Lecture 12 (Viral Diseases of Cattle I)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
colostrum
what is the first "vaccine" every calf should get
-if there's low risk in the herd
-pregnancy status
-shedding into the environment
*you don't have to vaccinate for everything so think if the herd is even going to come into contact with a disease in the first place
provide a reason we may not vaccinate for a disease in cattle even though it has a high mortality rate
start with clinical presentation then go to virus families (not the other way around)
where does diagnosing a virus disease start?
-Cowpox (foreign animal disease)
-Pseudocowpox
-Bovine papular stomatitis
-Lumpy skin disease (foreign animal disease)
what are the 4 diseases of cattle caused by poxviruses worldwide?
-virus is resistant to the environment
-lesions proliferative and some "tumor-like"
-Orthopoxviruses & Capripoxviruses induce long lasting immunity
-Parapoxvirses often chronic infections and do not induce long lasting immunity
-diagnosis by clinical appearance confirmed by electron microscopy or virus isolation
-transmission by contact and mechanically by arthropods
-several viruses are zoonotic
discuss the properties/characteristics of Poxviruses
call the state vet
when in doubt, if you see oral ulcers in a cow you should always...
Pseudocowpox
-mild often recurrent disease in dairy cattle
-often associated with poor hygiene
-secondary bacterial mastitis occurs
-causes bovine papular stomatitis and milker's nodules
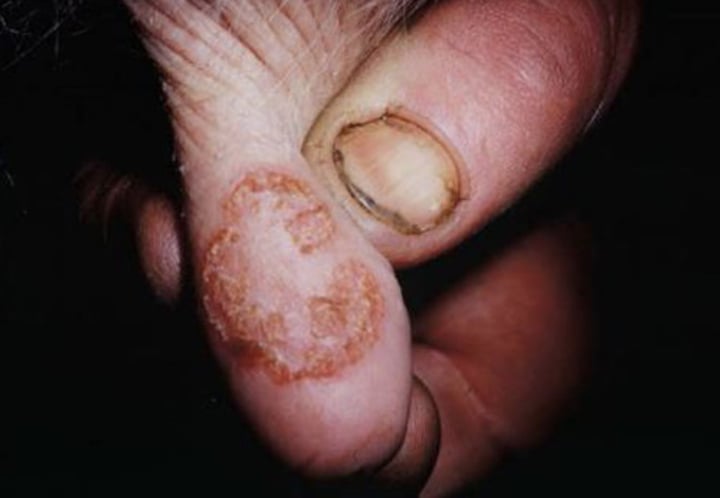
d) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
-common incidental infection in beef cattle
-suckling calves or up to 1 year of age
-no treatment necessary
-can become dangerous if it produces esophageal diseases
a) BVD
b) Blue tongue
c) Vesicular Stomatitis
d) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
a) Herpesviruses
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR), Malignant Catarrhal Fever (MCF), Pseduorabies, and Pseudo-Lumpy Skin Disease are all caused by:
a) Herpesviruses
b) Poxviruses
c) Adenoviruses
d) Papovaviruses
false - can cause lesions in humans (milker's nodules)
t/f: Pseudocowpox is not zoonotic
diagnosis by clinical appearance confirmed by electron microscopy or virus isolation
what is the definitive diagnosis for Poxviruses in cattle?
-Foot and Mouth Disease
-Vesicular Stomatitis
Bovine Papular Stomatitis is a concern to producers in the sense that it looks like what two CONCERNING viruses in cattle:
if it persists and causes esophageal disease
when would Bovine Papular Stomatitis be considered lethal?
-virus is unstable in environment
-wide range of clinical presentations
-latent infections in presence of serum antibody
-diagnosis confirmed by virus isolation and PCR
-transmission by direct contact and droplet/aerosol
-some viruses are zoonotic or "jump species"
discuss the properties/characteristics of Herpesviruses
diagnosis confirmed by virus isolation and PCR
how do you diagnose Herpesviruses in cattle?
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
economically speaking, what is the most important disease complex in cattle?
1. Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
2. Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitis (IPV)
3. Infectious Pustular Balanoposthitis (IPB)
4. abortion
5. generalized (systemic) disease in newborn calves
6. Encephalitis (BHV5)
list the diseases caused by Bovine Herpes Virus 1 (6)
Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) complex
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR) is often part of a shipping fever complex which is also known as...
a) IBR - Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
part of the "shipping fever" complex known as the bovine respiratory disease (BRD) complex:
a) IBR
b) BVD
c) Blue Tongue
d) MCF
1. ocular discharge
2. nasal discharge
3. ear droop and head tilt
4. cough
5. breathing
6. temperature
list some clinical signs we can look for and grade to determine if a cow has Bovine Respiratory Disease
d) ear droop or head tilt
according to the Bovine Respiratory Disease scoring system for pre-weaned dairy calves, which sign is attributed 5 points itself and thus automatically suggests the animal is positive for BRD?
a) eye discharge
b) nasal discharge
c) cough
d) ear droop or head tilt
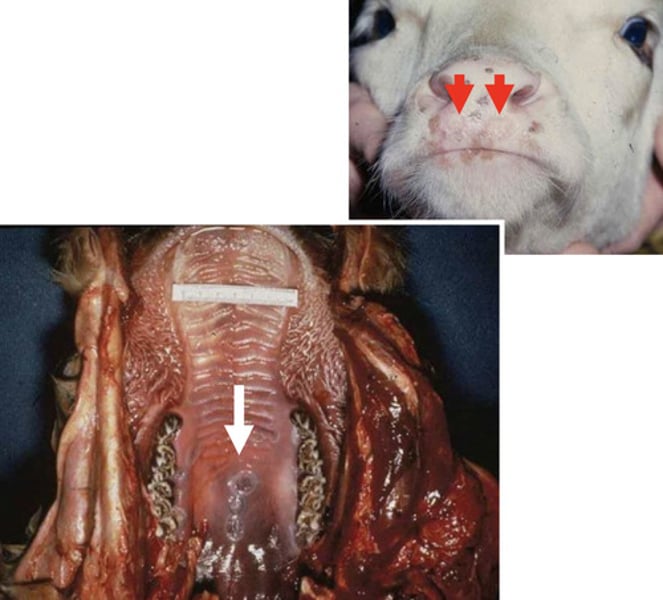
a) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
-this disease is part of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex and is noted for the pustular characteristic of lesions
-excessive salivation and pneumonia are also associated with this respiratory virus
-pneumonia is typically cause of death
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
d) Pseudorabies (Mad Itch/Aujezsky's disease)
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
which of the following is a disease linked to Bovine Herpes Virus 1?
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
d) Pseudorabies (Mad Itch/Aujezsky's disease)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
which of the following is a disease linked to Bovine Herpes Virus 2?
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
d) Pseudorabies (Mad Itch/Aujezsky's disease)
-conjunctivitis
-corneal keratitis
-ulceration
-possible association with "cancer eye"
what type of eye infections will you see with BHV1?
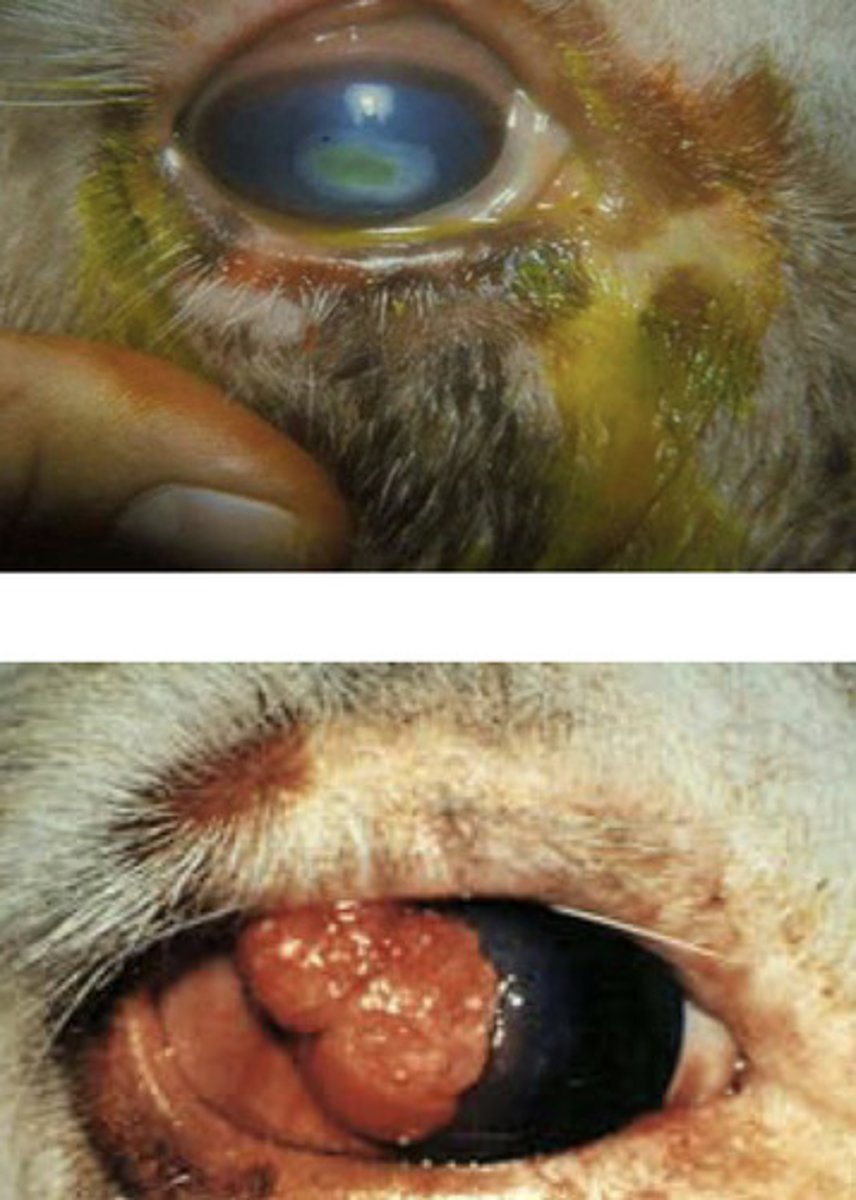
a) BHV1
associated with conjunctivitis, corneal keratitis & ulceration // possible associations with cancer eye
a) BHV1
b) BHV2
false - does not lead to abortion
t/f: Infectious pustular vulvovaginitis and infectious balanoposthitis lead to abortion
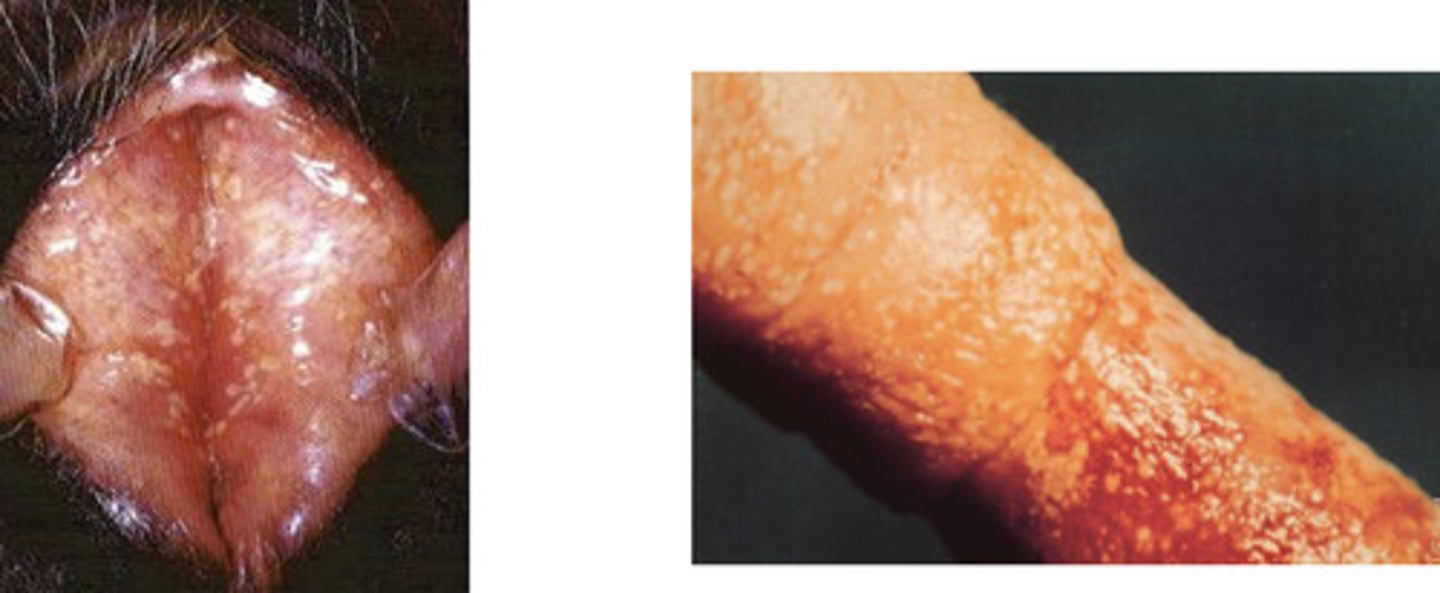
a) tied to abortion
*not known to cause abortions
which of the following is NOT accurate about Infectious pustular vulvovaginitis / Infectious balanoposthitis?
a) tied to abortion
b) may be the historical form of BHV1 before it became respiratory
c) caused by BHV1
d) causes lesions of epithelial necrosis
Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitis (IPV) and Infectious Pustular Balanoposthitis (IPB)
these were the historical forms of BHV1 before tropism occurred to cause respiratory disease in cattle
c) Tropism
BHV1 historically was just the IPV/IPB spread by coitus, it then emerged in feedlots in the 1960s and now spreads by aerosols // the idea of a virus previously of the genital tissues now colonizing respiratory tissues is a feature of the virus changing:
a) Virulence
b) Pathogenicity
c) Tropism
a) IBR
calves sent to feed lots should be vaccinated against BHV1 3 weeks before shipping to prevent:
a) IBR
b) IPV
c) IPB
d) MCF
true
t/f: the control and prevention of BHV1 utilizes marker vaccines (at least in Europe)
-infection is acquired shortly after birth
-pustular lesions affecting the reticulum
-may lead to a systemic infection and death with microscopic lesions throughout the body in addition to respiratory signs
talk about BHV1 infection in young calves
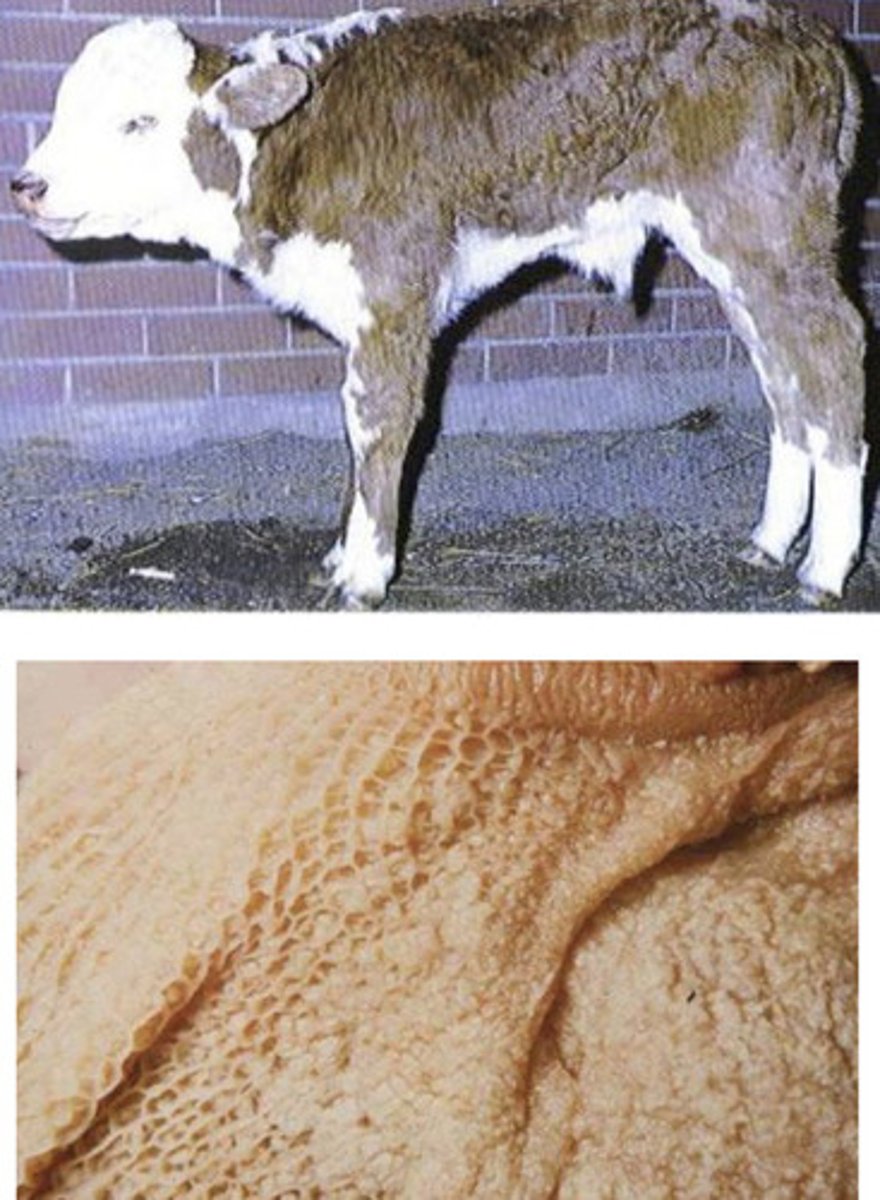
d) microscopic lesions throughout the body + respiratory signs
which of the following symptoms of BHV1 is seen in young calfs when they develop a systemic infection that can be lethal?
a) intense rhinitis and tracheitis
b) pneumonia
c) excessive salivation + respiratory signs
d) microscopic lesions throughout the body + respiratory signs
-follows from respiratory infection and spreads to the fetus → induces abortion
-not a distinct virus from that causing IBR
-a liver sample is the best source of virus for diagnosis
talk about abortion from BHV1
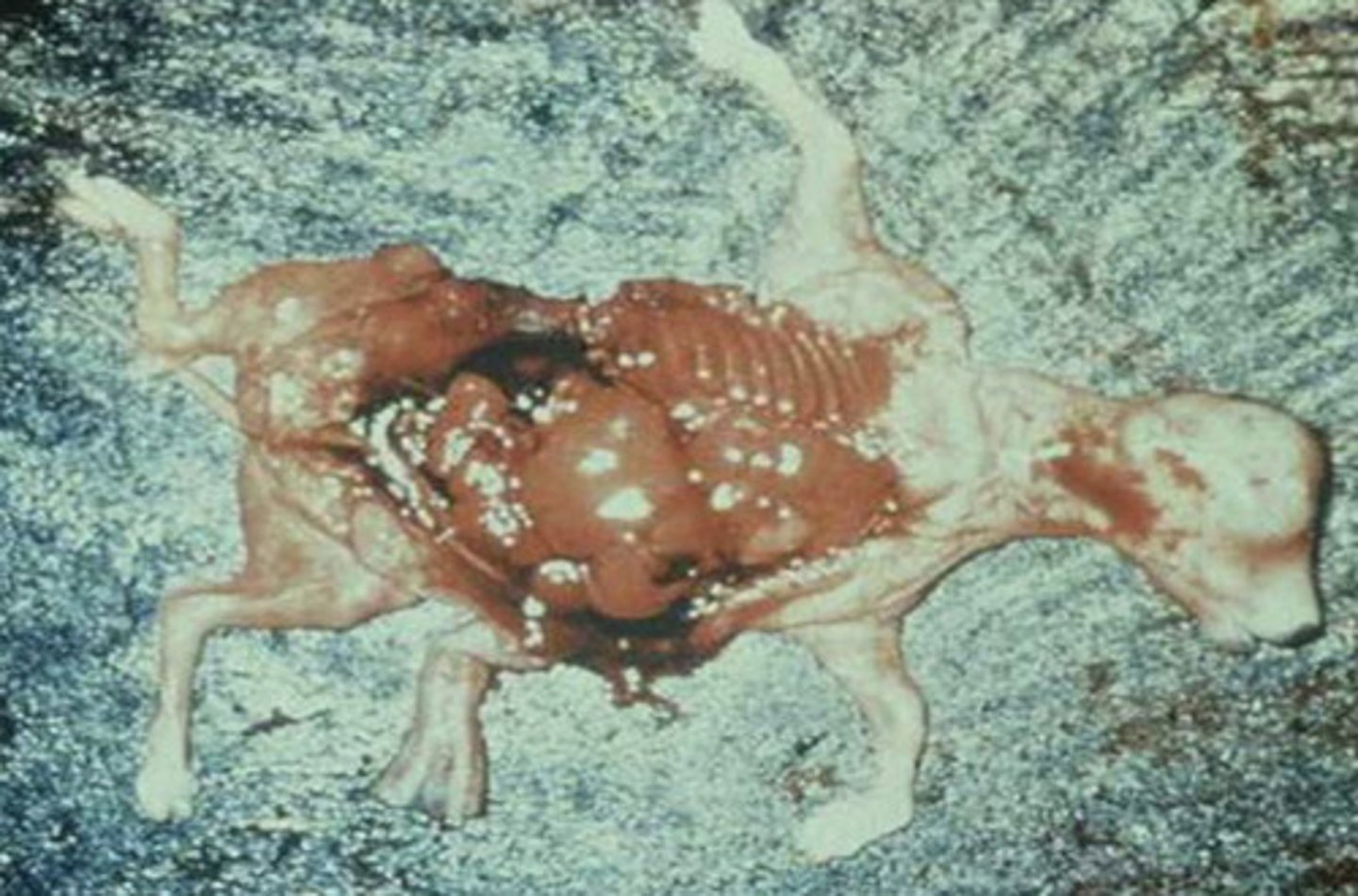
b) respiratory BHVI such as the causative agent of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
which is known to cause abortion:
a) historical BHVI such as the causative agent of Infectious pustular vulvovaginitis & Infectious balanoposthitis
b) respiratory BHVI such as the causative agent of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
d) live vaccines of IBR can be used as an abortigen in feed lots
which of the following is true regarding Abortion tied to BHV1
a) it is a distinct virus from that causing IBR
b) the placenta is the best source of virus for diagnosis
c) usually do not expect a previous respiratory infection
d) live vaccines of IBR can be used as an abortigen in feed lots
-spreads by aerosol in feedlots
-spread by coitus for IPV/IPB (village bull)
how is BHV1 spread?
vaccinate (many are attenuated and combined with other vaccines)
*gene deleted vaccines are available and used in Europe to eradicate disease
talk about the best ways to control and prevent BHV1
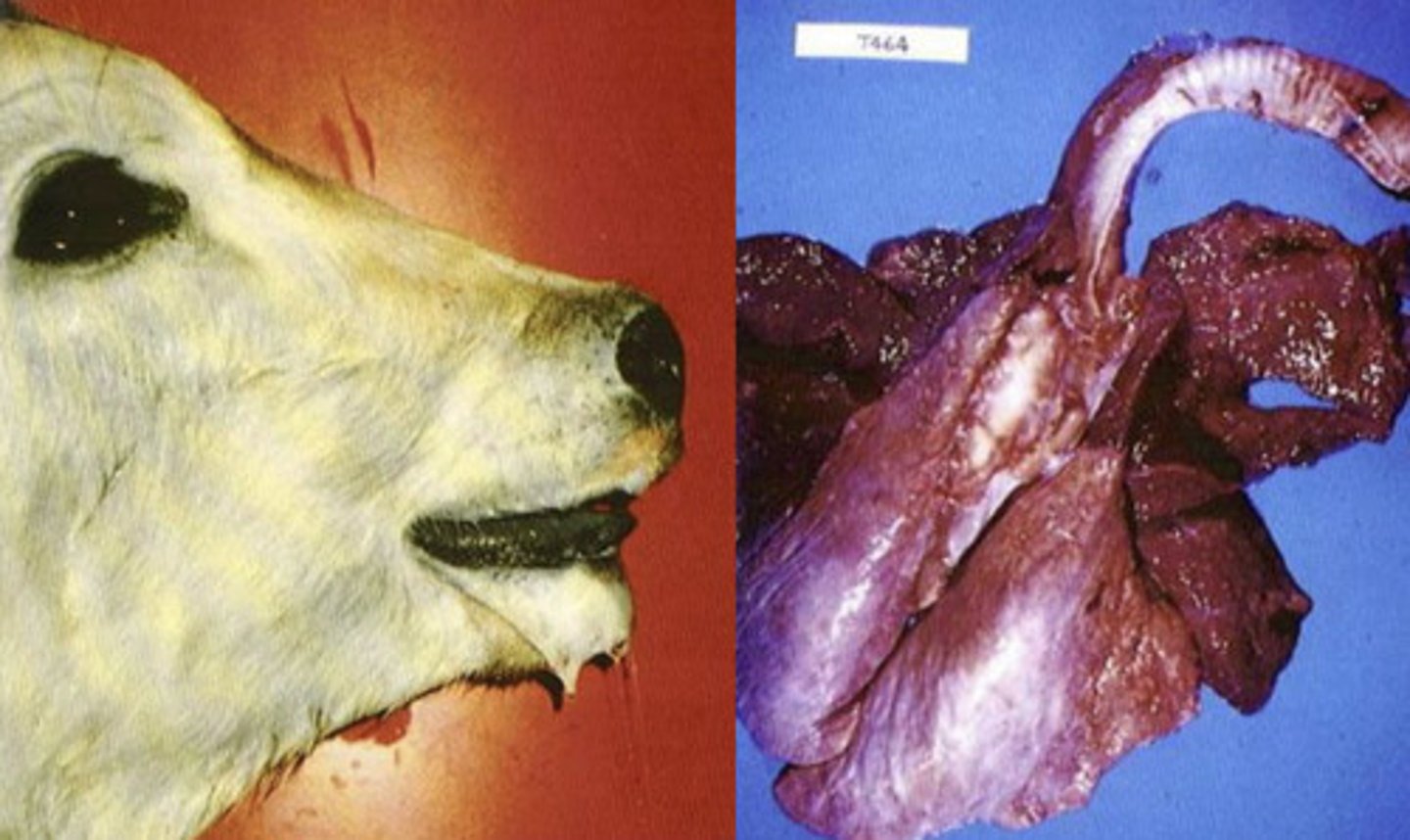
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
-caused by a cell associated herpes virus
-has an African and North American types of virus (both types occur in the USA)
-North American type is mostly associated with sheep; virus has not been isolated
-can occur in American Bison
-100% mortality rate
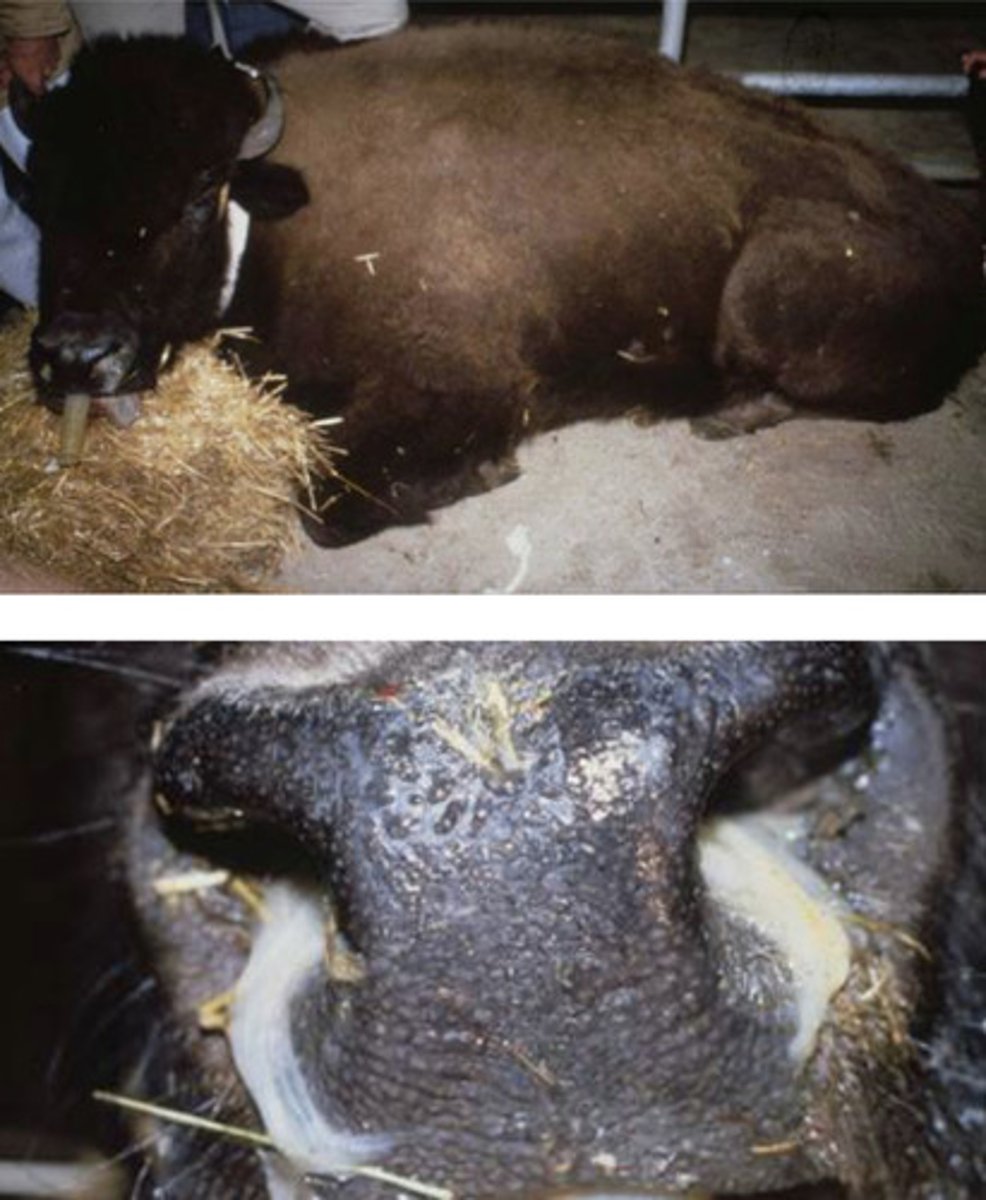
b) Sheep
Malignant Catarrhal Fever is found in two types (African and N. American) in the USA // the North American type is mostly associated with:
a) Cows
b) Sheep
c) Goats
d) Buffalo
bilateral corneal opacity (eyes appear white)
this is a diagnostic indicator for Malignant Catarrhal Fever
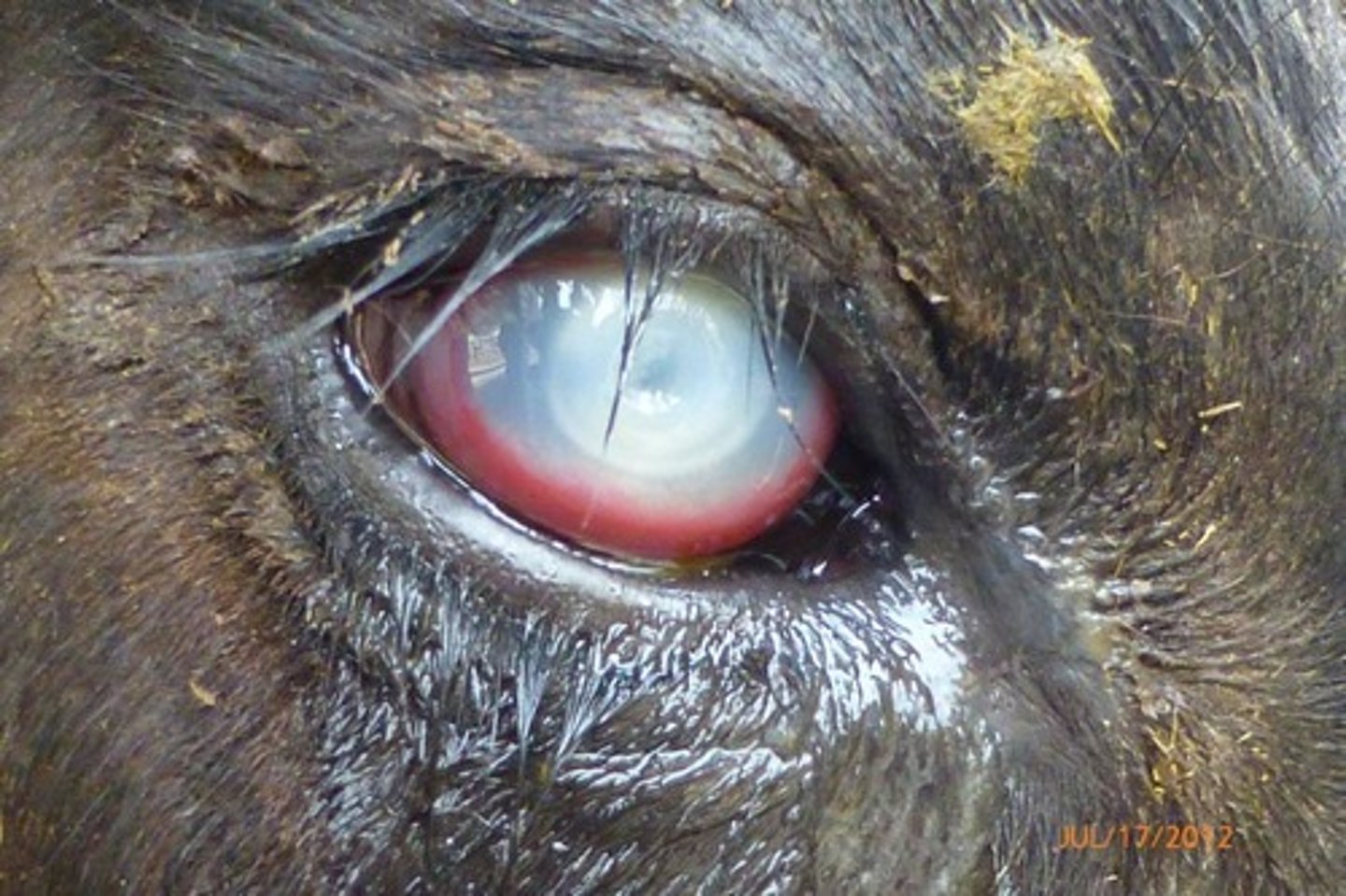
Bovine Herpesvirus 2
-not an important disease
-transmitted by flies
-disease is indicated by umbilicated skin lesion
-commonly seen in the fall
-outbreak of teat lesions without generalized skin lesions
-springing heifers most severely affected
-production losses due to mastitis
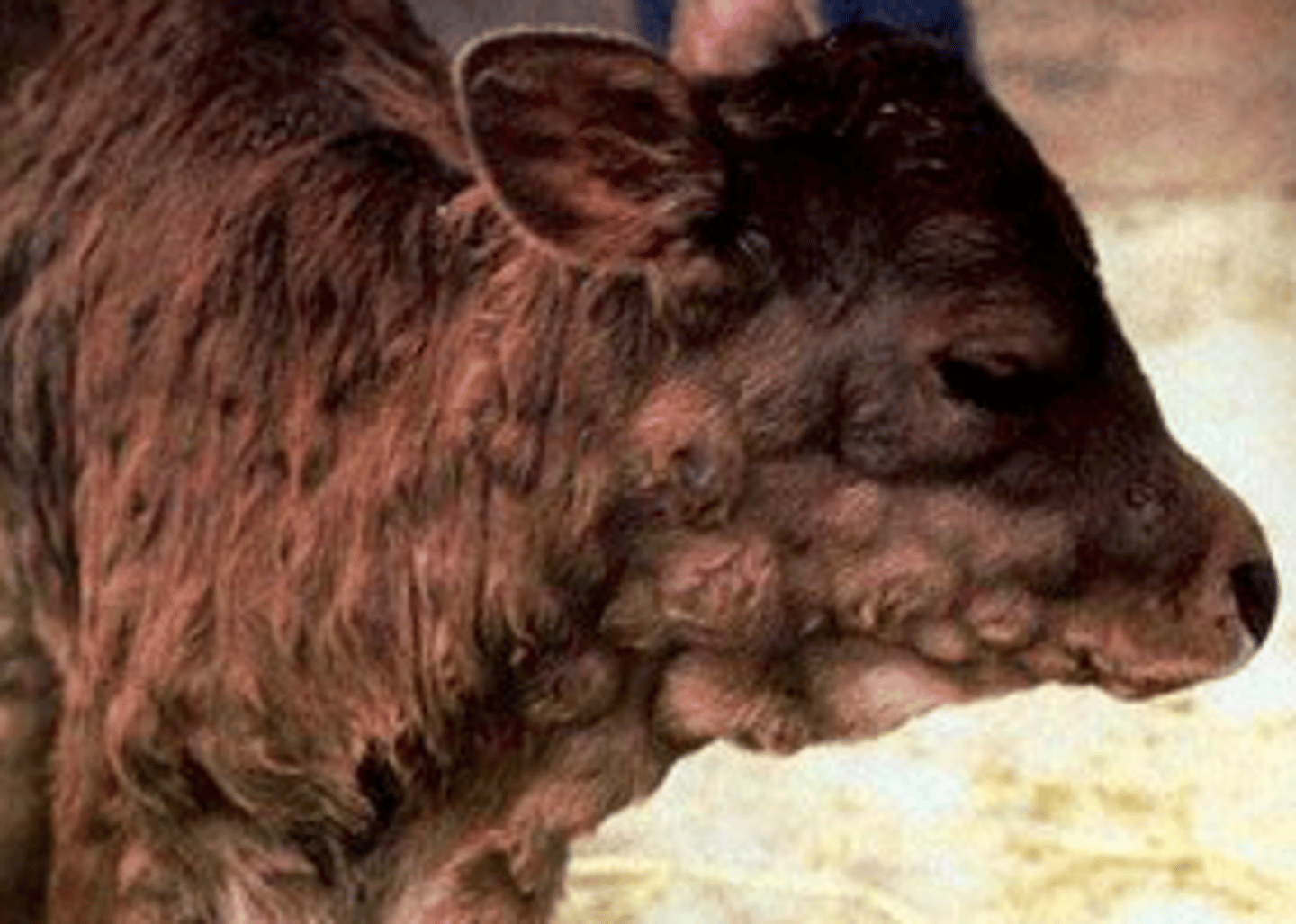

a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
heavy nasal secretions, 100% mortality, bilateral corneal opacities, pneumonia, and low morbidity are signs or characteristics of:
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
d) Pseudorabies (Mad Itch / Aujezsky's disease)
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
this viral disease is acquired from Wildebeest both at calving or by young sheep when stressed (such as food shortage stress) // both are examples of resource partitioning or biological warfare that can kill off competition for resources
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection (Pseduo-Lumpy Skin)
d) Pseudorabies (Mad Itch / Aujezsky's disease)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection
this disease is not an important disease per se, but is important in the differentiation of Lumpy Skin Disease
a) Malignant Catarrhal Fever
b) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
c) Dermopathic Bovine Herpesvirus Infection
d) Pseudorabies
c) Pseudo Lumpy Skin Disease
commonly seen in the fall as an explosive outbreak of teat lesions with spring heifers most severely infected; caused by a BHV2:
a) Pseduo-Cowpox
b) Cowpox
c) Pseudo Lumpy Skin Disease
d) Lumpy Skin Disease
-clinically (but need to differentiate other conditions in the herd)
-virus isolation in cell culture
-electron microscopy
*ulcerated vesicles: you need to be differentiating against Foot-and-Mouth Disease
how do you diagnose BHV2?
Pseudorabies (Mad Itch/Aujeszky's Disease)
-clinical presentation similar to rabies
-acquired through contact with pigs but this virus is now eradicated from domestic pigs in the USA
-clinical signs: self-mutilation // bellowing // look like they're choking // aggression
-no virus excretion at site of self mutilation (hence no transmission)
-virus can be isolated from the brain
-don't typically vaccinate cattle against this virus
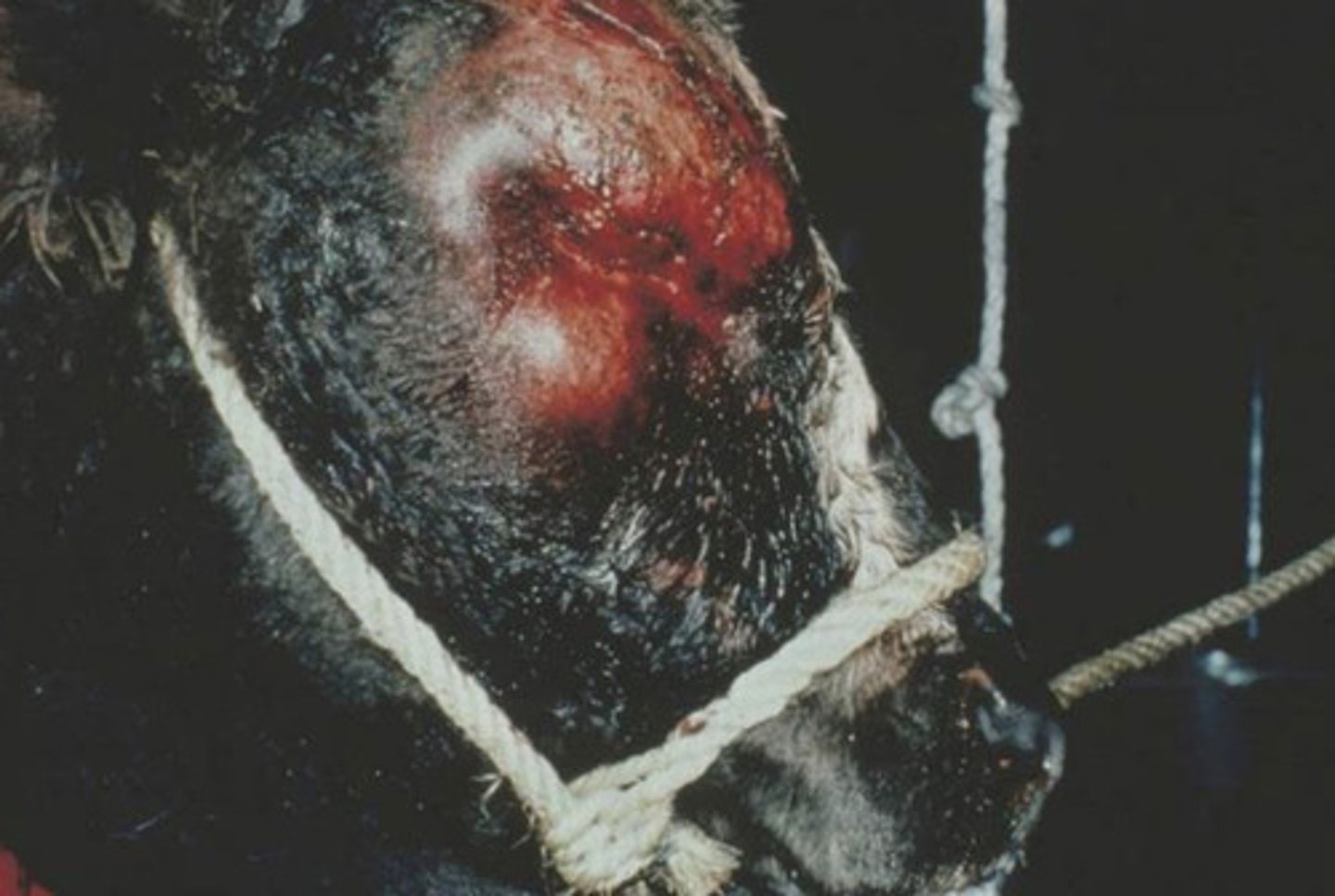
b) Pseudorabies
this disease that can affect cattle is also called "Aujezsky's disease" or "Mad Itch" // it is endemic in USA feral swine populations and then spills over to cattle
a) Rabies
b) Pseudorabies
c) Lumpy Skin Disease
d) Pseudo Lumpy Skin Disease
c) virus is excreted at sites of self mutilation which worsens transmission
*there is no virus excretion, hence no transmission
which of the following is FALSE in regards to Pseduorabies in cows:
a) clinical presentation similar to rabies
b) acquired through contact with feral pigs
c) virus is excreted at sites of self mutilation which worsens transmission
d) the virus can be isolated from the brain, like rabies
Bovine Papillomatosis
-very common infection in young animals and humans
-self healing
-teat warts may need to be removed
-related to bladder cancer with co-carcinogen
-cannot be grown in cell culture
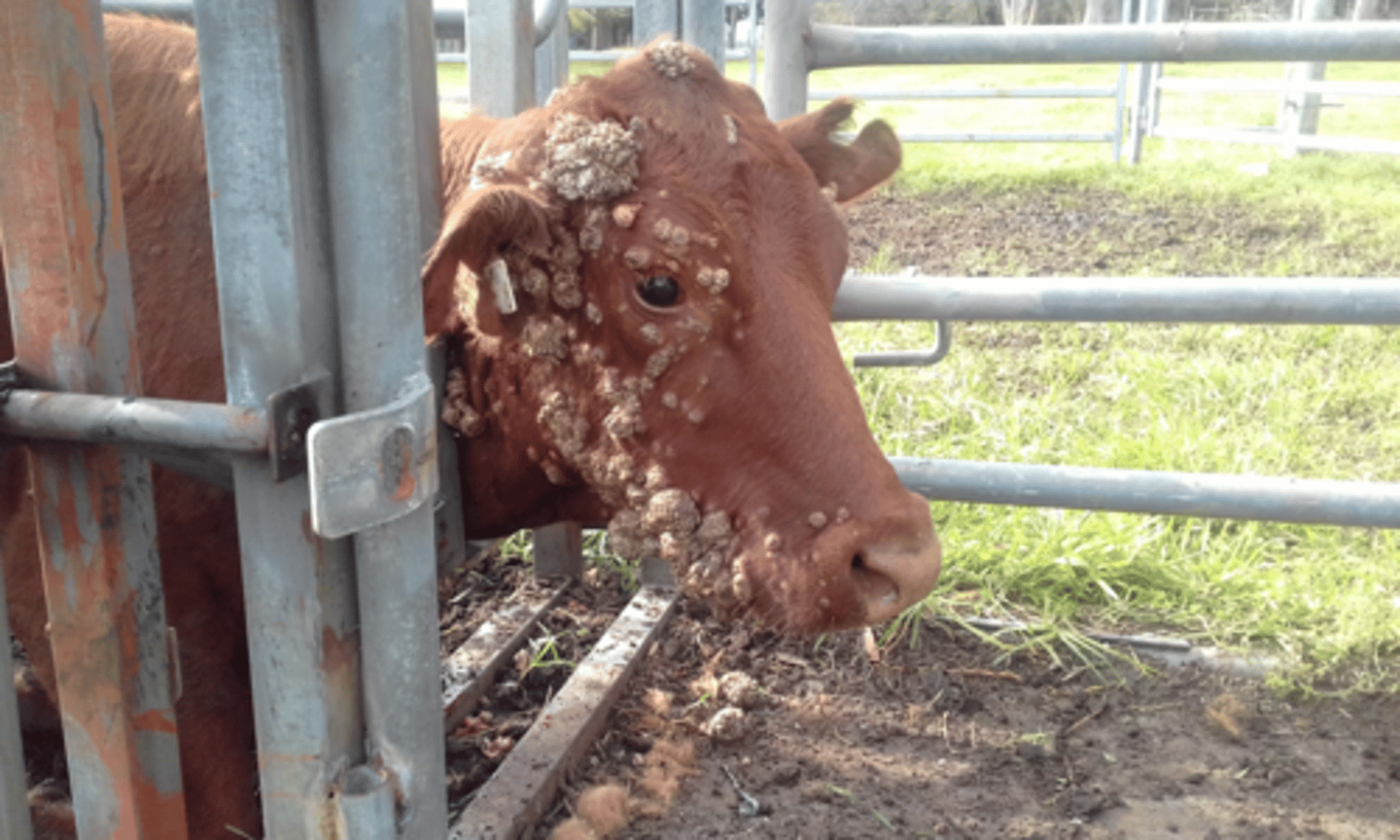

-virus is resistant to environment
-lesions proliferative and some "tumor like"
-no serum antibody response
-chronic infections and do not induce long lasting cellular immunity
-diagnosed by clinical appearance confirmed by electron microscopy or PCR
-virus very difficult to isolate in cell culture
-transmission by contact and fomites
discuss the properties/characteristics of Papillomaviruses
true
t/f: Adenoviruses are not considered of any clinical relevance in cows, and have only been isolated in cases of mild respiratory disease
sarcoids
Bovine Papillomatosis causes _________ in horses
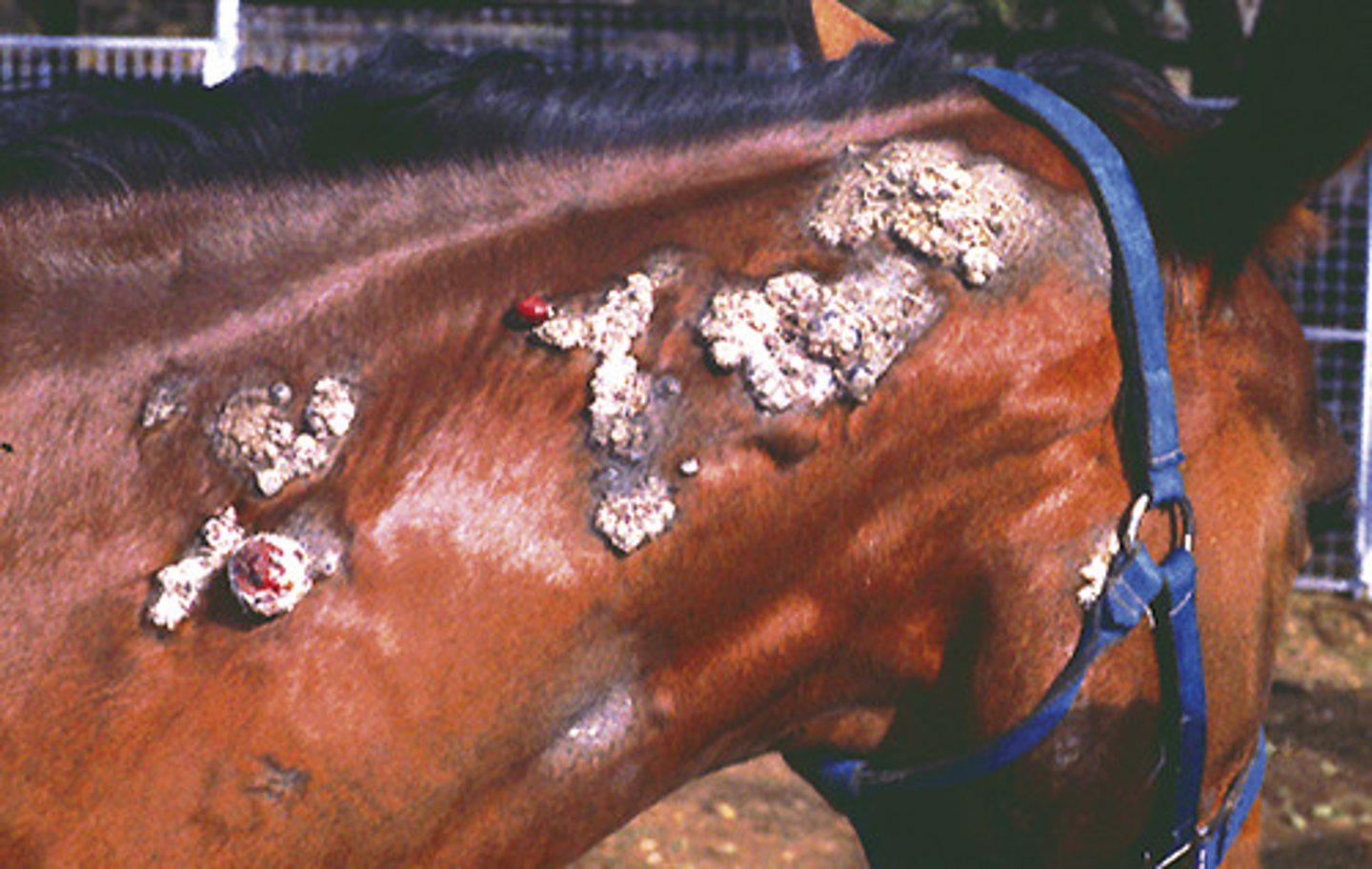
by contact and fomites: curry combs especially
how is Bovine Papillomatosis typically spread?
b) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
*this was the incidental suckling lesions that don't require treatment
which is caused by a Poxvirus?
a) Bovine Papillomatosis
b) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
a) Bovine Papillomatosis
*these are the self-healing warts (although teat ones need removed often) that also cause Sarcoids in Horses
which is caused by a Papovavirus?
a) Bovine Papillomatosis
b) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
Rotaviruses
__________ are a major cause of viral gastroenteritis in young animals
Rotavirus diarrhea
-virus cannot be easily isolated
-diagnosed by EM
-transmission is primarily via the fecal-oral route
-infection results in diarrhea and fever (occasionally abdominal pain)
-severe dehydration due to major loss of fluids and electrolytes
-infections are common in crowded facilities
-no specific treatment available
fluids are given to combat the severe dehydration due to major loss of fluids/electrolytes
there is no specific treatment available for Rotavirus diarrhea in cattle, so how can you "lessen symptoms" per se?
diagnosis by clinical presentation confirmed by ELISA, PCR, or virus isolation
how can you diagnose Paramyxoviruses in cattle?
Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV)
-related to RSV in children
-infections are common in the U.S.
-this virus is present in 38-76% of beef and dairy herds
-lungs appear very wet
-cows can die very quickly
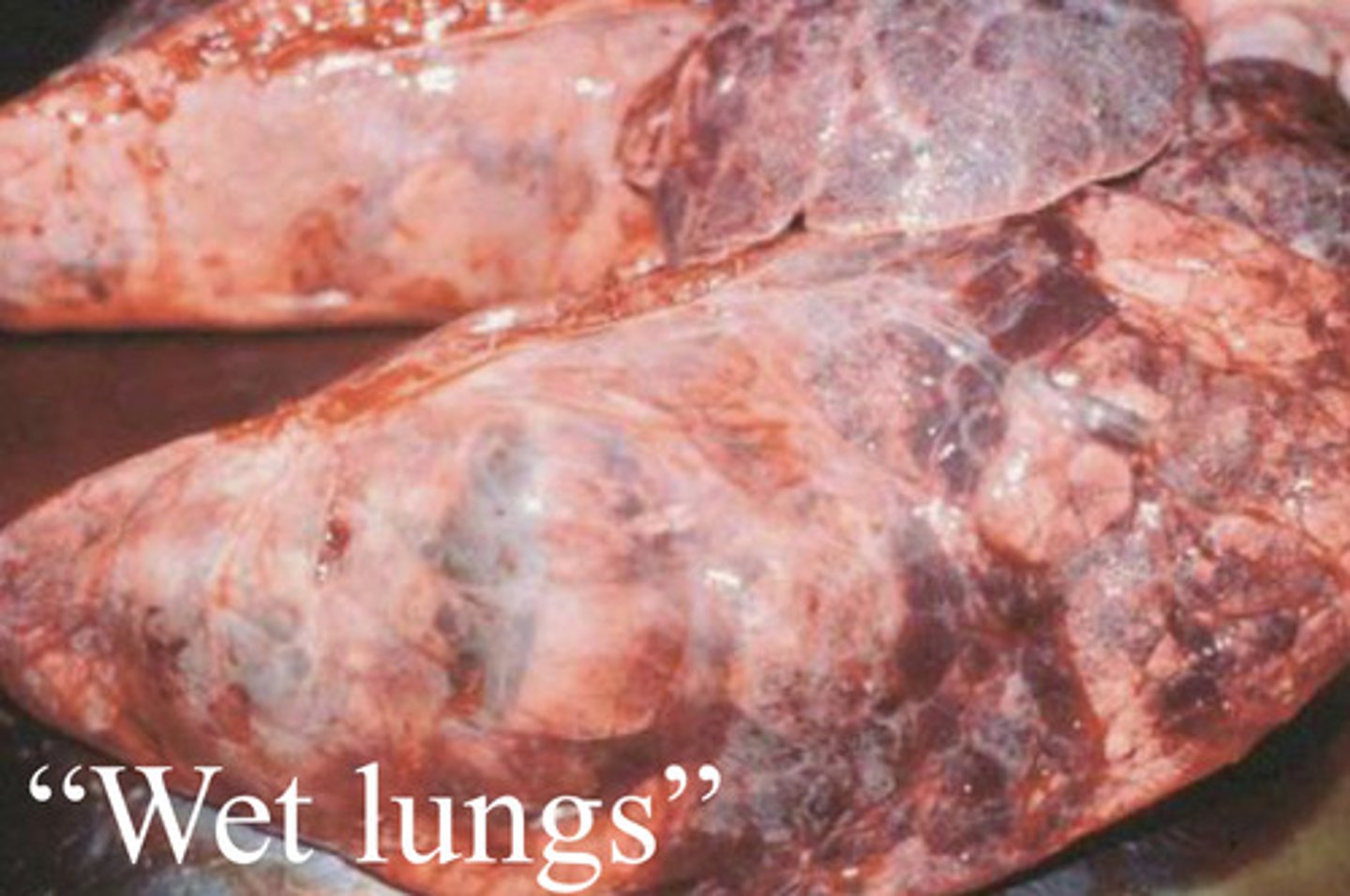
attenuated vaccines are available
talk about the vaccinations against BRSV
-virus is unstable in the environment
-respiratory and systemic clinical presentations
-diagnosis by clinical presentation confirmed by ELISA, PCR, or virus isolation
-transmission by direct contact and droplets
discuss the properties/characteristics of Paramyxoviruses
1. Rabies
2. Vesicular Stomatitis
3. Bovine Ephemeral Fever
disease caused by Rhabdoviruses in cattle (3)
Rabies
-frequent bellowing
-often present as if they have a foreign body in their throat
-signs may be subtle // knuckling over or tail head carried high
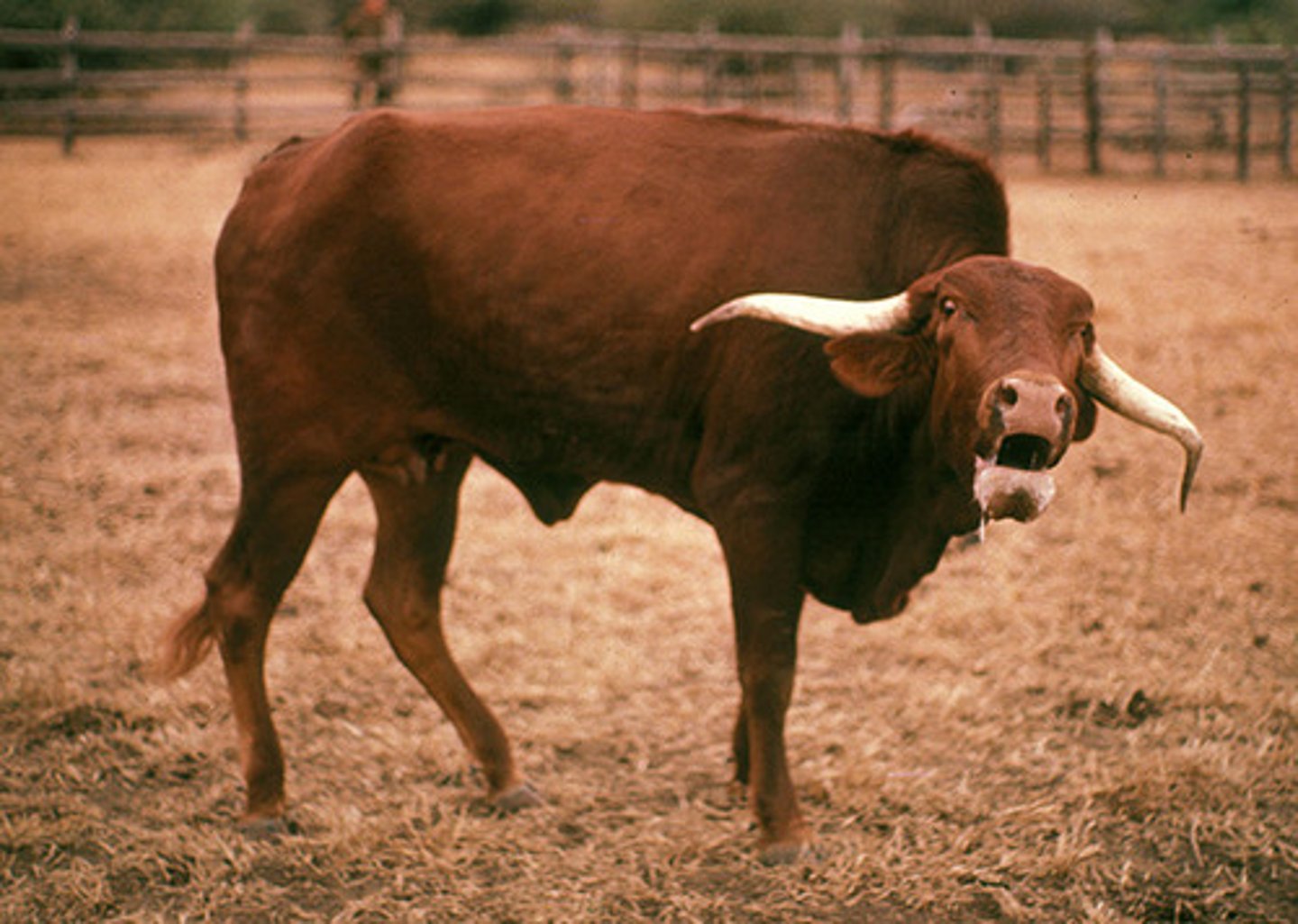

no
is rabies a core vaccine with cows?
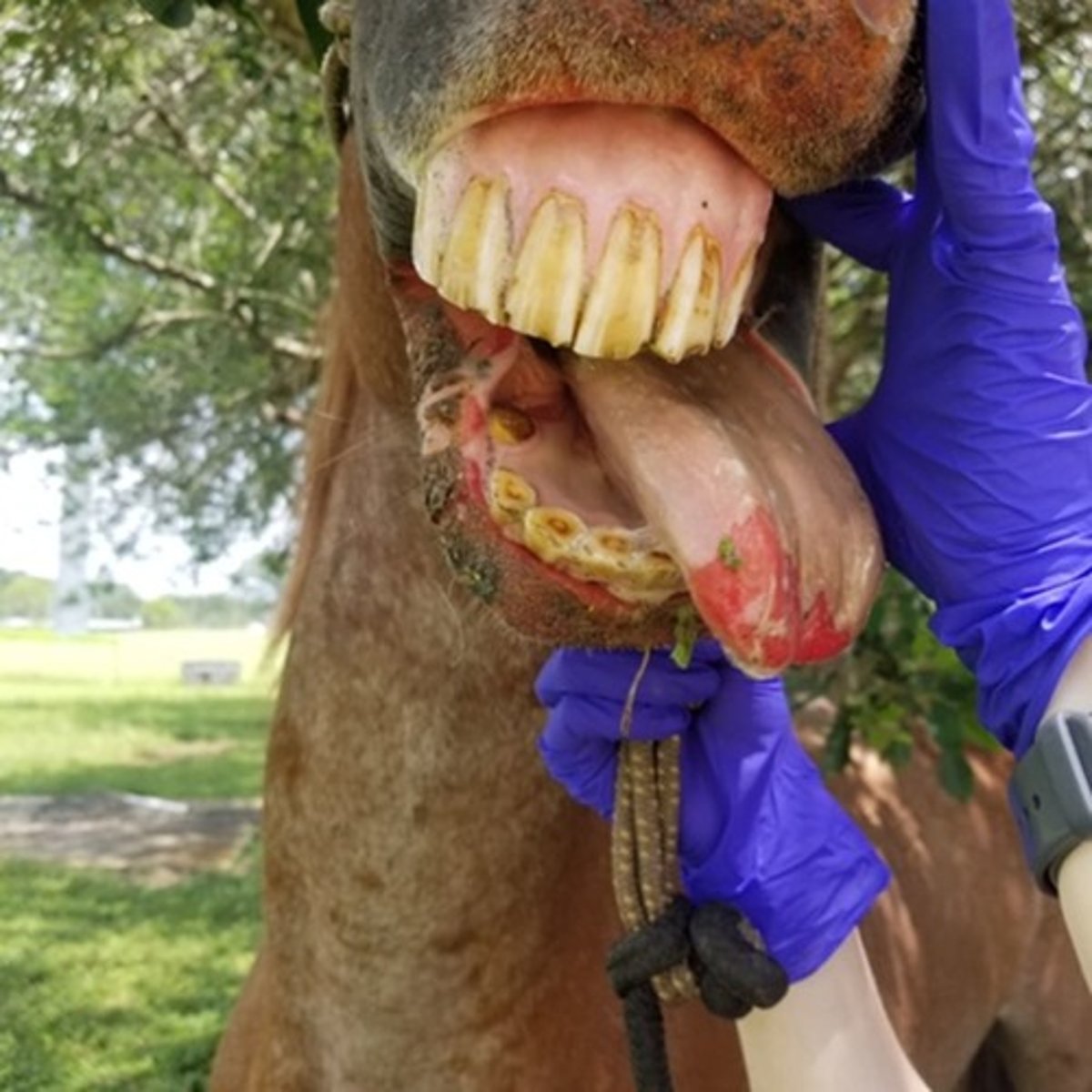
Vesicular Stomatitis
-an important disease "per se" because it may be confused with Foot-and-Mouth Disease
-affects cattle, horses, and pigs
b) the clinical presentation of viral disease is interpreted to diagnose the virus family or species
which is more accurate:
a) the virus's family / phylogenetic relationship tells us what to expect as clinical signs
b) the clinical presentation of viral disease is interpreted to diagnose the virus family or species
a) BVD
which of the following cattle viruses was ranked the most important by Dr. Center's +++ scale?
a) BVD
b) IBR
c) MCF
d) RSV
b) Poxvirus
Bovine Papular Stomatitis is a...
a) Herpesvirus
b) Poxvirus
c) Adenovirus
d) Papovavirus
b) Pseudocowpox
which of the following would you most expect to find in a U.S. cow?
a) Cowpox
b) Pseudocowpox
c) Lumpy Skin Disease
b) Pseudocowpox
Bovine Papular Stomatitis is caused by:
a) Cowpox
b) Pseudocowpox
c) Lumpy Skin Disease
c) Pseudocowpox
"Milker's Nodules" are caused by:
a) BVD
b) BHV
c) Pseudocowpox
d) Bovine Papillomatosis
warts on the teats is characteristic of:
a) Cowpox
b) Pseudocowpox
c) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
d) Bovine Papillomatosis
d) Bovine Papillomatosis
which of the following is a very common infection in young cattle and humans, generally self healing, but can cause sarcoids in horses:
a) Cowpox
b) Pseudocowpox
c) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
d) Bovine Papillomatosis
a) Rotavirus diarrhea
this disease, caused by an RNA virus, is a major cause of viral gastroenteritis in young animals, primarily transmitted fecal orally // the major loss of fluids and electrolytes can be lethal if not given supportive fluids
a) Rotavirus diarrhea
b) Paramyxovirus diarrhea
c) Rhabdovirus diarrhea
d) Bovine Viral Diarrhea
a) Paramyxovirus
Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV or bovine RSV) is a:
a) Paramyxovirus
b) Herpesvirus
c) Poxvirus
d) Adenovirus
b) Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus
this part of the complex of shipping fever is present in 38-76% of beef and dairy herds, may cause severe bronchitis & interstitial pneumonia, and is a paramyxovirus
a) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
b) Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus
b) Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus
multinucleated cells from fused cytoplasm in infected cells is characteristic of:
a) Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
b) Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus
b) RSV
this bovine virus is associated with "Wet Lungs" or interstitial pneumonia and is related to its counterpart in human children
a) IBR
b) RSV
c) IPB
d) IPV
c) Parainfluenza 3 virus
the only thing mentioned about this disease is that it has been known for many years, may be part of "shipping fever" / BRD but it has not been established, and that there are multivalent vaccines against shipping fever that include protection against this too
a) IBR
b) RSV
c) Parainfluenza 3 virus
c) Rhabdovirus
Rabies is caused by a:
a) Paramyxovirus
b) Herpesvirus
c) Rhabdovirus
d) Adenovirus
a) Rabies
this disease is caused by a rhabdovirus and its signs include frequent bellowing, presenting like a choke, and carrying the tail head high
a) Rabies
b) Pseudorabies
c) Vesicular Stomatitis
Lumpy Skin = Pox
Pseduo-Lumpy Skin = Herpes (BHV2)
Lumpy Skin vs. Pseduo Lumpy Skin
what type of virus?
Rabies = Rhabdovirus
Pseduorabies = Herpes (Suid Herpesvirus 1)
Rabies vs. Pseudorabies
what type of virus?
both are pox viruses
*Cowpox is a foreign disease
Cowpox vs. Psuedocowpox
what type of virus?
c) Vampire Bats as a vector
increased occurrence of rabies in Central & South America is thought to be tied to:
a) Political Sabotage
b) Different Serotypes
c) Vampire Bats as a vector
d) Shipping practices
b) Bovine Vesicular Stomatitis
this disease is caused by a rhabdovirus and is important in that it may be confused with Foot-and-Mouth disease:
a) Bovine Papular Stomatitis
b) Bovine Vesicular Stomatitis
c) Bovine Syncytial Virus
d) Blue Tongue
BVS = Rhabdovirus
FMD = Picornovirus
Bovine Vesicular Stomatitis should be differentiated from FMD
what type of virus causes each?