Ap World Unit 8 review
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Tiananmen Square
Beginning and end of democracy in China
Leader of China cut off all western media and suppressed demonstrations of western culture
Nationalist movements in Africa and Asia
Decolonization
after britain and france lost strength after war, Russia helped other rise up with weapons, america came with food, they sided with russia
WWII and Communism- relationship
WWII facilitated the spread of communism
Scenes of genocide in 20th century
Armenian genocide WWI by turks, holocost, bosnian,
Gandhi’s goal
To achieve indian independence from britain
Ghandi’s method
Satyagraha- no violence, would do nothing until their goal was reached
Satyagraha
steadfastness in truth
WWI epidemic
Spanish Flu
Appeasement
thought that giving him what he wants will stop it, but leads to a consequence
Who is appeasement associated with?
Hitler
Partition of India- cause
Prompted by demand for separate muslim homeland,
What did the partition of India split India into?
india (muslim) and pakistan (hindu)
Marshall plan
US bringing supplies to Europe to rebuild after WWII
What was the purpose of the marshall plan
to prevent communism in weakened countries
Economic competition to the West
China
How did world wars affect the status of women?
Enhanced value and status
Let them join the workforce, increased independence, feminism rise
Latin American antagonists to US
Cuba, allied w russia and had large military
Nicaragua
Soviet Leaders (order)
Lenin, Stalin, Khrushchev, Brezhnev, Andropov, Chernenko, Mikhail Gorbachev
International migration
From global south to global north +australia and new zealand
When did the Soviet Union fall
1991
Suffrage
Right to vote
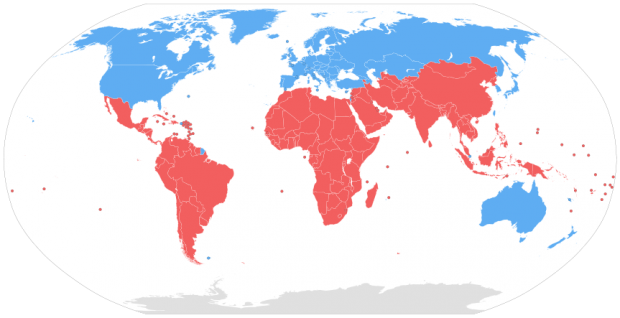
Global South
Central and South America, Africa, Asia and Oceania
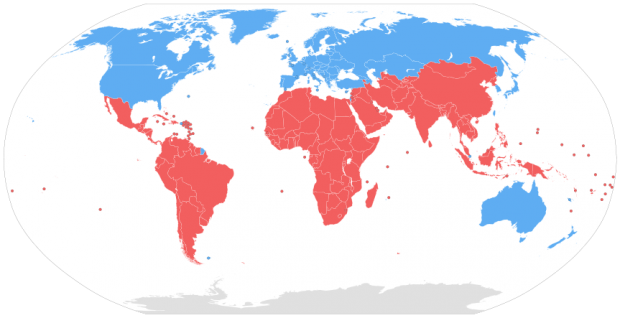
Global North
North America, Europe, and parts of East Asia
Socialism vs. communism
socialism was less severe version of communism
socialism allowed private property and control of own labor
Perestroika
Reforming economy
Glasknost
Transparency in government
what was the purpose of perestroika and glasnost
Mikhail Gorbachev way of reforming soviet union back into russia
Comintern
Advocated/ spread communism
Globalization
increased interconnection of people around the world as technology advances
What technology advanced globalization
internet, social media, and transportation, free market policy,
Major reforms
Civil right, feminism, and environmental
Free market policies
economic system with limited government interference, reduced trade barriers