Lab 4: Heart Physiology
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1) c. Aortic SL valve
2) a. Pulmonary SL valve
3) b. Mitral AV valve
4) d. Tricuspid AV valve
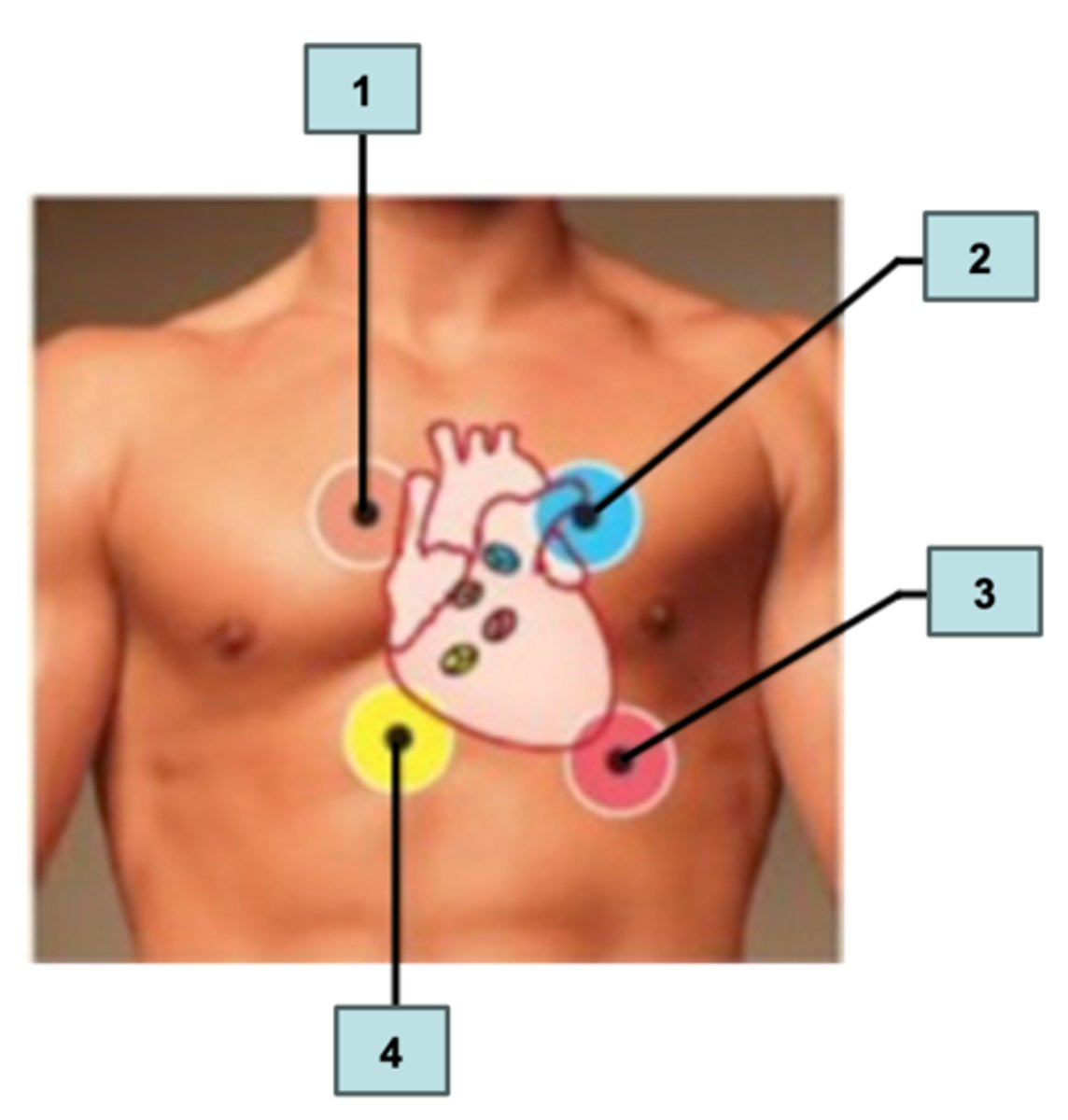
Label the four areas for auscultating heart sounds.
a. Pulmonary SL valve
b. Mitral AV valve
c. Aortic SL valve
d. Tricuspid AV valve
1) c. Tricuspid Valve
2) b. Aortic Valve
3) d. Pulmonary Valve
4) a. Mitral Valve
Select the choice that best describes proper placement of the stethoscope to listen to certain valves.
1) right sternal margin of the 5th intercostal space
2) right sternal margin of the 2nd intercostal space
3) left sternal margin of the 2nd intercostal space
4) in line with the middle of the clavicle of the 5th intercostal space
a. Mitral Valve
b. Aortic Valve
c. Tricuspid Valve
d. Pulmonary Valve
1) lubb
2) AV valves
3) apex
First heart sound S1: "_[1] " is caused by the rebound of blood on the closed _[2] & heard best at the _[3] area.
4) dubb
5) SL valves
6) aortic
Second heart sound S2: "_[4] " is caused by the rebound of blood on the closed _[5] & heard best at the _[6] area.
Ken-tuck-y; S1-S2-S3
S3 sounds like _____ or _____-_____-_____ sequence
Ten-nes-see; S4-S1-S2
S4 sounds like _____ or _____-_____-_____ sequence
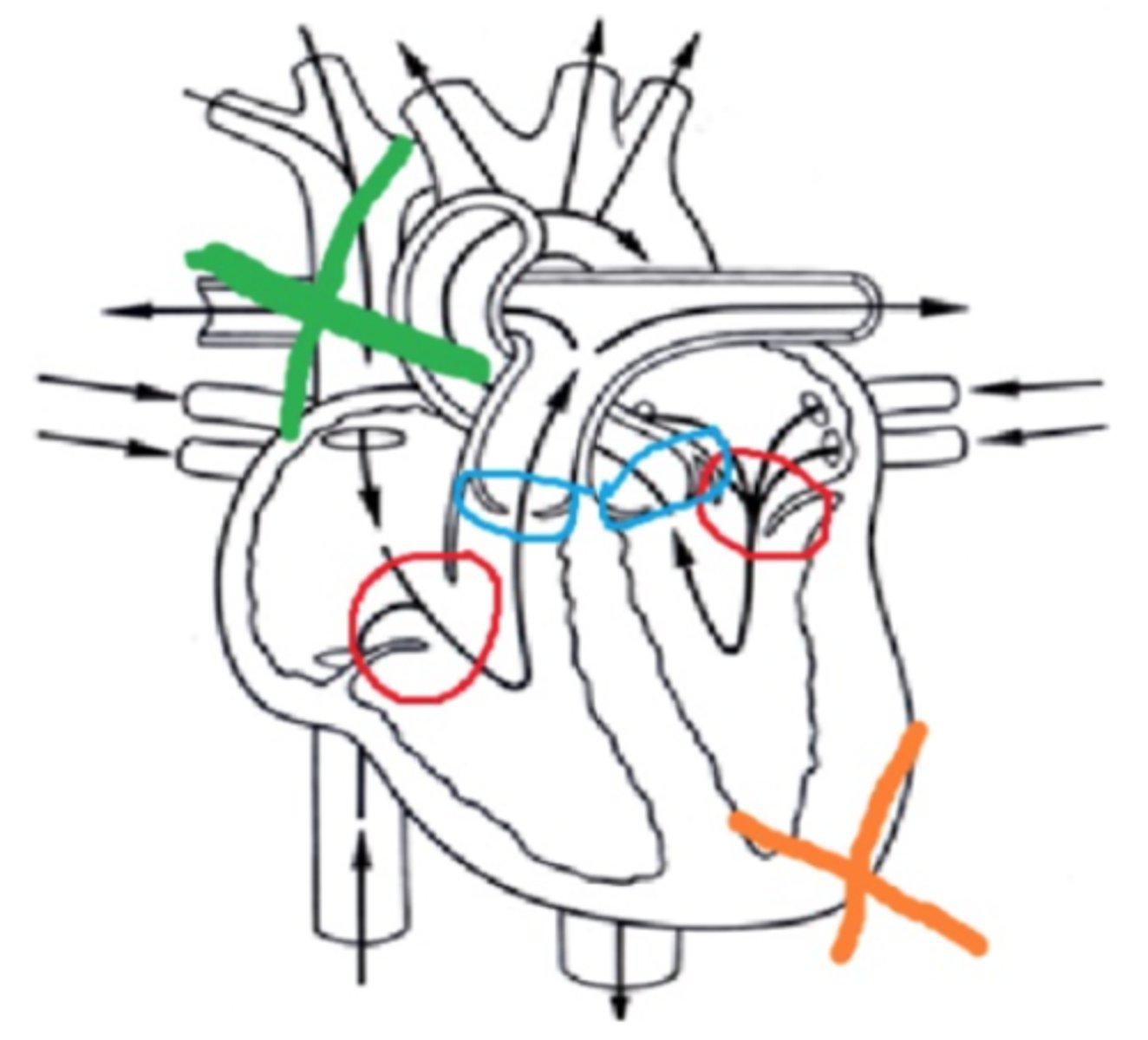
1) b. red circles
2) c. blue circles
3) d. orange X
4) a. green X
Match the coloring on the heart to the correct description:
1) S1 is produced when these valves shut
2) S2 is produced when these valves shut
3) S1 is heard best by placing the stethoscope here
4) S2 is heard best by placing the stethoscope here
a. green X
b. red circles
c. blue circles
d. orange X
murmur; valves
A heart _____ is any abnormal heart sound that is caused by turbulent blood flow
- mostly commonly caused by leaky _____
Pulse
_____: alternating surges of blood pressure in a major artery during heart contraction & relaxation
Bradycardia
_____: slow heart rate; below 60 beats/min
Tachycardia
_____: fast heart rate; above 100 beats/min
- 60-100
- 75
Normal heart rate:
- At rest: # - # bpm
- Average: # bpm
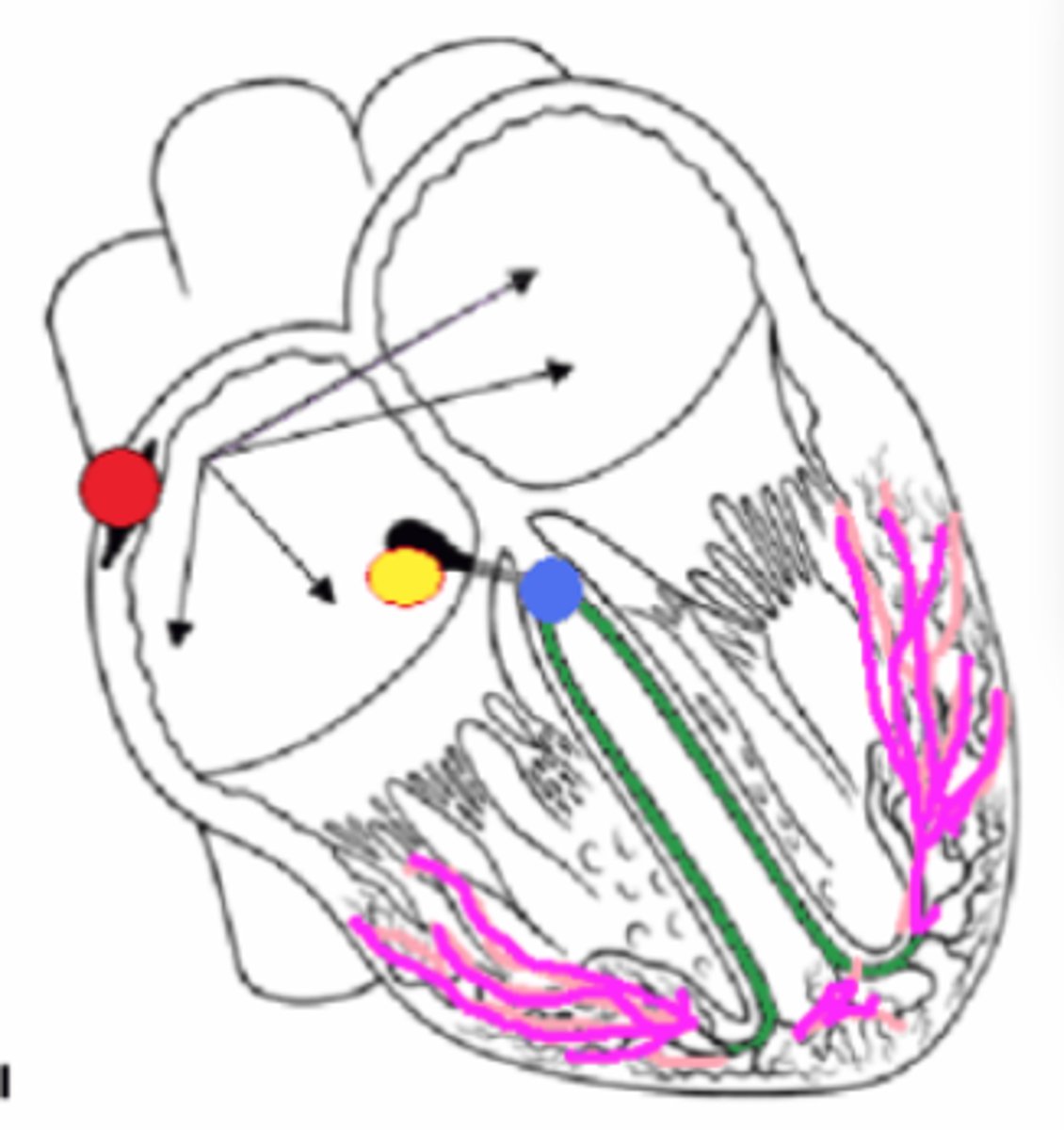
1) d. Green
2) c. Yellow
3) b. Red
4) f. Blue
5) a. Pink
6) b. Red
7) e. Black
8) c. Yellow
Match the conduction pathway structure. (two letters used twice)
1) Right and Left Bundle Branches
2) AV Node
3) SA Node
4) AV Bundle or Bundle of HIS
5) Purkinje Fibers or Myofibers
6) Pacemaker
7) Atrial Nodal Pathway
8) Impulse hesitates here 0.1 seconds
a. Pink
b. Red
c. Yellow
d. Green
e. Black arrows
f. Blue
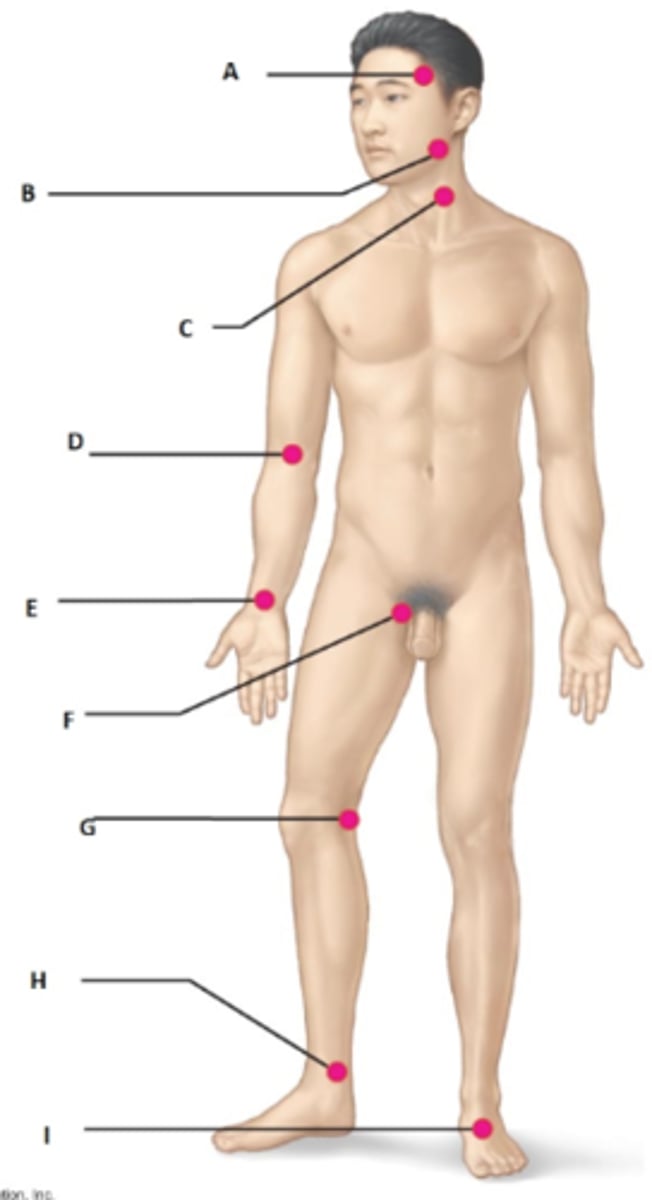
A) f. Superficial Temporal
B) d. Facial
C) h. Common carotid
D) b. Brachial
E) e. Radial
F) a. Femoral
G) i. Popliteal
H) g. Posterior tibial
I) c. Dorsalis pedis
Match the major sites for palpating pulse to the correct location. #A-I
a. Femoral
b. Brachial
c. Dorsalis pedis
d. Facial
e. Radial
f. Superficial Temporal
g. Posterior tibial
h. Common carotid
i. Popliteal
a. Common Carotid & Radial
Which two arteries are the most common arteries used to palpate pulse?
a. Common Carotid & Radial
b. Common Carotid & Femoral
c. Superficial Temporal & Facial
d. Brachial & Dorsalis pedis
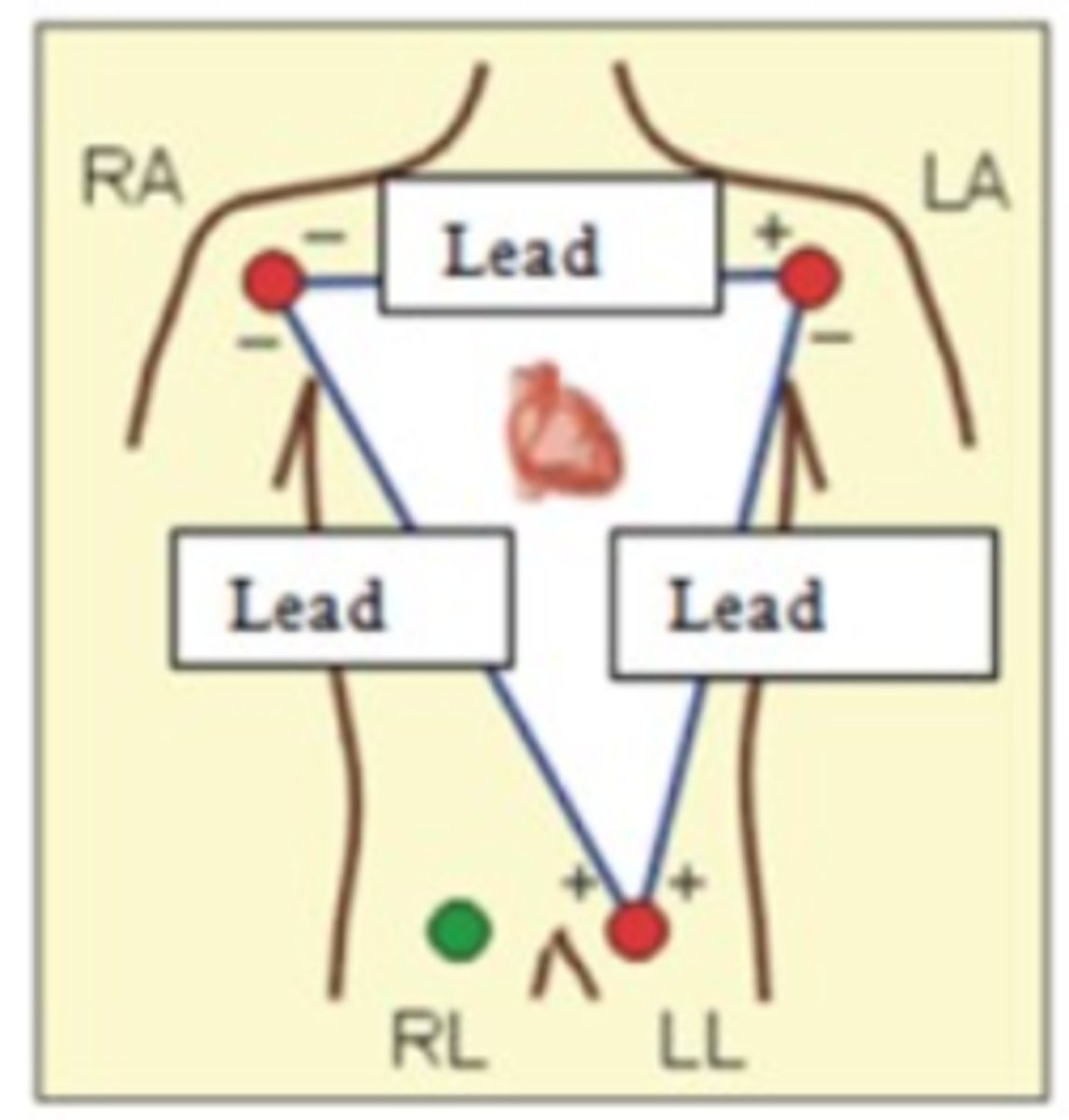
1) c. From right arm to left arm
2) a. From right arm to left leg
3) b. From left arm to left leg
Match the lead to the description.
1) Lead One
2) Lead Two
3) Lead Three
a. From right arm to left leg
b. From left arm to left leg
c. From right arm to left arm
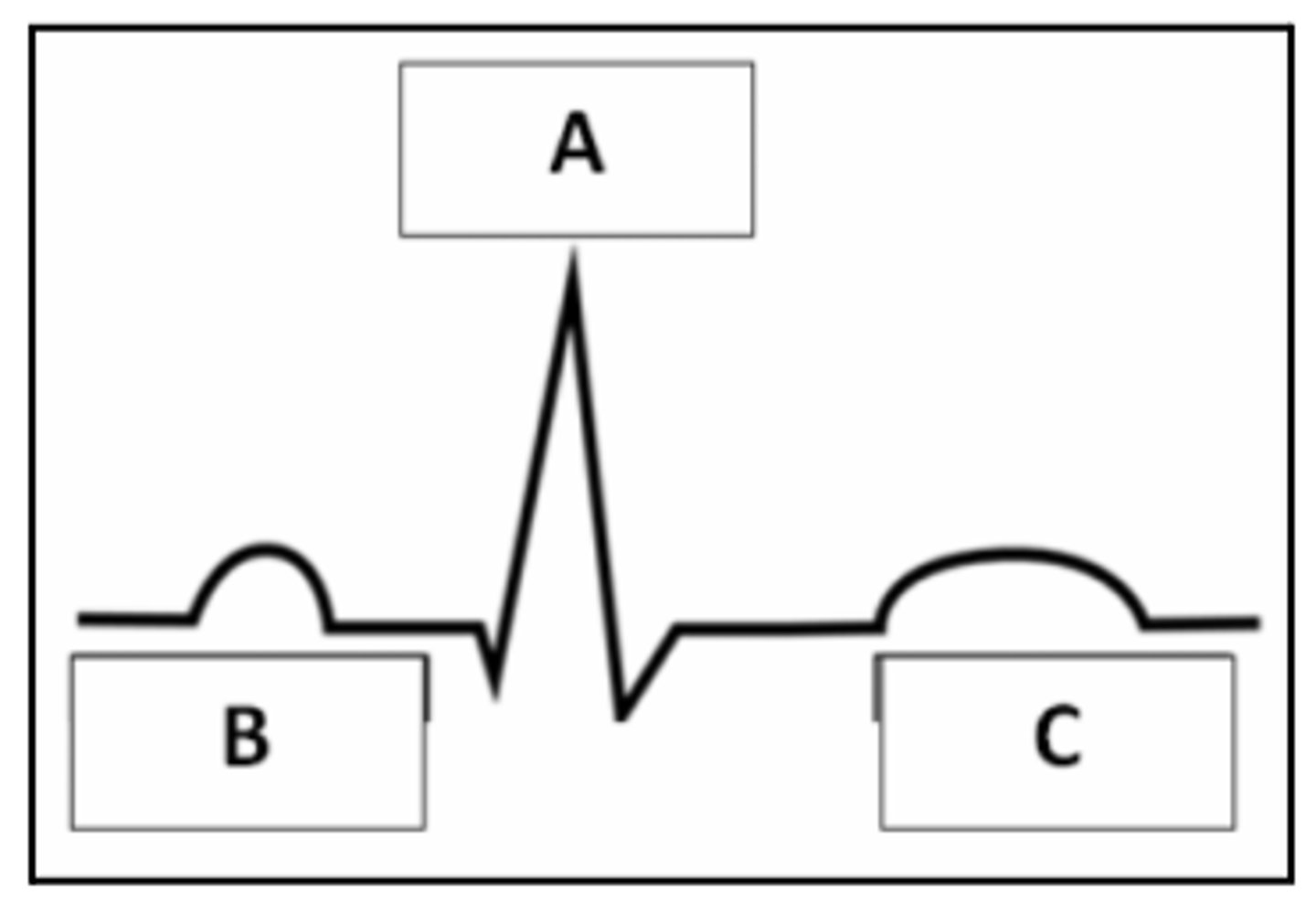
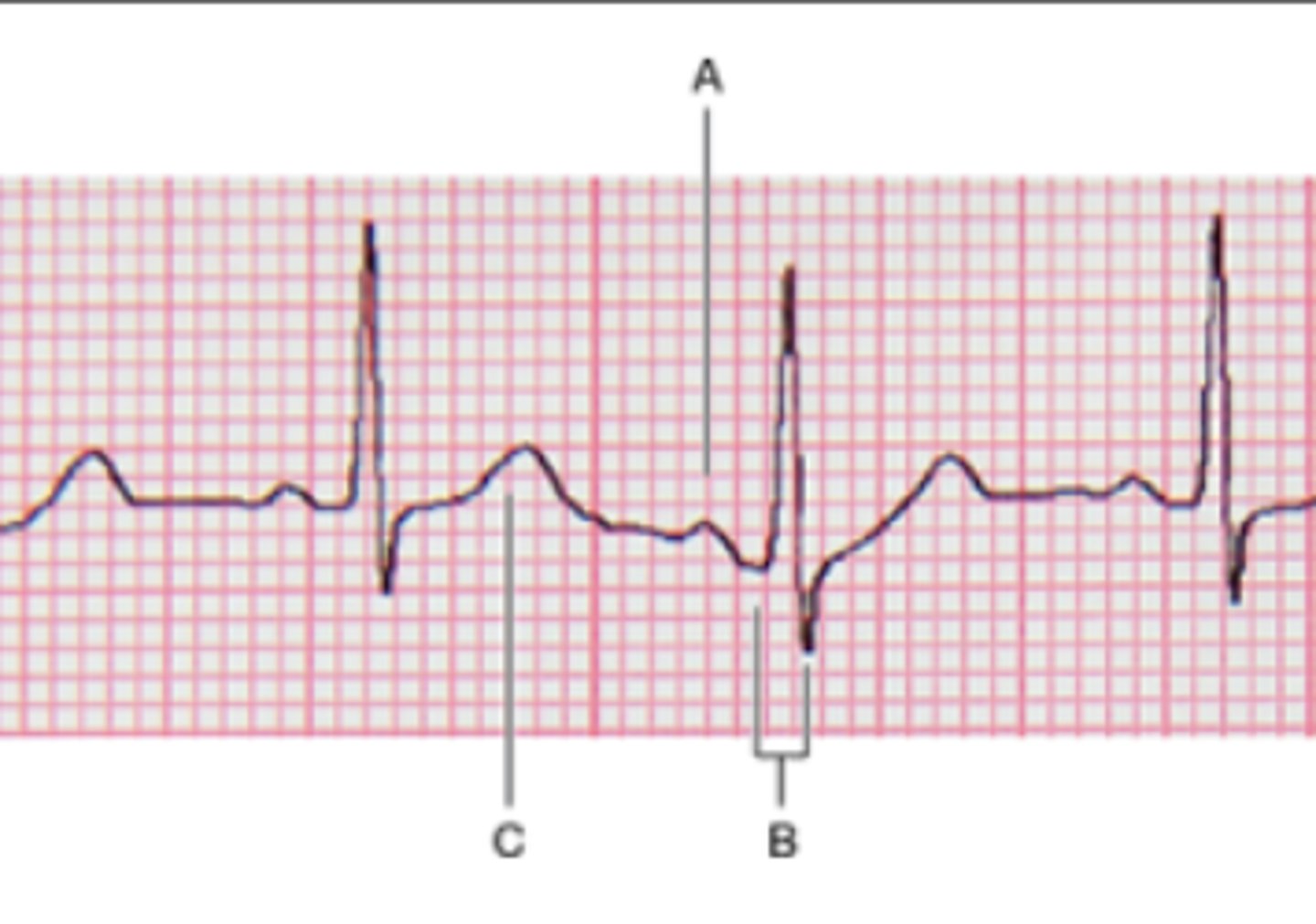
1) B
2) A
3) C
4) A
5) C
6) B
7) Masked by the QRS complex
Match the parts of an EKG/ECG to the correct description.
1. P wave
2. QRS complex
3. T wave
4. Ventricular depolarization
5. Ventricular repolarization
6. Atrial depolarization
7. Atrial repolarization
A
B
C
Masked by the QRS complex
D, C, B, A, E, F
Put the following conduction pathway structures in order of the impulse:
A - AV bundle
B - AV Node
C - Atrial nodal path
D - SA node
E - Bundles Branches
F - Purkinje fibers
b. Lead Two
Which lead is most commonly used because it runs obliquely across the heart just like the conduction pathway?
a. Lead One
b. Lead Two
c. Lead Three
d. Lead Four
b. Ensure heart beats as a coordinated unit.
c. Ensures the heart muscle depolarizes in an orderly and sequential manner.
Select the TRUE statements about the critical role of the intrinsic conduction system in heart physiology.
a. Depends on the impulse from the nervous system.
b. Ensure heart beats as a coordinated unit.
c. Ensures the heart muscle depolarizes in an orderly and sequential manner.
1) c. AV node
2) g. Interval
3) e. P Wave
4) a. QRS Complex
5) b. SA Node
6) f. Segment
7) d. T Wave
MATCHING:
1) The intrinsic conduction system structure where the conduction of the impulse is delayed
2) A region on an ECG tracing that includes a segment and at least one wave
3) The deflection on the ECG that is a result of atrial contraction
4) The deflection on the ECG that is a result of ventricular contraction
5) The intrinsic conduction system structure that initiates atrial depolarization
6) A region on an ECG tracing that is between two waves but doesn't include a wave
7) The deflection on the ECG that is a result of ventricular relaxation
a. QRS Complex
b. SA Node
c. AV node
d. T Wave
e. P Wave
f. Segment
g. Interval
1) b. Fibrillation
2) d. Systole
3) c. Diastole
4) a. Cardiac Cycle
Define the following terms.
1) Rapid uncoordinated heart contractions
2) Ventricular contraction
3) Ventricular relaxation
4) Both atria and ventricles contract and then relax which is equivalent to one complete heartbeat
a. Cardiac Cycle
b. Fibrillation
c. Diastole
d. Systole
1. i
2. k
3. n
4. o
5. p
6. g
7. m
8. h
9. f
10. b, d
11. j
12. l
13. a, e
14. c
Match the correct letter to the proper description. (a-p: two questions have two answers)
1. aortic pressure
2. atrial pressure (left)
3. ECG
4. first heart sound
5. second heart sound
6. ventricular pressure (left)
7. ventricular volume
8. aortic (semilunar) valve closes
9. aortic (semilunar) valve opens
10. AV & Semilunar valves closed
11. AV valves closes
12. AV valves open
13. Ventricular diastole
14. Ventricular systole
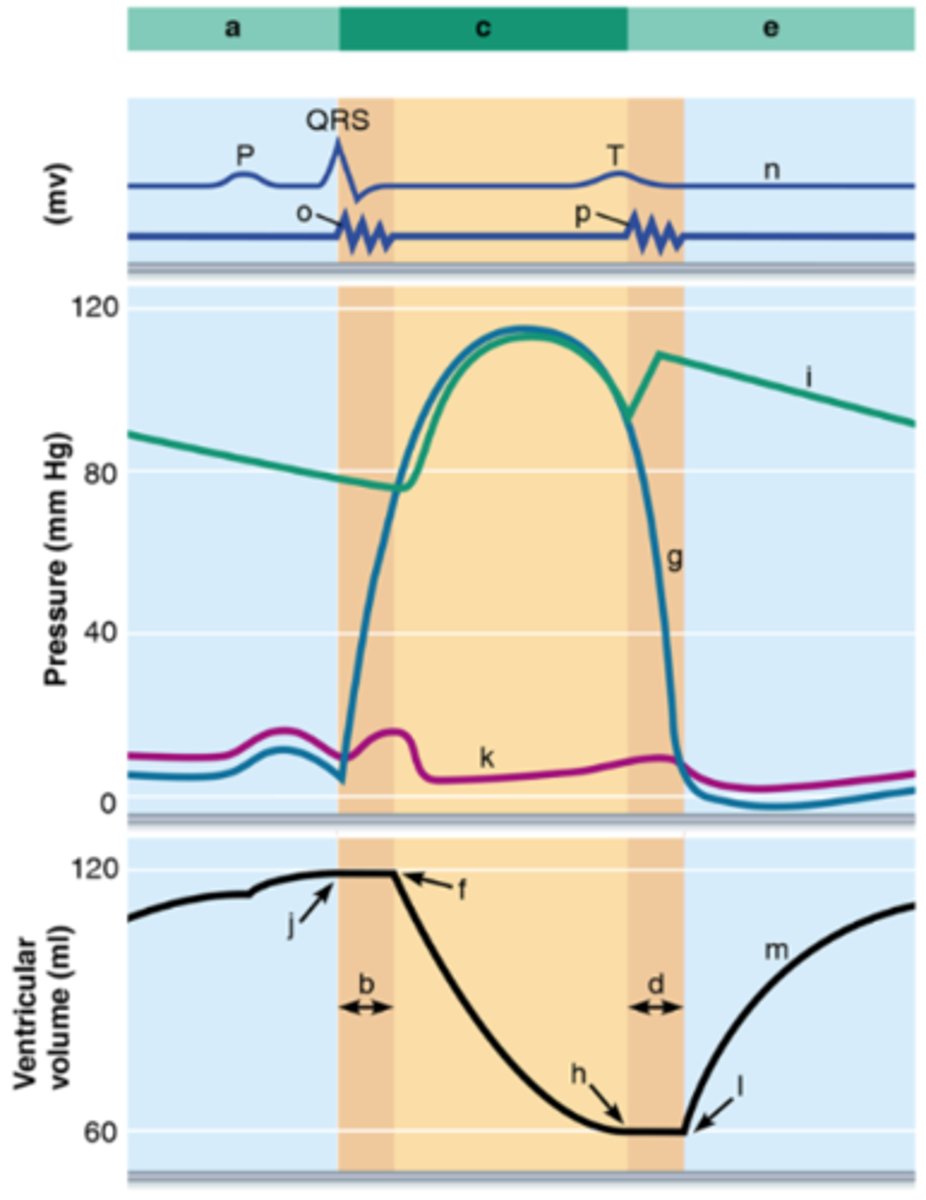
1) d. During atrial systole
2) a. Atrial pressure greater than ventricular pressure
MATCHING:
1) Phase of the cardiac cycle when the AV valves are opened
2) Pressure difference that causes AV valves to open
a. Atrial pressure greater than ventricular pressure
b. Ventricular pressure greater than pressure in great arteries
c. Increase in aortic pressure that occurs when its SL valve snap shut
d. During atrial systole
e. During ventricular systole
f. After atrial contraction and ventricular systole
3) e. During ventricular systole
4) b. Ventricular pressure greater than pressure in great arteries
MATCHING:
3) Phase of the cardiac cycle when the SL valves are opened
4) Pressure difference that causes SL valves to open
a. Atrial pressure greater than ventricular pressure
b. Ventricular pressure greater than pressure in great arteries
c. Increase in aortic pressure that occurs when its SL valve snap shut
d. During atrial systole
e. During ventricular systole
f. After atrial contraction and ventricular systole
5) f. After atrial contraction and ventricular systole
6) c. Increase in aortic pressure that occurs when its SL valve snap shut
MATCHING:
5) Phase of cardiac cycle when both sets of valves (AV & SL) are closed
6) Phase of the cardiac cycle that causes the dicrotic notch
a. Atrial pressure greater than ventricular pressure
b. Ventricular pressure greater than pressure in great arteries
c. Increase in aortic pressure that occurs when its SL valve snap shut
d. During atrial systole
e. During ventricular systole
f. After atrial contraction and ventricular systole
ventricles; atria
The heart chambers that have just been filled when you hear the first heart sound are the _____, and the chambers that have just emptied are the _____
atria; ventricles
Immediately after the second heart sound, both the _____ and _____ are filling with blood.
a. True
The mitral valve is heard most clearly when the apical heartbeat is auscultated.
a. True
b. False
1) d. Pulse Pressure
2) a. Apical Pulse
3) e. Blood Pressure
4) c. Systolic Pressure
5) b. Diastolic Pressure
MATCHING:
1) the difference in systolic and diastolic pressure
2) the actual counting of heartbeats
3) pressure the blood exerts against any unit area of the blood vessel walls
4) pressure in the arteries at the peak of ventricular contraction
5) pressure during ventricular relaxation
a. Apical Pulse
b. Diastolic Pressure
c. Systolic Pressure
d. Pulse Pressure
e. Blood Pressure
1) b. radial artery
2) e. temporal artery
3) d. dorsalis pedis artery
4) a. carotid artery
5) c. posterior tibial artery
What artery is palpated at each pressure point?
1) wrist
2) front of the ear
3) dorsum of the foot
4) side of neck
5) inside ankle
a. carotid artery
b. radial artery
c. posterior tibial artery
d. dorsalis pedis artery
e. temporal artery
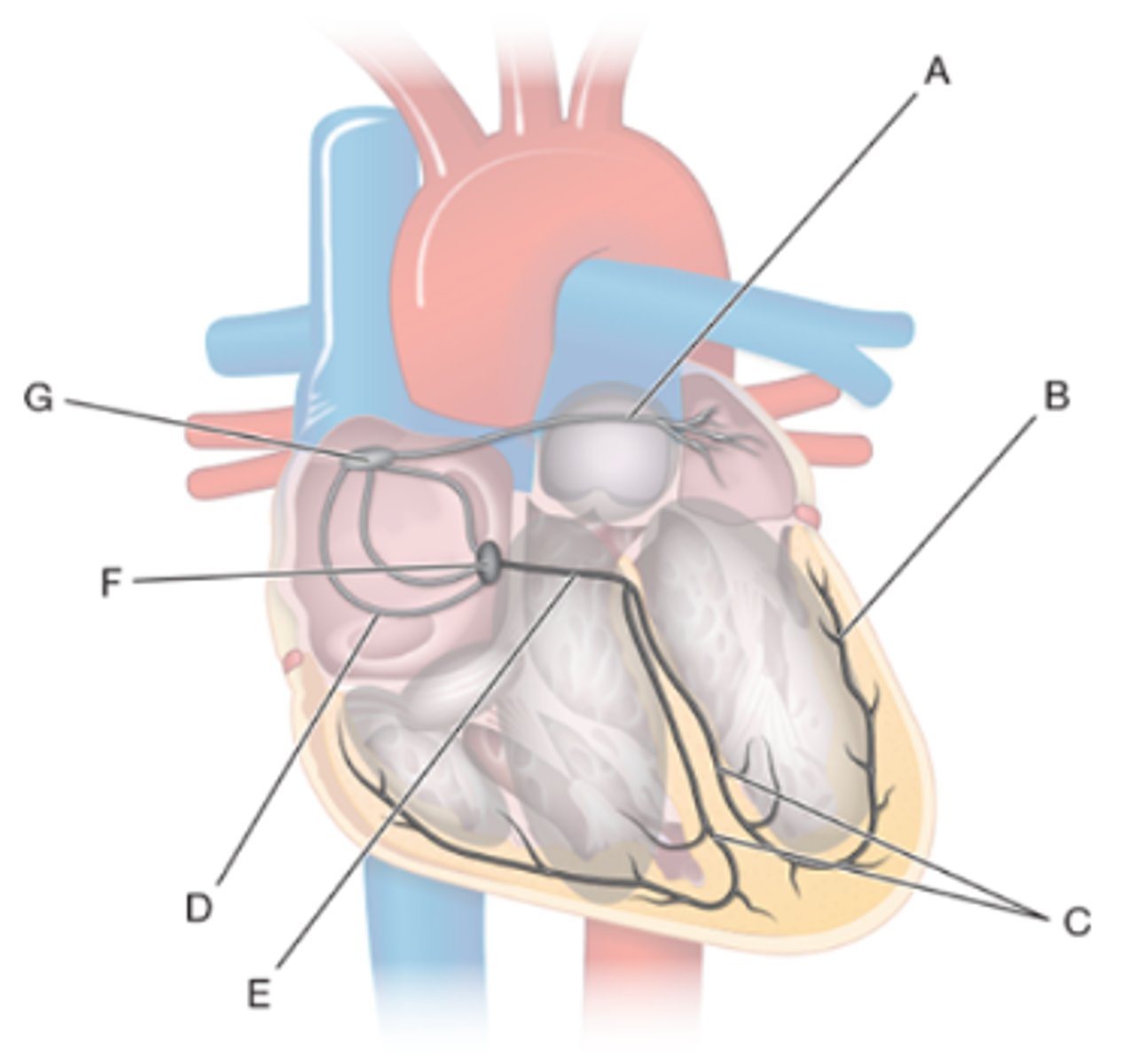
A) f. Bachmann's bundle
B) a. Purkinje fibers
C) d. bundle branches
D) g. internodal pathway
E) b. bundle of His
F) e. atrioventricular node
G) c. sinoatrial node
Anatomy of the conduction system of the heart. Label the figure. #A-G
a. Purkinje fibers
b. bundle of His
c. sinoatrial node
d. bundle branches
e. atrioventricular node
f. Bachmann's bundle
g. internodal pathway
A) P wave
B) QRS complex
C) T wave
Use the matching question to identify one P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
A)
B)
C)
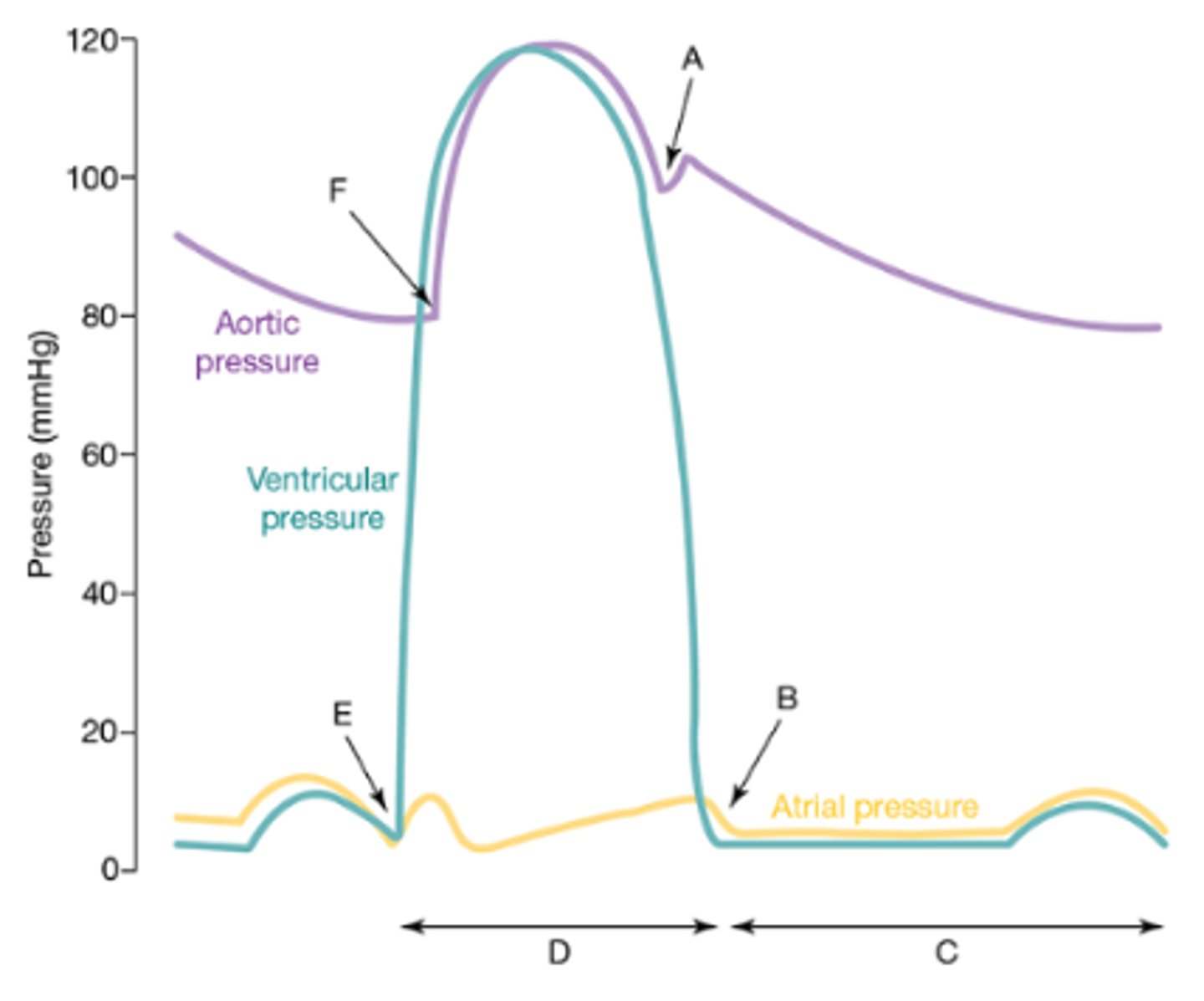
A) b. Aortic SL valves close
B) e. AV valves open
C) f. Diastole
D) c. Systole
E) d. AV valves close
F) a. Aortic SL valves open
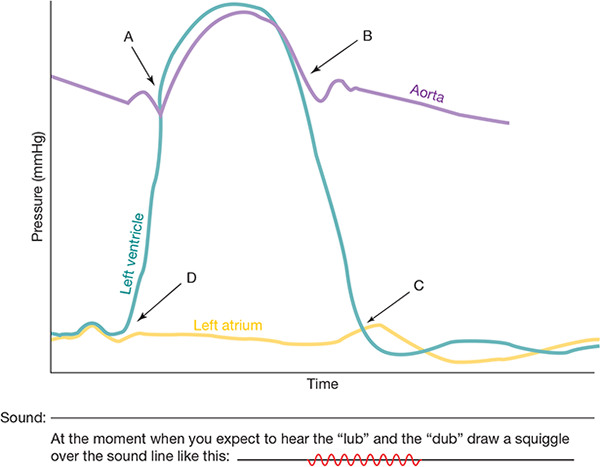
Identify the following areas of the Wiggers diagram. #A-F
a. Aortic SL valves open
b. Aortic SL valves close
c. Systole
d. AV valves close
e. AV valves open
f. Diastole
1) e. a-
2) a. cardi-
3) b. diastol-
4) d. systol-
5) c. tachy-
Match each of the roots with its definition.
1) without
2) heart
3) relax
4) contract
5) rapid
a. cardi-
b. diastol-
c. tachy-
d. systol-
e. a-
hydrostatic pressure
_____ _____: the pressure exerted by a fluid onto the walls of its container
c. The closure of the flaps of the heart valves against each other
The heart sounds are caused by what event?
a. The expansion of the walls of the elastic arteries as blood is forced into them
b. The smack of blood against the walls of the atria as it enters the heart
c. The closure of the flaps of the heart valves against each other
a. The pressure is greater on the left side.
The left AV valve closes slightly before the right AV valve. Which of the following statements correctly explains why?
a. The pressure is greater on the left side.
b. The left AV valve has four cusps, making it easier to close.
c. The ventricular walls do not depolarize at the same time, as evidenced by the different waveforms for each ventricle on the ECG.
to supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle itself
coronary vessels
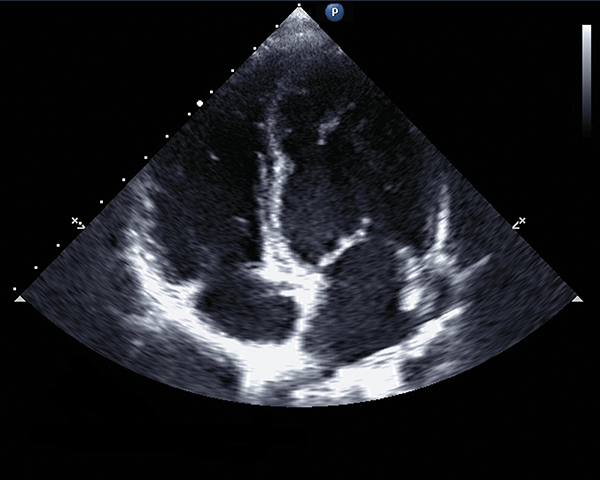
an ultrasound of the heart
echocardiogram
best tool to visualize and understand the electrical signals within the heart that
detects the disruptions in the concentration of ions in the interstitial fluid that are caused when the heart contracts
arrhythmia = heart doesn’t follow normal pattern diagnosed using this test
electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
listening to the heart with a stethoscope to hear each heart valve closing
auscultation
on the proximal region of the brachial artery
When measuring blood pressure, which of the following is the correct location to place your stethoscope?
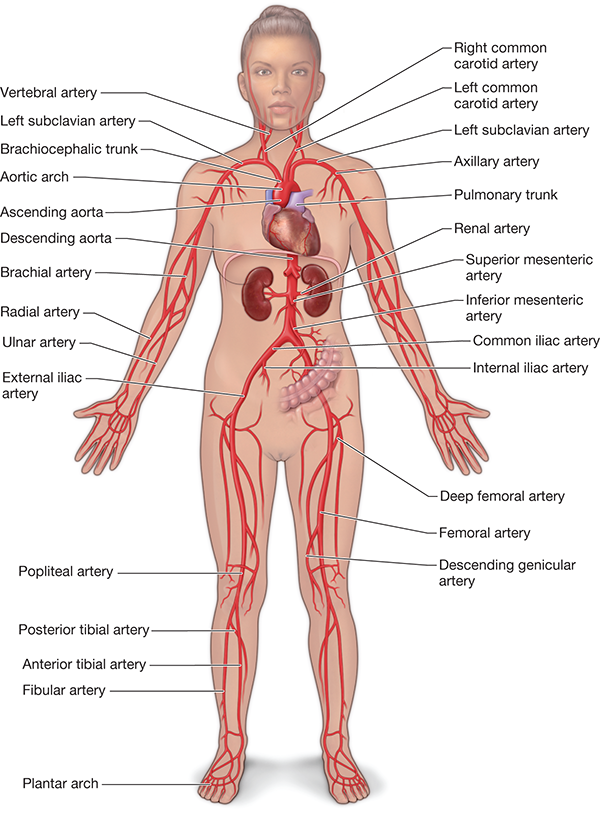
the major arteries of the systemic circuit
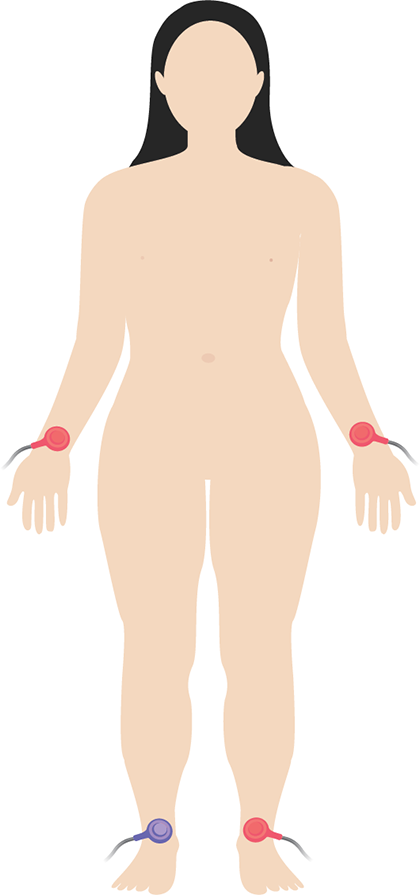
four electrode placements for ECG
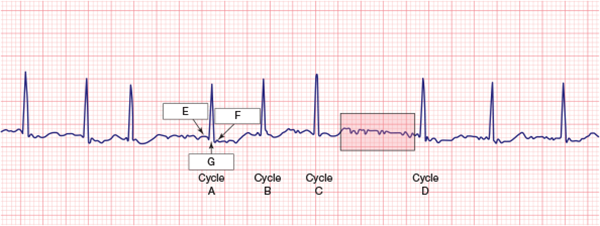
The extra waveforms indicate that the ventricles are depolarizing additional times between cycle C and cycle D.
ventricular fibrilliation
Examine the region shaded in red between cycles C and D. It should be clear that there is extra electrical activity there, so which of the following seems the most plausible?
The extra waveforms indicate that the ventricles are depolarizing additional times between cycle C and cycle D.
The extra waveforms indicate that the atria are depolarizing additional times between cycle C and D.
No, the fibrillation contractions will not eject as much blood as the normal contractions because the chamber did not have enough time to fill with blood.
In a given fibrillation contraction, do you think the chamber will eject as much blood as during a normal contraction?
Yes, there will be more contractions, but each one will be as powerful as a normal contraction.
No, the fibrillation contractions will not eject as much blood as the normal contractions because the chamber did not have enough time to fill with blood.
3
If this was atrial fibrillation, do you think that the ventricles would fill with as much blood as they would if the patient was not experiencing fibrillation?
1) Yes, there would be as much blood filling the ventricles as during times when the patient is not experiencing fibrillation because the atria are still contracting.
2) No, due to inadequate atrial filling time or incomplete atrial contraction, there would be very little blood that reached the ventricles.
3) Because the majority of blood reaches the ventricles through gravity alone, atrial fibrillation may reduce, but only slightly reduce, the amount of blood reaching the ventricles.
regular rhythms:
1) count the number of large squares between two consecutive R waves
2) 300/# squares
irregular rhythms:
1) count the number of R waves in a set time period (like 10 secs) and multiple by 6 to get the average bpm
How to calculate HR in bpm using ECG?
pulmonary veins
In atrial fibrillation, the _ _ are often the source of abnormal electrical signals. Ablation frequently focuses on isolating these veins from the atria.
Because the vessels cross at the midline as they ascend
In Activity 25.1, heart sounds, you heard the left AV valve on the left side of the heart, and the right AV valve was clearer on the right side of the heart. But the pulmonary semilunar valve, which is connected to the right ventricle, was more clearly auscultated on the left. Why do you think that may be? (hint: reviewing the heart anatomy may help!)
Because the vessels cross at the midline as they ascend
Because the pulmonary semilunar valve is located far into the pulmonary arteries
Because the sternum prevents auscultation of the pulmonary valve
A Aortic valve opens
B Aortic valve closes
C Mitral/bicuspid valve opens
D Mitrial/bicuspid valve closes
Match each letter to the valve and whether it is opening or closing.
120/55
The arteries of young people and athletic individuals tend to be quite elastic, but as we age (and especially in sedentary individuals) elasticity decreases over time. Below are two blood pressure measurements. One is from a 38-year-old athlete, and the other is from a 62-year-old sedentary individual. Which one do you think is from the athlete?
120/55
125/85
sinoatrial node
AV node reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) is a type of arrhythmia which can cause sudden (and potentially fatal) increases in heart rate. AVNRT is caused by miscommunication between the sinoatrial node and the atrioventricular node. In a healthy heart, which of these nodes fires first?
Sinoatrial node
Atrioventricular node
They fire at the same time
Autorhythmic cells
AV node reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) is a type of arrhythmia which can cause sudden (and potentially fatal) increases in heart rate. AVNRT is caused by miscommunication between the sinoatrial node and the atrioventricular node. AVNRT can be cured through a surgical procedure in which the cells causing this miscommunication are burned with a laser. Which type of cells are the target of this procedure?
Autorhythmic cells
Contractile cells
Neither of these types
gap
Cardiac muscle cells contract as a single unit because the cells share ions for depolarization via _______ cell junctions.
gap
tight
desmosome
radial artery
Imagine the cuff of a sphygmomanometer that is occluding (blocking) blood flow through the brachial artery, as occurs during a blood pressure measurement. As the cuff loosens, flow is restored through the artery. In which distal artery is blood flow restored immediately after deflating the cuff?
Palmar artery
Proximal brachial artery
Radial artery
Axillary artery
Blood is ejected from the heart into arteries, whereas veins receive blood from capillary beds, therefore the pressure generated by the heart can be measured more easily.
Why is blood pressure measured in arteries and not veins?
Arteries have thicker walls and can better withstand the pressure of the sphygmomanometer.
Blood is ejected from the heart into arteries, whereas veins receive blood from capillary beds, therefore the pressure generated by the heart can be measured more easily.
Arteries have more elastic fibers in their walls and so they expand and contract with the systole and diastole phases more than veins, which have fewer elastic fibers.
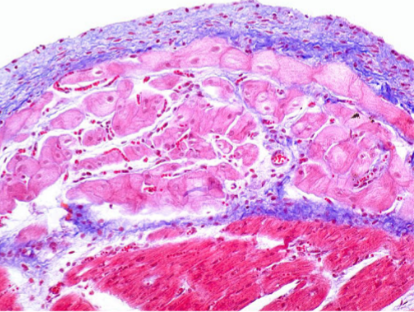
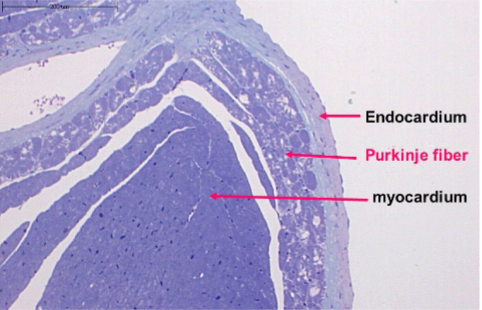
What are these structures?
endocardium
purkinje fiber
myocardium
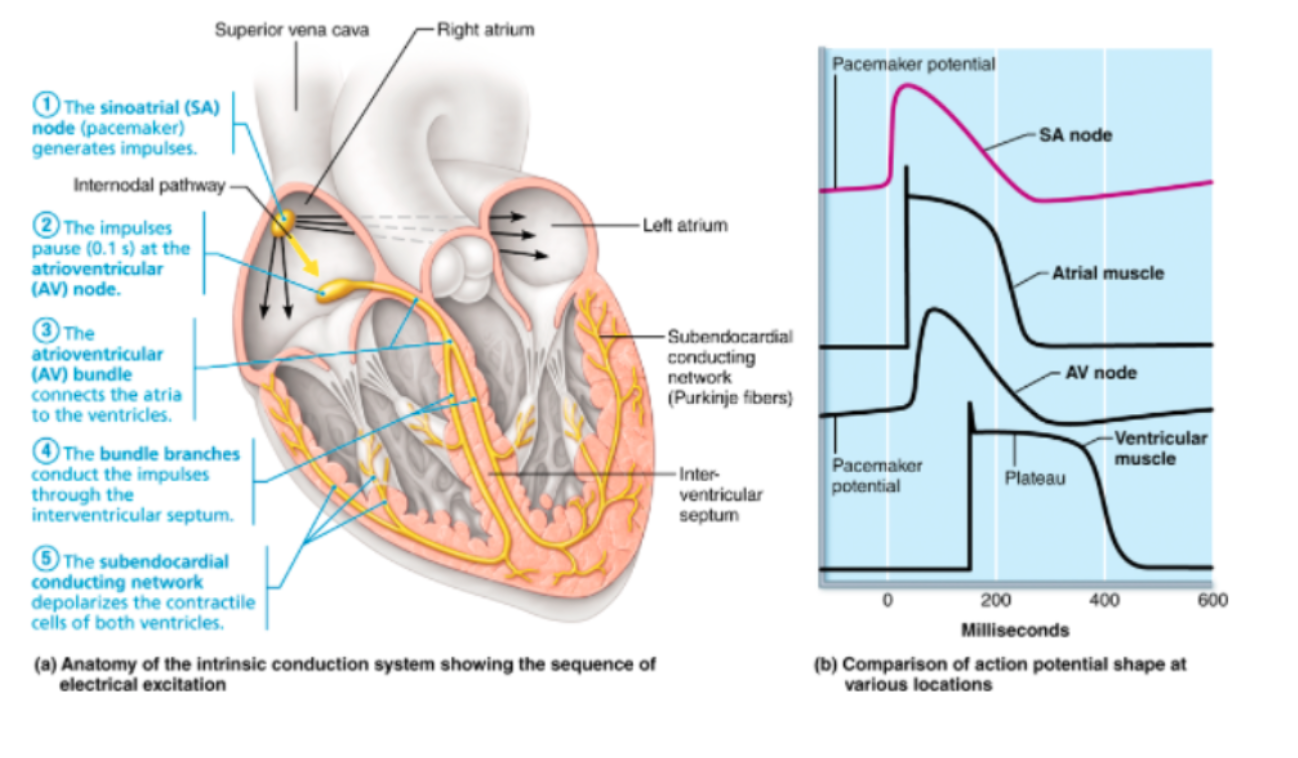
cardiac intrinsic conduction system
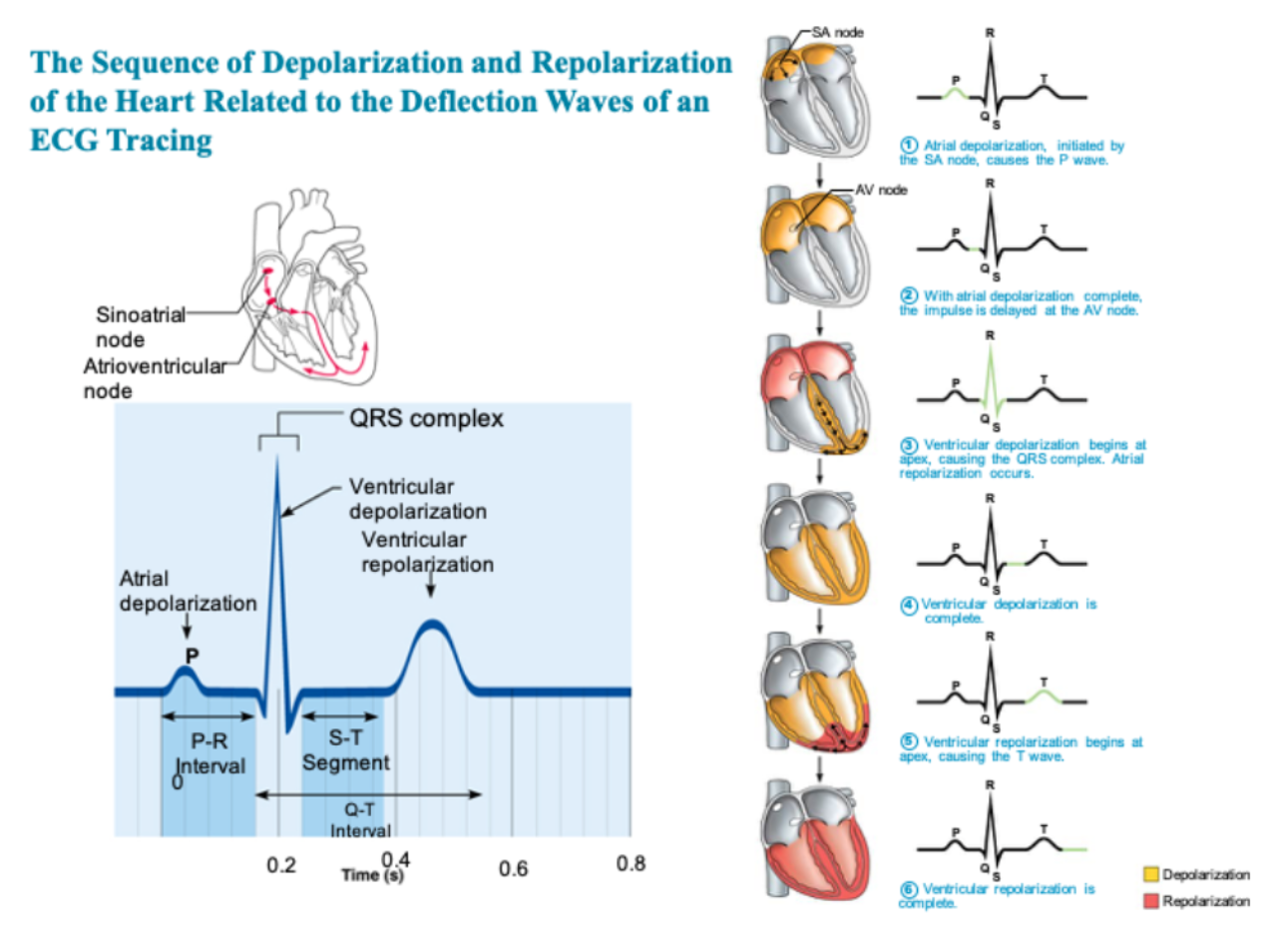
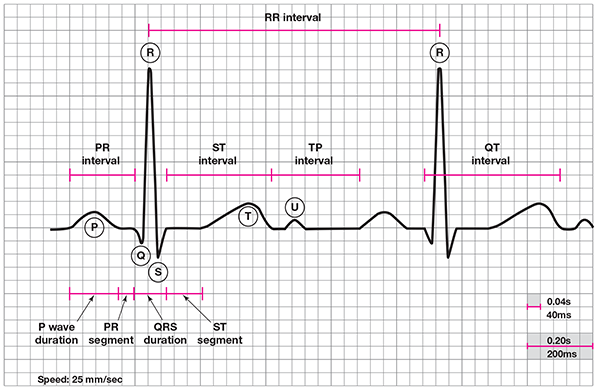
Deflection waves of ECG tracking
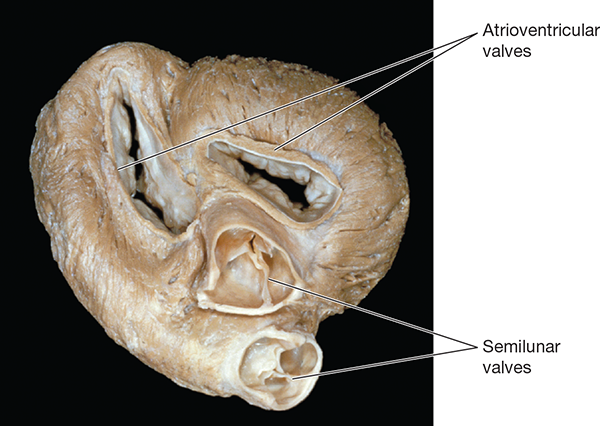
AV valves and Semilunar Valves
enlarged ventricles
enlarged R wave
First-degree heart block. The signal from the SA node to the AV node is delayed longer than normal
Prolonged P-R interval
Increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias. This interval corresponds to the beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization
Prolonged Q-T interval (when compared to the R-R interval)
Myocardial infarction (heart attack).
S-T segment elevated from baseline
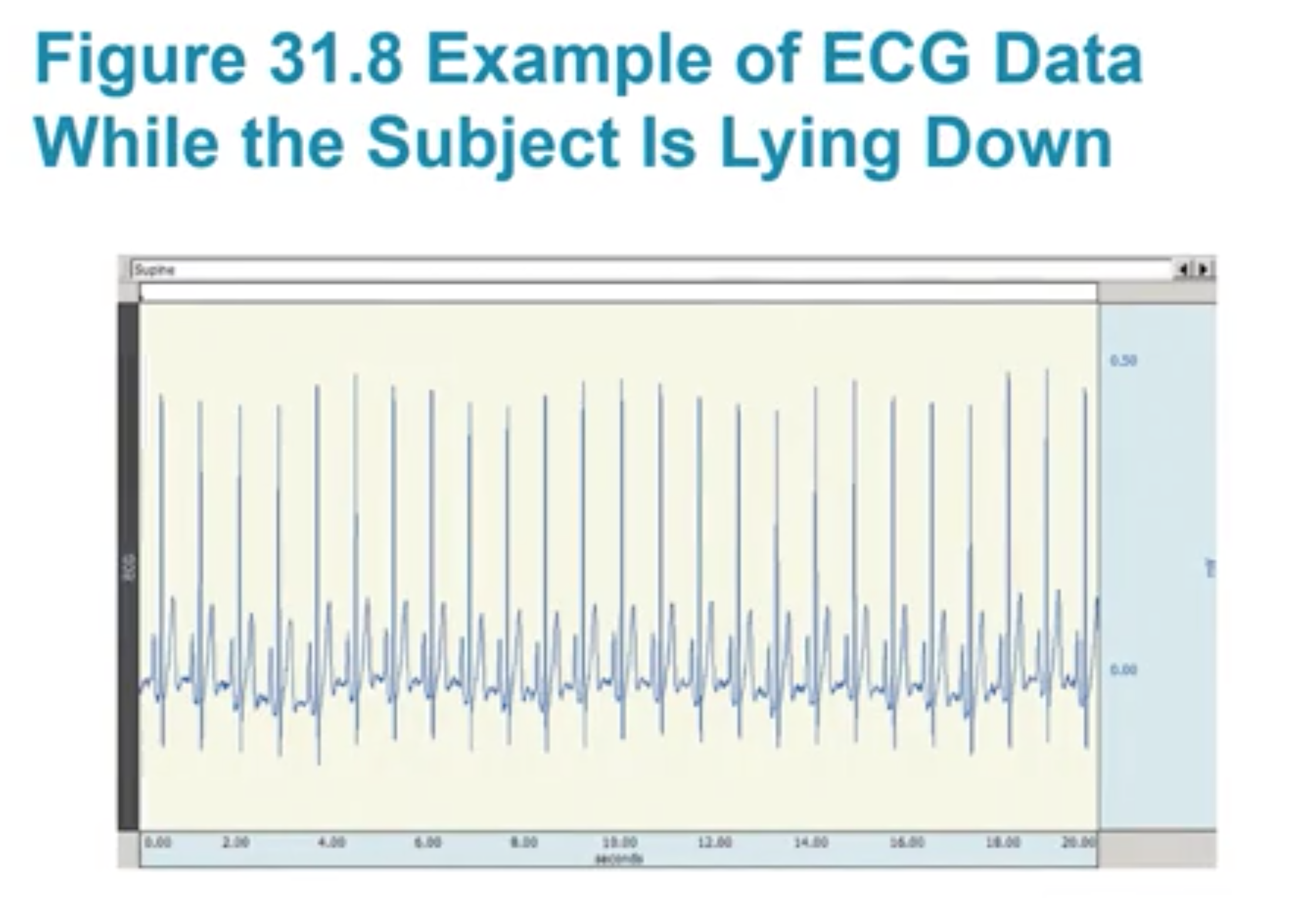
Example of ECG Data for someone lying down
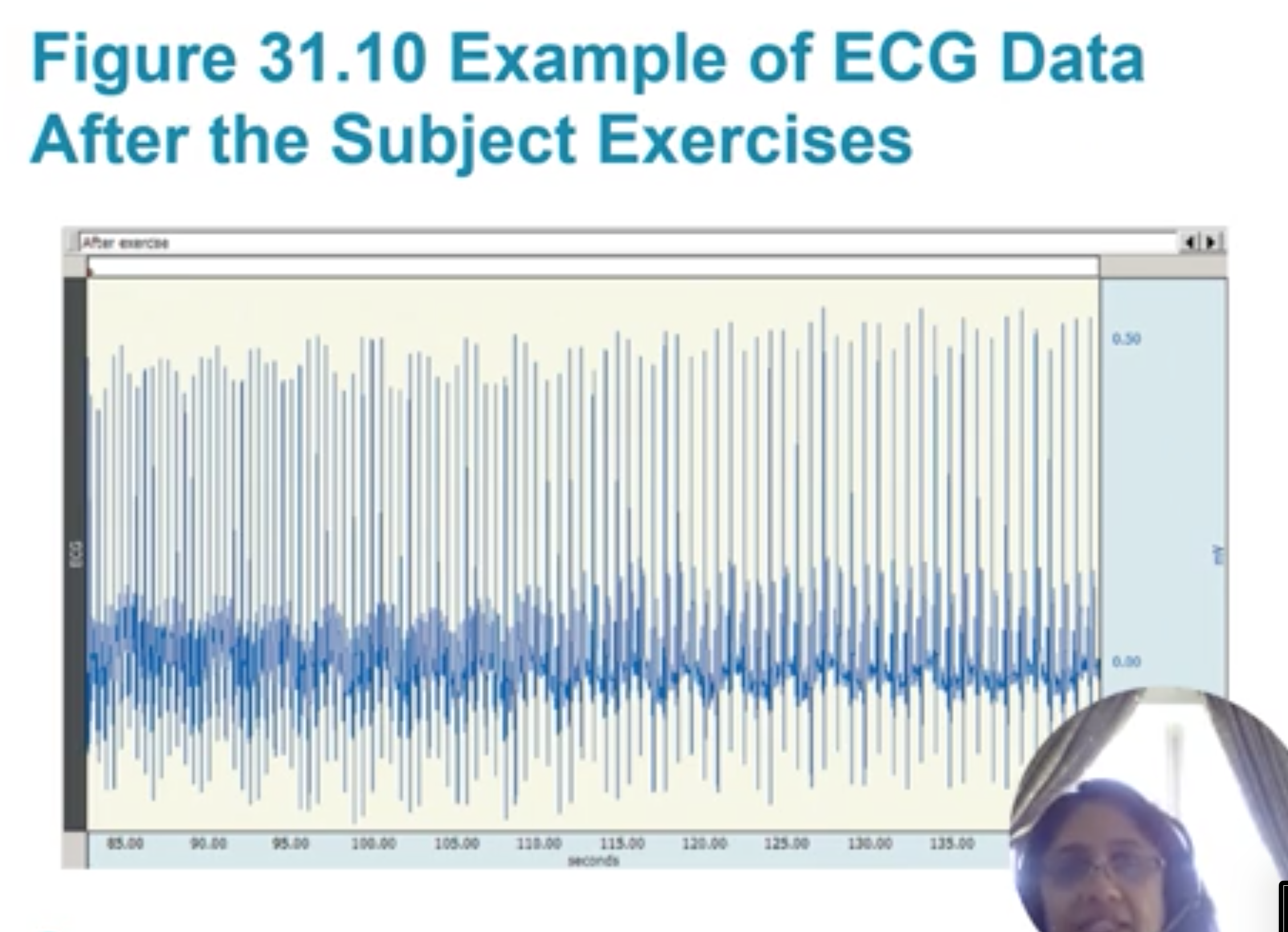
example of ECG data for someone exercising
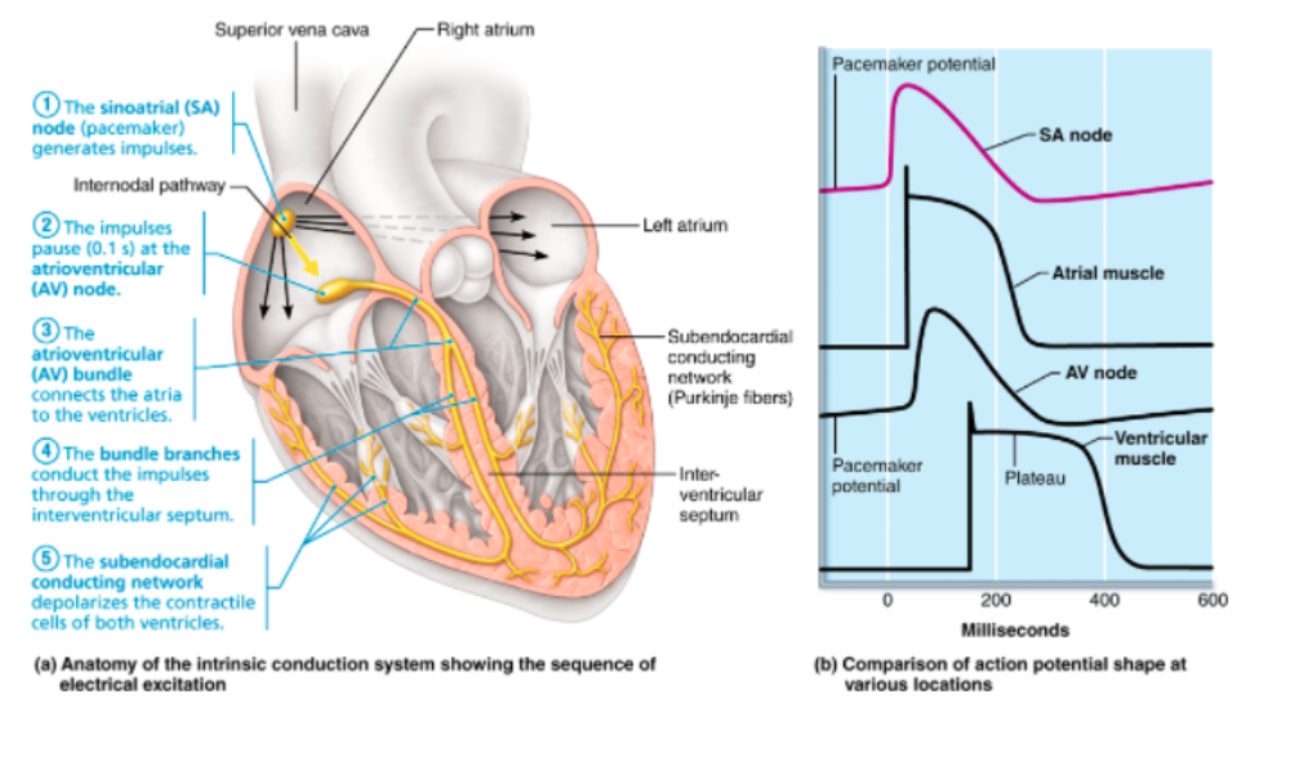
action potential at various spots of intrinsic conduction system
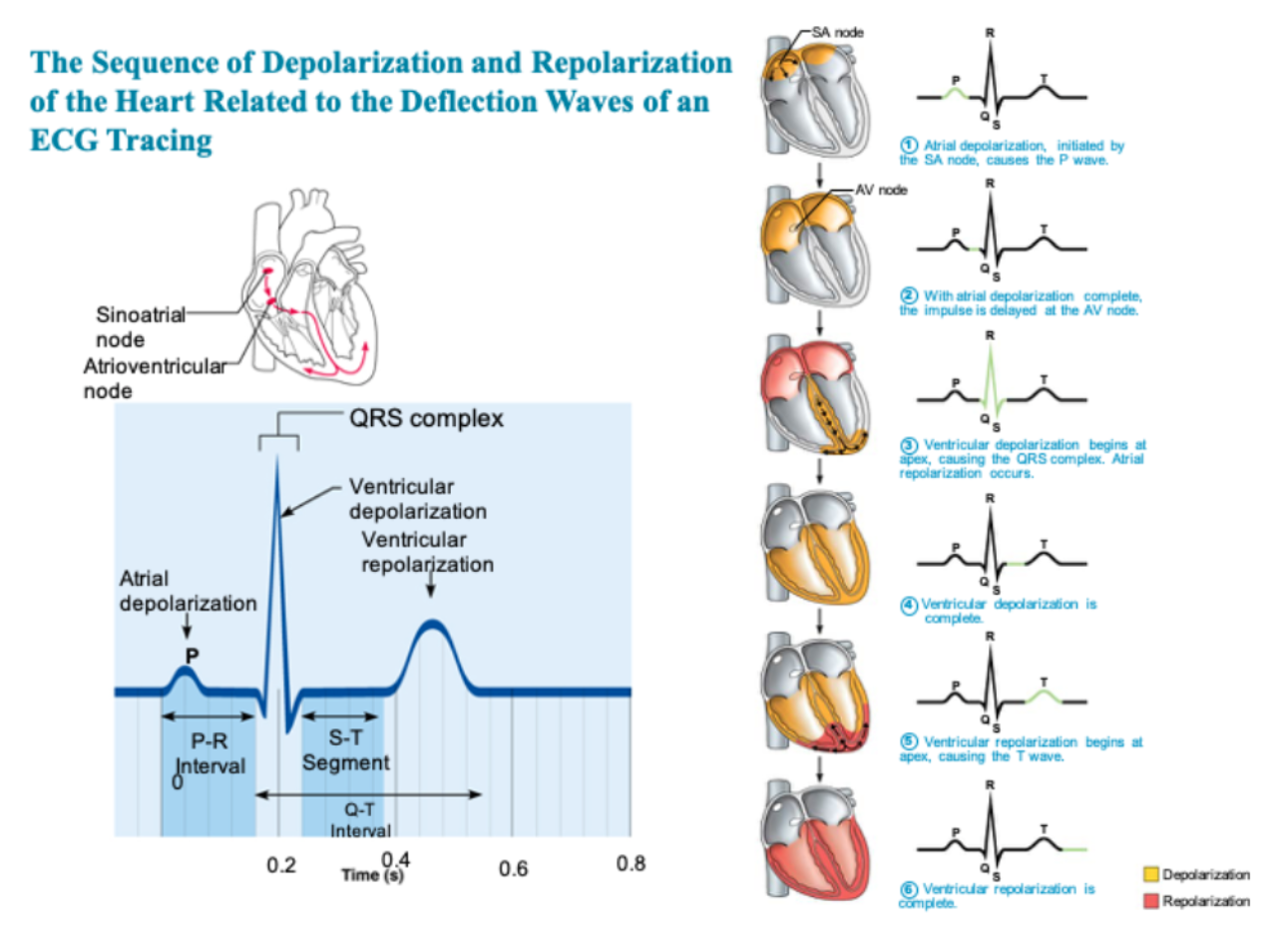
ECG diagram with definitions