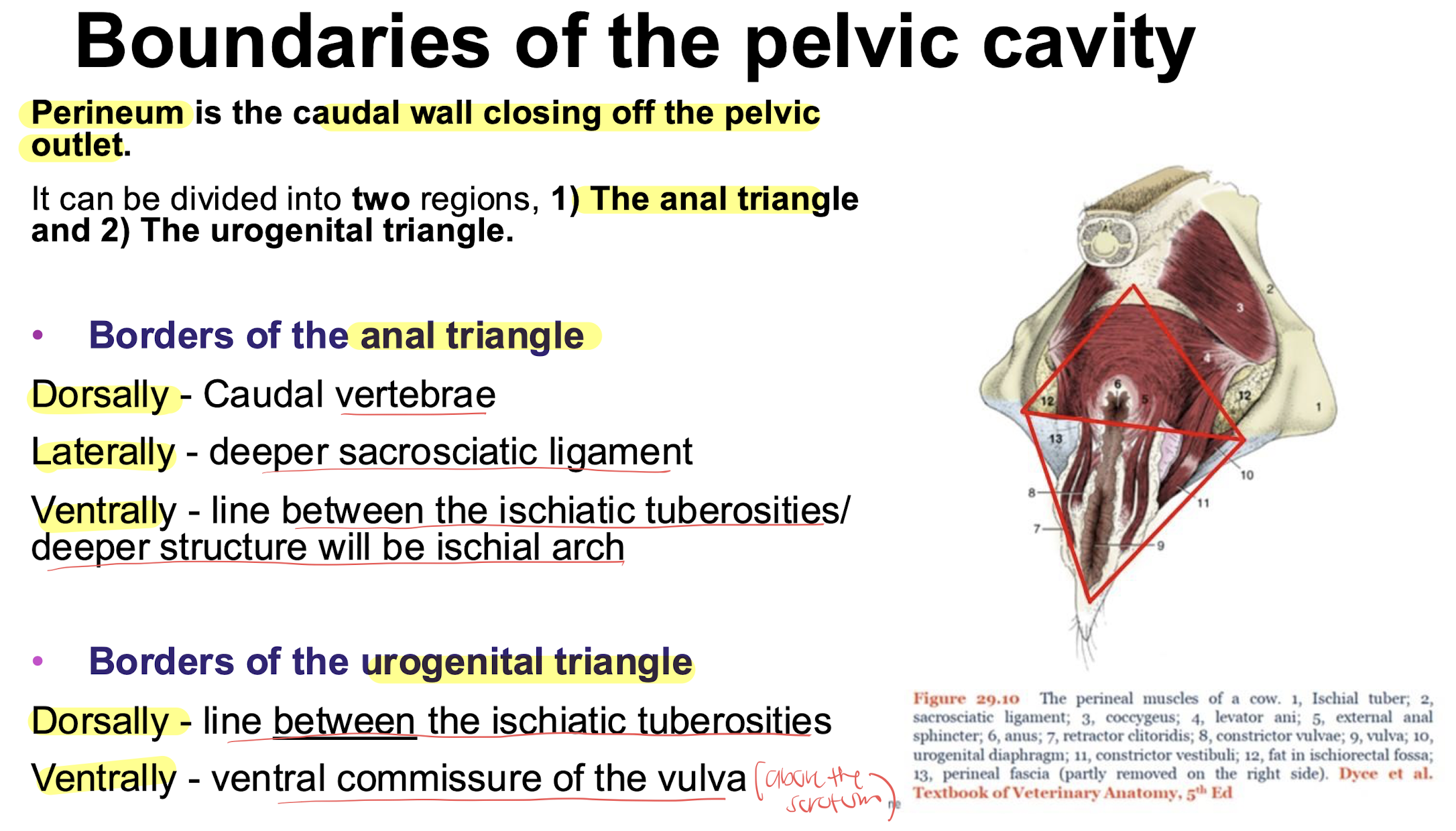
borders of the anal triangle and urogenital triangle
Pelvic diaphragm is composed of what muscles
coccygeus muscle
levator ani muscle
external and internal fascia
some consider the external anal sphincter m
urogenital diaphragm closed off by these muscles
retractor clitoridis muscles
constrictor vulvae muscles
constrictor vestibuli muscles
compartments of the pelvic cavity
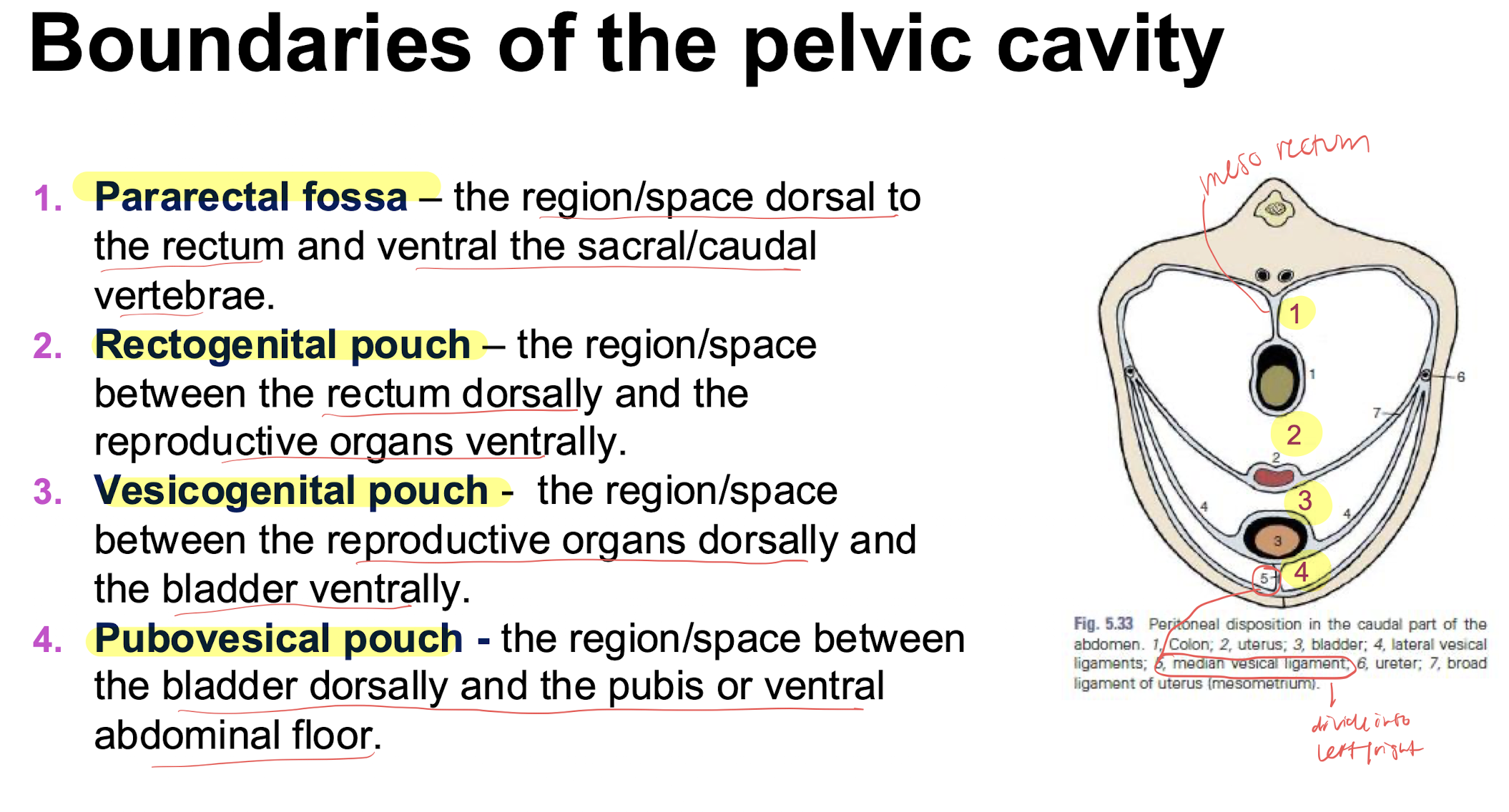
renal recesses vs renal sinus
recesses= depressions in the renal pelvis
sinus= fat filled space surrounding the renal vessels and ureters
ultrasound of the kidneys echogenictiy
renal cortex: hypoechoic or isoechoic
renal medulla: hypoechoic or anechoic
renal pelvis: hyperechoic bc of the fat/fibrous tissue
species variations kidneys
dog- fused both cortex and medulla
bovine- unfused both cortex and medulla, 18-20 lobes, NO crest or pelvis right kidney= flattened and oval left kidney= slightly twisted displaced to the right by rumen; contains renal calices (major (2) and minor(lobe #))
porcine= no external lobation bc cortex fused but internal lobation present; kidneys at same level T-13-L4; no contact with liver; calyces present (10 minor and two major); cranial of both associated with pancreas (left/body)
goats/sheep= similar to canine species fused cortex/medulla, bean shaped (color slightly lighter than canine)
equine= right kidney: T16-L1 touches liver heart shaped; left: T17-L2 figure of 6; has a unipyramidal (fused pyramids with a common renal crest); renal pelvis is expanded with two polar terminal recesses with papillary ducts that open into the terminal recesses
internal kidney supply
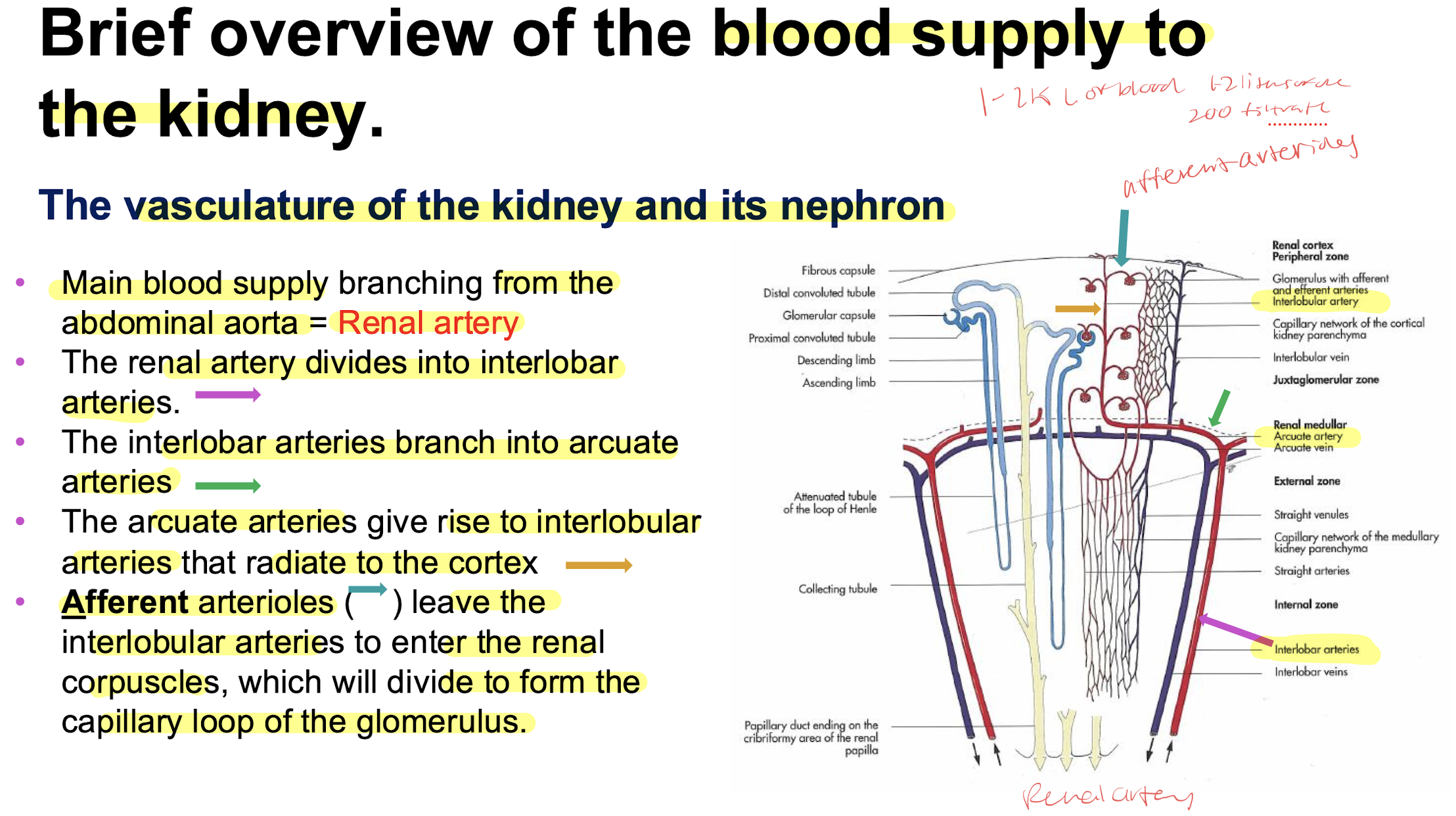
afferent into glomerulus then out via efferent then into peritubular capillaries
pars convoluta vs pars radiata
convoluta= proximal and distal convoluted tubules
radiata= collecting ducts (part of cortex part in medulla)
cortical nephron vs juxtamedullary nephron
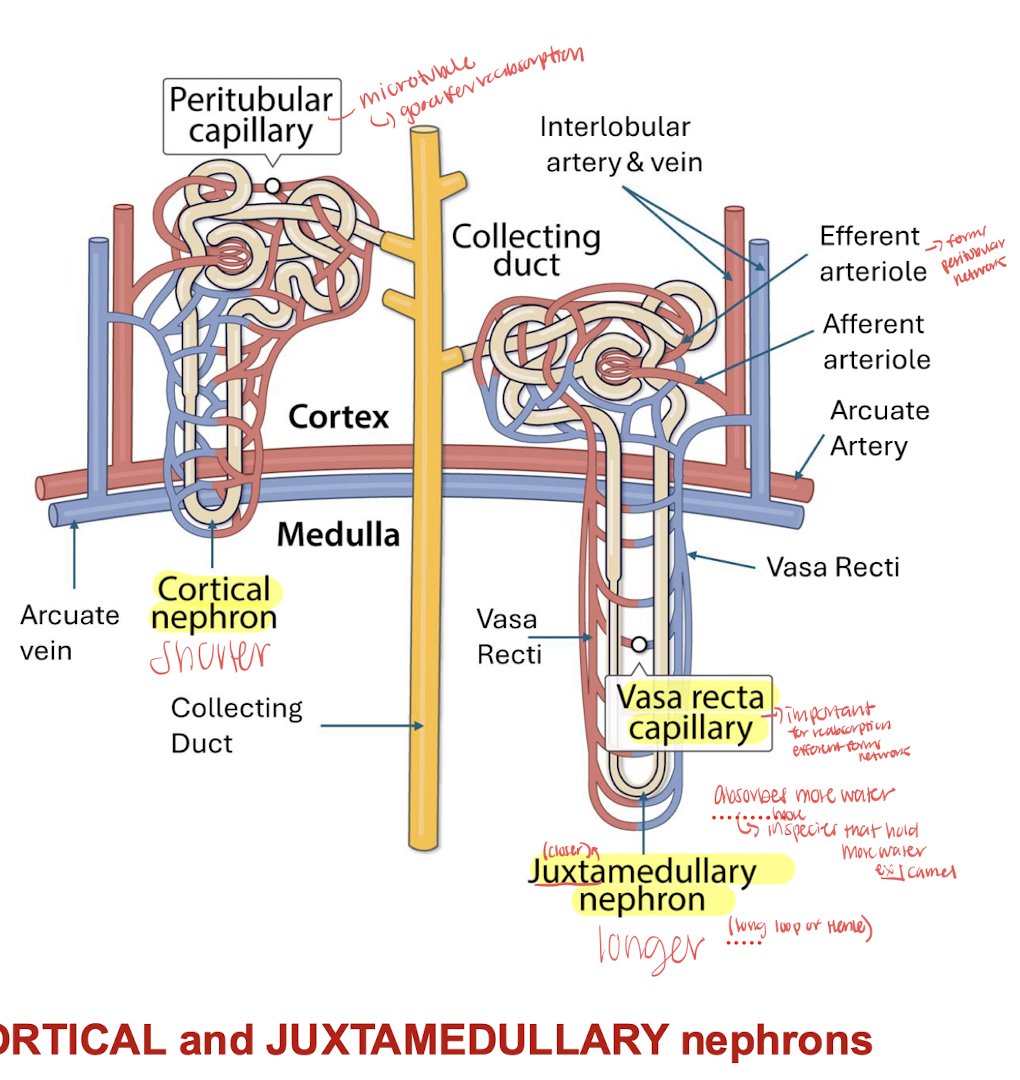
Juxtaglomerular apparatus= distal tubule is connected to afferent arteriole with macula densa cells within the distal tubule and sensitive to chloride ions to help regulate the filtration rate
Juxtaglomerular cells are in the afferent arteriole which produce RENIN
juxtaglomerular nephrons are known to conserve more water (camels have more of this type of nephron
capillary network within the glomerulus: what are the three barriers for filtrate
100 liters of blood are circulated through the kidney producing 1 liter f urine
the three barriers:
porous capillaries
basement membrane
podocytes= cells surround glomerular fenestrated capillaries forms the visceral layer of the bowman’s space, controls amount of filtrate produced primary and secondary processes (form filtration slits)
the nephron tubule micro anatomy
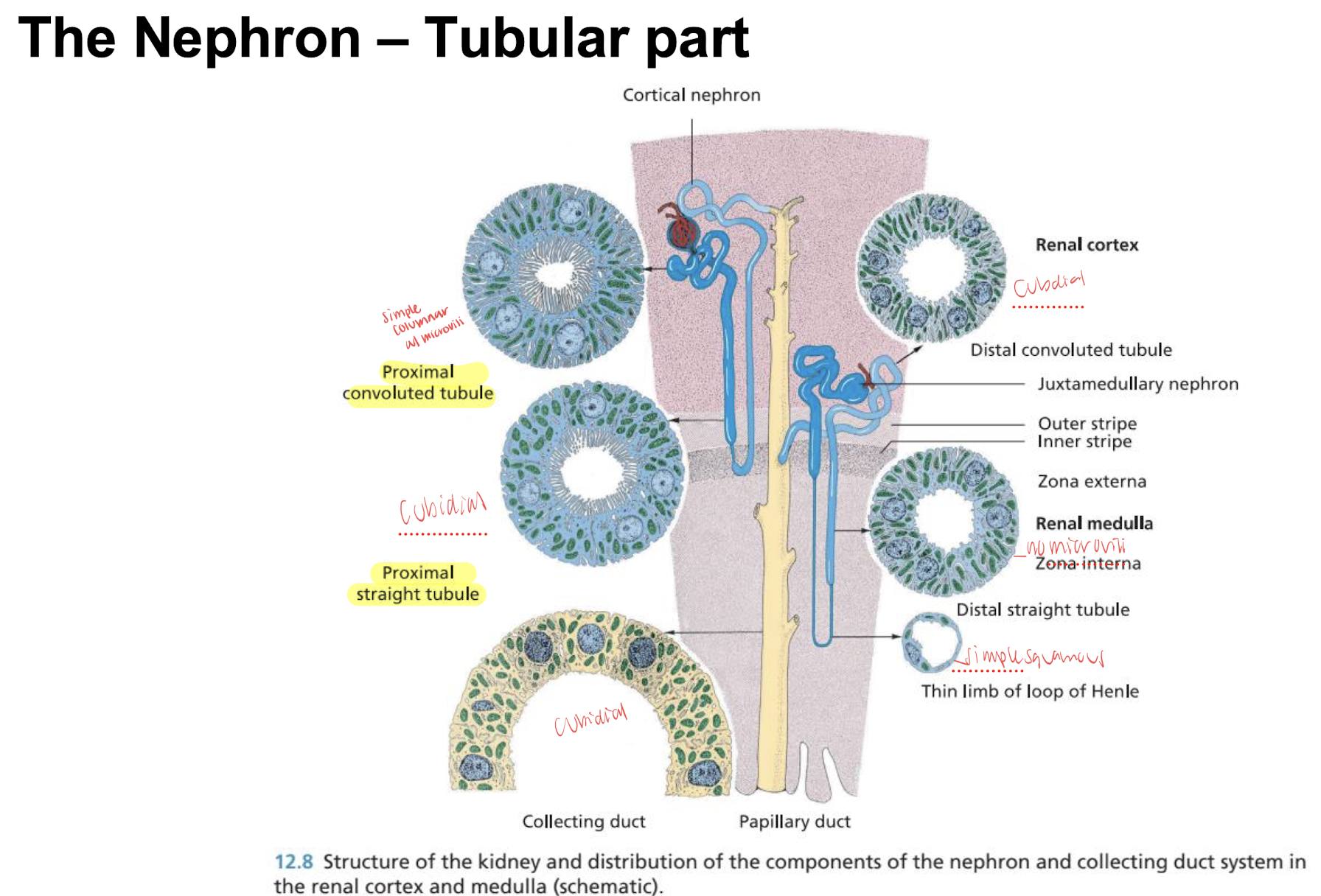
proximal: simple columnar with microvilli (for reabsorption)
henle: simple squamous epithelium nuclei flattened and nuclei protrude into lumen
distal: simple cuboidal epithelium lumen in larger with no brush border
papillary duct: epithelium two layered and later transitional epithelium
renal calices and pelvis: lined by transitional epithelium and undergoes loose connective tissue layer (in horse the mucous glands are present under the epithelium responsible for the mucous in the equine urine)
toxins and hypoxia affects which parts of the kidneys
cortex= toxins reach this more bc more perfusion
medulla=hypoxia bc its main job is to maintain hyperosmolarity
renal circulation-pressures
glomerulus is high pressure while peritubular capillaries is low pressure to promote reabsorption
1-2% of total renal blood flow is flowing through the vasa recta and promotes reabsorption
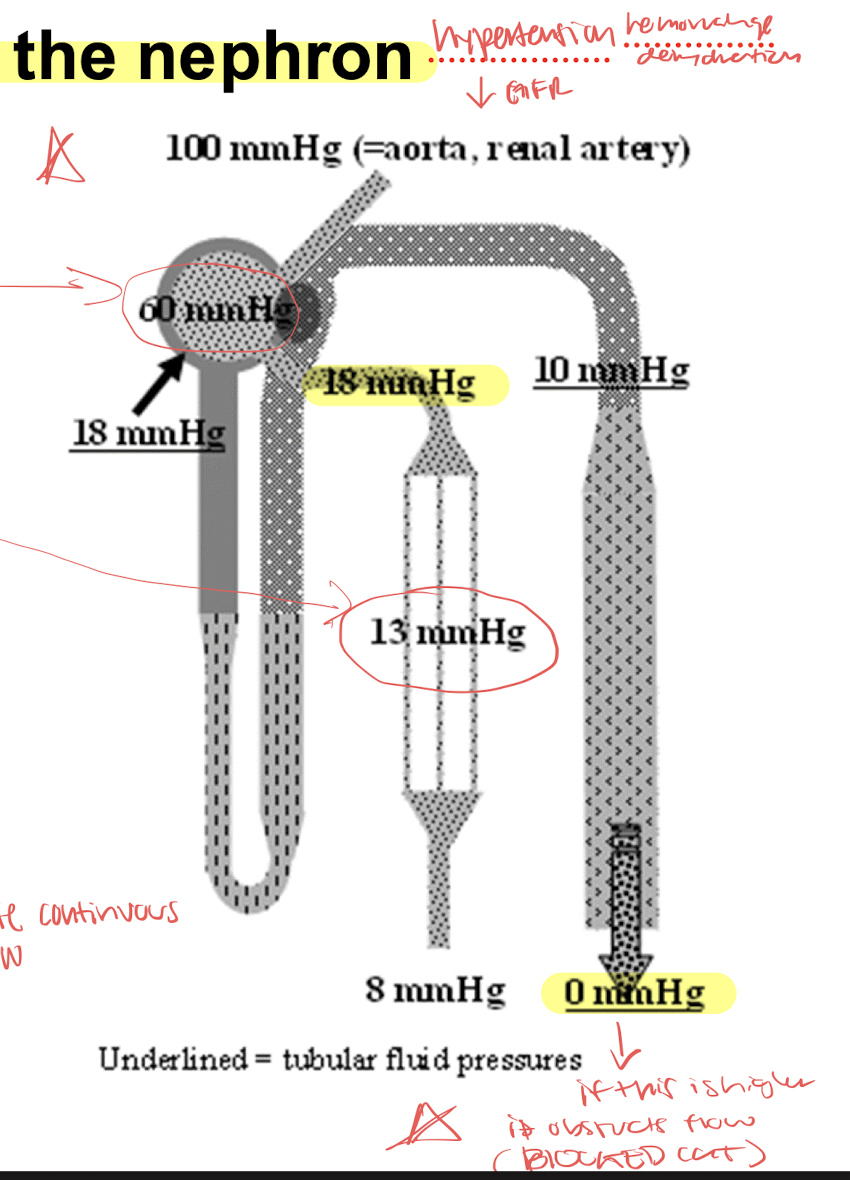
PROMOTES CONTINUOUS FLOW
glomerular filtration offers filtration to what and happens during dz?
glomerular basement membrane offers high permeability for the filtration of water and small solutes
molecular weight= <5,200; almost impermeable to plasma proteins
molecular charge= glom pores lined with negative charges and reject neagtively charged molecules like proteins (even of a smaller diameter of the pore)
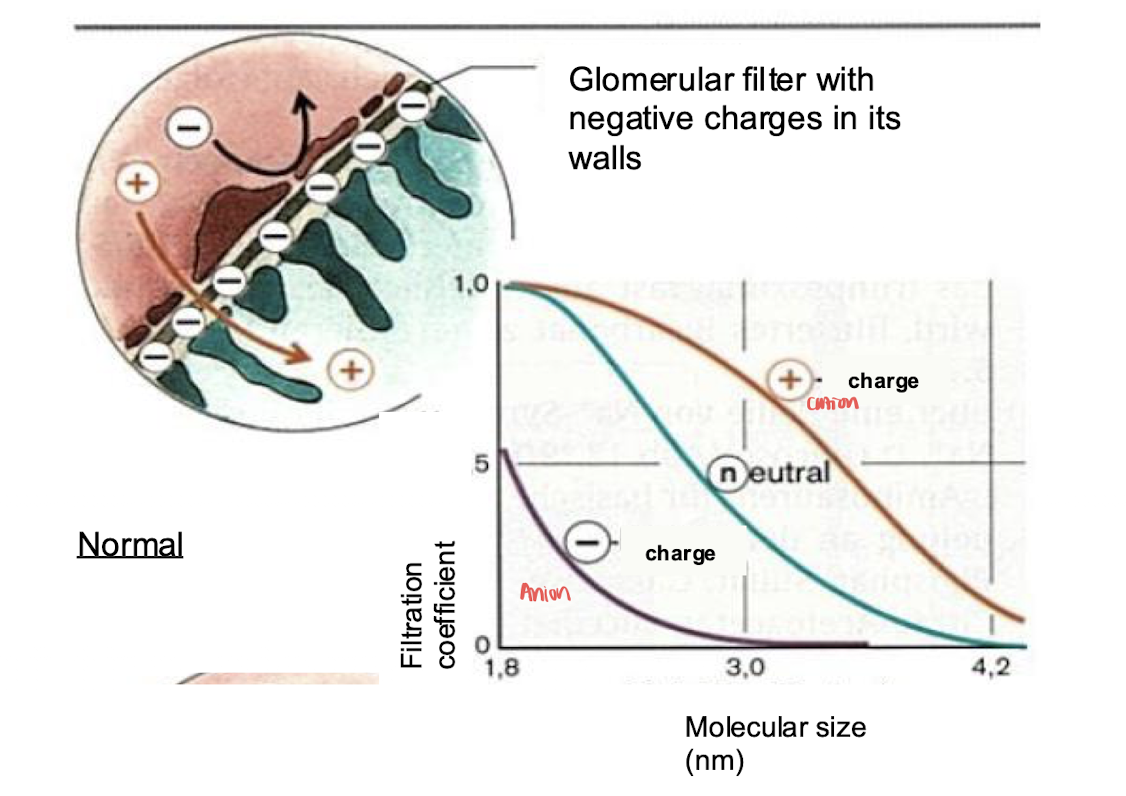
In glomerulonephritis the negative charges are neutralized and allows negative macromolecules like albumin to increase resulting in proteins in the urine= proteinuria
filtrate = ?; and what is the glomerular filtration rate
plasma without proteins bc the glomerulus filters everything except over 5.2weight and negative charged molecules
glomerular filtration rate= volume of filtrate into bowman’s capsules by both the kidneys each minute
slow speed= increased absorption of waste products
fast speed= reabsorption decreases and miss valuable substances are lost
filtration speed depends on glomerular filtration rate which si controlled by increasing and decreasing resistance of the afferent and efferent arteriole blood flow
pressures altering flow of glomerular filtration
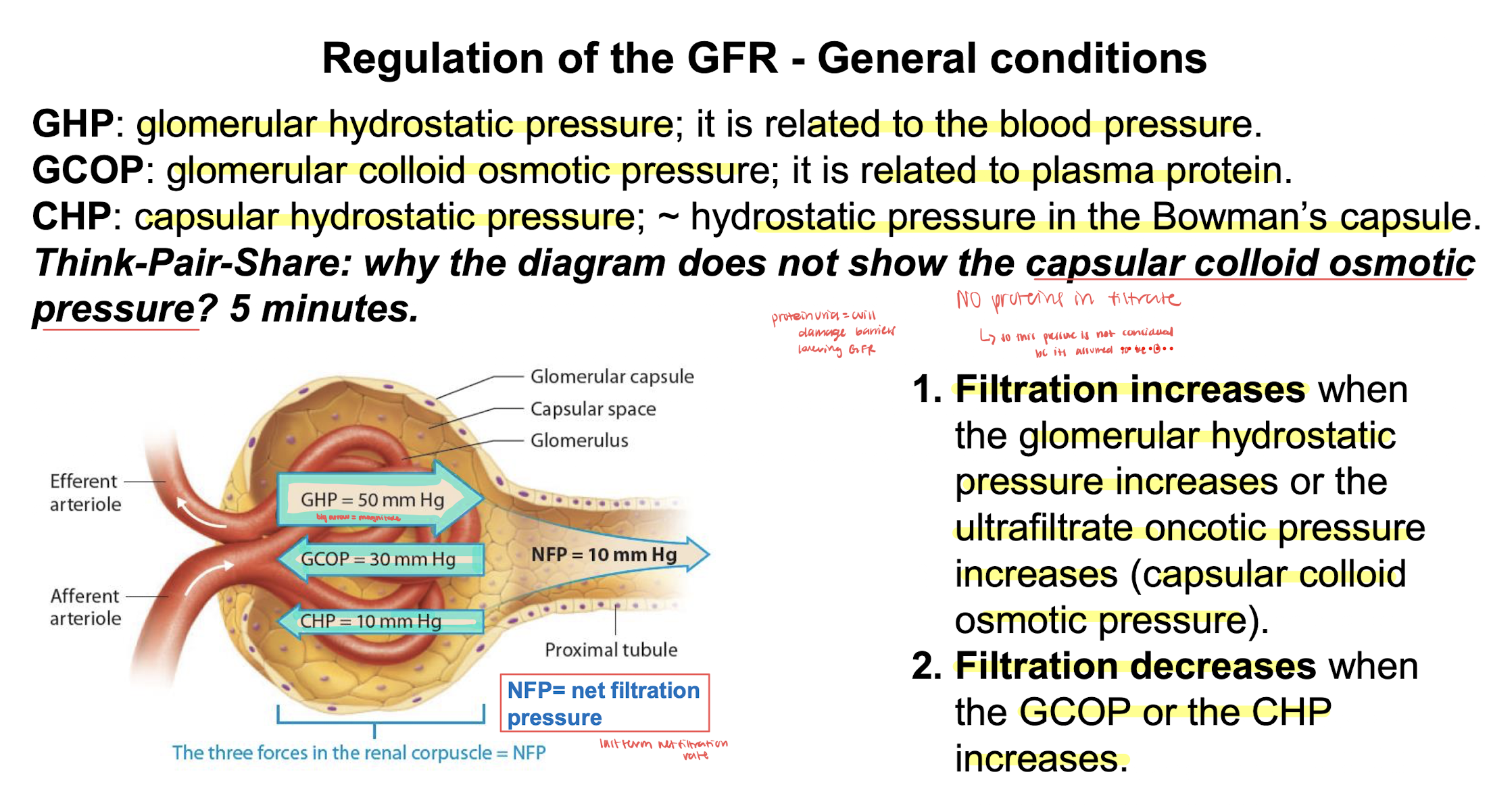
angiotensin 2 regulates the vasocontriction of the efferent arteriole
severe vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole has paradoxical effect decreases flow GCOP counters the increased GHP which decreases GFR
afferent vasoconstrict= low pressure and filtration
afferent vasodilate=high pressure and filtration
how does NSAIDS, tying up in horses, and lower urinary tract obstruction affect GFR?
NSAID= decrease GFR because it causes severe vasocontriction in efferent arteriole
tying up= decrease GFR myoglobin released from muscles into the urine cause tubular obstruction and reduced filtration efficiency (earthquake survivors)
obstruction= decrease GFR causes pressure changes lowering GFR backward pressure cascade
pressure diuresis
GFR is almost but not perfectly constant so an increase in blood pressure will increase GFR resulting in higher urine output
autoregulation
autoregulation maintains the GFR within a 5% deviation any more too high or too low causes wither excess waste absorption or excess excretion of valuable solutes
myogenic reflex: baroreceptors in the arterioles cause an auto regulation stretch=vasoconstrict no stretch= vasodilation in order to maintain adequate pressures this system works for a specific range of pressures (80-189 mmhg) if out of these ranges then myogenic reflex is limited
tubulogomerular feedback=
GFR low→ afferent arteriole vasodilates and efferent vasocontricts (more NaCl are reabsorbed and in the distal tubules the macula densa cells detect that NaCl is too low in the filtrate and responds by DILATION of the AFFERENT arteriole with NITRIC OXIDE; in the EFFERENT arteriole that angiotensin 2 (formed from the release of renin from the JG cells) is used to constrict the efferent arterioles
GFR high→ leads to an increase in NaCl delivery to Macula densa cells so macula release ADENOSINE which diffuses through the interstitial fluid to the afferent arteriole causing vasoconstriction and also signal to REDUCE the release of renin causing efferent vasodilation
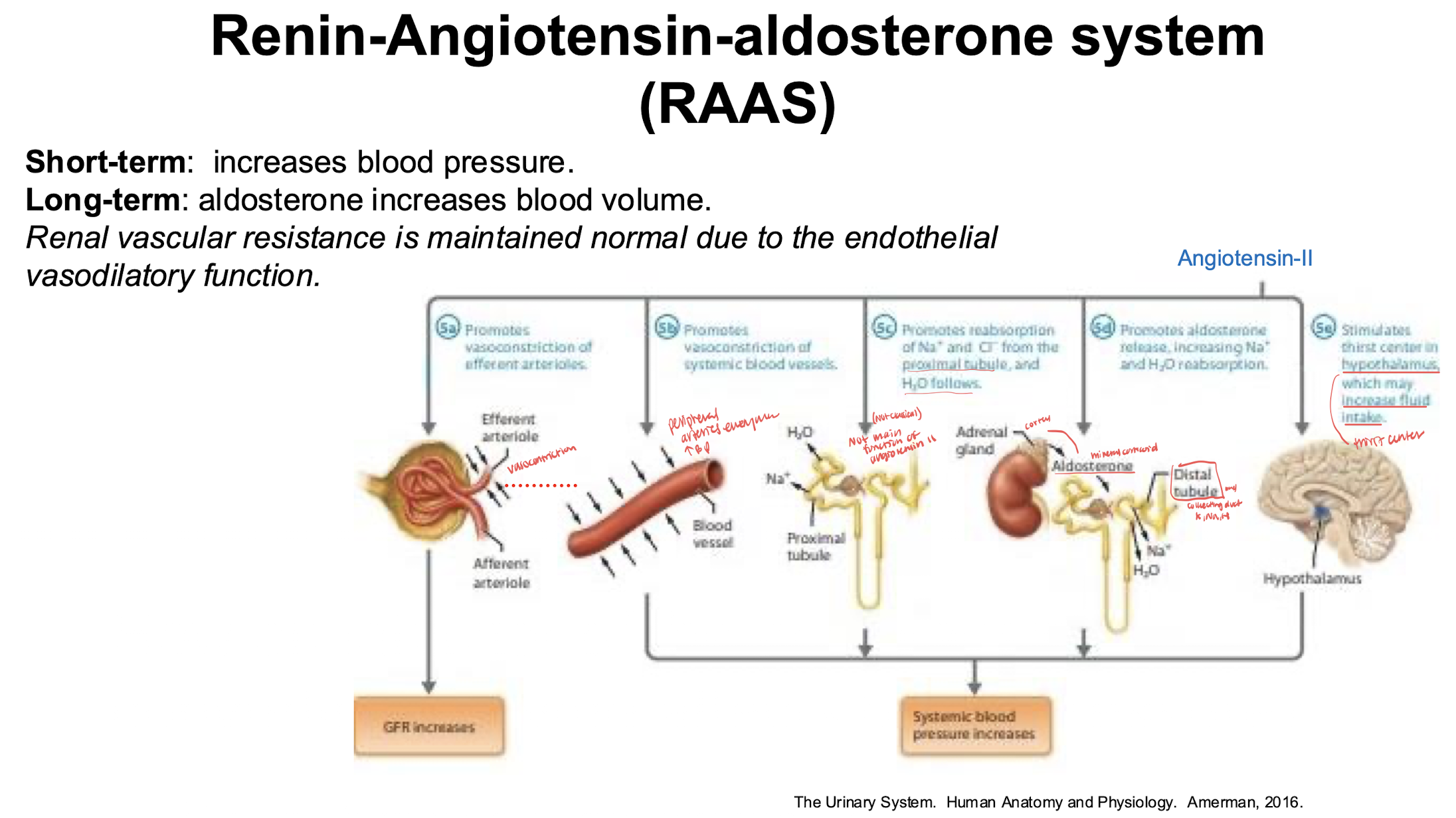
RAAS stumli and short/long term effects
short= increase blood pressure
long= aldosterone increases blood volume
stimuli= hypotension, hyponatremia, increase sympathetic activation, hyperkalemia
effects of angiotensin
reabsorption of substances in the proximal tubule
GLUCOSE= Na and glucose CO-transporter with the NaK+ATPase pump on basolateral border is SATURABLE facilitated diffusion into the peritubular capillary
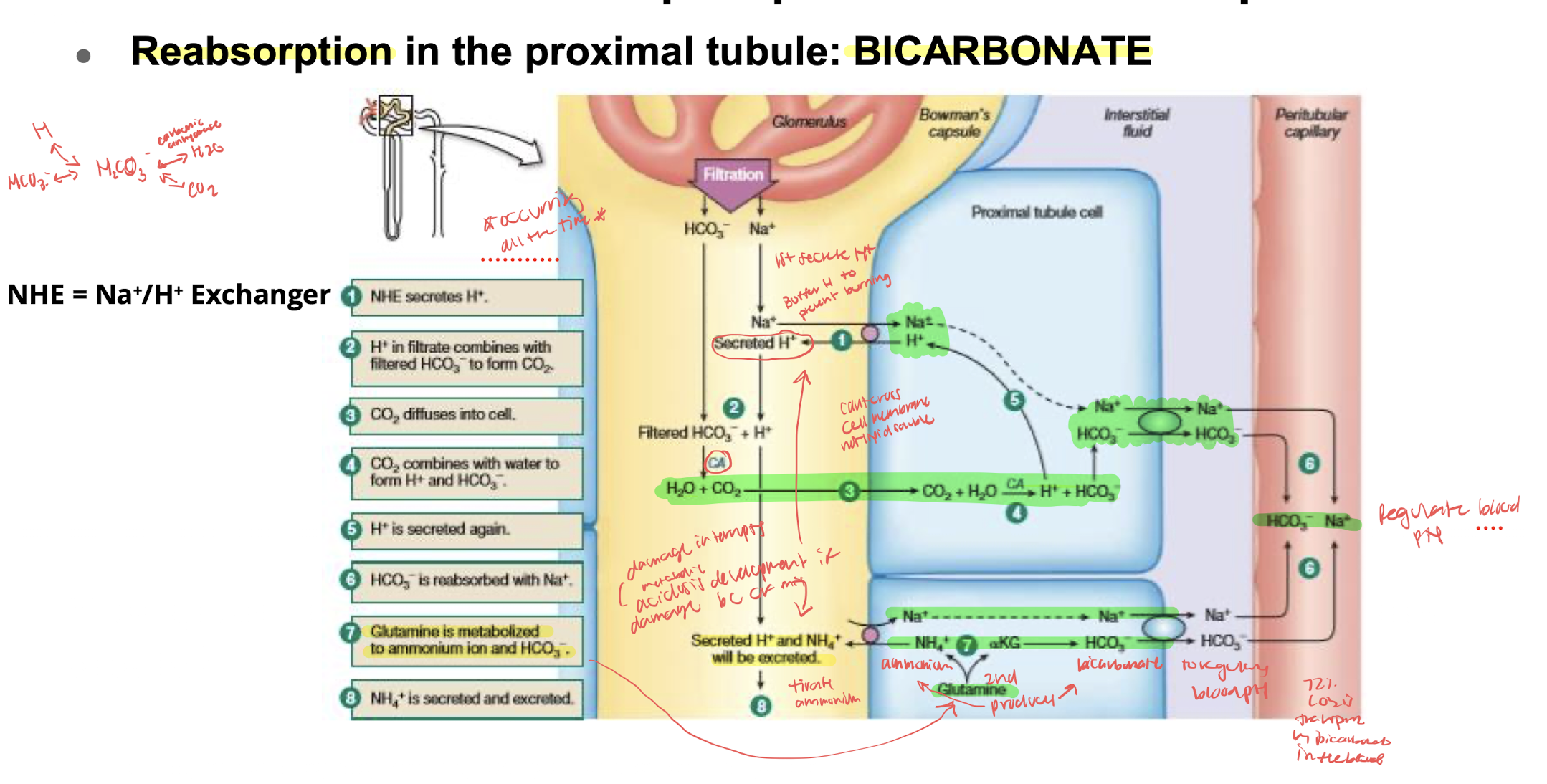
SODIUM and BICARBONATE:
CALCIUM/WATER: 2/3rds is absorbed in the proximal tubule; 90% being paracellular by solvent drag driven by the active transcellular reabsorption of sodium provides a driving force for the osmotic reabsorption of water; small amount is transcellular mediated by the voltage gated calcium channel sensitive to hormones (PTH)
PHOSPHATE: 80% of filtered phosphate is reabsorbed from prox. tubule but is exclusively transcellular process with 3 sodium coupled phosphate transporters mediate phosphate influx; apical phosphate entry is driven by the inward gradient for sodium maintained by the activity of the basolateral Na-K-ATPase→ PTH INHIBITS tubular phosphate reabsorption by decreasing the apical membrane expression of sodium-phosphate transporters
MAGNESIUM: is unusual because it is primarily reabsorbed along the thick ascending limb (50-70%) rather than proximal tubule which only reabsorbs 10-25% of the filtered load but plays an important role in fine tuning mg2+ homeostasis; paracellular mechanism that is likely to be largely unregulated