Orgo Functional Groups (copy)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
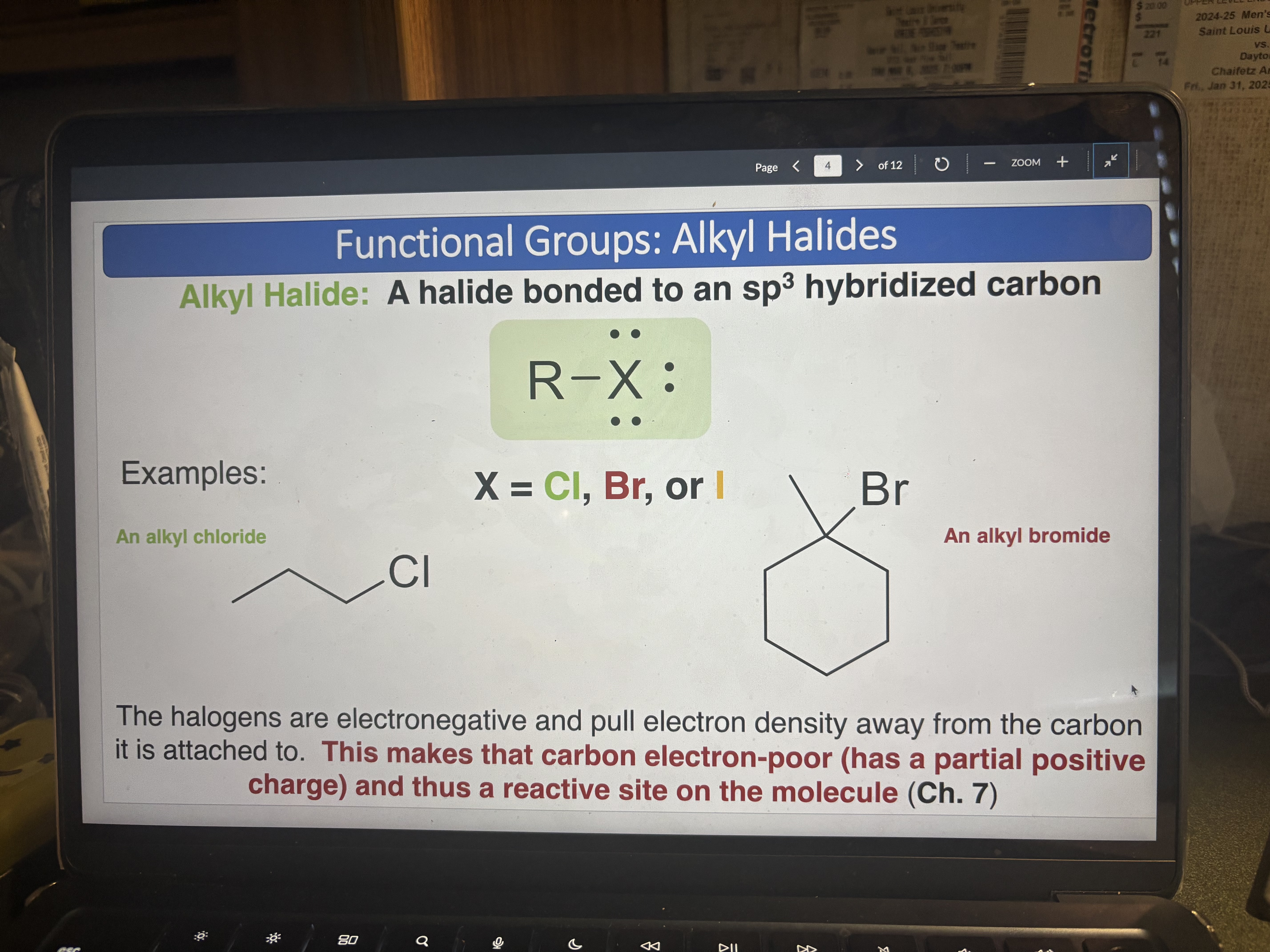
Alkyl Halide
Halide (Cl, Br, or I) bonded to a sp3 hybridized carbon. makes carbon e- poor and a good reactive site.
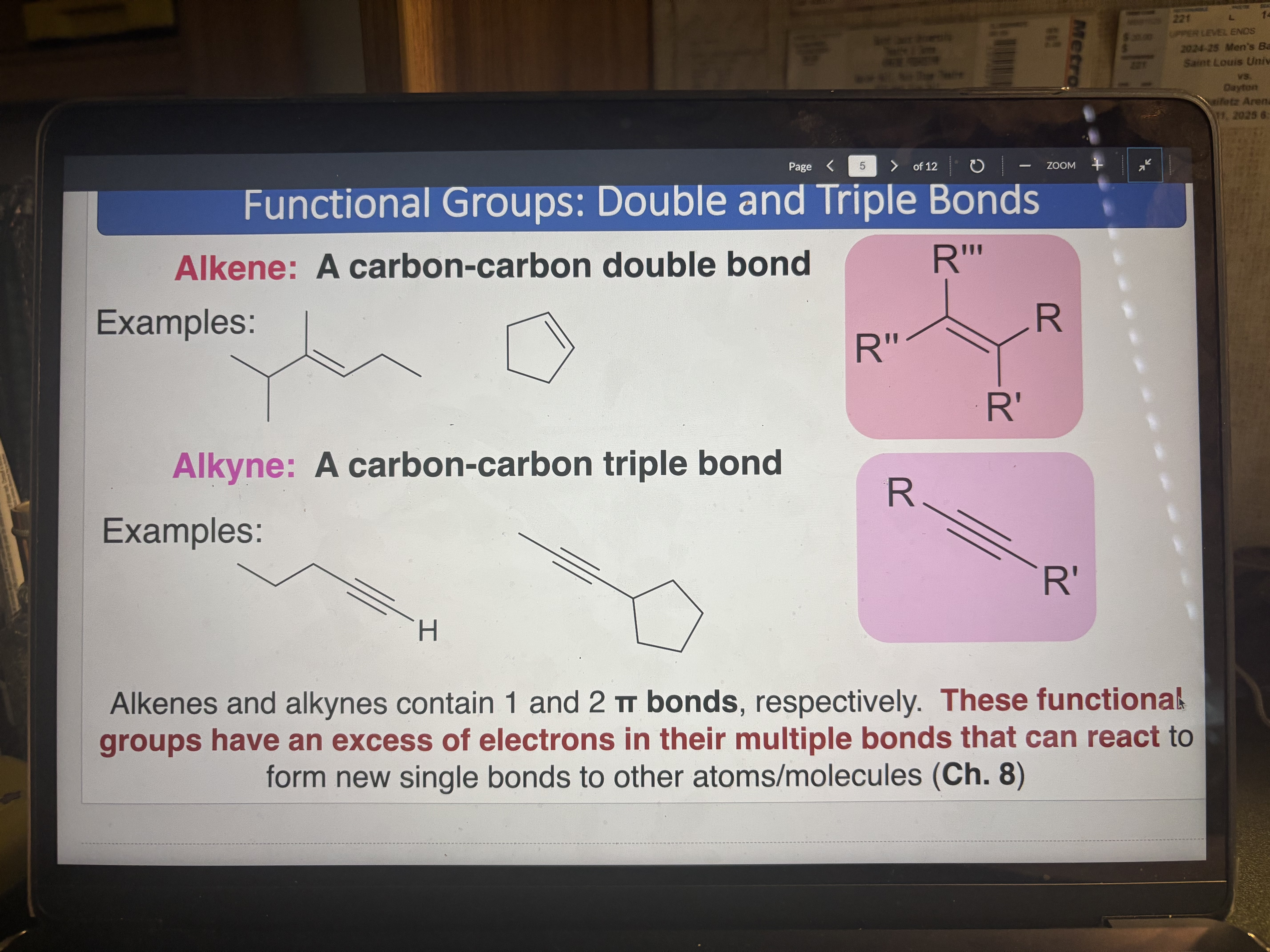
Alkene
A carbon-carbon double bond (1 π bond)
pKa = 43-44
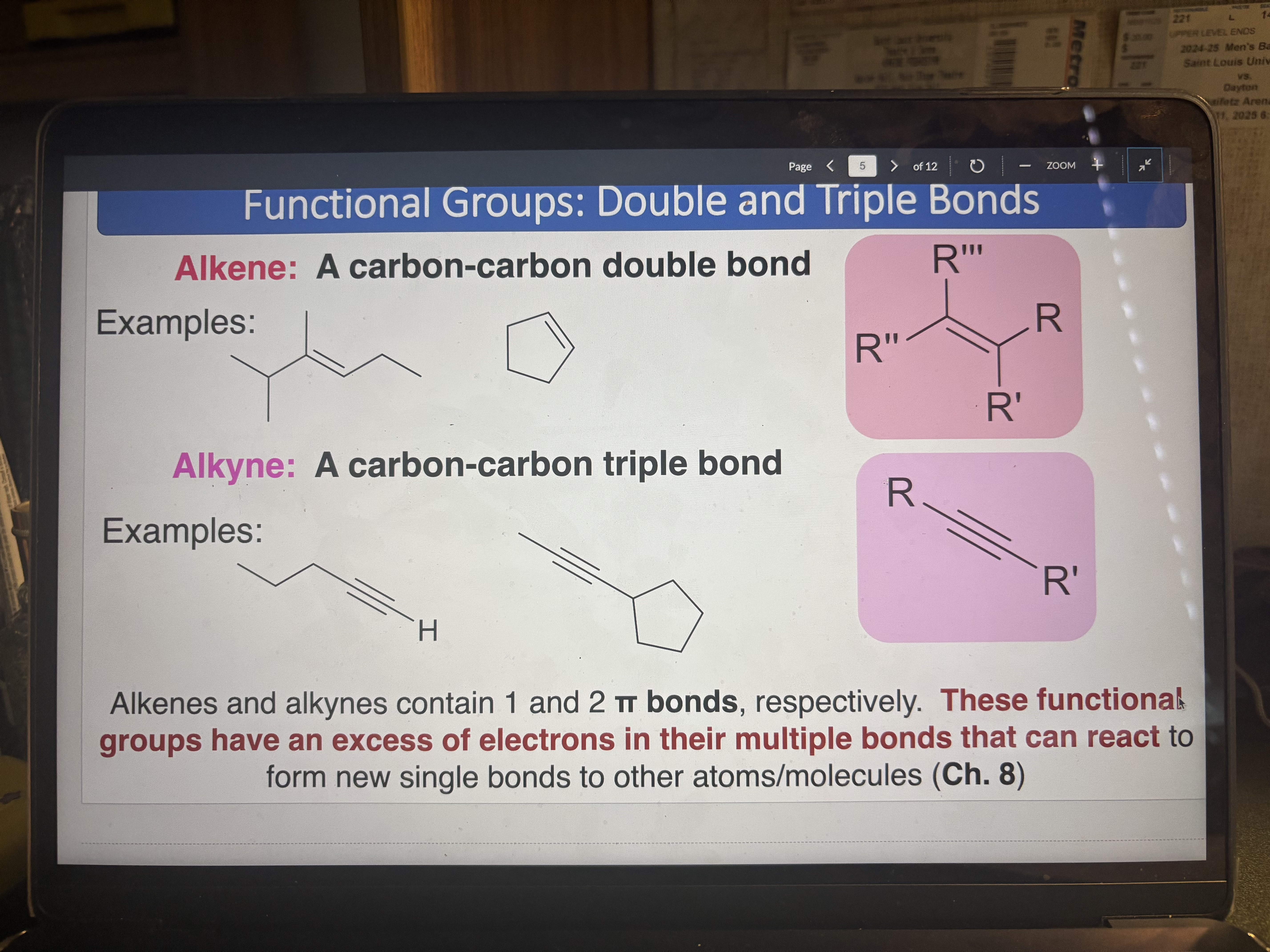
Alkyne
pKa = 25
A carbon-carbon triple bond (2 π bonds)
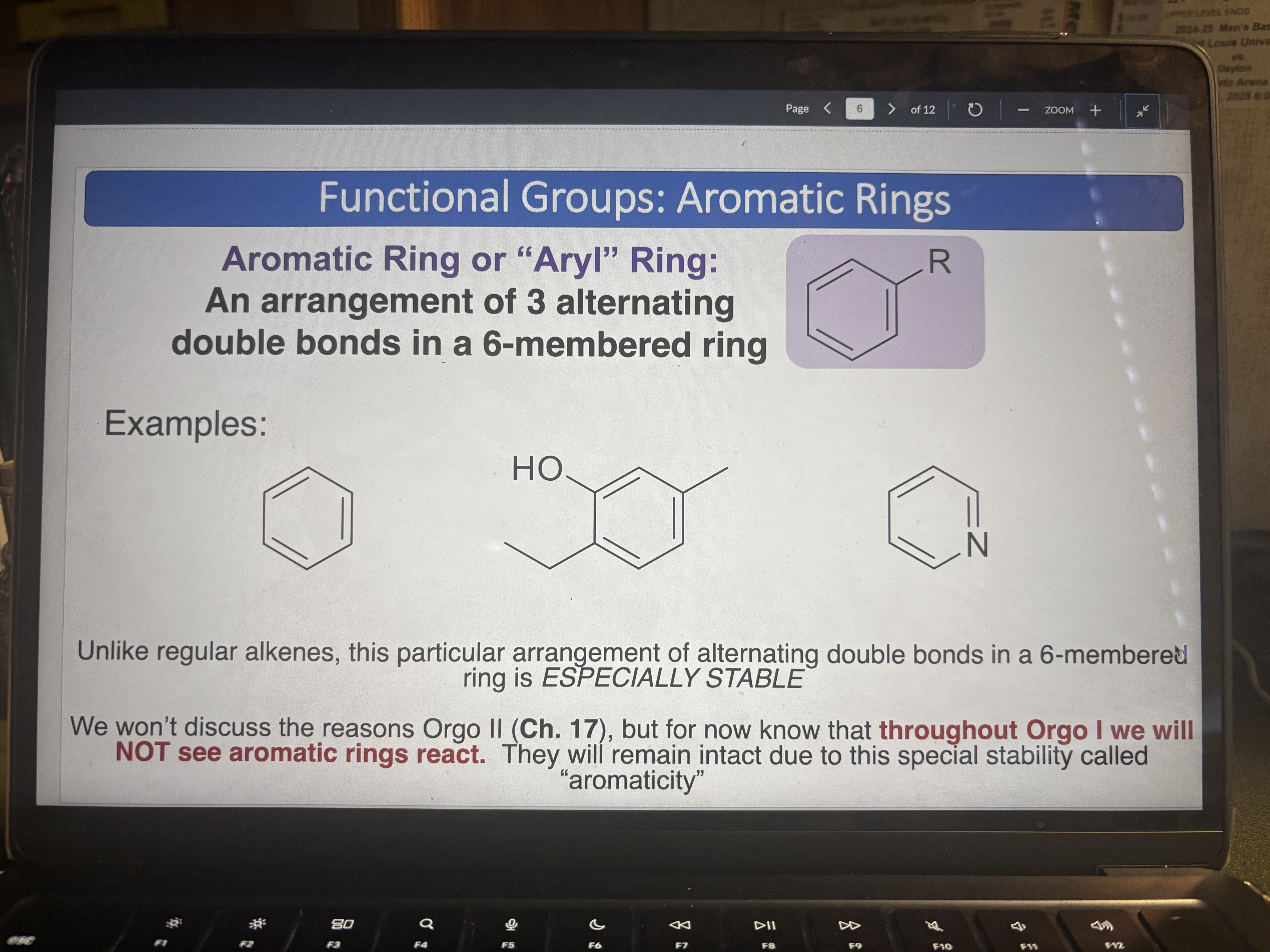
Aromatic Rings
An arrangement of 3 alternating double bonds in a 6-members ring (ESPECIALLY STABLE)
Benzene pKa = 43
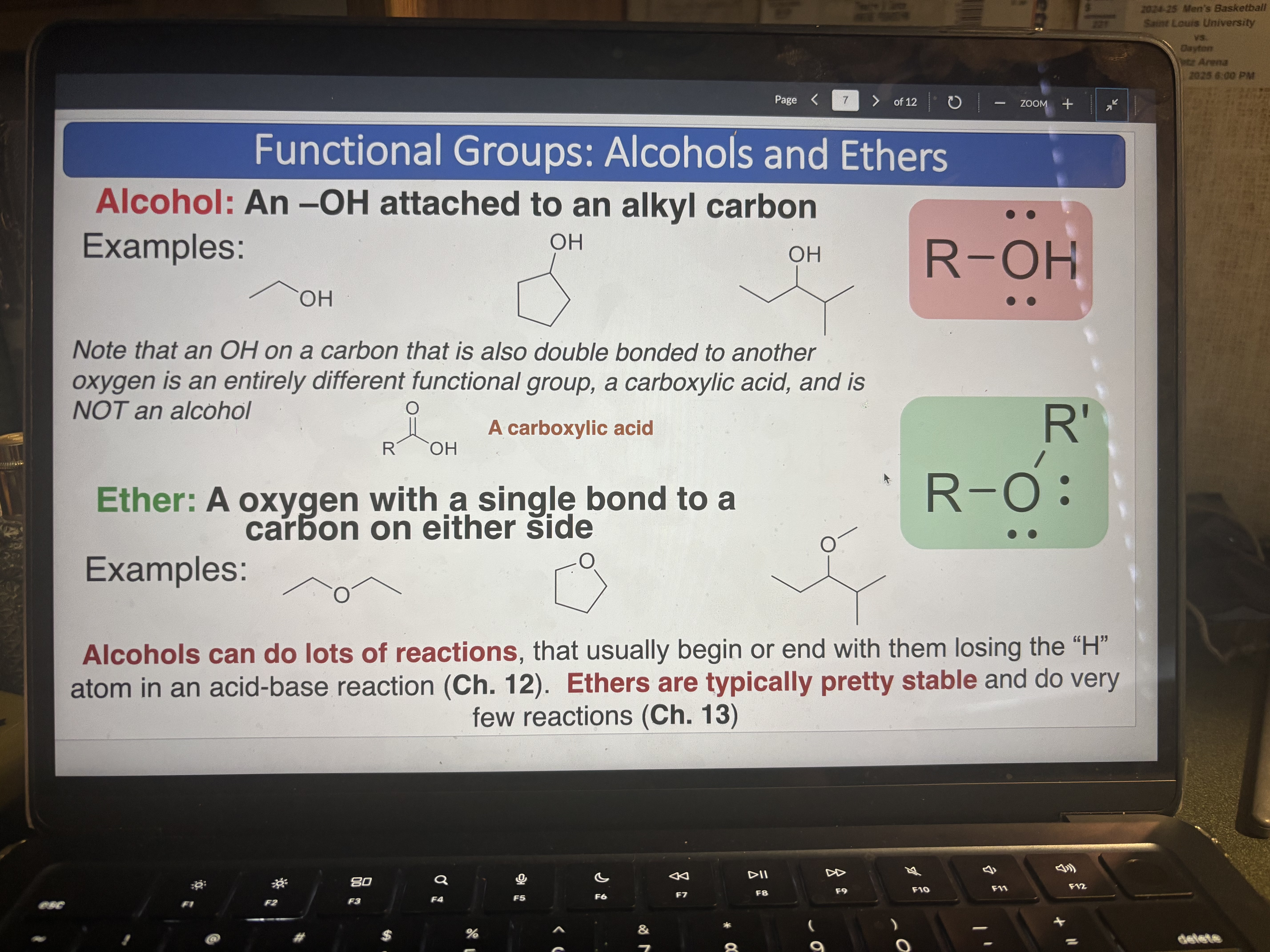
Alcohol
pKa = 17
An -OH attached to an alkyl carbon (can do lots of reactions, usually losing the H)
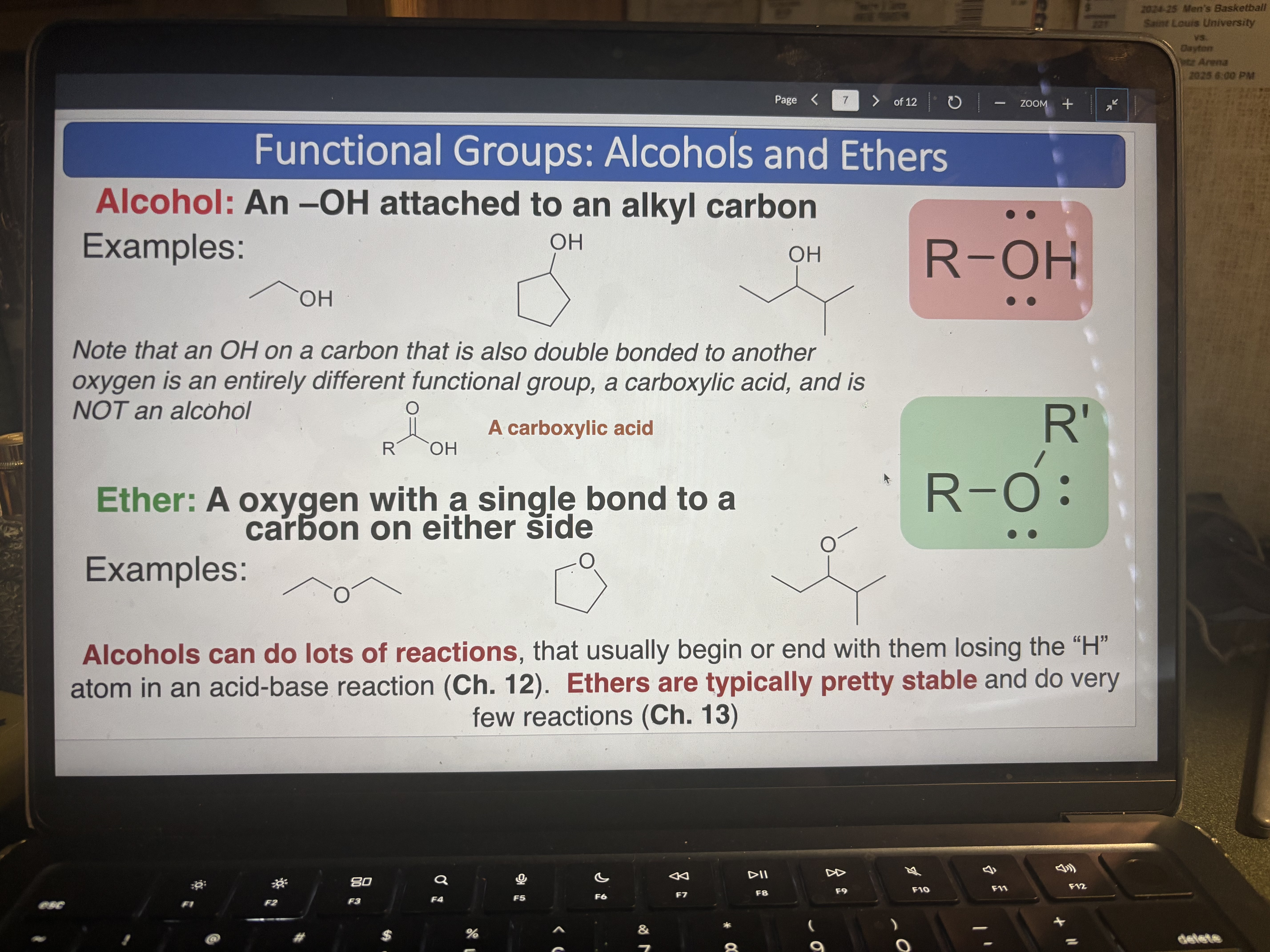
Ether
An oxygen with a single bond to a carbon on either side (typically pretty stable)
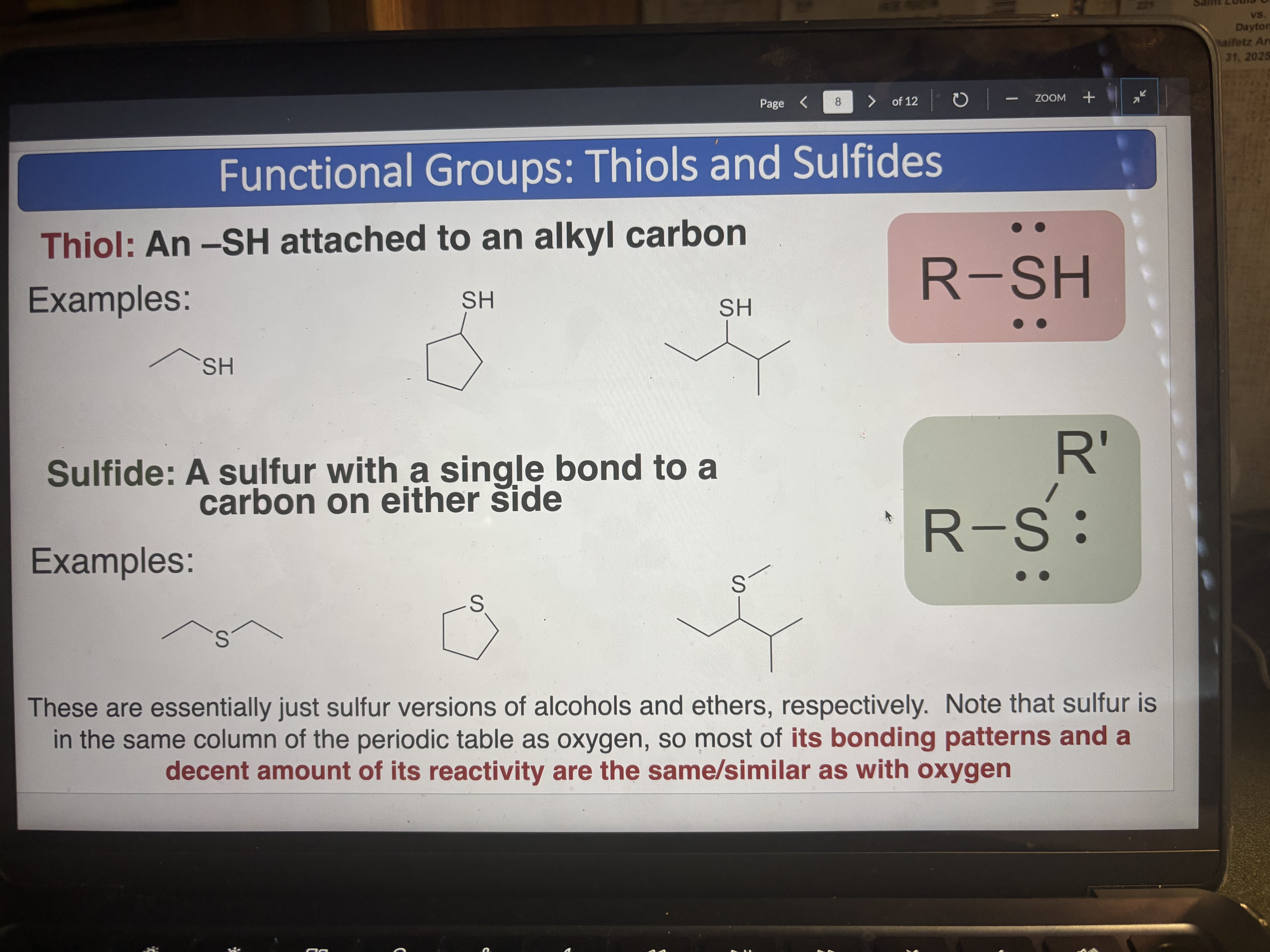
Thiol
An -SH attached to an alkyl carbon
pKa = 10
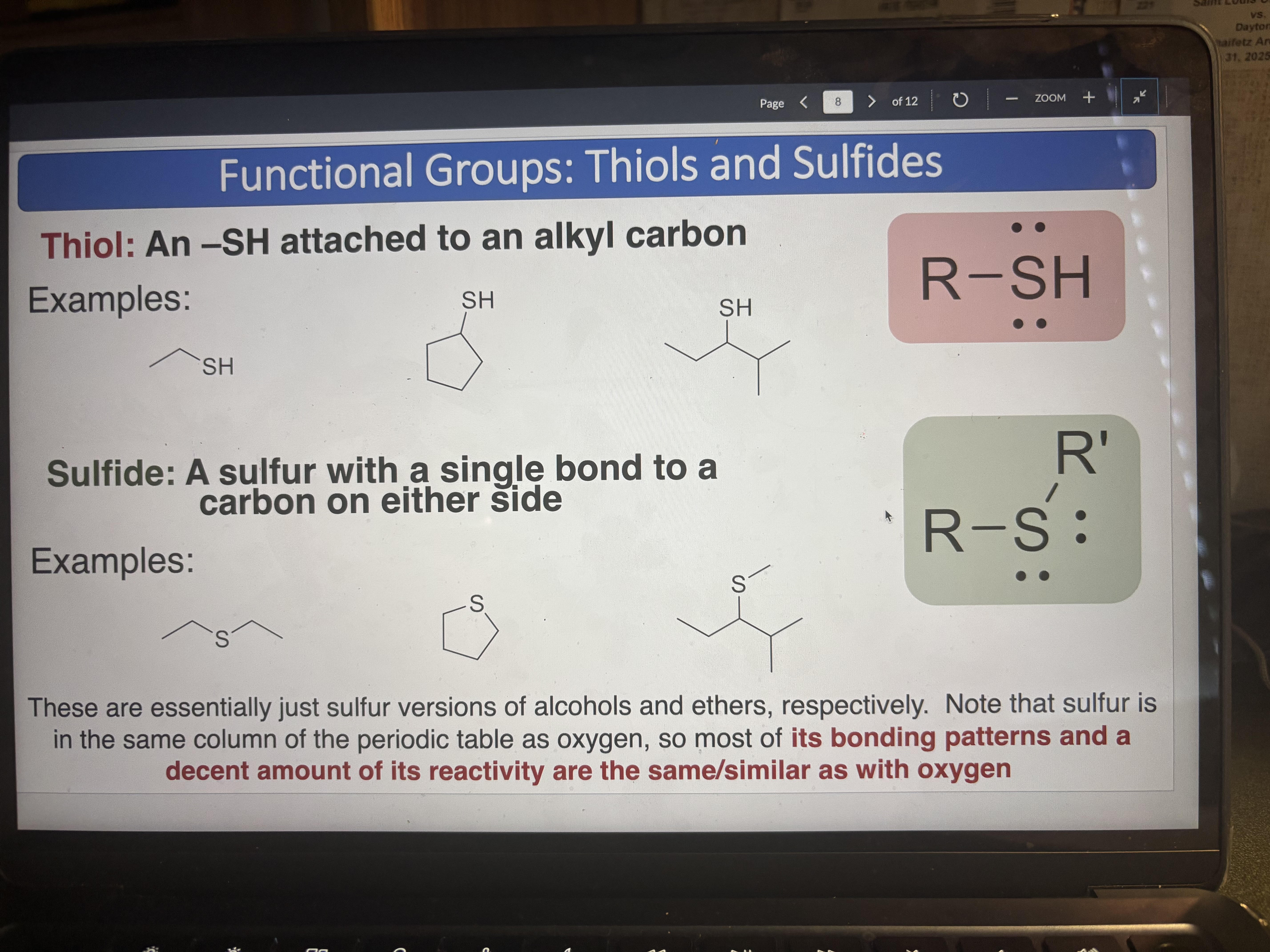
Sulfide
A sulfur with a single bond to a carbon on either side
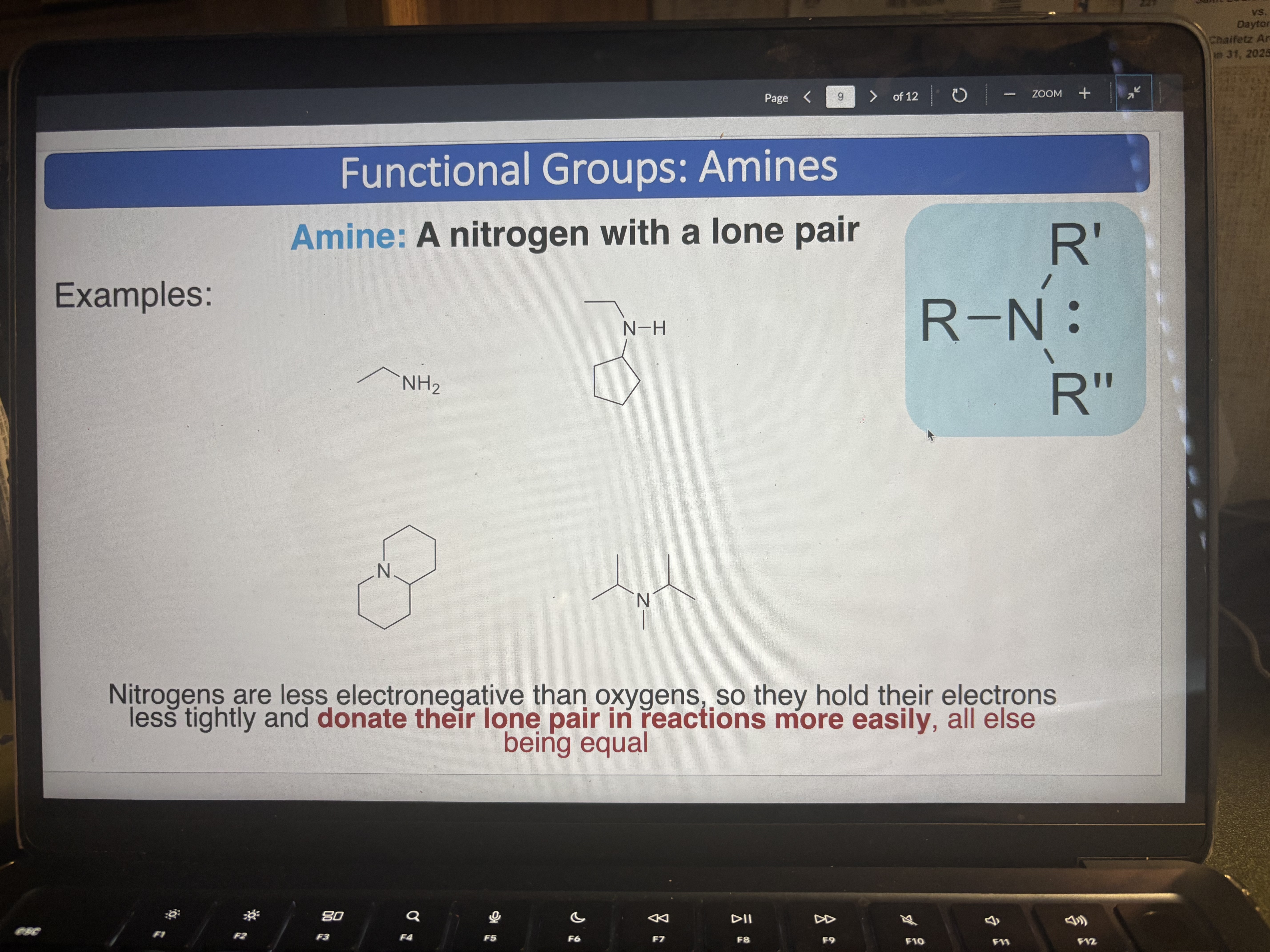
Amine
A nitrogen with a lone pair (donate e- more easily than oxygen), can be NH or NH2
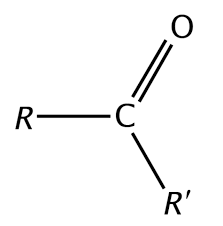
Carbonyl
Any functional group that contains a C=O double bond
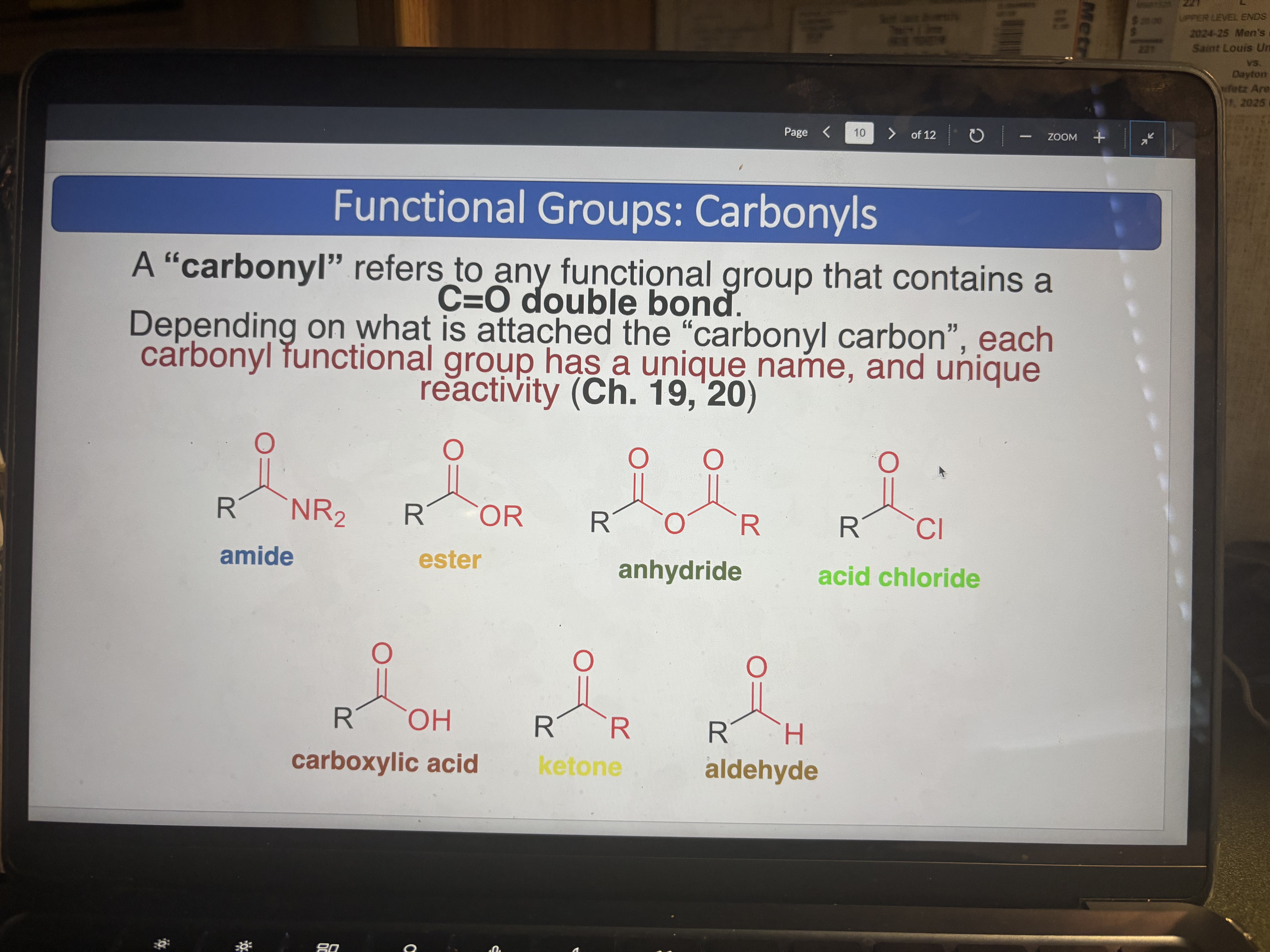
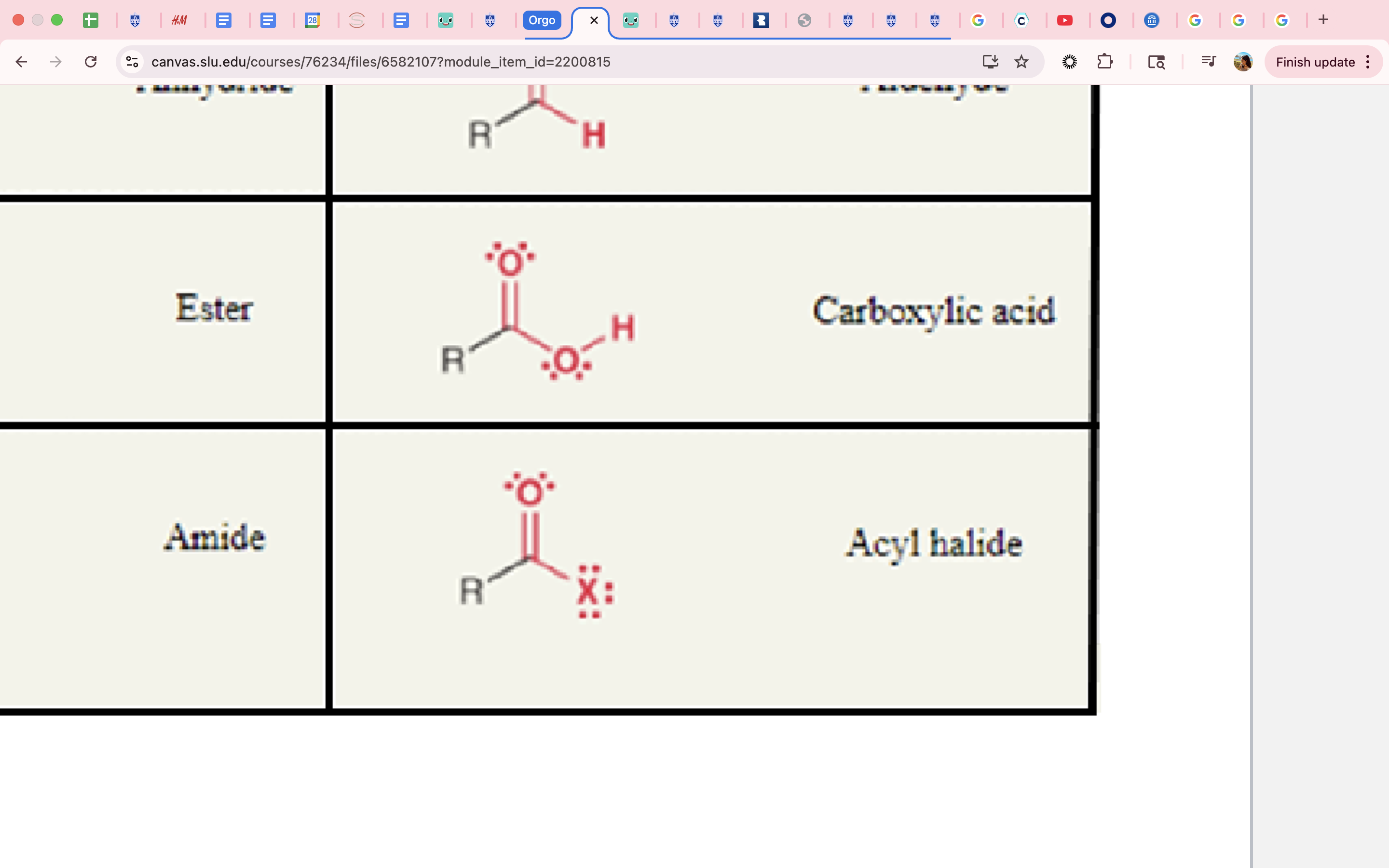
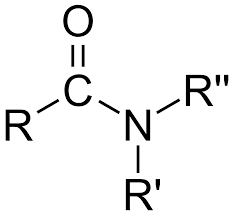
amide
carbonyl
ester
cabonyl
pKa = 25
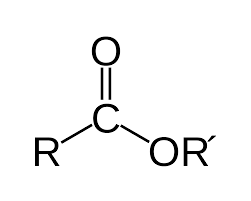
anhydride
carbonyl
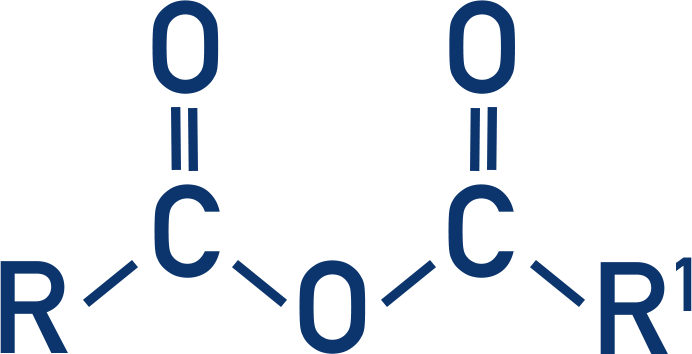
acid chloride
carbonyl
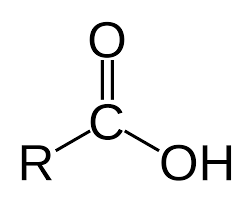
carboxylic acid
carbonyl
pKa = 4-5
ketone
carbonyl
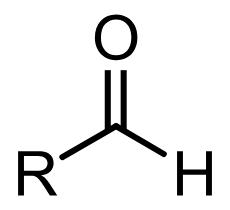
aldehyde
carbonyl
pKa = 17
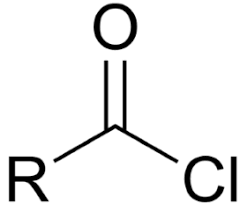
acyl halide