Practice Question Set 9 Meiosis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the costs and benefits of sexual versus asexual reproduction?
Sexual: more variation but slower and needs two parents.
Asexual: faster, one parent needed, but no variation.
Asexual reproduction results in identical offspring unless which occurs?
a. Natural selection
b. Cloning
c. Crossing over
d. Mutation
e. Environmental change
d. Mutation
What is a “gene”? What is an allele?
Gene: a piece of DNA for a trait.
Allele: a different version of a gene.
What is meant by “homologous” chromosomes? What is a tetrad?
Homologous: same size and genes, one from each parent, but different allels.
Tetrad: 2 homologous chromosomes paired up.
Sex chromosomes are:
a. completely different between the two sexes.
b. partially homologous but also have unique regions.
c. found only in males.
d. unable to line up properly at the metaphase plate.
e. completely homologous but always have different alleles.
b. Partially homologous but also have unique regions.
Define diploid and haploid. Will meiosis necessarily lead to haploid gametes?
Diploid: two sets of chromosomes.
Haploid: one set.
Meiosis usually makes haploid gametes.
If a diploid cell has DNA content x in G1, what is it at anaphase of meiosis I?
a. 0.25x b. 0.5x c. x d. 2x e4x
d. 2x
What is synapsis?
Homologous chromosomes pair up.
What is the synaptonemal complex?
A protein structure that helps chromosomes stick together during synapsis.
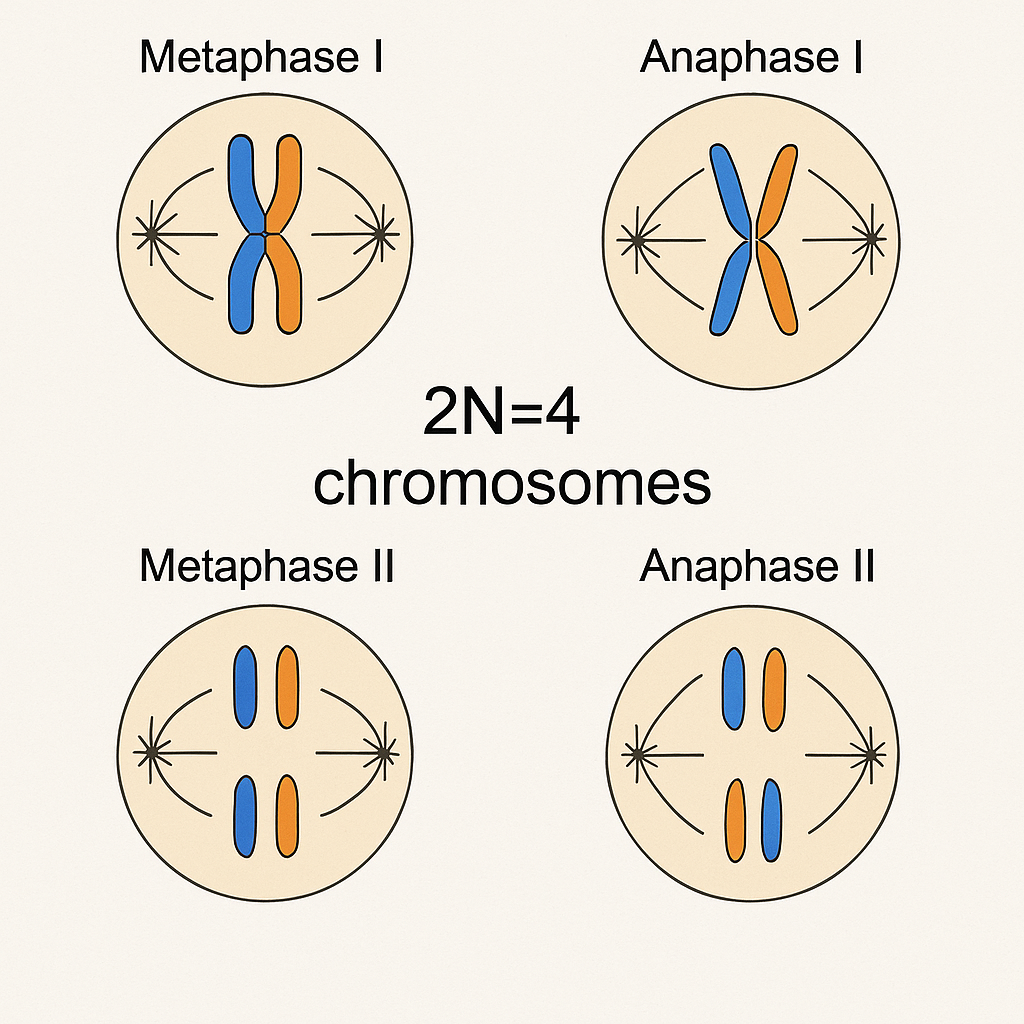
Draw 2N=4 chromosomes during Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Metaphase II, and Anaphase II.
Why is there no DNA replication between Meiosis I and II?
DNA is already copied before meiosis starts.
How many duplicated chromosomes in Metaphase I and Anaphase I? How many chromosomes in Metaphase II and Anaphase II?
Metaphase I: 4 duplicated chromosomes.
Anaphase I: 2 duplicated chromosomes per cell.
Metaphase II: 2 duplicated chromosomes.
Anaphase II: 2 single chromosomes per cell.
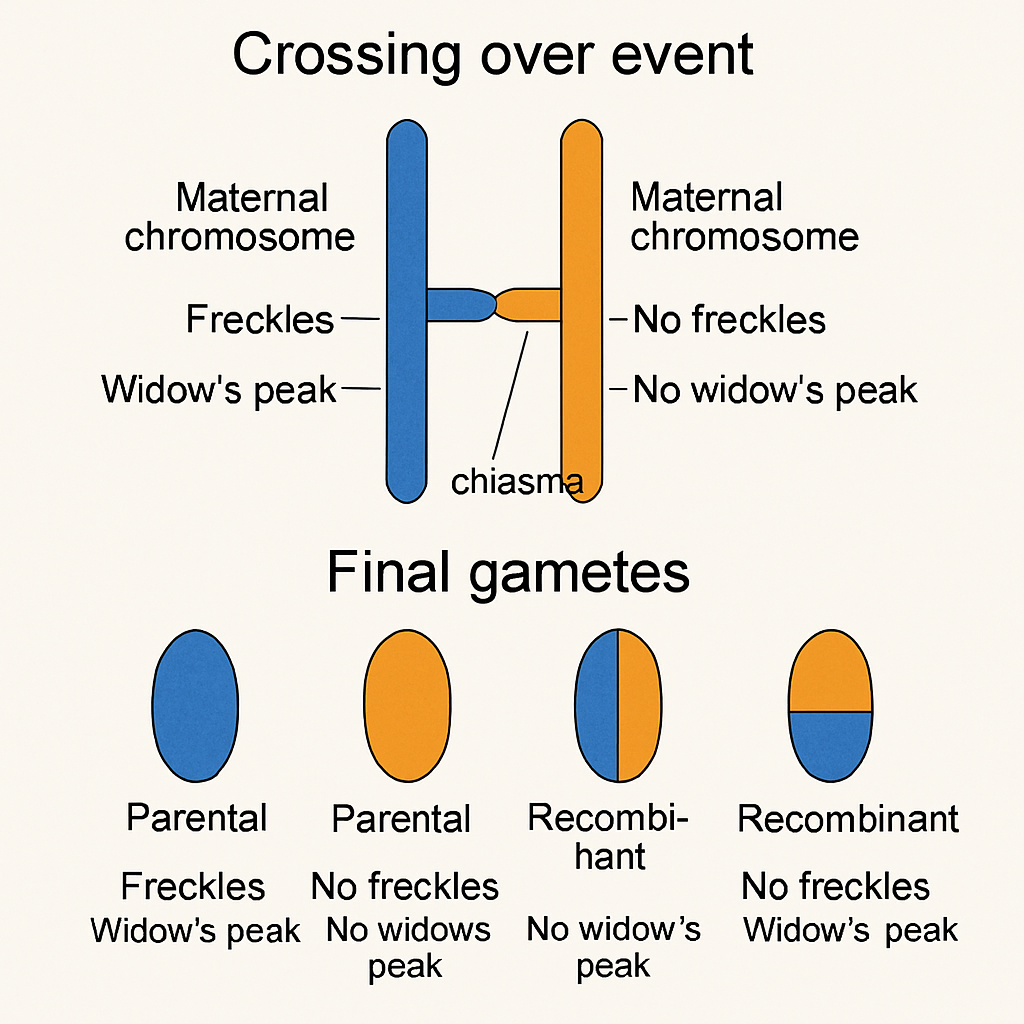
Briefly describe the function of the recombination nodule.
Helps crossing over happen between chromosomes.
Draw one crossing over event and final gametes (freckles and widow's peak genes).
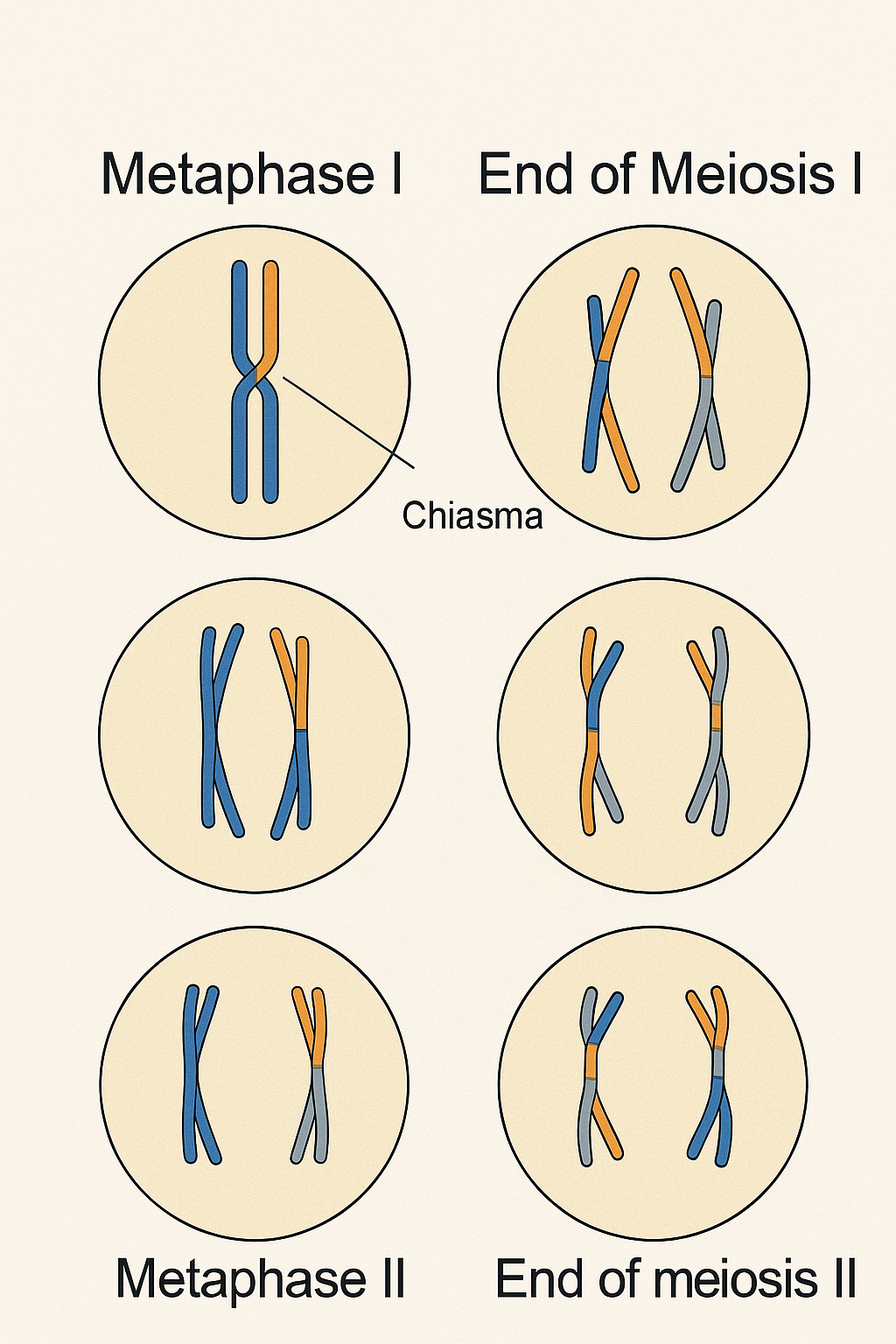
Be able to draw the cells in metaphase I, at the end of meiosis I, metaphase II, and at the end of meiosis II. Do the same for N=3
During what stages of meiosis are tetrads present?
Prophase I and Metaphase I.
What are the unique events in Meiosis I that lead to variation in gametes?
Crossing over and independent assortment.
An organism has 2N=16 chromosomes. How many different gamete types?
2⁸ = 256 types.
Why are garden peas good model organisms for genetics?
Easy to grow, reproduce fast, and have simple traits.
Define a gene, an allele, and a locus.
Gene: DNA code for a trait.
Allele: version of a gene from a mutation.
Locus: location of a gene.
What are the commonalities among the 7 characters Mendel studied?
Each had two clear traits, and one trait dominated.
What are Mendel’s four concepts and additional law?
Genes exist in pairs.
One allele is dominant.
Alleles separate during gamete formation.
Law of Segregation.
For two characters: Law of Independent Assortment.
How does Meiosis explain segregation?
Homologous chromosomes (and their alleles) separate in Meiosis I.
When crossing homozygous recessive × heterozygote, chance of homozygous recessive offspring?
50%.
Two straight hairline parents. Chances of a child with widow’s peak?
0% — both parents have no widow's peak allele.
Freckles dominant. Child has freckles. Mother has no freckles. Possible father genotypes?
Must be Ff (heterozygous).
Define genotype and phenotype.
Genotype: the genetic makeup.
Phenotype: the physical appearance.
How many unique gametes from AaBbCCDdEe?
16 types. (count the amount of hetero and then 2 to that power)