Dentistry
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
3I:1C:4P:3M on all 4 quadrants
In the standard system how many I:C:PM:M do horses have?
Wolf tooth (First PM x05)
Most mares are missing what tooth?
Towards the crown
Define Coronal?
Between adjacent teeth
Define interproximal?
Near gingival margin
Define Marginal?
Hypsodont - continuous eruption (4mm a year)
What kind of eruption patten do horses have?
A palpable evidence of erupting teeth on the mandible
What is an eruption bump?
Birth or in the first week
No deciduous molars are present
When do equine deciduous premolars erupt? When do deciduous molars?
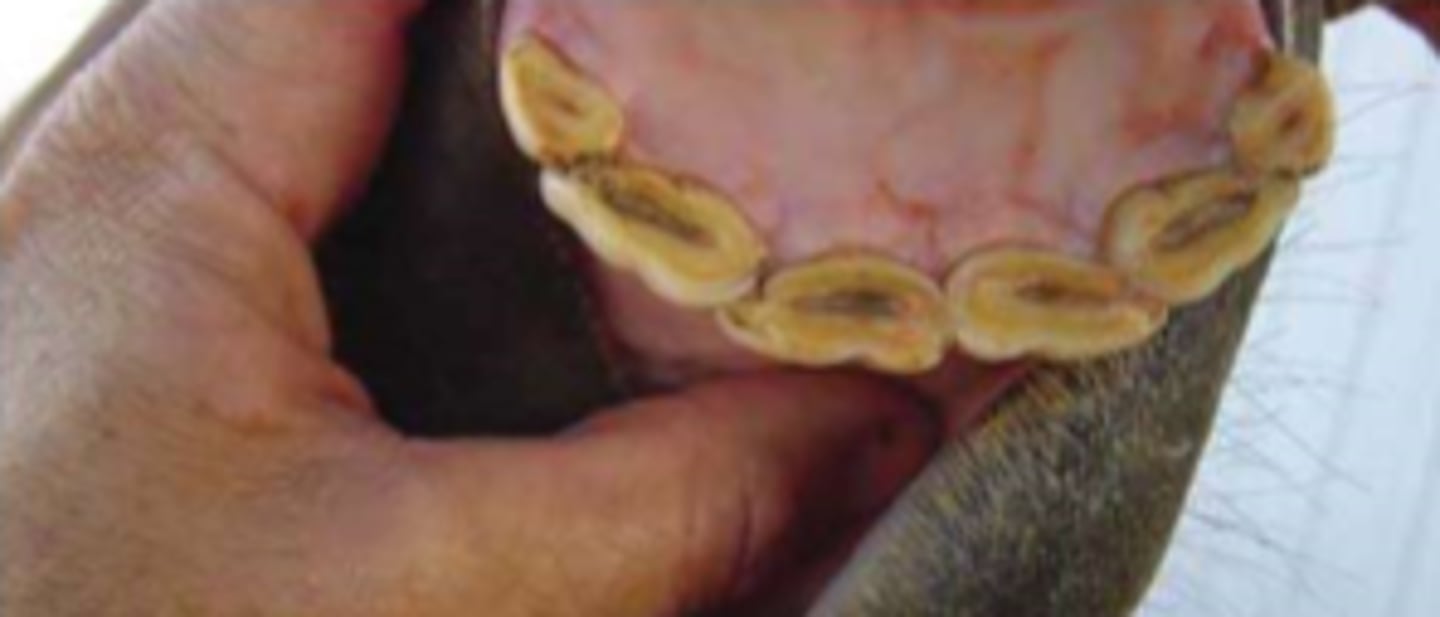
The center of the infundibulum disappear w/ age (12-18y) going from transverse to round to straight
Where do we see cups (shape)?
-Teeth protrude and incisors are more vertical
-Become more rectangular w/ time
What are some changes we see in teeth aging?
Detomidine (lasts 20mins) (A2 Agonist)
Butrorphanol
What is standard for sedation for standing horse exam?
NO must be used w/ A2 agonist
Can you use butorphanol by itself?
Carefully or not at all (small quantities)
How should reversal agents be given to horses on sedation?
Muscle symetry
TMJ
anisognathic (grind/ lateral excursion)
cranial caudal movements
flush the mouth
Scent of mouth
What are we looking at in a sedated dental exam?
Match the facial crest
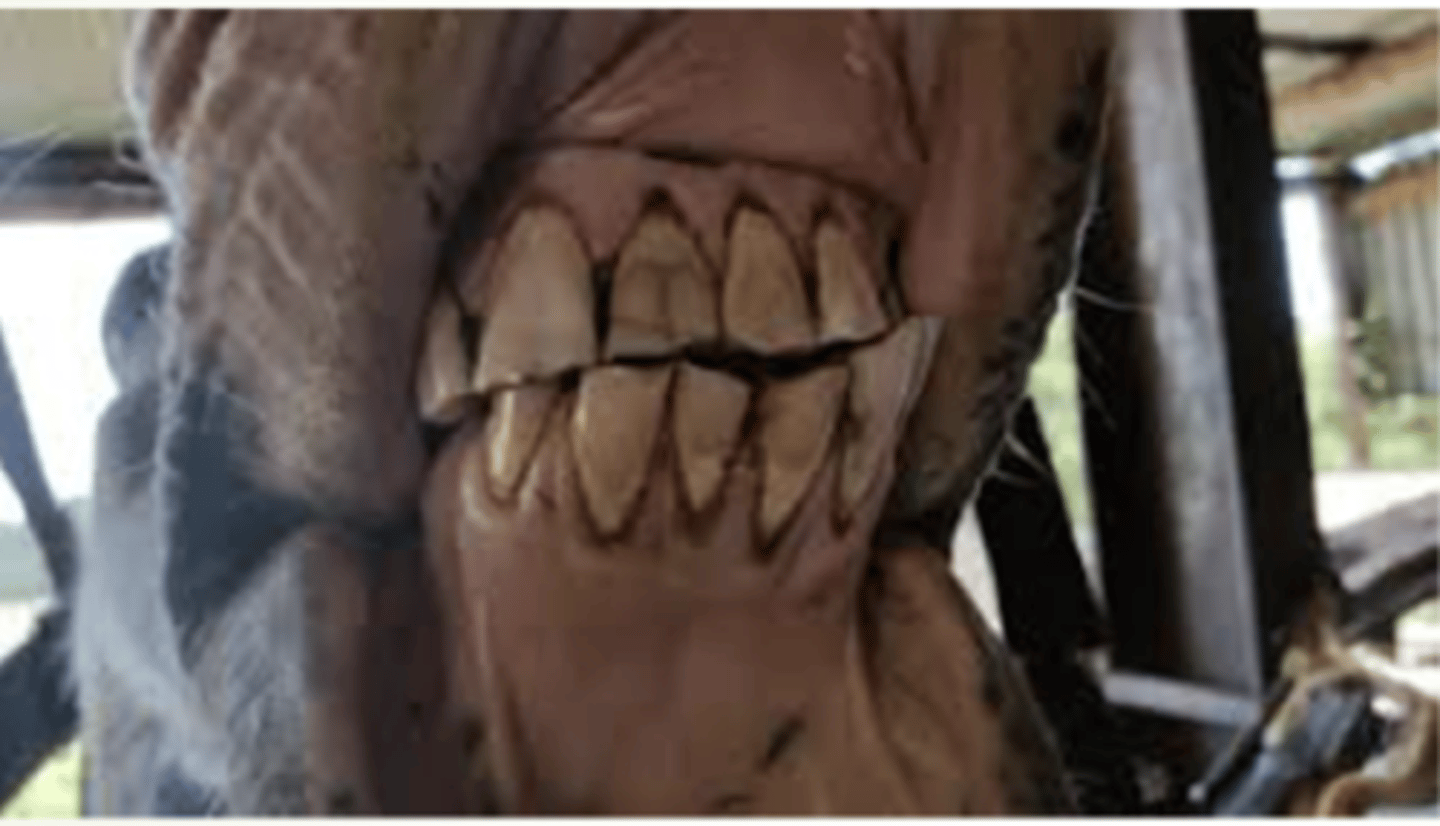
What should a normal incisor do?
Incisor pathology, diagonal mouth (due to skull asymmetry)
Identify the pathology?
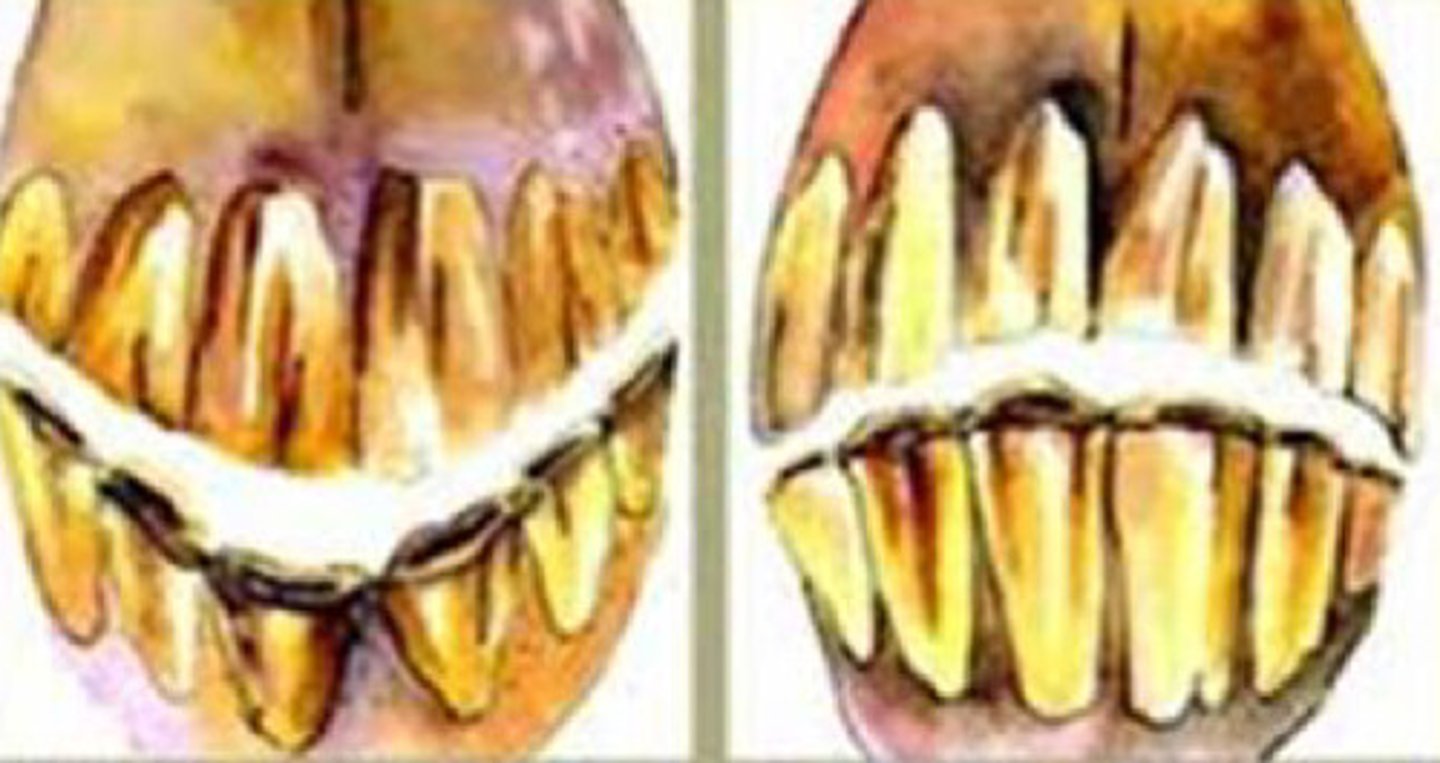
Incisor pathology, ventral and dorsal curvature
Identify the pathology?
partial tooth sticking out
Entire tooth sticking out
Jet is a ___ where as bite is an ___?
equine odontoclastic tooth resorption and hypercementosis
What is the pathology
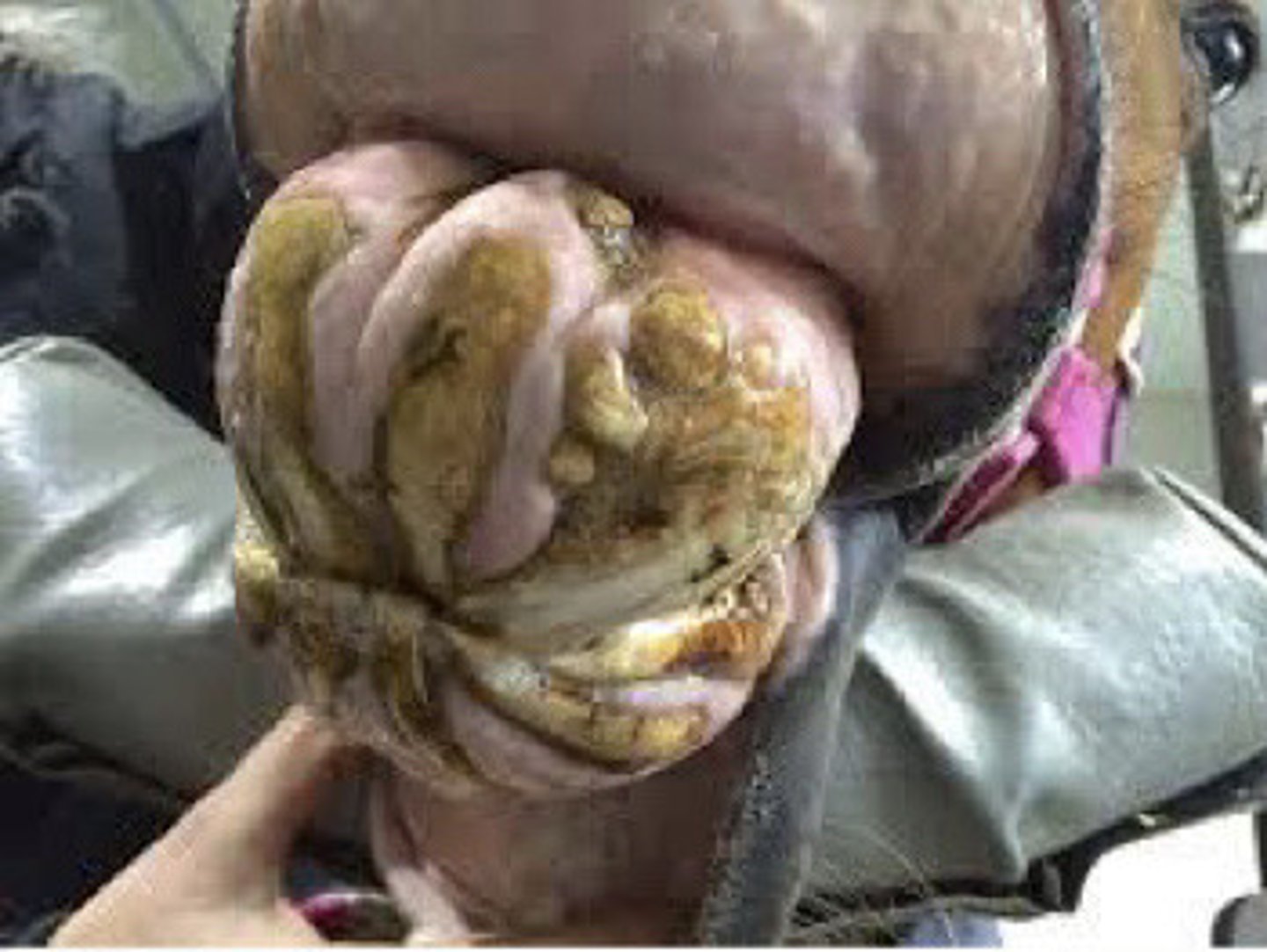
Absorption of alveolar bone and excessive production of cementum - must remove teeth
What is equine odontoclastic tooth resorption and hypercementosis?
Missing teeth
Define Oligodontia?
Infundibular carries (cavities)
Identify the pathology?
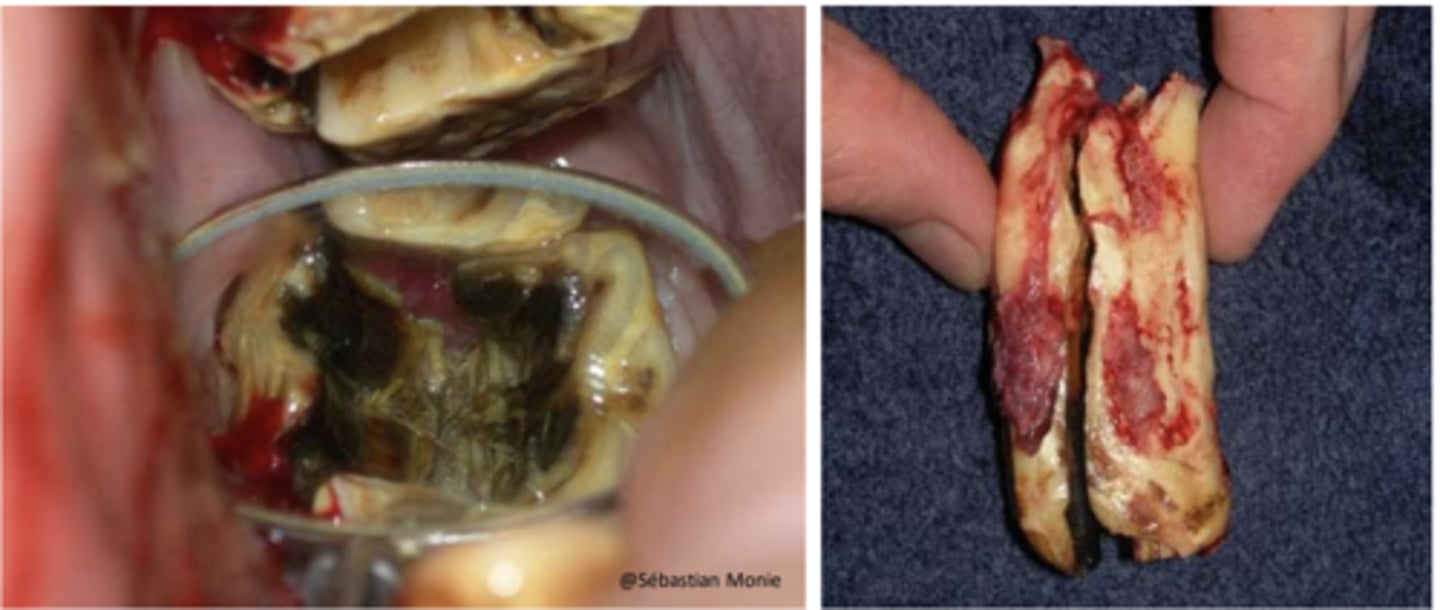
Maxillary teeth, packed w/ feed
Where do we see Infundibular carries?
Wave mouth (most common in older)
What is the pathology?
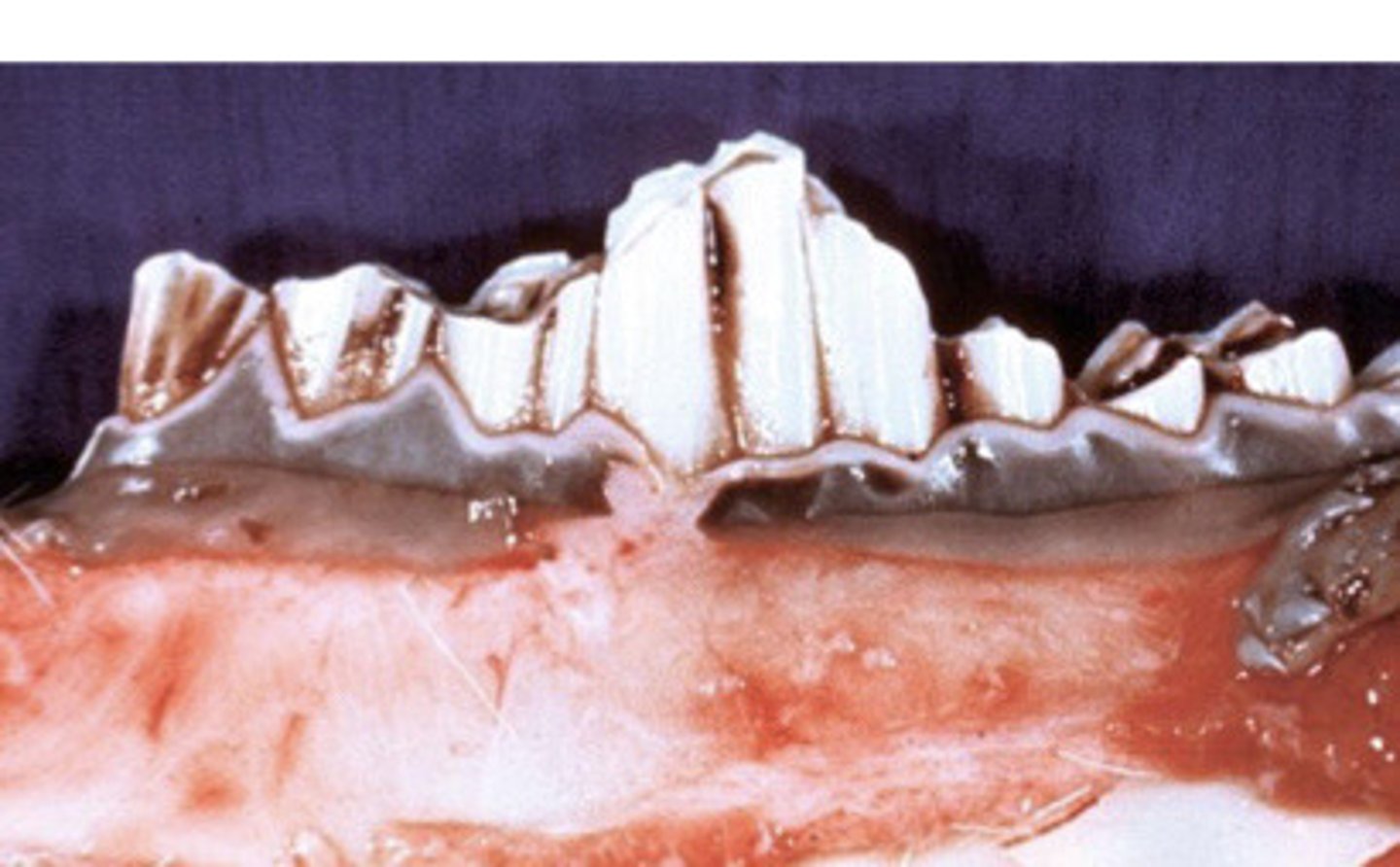
109/209- erupt and wear out cup 308/408 lose cups last
When does wave mouth occur?
Excessive transverse ridges (need floated every 6m)
What is the pathology
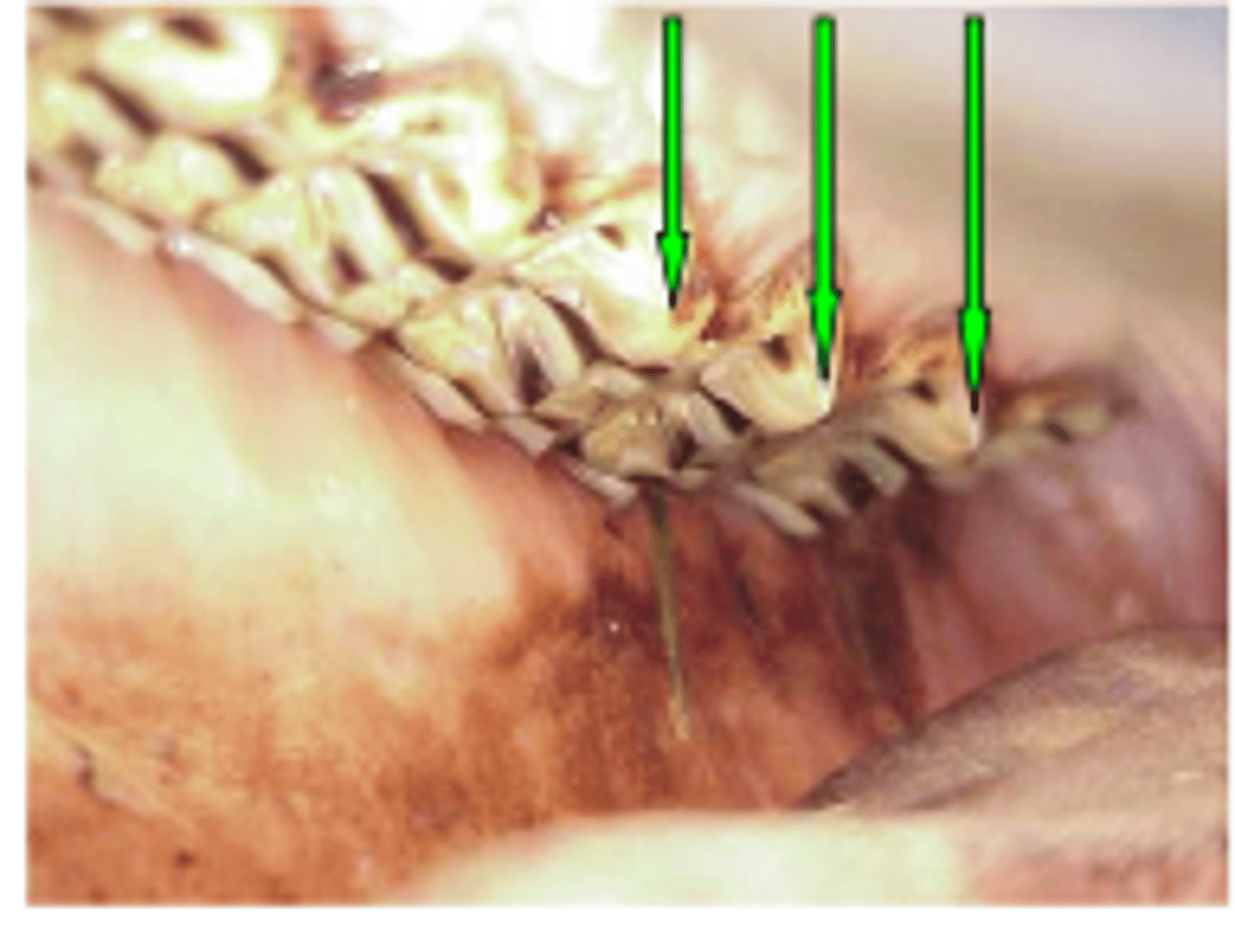
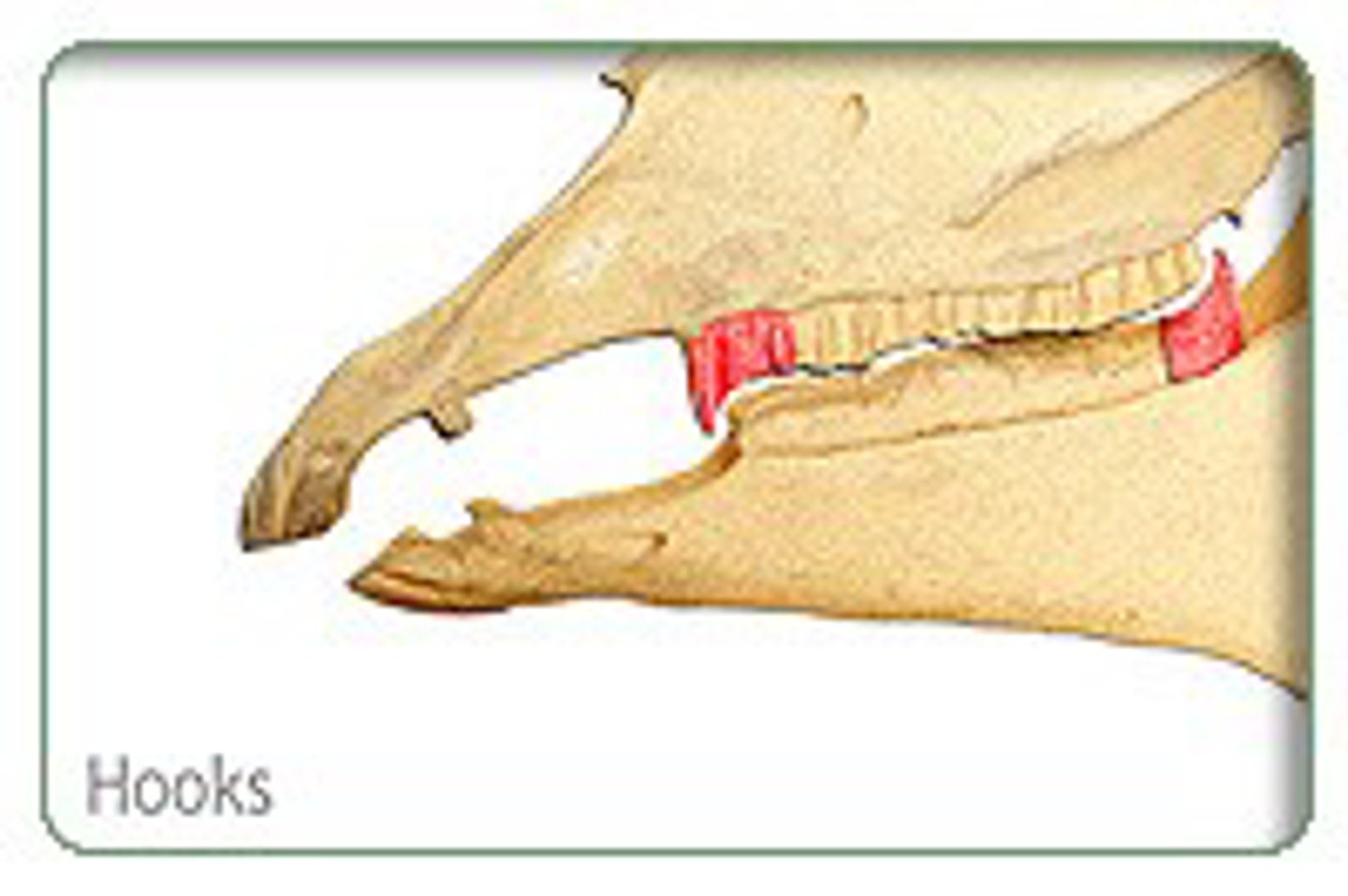
Hooks (106/206 or 311/411 common)
What is the pathology?
Ramps (most common 306/406) Dont open pulp
What is the pathology?
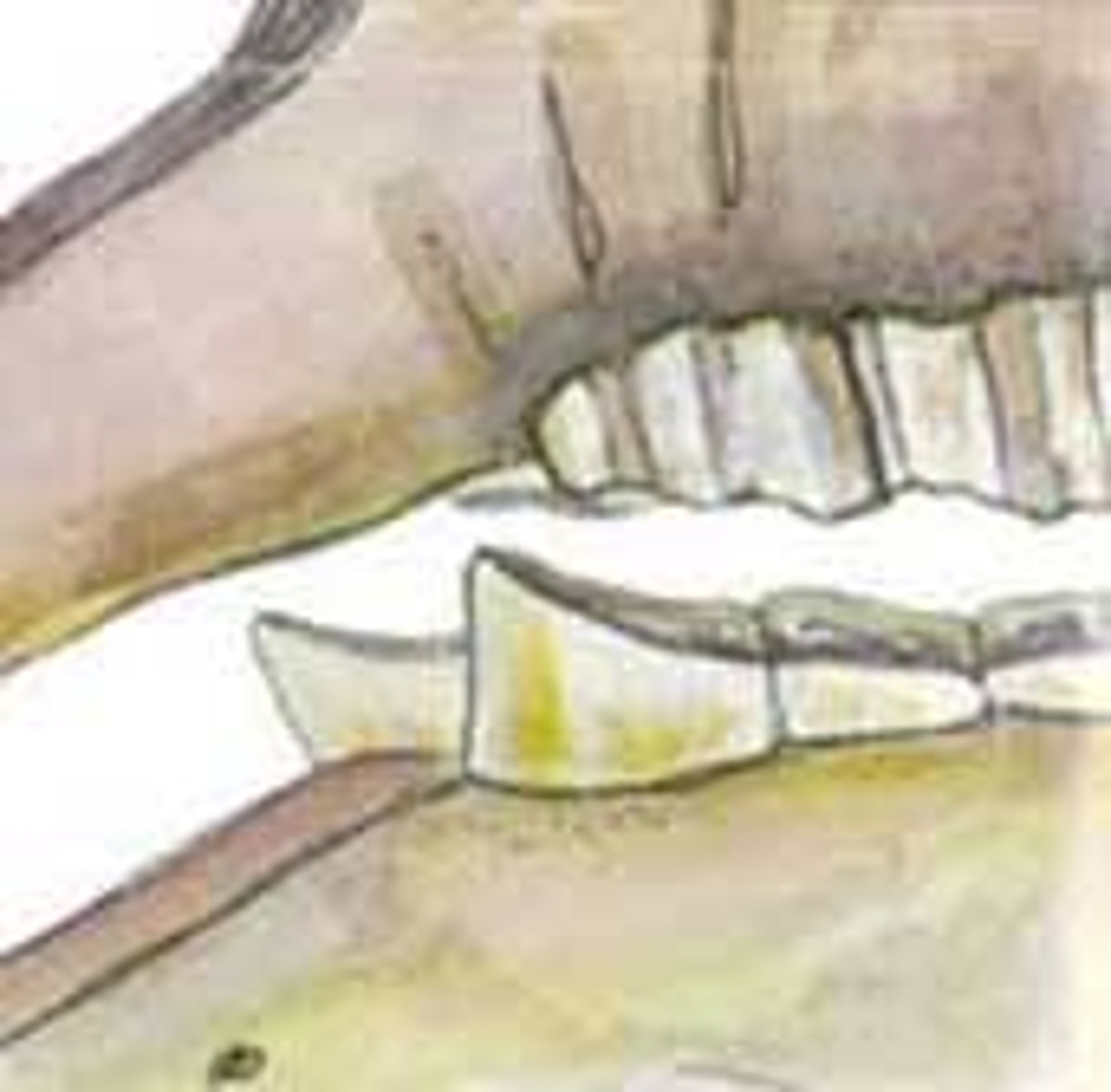
Step mouth - Float yearly , due to missing tooth or malocclusion
What is the pathology?
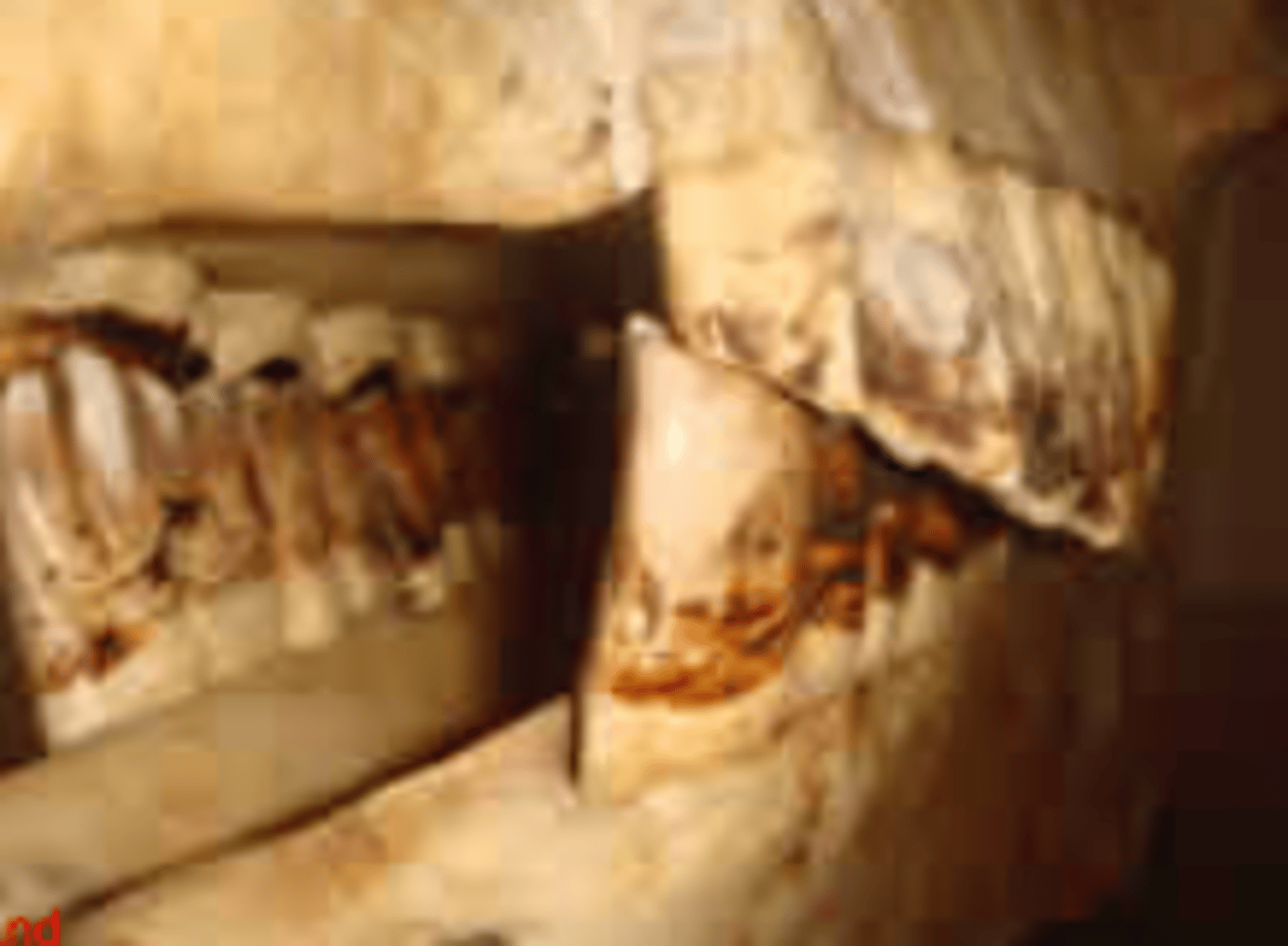
Shear mouth, - total loss of normal jaw motions
What is the pathology?

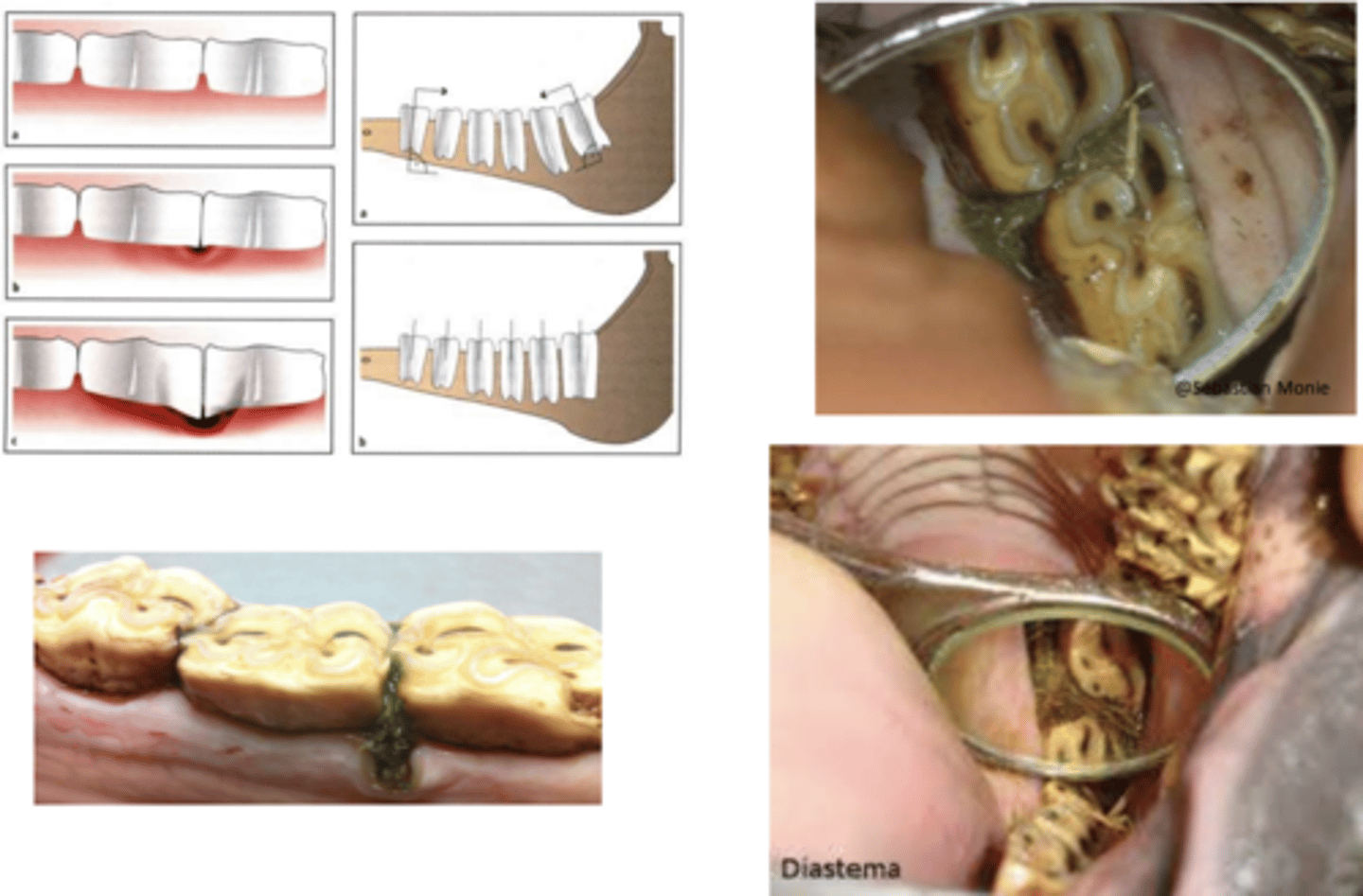
Diastema - Can be open/ closed and can cause food impaction
What is the pathology?
Cementum not filling in the infundibula - tx w/ removal causing pulpits
What is a patent infundibulum?
Grind down and round teeth that need it. When brown becomes white stop.
How do you float teeth?
Every 6-12 m : young horses
Every 12-36m : gERIATRIC HORSES
How often should teeth be floated?
Wolf tooth,
What tooth is commonly removed in horses?
Local block
Burgess extractor,
Elevators
Dental forceps
What is used to remove a wolf tooth?
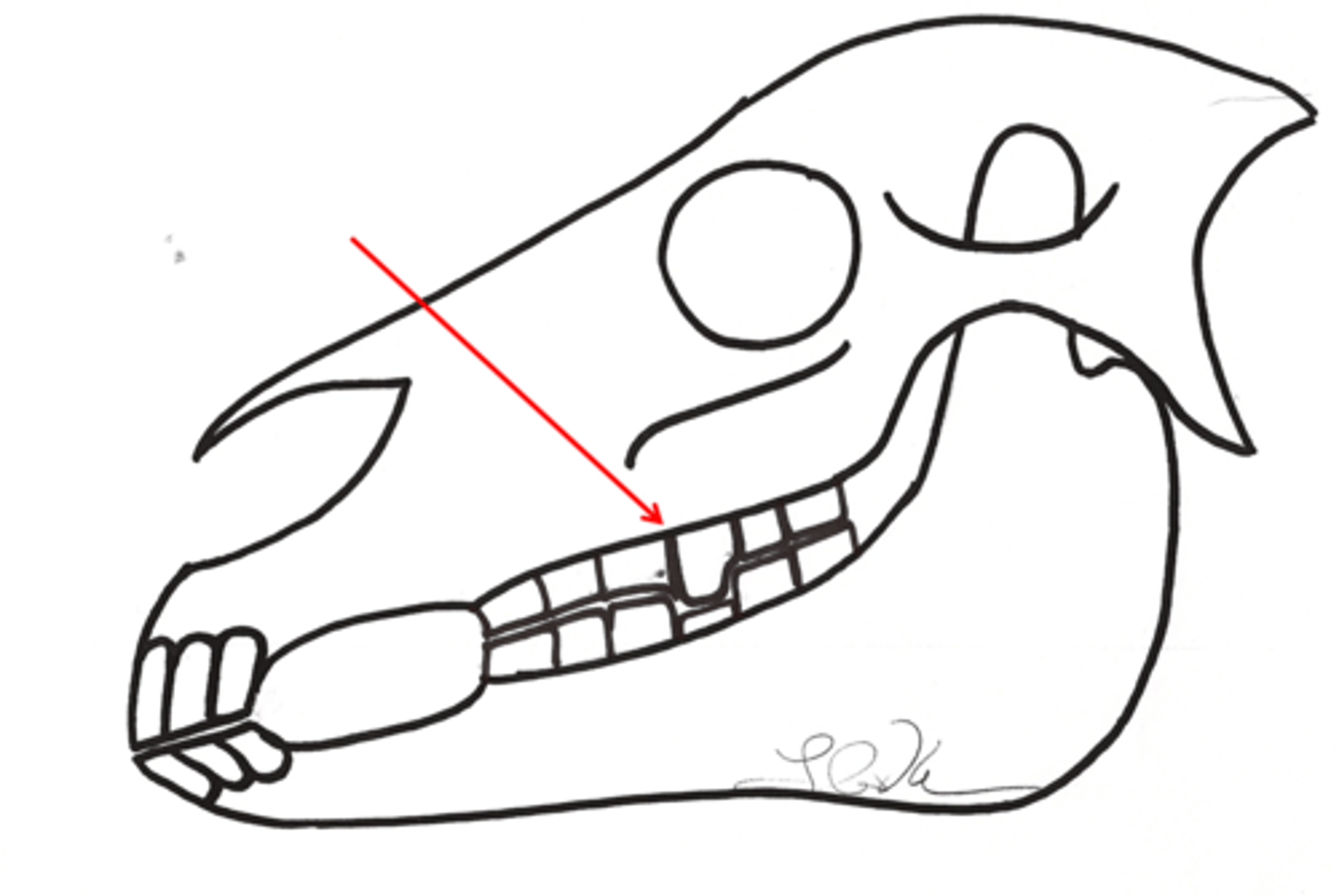
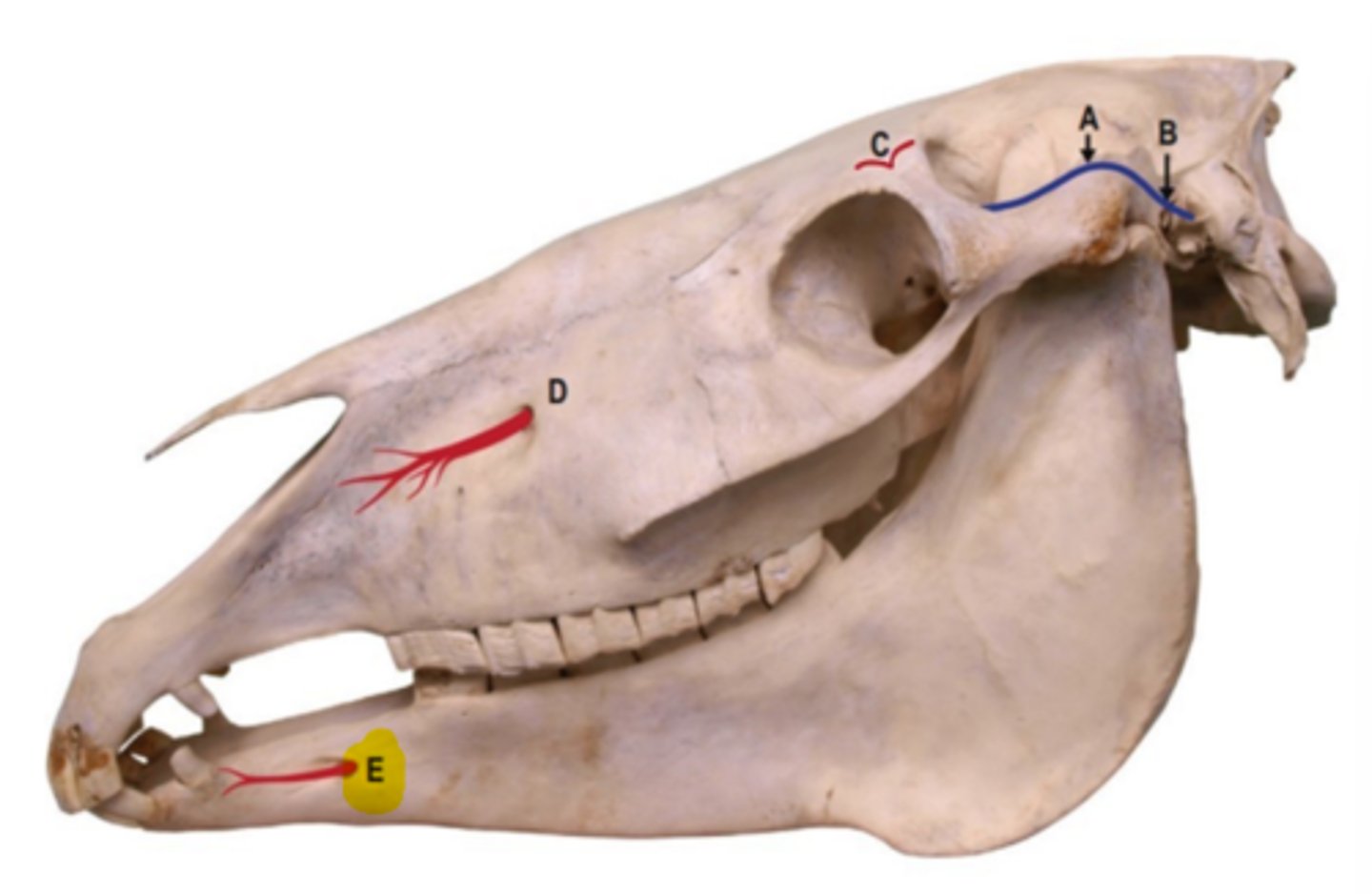
Infraorbital
What block would be performed here?
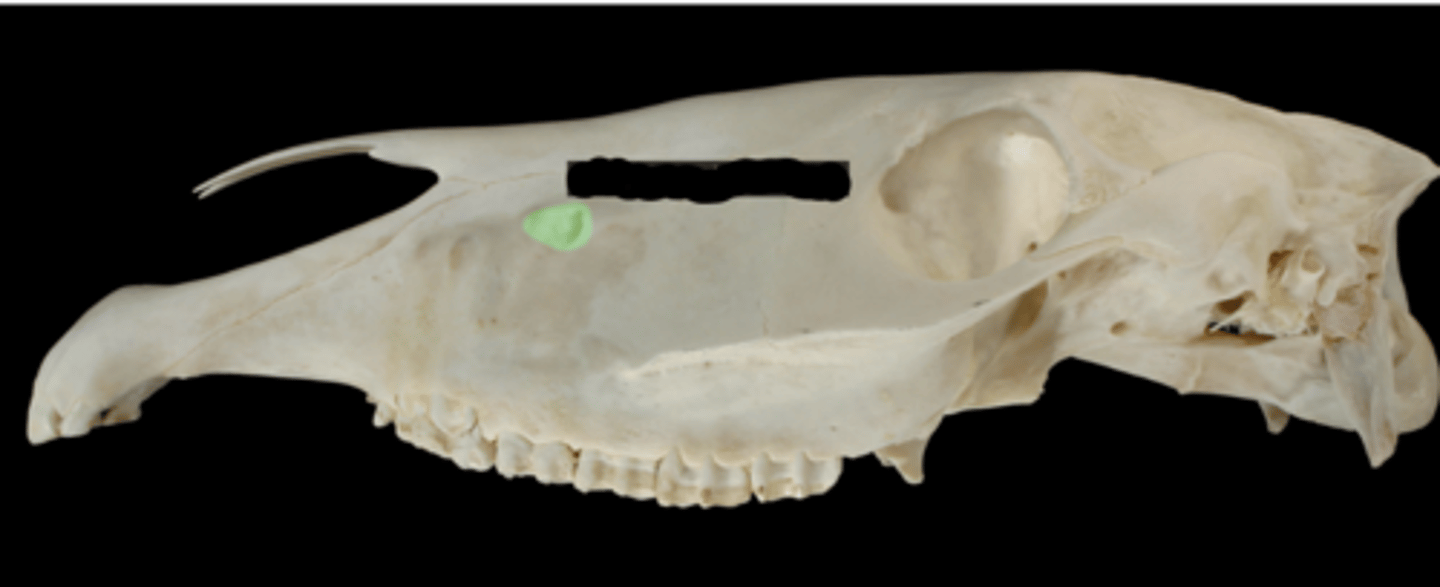
Maxillary block
What block would be performed at the yellow spot?
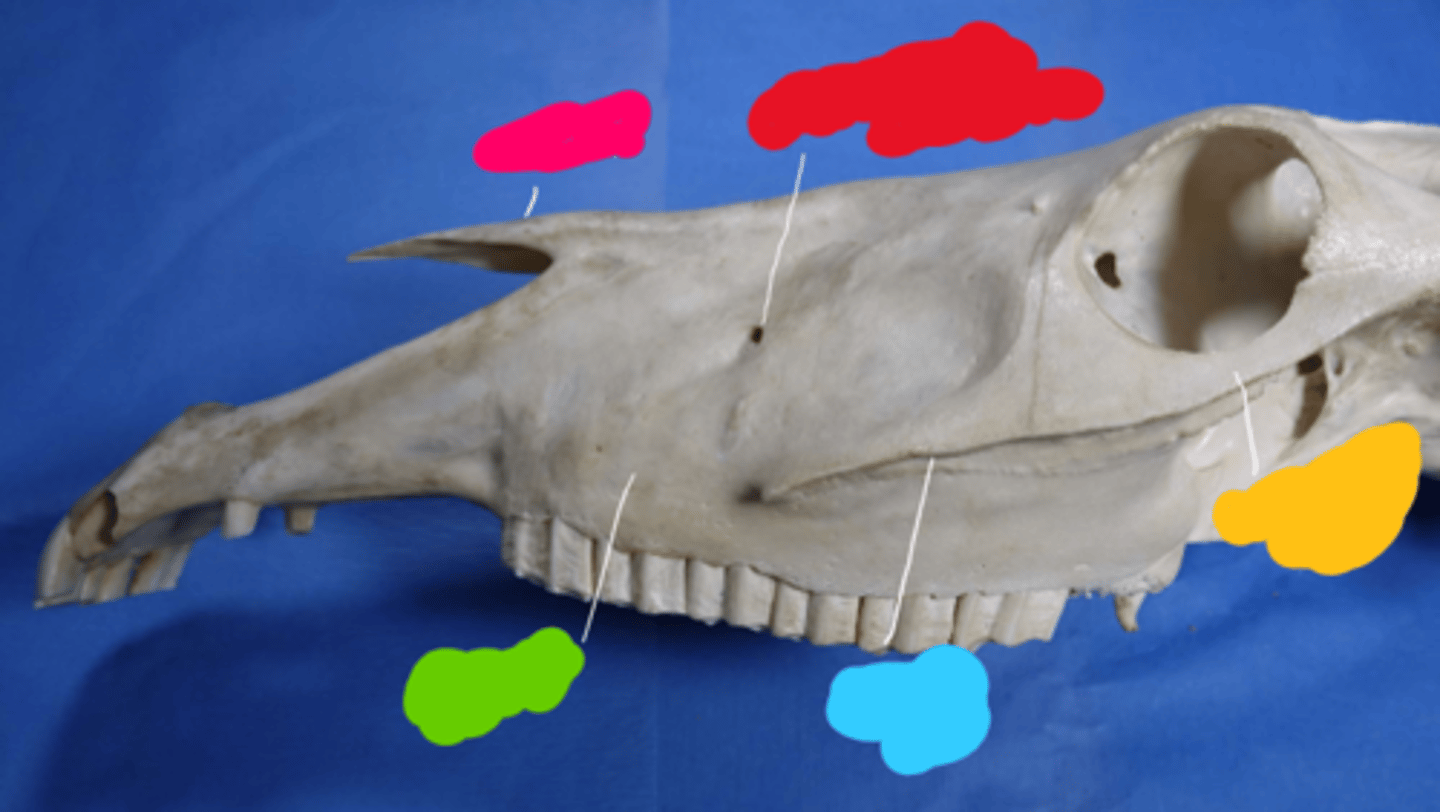
Mental block
What block is performed at E?
Lidocaine
What blocking agent will work the w/in 4minutes and blocks voltage gate sodium channels of neurons?
Bupivicane
Which local anesthetic will prevent depolarization within 15 minutes of administration?
A cap (will be 500-800)
Deciduous teeth are also known as what?
a prolongation of the pulp extending toward the cusp of a tooth. (will have 5-7)
What is a pulp horn?
09 (1y of age wears out first)
What is the oldest tooth in the horses mouth?
18y
If the dental star is still present but infundibular cups are missing, what age does the horse at least have to be?
20Y
If a horses teeth are rectangular what age is the horse?
75%
Excellent occlusion is usually what percent?