AICE ENVIRONMENTAL-UNIT 7
Acid Deposition
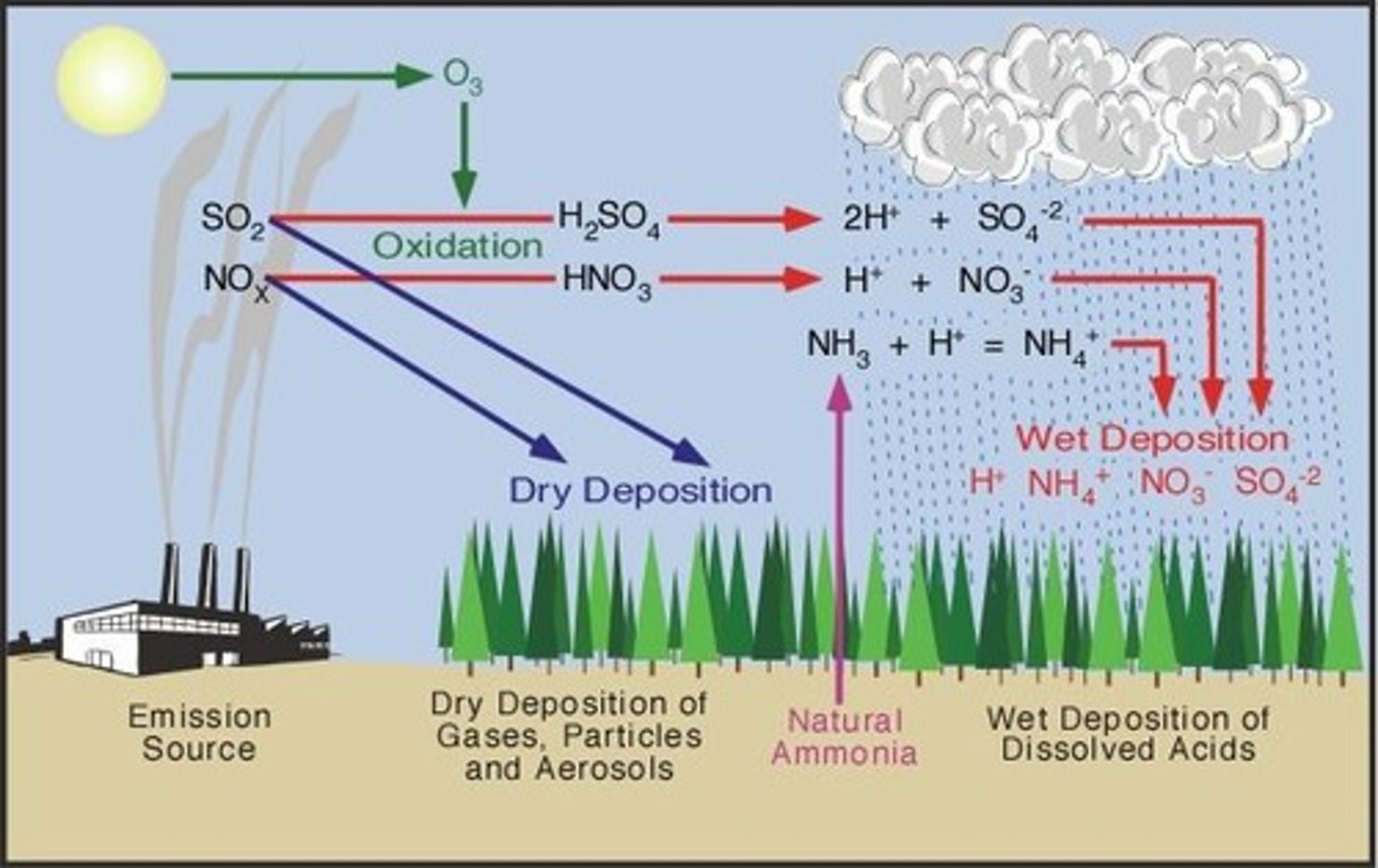
Mix of pollutants depositing as wet or dry acid.
Wet Deposition
Acids in precipitation like rain or snow.
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pollution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Acid Deposition
Mix of pollutants depositing as wet or dry acid.
Wet Deposition
Acids in precipitation like rain or snow.
Dry Deposition
Dust and gases depositing near pollution sources.
Acid Rain
Precipitation with pH less than 5.6.
Primary Pollutants
Directly emitted pollutants from sources.
Secondary Pollutants
Formed from reactions of primary pollutants.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Primary pollutant from burning fossil fuels.
Nitrogen Monoxide (NO)
Primary pollutant from vehicle emissions.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
Primary pollutant from combustion processes.
Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
Secondary pollutant formed from sulfur dioxide.
Nitric Acid (HNO3)
Secondary pollutant formed from nitrogen monoxide.
Aluminum Leaching
Acid rain leaches aluminum from soil into water.
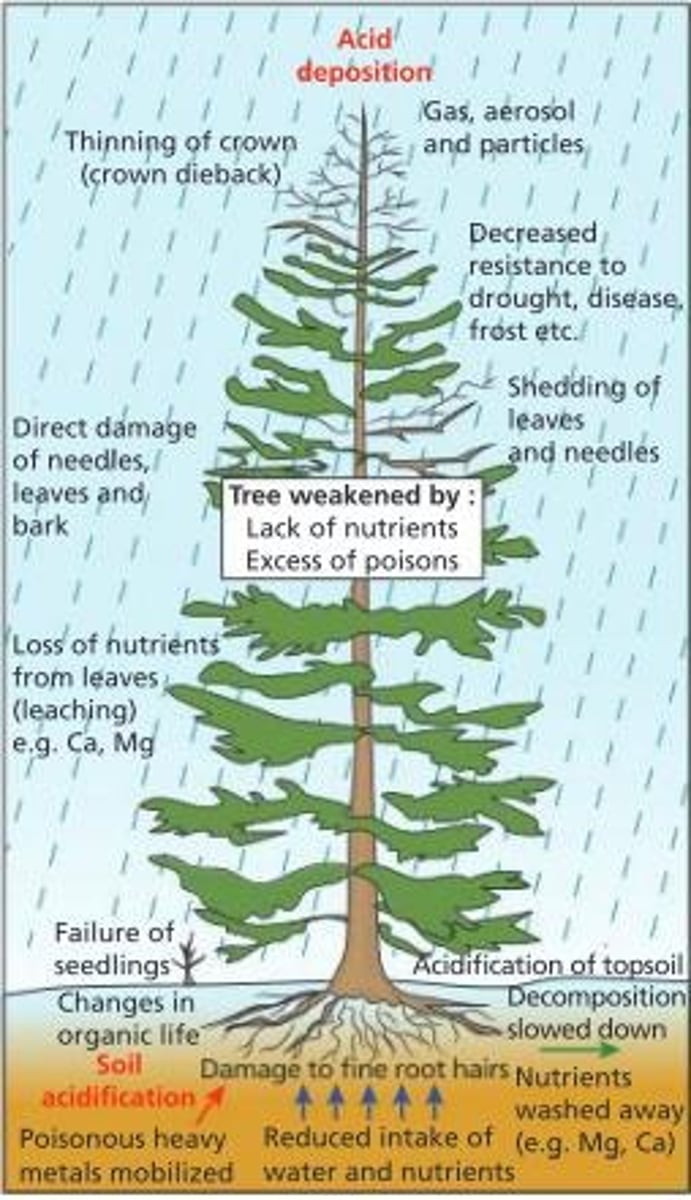
Acid-Sensitive Species
Organisms vulnerable to low pH environments.
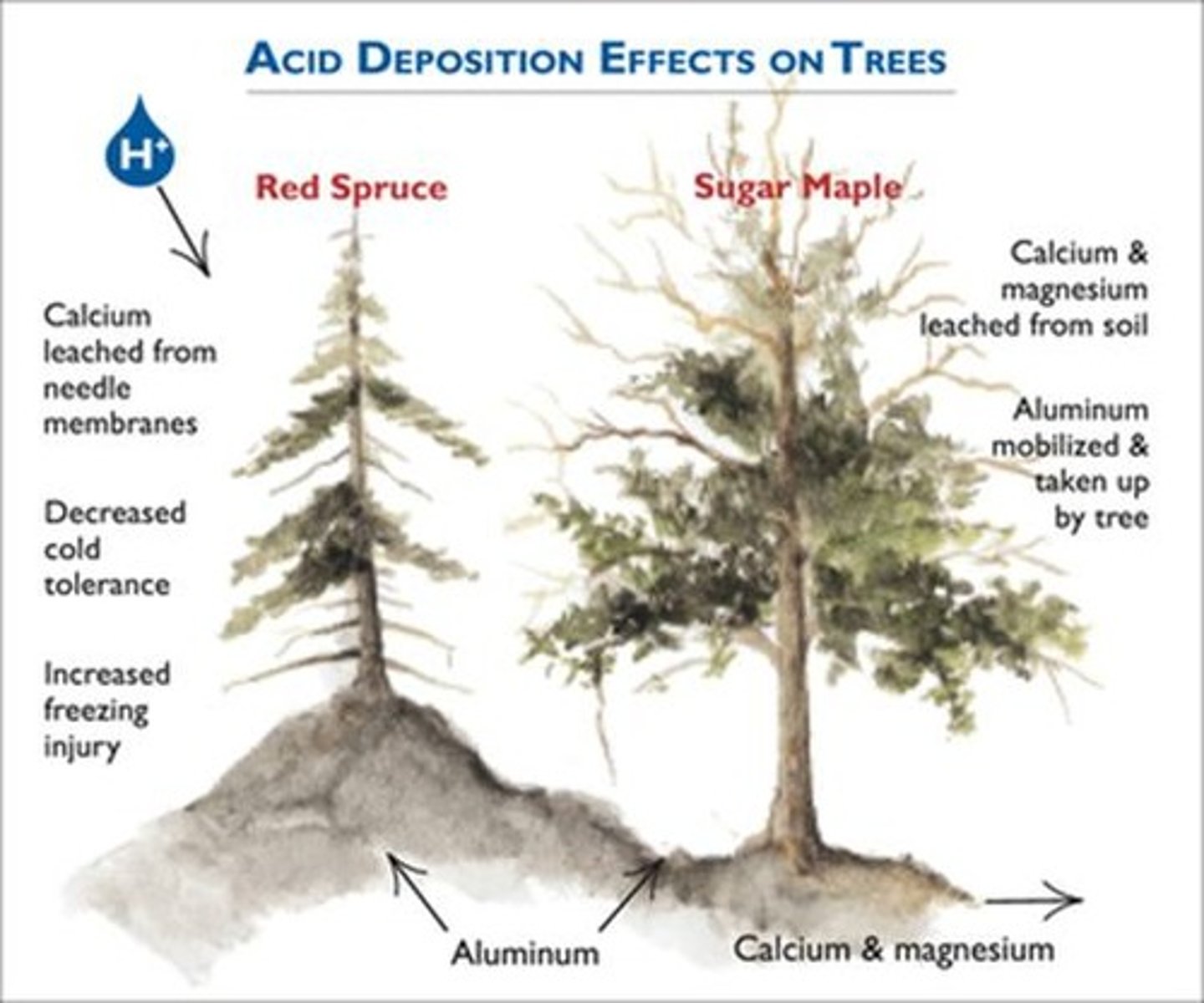
Critical pH for Fish Eggs
Most fish eggs fail to hatch below pH 5.
Dissolved Aluminum
Toxic to fish, damages gills and respiration.
Nutrient Leaching
Loss of essential nutrients from acidic soil.
Crop Yield Reduction
Lower pH leads to decreased agricultural productivity.
Defoliation
Loss of leaves due to acid deposition.
pH and H+ Concentration
Lower pH indicates higher hydrogen ion concentration.
Aquatic Ecosystem Impact
Acid rain harms fish and wildlife in water.
Tolerance to Acidity
Some species withstand acidic conditions better.
Root Hair Damage
Acidic soil harms water uptake in plants.
Acidic Lakes
Lakes with low pH may lack fish.
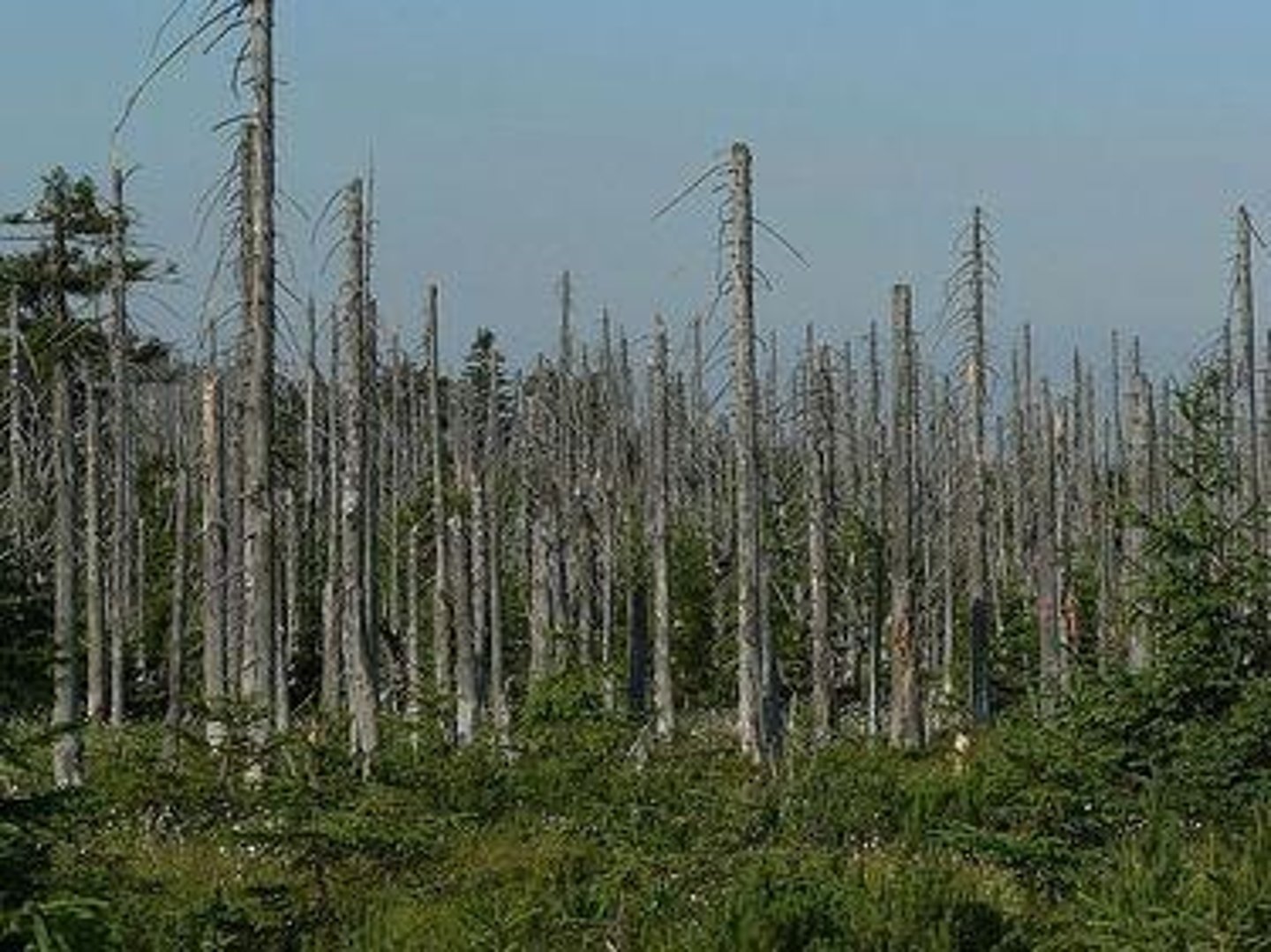

Acid Deposition
Process where acids strip nutrients from foliage.
Photosynthesis
Process by which trees convert sunlight into energy.
Chemical Weathering
Weathering caused by chemical reactions, like acids.
Limestone
Type of rock that dissolves in acid rain.
Photochemical Smog
Air pollution formed by sunlight-driven reactions.
Ground Level Ozone
Ozone formed at Earth's surface, harmful to health.
NOx
Nitrogen oxides, pollutants from combustion processes.
VOCs
Volatile organic compounds, contribute to smog formation.
Industrial Smog
Smog from burning coal, includes soot and sulfur dioxide.
Sulfur Dioxide
Gas produced from burning fossil fuels, contributes to acid rain.
Tropospheric Ozone
Ozone in the lower atmosphere, a major smog component.
Asthma
Chronic respiratory condition worsened by air pollution.
Flue Gas Desulfurization
Process to remove sulfur dioxide from exhaust gases.
Dry Scrubbers
Devices using chemicals to absorb pollutants from emissions.
Wet Scrubbers
Devices that use liquid to remove pollutants from gases.
Mass Transit
Public transport systems to reduce private vehicle use.
Renewable Energy
Energy from sources that do not pollute, like solar.
Urban Air Pollution
Air pollution concentrated in city environments.
Particulate Matter
Small particles in the air that can harm health.
Crop Yield
Amount of crop produced, affected by air quality.
Heart Problems
Health issues exacerbated by exposure to smog.
Legislation
Laws aimed at reducing air pollution.
Local Food Consumption
Eating locally sourced food to reduce carbon footprint.
Wet Scrubbers
Devices that absorb pollutants using water droplets.
Hydrodesulfurization (HDS)
Process to remove sulfur from petroleum products.
Sulfur Dioxide (SOx)
Pollutants produced from burning sulfur-containing fuels.
Catalytic Converters
Devices converting harmful exhaust pollutants to less harmful substances.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that easily evaporate at room temperature.
Electrostatic Precipitators
Devices that remove particles from gas streams using electric charge.
Particulate Matter (PM)
Tiny particles in the air that can harm health.
Formaldehyde
Common VOC and indoor air pollutant, measurable in air.
Sludge Collection System
System for trapping and disposing of polluted water.
Mist Eliminator
Device that captures mist droplets in scrubbers.
Hydrotreating Facility
Plant where hydrodesulfurization processes occur.
Carbon Footprint
Total greenhouse gas emissions caused by an individual.
Geneva Convention
1979 agreement to control transboundary air pollution.
Montreal Protocol
1987 treaty to phase out CFCs for ozone protection.
Rio Earth Summit
1992 conference aimed at reducing environmental pollution.
Kyoto Protocol
International agreement to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Economic Incentives
Financial benefits to encourage environmentally friendly practices.
Educational Campaigns
Programs to inform public about pollution reduction.
Air Fresheners
Household products that can emit VOCs into the air.
Aerosol Sprays
Common VOC sources found in household products.
Proper Disposal
Following guidelines for safe waste management.
Ventilation Increase
Improving air flow to reduce VOC exposure.
Gothenburg Protocol
Targets reduction of pollutants and acid rain.
Copenhagen Conference
2009 agreement on greenhouse gas emission limits.
$30 billion aid
Initial financial support for LICs from HICs.
Paris Climate Conference
2015 agreement to limit global temperature rise.
2° C limit
Goal to restrict global temperature increase.
Polluter Pays Principle
Polluters bear costs of environmental damage.
Ozone Depletion
Reduction of ozone layer due to pollutants.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Unreactive compounds causing ozone depletion.
Dobson Unit
Measurement unit for ozone concentration.
Ozone hole
Area with ozone concentration below 100 Dobson Units.
Polar vortex
Weather phenomenon affecting ozone depletion in Antarctica.
Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs)
Clouds contributing to ozone depletion processes.
Increased UV radiation
Result of ozone layer deterioration.
Cataracts
Eye condition exacerbated by UV radiation.
Montreal Protocol
Successful agreement to phase out ozone-depleting substances.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
Greenhouse gases used as CFC alternatives.
Global warming potential (GWP)
Measure of a substance's heat-trapping ability.
Fluorinated Gases (F-GHGs)
Potent greenhouse gases from industrial processes.
Rowland and Molina
Scientists who confirmed CFCs' role in ozone depletion.
Experimental evidence
Data supporting scientific hypotheses on ozone destruction.
Auxiliary hypotheses
Supporting ideas tested alongside main scientific hypotheses.
Skin cancer
Health risk increased by exposure to UV radiation.
Decreased biodiversity
Loss of species diversity due to environmental changes.