D1.1 DNA replication
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is DNA replication?
When new strands of DNA are made from existing DNA
What may DNA replication be useful for?
For reproduction - the DNA has to be passed on from parents to offspring
For growth and tissue replacement - the DNA has to be in each cell before it splits
What does it mean that DNA is semi-conservative?
Half of the DNA is conserved, and the new half is added onto it
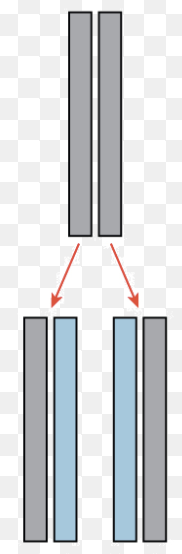
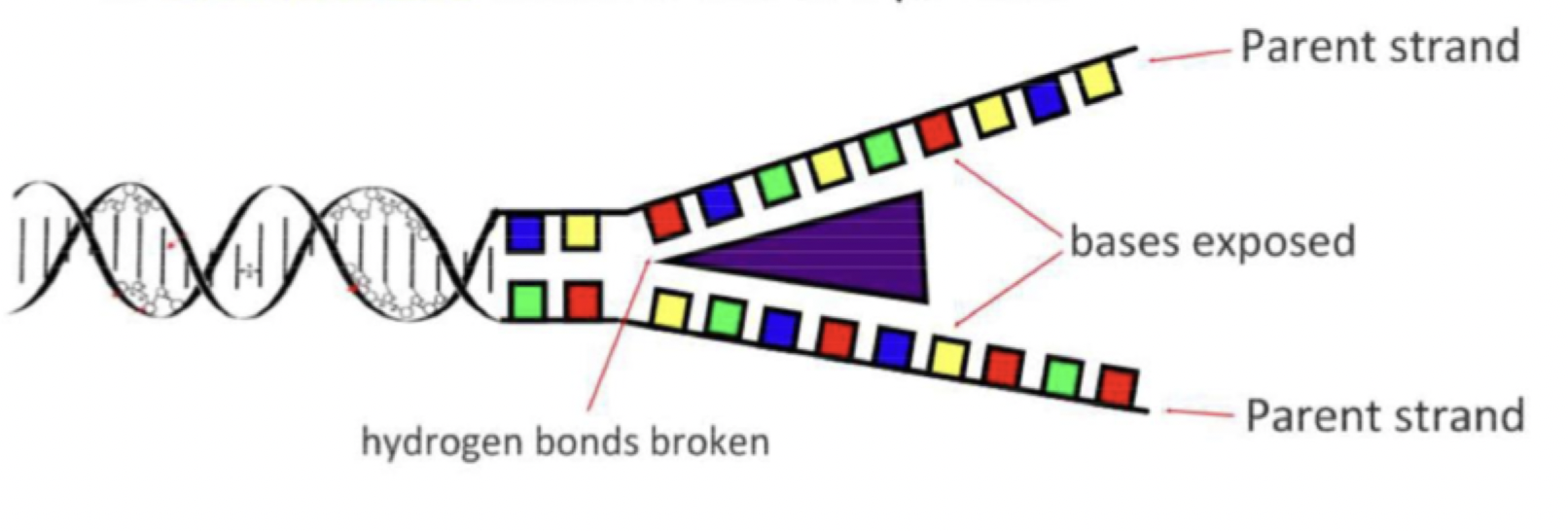
How is the DNA split into two strands?
The enzyme Helicase unwinds and separates the 2 strands, by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. Helicase uses ATP to get the energy to break the hydrogen bonds
How are the complementary strands for each DNA strand created?
The enzyme DNA polymerase runs in opposite directions on each strand and collects free nucleotides in order to pair them with their complementary bases
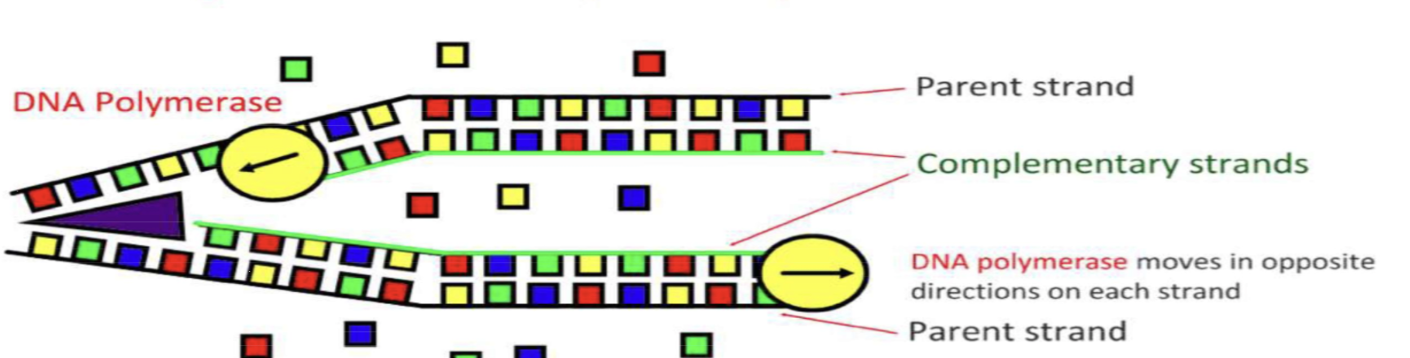
The free nucleotides are nucleotide triphosphates. Where do the extra two phosphates go?
The breakdown of the two phosphates releases energy which is used to form covalent bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone
What is the polymerase chain reaction?
It is an artificial way to replicate DNA if you only have a small sample of DNA at a crime scene. Instead of just normal DNA polymerase, taq polymerase is used to create the new DNA strands, as this is heat resistant
How does it work?
DNA is separated into 2 strands by heating it up in order to break the hydrogen bonds between base pairs. Then it is cooled down, allowing primers (short fragments of DNA) to attach. Then taq DNA polymerase (heat resistant polymerase) copies the strands at a much quicker pace.
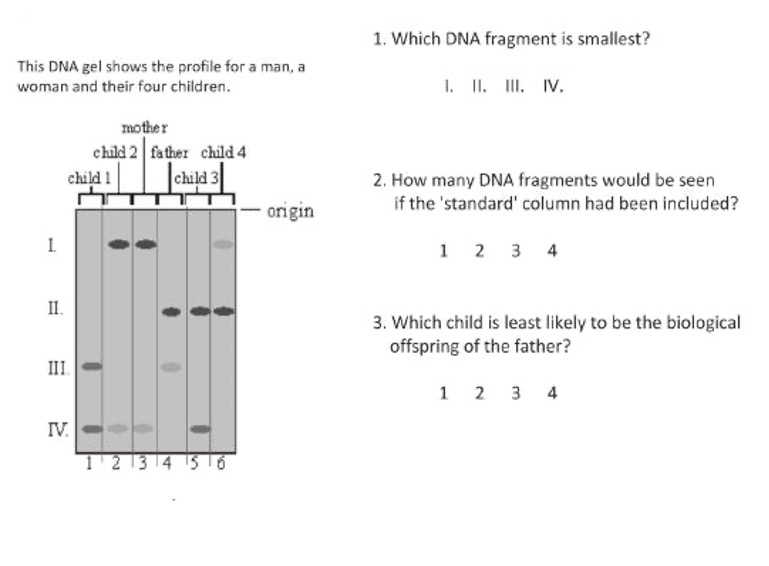
How can DNA sequences be visualized?
Through Gel electrophoresis.
How does gel electrophoresis work?
DNA is cut into fragments of various lengths. These are placed in a gel box in which a current runs through. One side is negative and the other is positive. As DNA is negative, it is attracted to the positive side. These fragments will move through the gel based on their size and charge. The smallest fragments and the most charged fragments travel the furthest
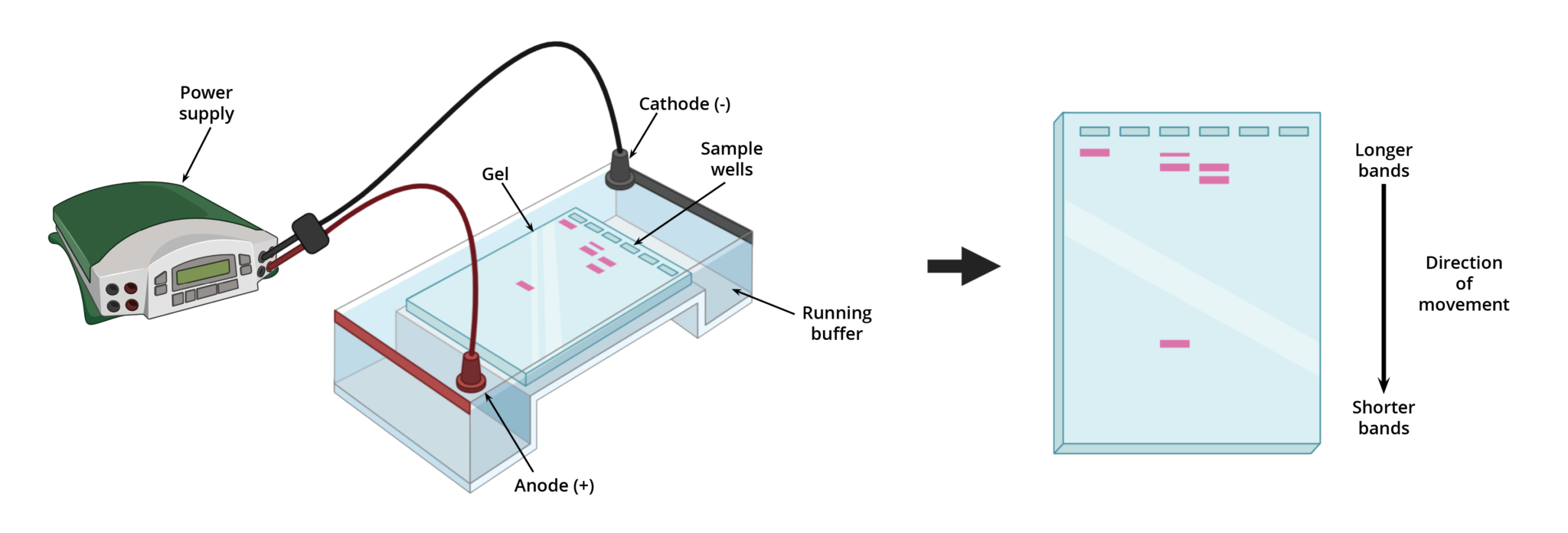
What are the polymerase chain reaction and gel electrophoresis used for?
Corona virus testing (this is very expensive though, but it work well as it is sensitive) and DNA profiling (identifying family members in DNA with small DNA sample)
DNA Profiling
You should be able to answer DNA profiling questions