HISTEM W1: The Cell
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are examples of binucleated cells?
cardiac muscle cells, parenchymal liver cells
What are examples of multinucleated cells?
Osteoclasts, skeletal muscle cells
What cells do not have a nucleus?
RBC and platelets
What are the components of a nucleus?
Nuclear envelope (double layered membrane), Nucleoplasm (fluid), Nucleolus (produces rRNA), Chromatin (contains DNA)
What is the primary function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
modification, storage, segregation and transport of proteins manufactured by the cell
*rough ER and smooth ER
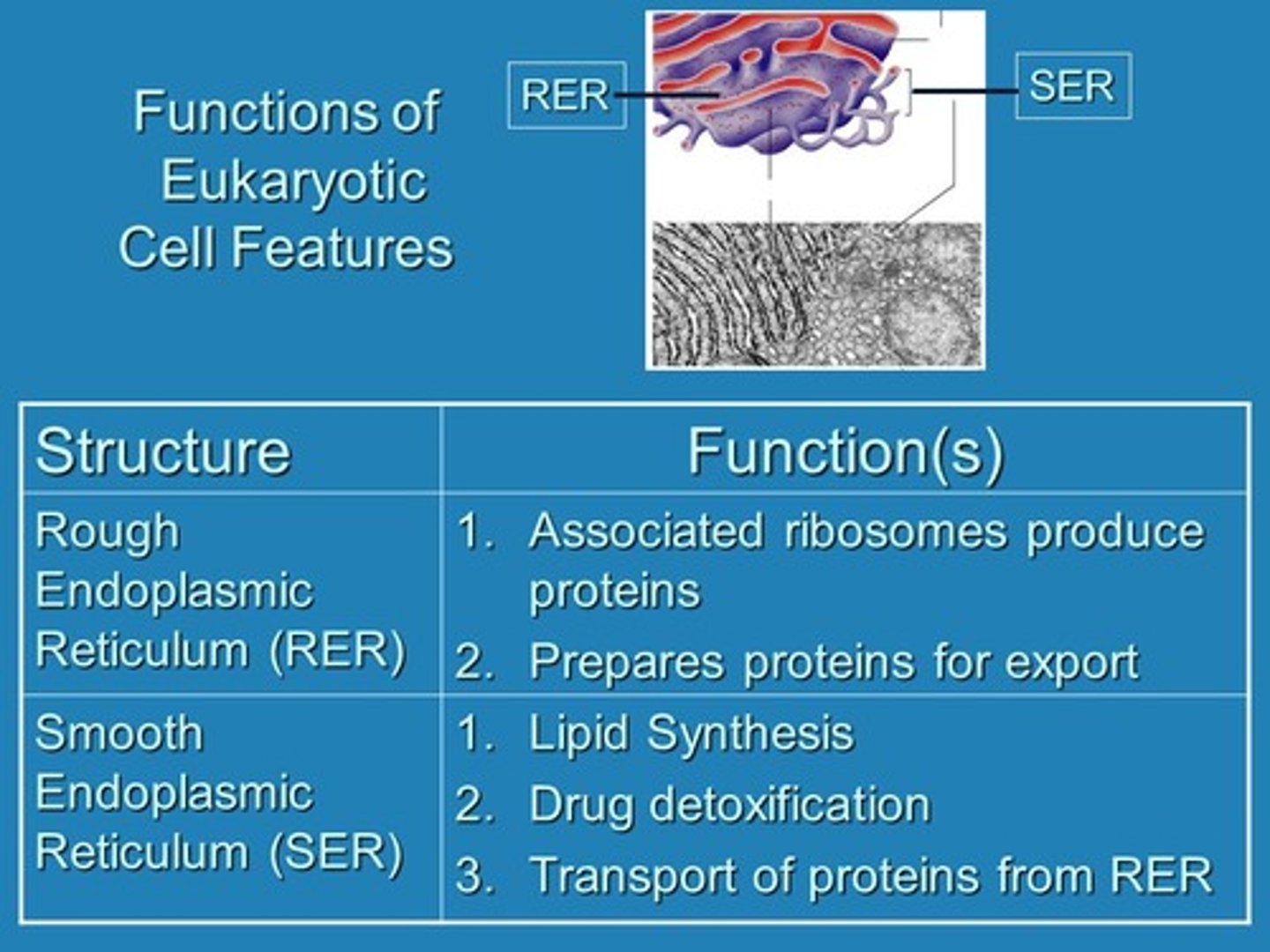
Compare and contrast rough ER and smooth ER
Rough ER:
- studded with ribosomes
- fx is to synthesize protein and RNA
Smooth ER:
- contains enzymes involved in manufacturing lipids and steroid hormones
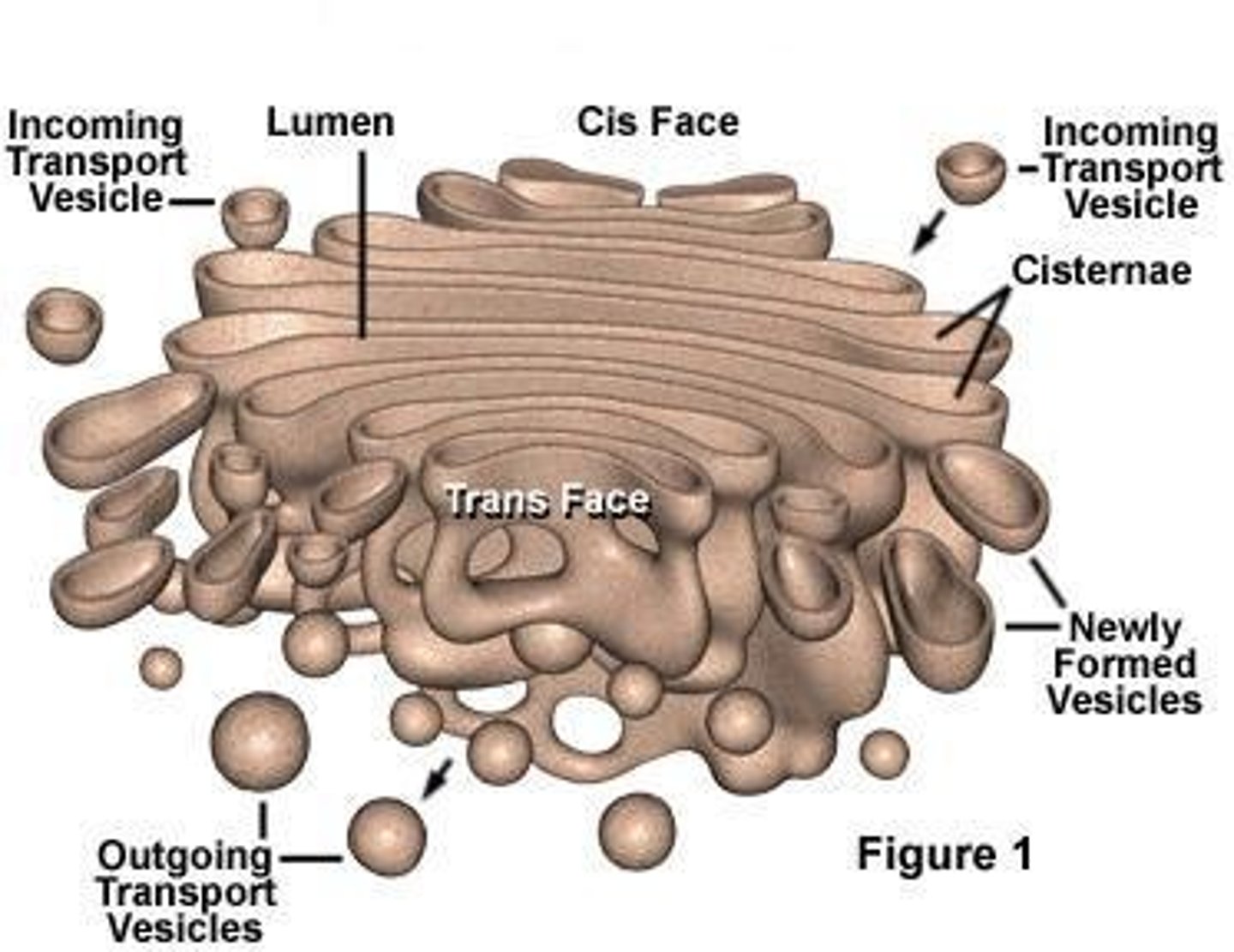
What is the golgi apparatus? what is its function?
Golgi apparatus is the chemical processing and packaging center.
- its a stack of 3-20 flattened membranous sacs attached to the cell membrane
fx:
- sort, condense, package and delivers protein from RER
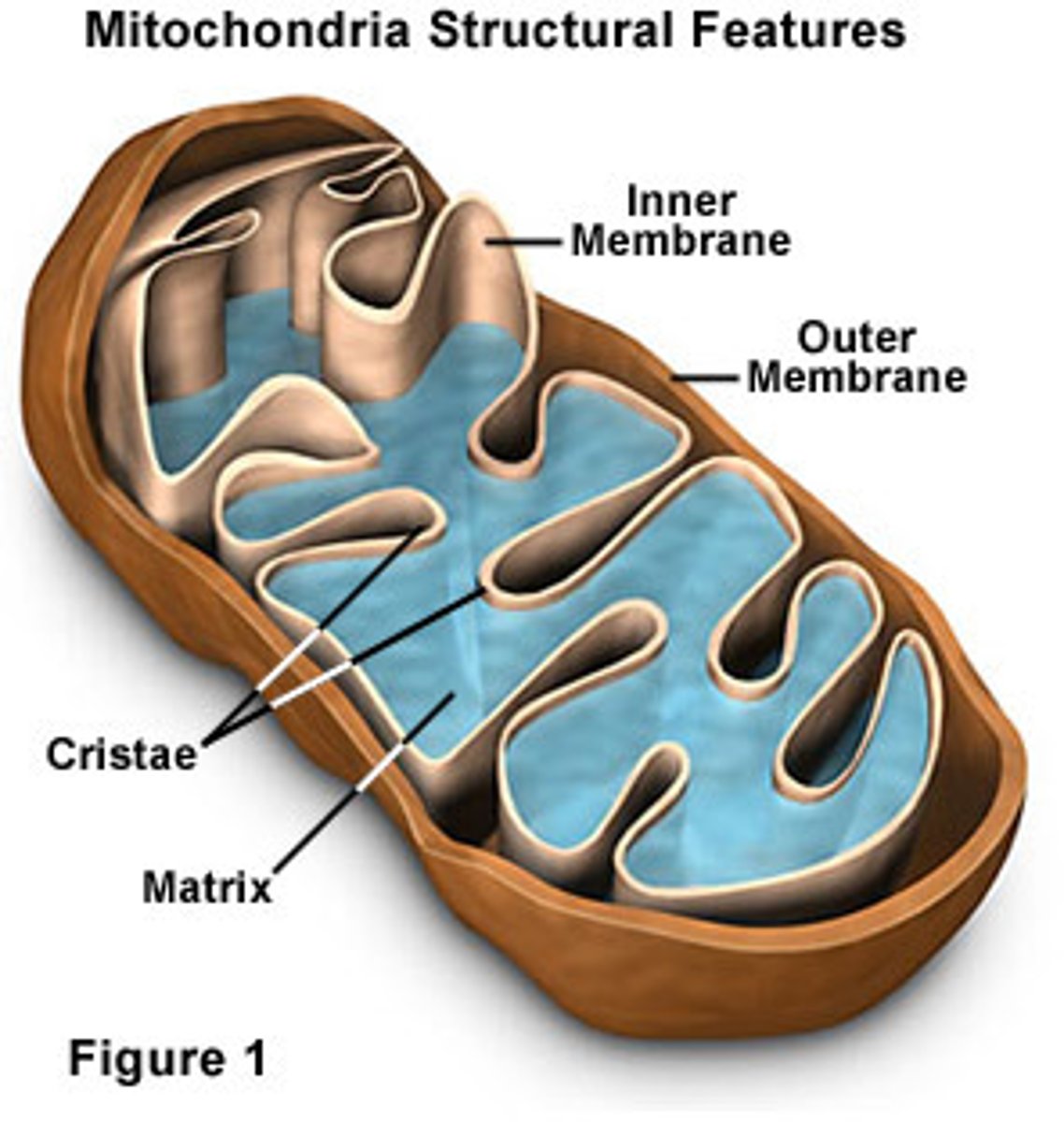
The mitocondria has 2 membranes. Which one contains cristae?
Inner membrane is folded to increase SA forming cristae.
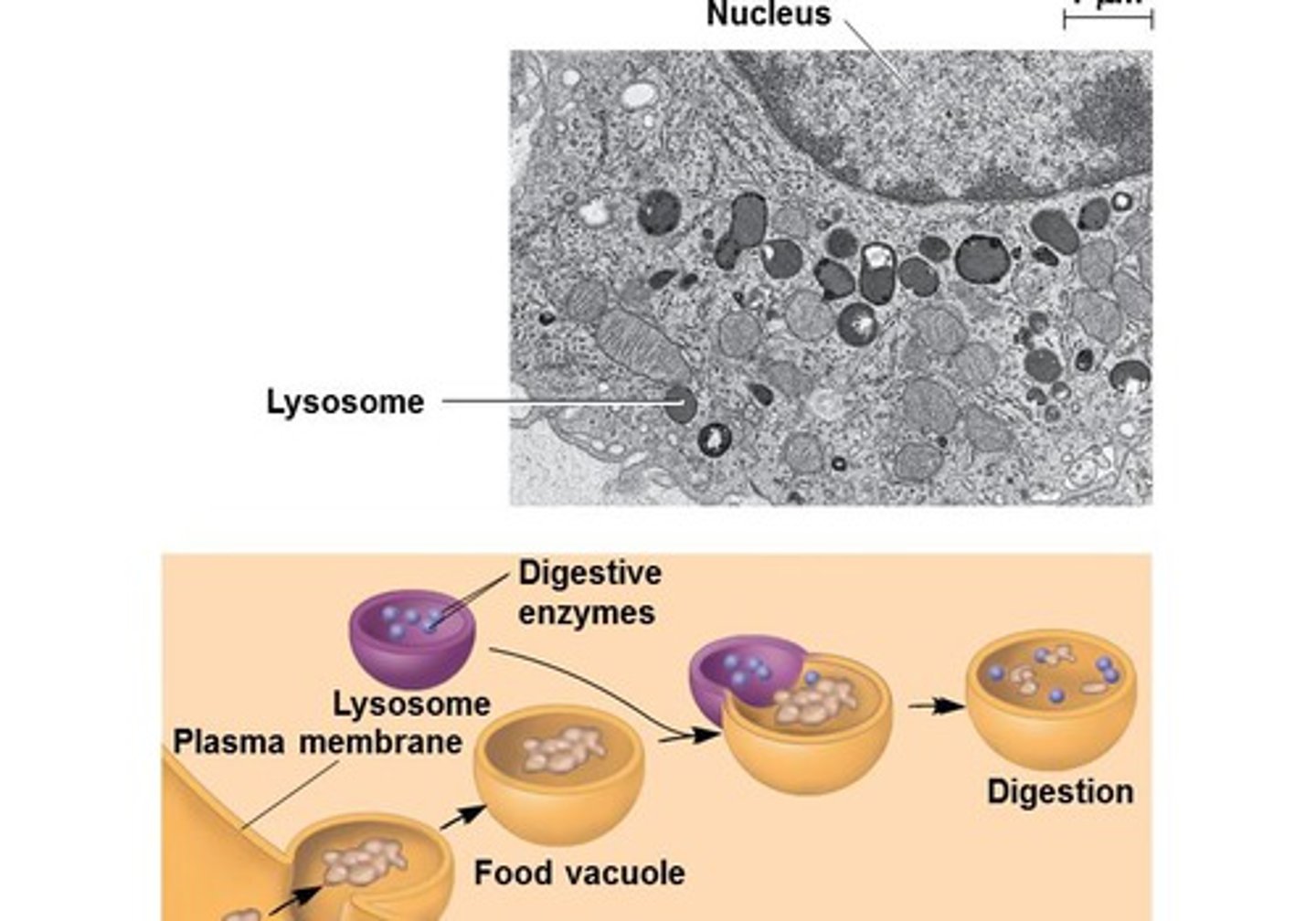
What is a lysosome?
Membranous sacks produced by the Golgi apparatus that contains hydrolytic acid and digestive enzymes.
Lysosomes destroy worn out cell parts
What are the 3 components that make up the cytoskeleton?
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
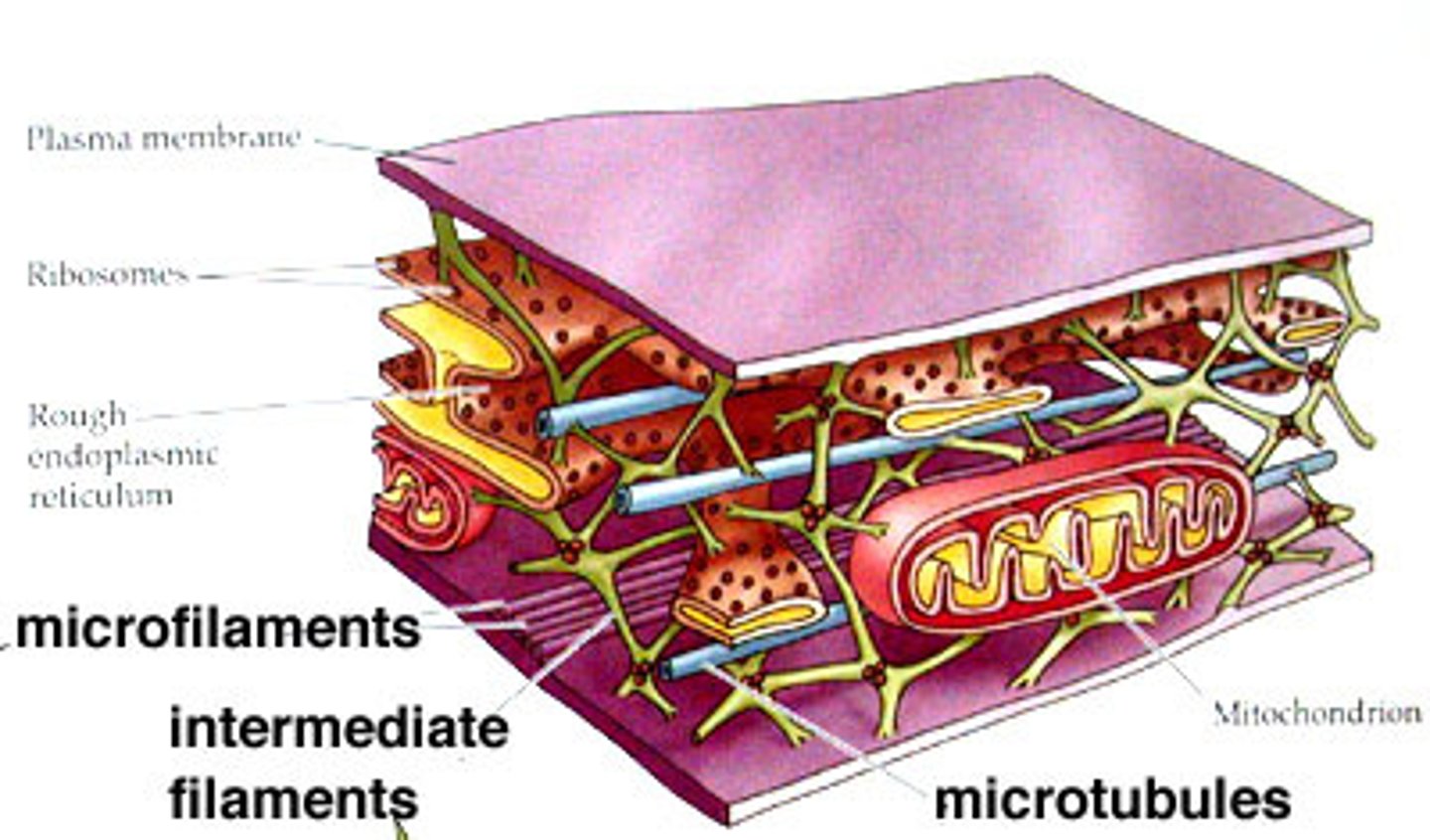
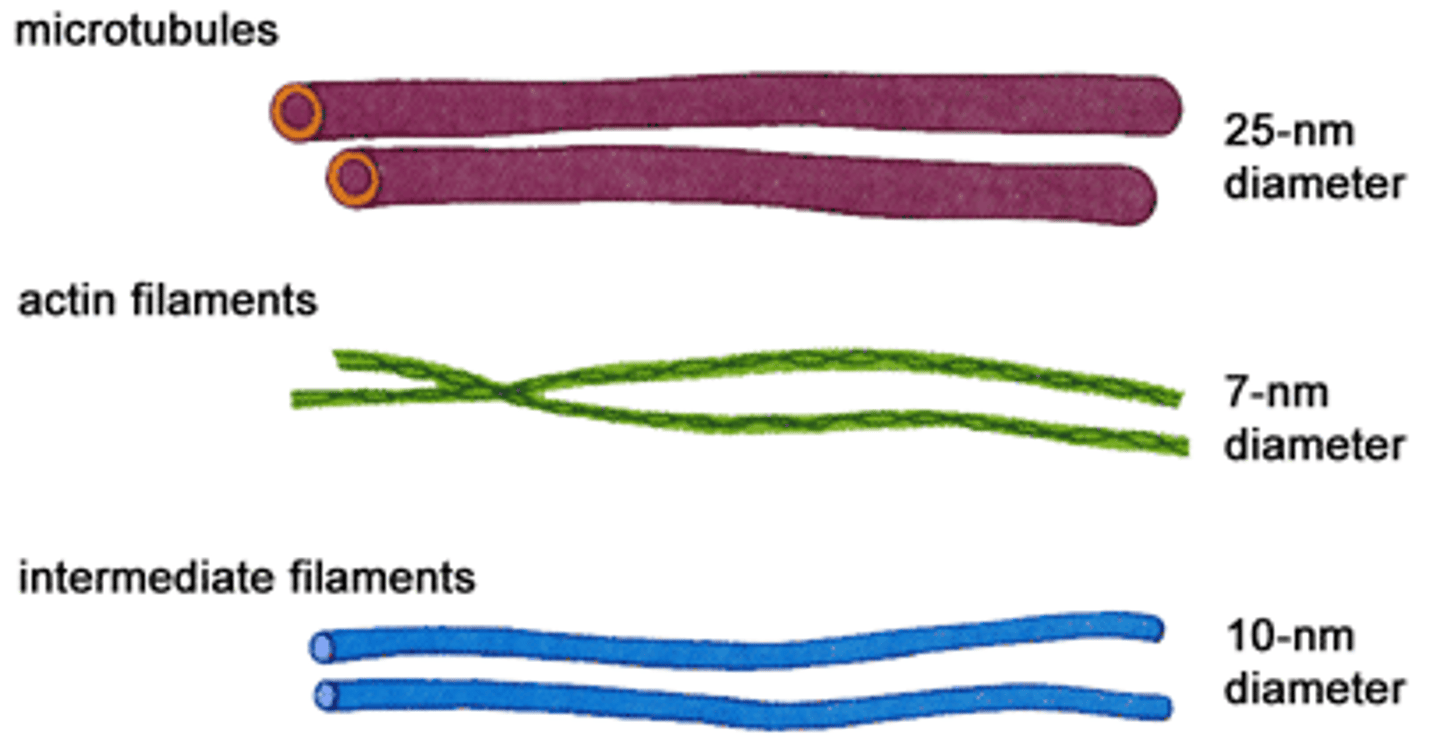
Describe microfilaments and its function.
Contractile fibres formed from actin (specialized protein).
- Fx: Responsible for cell movement and contraction.
- smallest diameter component of cytoskeleton
- sometimes called actin filaments
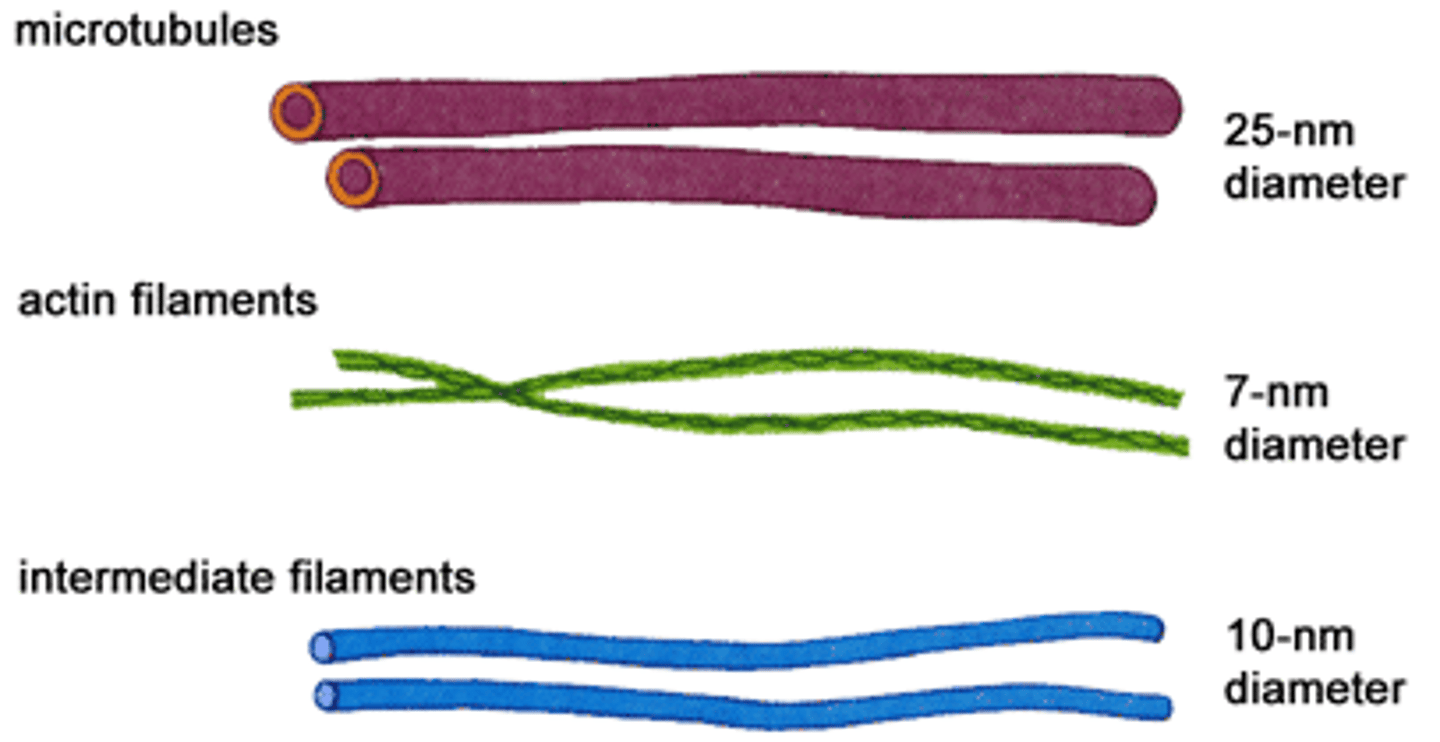
Describe microtubules and its function.
- Hollow, tube-like structures
- They are composed of protein subunits called tubulin
- Fx: Crucial roles in maintaining cell shape, facilitating cell movement, and intracellular transport
Fx: Provide strength to the structure of: cilia, flagella, centrioles, mitotic spindle
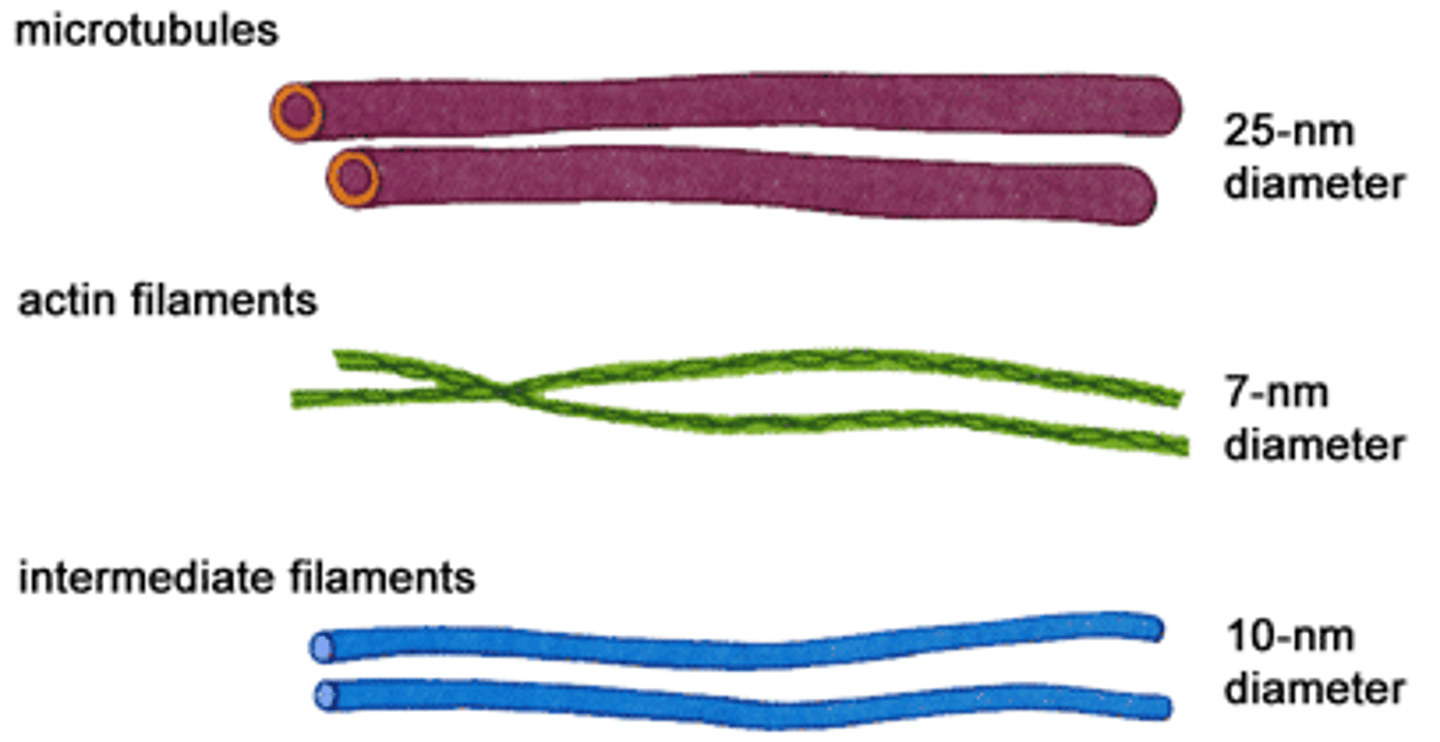
Describe intermediate filaments and its function.
Thicker filament compared to microfilament, but thinner than microtubules.
fx: Has roles in resisting tension , maintaining cell shape, and anchoring organelles
*not involved in cell motility
What is tonofilament?
A intermediate filament that is important in intercellular junctions.
What are cellular inclusions?
Cellular inclusions are metabolically inert (not active in metabolism) substances that are transient (exist for a short time) over time in the cell.
-> consists of cellular products that remain in a cell only temporarily
ex. nutrients like glycogen, lipids, melanin
Describe tight junctions
Tight junctions are tight intercellular connections that fuse adjacent cell membranes together.
- prevents movement or loss of fluid -> nothing can pass through or leave//tight seal)
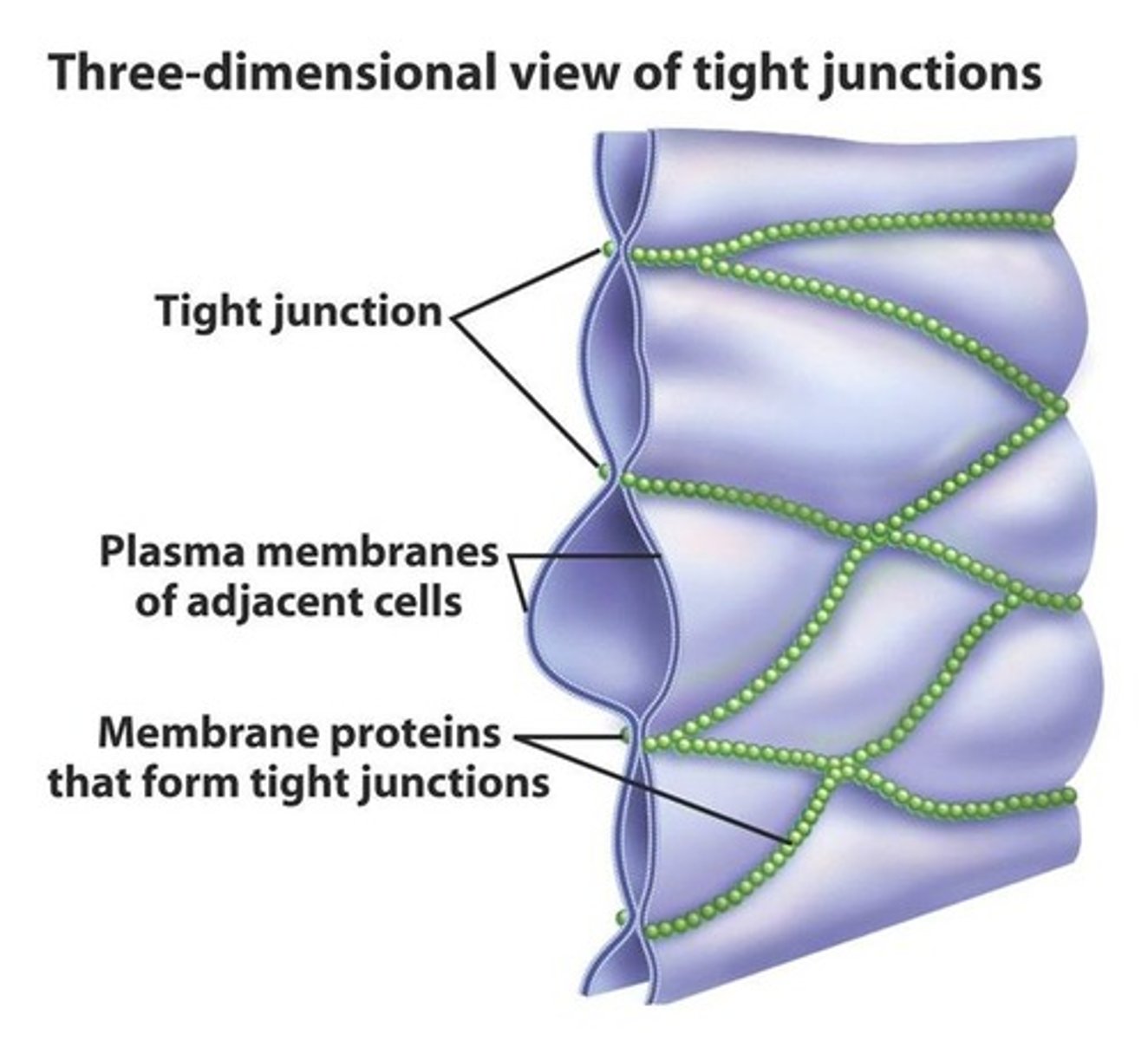
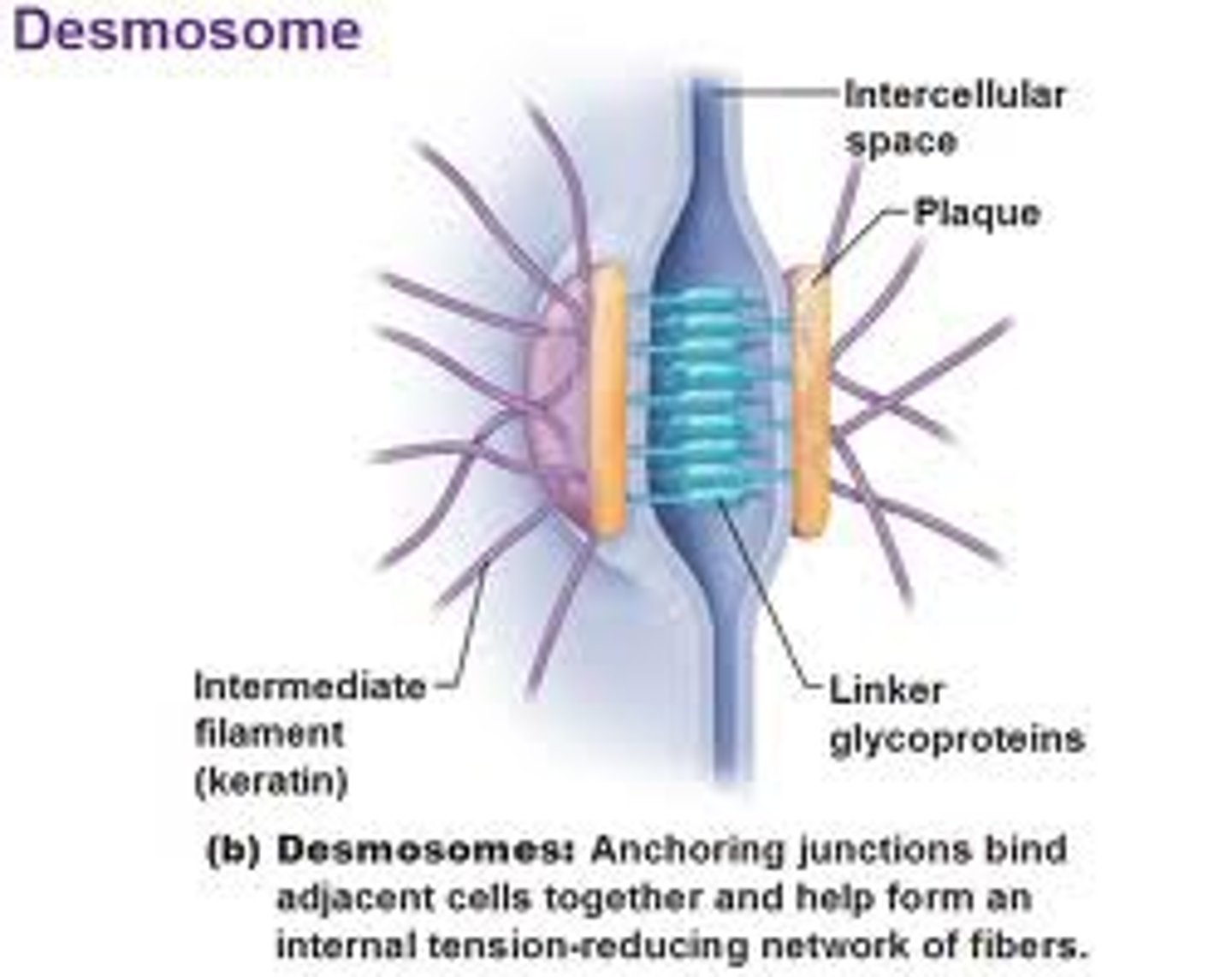
What are desmosomes?
Desmosomes are the protein complex responsible for binding adjacent cell membranes together at a TIGHT JUNCTION.
-> also known as tonofilament complexes
- Desmosomes are found in the outer skin (epithelium) and oral mucosa
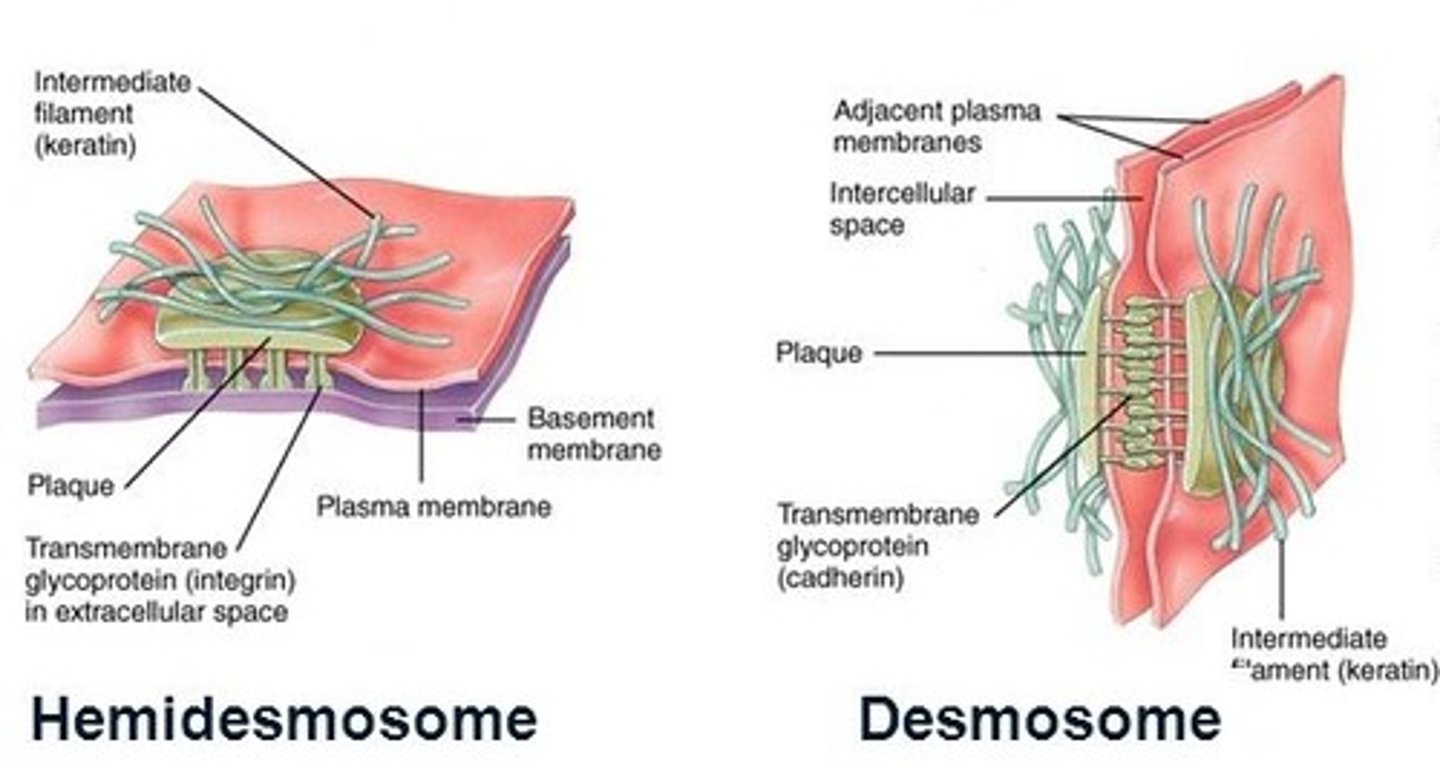
What are hemidesmosomes?
Hemidesmosomes are a protein complex attach cells to an adjacent NON-CELLULAR surface (i.e. basement membrane)
- often used in attachment of the epithelium to connective tissue
**Responsible for gingival tissue adhering to the tooth surface by epithelial attachment
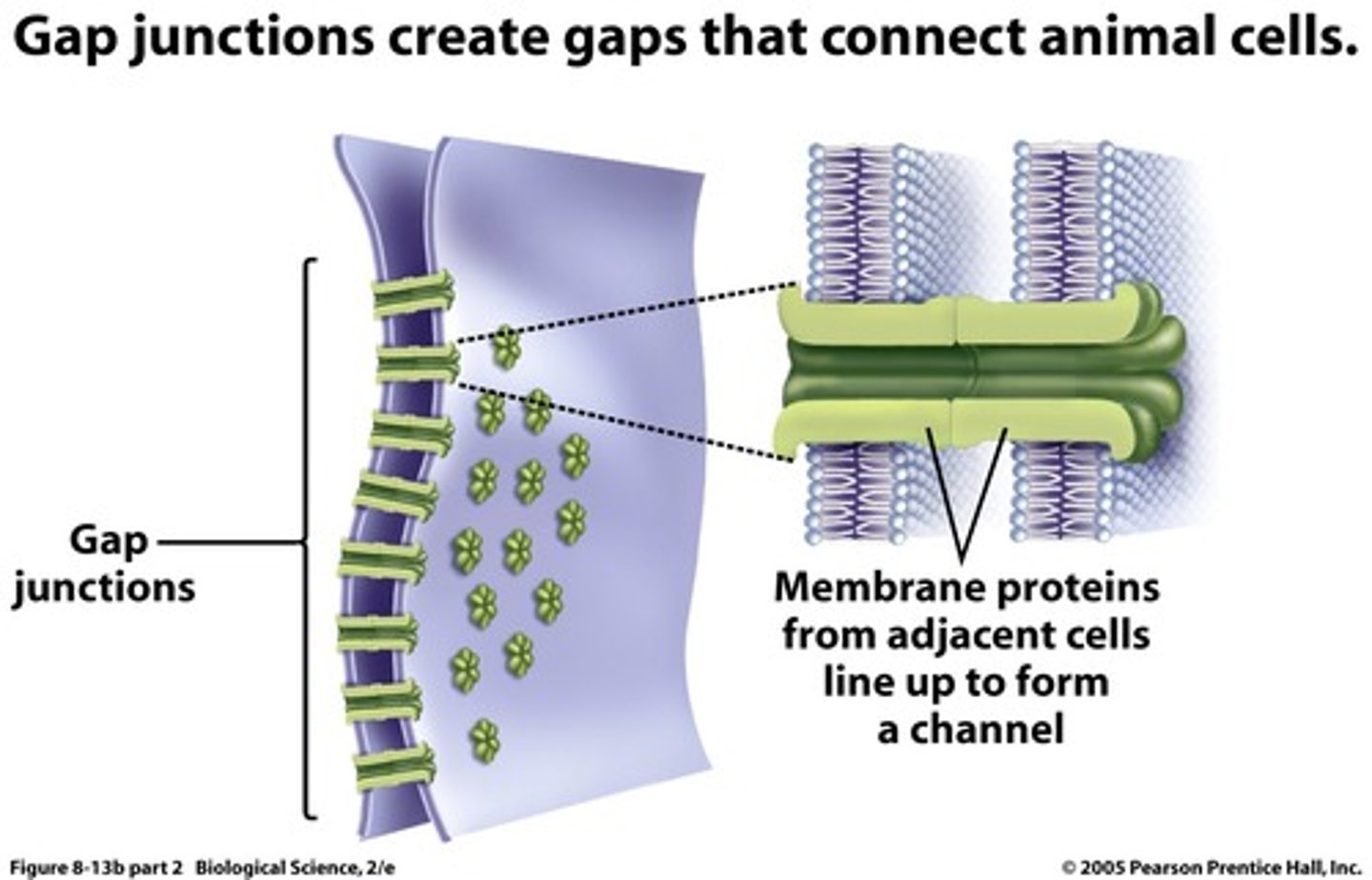
What are gap junctions?
Gap junctions are a specialized intercellular connection between cells that allow for substances to be exchanged. (Tubular channel)
What are the 4 stages of Mitosis?
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
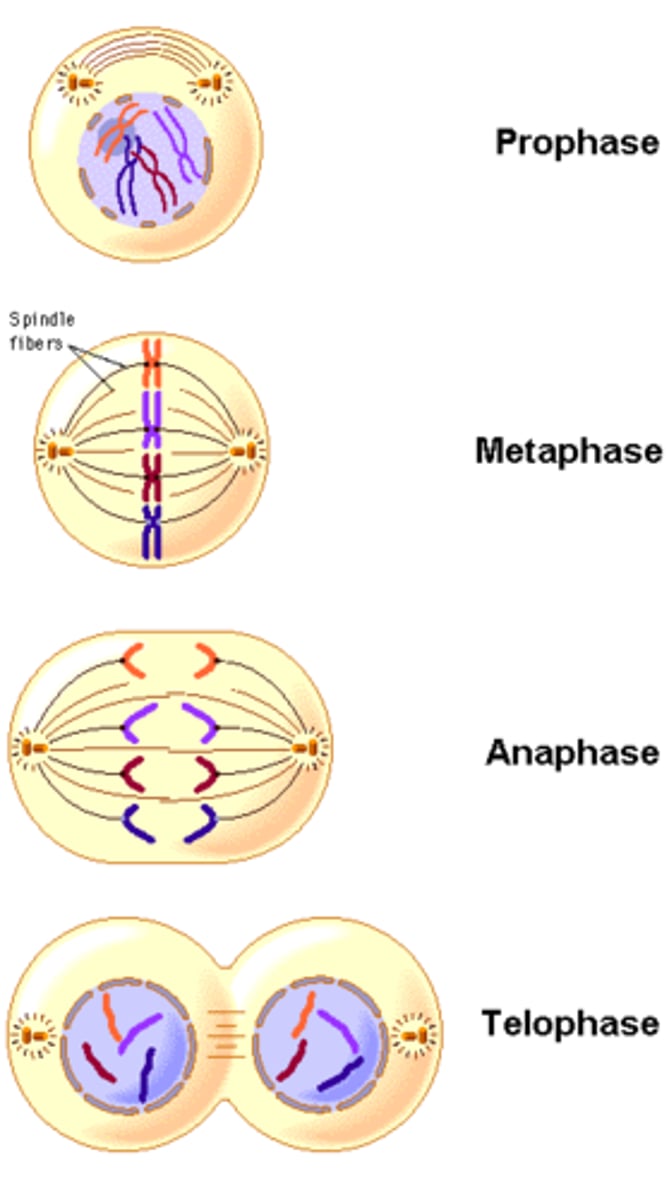
What happens during Prophase?
- chromatin condenses into chromosomes
- nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
- centrioles move towards opposite poles
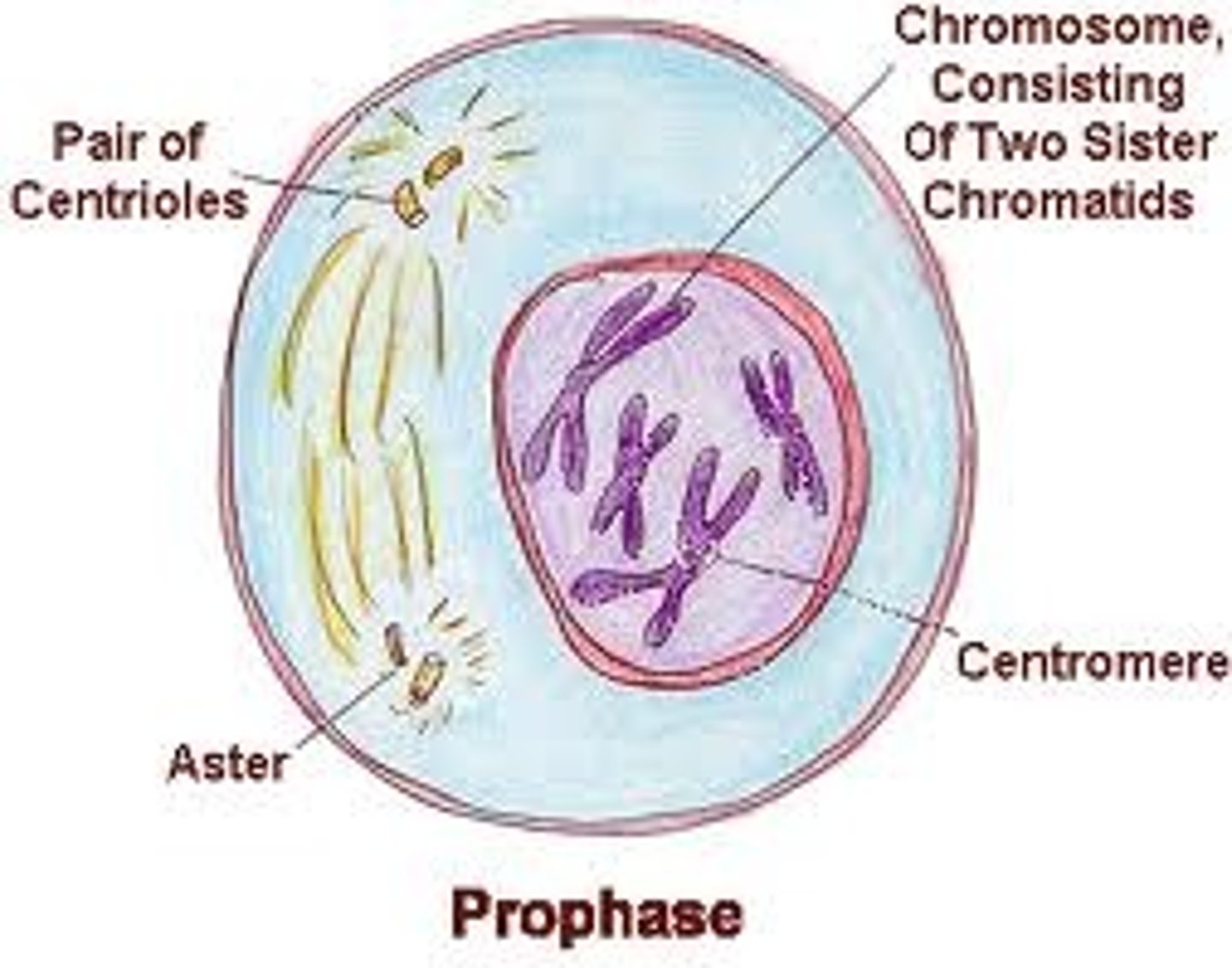
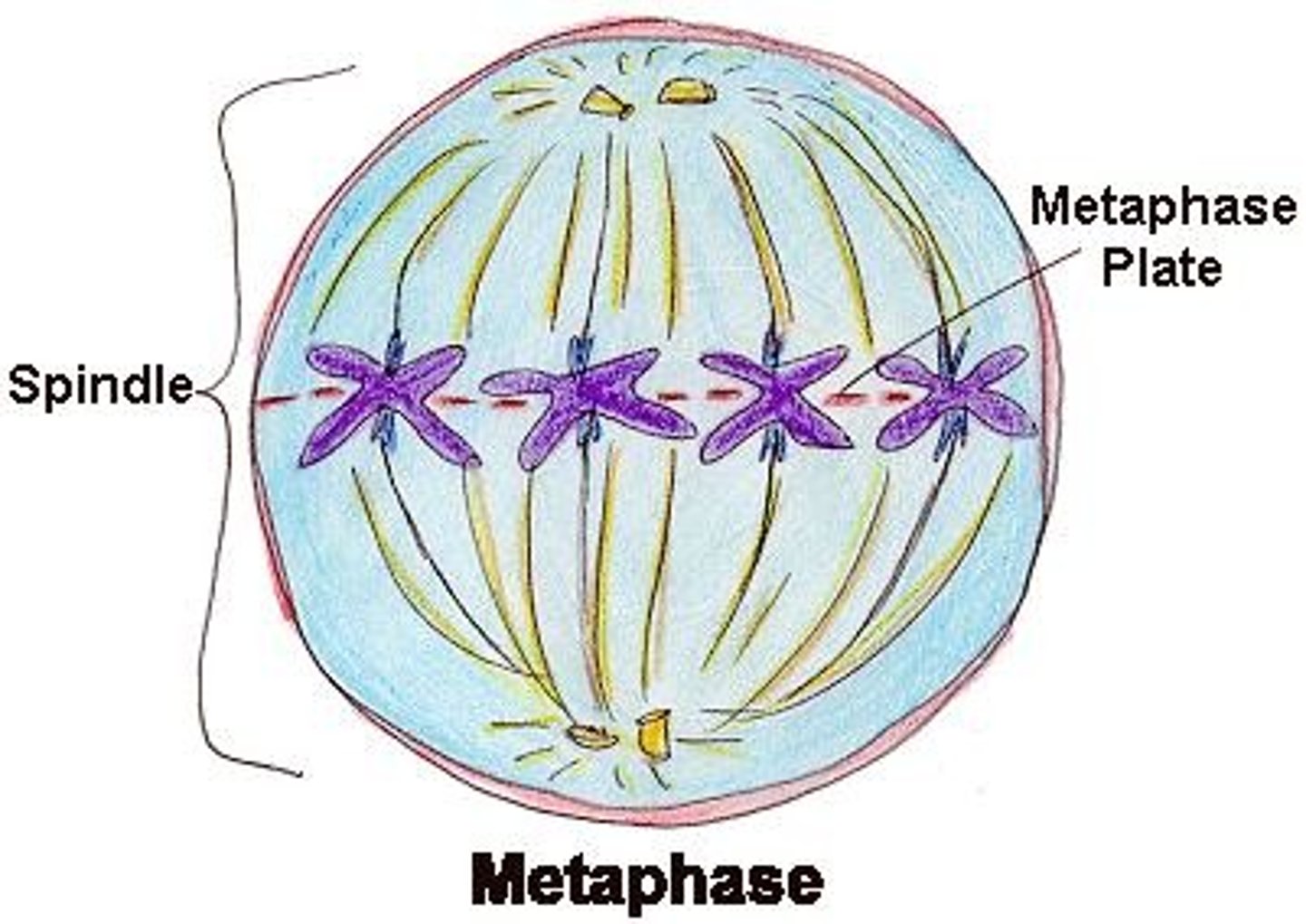
What happens during Metaphase?
- chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (midway between centrioles)
- Spindle fibres from centrioles attach to the centromeres (center) of each chromosome
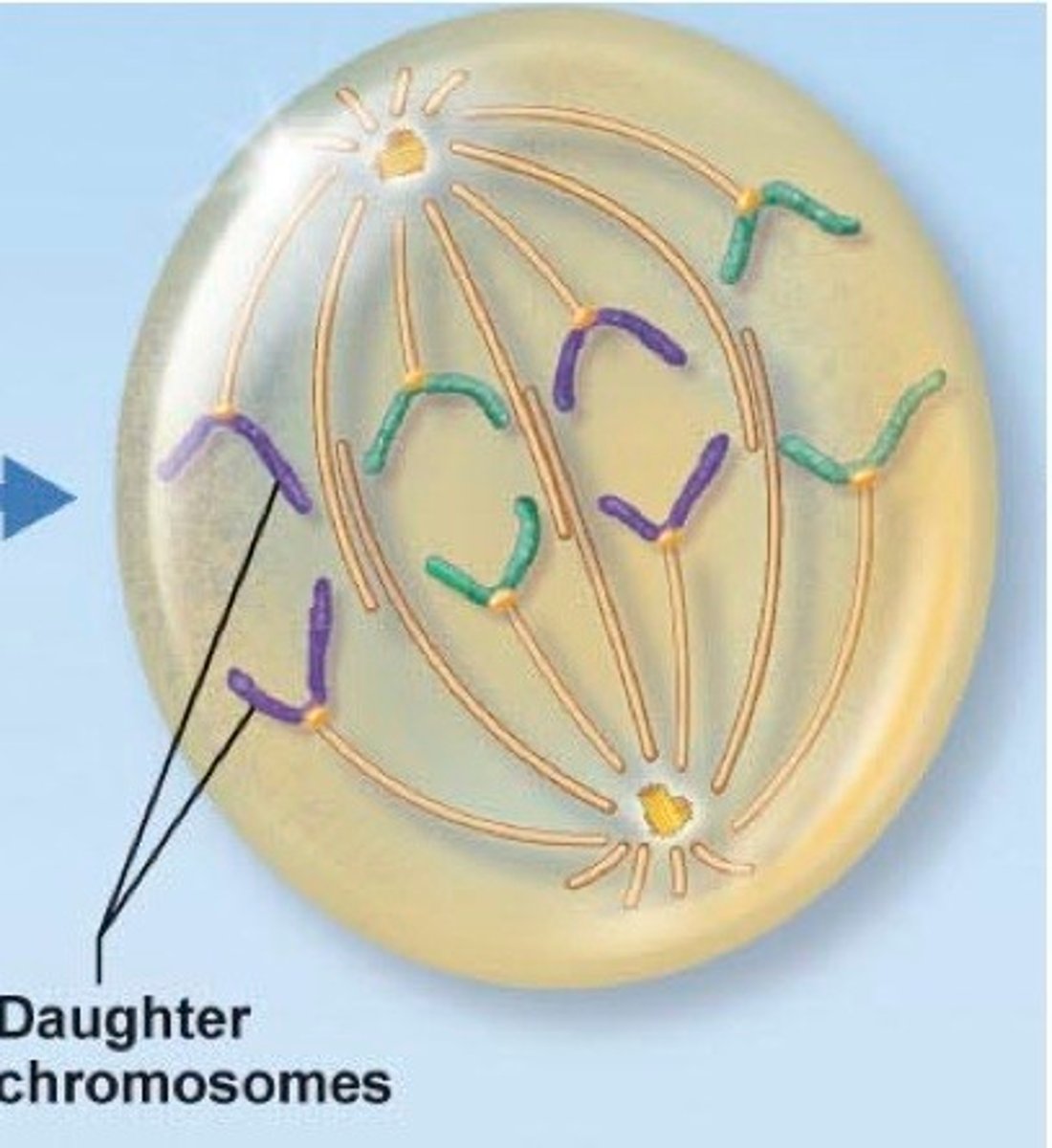
What happens during Anaphase?
- Centromeres split and each chromosome separates into 2 chromatids
- Chromatids migrate to each pole by mitotic spindle
- spindle fibres shorten to pull chromatids
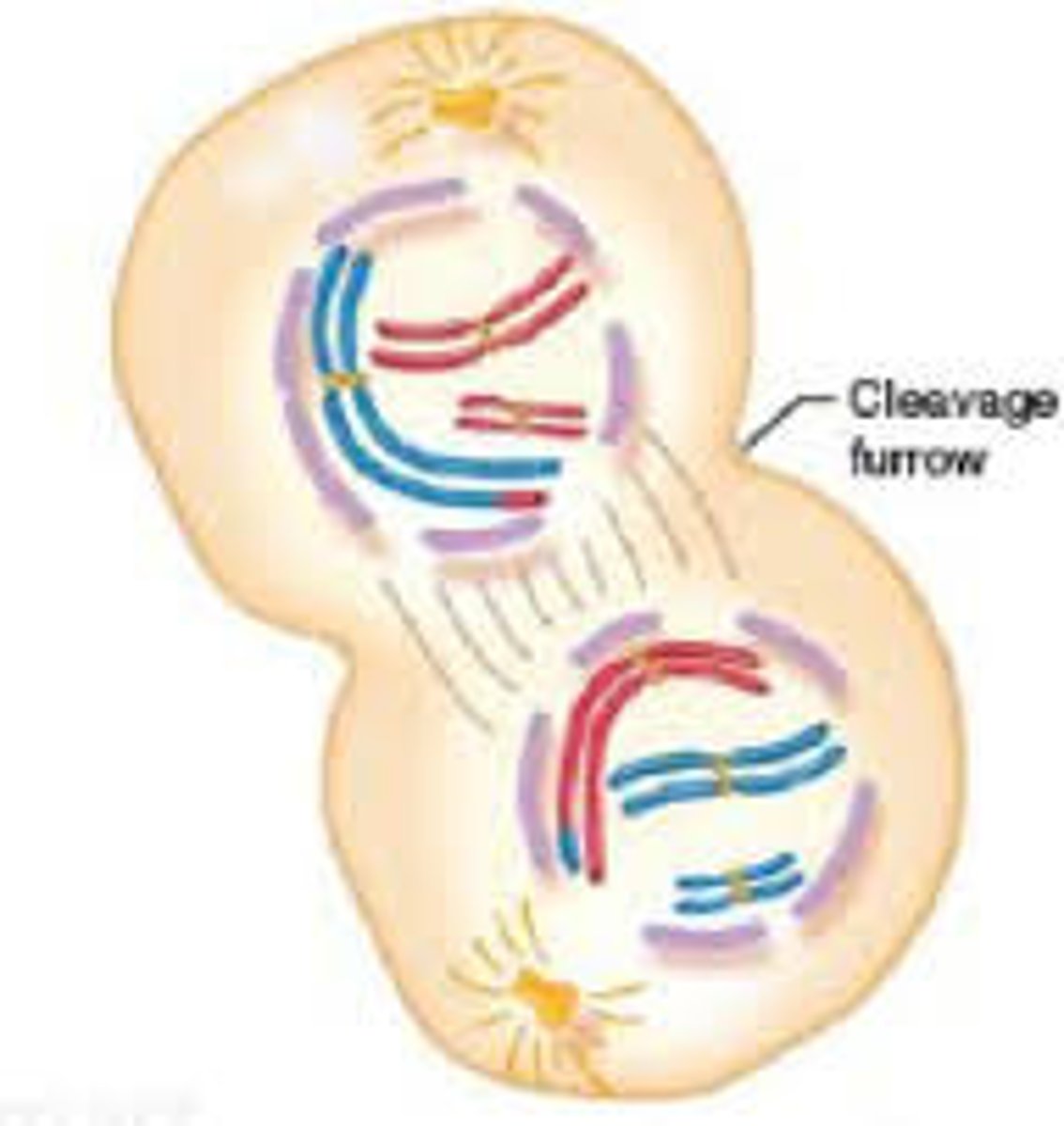
What happens during Telophase?
- Cytoplasmic division begins (cytokinesis) -> forming 2 daughter cells
- Chromosomes elongate and form chromatin threads
- Nuclear membranes appear around each set of chromosome
- Nucleoli appear
- Microtubules disappear (bye, centrioles)
Define cellular differntiation.
Process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type