ANAPHY- INTERGUMENTARY SYSTEM
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
- is your body’s outer layer. It’s made up of your skin, nails, hair, and the glands and nerves on your skin.
- acts as a physical barrier — protecting your body from bacteria, infection, injury, and sunlight. It also helps regulate your body temperature and allows you to feel skin sensations like hot and cold.
Intergumentary System
- is the largest and heaviest organ in your body.
- It weighs about six pounds (or more) and is approximately 2 millimeters thick — thinner on sensitive areas like eyelids, and thicker on surfaces that take more stress, like the soles of your feet. One inch of your skin contains nearly 19 million cells.
SKIN
Your skin is composed of three layers, with nerves that recognize different sensations in each layer:
epidermis
dermis
hypodermis
The top layer of your skin. This is the part of your skin that you can see and touch. It’s made up of three types of cells: melanocytes, keratinocytes and Langerhans. It gives your skin its color and provides a waterproof barrier.
epidermis
The middle layer of your skin. This layer is the thickest. It contains sweat and oil glands and hair follicles.
dermis
The bottom layer of your skin. It’s the fatty layer of your skin that helps insulate your body.
hypodermis
is the result of relative amount of melanin
skin color
is a yellow-orange pigment present primarily in the stratum corneum
carotene
flush skin may indicate_________
hypertension or fever
pale skin seen in ____________
anemic individuals
bluish cast
cyanosis
tissues become yellow
jaundice
bronzing of the skin
addison’s disease
protect the ends of your fingers and toes
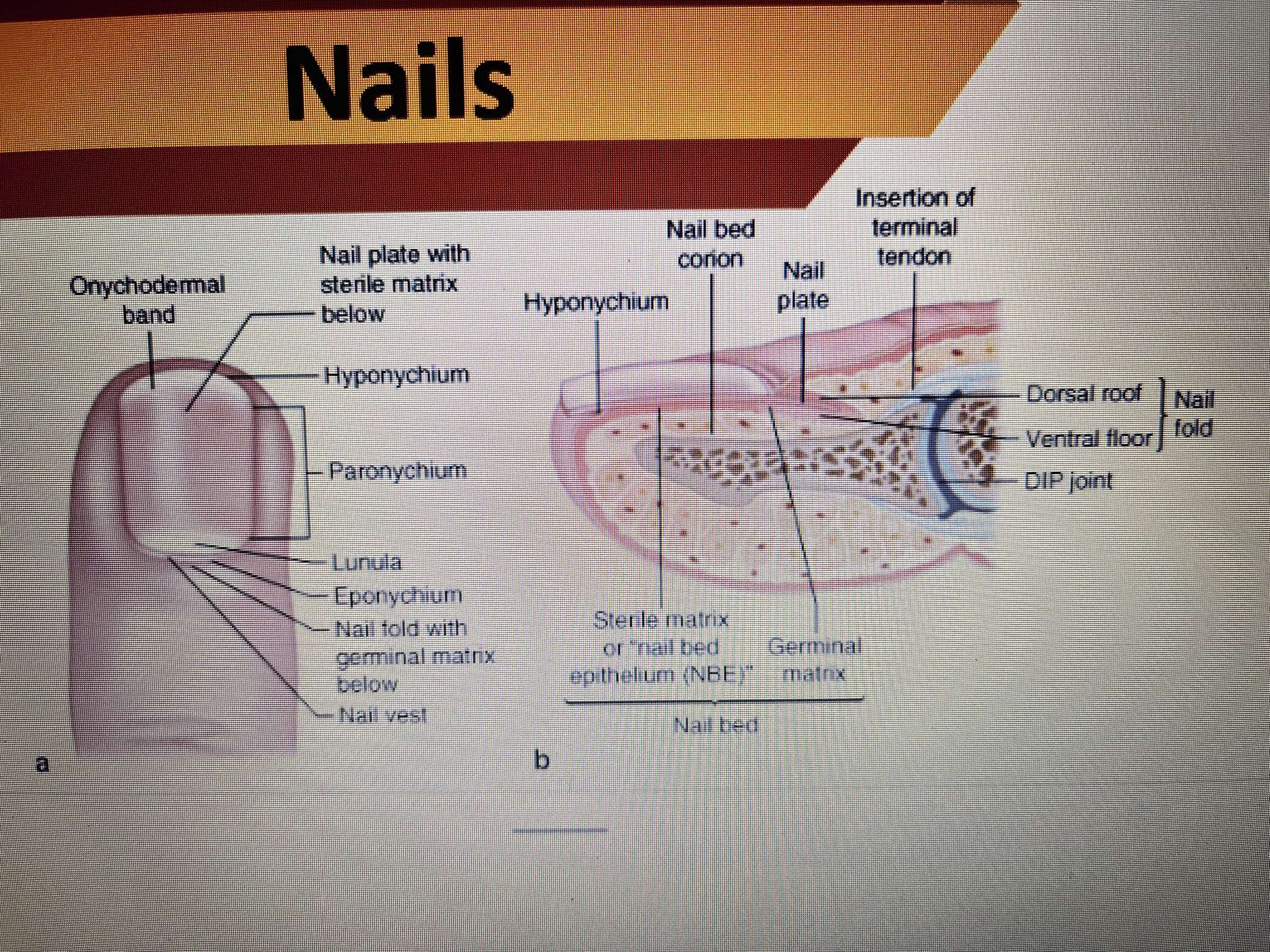
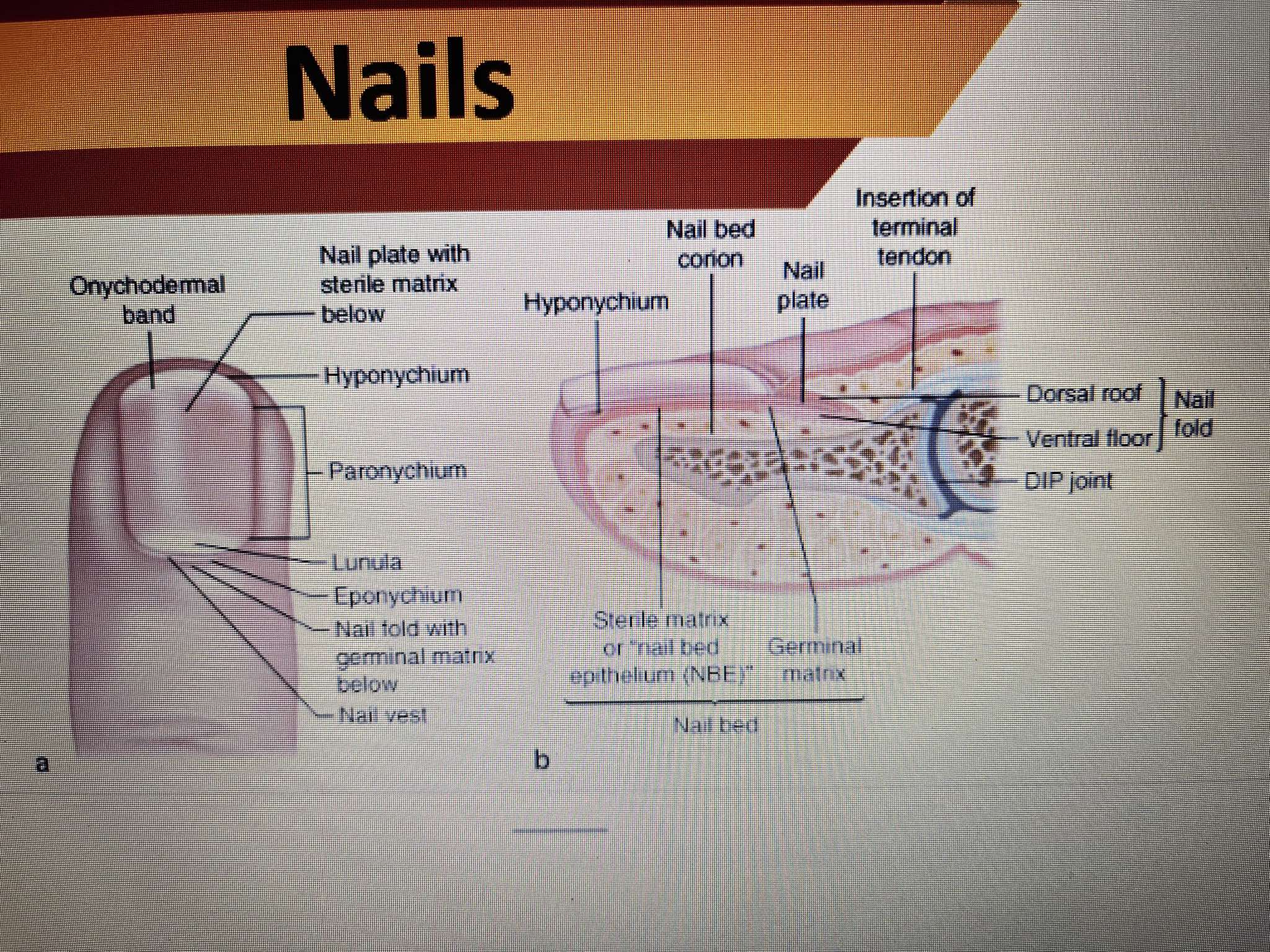
NAILS
The anatomy of your nail consists of:
Nail plate: The hard part of your nail you can see.
Nail bed: The skin under your nail plate.
Cuticle: The thin skin at the base of your nail plate.
Matrix: The “root” of your nail responsible for making it grow.
Lunula: The white, moon-shaped part of your nail plate.
helps keep heat in your body. Your eyelashes and eyebrows help protect your eyes from dirt and water.
HAIR
our hair is made of a protein called_________
keratin
.Your hair consists of three parts: the shaft, follicle, and bulb.
Hair shaft: The part of your hair you can see, touch, and style.
Hair follicle: The tube-like structure that keeps your hair in your skin.
Hair bulb: Located under your skin and responsible for hair growth.
are caused by your integumentary system. We all have hair erector muscles connected to our hair follicles and skin. When it contracts, it makes your hair stand up
goosebumps
They release materials like water, salt or oil from under your skin to the surface of your skin
Glandas
our integumentary system consists of the following glands:
Sudoriferous glands: These are the glands that secrete sweat through your skin. There are two types of sweat glands: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. Eccrine glands are all over your body and open to your pores, while apocrine glands open into your hair follicles.
Sebaceous glands: These glands produce sebum (oil) and give your face its oil.
Ceruminous glands: These are the glands in your ear that secrete ear wax.
Mammary glands: These are the glands on a person’s chest. In people assigned female at birth (AFAB), mammary glands produce milk after giving birth.
What is the purpose of the integumentary system?
Your integumentary system protects your body from infection and injuries you could get from your external environment
It’s your body’s coat of armor and the defense against viruses, bacteria and other microbes.
It shields your body from harmful light and helps regulate your body temperature
HOW A SKIN INJURY GETS REPAIRED BY THE BODY
the wound breaks open cells and release their contents
injury
blood seeps from the vessels and forms a cloth
clotting
fibroblast produce a plug of fibrous tissue within the clot, which contracts and shrink
plugging
the plug hardens and dries into scab which eventually detaches
scabbing
the suns rays include a spectrum of color wavelengths including infrared or IR rays
Ultraviolet defenses
melanocytes are melanin-producing cells in the base of the epidermis
melanin production
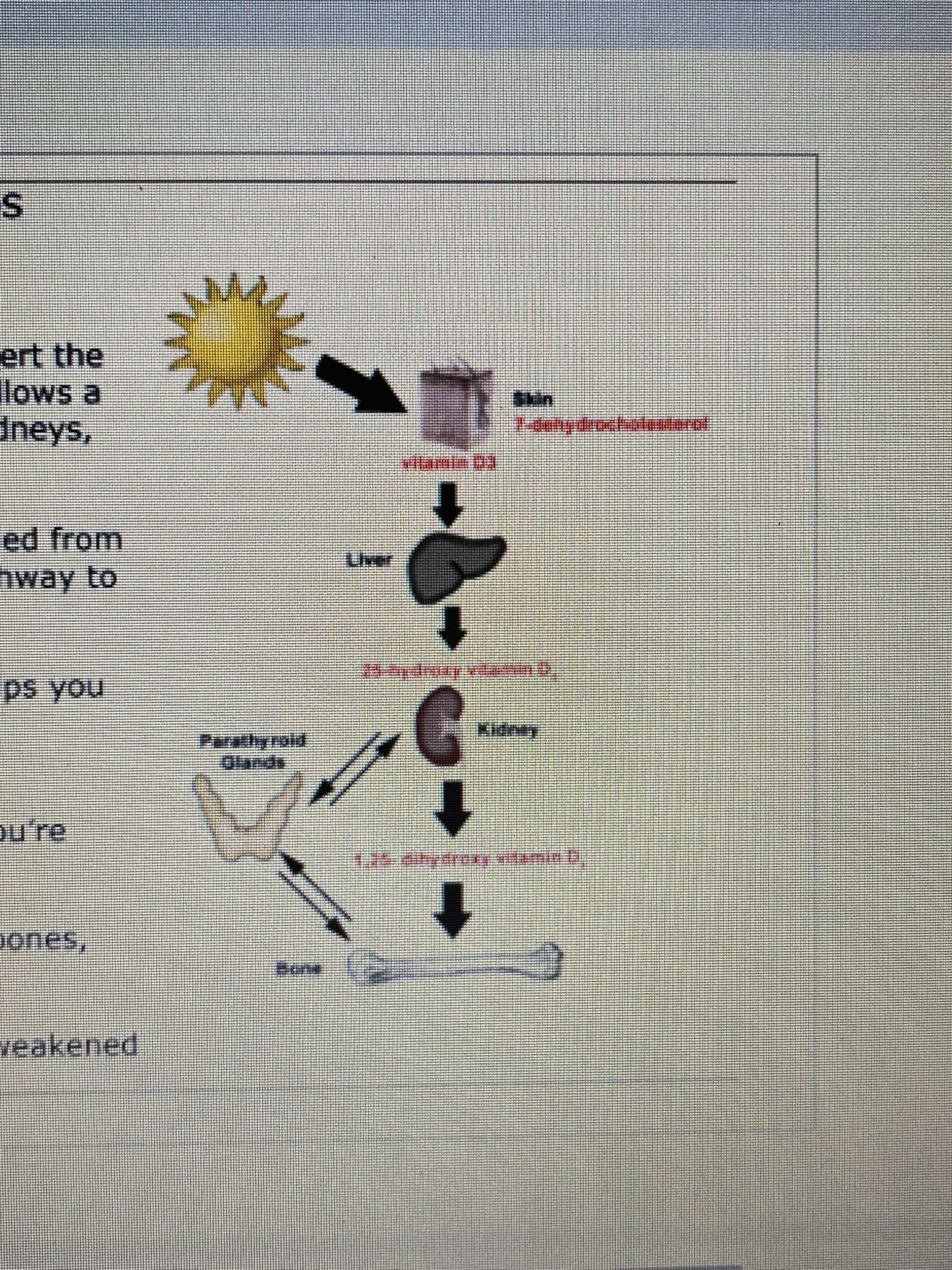
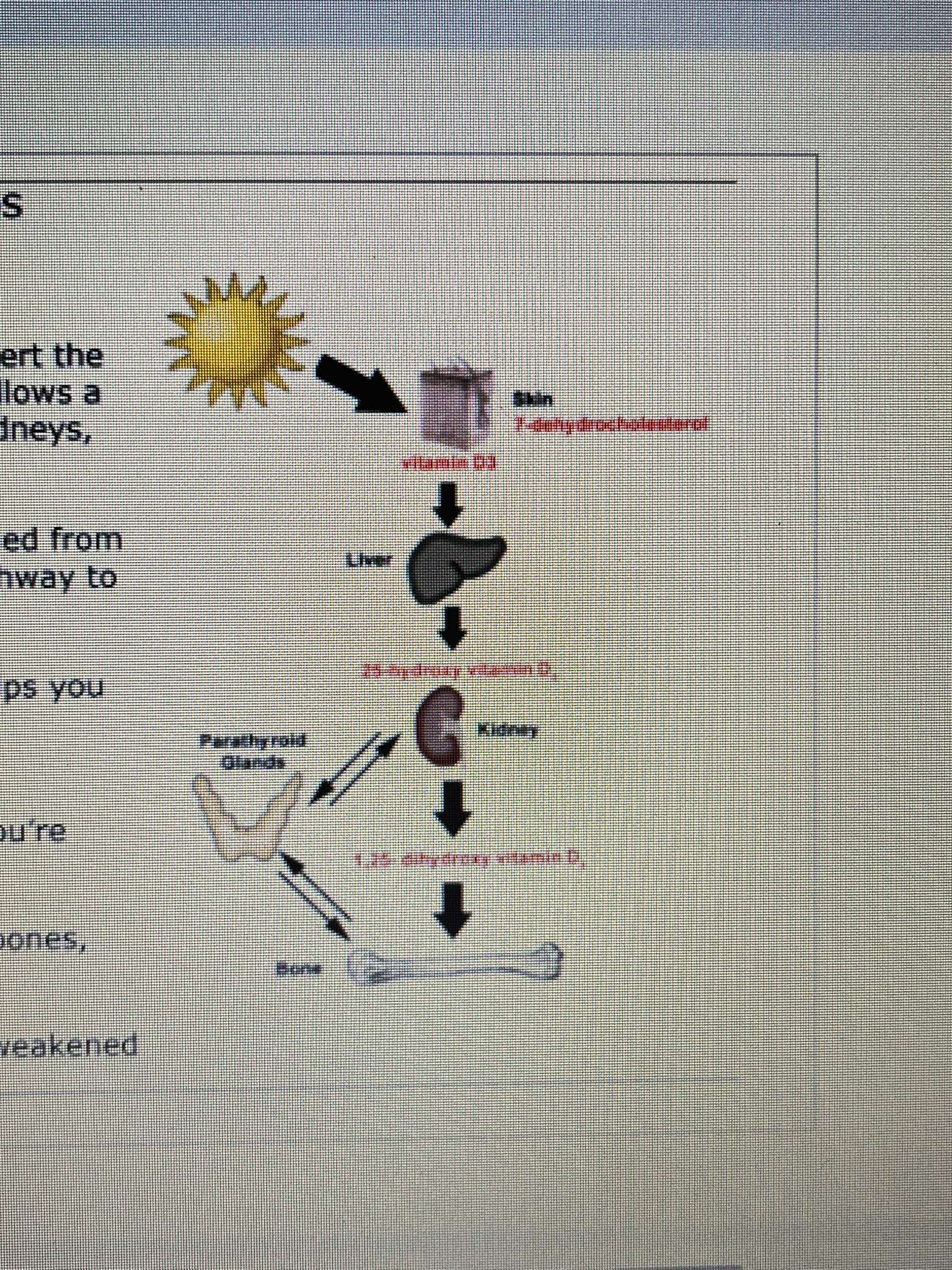
GETTING VITAMIN D FROM SUNLIGHT AND FOODS
our skin is naturally contains precusor to vitamin D, when the suns ultraviolet touch the skin they convert the precursor to a molecule called vitamin D3, which the follows a metabolic pathway through the liver and finally to the kidneys, where its converted into a molecule called calcitrol.
HAIR GROWTH
different kinds of hair grow at varying rates with scalp hairs lengthen about 1/100 inch each day. However hair does not grow continuously after 3 to 4 years the follicle goes to resting phase- activity in the hair follicle stops and the hair dies. Growthphase - a new hair spouts at the base of the follicle as it grows the dead hair is shed
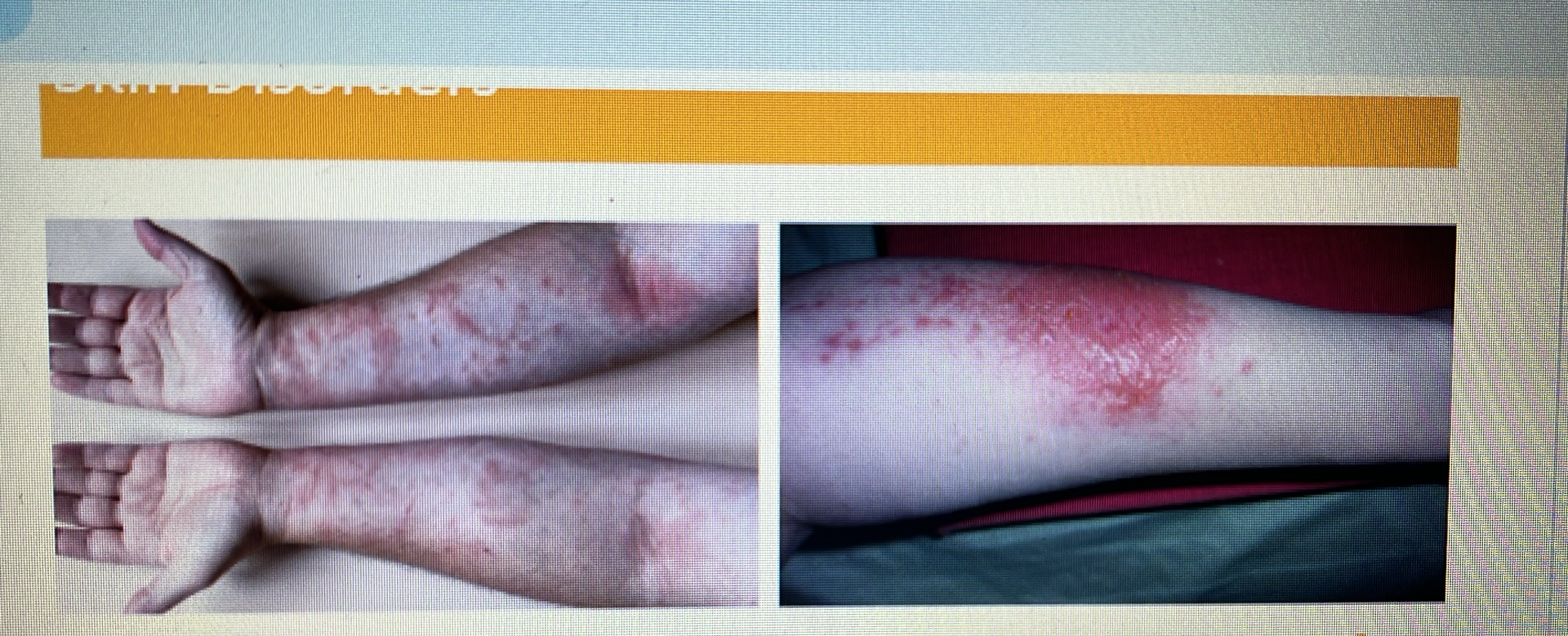
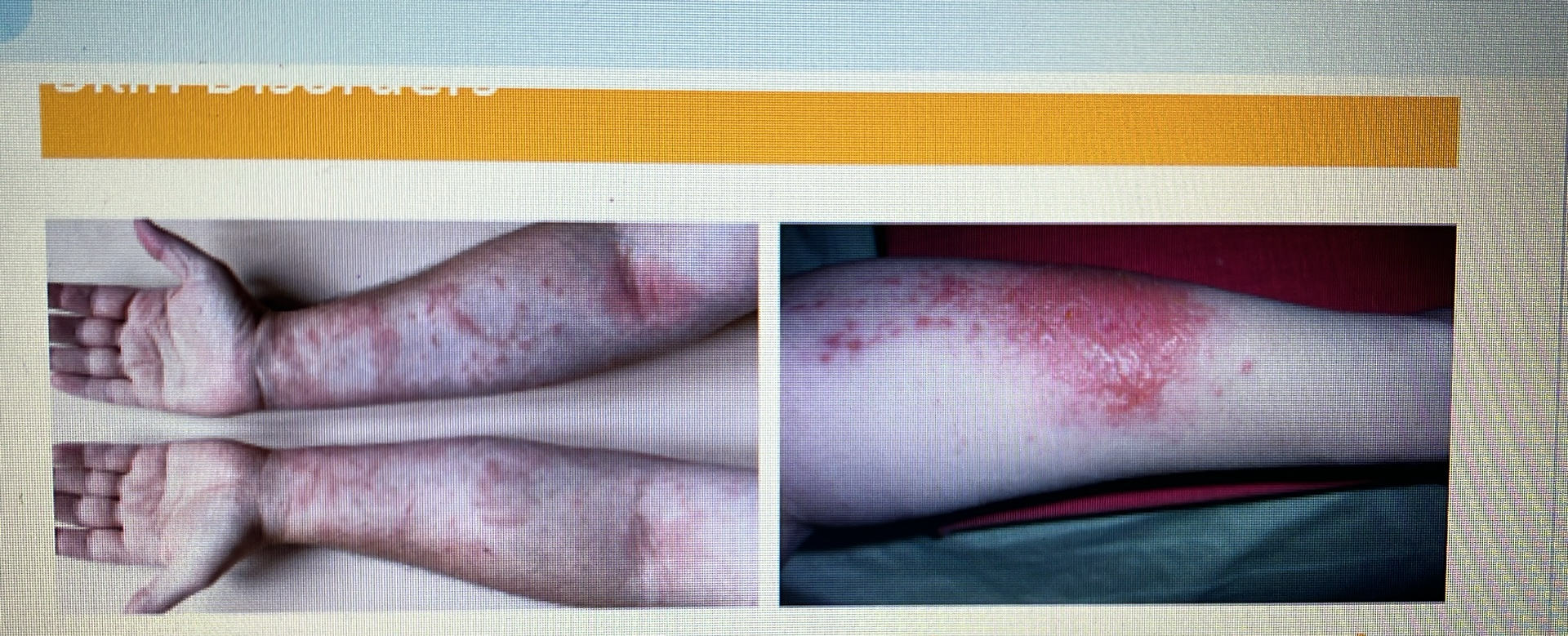
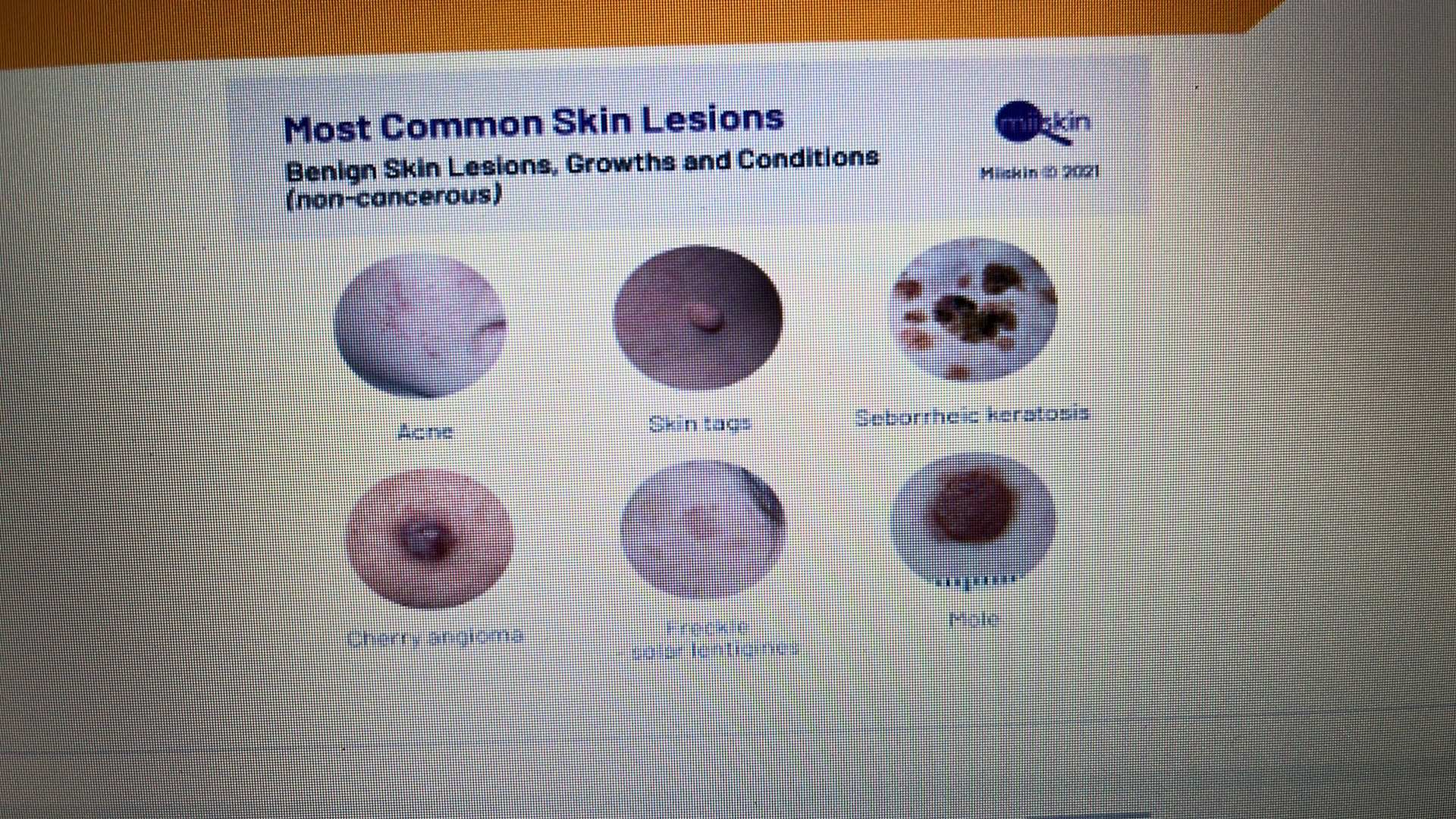
SKIN DISORDERS
Contact dermatitis and Poison Ivy Rash
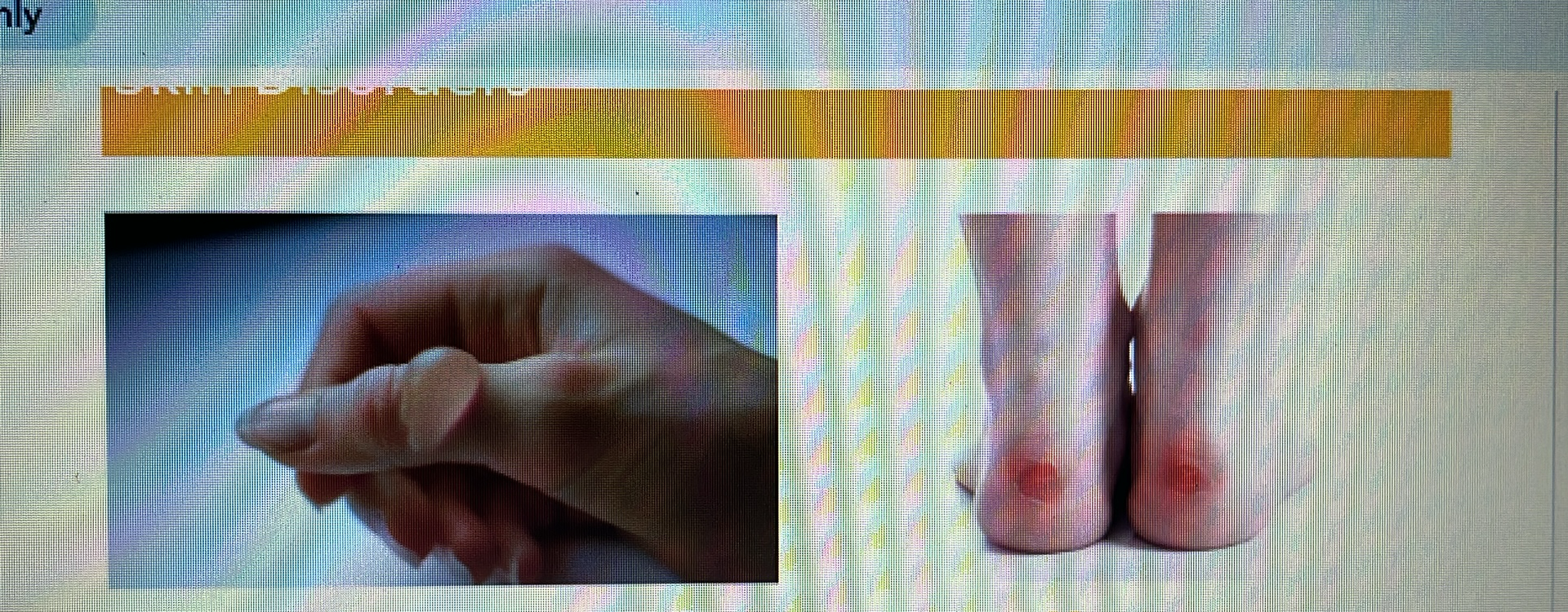
SKIN DISORDER
blister
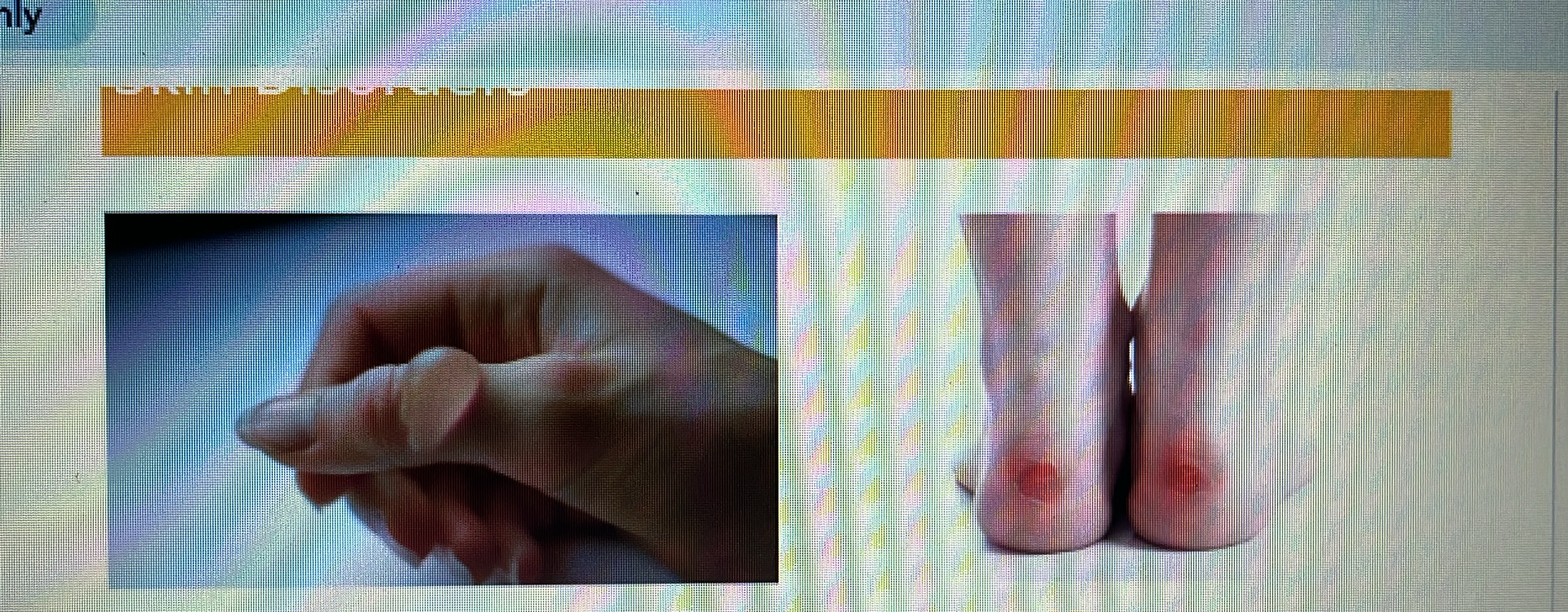
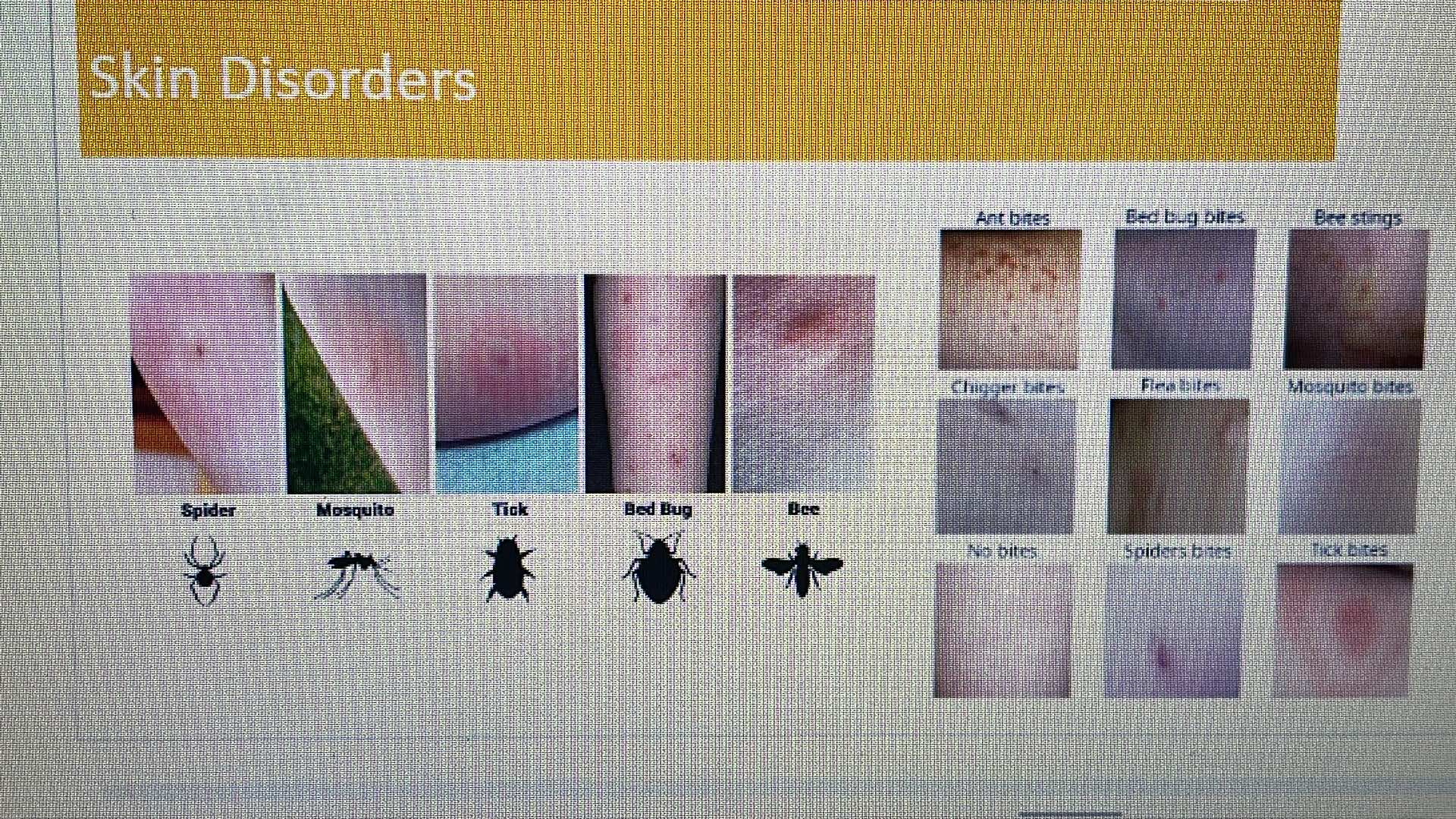
SKIN DISORDER
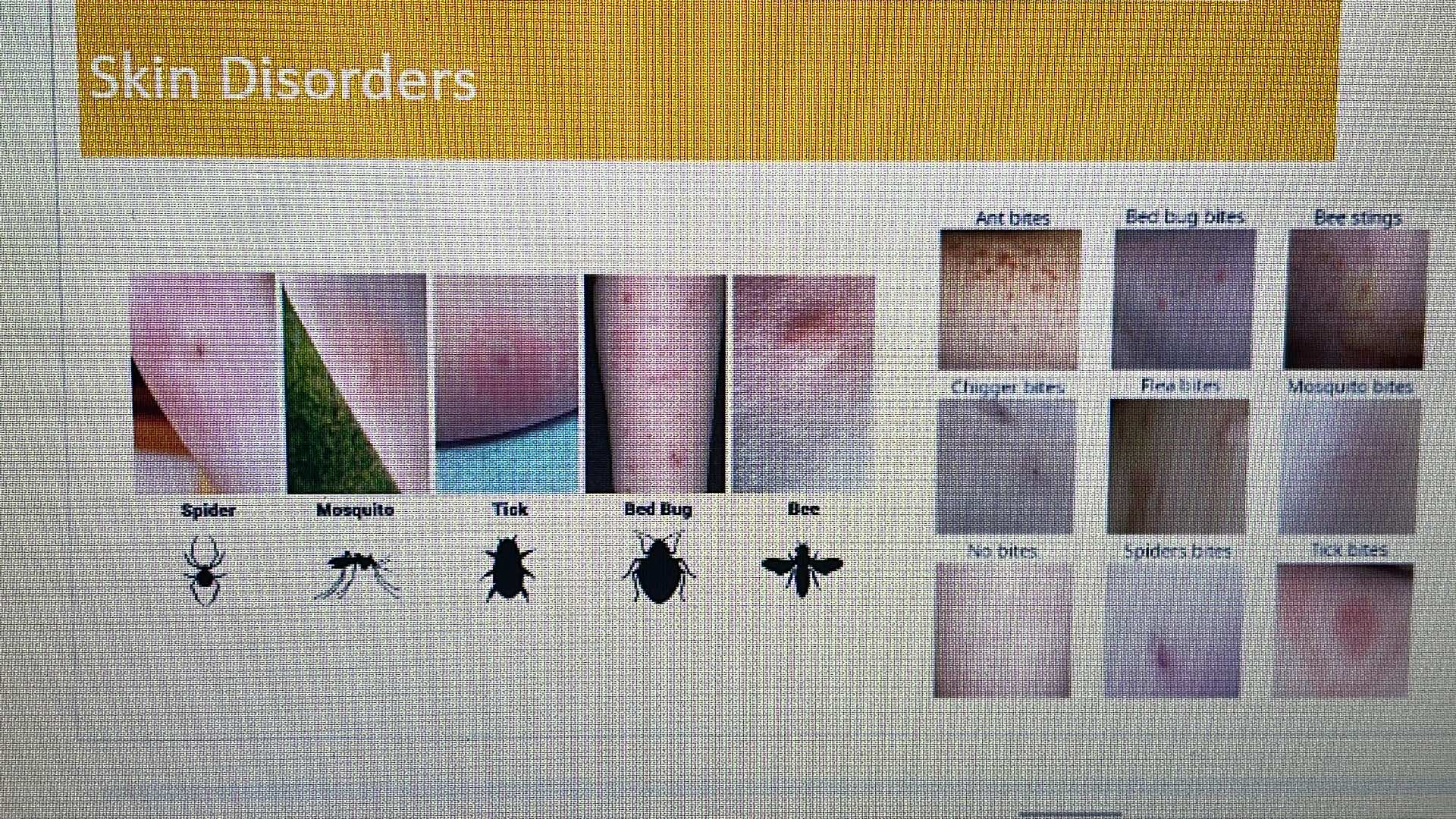
SKIN DISORDER
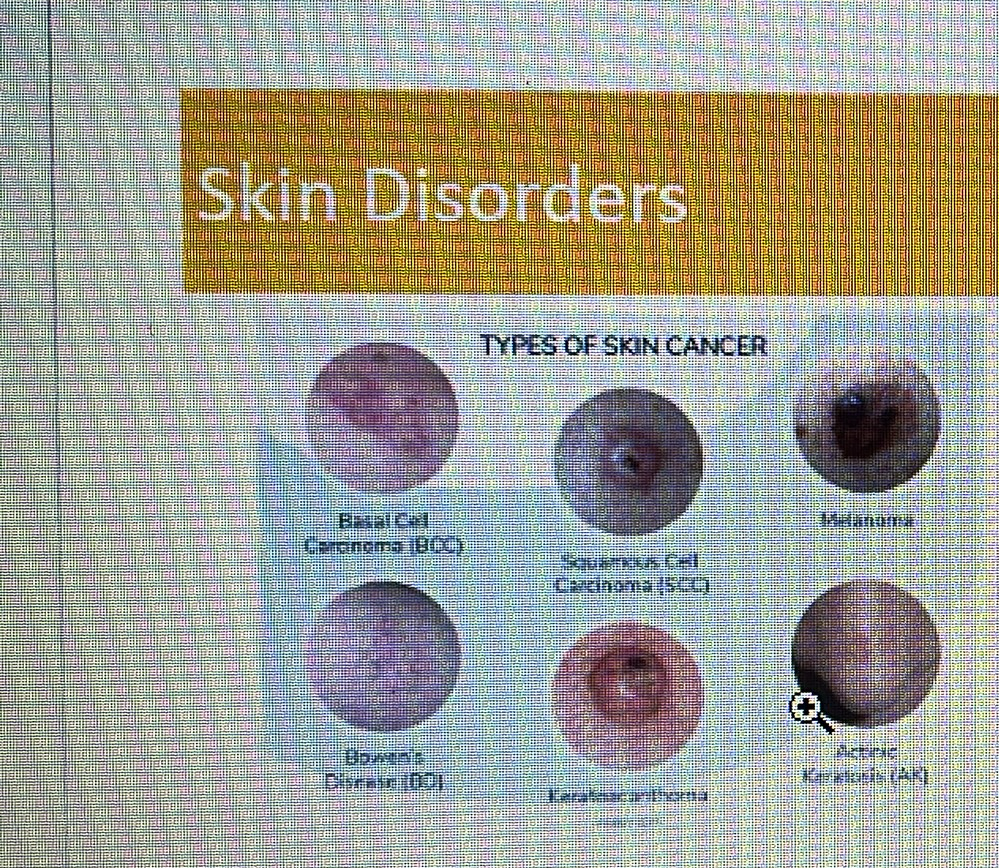
Skin cancer
melanoma
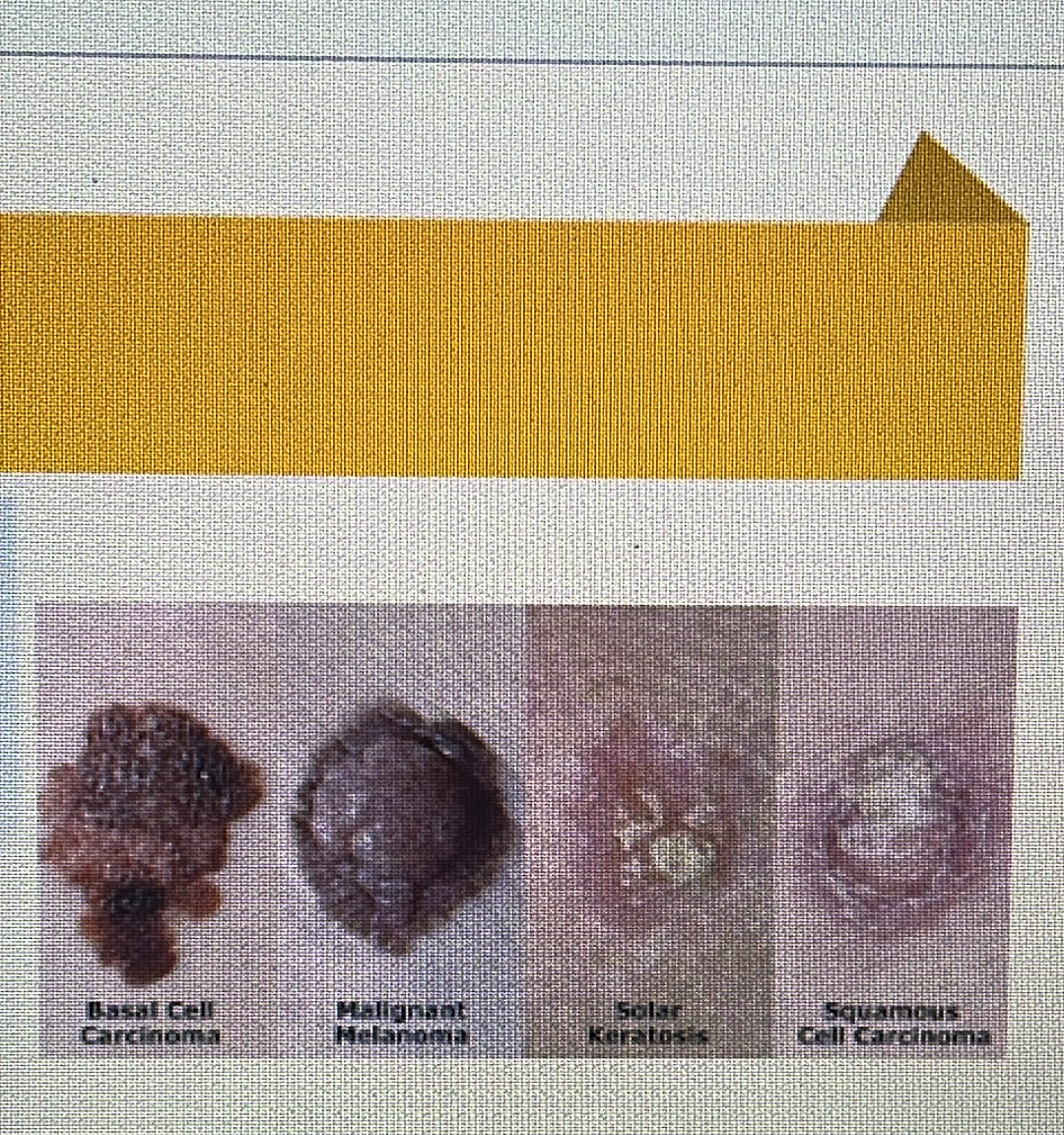
SKIN DISORDER
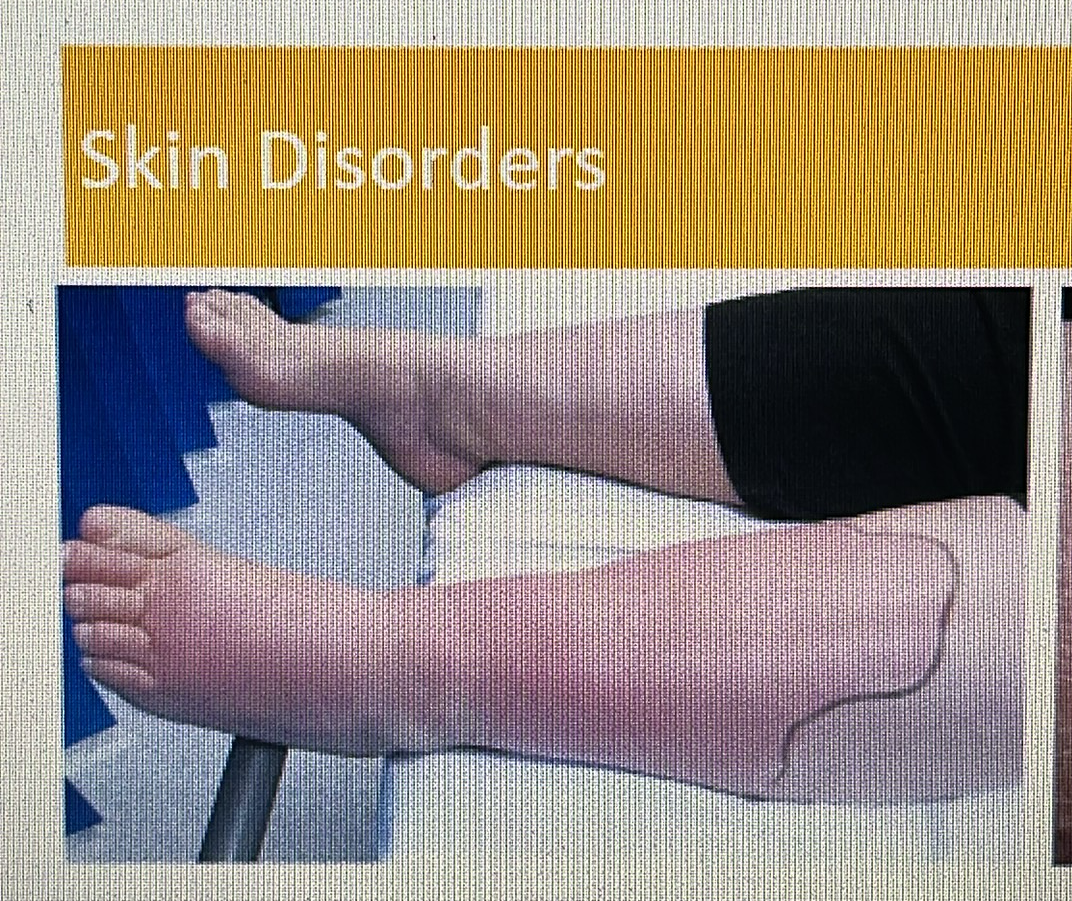
Cellulitis
dry skin rash
SKIN DISORDER
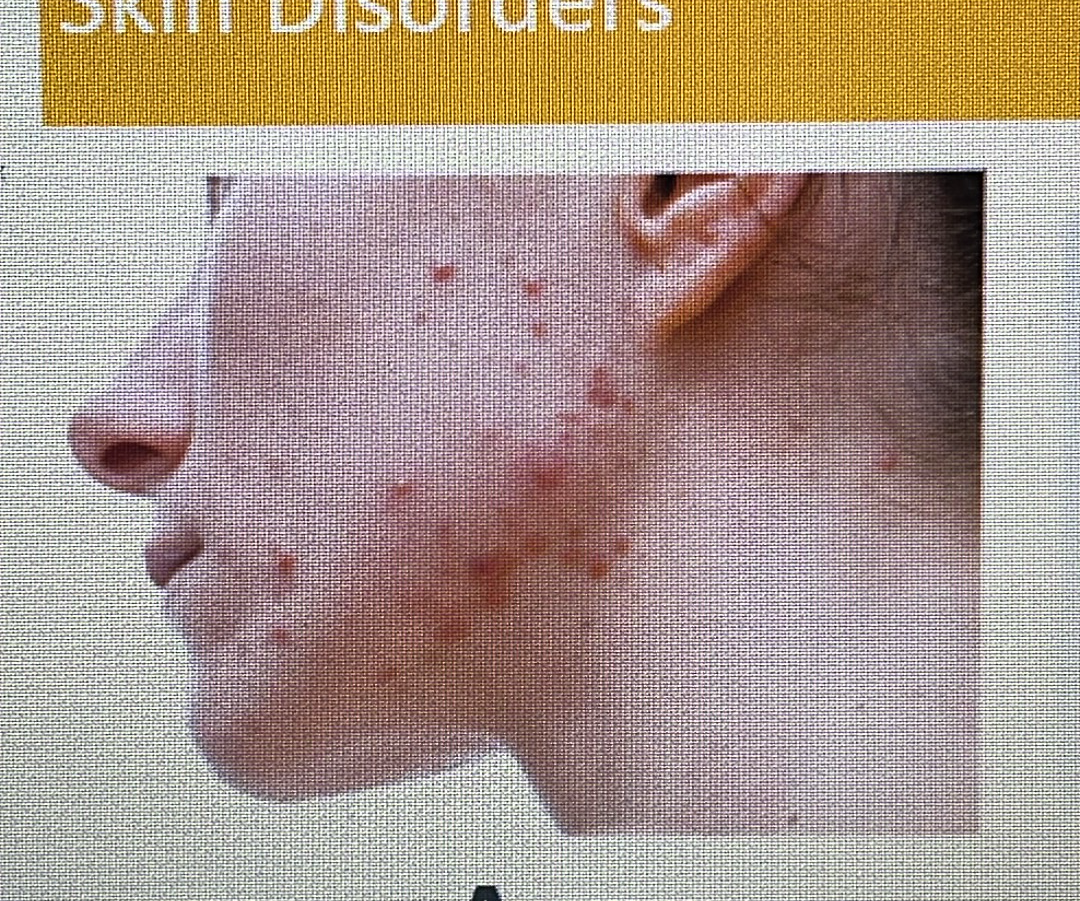
acne
eczema
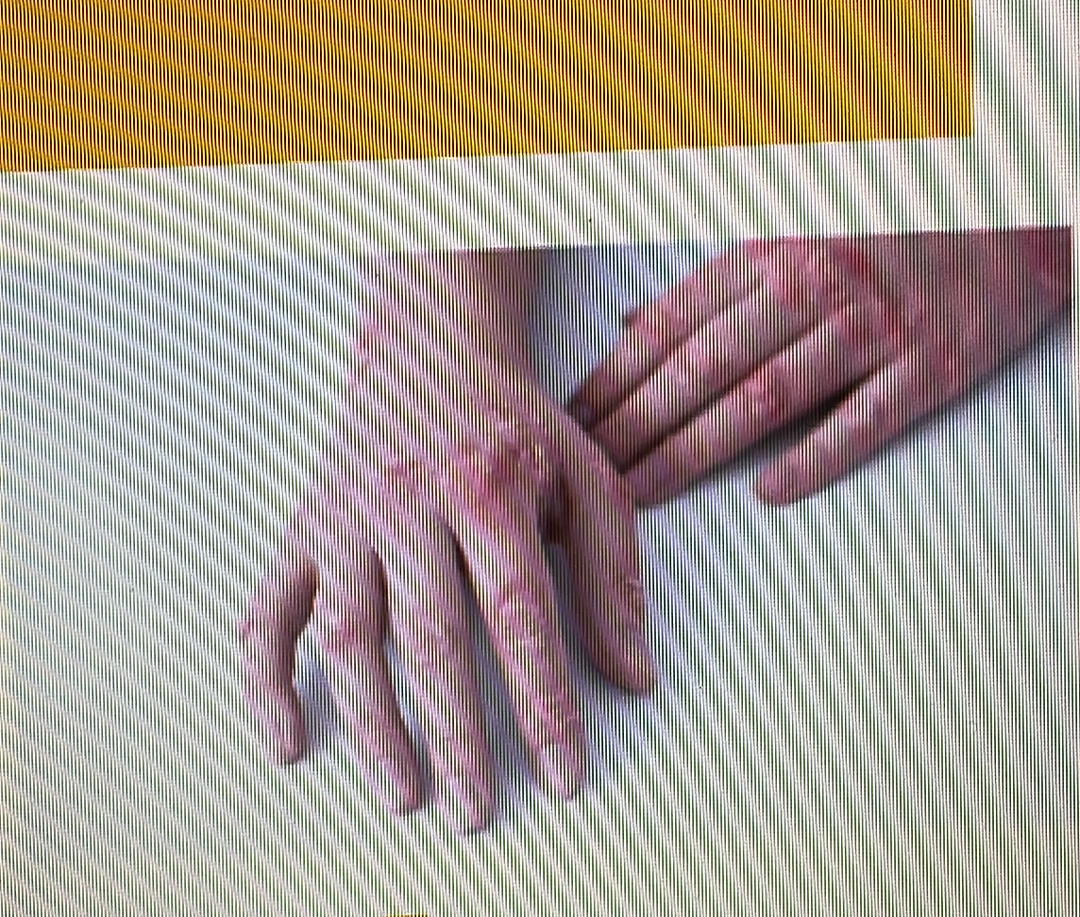
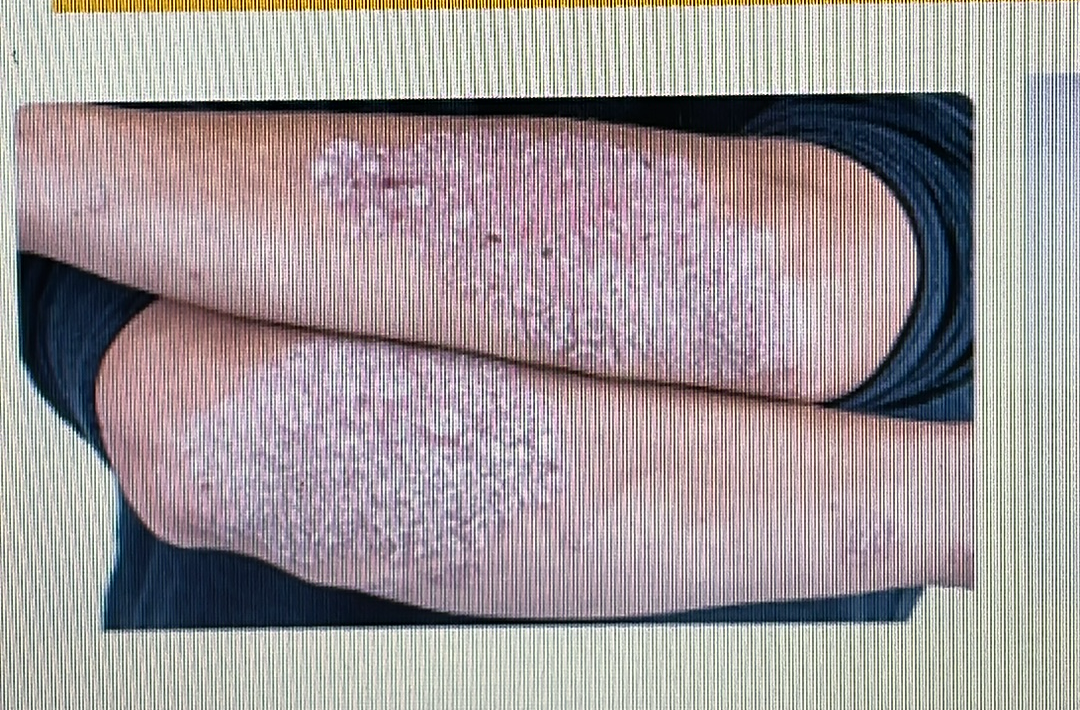
SKIN DISORDER
psoriasis
vitiligo
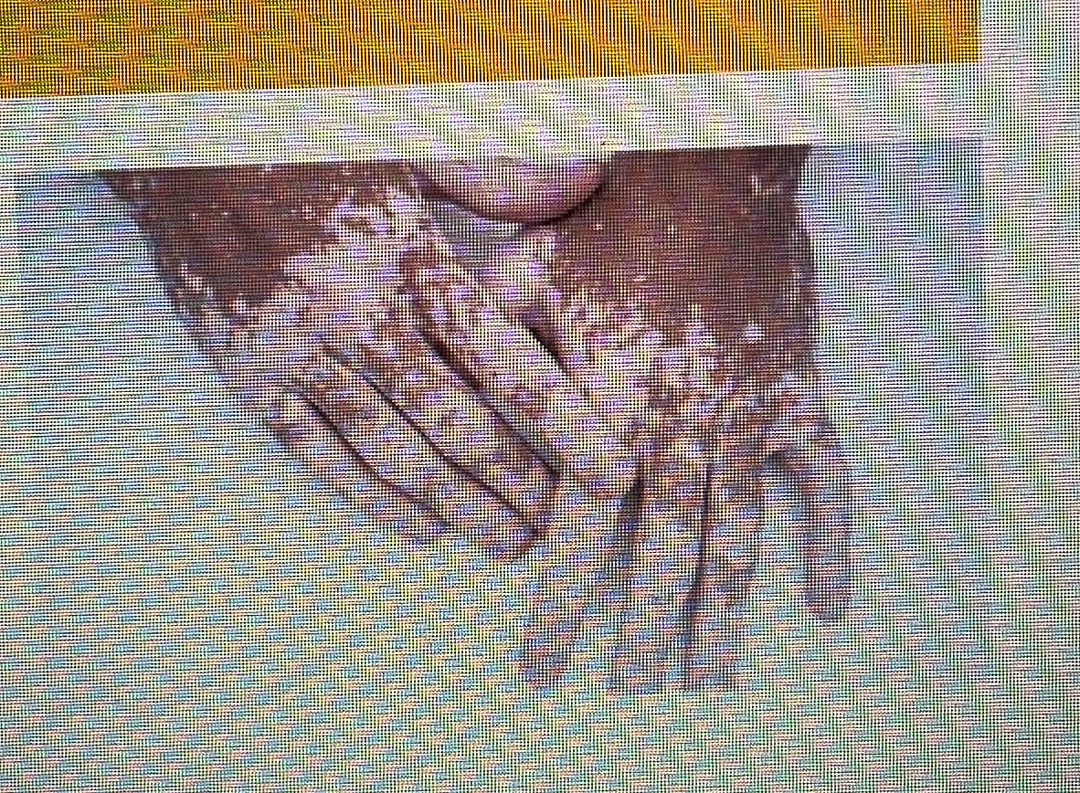
SKIN DISORDER
WOUNDS
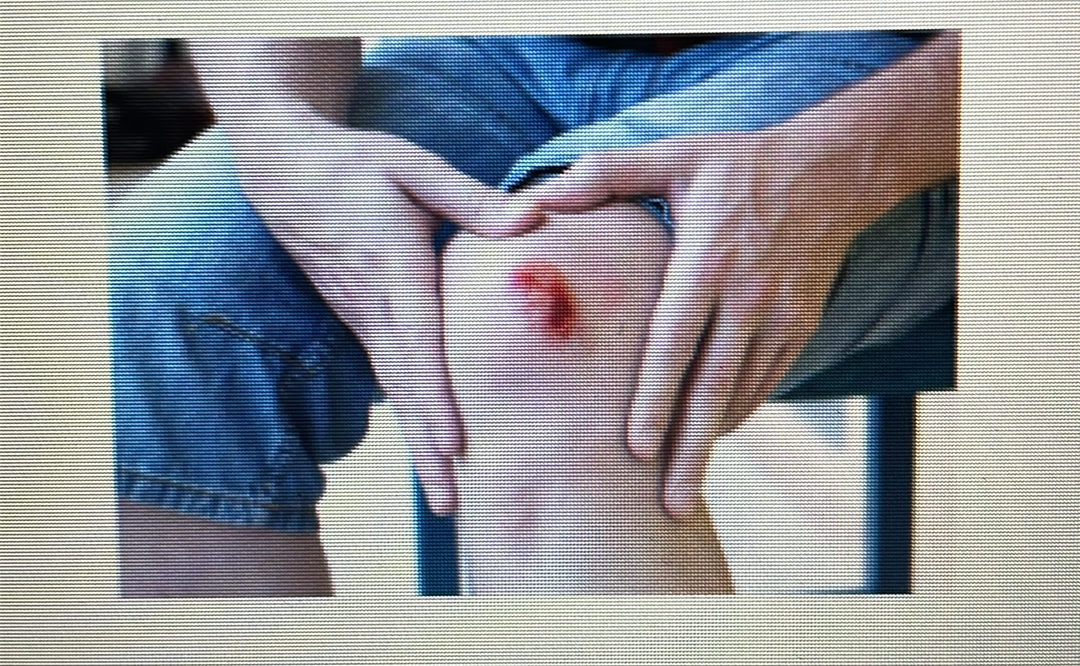
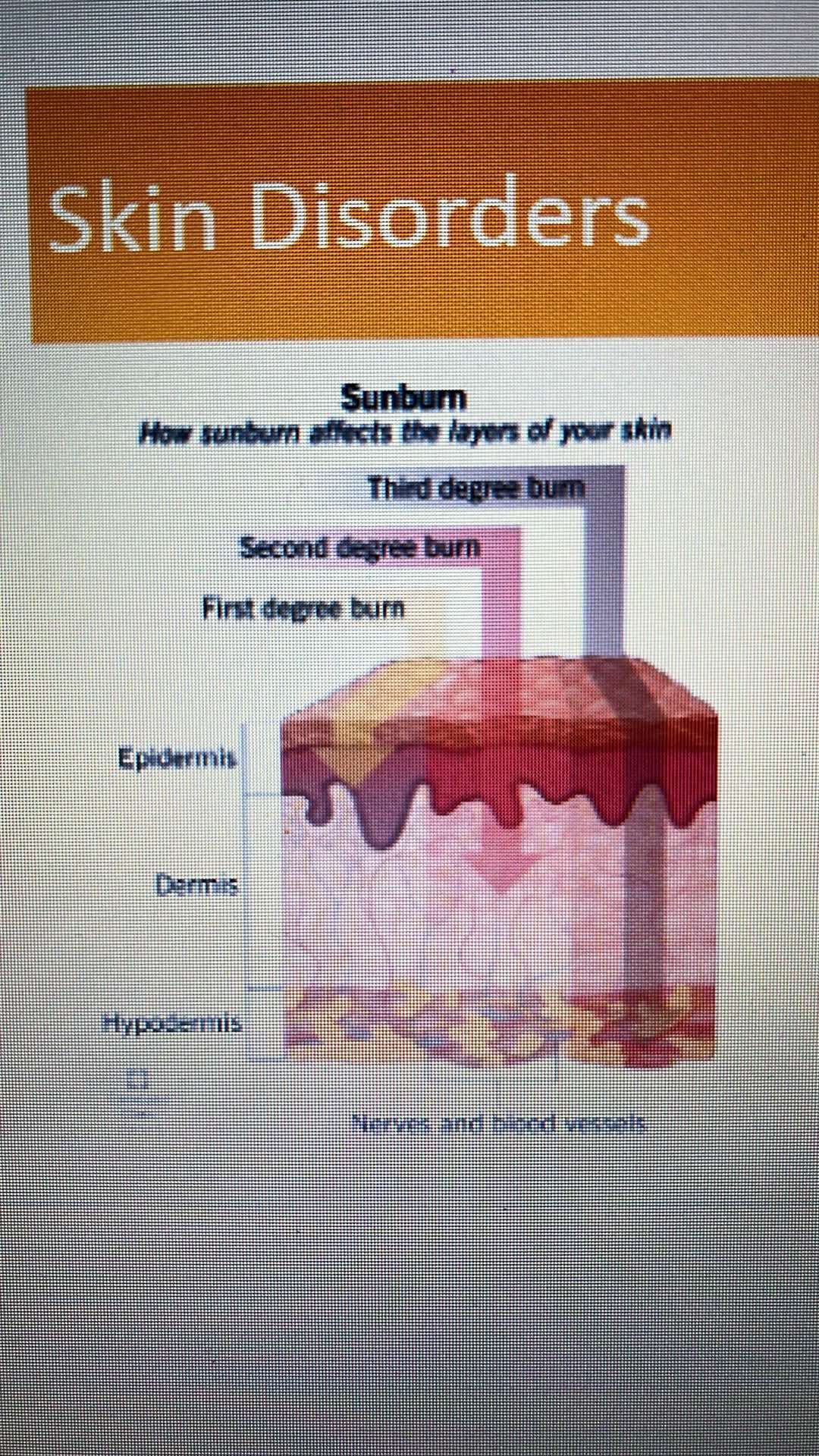
1st degree burn - epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
2nd degree burn - nerves and blood vessels
3rd degree burn - including fats
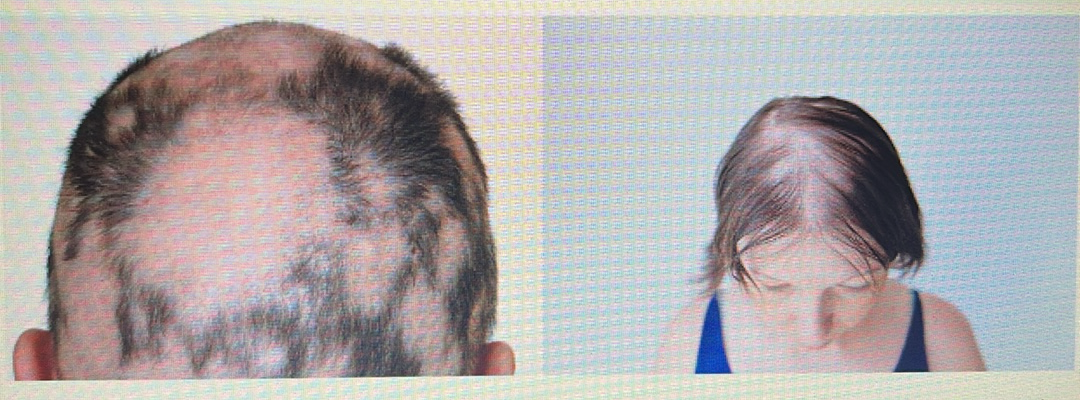
HAIR DISORDER
Alopecia areata: Patches of hair loss caused by an autoimmune disease
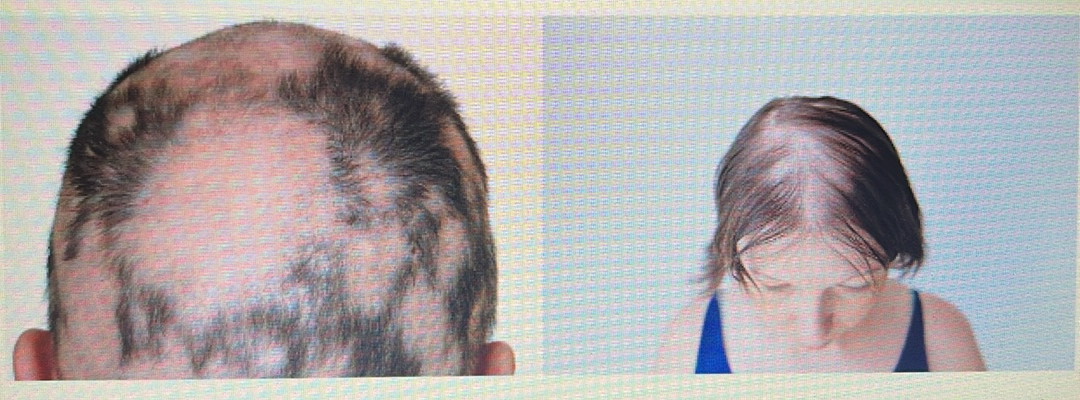
HAIR DISORDER
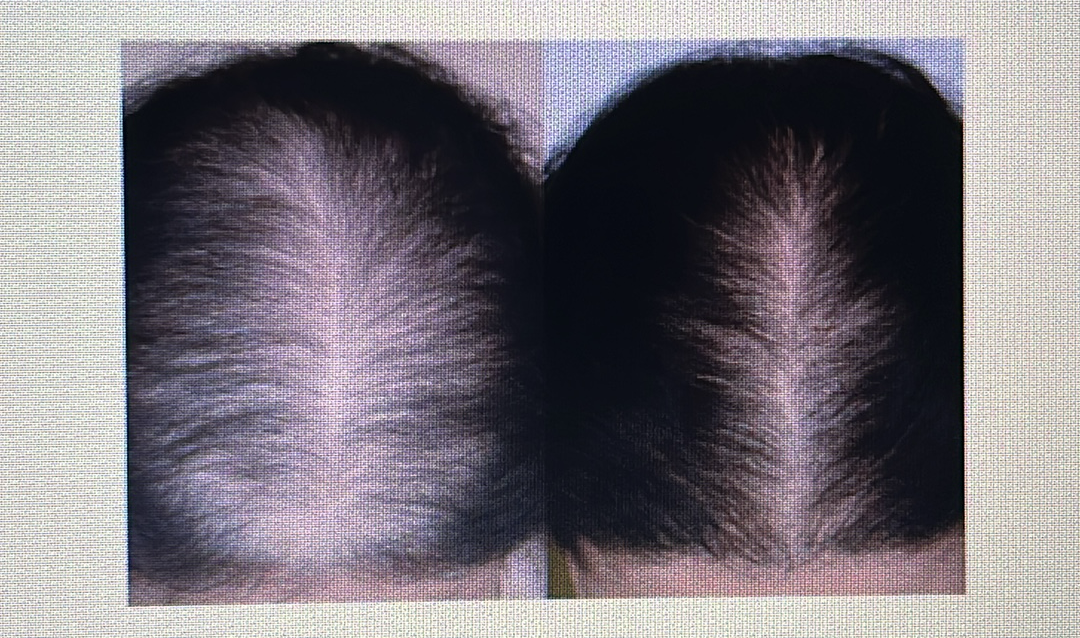
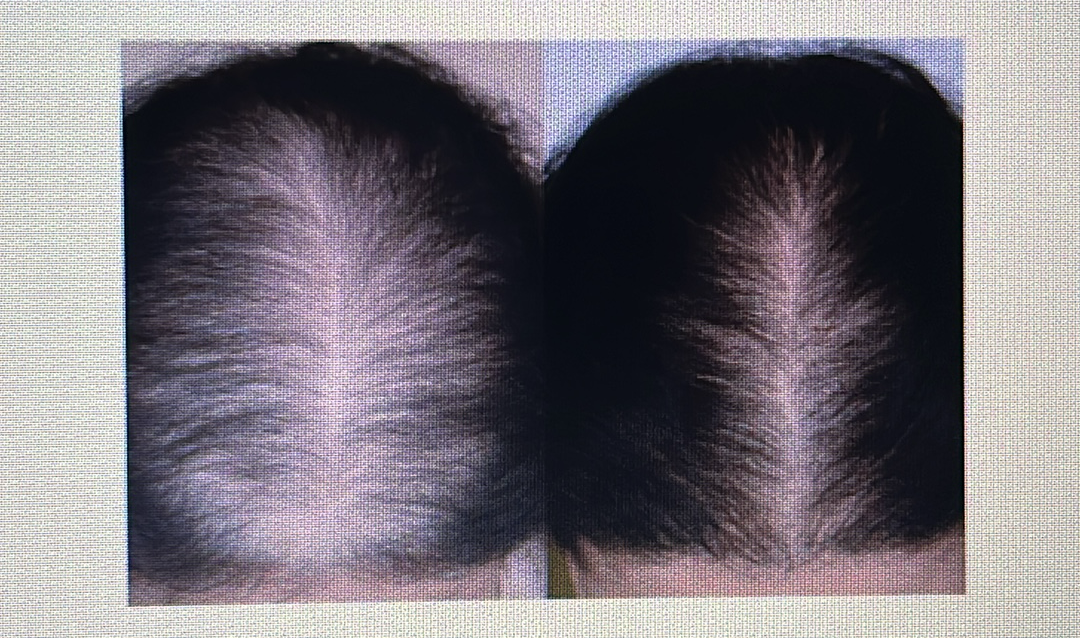
Androgenic alopecia: Baldness in both genders/sexes that’s based on genetics.
HAIR DISORDER
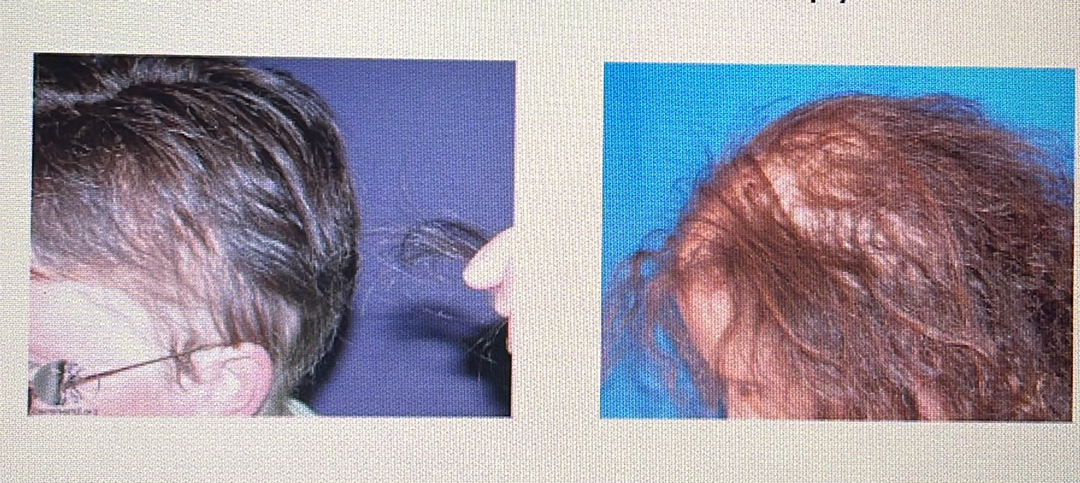
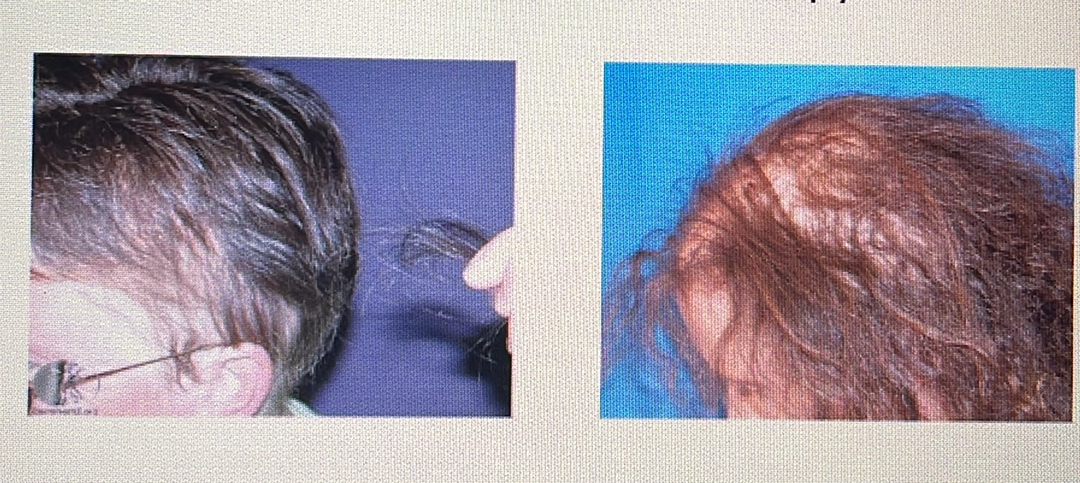
Anagen effluvium: Loss of hair during its growth phase; this often occurs during medical treatments like chemotherapy

HAIR DISORDER
Telogen effluvium: Loss of hair during its rest phase. It typically shows up a few months after your body goes through something stressful or from hormonal changes.


HAIR DISORDER
Traumatic alopecia: Hair loss due to damage to your scalp from hair styling, through rubbing your scalp repeatedly against a surface or hat or by playing with and breaking your hair.

HAIR DISORDER
Dandruff: It causes white or yellow flakes on your scalp and hair shaft. It’s also known as seborrheic dermatitis.
HAIR DISORDER
Head lice: Tiny, crawling insects that live in a person’s head hair.

HAIR DISORDER
Hirsutism: Excessive hair growth in people assigned female at birth.

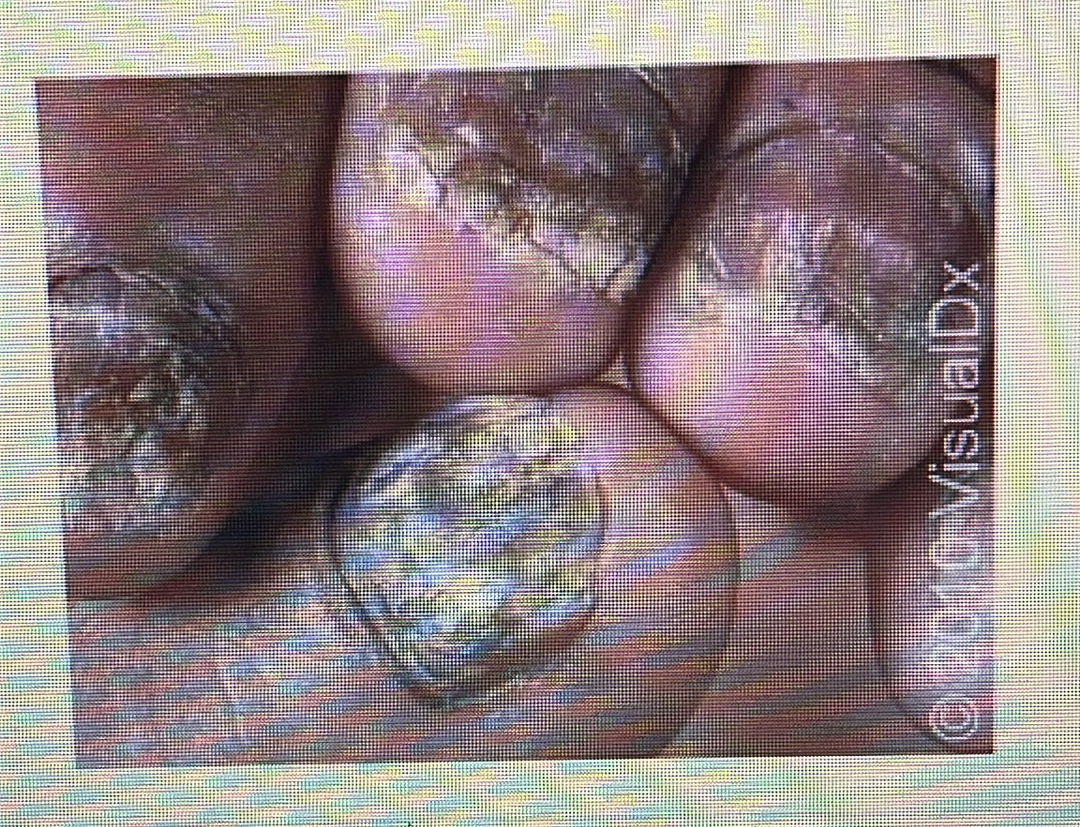
NAIL DISORDER
Onychomycosis: Nail fungus in your fingernails or toenails.
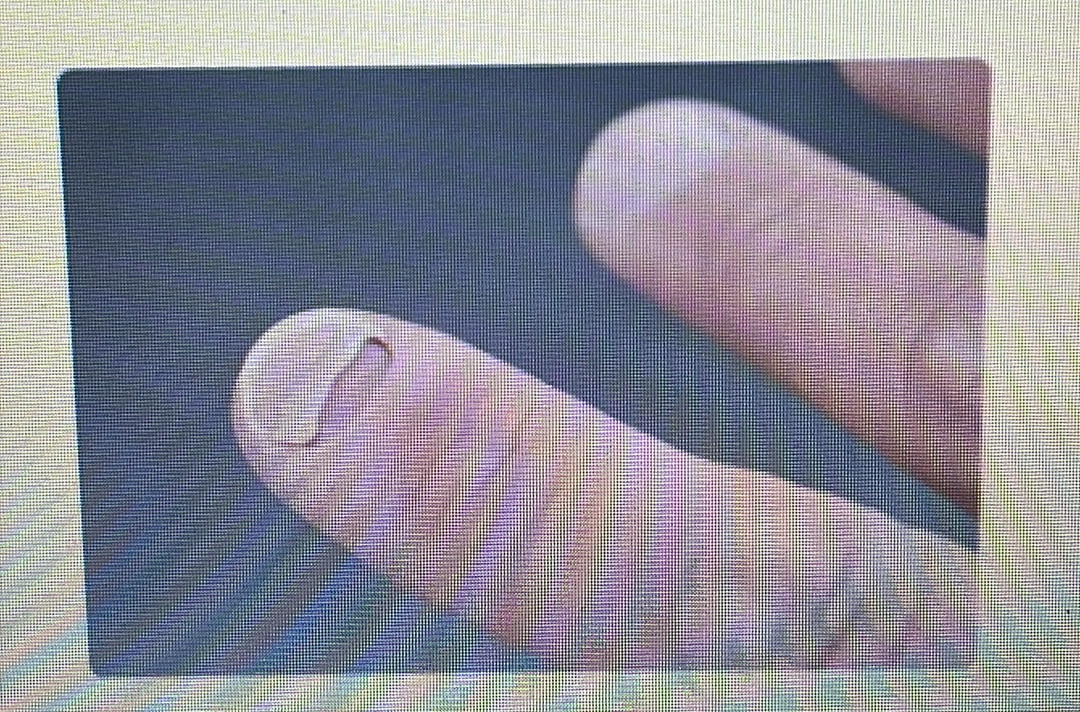
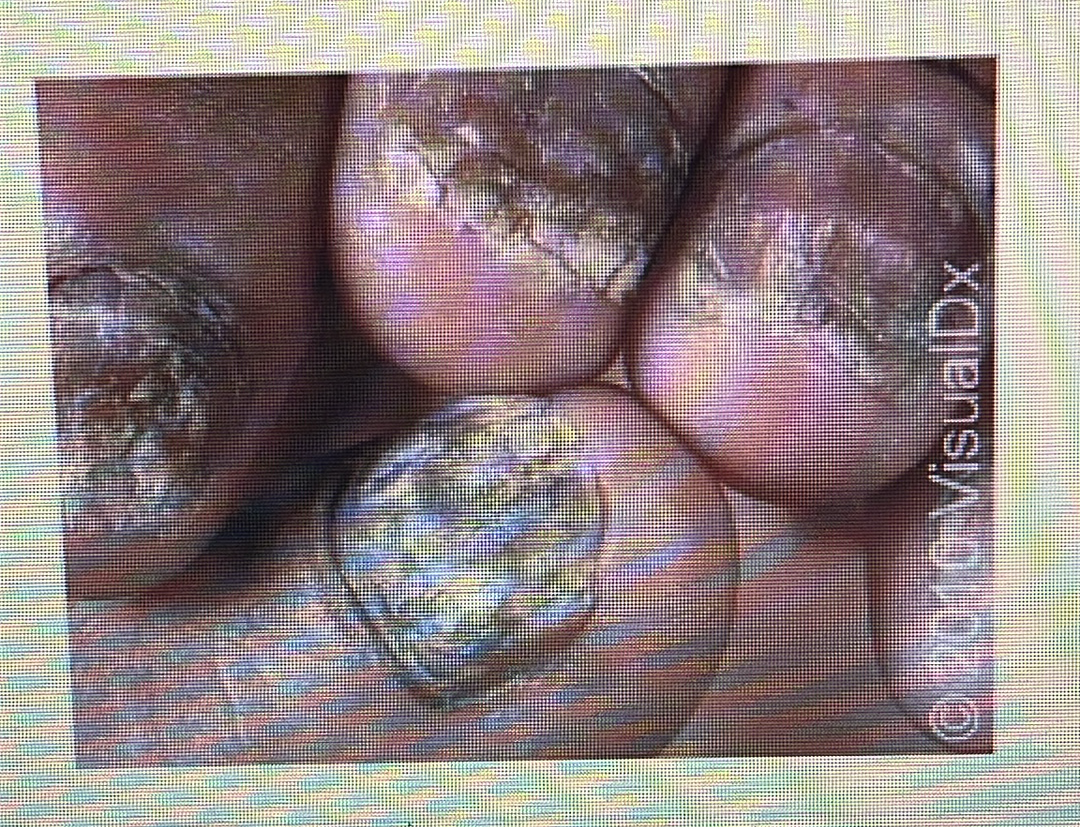

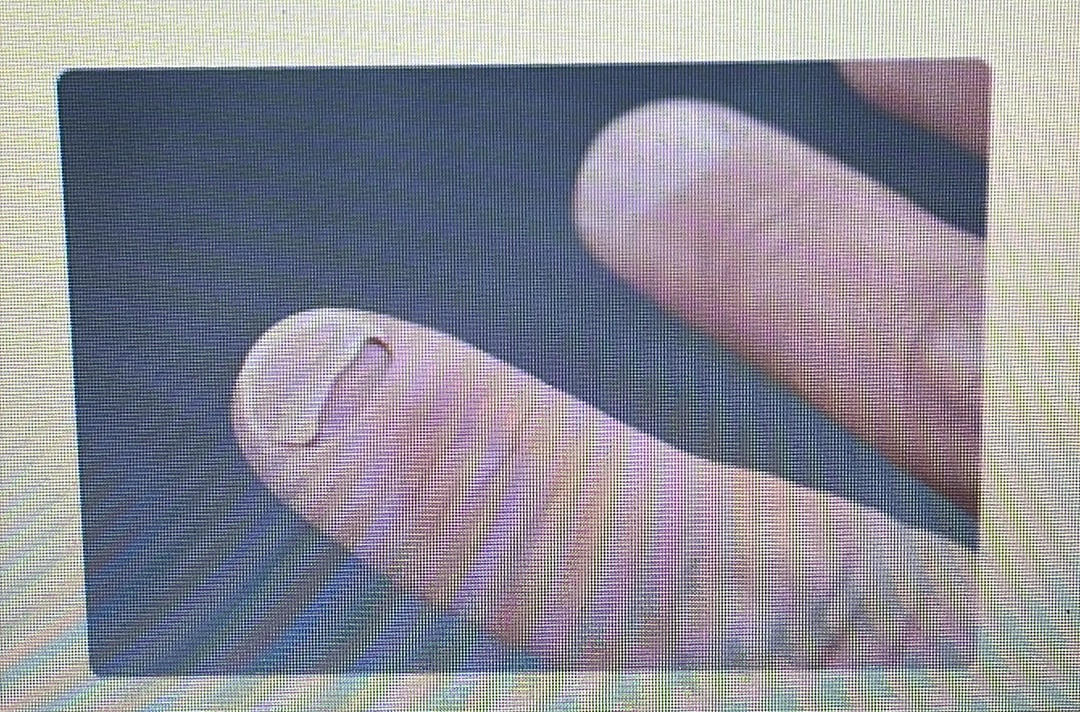
NAIL DISORDER
Onycholysis: When your nail separates from your nail bed.

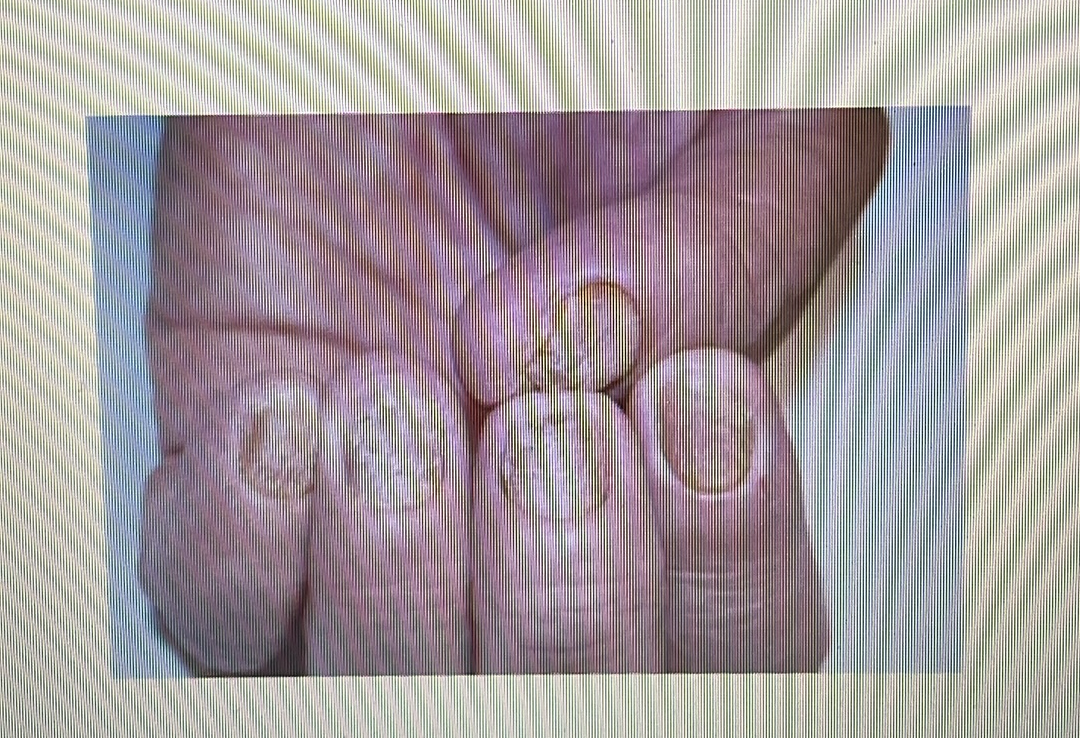
NAIL DISORDER
Psoriasis of the nails: A skin condition that causes pitting, nail discoloration and other symptoms.
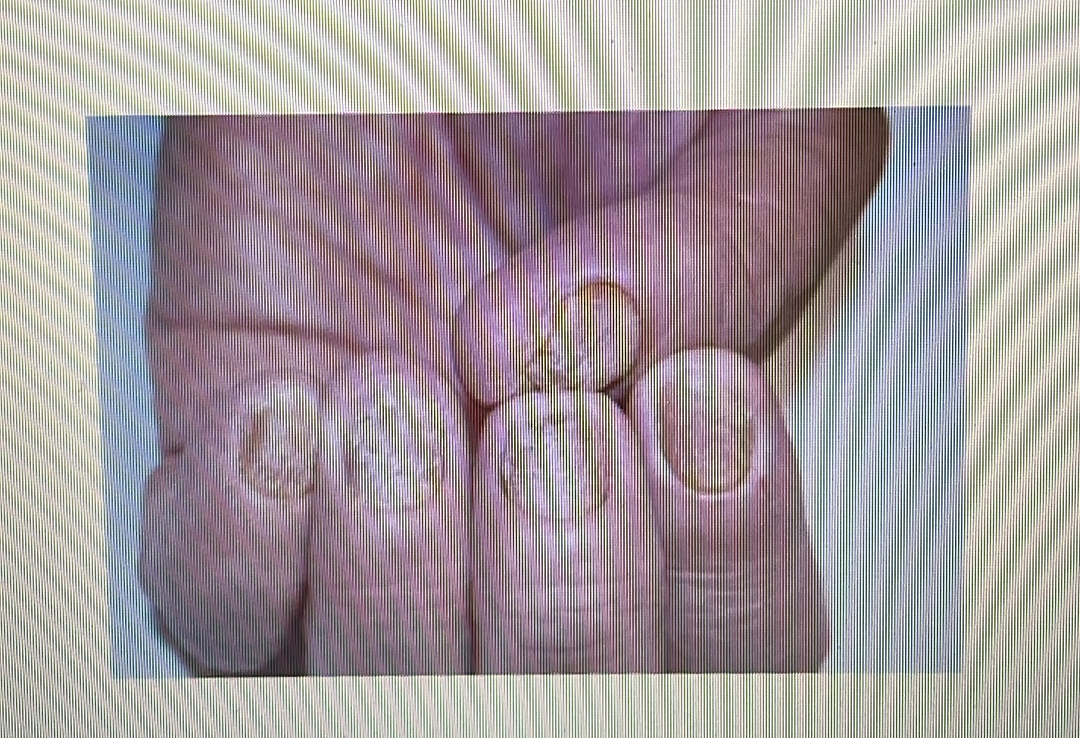
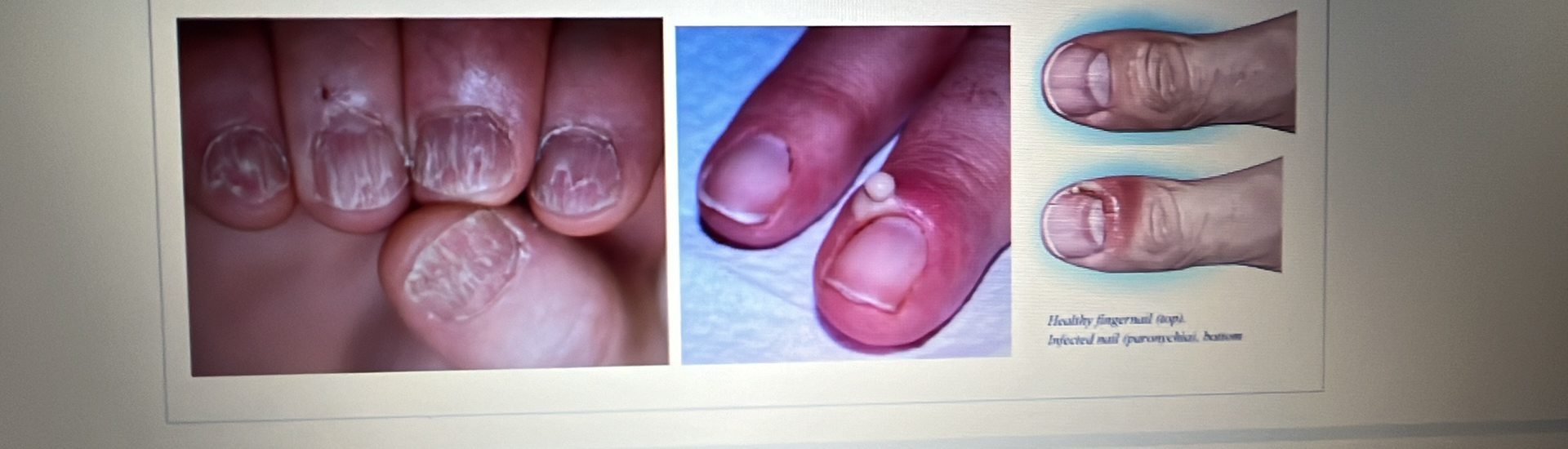
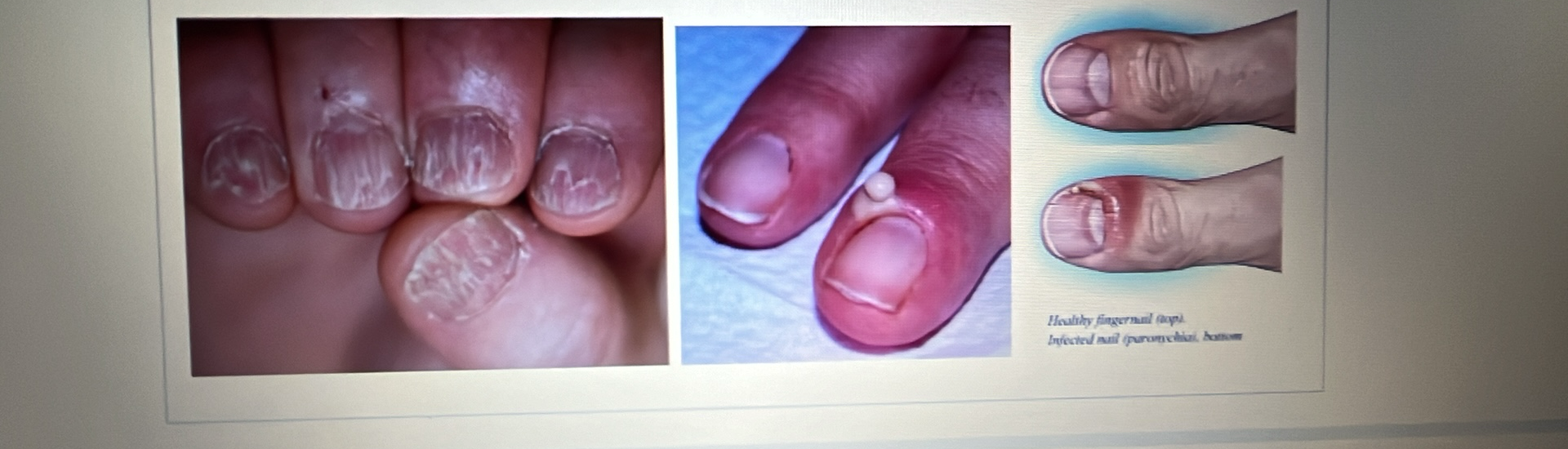
NAIL DISORDER
Lichen planus: A rash that appears as ridges or grooves on your nail.
Paronychia: An inflammation or infection of the tissue directly surrounding your nail
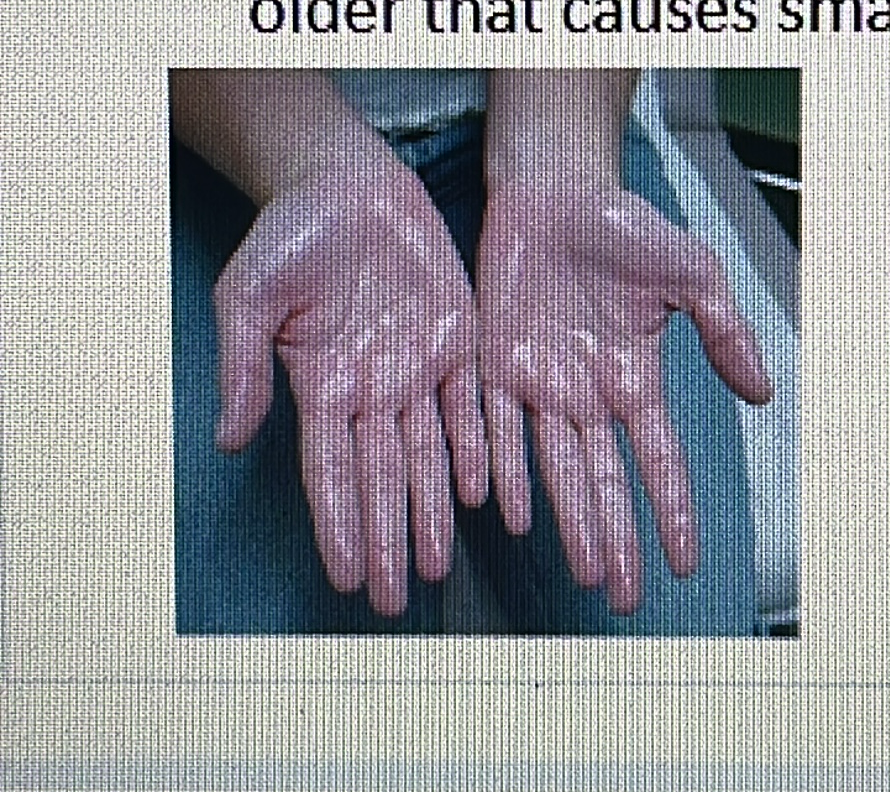
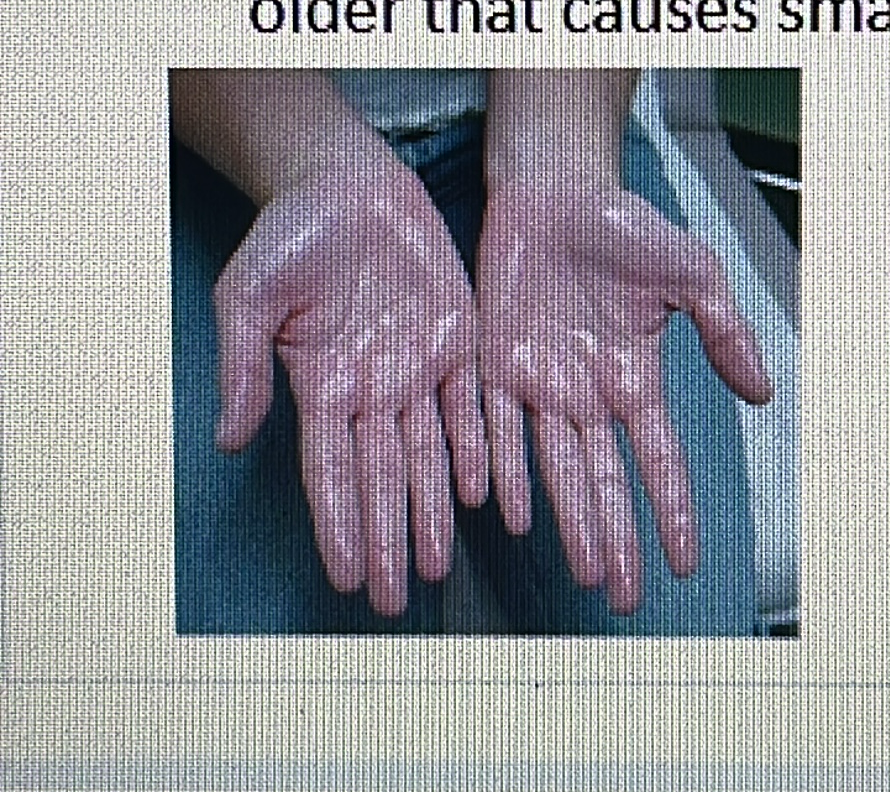
GLAND DISORDER
Hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating.
GLAND DISORDER
Seborrheic dermatitis: Scaly, red patches that affect your face, chest or back. When it’s on your head, it’s called dandruff.
GLAND DISORDER
Sebaceous hyperplasia: A skin condition common in people who are older that causes small, yellowish bumps on your skin.