Mass Spec Fragmentation Patterns
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
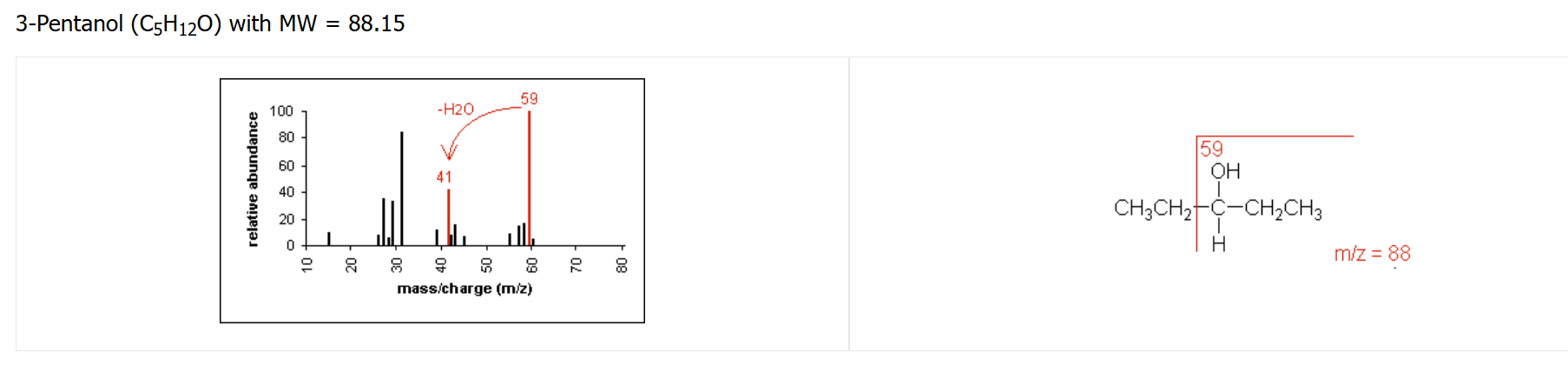
alcohol fragmentation pattern
cleavage of C-C bond next to C-OH
loss of H₂O may also occur
aldehyde fragmentation pattern
cleavage of H off of carbonyl results in molecular ion -1 peaks
cleavage of C-OH results in molecular ion -29 peaks

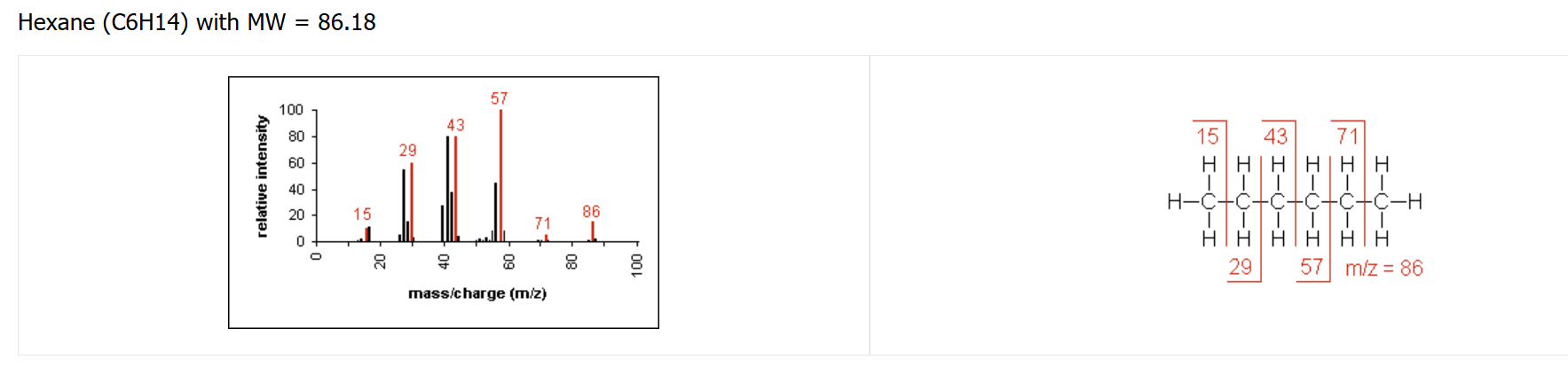
alkane fragmentation pattern
contains clusters of peaks 14 mass units apart, representing the loss of CH₂
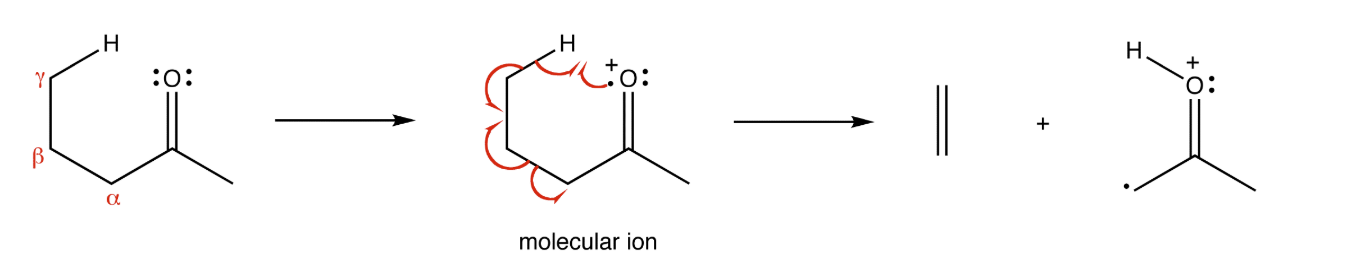
McLafferty rearrangement
gamma hydrogen attacks carbonyl
amide fragmentation pattern
can show in the base beak due to McLafferty rearrangement
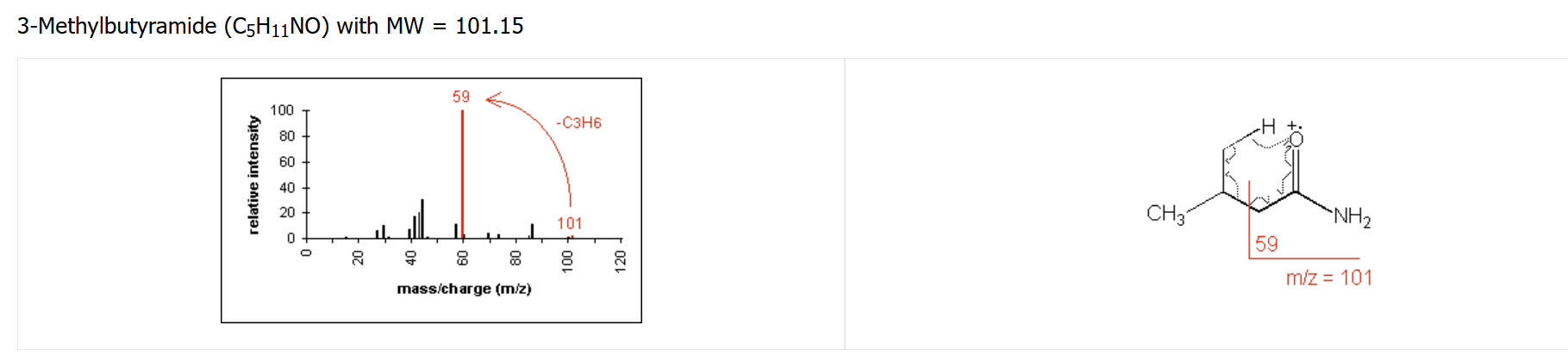
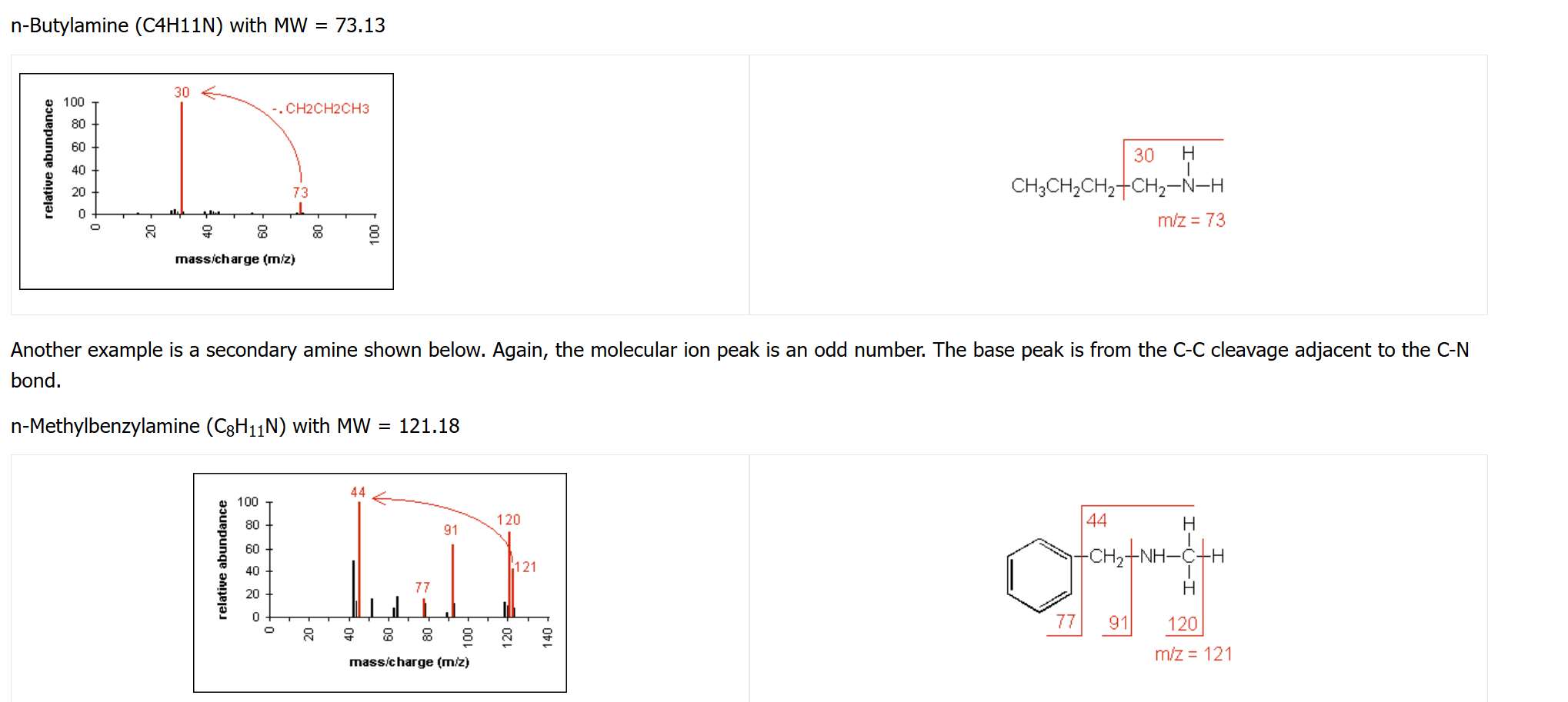
amine fragmentation pattern
molecular ion peak will be odd number (if only one amine is present)
for aliphatic amines, cleavage at the alpha carbon often occurs
aromatic fragmentation pattern
ring structure peaks are strong

carboxylic acid fragmentation pattern
for short chain acids, peaks due to the loss of OH (molecular ion -17) and COOH (molecular ion -45) are prominent due to cleavage of bonds next to C=O

ester fragmentation pattern
bond cleavage next to carbonyl

ether fragmentation pattern
tend to occur at alpha carbon from oxygen

halide fragmentation pattern
halogens will cleave off to form recognizable peaks
be careful of multiple isotopes

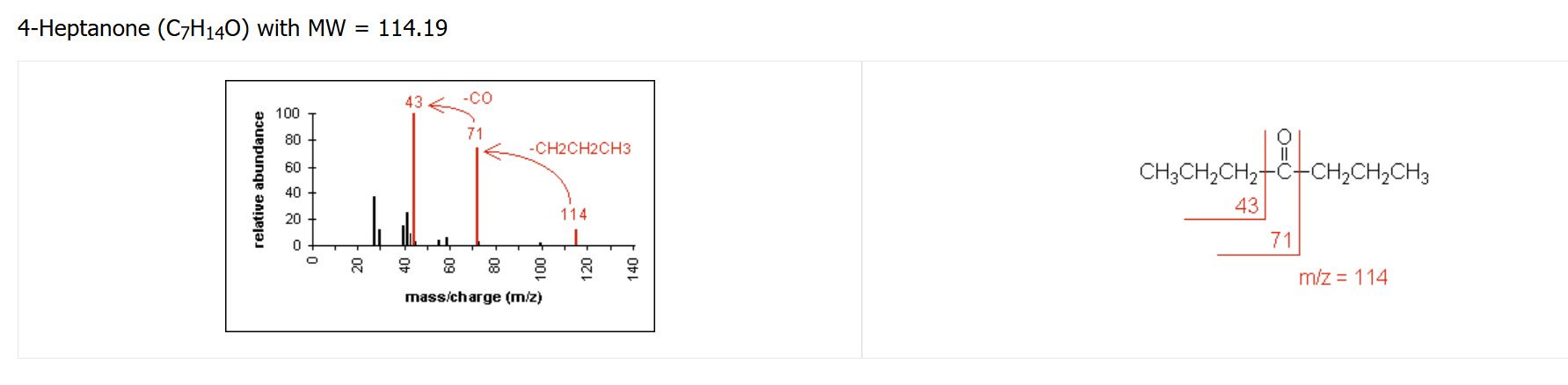
ketone fragmentation pattern
Major fragmentation peaks result from cleavage of the C-C bonds adjacent to the carbonyl