Kaplan Biochemistry - Chapter 7: RNA and Genetic Code
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
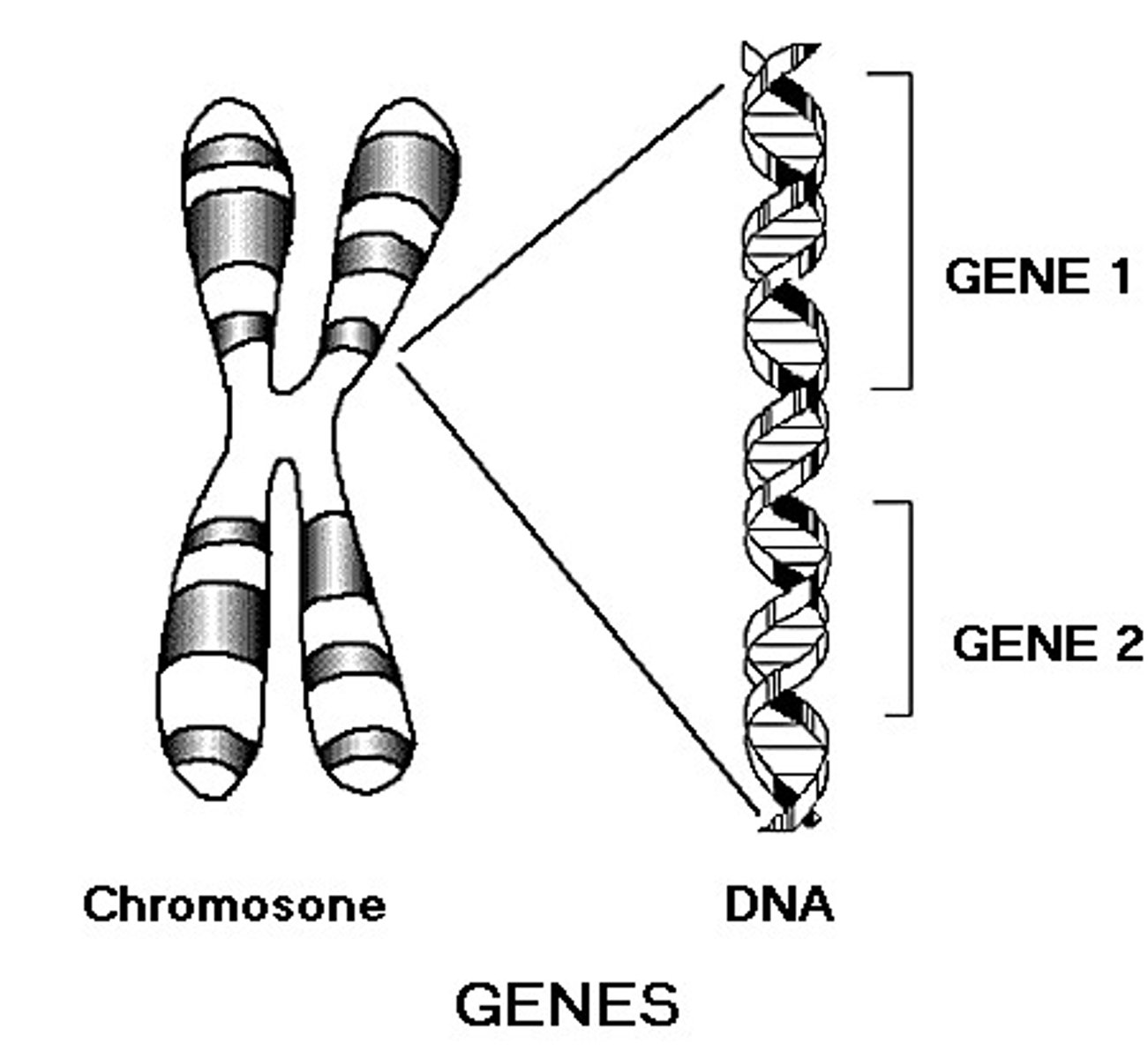
A unit of DNA that encodes for a specific protein or RNA molecular, which can be expressed via transcription and translation
Gene
Carries the message from DNA in the nucleus via transcription of the gene; it travels into the cytoplasm to be translated.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
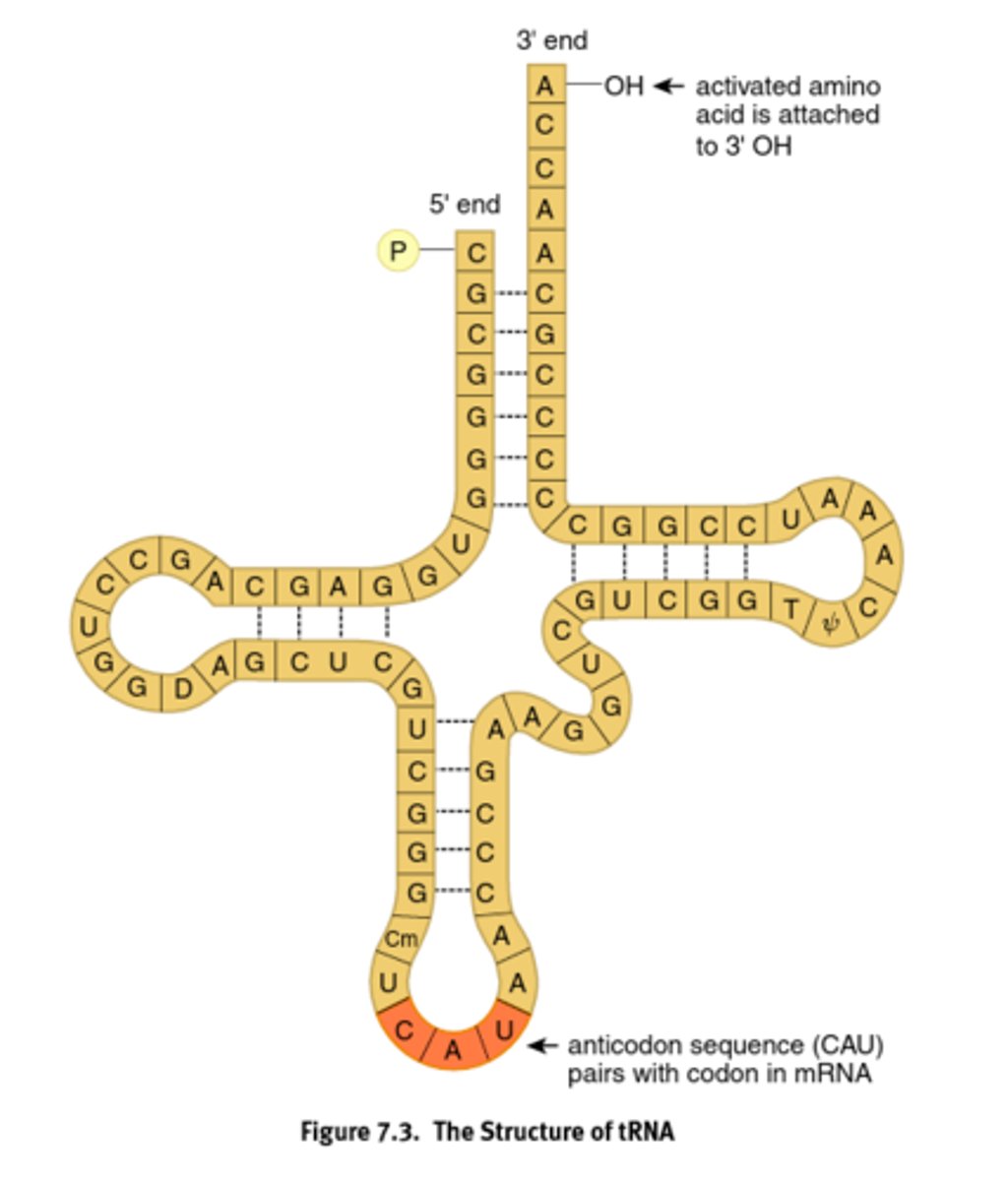
Bring the amino acids and recognizes the codon on the mRNA using its anticodon.
When bound to AA, it is charged, and is a high energy bond
Transfer RNA (rRNA)
Synthesized in the nucleolus and functions as an integral part of the ribosomal machinery used during protein assembly in the cytoplasm.
Makes up the ribosome and its enzymatically active.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code.
Codon
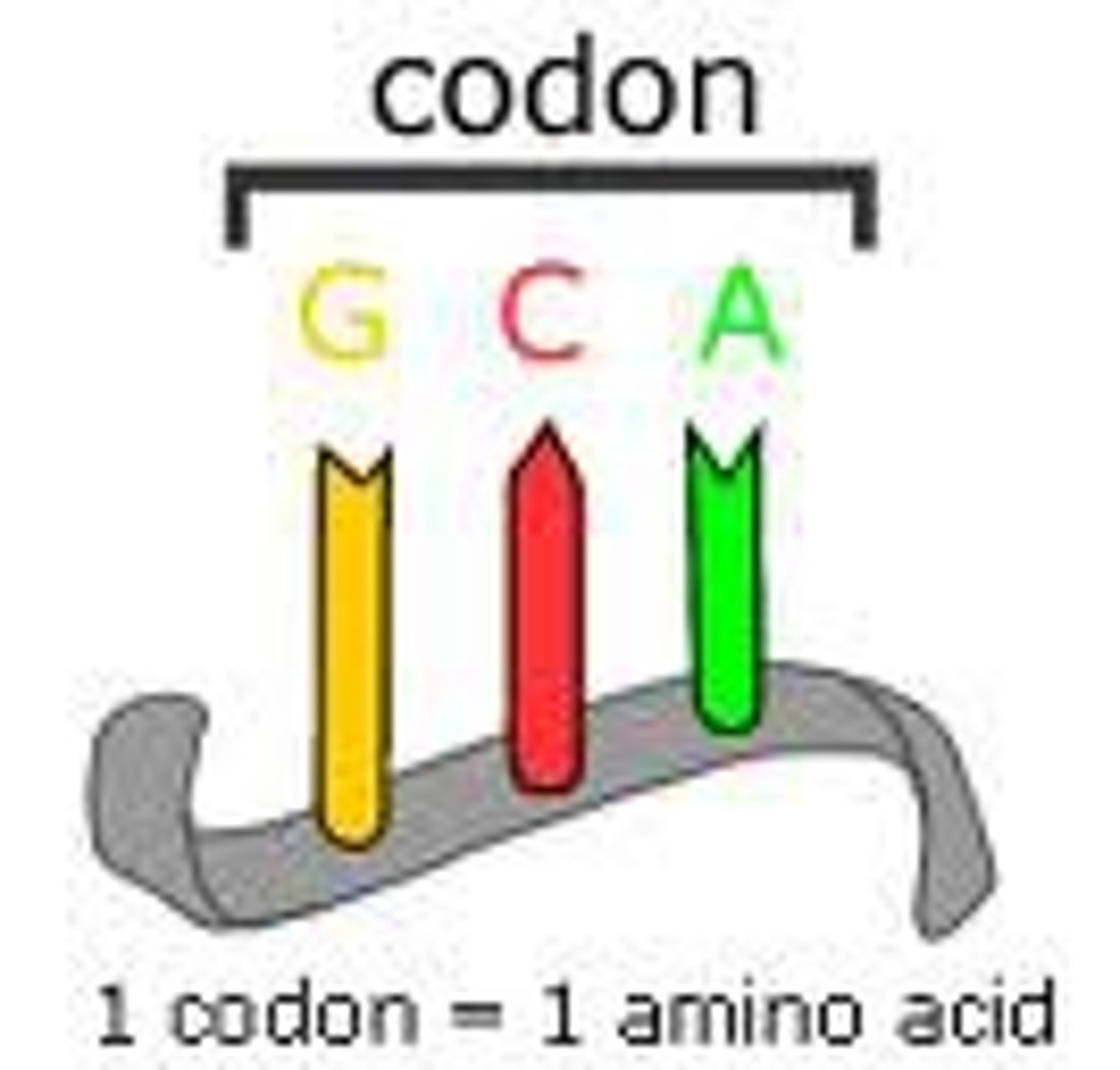
AUG
think starts school in AUGest
Start codon

1) UGA - U Go Away
2) UAG - U Are Gone
3) UAA - U Are Annoying
Stop codons

Specific mutations one piece of a codon:
1) Silent
2) Nonsense
3) Missense
Point mutations
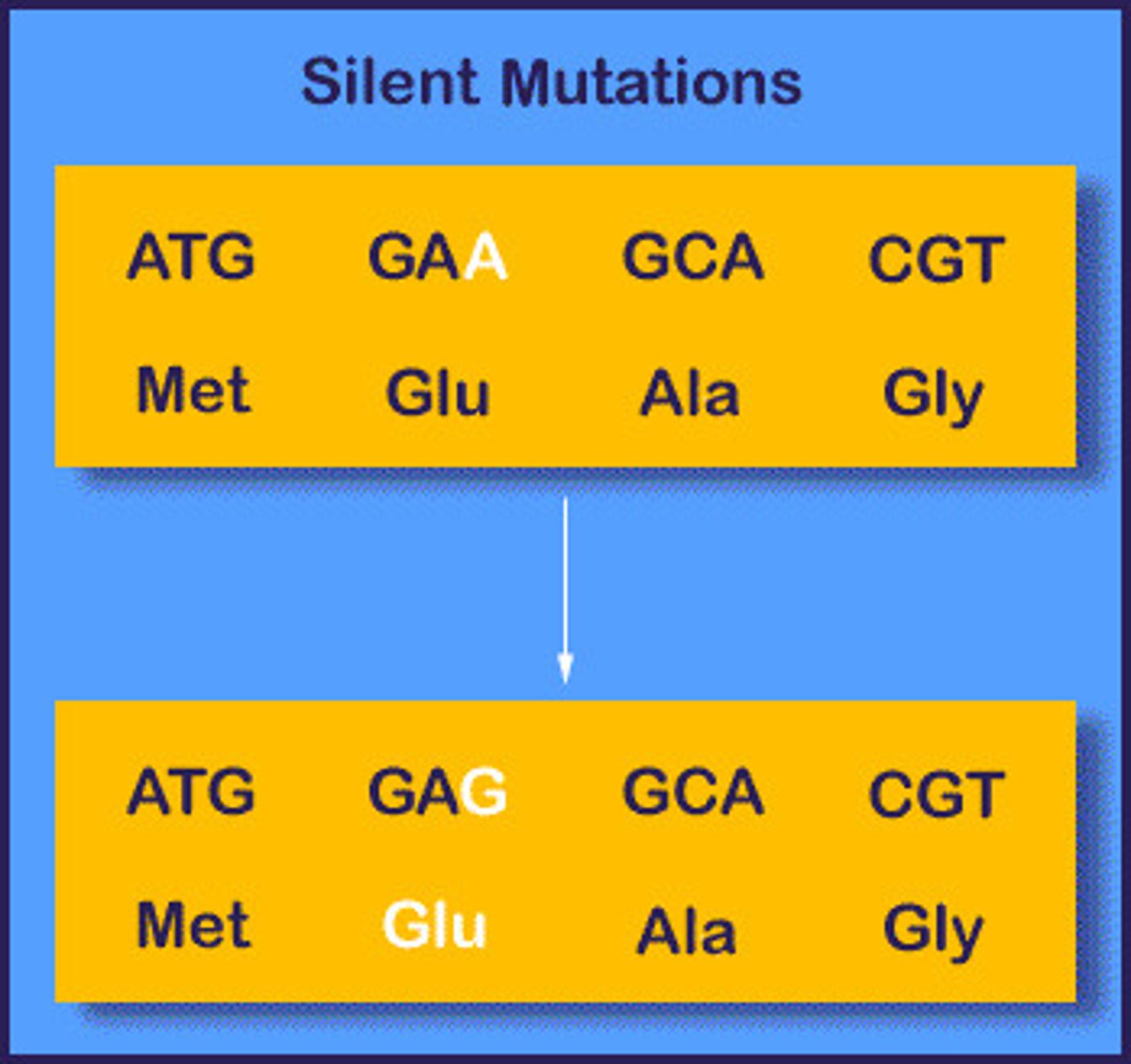
Causes no effect in the protein sequence due to redundancy in the wobble position (third base in codon)
Silent mutations
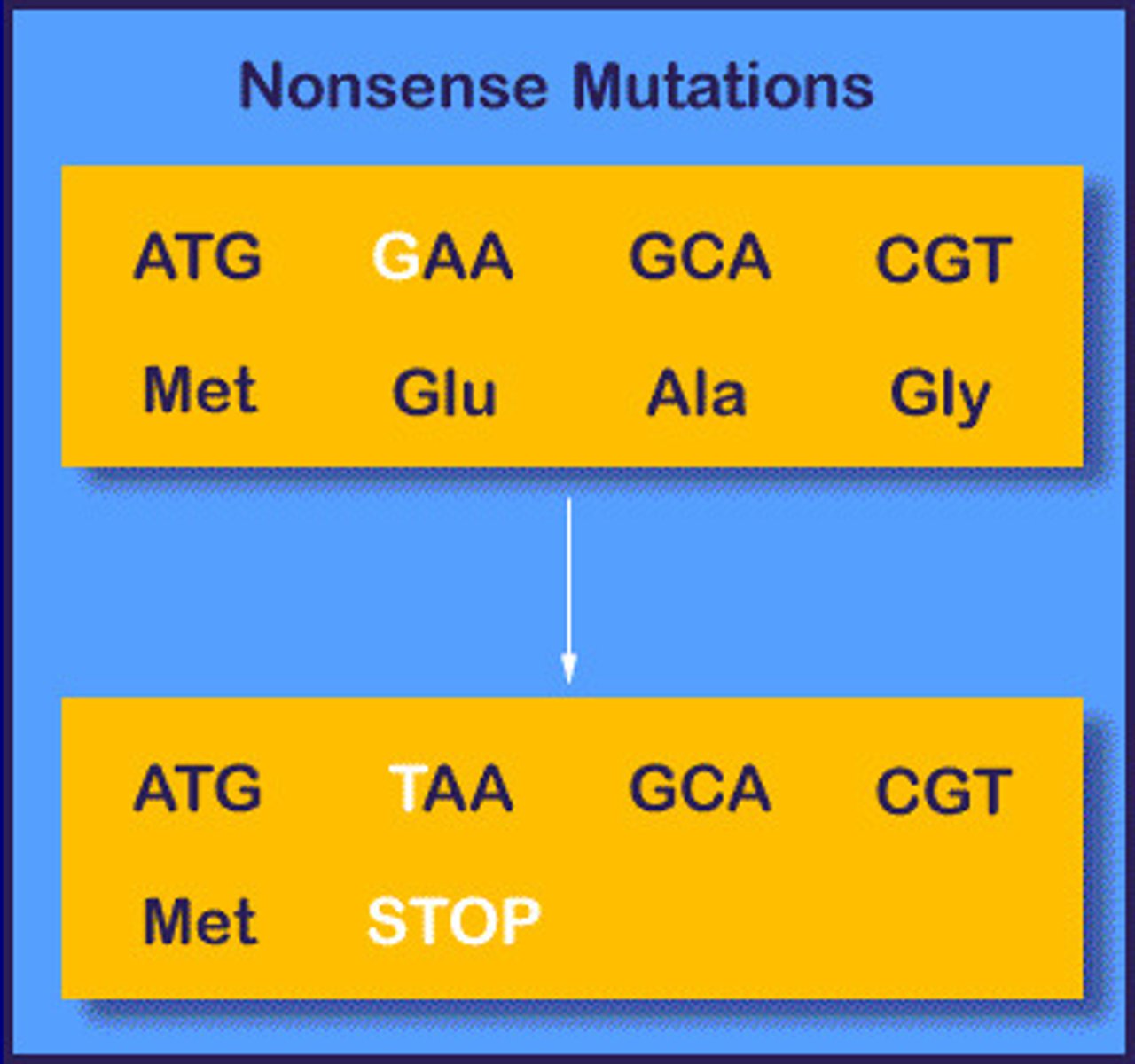
Mutation that produces a premature stop codon.
Nonsense (truncation)
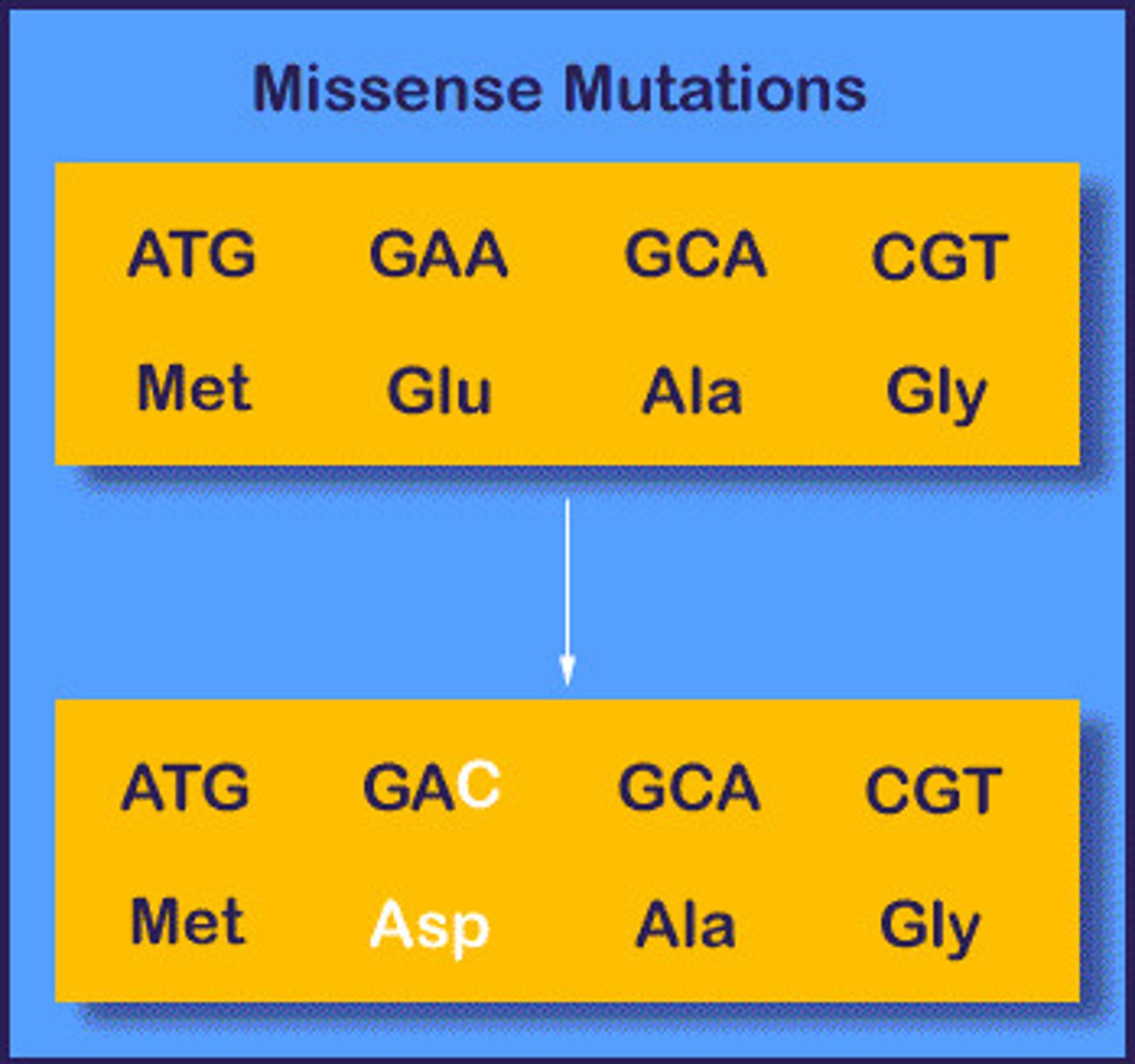
Mutation that produces a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
Missense mutation
Mutation that results from nucleotide addition or deletion, and change the reading frame of subsequent codons.
Frameshift mutation
RNA has:
1) A ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose
2) Substitution of uracil for thymine
3) Single-stranded instead of double-stranded
RNA vs DNA
The coding pattern of eukaryotes in which one mRNA molecule codes for only one protein.
Monocistronic
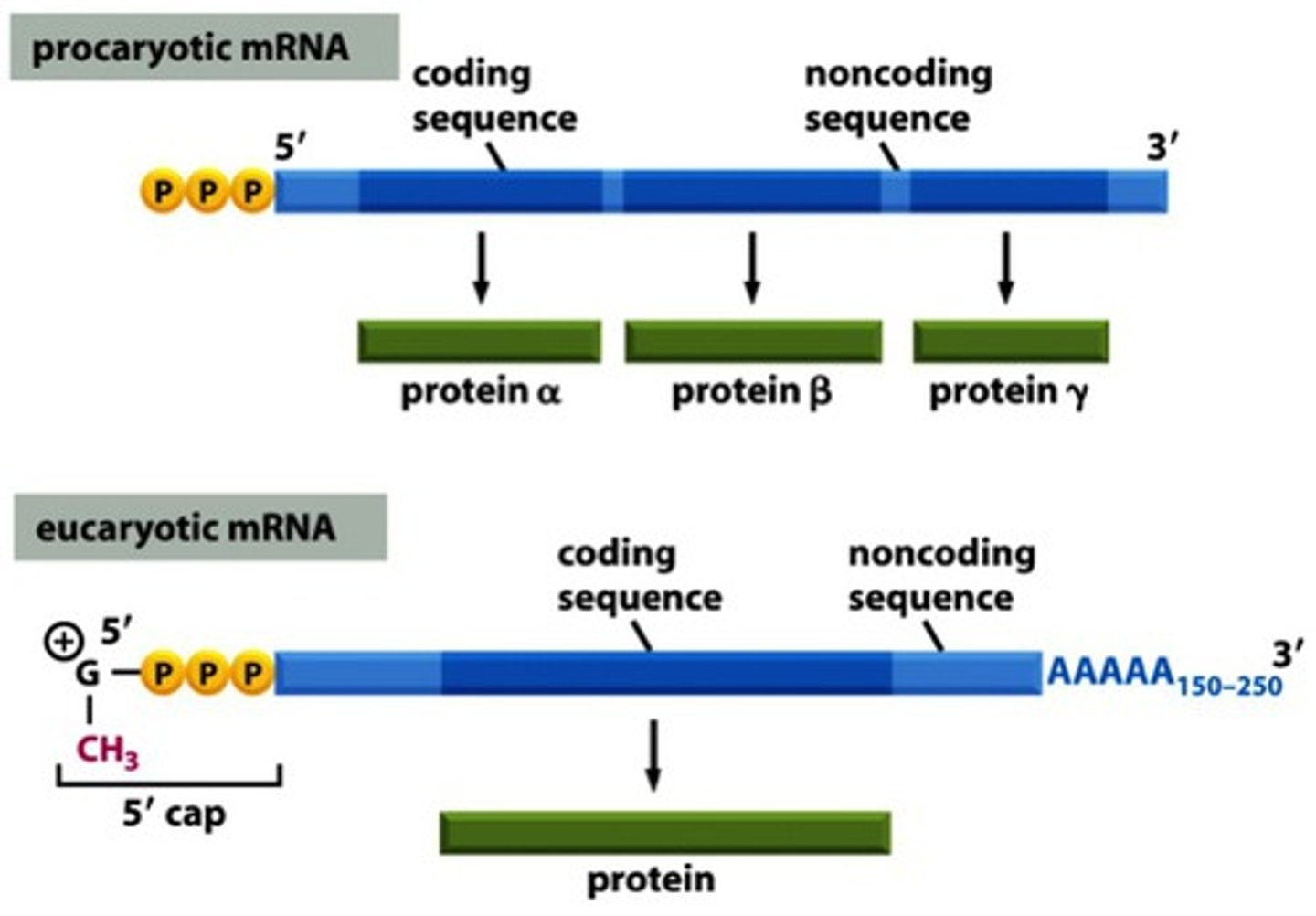
The coding pattern of prokaryotes, in which one mRNA may code for multiple proteins.
Polycistronic
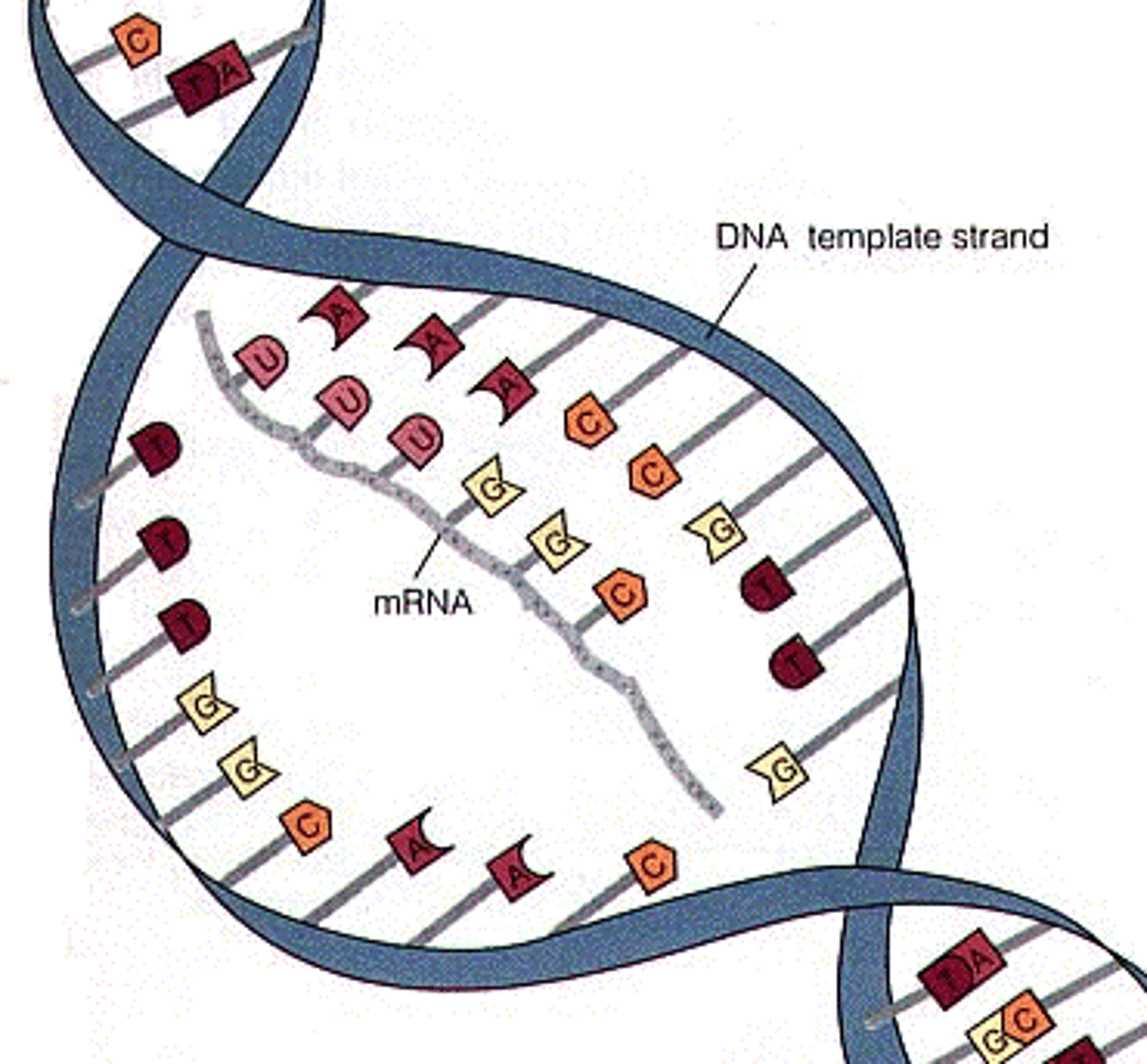
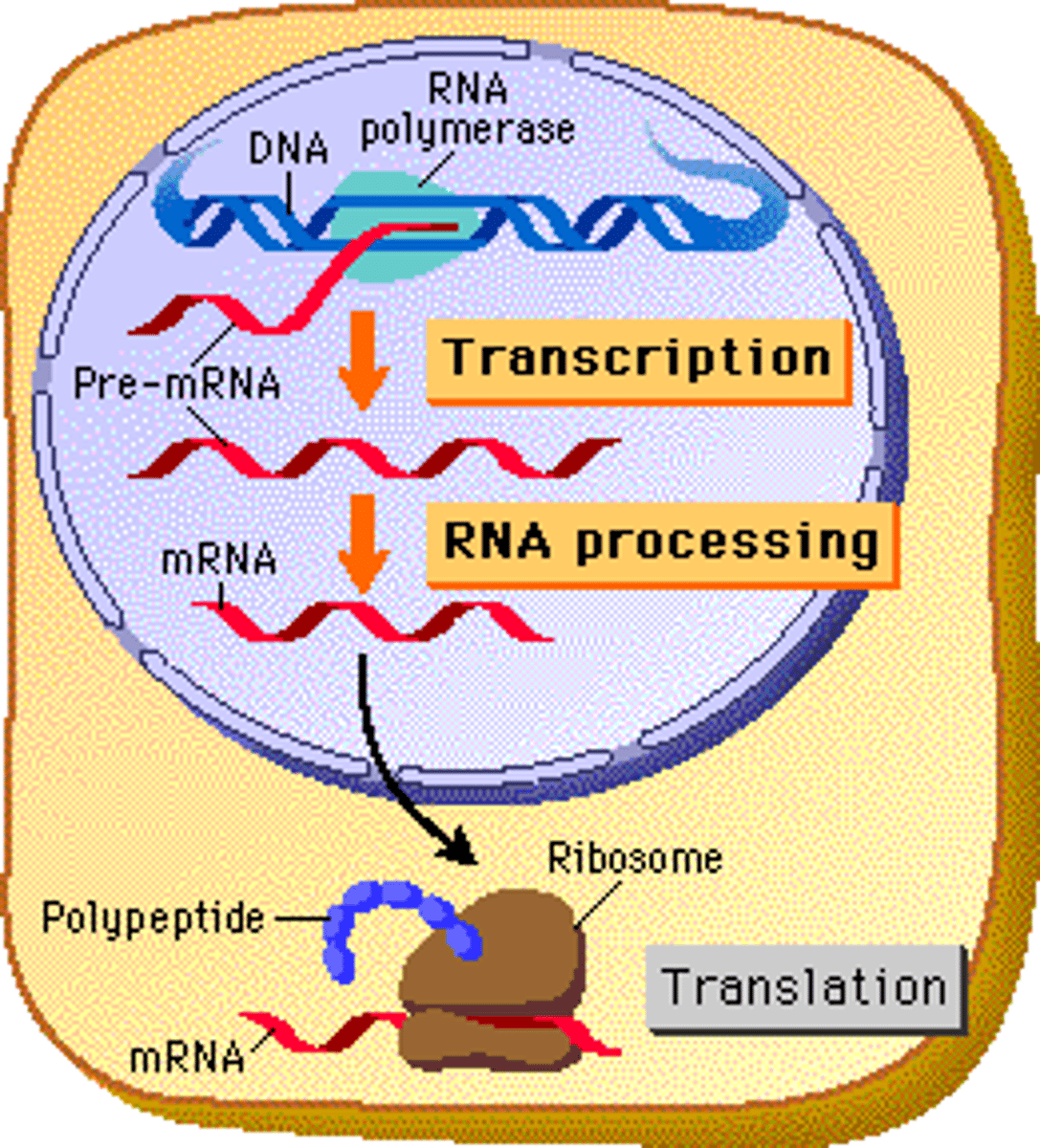
The creation of mRNA from a DNA template.
Transcription
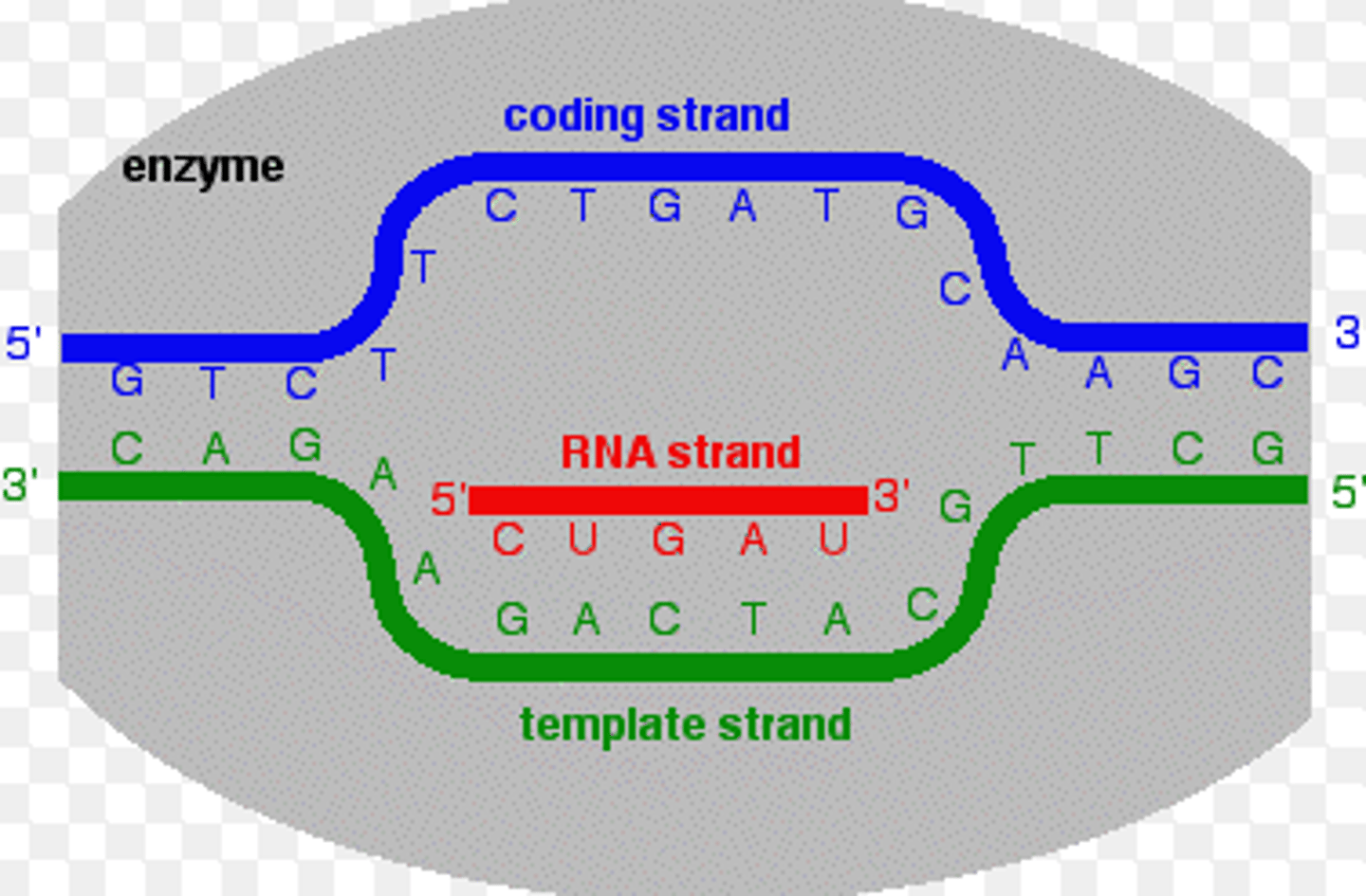
1) Coding strand
2) Template strand
DNA strands to be transcribed
Enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
1) Reads 3' to 5' but adds 5' to 3'
2) Does no proof reading
3) Continues until it reaches a termination signal.
RNA polymerase
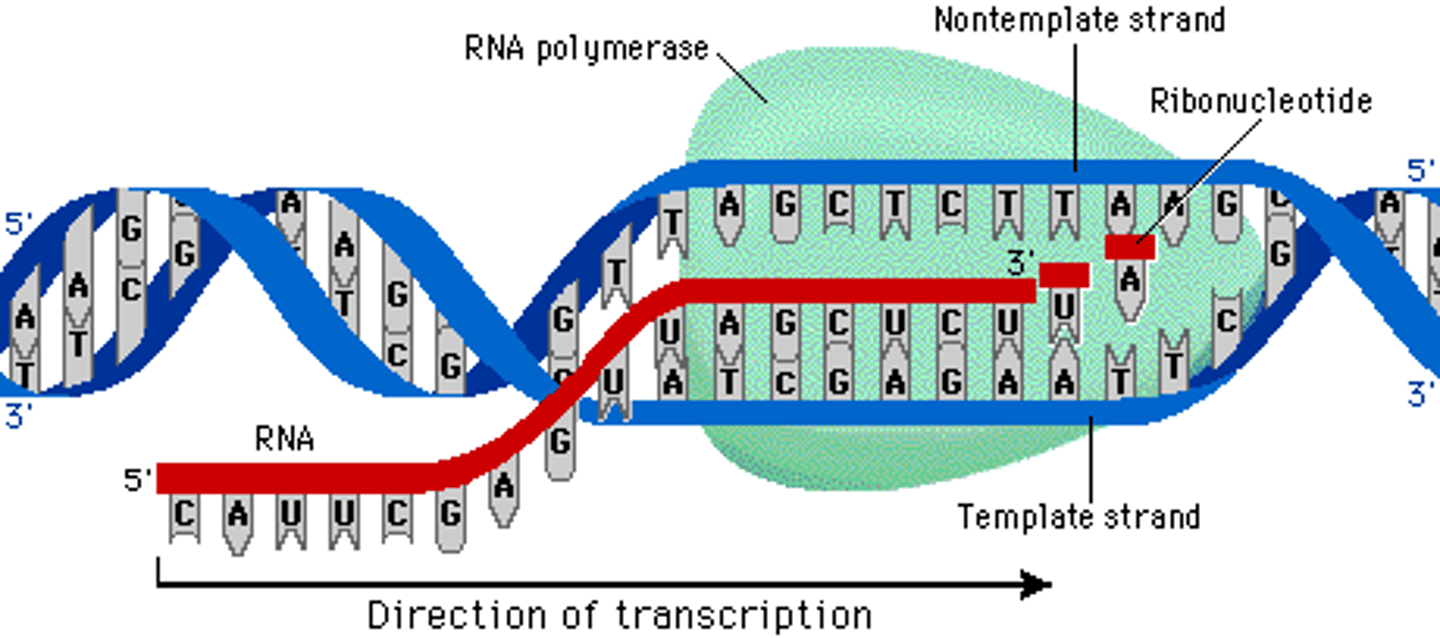
Heterogeneous RNA.
RNA that has been freshly transcribed and has not underwent any post transcriptional modifications.
hnRNA
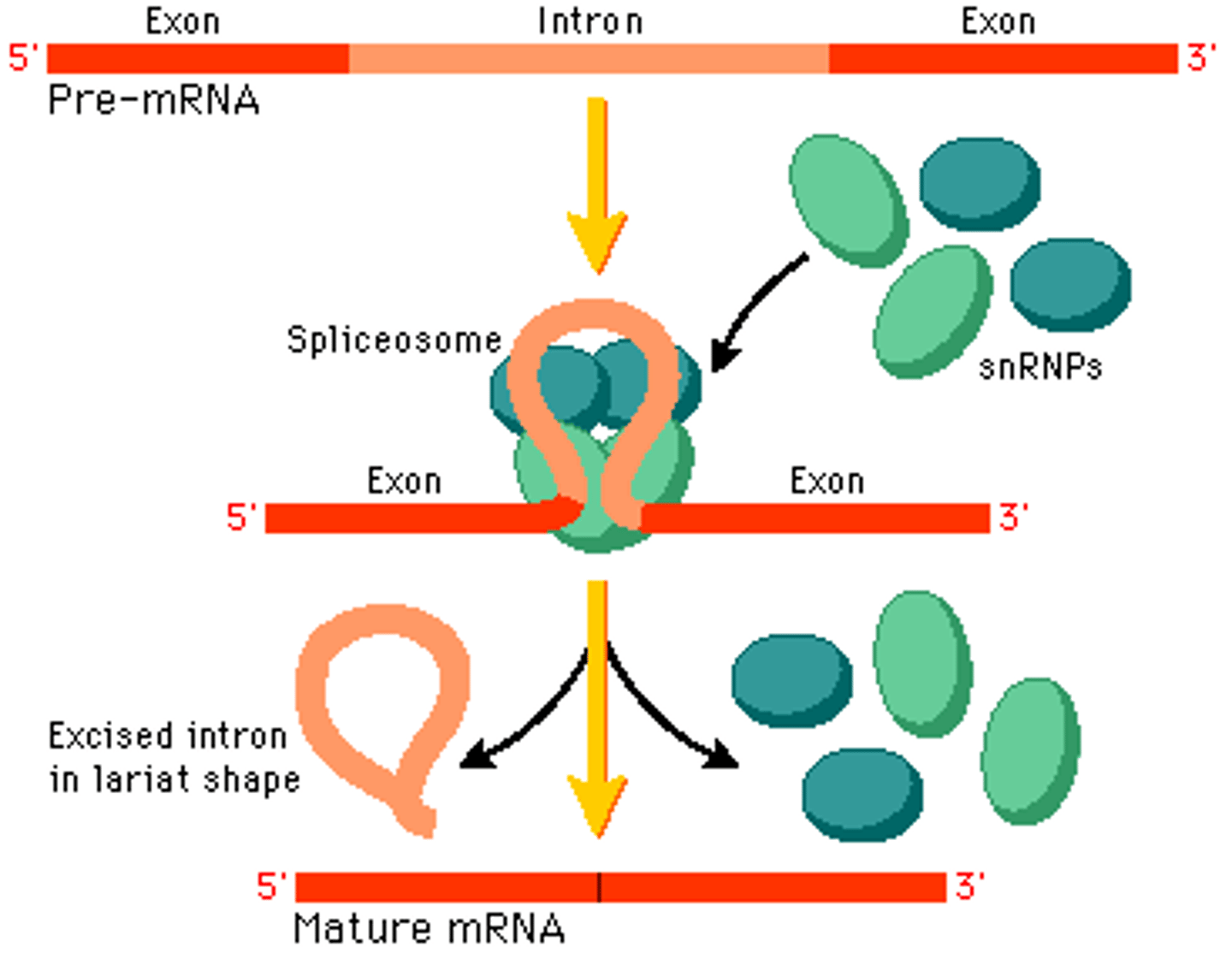
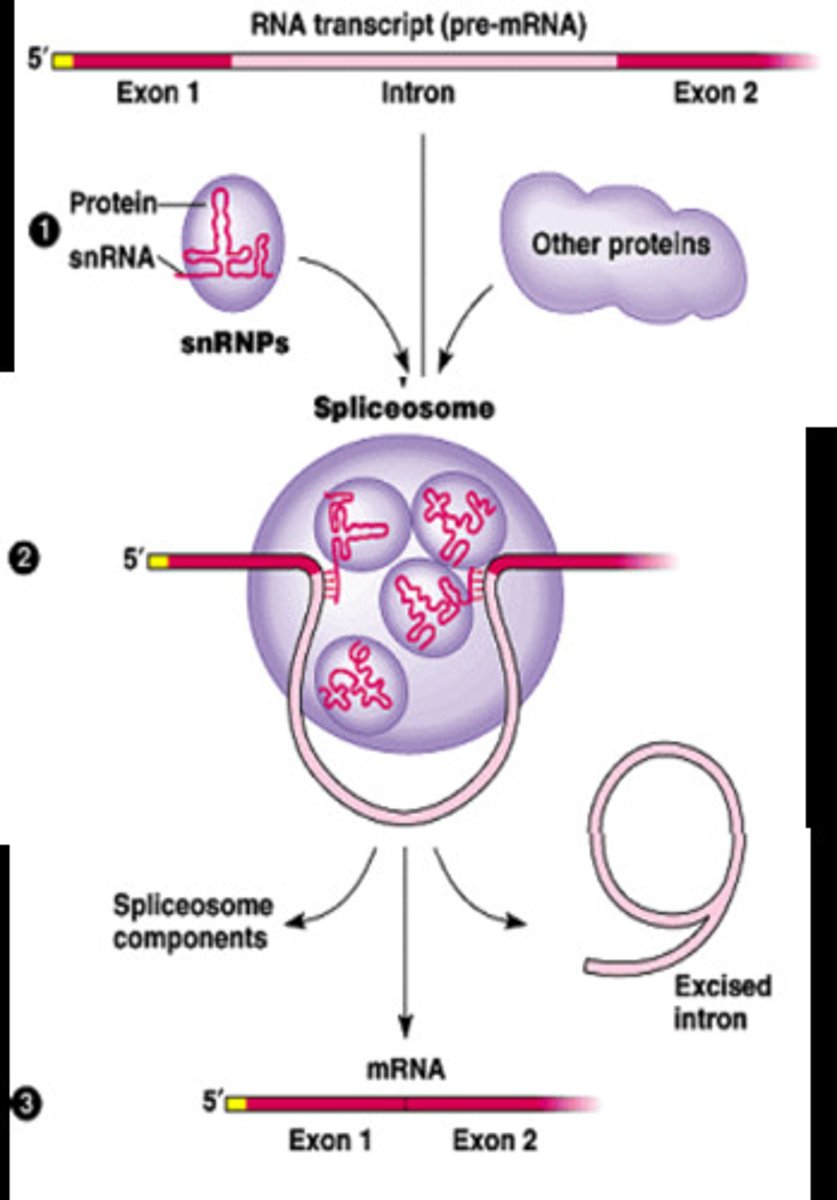
a complex of specialized RNA and protein subunits that removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA segment.
Contain:
1) snRNA
2) snRNPs or "snurps"
Splicesome
A 7-methylguanylate triphosphate cap that protects mRNA from degradation in cytoplasm and is a recognized binding site for ribosomes.
5' Cap
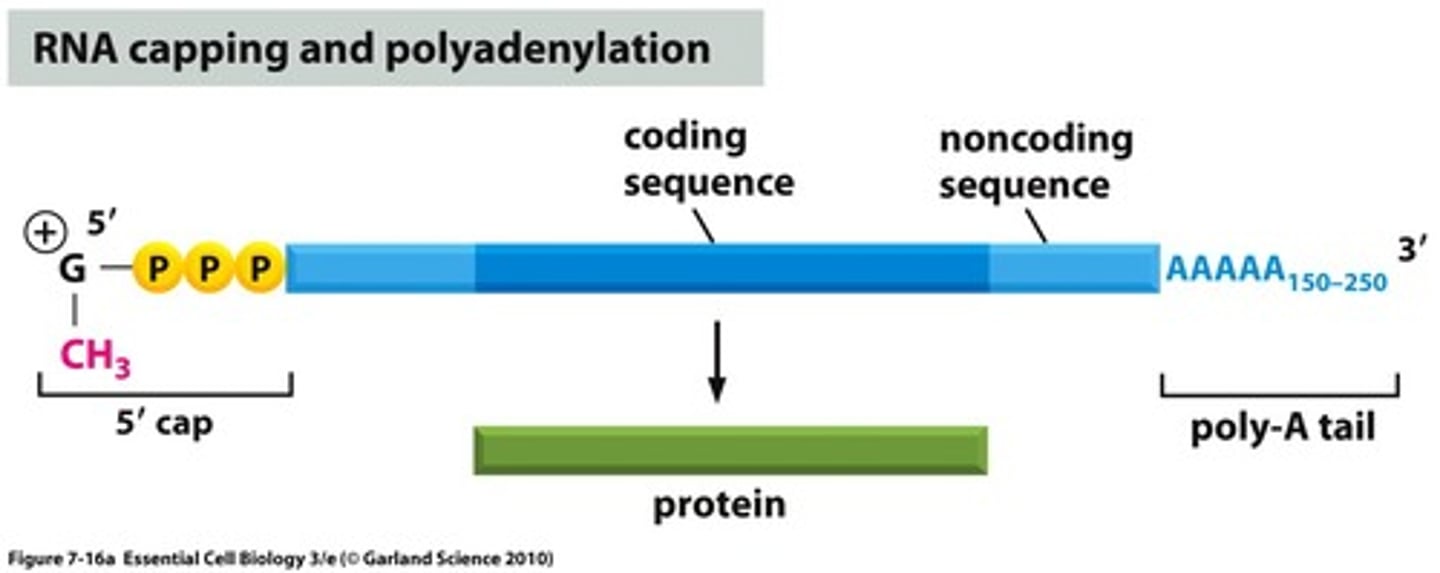
A poly-A tail is composed of adenine and is added to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript and protects the message against rapid degradation.
Longer the poly-A tail = longer time before degradation.
3' Poly-A tail
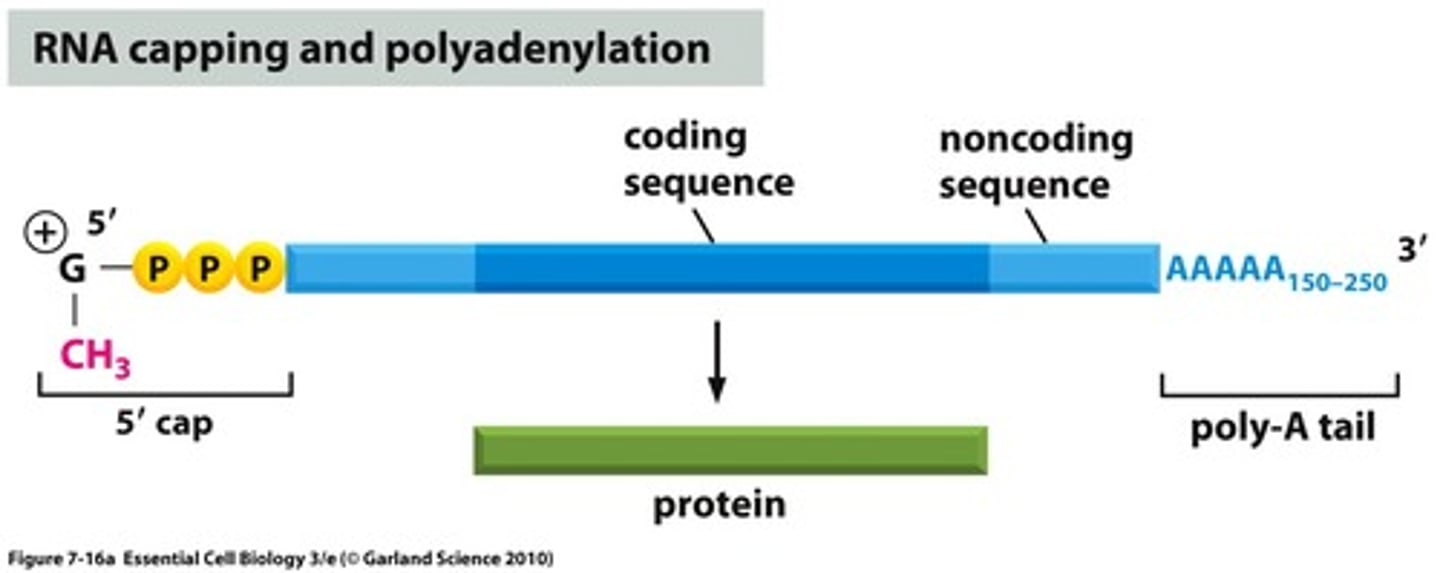
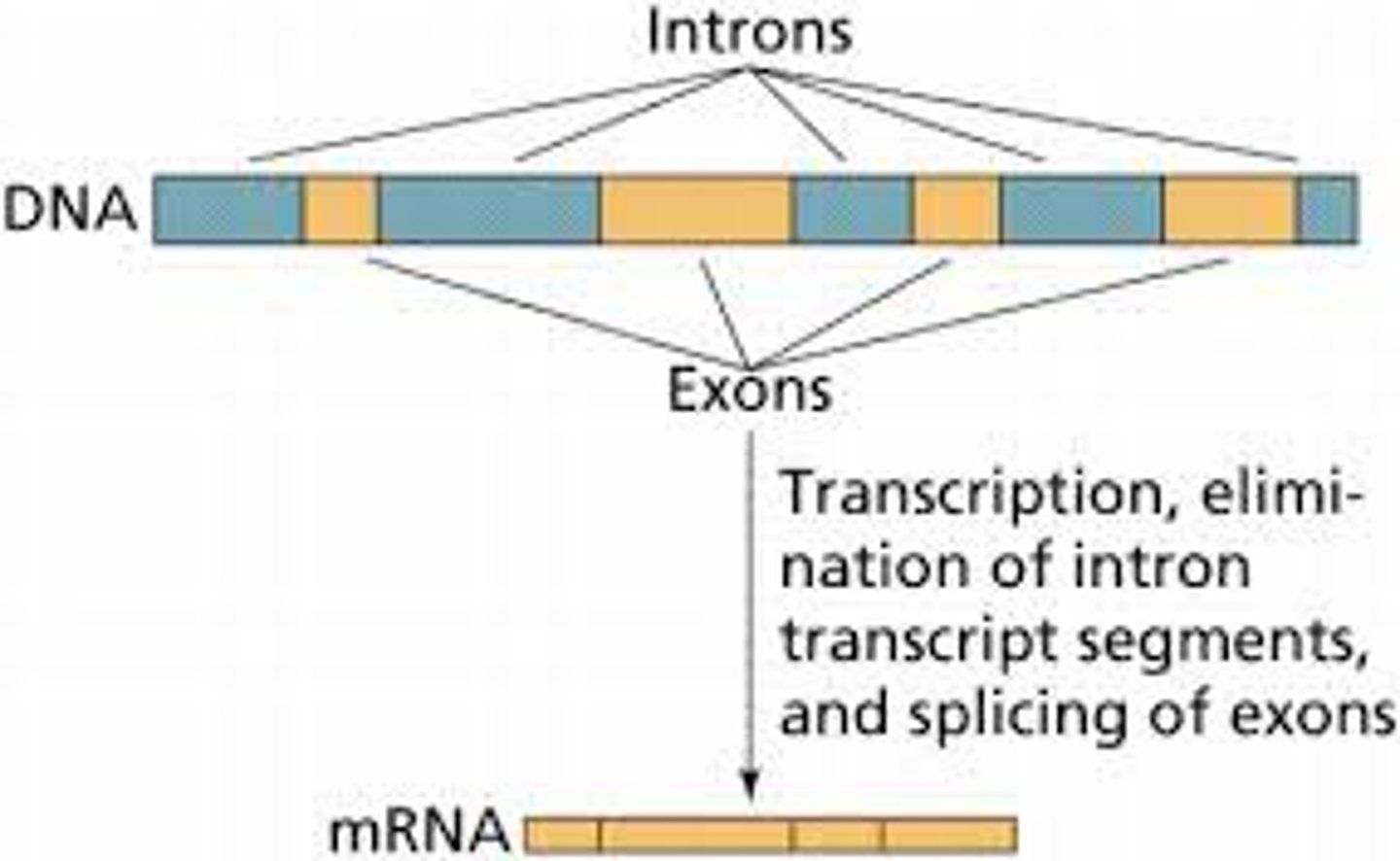
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
Introns
1) Helicase and topoisomerase unwind the dsDNA.
2) RNA polymerase II binds to TATA box within the promoter region of the gene (25 base pairs upstream)
3) hnRNA is synthesized from the DNA template (antisense) strand and stopped once termination signal.
Post-translational modifications
4) A 7-methylguanylate triphosphate cap added to 5' end.
5) Poly-A tail added to 3' end
6) Splicing done by snRNA and snRNPs in the spliceosome. Process removes introns.
7) Alternative splicing (combining of exons) allows more variability of gene products
8) Leave nucleus and into cytosol.
Mechanism of transcription
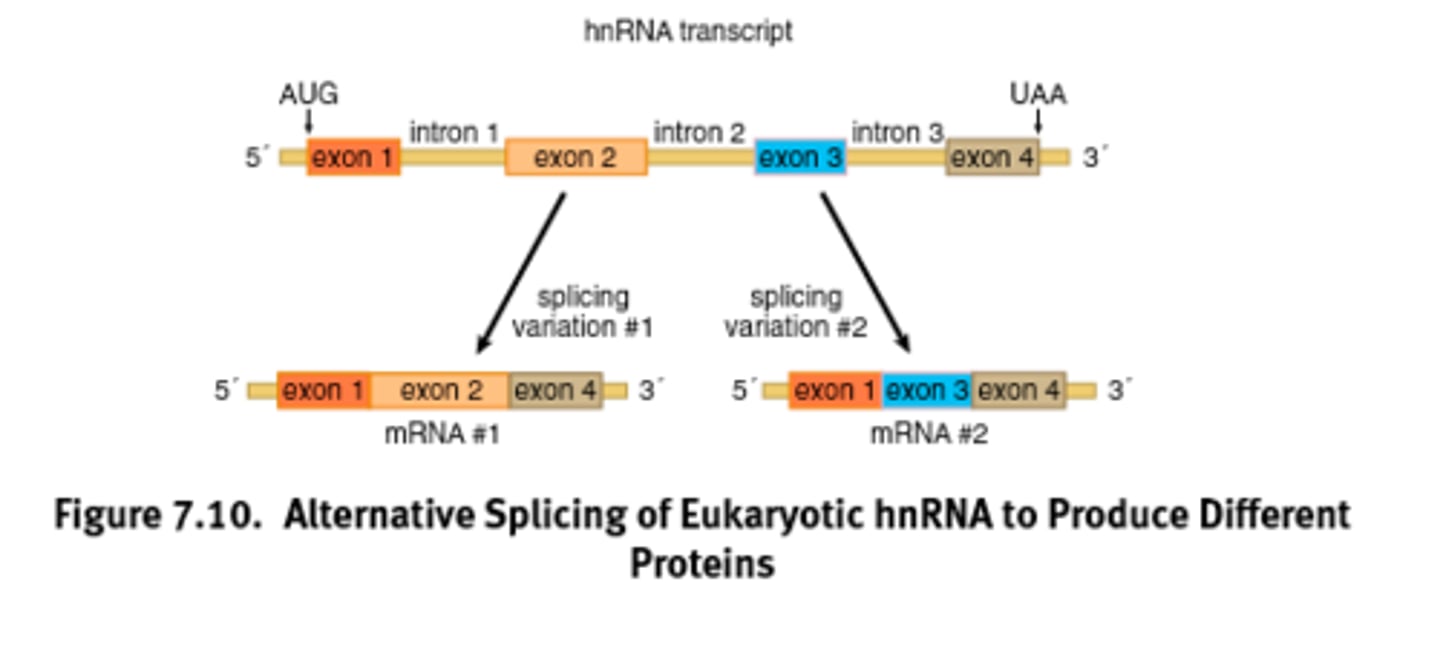
Splicing of introns in a pre-mRNA that occurs in different ways, leading to different mRNAs that code for different proteins or protein isoforms. Increases the diversity of proteins.
Alternative splicing
A coding region of a eukaryotic gene. Exons, which are expressed, are separated from each other by introns.
Exons
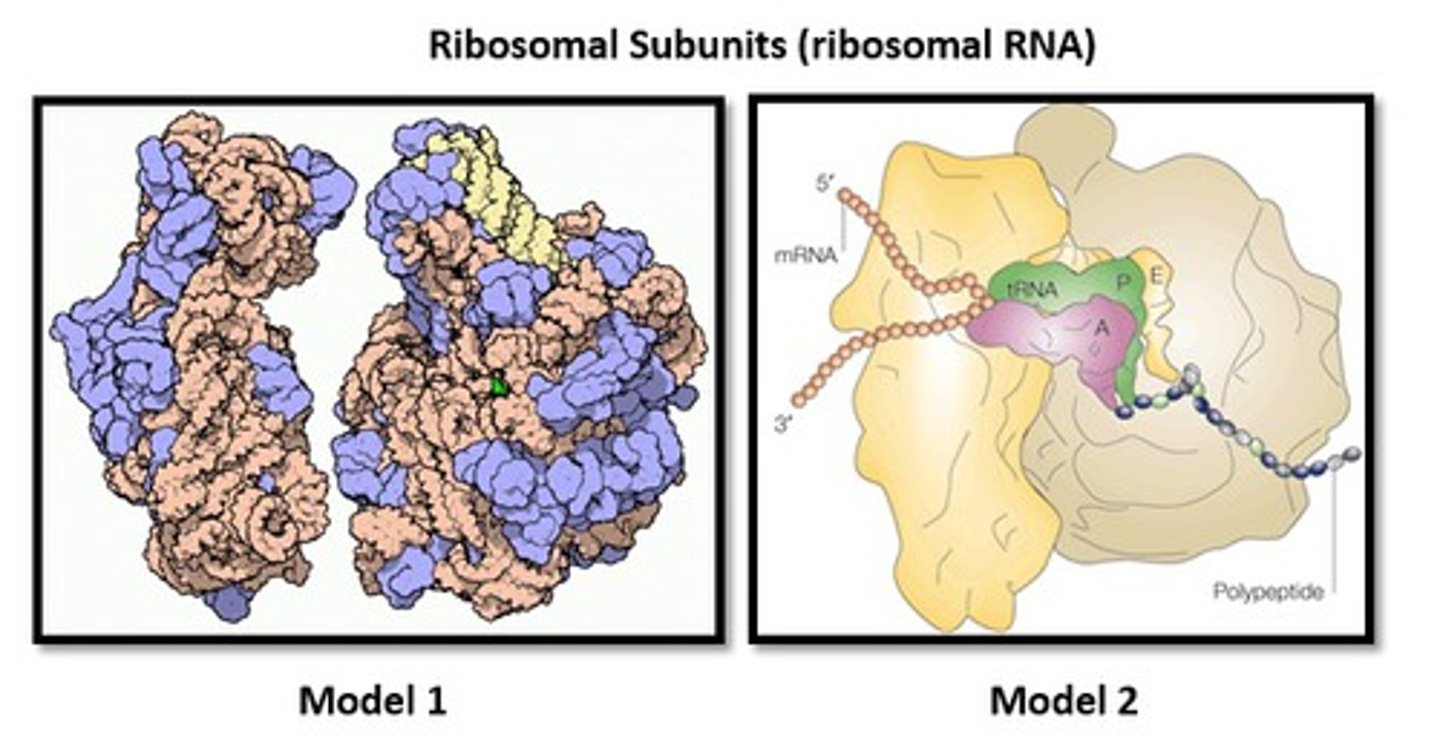
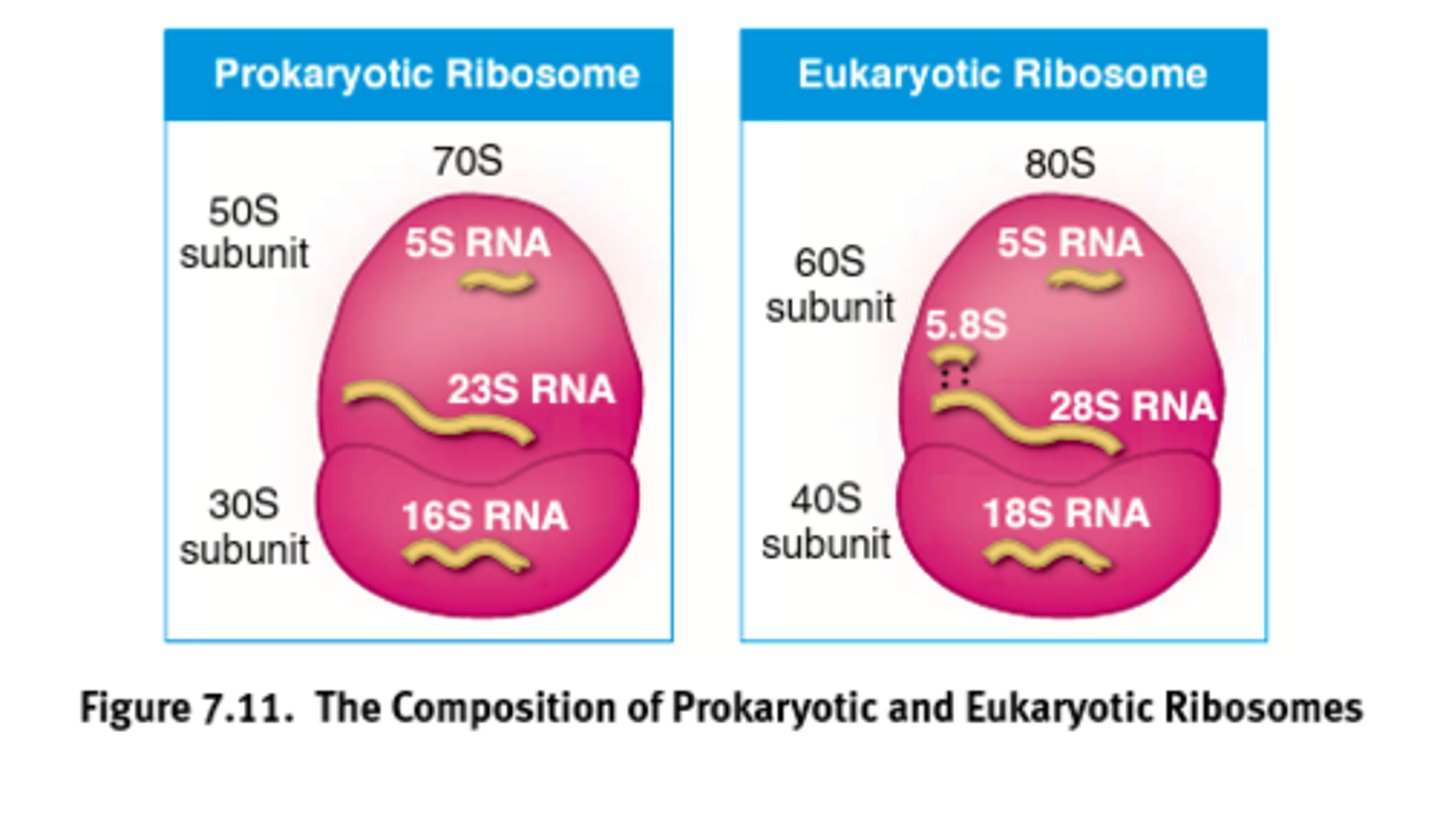
Factories for the translation of mRNA into proteins.
Composed of proteins and rRNA with variability among prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Ribosome
Eukaryotic Ribosome = 80 S
Prokaryotic Ribosome = 70 S
Where S value is determined experimentally by studying the behavior of particles in a centrifuge.
Ribosomal sub-weight
(Two domains)
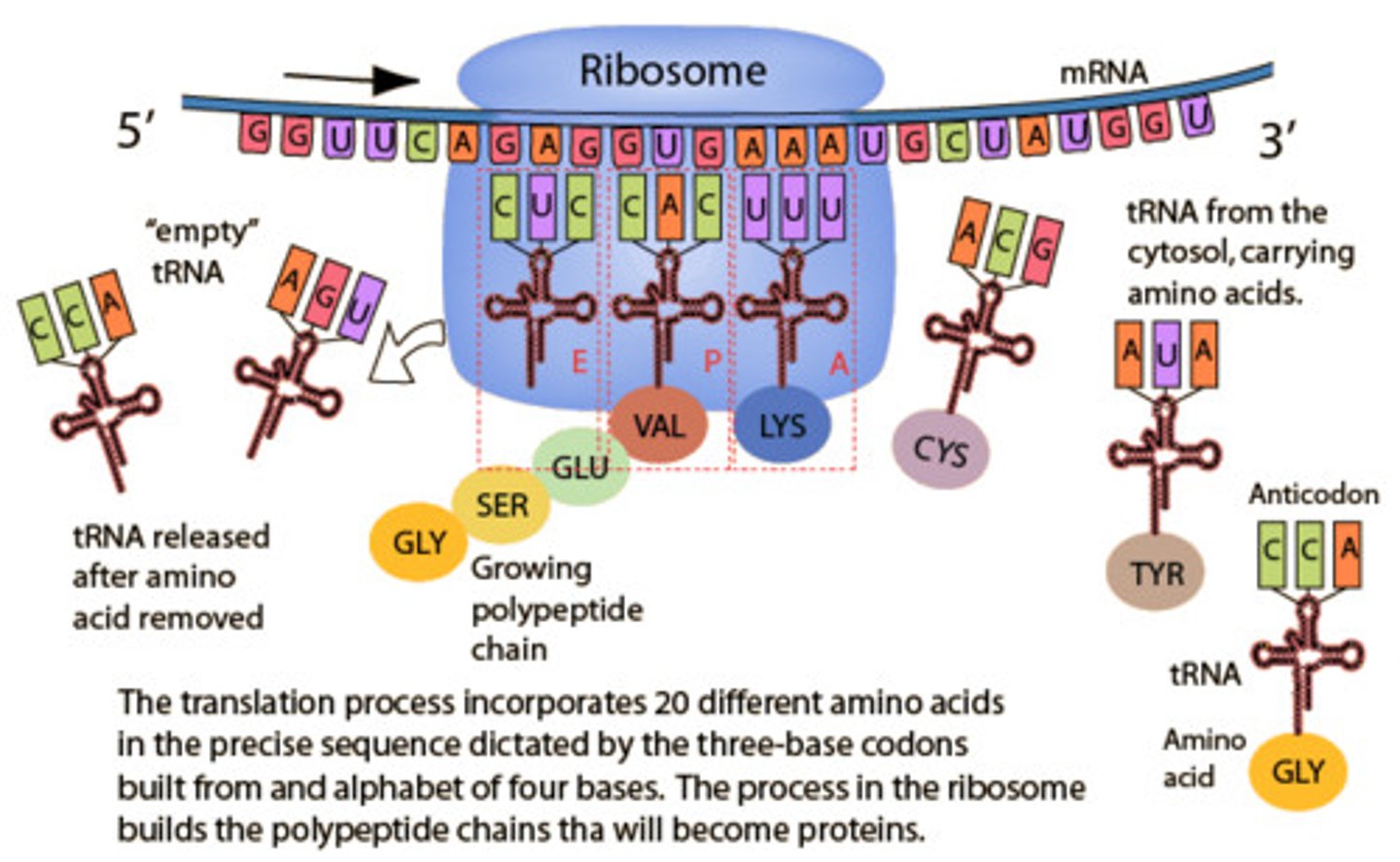
1) Initiation begins for eukaryotes when 40S ribosome attaches to 5' cap and begins scanning for a start codon.
2) Once AUG is found, it lays down a methionine in the P site of the ribosome.
3) Elongation begins and new tRNA come into site A of the ribosome and transfer growing polypeptide chain from tRNA in the P site to tRNA in the A site.
4) The now uncharged tRNA exits the ribosome via the E site.
5) Process continues until stop codon is reached and a release factor places a water molecule on the polypeptide chain causing release of protein.
Post-translational modifications
6) Folding by chaperones, formation of quaternary structure, cleavage of protein or signal sequences, or the covalent addition of other biomolecules.
Mechanisms of Translation
The addition of phosphate group by protein kinases to activate deactivated proteins.
Phosphorylation
Addition of a carboxylic acid group, usually serves as calcium binding sites.
Carboxylation
Addition of oligosaccharides as proteins pass through the ER and Golgi apparatus to determine cellular destination.
Glycosylation
Addition of lipid groups to certain membrane-bound enzymes.
Prenylation
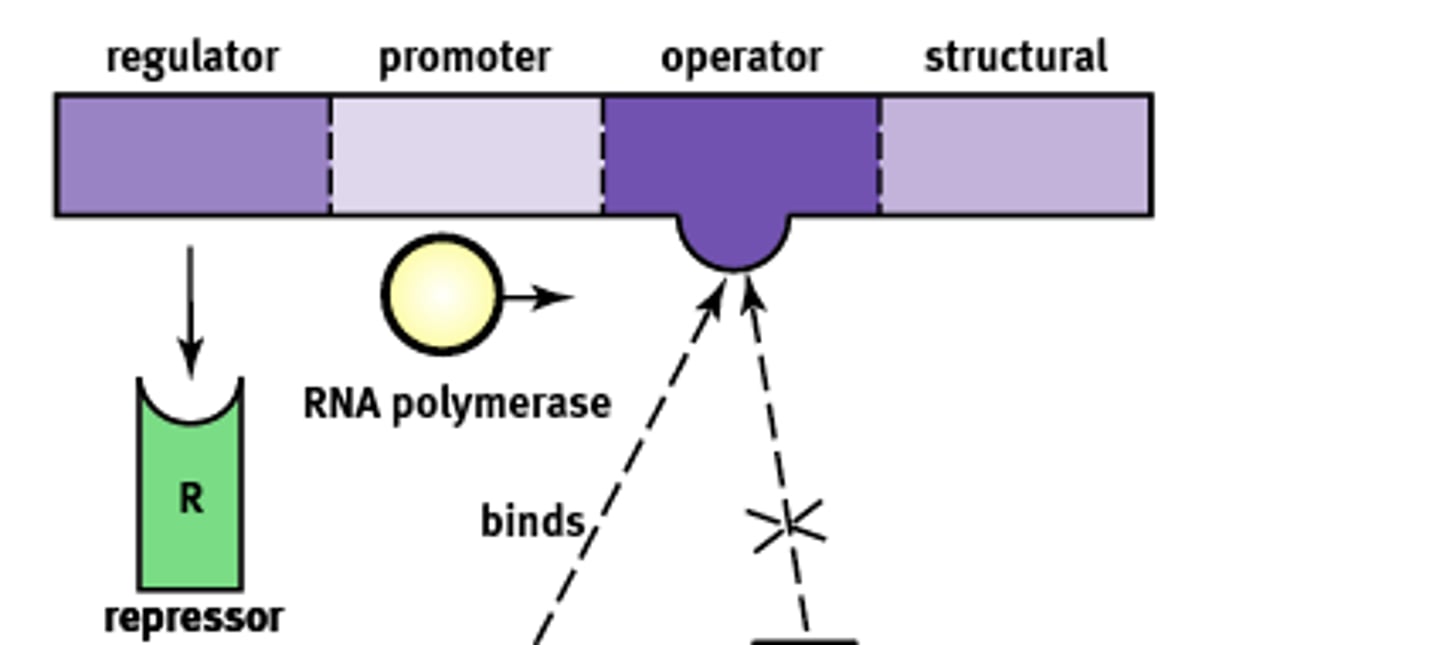
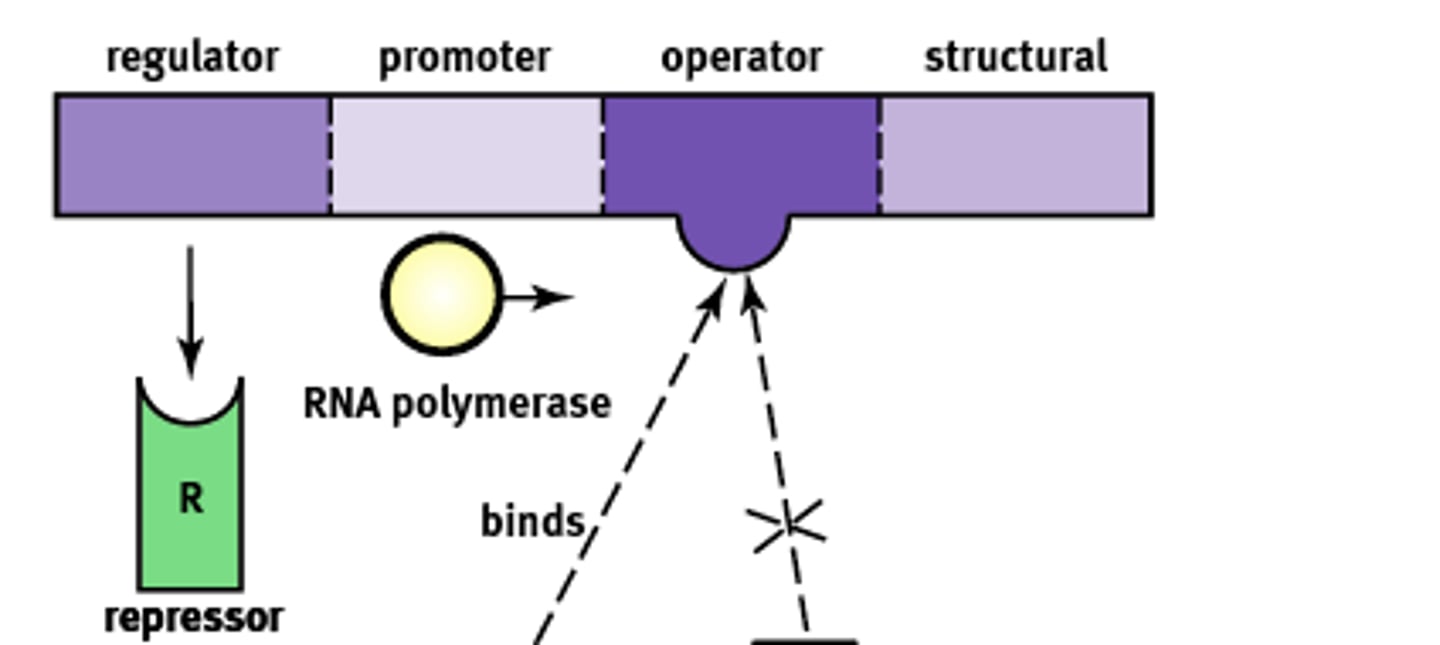
Essentially an "on-off" switch that regulates gene expression. Composed of:
1) Regulator
2) Promoter
3) Operator
4) Structural
Operon Structure
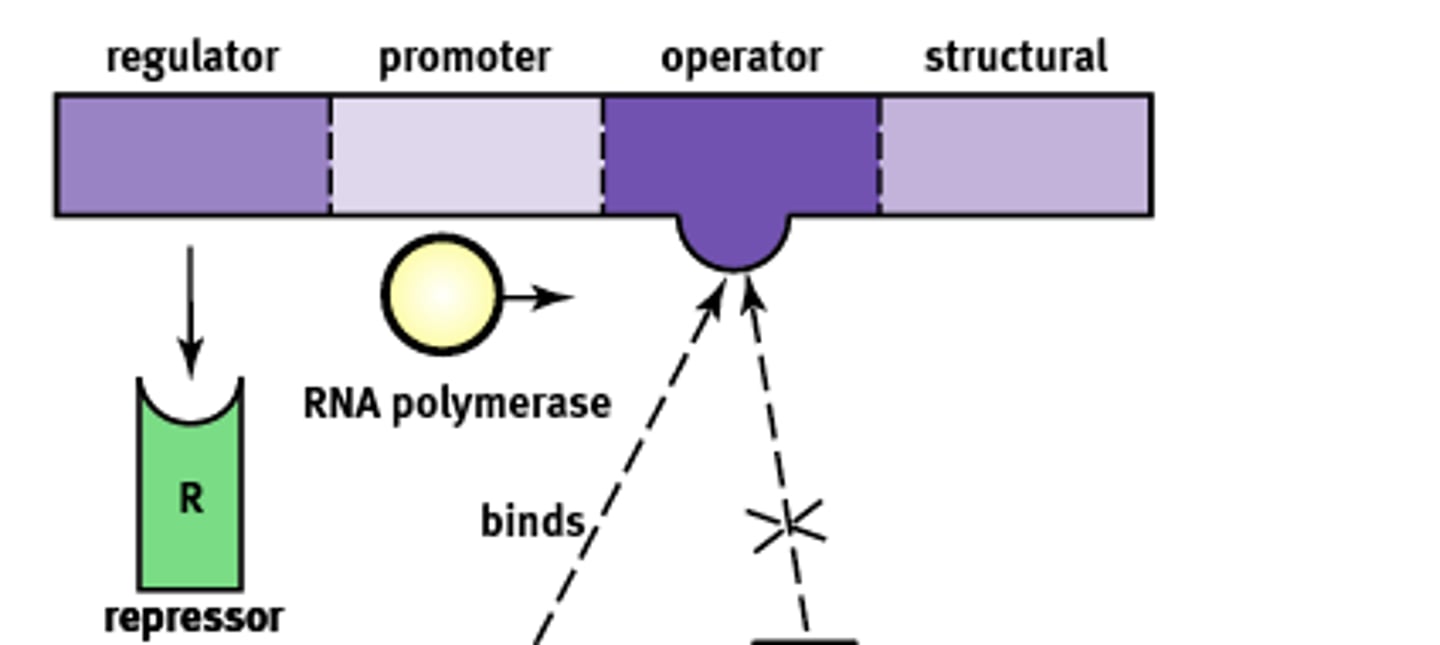
Codes for the protein known as a repressor that prevents gene transcription.
Regulator gene
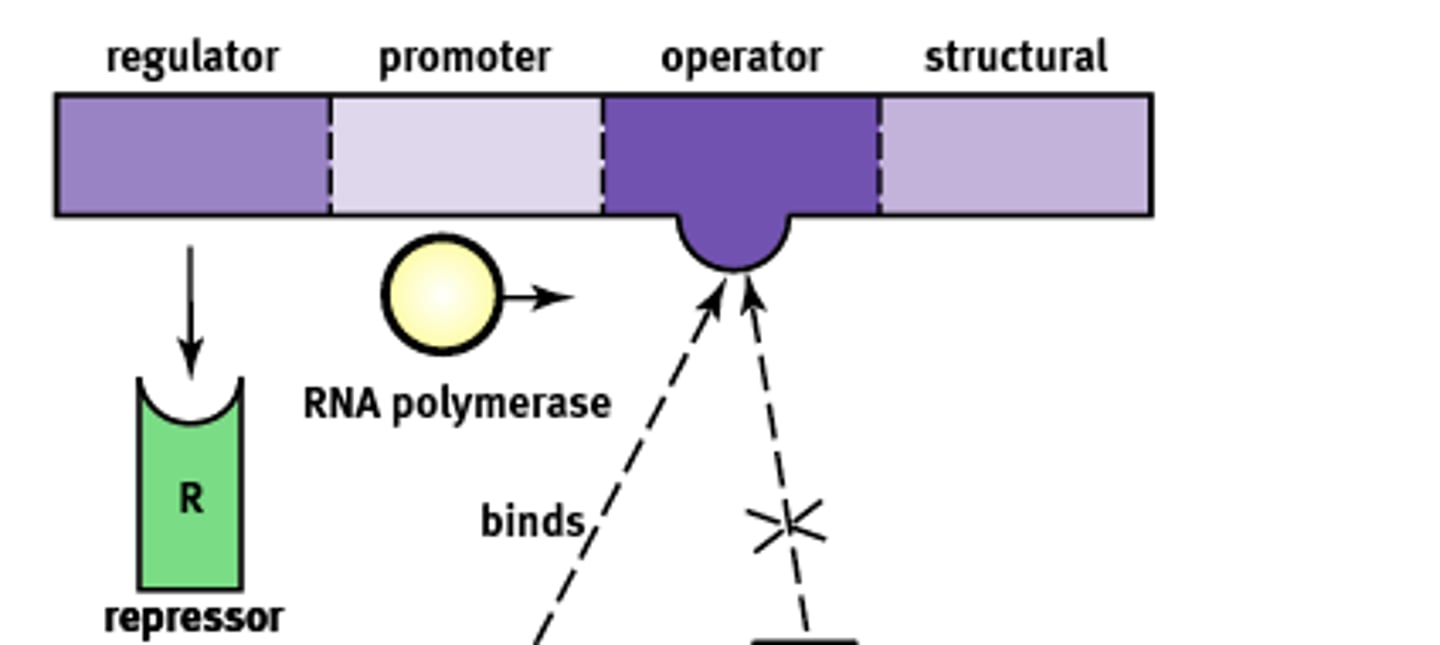
Site where RNA polymerase will bind to begin transcription. About ~25 base pairs upstream
Promoter site
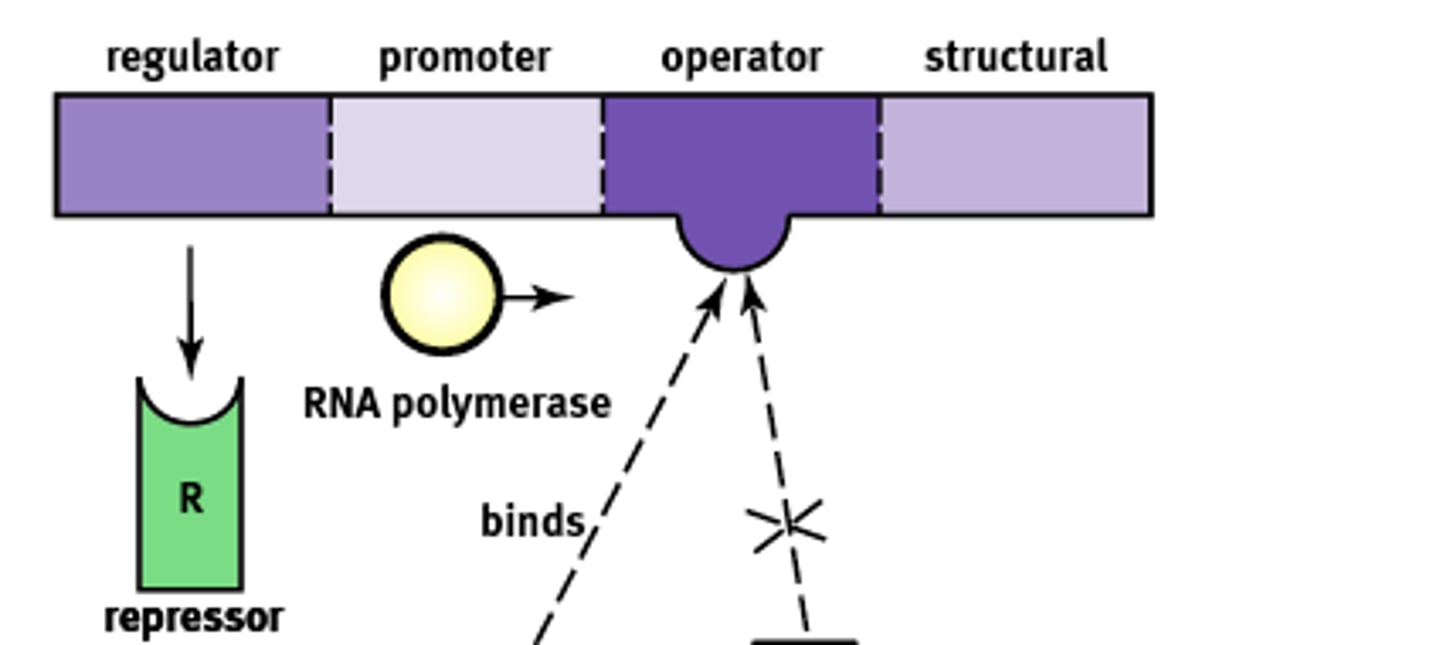
A non transcribable region of the DNA that is capable of binding a repressor protein and preventing transcription.
Operator
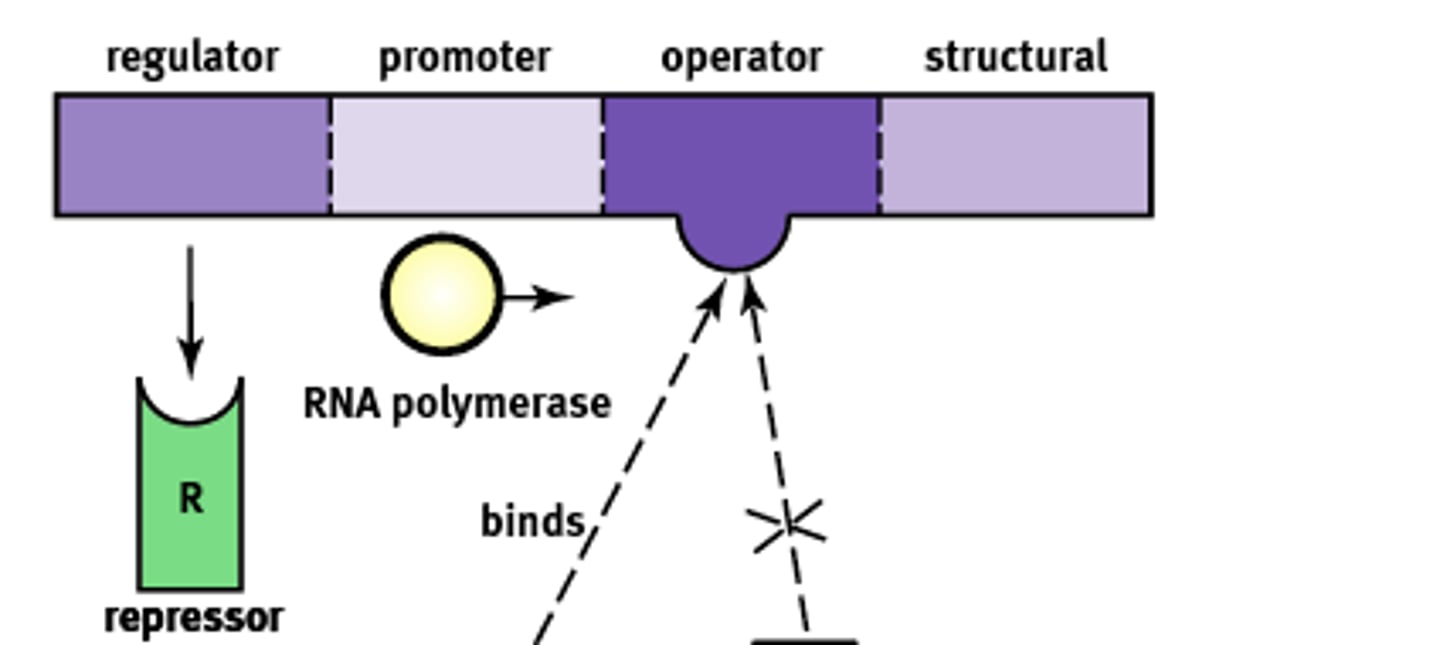
Codes for the protein of interest
Structural gene
Systems that are bonded to a repressor under normal conditions.
1) They can be turned on by an inducer pulling the repressor from the operator site.
Ex) lac operon.
Inducible system
System that is transcribed under normal conditions.
1) Can be turned off by a corepressor coupling with the repressor and binding to the operator.
Ex) Trp operon
Repressible system
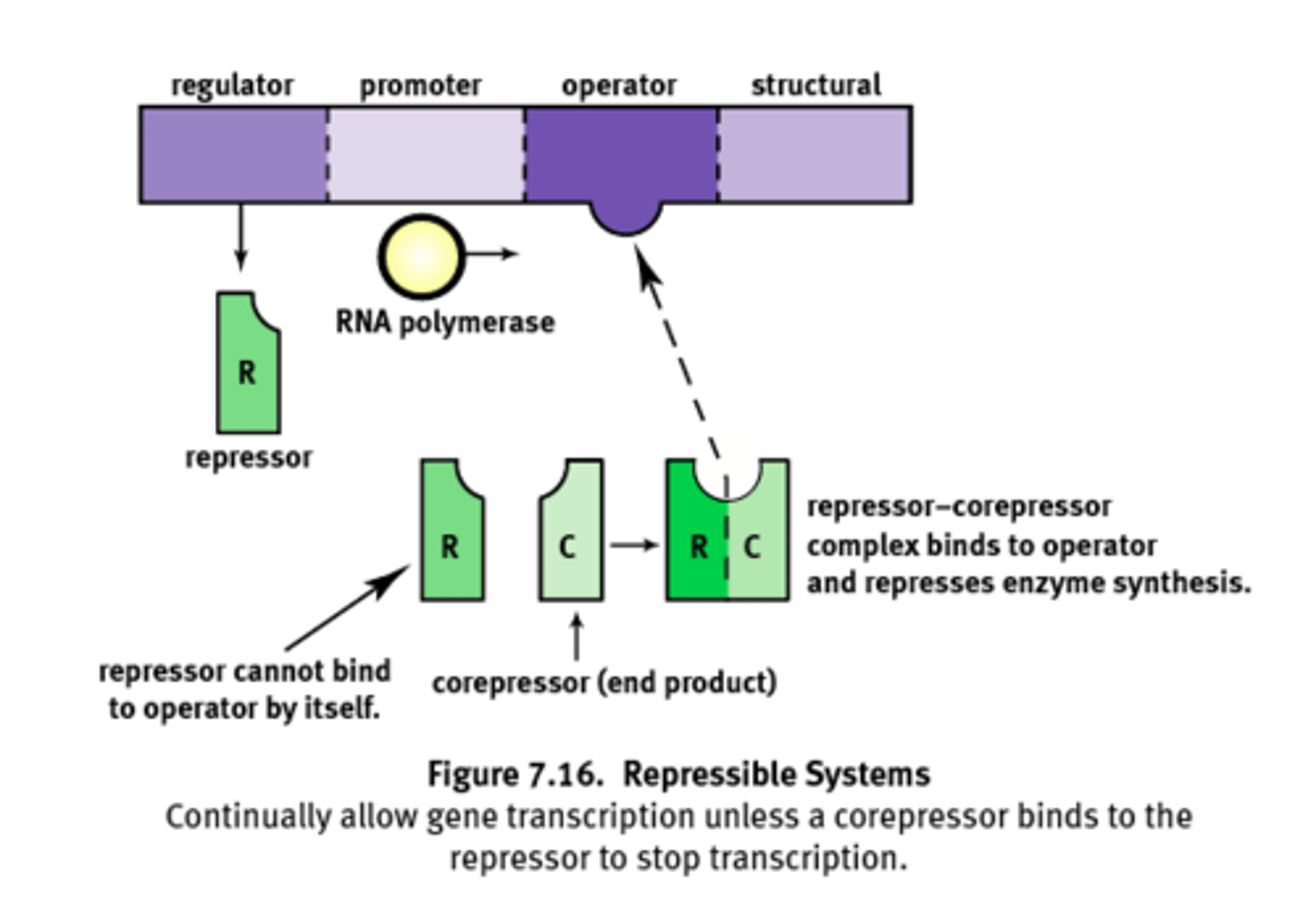
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
Transcription factors
Are more than 25 base pairs away from the transcription start site.
Enhancers
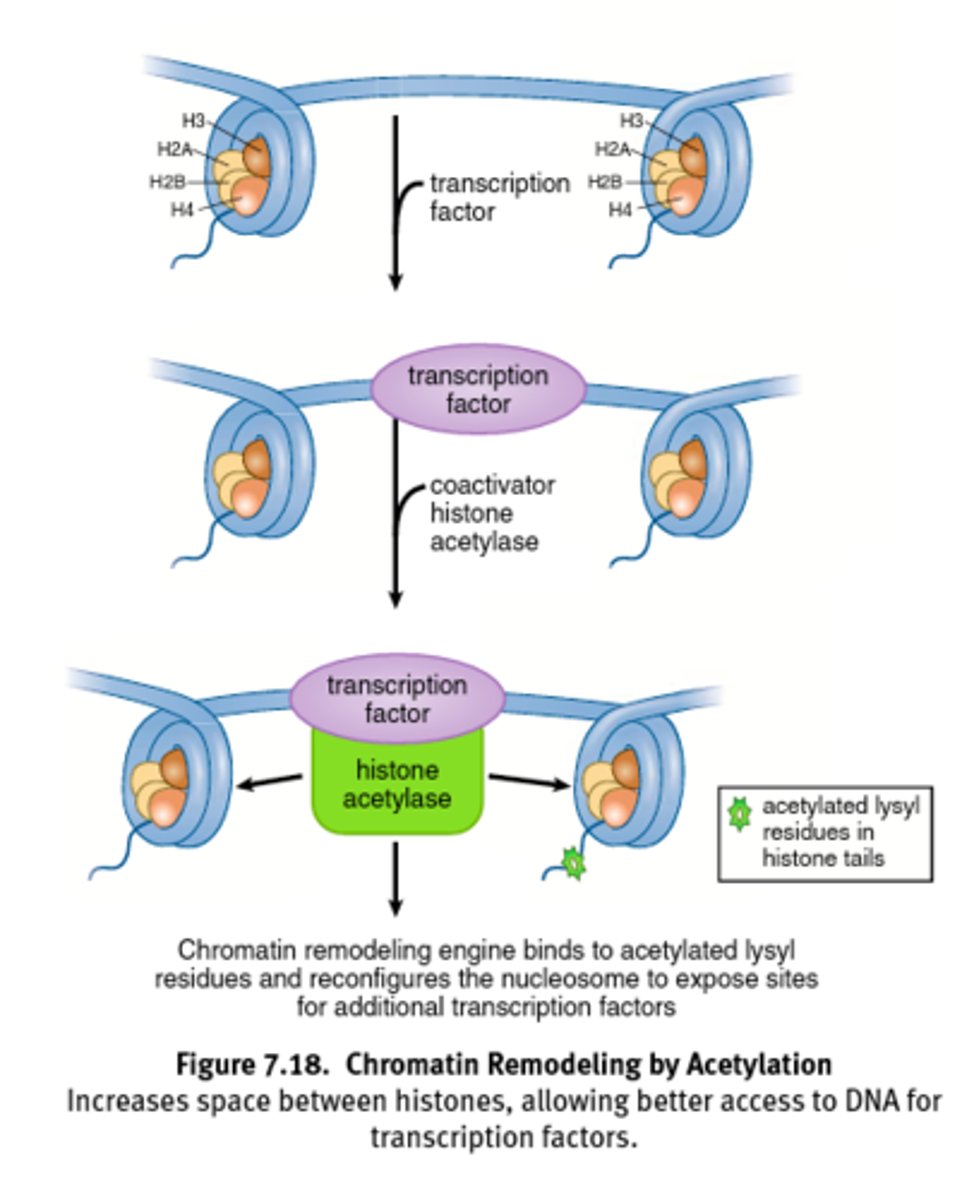
Acetylation of histones decreases positive charge on lysine residues and weakens histone-DNA interactions.
Results in open euchromatin formation that allows for easier asses for transcription factors.
Acetylation = Access
Histone Acetylation
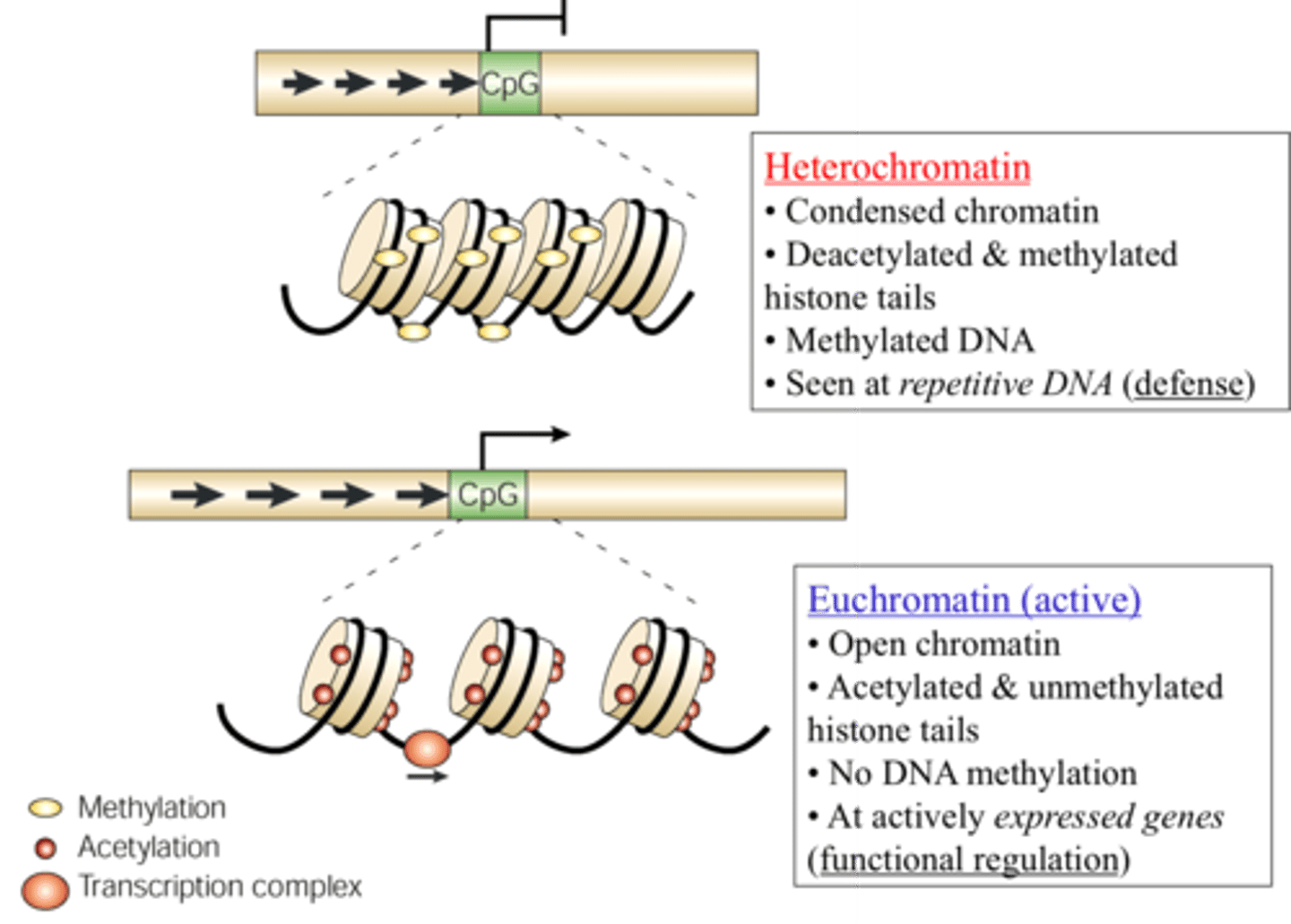
Add methyl groups to cytosine and adenine nucleotides. Methylation of genes is often linked with silencing gene expression.
The heavily methylated DNA hinders transcriptional machinery.
DNA methylation
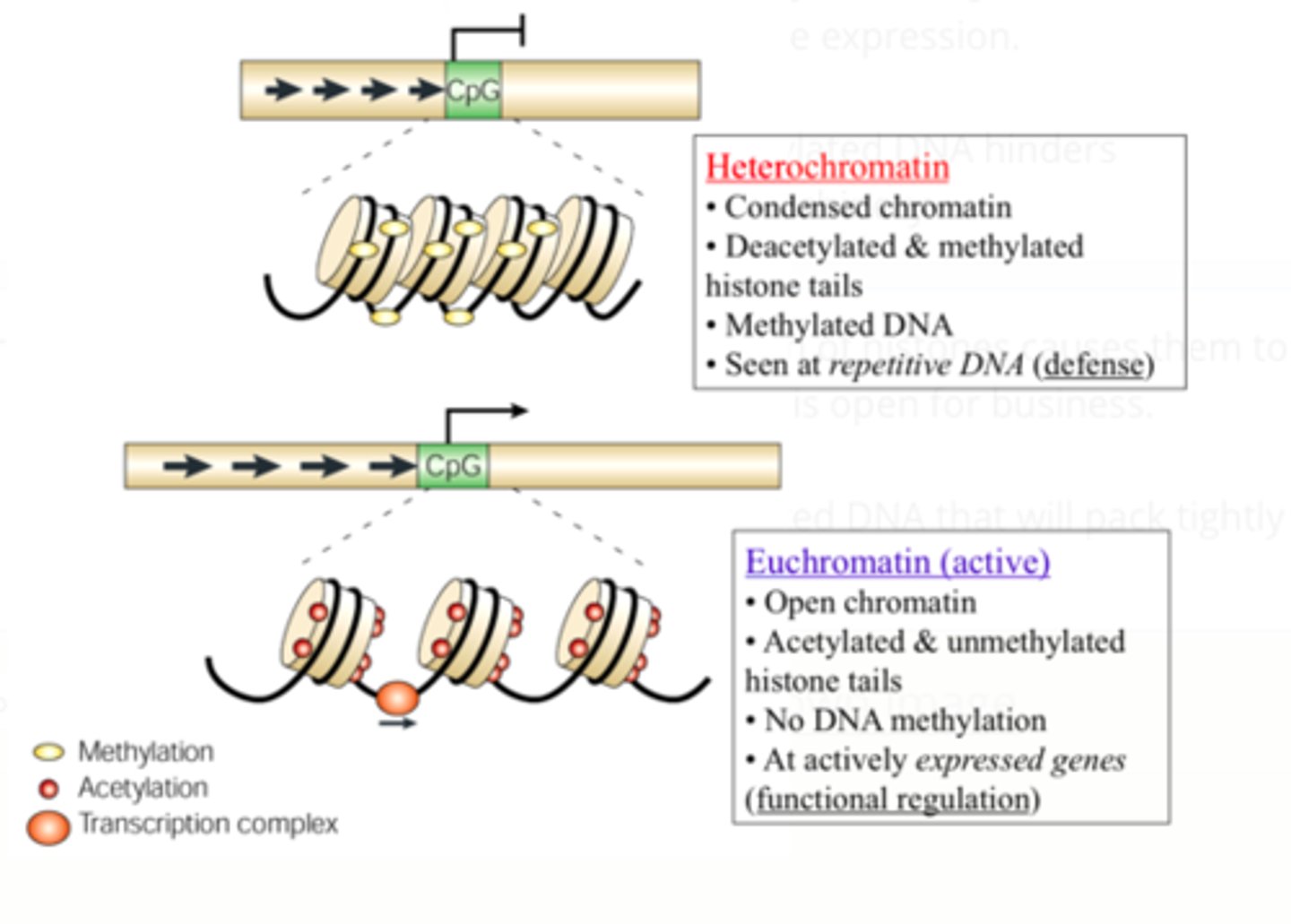
Open = acetylation of histones causes them to form euchromatin that is open for business.
Closed = methylated DNA that will pack tightly into heterochromatin.
How to make DNA open/ closed for transcription?
5' - CAAAGA - 3' because mRNA is antiparallel to DNA
If a DNA sequence is 5' - TCTTTG - 3', what is the transcribed RNA strand?