Principles of Biochemistry Chapter 2 Water
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
water is a ________ molecule
polar; contains a positive and negative end
in water, oxygen has a slightly ________ charge
negative
in water, hydrogen has a slightly ________ charge
positive
one water molecule can bind with ______ other water molecules at the same time
4
cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
cohesion is made possible due to
hydrogen bonds
adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
adhesion is made possible due to
hydrogen bonds that bind to electronegative Os
surface tension
linking together of water molecules on the surface of a body of water
surface tension is made possible due to
hydrogen bonds
heat
total amount of kinetic energy
temperature
intensity of all the heat in a substance as the molecules move
water's ability to regulate temperature is due to
hydrogen bonds
evaporative cooling
The property of a liquid whereby the surface becomes cooler during evaporation, owing to a loss of highly kinetic molecules to the gaseous state.
water __________ when it freezes
expands
four properties of water
1. cohesion/adhesion
2. evaporative cooling
3. temperature regulation
4. water expands when it freezes
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
universal solvent
water
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solution
A mixture in which one or more substances are evenly distributed in another substance
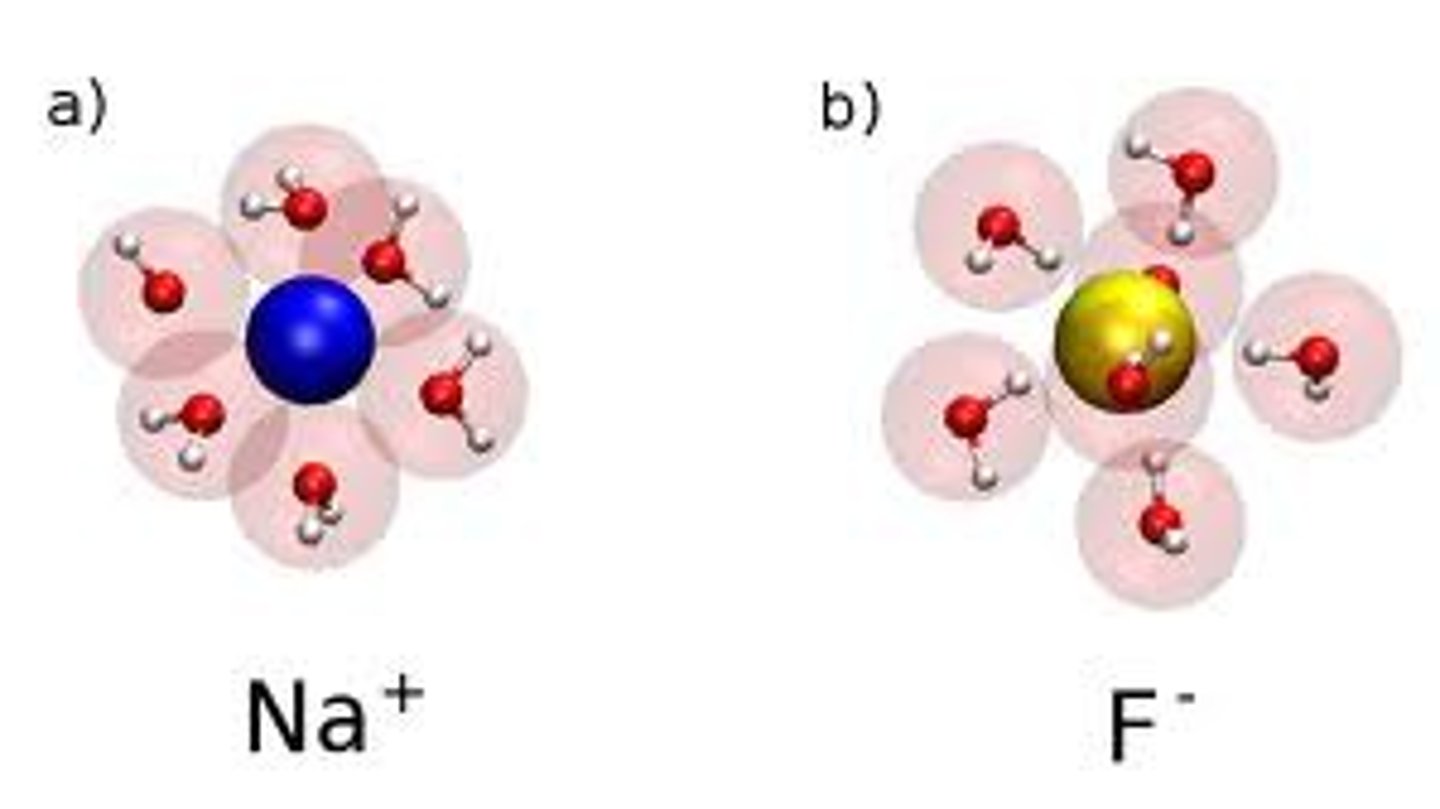
hydration shell
The sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion
water can not grab and dissolve ________ molecules
non-polar (oils, grease, fats)
hydrophobic
"water fearing"
hydrophilic
"Water loving"
dissociation
splitting of water into H+ (proton) and an OH- (hydroxide ion)
acid
substance gives away H+
base
substance gives away OH-
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14 pH =(-)logH+. A log scale.
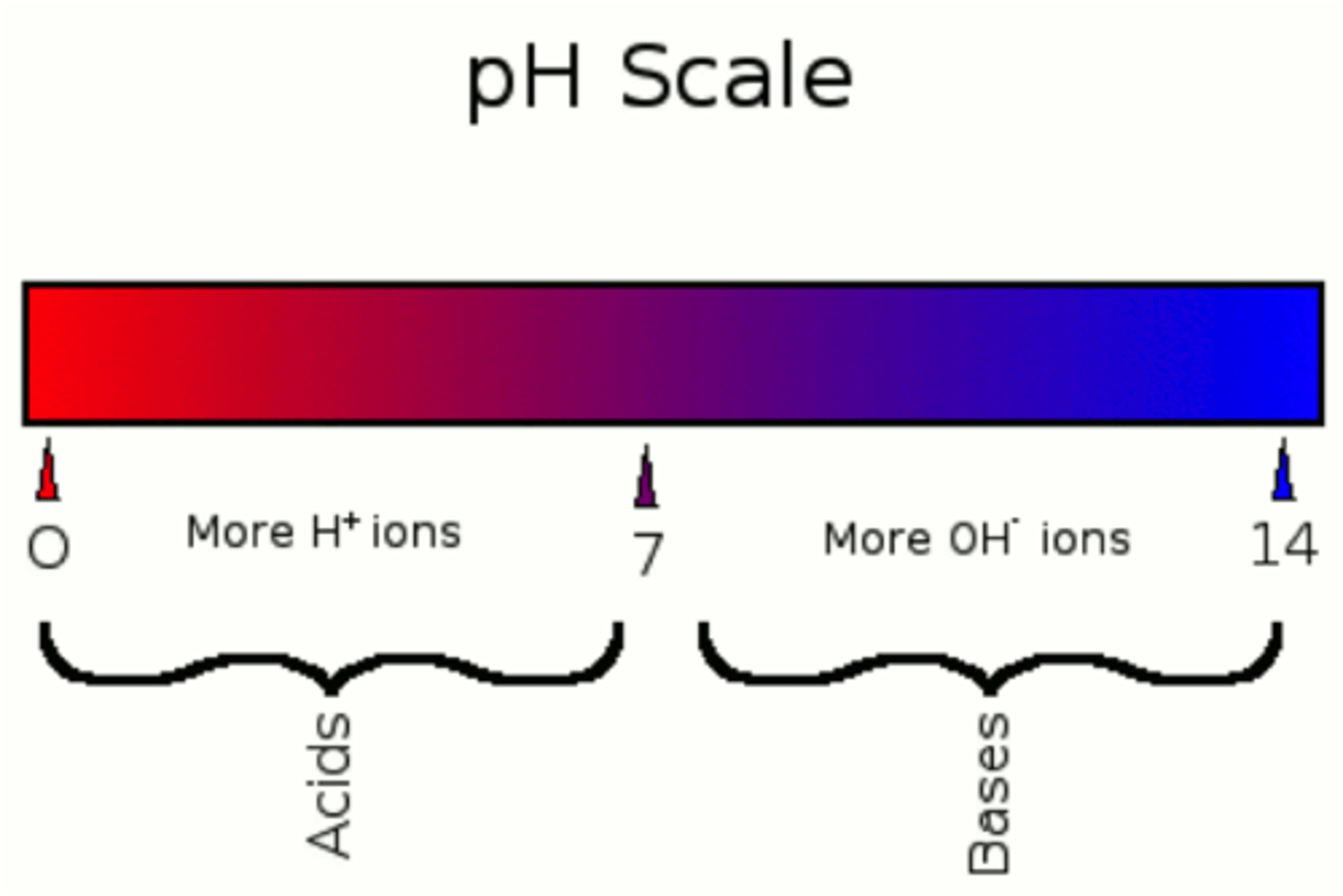
buffer
A solution that resists changes in pH when limited amounts of acid or base are added.
biocarbonate
buffer found in human blood; keeps blood at a pH of 7.4
acid precipitation
Rain, snow, or fog that is more acidic than pH 5.6.
causes of acid precipitation
burning of fossil fuels; sulfur oxide and nitrous oxide combine with water
what bond makes water possible
polar covalent
what bond provides the properties of water
hydrogen
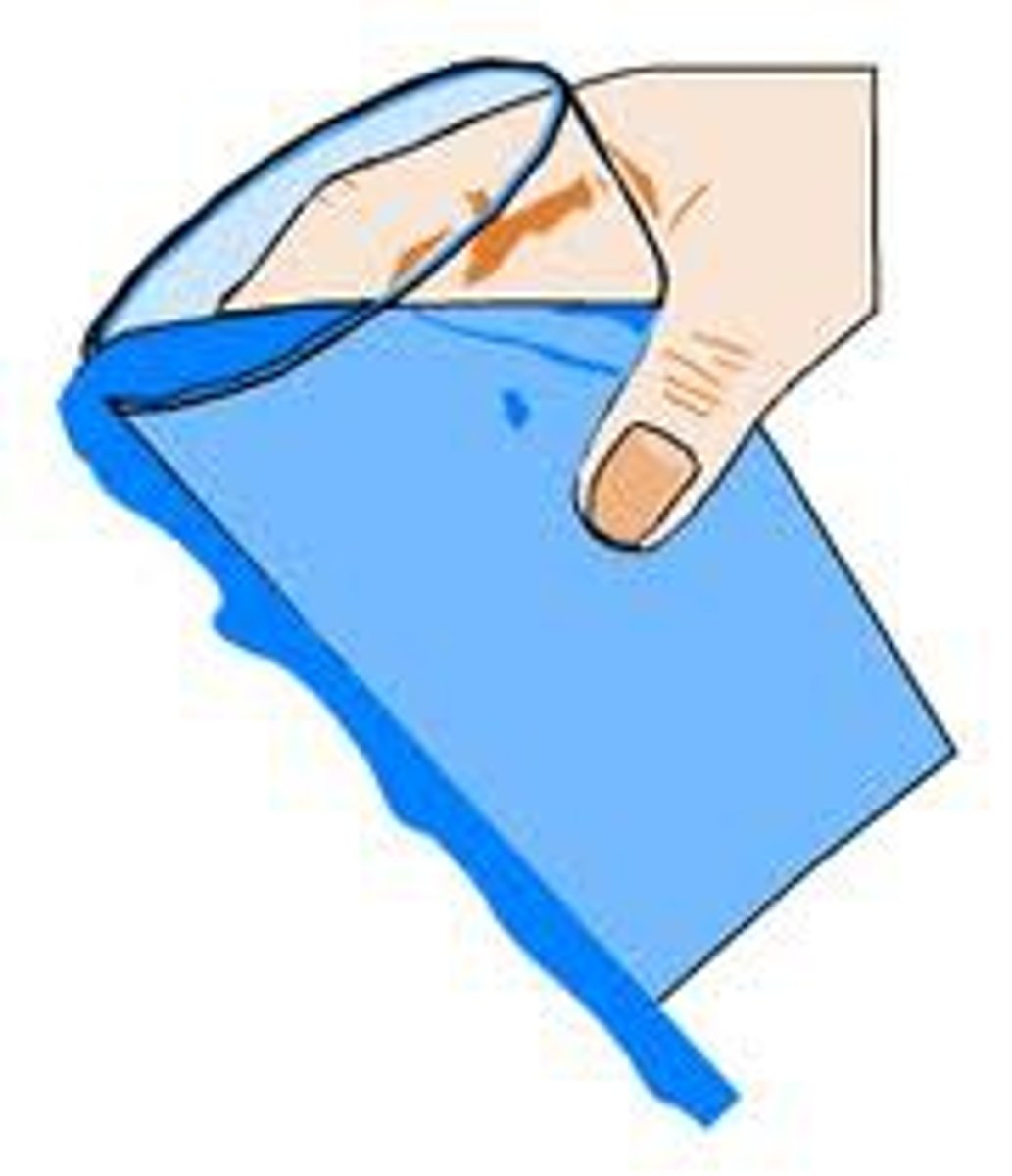
adhesion of water
the water is attracted to the glass
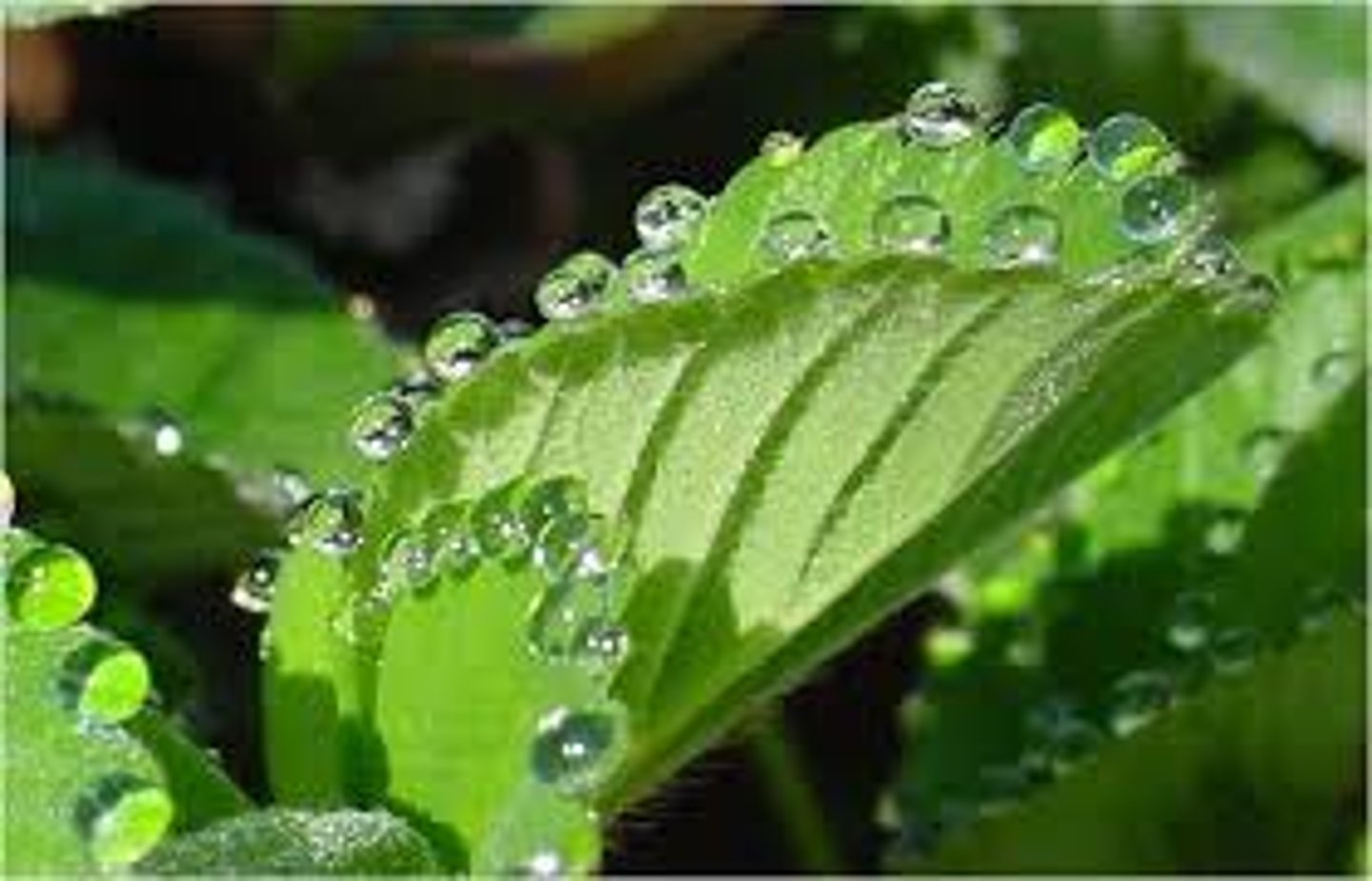
cohesion of water
water molecules are attracted to each other and form droplets

example of hydration shell
the water molecules surround the molecules
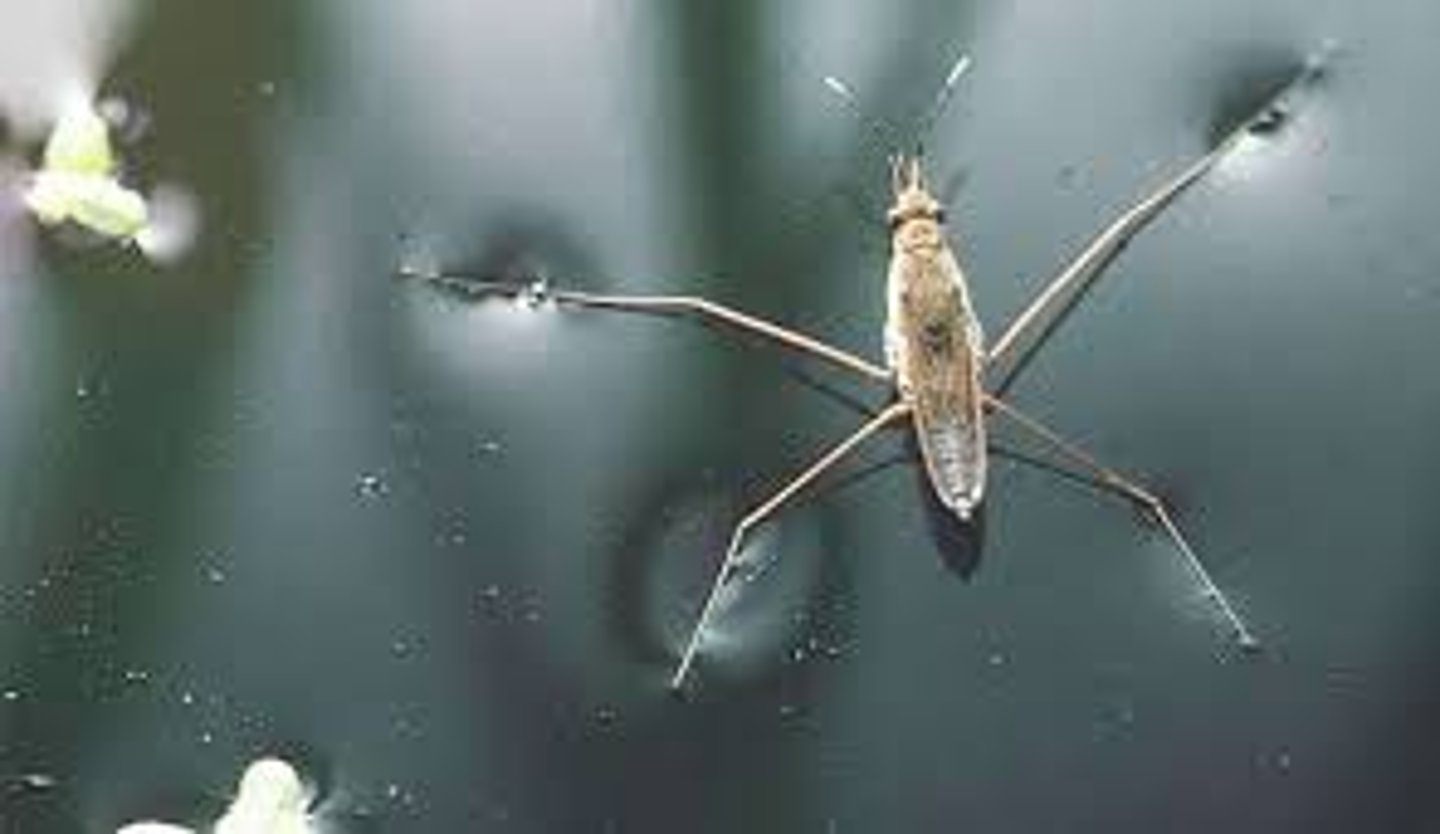
surface tension of water
Water molecules want to cling to each other. At the surface, however, there are fewer water molecules to cling to since there is air above (thus, no water molecules). This results in a stronger bond between those molecules that actually do come in contact with one another, and a layer of strongly bonded water. This surface layer creates a considerable barrier between the atmosphere and the water.

hydrogen acceptor
atom, ion, or molecule component of a hydrogen bond which does not supply the bridging (shared) hydrogen atom Ie O or N
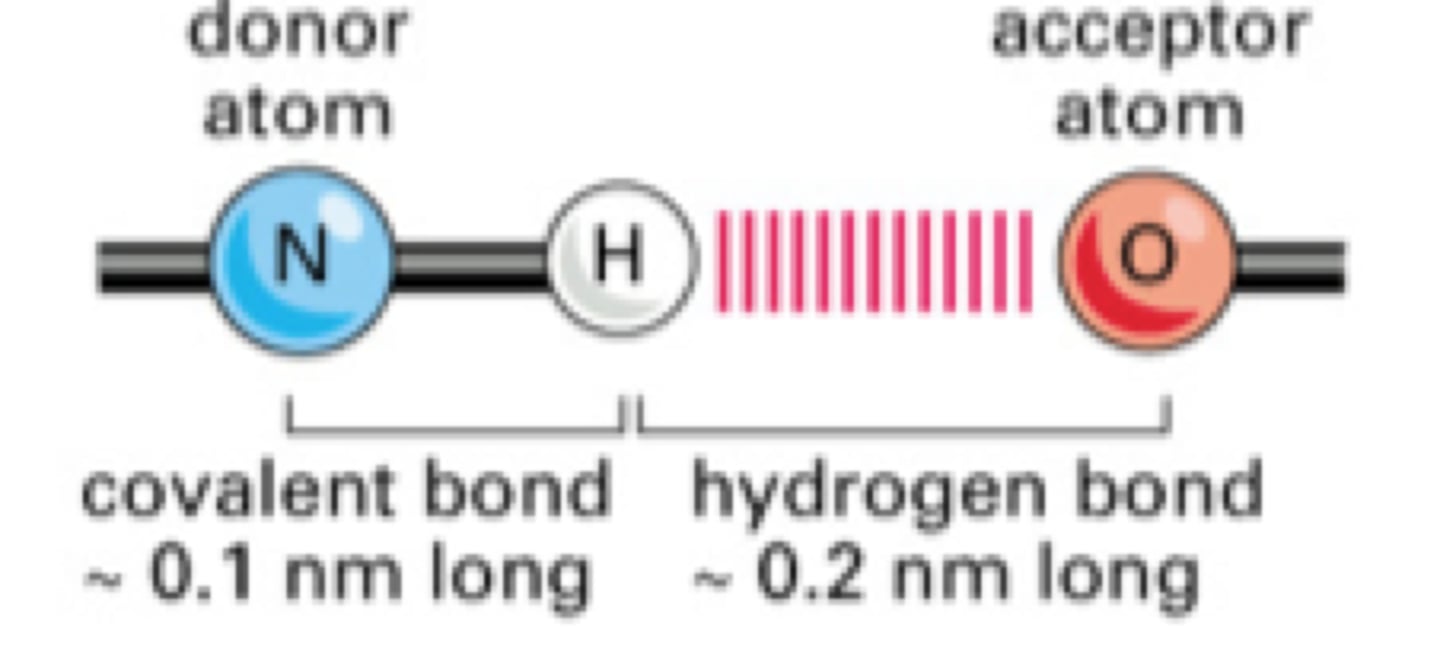
hydrogen donor
the Hydrogen atoms that are ATTACHED to the electronegative atom (O N or F)
Hydrogen bonds
The two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ that form between pairs of nitrogenous bases.
dielectric constant
Solvent polarity is a measure of solvent ability to separate opposite charges, which is expressed as _________. (E)
cathrate
shell created around nonpolar substance by polar substances, decreases entropy
ampipathic
Both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
micelles
-consist of bile salts, fatty acids, monoglycerides and phospholipids all clustered together with the polar ends of each molecule oriented towards the micelle's surface and the nonpolar portions forming the core.
van der waals interactions
weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges
proton hopping
Hydrogen bonded networks form natural chains for rapid proton transfer. Covalent and hydrogen bonds are interchangeable. Much faster than true diffusion, and results in extremely fast acid-base rxns.
colligative
a property that is determined by the number of particles present in a system but that is independent of the properties of the particles themselves

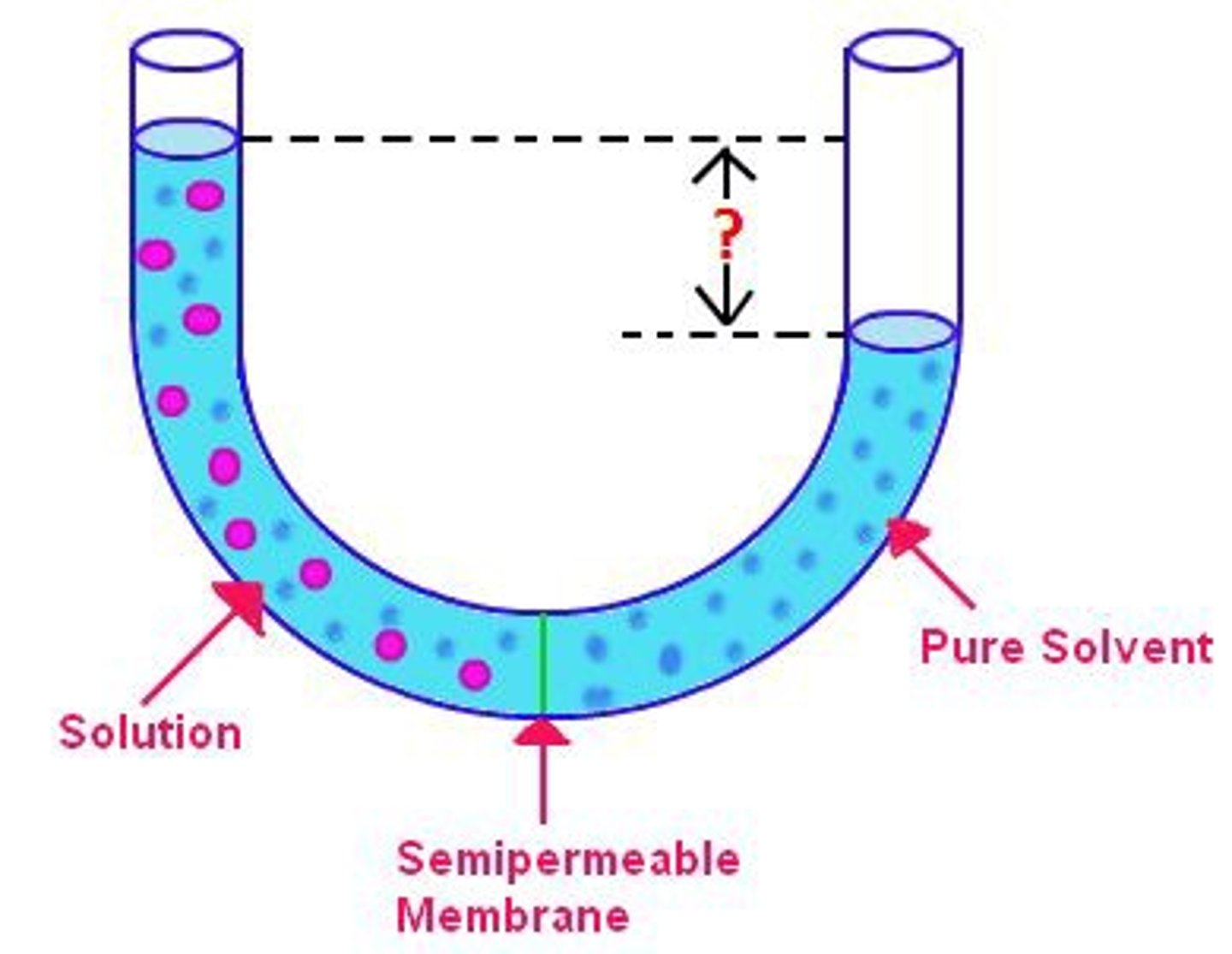
osmotic pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane when solutes are in water solution.
equilibrium constant
a ratio of products formed at equilibrium to reactants formed at equilibrium. Products/Reactants
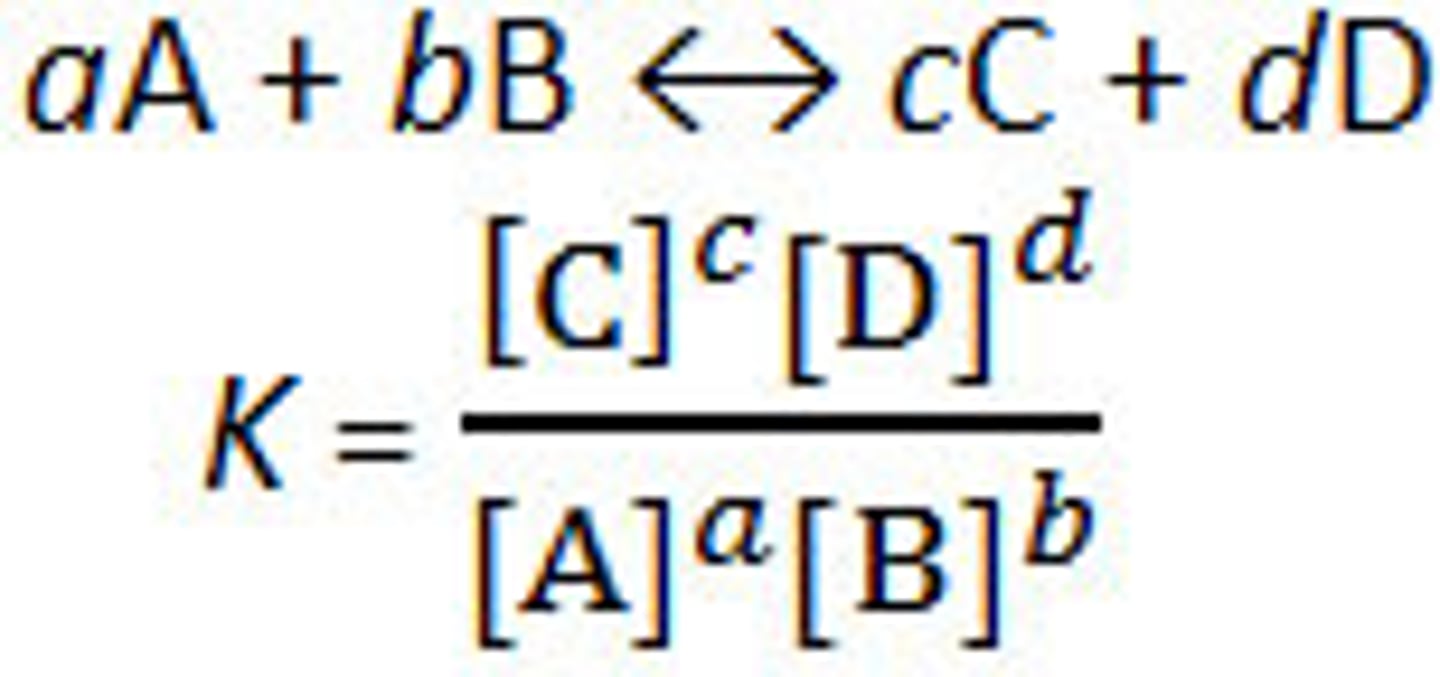
titration curve
a graph of pH of a solution as titrant is added, expressed by a weak acid proton donor dissociates to become its conjugate base a proton acceptor. CH3COOH --> CH3COO- + H+. At equilibrium pKa = pH because changes in H+ concentration are buffered and line is stable.
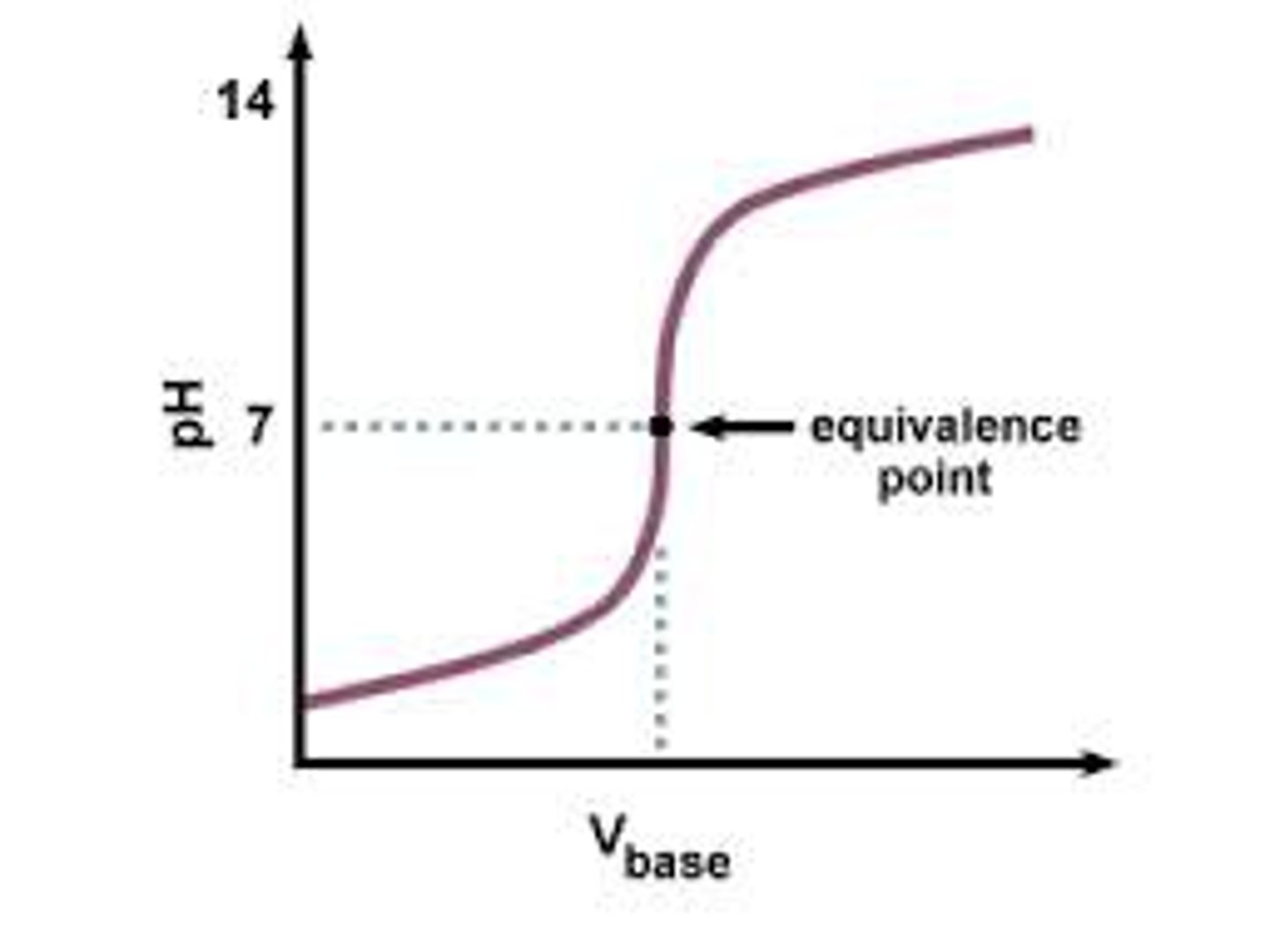
Henderson Hasselbach
pH= pKa + log (base(A-)/acid(HA))
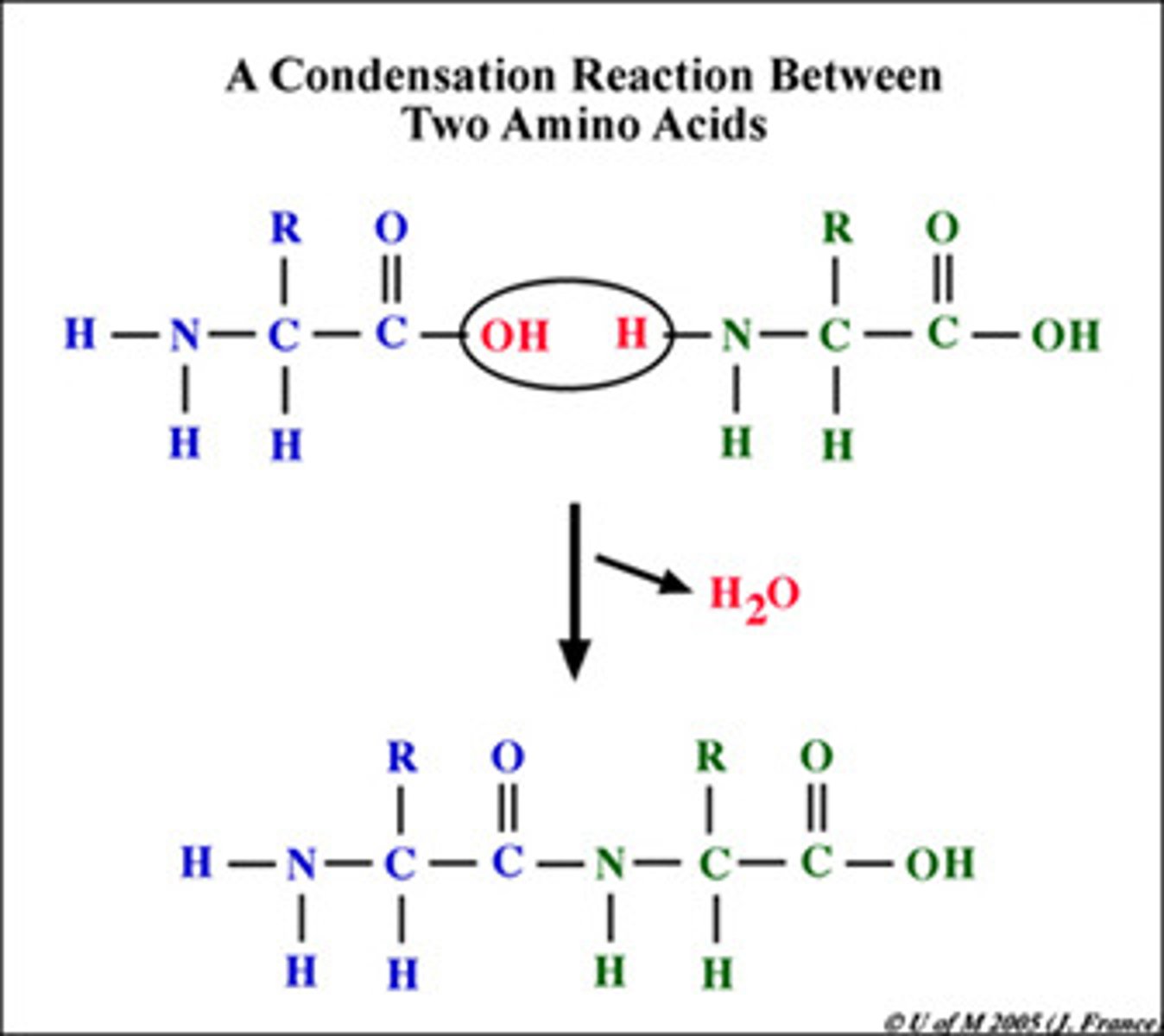
condensation reaction
A reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water; also called dehydration reaction.
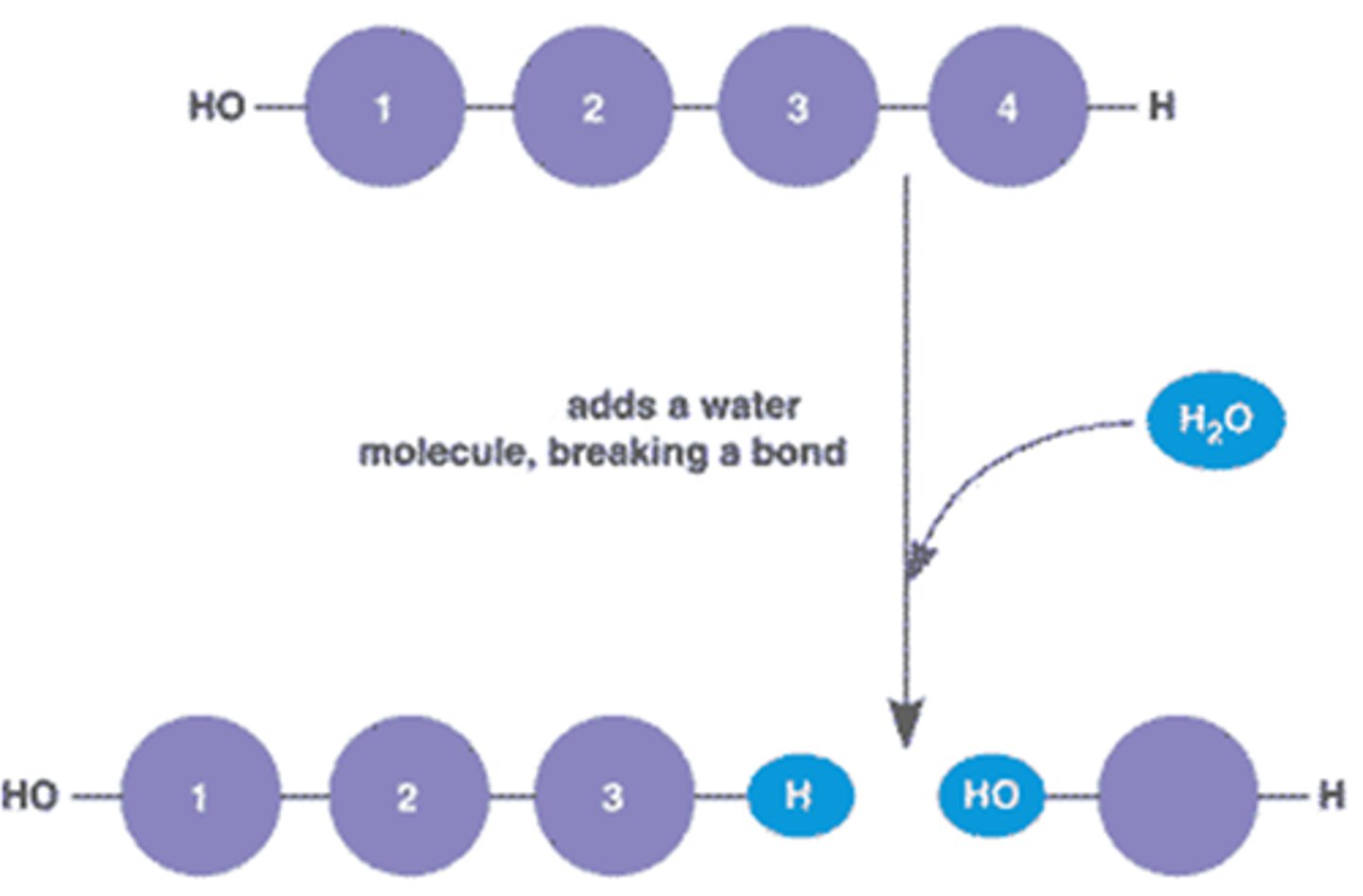
Hydrolysis reaction
this is when water (H2O) is added to a substance in order to break it up into smaller molecules. You can identify this as having a H2O reactant.
specific heat of water
High compared to other substances. Allows Earth's large bodies of water to store heat and not be changed by small temp increases. Acts as a buffer. 1 Joule(Calorie) of heat energy needed to raise 1 Gram, 1 Degree higher.
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1x10^-14
Ion product of H2O
pH of a solution
pH = -log_10[H+]
Logarithmic functions are closely related to exponential equations
log_b (x) = y says the same thing as b^y = x.