5.4 b Overview of Mood and Anxiety Disorders
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Mood Disorders
Psychological disorders with emotional extremes.
Depressive Disorders
Group of disorders with persistent sad mood.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Two weeks of depressed mood and loss of interest.
Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD)
Mild depression lasting at least two years.
Symptoms of MDD
Five or more symptoms required for diagnosis.
Depressed Mood
Feeling sad, empty, or irritable most of the time.
Loss of Interest
Dramatically reduced interest in most activities.
Appetite Regulation Problems
Significant challenges in appetite and weight.
Sleep Regulation Problems
Significant challenges in sleep patterns.
Physical Agitation
Restlessness or lethargy affecting daily functioning.
Feelings of Worthlessness
Perception of unwarranted guilt or low self-worth.
Cognitive Challenges
Problems with thinking, concentrating, or decision-making.
Suicidal Thoughts
Repetitive thoughts about death or suicide.
Anxiety Disorders
Disorders characterized by excessive fear or worry.
Specific Phobia
Intense fear of specific objects or situations.
Acrophobia
Fear of heights leading to avoidance behavior.
Arachnophobia
Fear of spiders causing significant distress.
Agoraphobia
Fear of situations where escape might be difficult.
Panic Disorder
Recurrent panic attacks causing significant anxiety.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Fear of social situations and being judged.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Chronic anxiety about various aspects of life.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Presence of obsessions and compulsions affecting daily life.
Hoarding Disorder
Persistent difficulty discarding possessions, leading to clutter.
Bipolar Disorder
Mood disorder with depression and mania episodes.
Mania
Hyperactive, euphoric state with impulsive behavior.
Bipolar Cycling
Alternating episodes of depression and mania.
Bipolar 1 Disorder
Severe form with more intense manic episodes.

Bipolar 2 Disorder
Less severe form with hypomania and depressive episodes.
Hypomania
Less severe manic episodes in Bipolar 2.
Genetic Predisposition
Increased risk if family has depressive disorders.
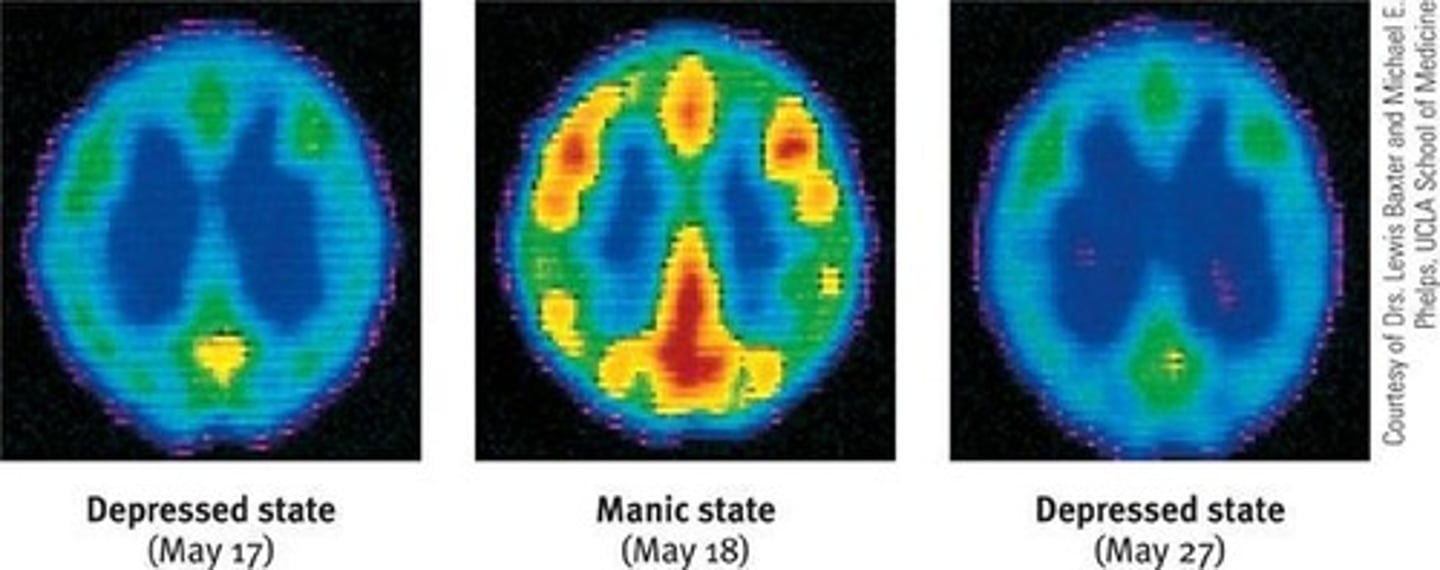
Brain Activity
Diminished during depression, increased in mania.
Frontal Lobes
Smaller in individuals with severe depression.
Hippocampus
Vulnerable to stress-related damage in depression.
White Matter
Less present in cerebral cortex of bipolar patients.
Norepinephrine
Low in depression, high during manic episodes.
Serotonin
Low levels associated with depressive disorders.
Reciprocal Determinism
Interaction of thoughts, actions, and environment.
Learned Helplessness
Condition where individuals feel powerless to change.
Rumination
Compulsive overthinking about problems and causes.
Explanatory Style
How individuals attribute successes and failures.
Stable Attribution
Belief that bad events will last forever.
Global Attribution
Belief that bad events affect all aspects of life.
Internal Attribution
Belief that failures are one's own fault.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Persistent, uncontrollable anxiety for 6 months.
Autonomic Nervous System
System in constant arousal state affecting anxiety.
Free-Floating Anxiety
Anxiety not linked to specific stressor.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Persistent anxiety lasting months without specific cause.
Panic Disorder
Unpredictable episodes of intense dread and fear.
Panic Attacks
Episodes of intense fear with physical symptoms.
Ataque de Nervios
Culture-bound disorder with panic-like symptoms in Latinx.
Specific Phobia
Irrational fear and avoidance of specific objects.
Arachnophobia
Fear of spiders causing panic responses.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Intense fear of judgment in social situations.
Taijin Kyofusho
Japanese social anxiety about body judgment.
Agoraphobia
Fear of public spaces leading to avoidance.
Learning Perspective
Anxiety disorders arise from conditioning and learning.
Classical Conditioning
Learning through association of stimuli and responses.
Operant Conditioning
Behavior reinforced by consequences, maintaining anxiety.
Stimulus Generalization
Fear extends to similar stimuli after a traumatic event.
Reinforcement in Anxiety
Avoidance behavior is reinforced by reduced anxiety.
Cognitive Behavioral Link
Perception of threats influences anxiety levels.
Cultural Influence on Anxiety
Cultural contexts shape expressions of anxiety disorders.
Age and Anxiety
Anxiety tends to decrease with increasing age.
Gender Differences in Anxiety
Higher prevalence of anxiety disorders in women.
Comorbidity with Depression
Depression often accompanies anxiety disorders.
Observational learning
Learning fear by observing others' reactions.
Hypervigilance
Enhanced sensory sensitivity to perceived threats.
Biological perspective
Evolutionary role of fears in survival.
Natural selection
Easily learned fears of relevant stimuli.
Evolutionarily relevant stimuli
Fears linked to survival threats like heights.
Genetic predispositions
Inherited traits affecting emotional reactivity.
Neurotransmitter (NT) production
Chemical signaling in the brain influencing anxiety.
Anterior cingulate cortex
Brain area overactive in OCD cases.
Amygdala
Brain region creating new fear circuits.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Anxiety disorder with obsessions and compulsions.

Obsessions
Repetitive, anxiety-provoking thoughts in OCD.
Compulsions
Repetitive behaviors to alleviate obsessive thoughts.
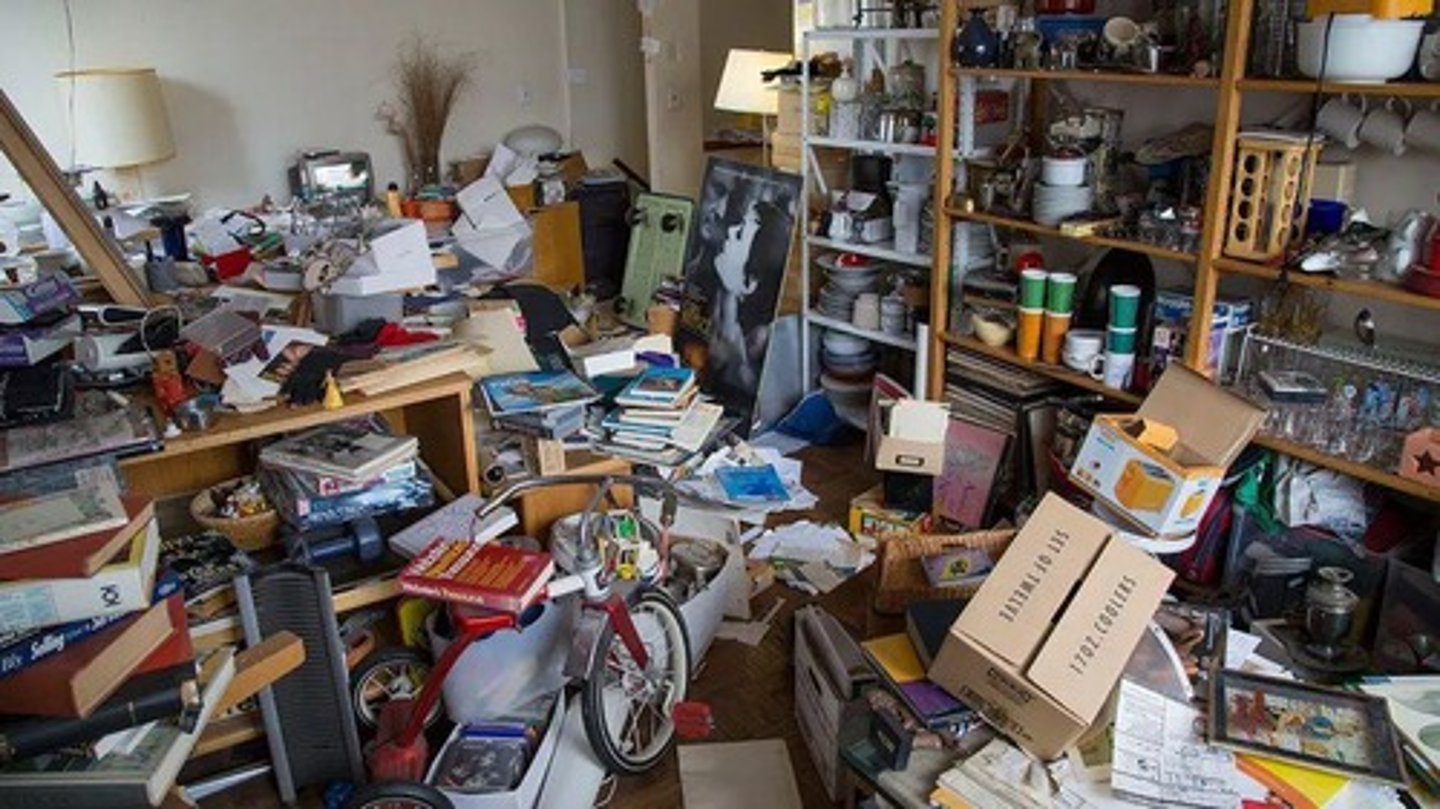
Hoarding Disorder
Compulsion to collect items causing distress.

Learned Associations
Connections between stimuli and emotional responses.
Maladaptive Thinking
Cognitive distortions worsening obsessive-compulsive symptoms.
Emotional responses
Feelings exacerbating maladaptive thought patterns.
Genetic factors
Hereditary components influencing OCD and anxiety.
Cognitive appraisals
Interpretations of uncertainty leading to anxiety.
Freudian conditioning
Psychodynamic theory linking repressed impulses to anxiety.
Avoidance conditioning
Learning to avoid anxiety-provoking stimuli.
Compulsive behaviors
Actions taken to manage anxiety or obsessions.
Clutter
Accumulation of items disrupting living space.
Distress
Emotional suffering due to compulsive behaviors.