midterm 2 bio 97
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
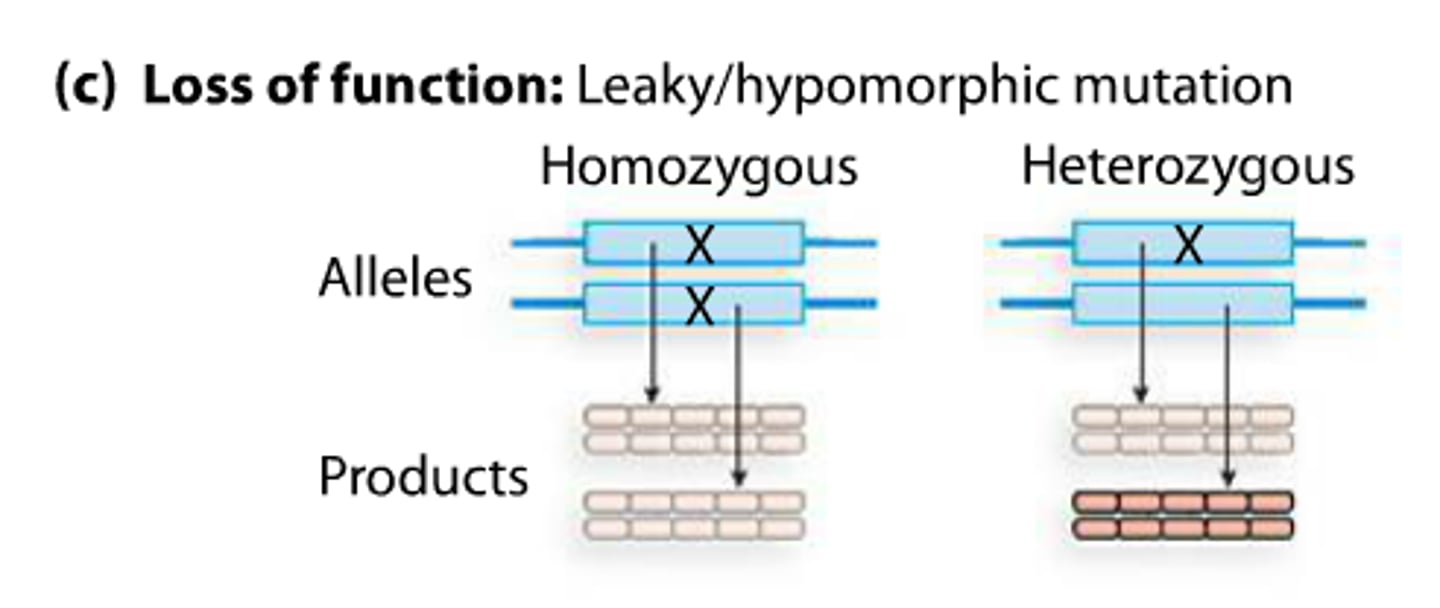
hypomorphic
Refers to a mutation that reduces but does not eliminate the activity of a particular gene product.
loss of function type of mutation
Make less of a gene product
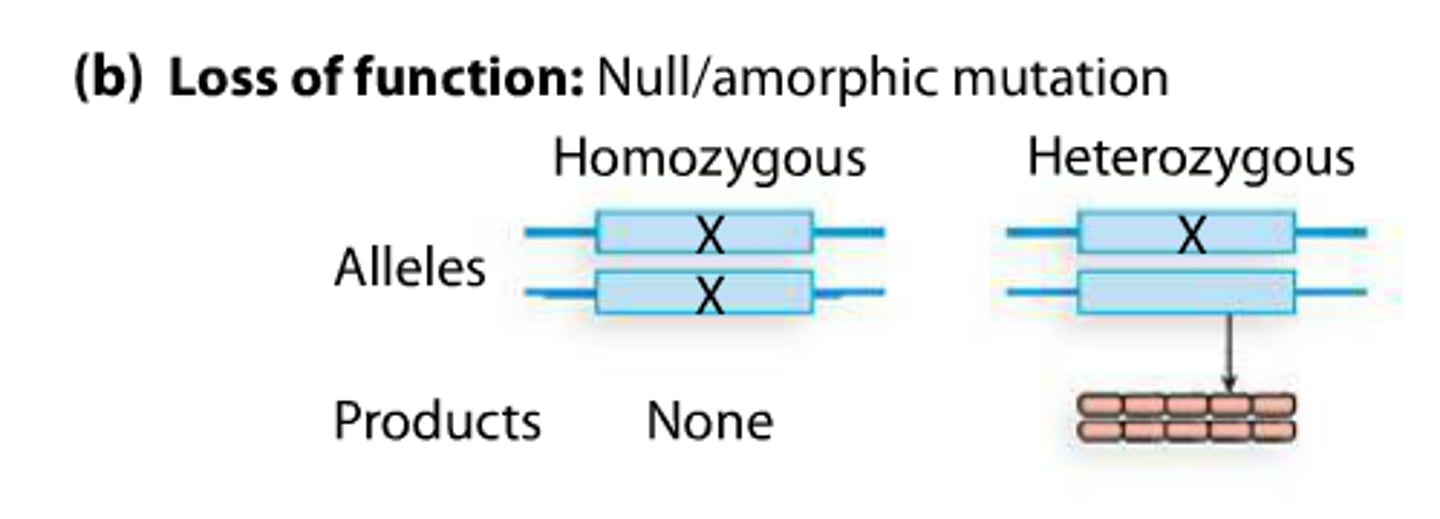
null or amorphic mutation
null alleles produce no functional product
loss of function type of mutation
Or nothing at all
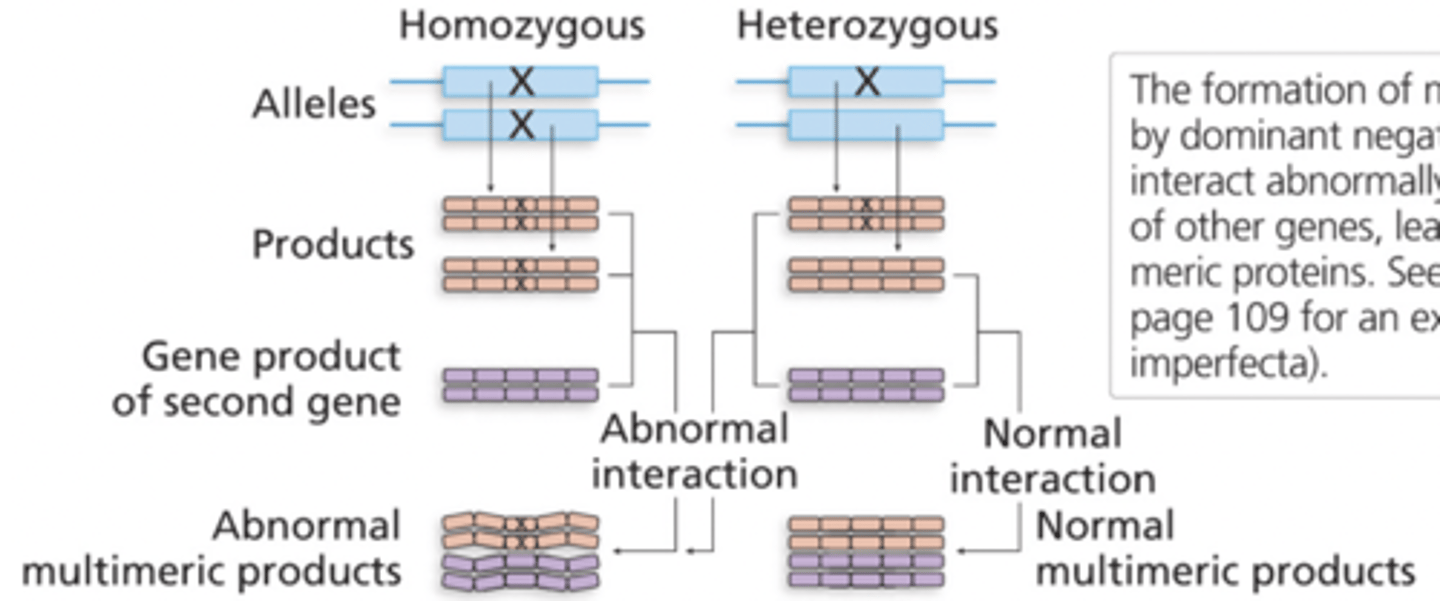
dominant negative mutation
A heterozygote produces a nonfunctional altered protein that also prevents the normal gene product from functioning
loss of function mutation
One copy of a disfunctional allele can destruct the other ones
characterized as negative due to the spoiler effect of the abnormal polypeptide on the multimeric protein
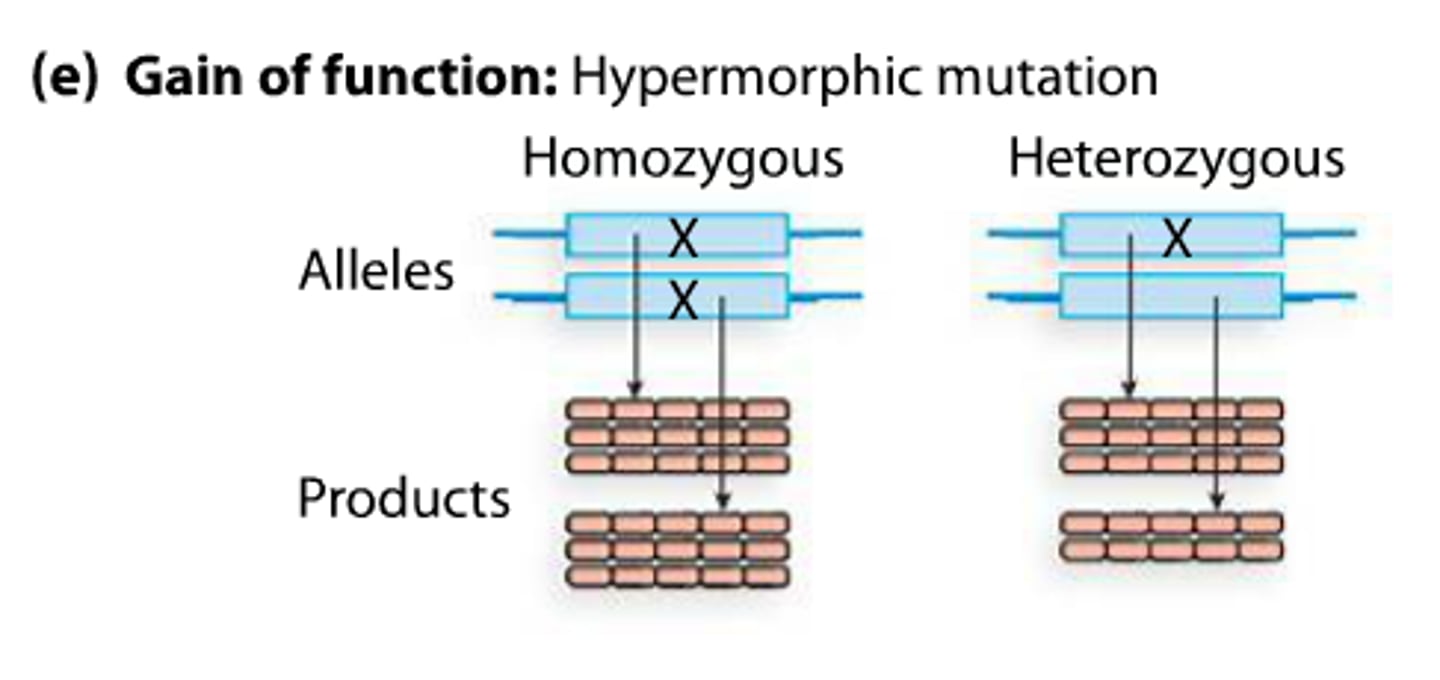
hypermorphic mutation
enhanced gene function (protein functions more efficiently)
-extremely rare
-usually dominant
gain of function mutation
Make more of a gene product
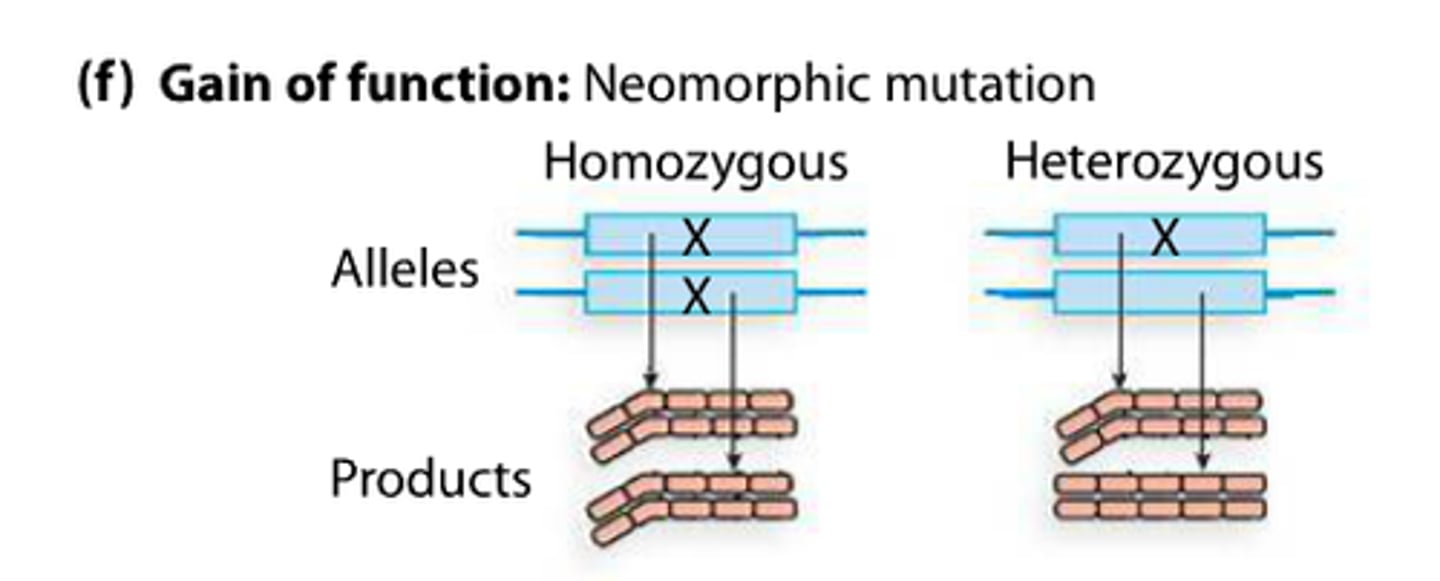
neomorphic mutation
a mutant expressing a new or novel function not seen in the wild type
gain of function mutation
Like insulin being produced in your toe
nonpenetrant
the phenotype is not consistent with the genotype
Sometimes an organism with a particular genotype fails to produce the corresponding phenotype
healthy individuals who are heterozygous for diseased mutations
penetrant
when the phenotype is consistent with the genotype
Showing the disease
haplosufficient
describes a gene that, in a diploid cell, can promote wild-type function in only one copy (dose)
1 copy is enough
haploinsufficient
when a single copy of a gene is not sufficient to produce a wild-type phenotype
a single copy of an allele is not enough to be healthy
incomplete penetrance
indicates that less than 100% of individuals with a mutant genotype have the mutant phenotype.
traits that are nonpenetrant in some individuals are characterized as displaying __________
e.g. polydactyly (many digits)
variable expressivity
indicates that the severity of a mutant phenotype differs among individuals with the same mutant genotype.
Epistasis
2+ genes have control over one trait
when it's NOT a 9:3:3:1 ratio
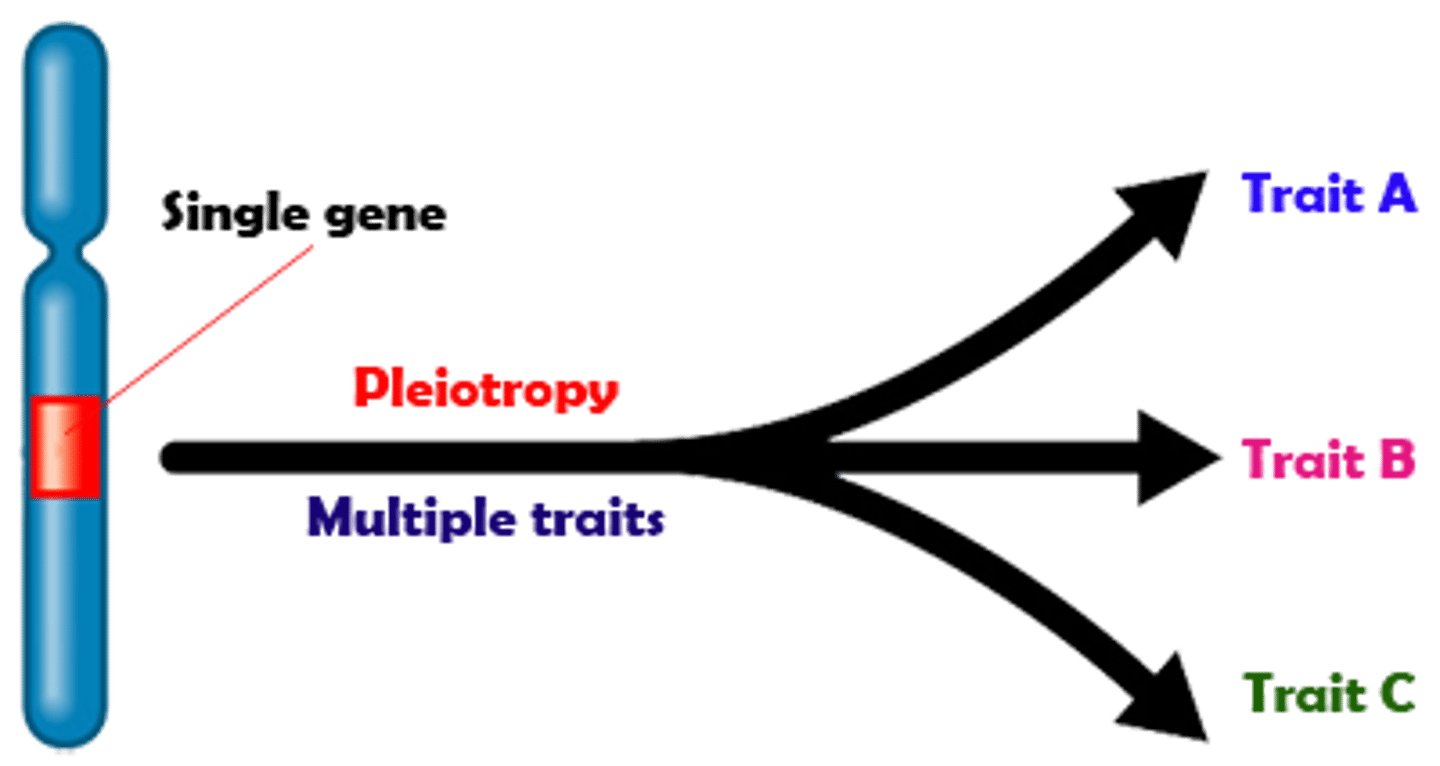
Pleiotropy
1 gene has control over many traits
somatic cells
cells in the body other than sperm or egg cells
totipotent cells
Stem cells with the potential to differentiate into any type of cell.
Pluripotent
Able to give rise to multiple, but not all, cell types.
differentiated cells
a cell is no longer able to differentiate into any type of tissue
hox genes
Class of homeotic genes. Changes in these genes can have a profound impact on morphology.
hox genes are a subset of homeobox genes which only regulate the formation of axes and appendages in organisms.
homeobox
homeobox genes are mainly involved in the regulation of the entire morphogenesis process, while hox genes are a subset of homeobox genes which only regulate the formation of axes and appendages in organisms.
Antennapedia complex
Cluster of five homeotic genes in fruit flies that affects the development of the adult fly's head and anterior thoracic segments.
bithorax complex
cluster of homeotic genes in Drosophila that control development of structures in the thorax & abdomen of the embryo
homeodomain
A conserved sequence of 60 amino acids used in the binding to DNA. Usually found in transcription factors, it is used to express genes that are related, more specifically in development to make tissues associated with one another.
the part of the protein that attaches (binds) to specific regulatory regions of the target genes
Complementation
Two different mutations in the heterozygous condition are exhibited as the wild-type phenotype; indicates that the mutations are at different loci.
testcross
cross between an organism with an unknown genotype and an organism with a recessive phenotype
1:1:1:1
aabb x ?
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
AaBb x AaBb
can only see epistasis in a _______
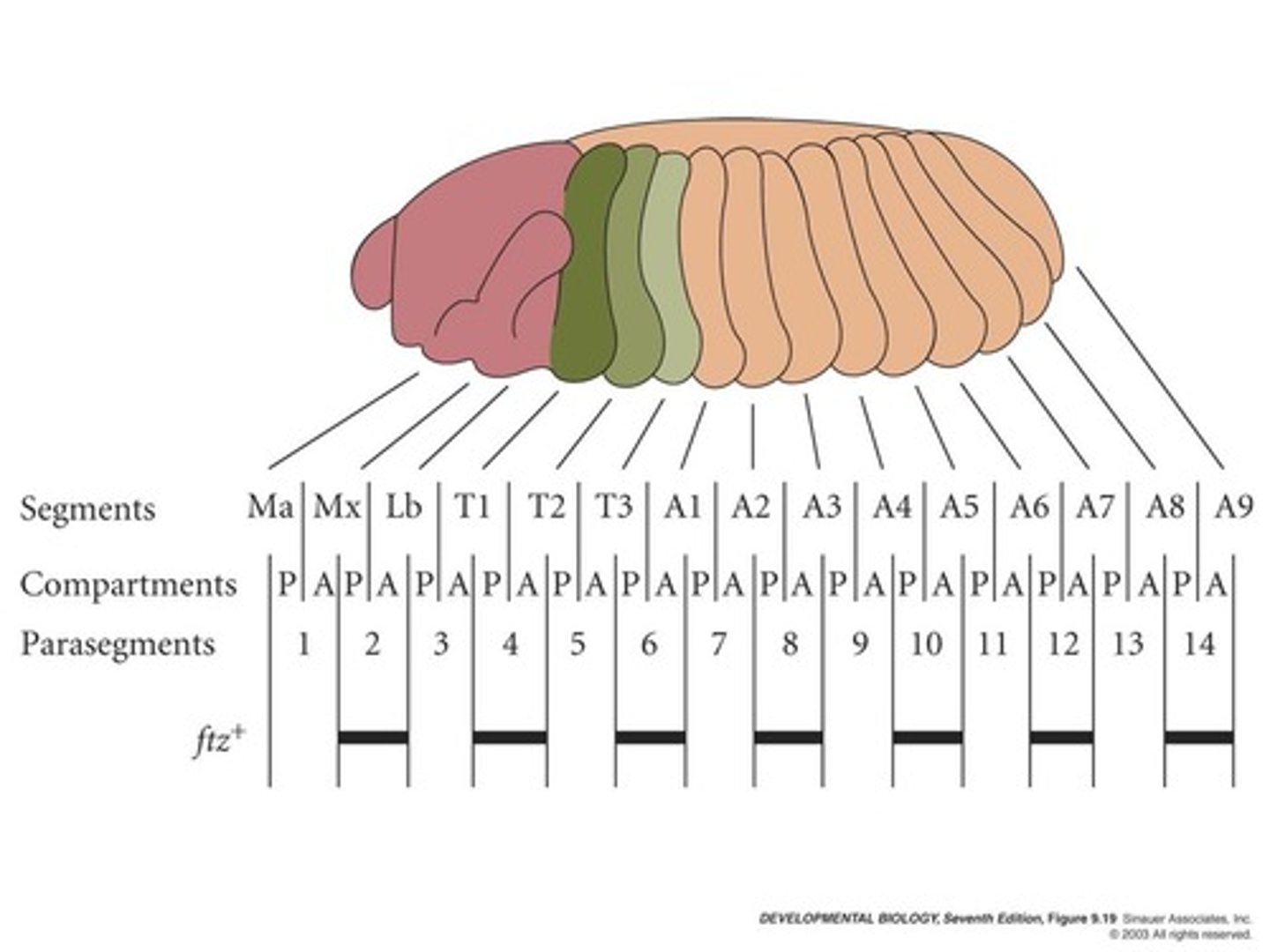
how do hox genes regulate embryonic development in drosophila?
Hox gene expression marks the boundaries of parasegments. Each parasegment expresses a unique combination of Hox gene products that give rise to the identity of each parasegment.
homeotic mutation
a mutation that causes a change in the placement of body parts, like causing a developing fly's antenna to be replaced by a leg
transcription factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
Most of the genes controlling development encode either signal molecules or transcription factors
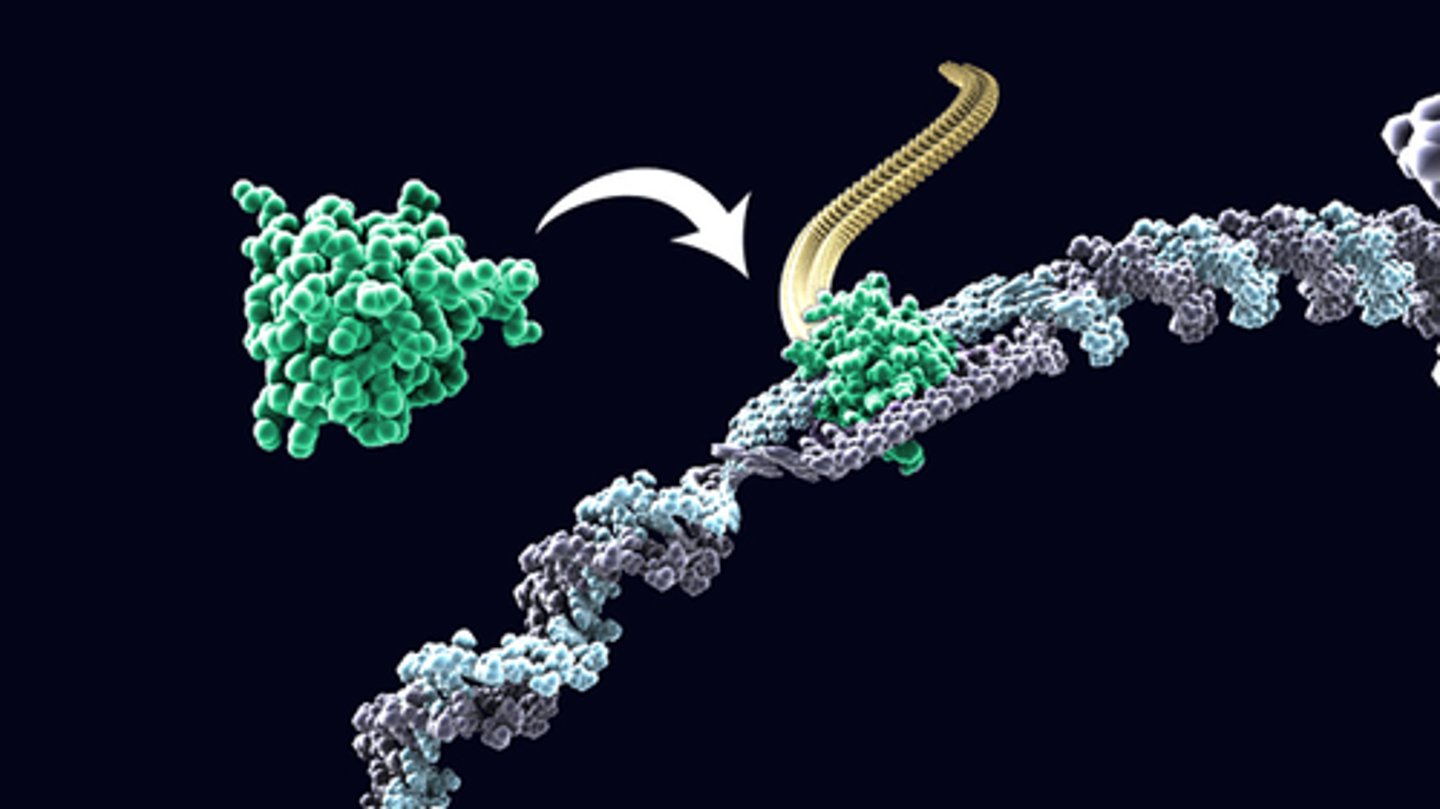
complementation group
all mutations present in any single gene
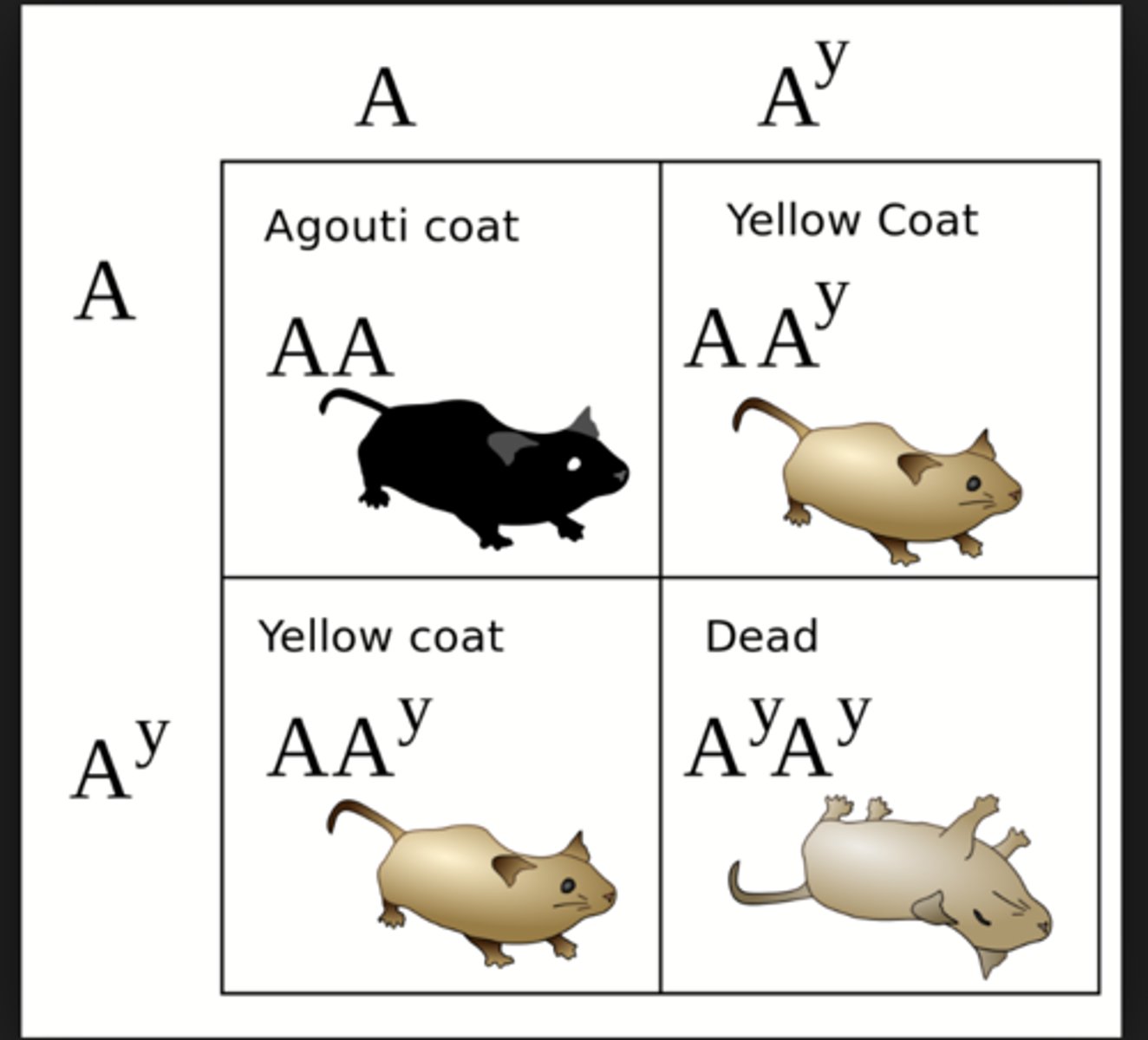
lethal allele
an allele whose expression results in the death of the individual organism expressing it
Some genes have alleles that prevent survival when homozygous or heterozygous.
results in 1/3 of progeny with dominant phenotypes and 2/3 recessive
allelic series
describes the dominance hierarchy of multiple alleles
a group of alleles of a gene that display a hierarchy of dominance relationship among them
Delayed age of onset
symptoms usually are not seen until 40 years of age or later
the abnormalities they produce do not appear until after affected organisms have had an opportunity to reproduce and transmit the mutation to the next generation.
e.g. Huntington's disease
temperature-sensitive allele
an allele whose product is functional only at certain temperatures
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that actually displays the phenotype associated with the genotype.
gene-environment interactions
influence of environmental factors (i.e., nongenetic factors) on the expression of genes and on the phenotypes of organisms.
e.g. arctic mammals coat color changes in winter (white), spring and summer (brown)
expressivity
the degree to which a trait is expressed
wildtype
original nucleotide sequence
law of independent assortment
Each member of a pair of homologous chromosomes separates independently of the members of other pairs so the results are random
incomplete dominance
Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another
heterozygotes with a novel phenotype between the dominant and recessive homozygotes
Need two functional red pigment copies, but if there's only one then there will be a pink flower
sex linkage
the presence of a gene on a sex chromosome
Genes carried on sex chromosomes, such as the X chromosome of humans, show different inheritance patterns than genes on autosomal (non-sex) chromosomes.
variations from classic mendelian genetics
multiple alleles, incomplete dominance, codominance, pleiotropy, lethal alleles, sex linkage
penetrance
the probability that a mutation will manifest its phenotype
rabbit allelic series order of dominance
C > c^ch > c^h > c
full color > chinchilla > himalayan > albino
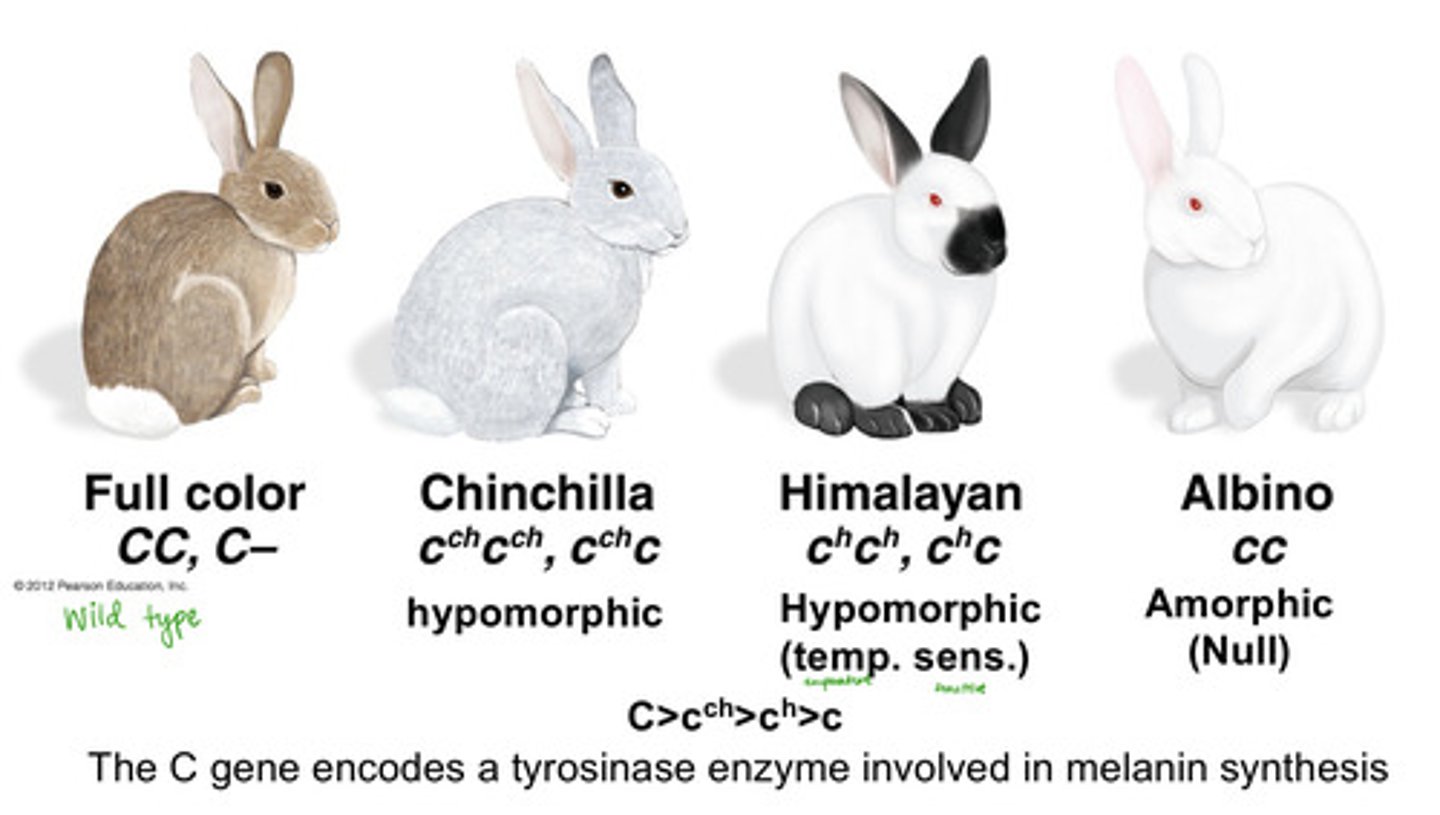
brown rabbit is dominant to
chinchilla, himalaya, and albino
chinchilla rabbit is partially dominant to
himalayan and dominant to albino
himalayan rabbit is dominant to
albino
Wildtype
Unaffected
Codominance
both traits are fully and separately expressed
null hypothesis
the normal hypothesis that COULD be proven wrong
it assumes that there is no real difference between the observed and expected values
chi squared test
it is a goodness of fit test
does the observed match the expected?
if it is a really good fit then you will have a very low x^2 value (not random chance)
the higher the chi-squared value, the lower chances are of it being random chance (it is random chance)
test cross
the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
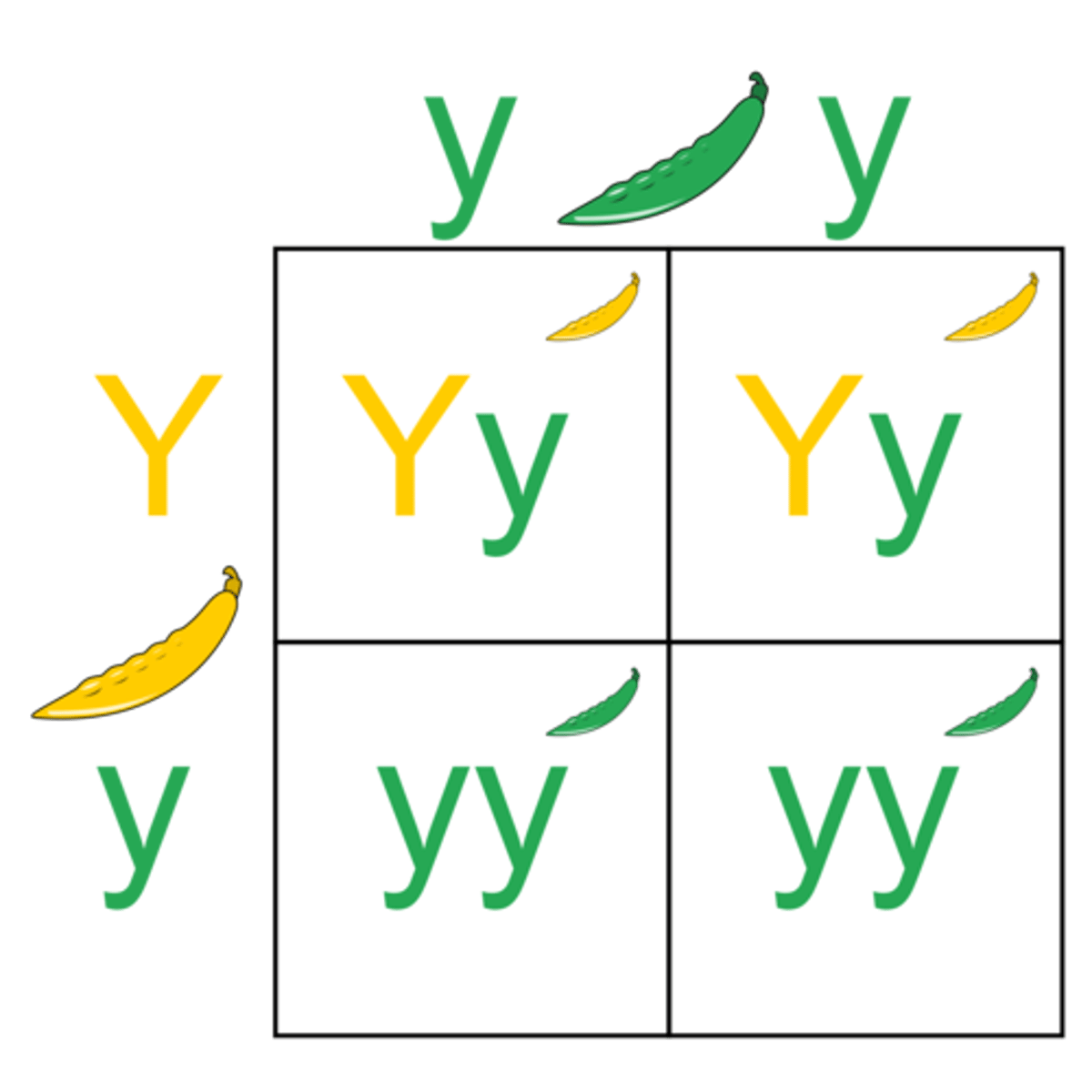
back cross
cross between an offspring (usually the F1) genotype and one of the parental genotypes
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
Aa x Aa
wild-type allele
natural or most common allele in a population
gain of function mutation
a mutation causing a gene to be overexpressed, to be expressed at the wrong time, or to encode a constitutively acting protein; usually inherited as a dominant mutation
certain gain of function mutations are lethal in a homozygous state
hypermorphic and neomorphic mutations
loss of function mutation
causes a complete or partial loss of function
both null and hypomorphic loss-of-function mutations are often recessive and homozygous lethal
multimeric proteins
A protein with more than one polypeptide chain; also said to have a quaternary structure.
particularly subject to dominant negative mutations
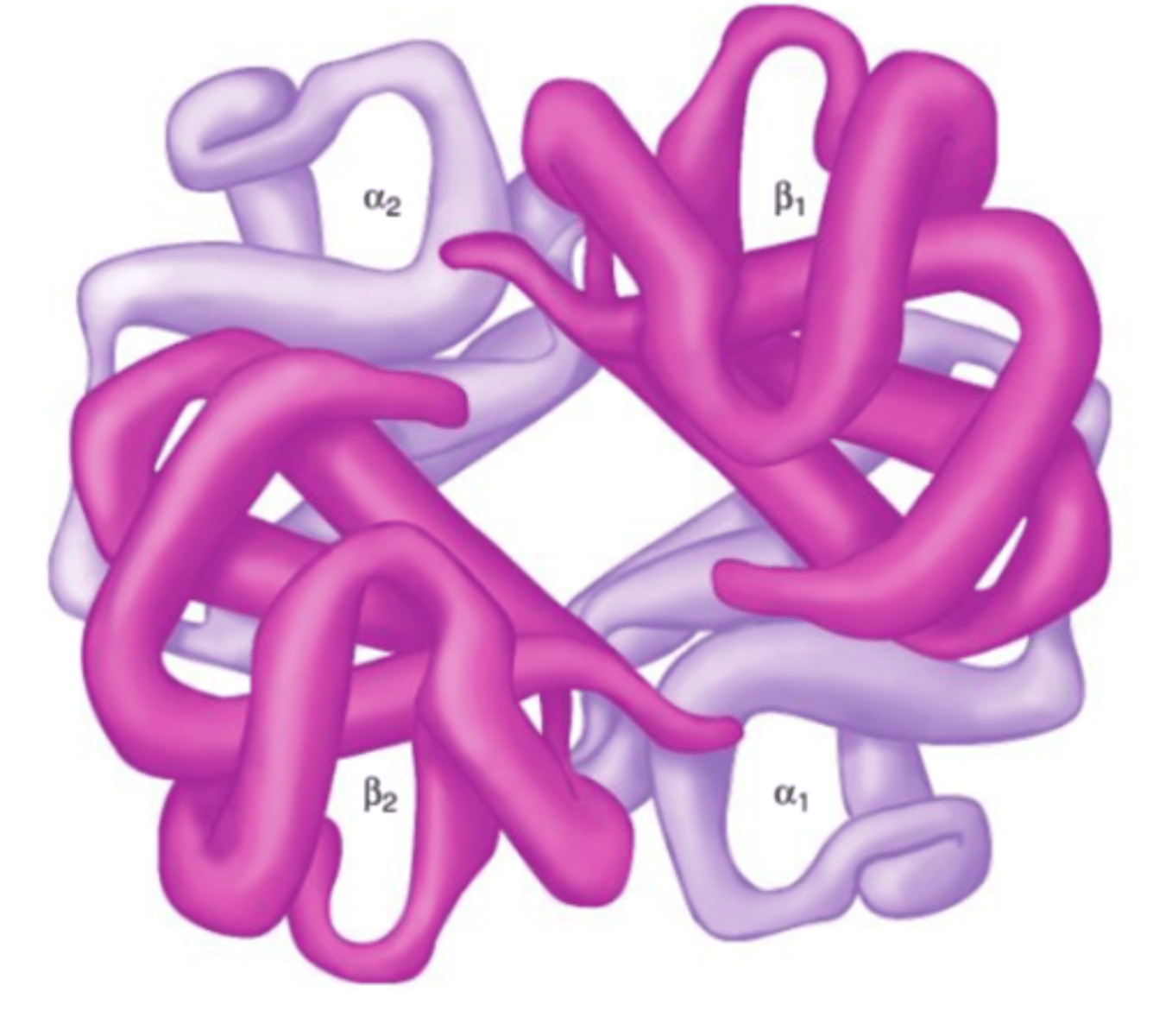
dimer
a molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together.
phenotypic ratio for complete dominance
3:1
phenotypic ratio for incomplete dominance
1:2:1
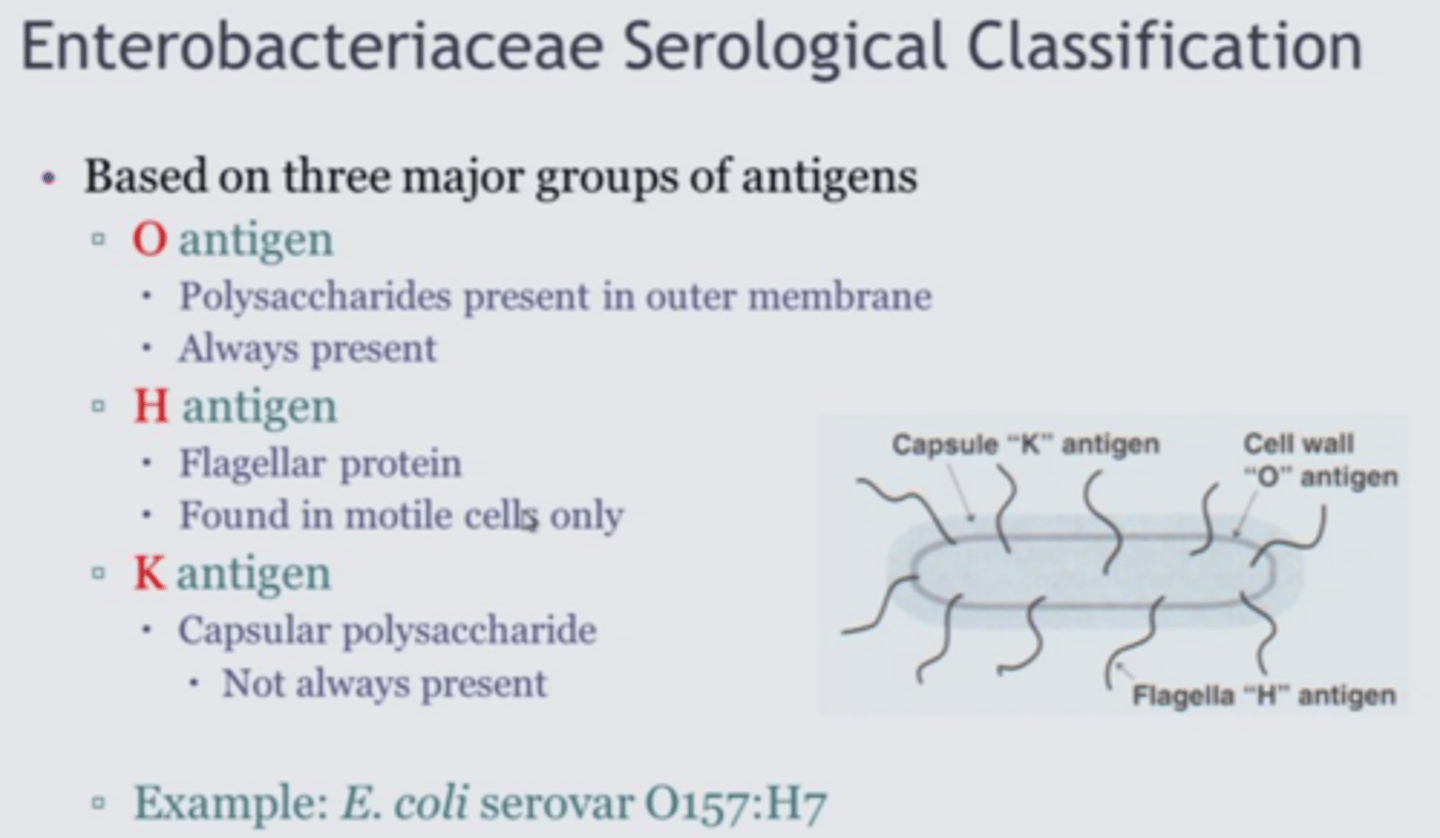
Antigen
A protein that, when introduced in the blood, triggers the production of an antibody
H antigen
flagellar antigen
locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome
fully penetrant
when the genotype is always expressed in the phenotype
genetic heterogeneity
mutations in different genes can produce the same or very similar mutant phenotypes
genetic complementation analysis
An experimental analysis of crosses designed to test alternative genetic explanations of an abnormal phenotype
Results can determine whether mutant organisms carry mutations of different genes that produce the abnormal phenotype or if the abnormal phenotype occurs due to allelic mutations on the same gene
Number of complementation groups = the number of genes
done by crossing pure breeding mutants for a recessive mutation and observing the phenotype of F1 progeny. If the F1 progeny have the wild type phenotype, genetic complementation has occurred, and the conclusion is that the mutant alleles are of different genes. But if the mutant alleles are of the same gene, the progeny of two pure-breeding mutants will have a mutant phenotype.
genetic complementation
(1) The observation of a wild-type phenotype in an organism or cell containing two different mutations.
(2) The cross of two pure-breeding mutants that yields progeny that are exclusively wild type.
syntenic genes
genes that are located on the same chromosome
Iinked genes are always
Syntenic
genetic linkage
tendency for genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together
homologous recombination
Exchange of genetic information between homologous DNA molecules.
recombinant chromosomes
A chromosome created when crossing over combines the DNA from two parents into a single chromosome.
recombination frequency
The rate of occurrence of recombination between a pair of linked genes.
r = number of recombinants/total number of progeny
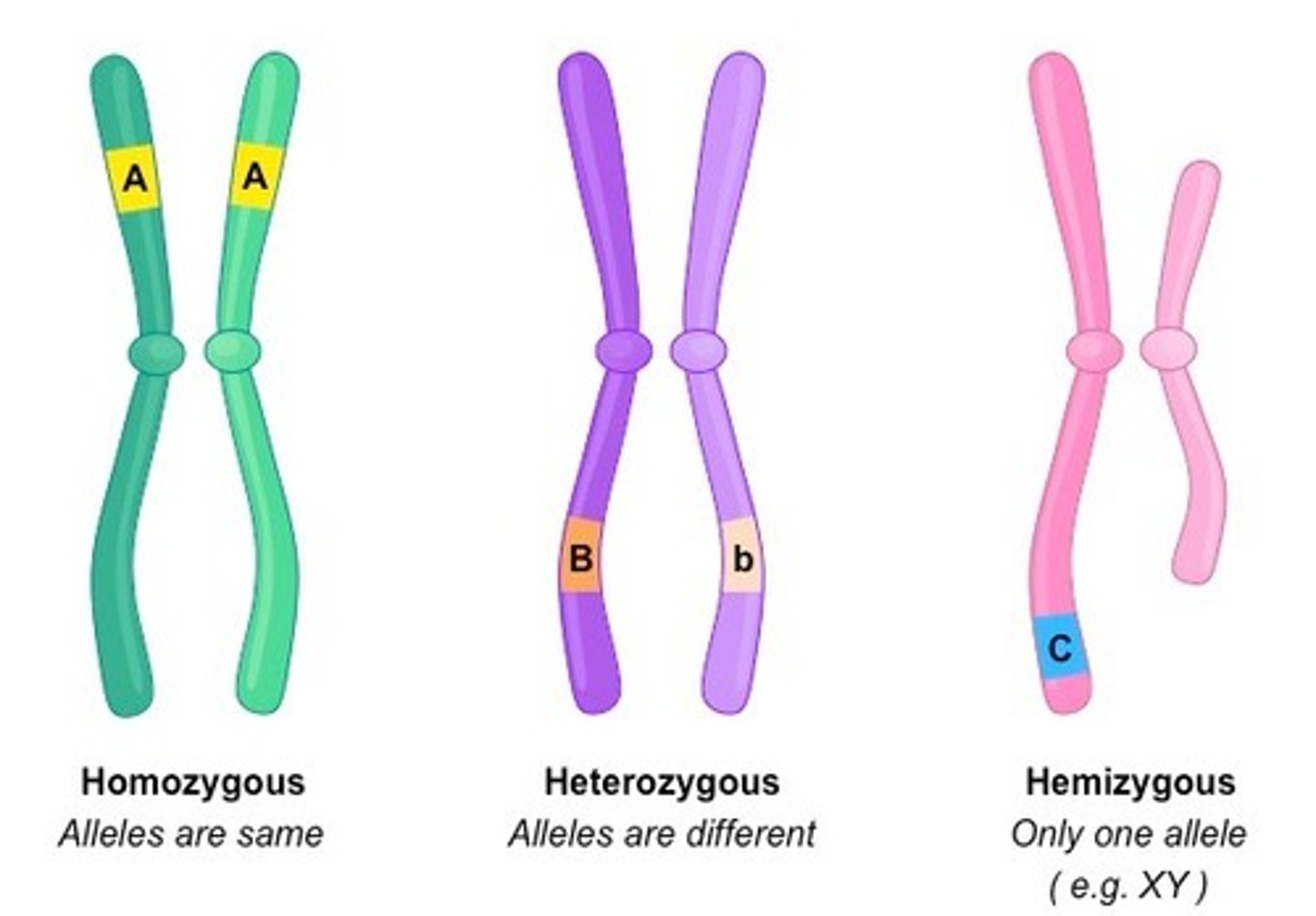
hemizygous
A gene present on the X chromosome that is expressed in males in both the recessive and dominant condition
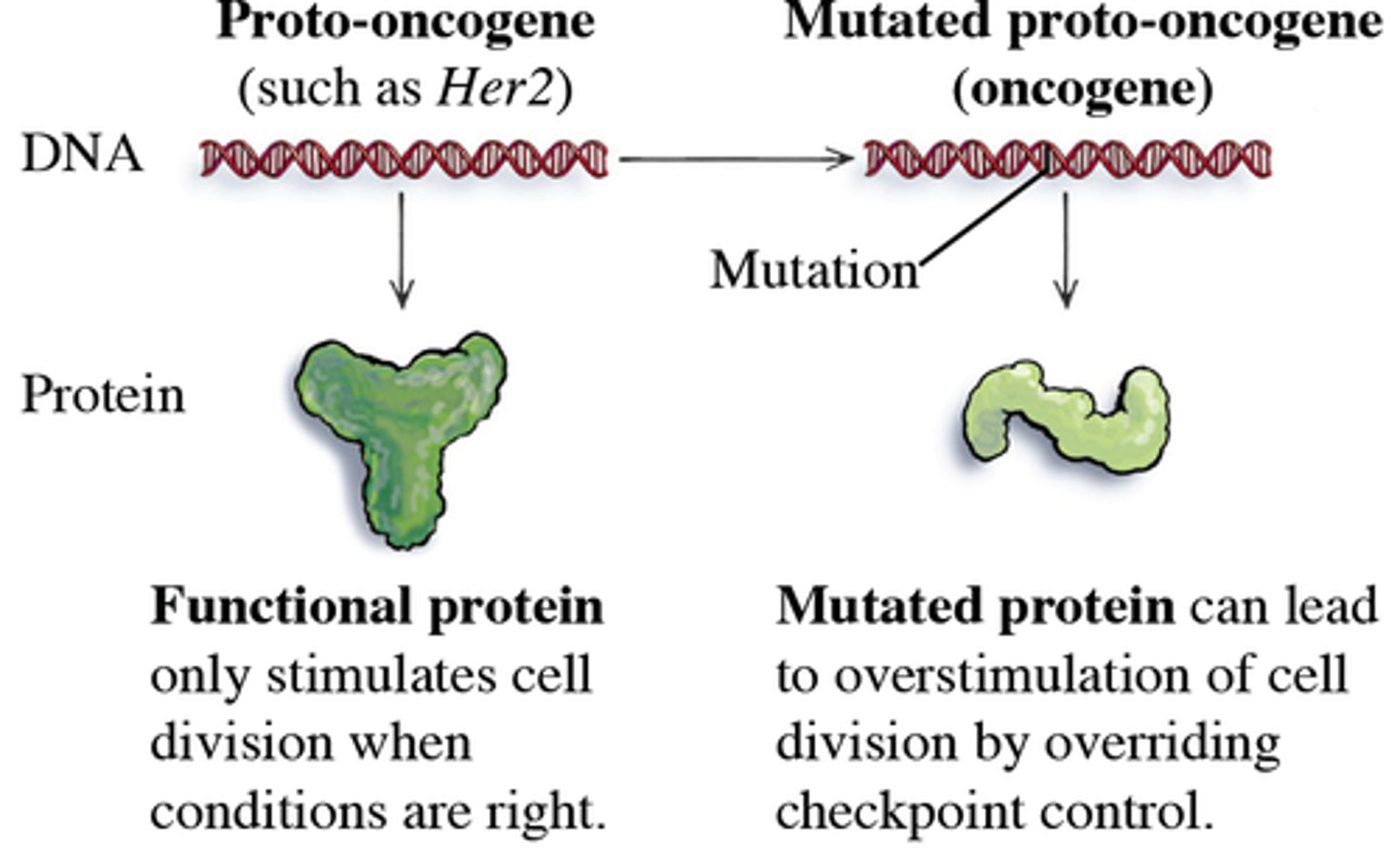
Proto-oncogenes
the corresponding normal cellular genes that are responsible for normal cell growth and division
tumor suppressor genes
encode proteins that help prevent uncontrolled cell growth
normal function involves preventing cell division
Dysplasia
abnormal development or growth of cells, tissues, or organs
Benign cell masses
noncancerous
SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism, change of base of single DNA nucleotide, makes up 90% of all human genetic variation
occurs every 300 bases in the human genome on average
there are about 10 millions SNPs in the human genome - most don't actually do anything
despite this, human genomes are very similar - they have 7x less genetic variation than in chimpanzees our closest relatives
number of SNPs where you match another person can therefore be used to tell how closely related you are
"typos" in the DNA sequence
dedifferentiated
loss of specialized cell characteristics, seen in cancer
act more like primordial cells than specialized cells
proliferation
active cell reproduction and tissue growth
primordial cells
undifferentiated cells (stem cells) that have the capacity to form into various systems
Hyperplasia
the enlargement of an organ or tissue because of an abnormal increase in the number of cells in the tissues
before cells become cancerous, they begin to look and grow abnormally
abnormality can first appear as hyperplasia
then progress to dysplasia
Neoplasia
dysplastic cells can progress to neoplasia - a general term for a cancerous condition or tumor
malignant tumor
cluster of cells that are cancerous
metastisis
The spread of cancer cells beyond their original site
proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
proto-oncogenes: start cell division, "gas"
tumor-suppressor genes: switch off cell division - "brake" mutations of these genes are like brake failure
Oncogenes
genes that cause cancer by blocking the normal controls on cell reproduction
"stuck accelerator"
sporadic
a term describing 90% or more of all cases of cancer, that develop as the result of the accumulation of multiple somatic mutations; these cancers occur without the inheritance of a specific mutation that increases an individual's susceptibility of cancer
germ-line mutation
a mutation occurring in gametes; passed on to offspring
leads to familial or hereditary cancer
de novo mutation
A new mutation that was not inherited from either parent
hereditary retinoblastoma
40% of retinoblastoma cases.
Onset typically is earlier than sporadic cases.
Multiple tumors involving both eyes.
Consistent pedigrees; siblings and offspring develop the same type of tumors.
two hit hypothesis
Tumor suppressor genes typically require both copies to be inactivated before an effect is seen.
Genotype of a normal cell in the retina in a person who has sporadic retinoblastoma?
RB1+ RB1+
What is the normal cell genotype if the person has hereditary retinoblastoma?
RB1+ RB1-
Hypermethylation
inactivates transcription of DNA
Methylation makes DNA mute
p <= 0.05
reject the null hypothesis
conclude that the observed experimental results are due to chance and the variable being tested had no effect. the results are "not significant" (due to chance)
little chance that the null hypothesis is true
null hypothesis assumes that there is no real difference between the observed and expected data
smaller X^2 value means that there are higher chances of it being due to random chance
p > 0.05
fail to reject (accept) the null hypothesis. The two groups are not statistically different.
big chance the null hypothesis is true
null hypothesis assumes that there is no real difference between the observed and expected data
bigger X^2 value means that there are lower chances of it being due to random chance