Antibiotics, Resistance, and the Human Microbiome
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Toxicity
Direct damage of tissues and organs through the effect of the drugs
Common toxic effects
Digestive issues, Headache, Joint pain
Uncommon toxic effects
Tetracycline → yellow teeth and bones; Ciprofloxacin/Levofloxacin → Light sensitivity

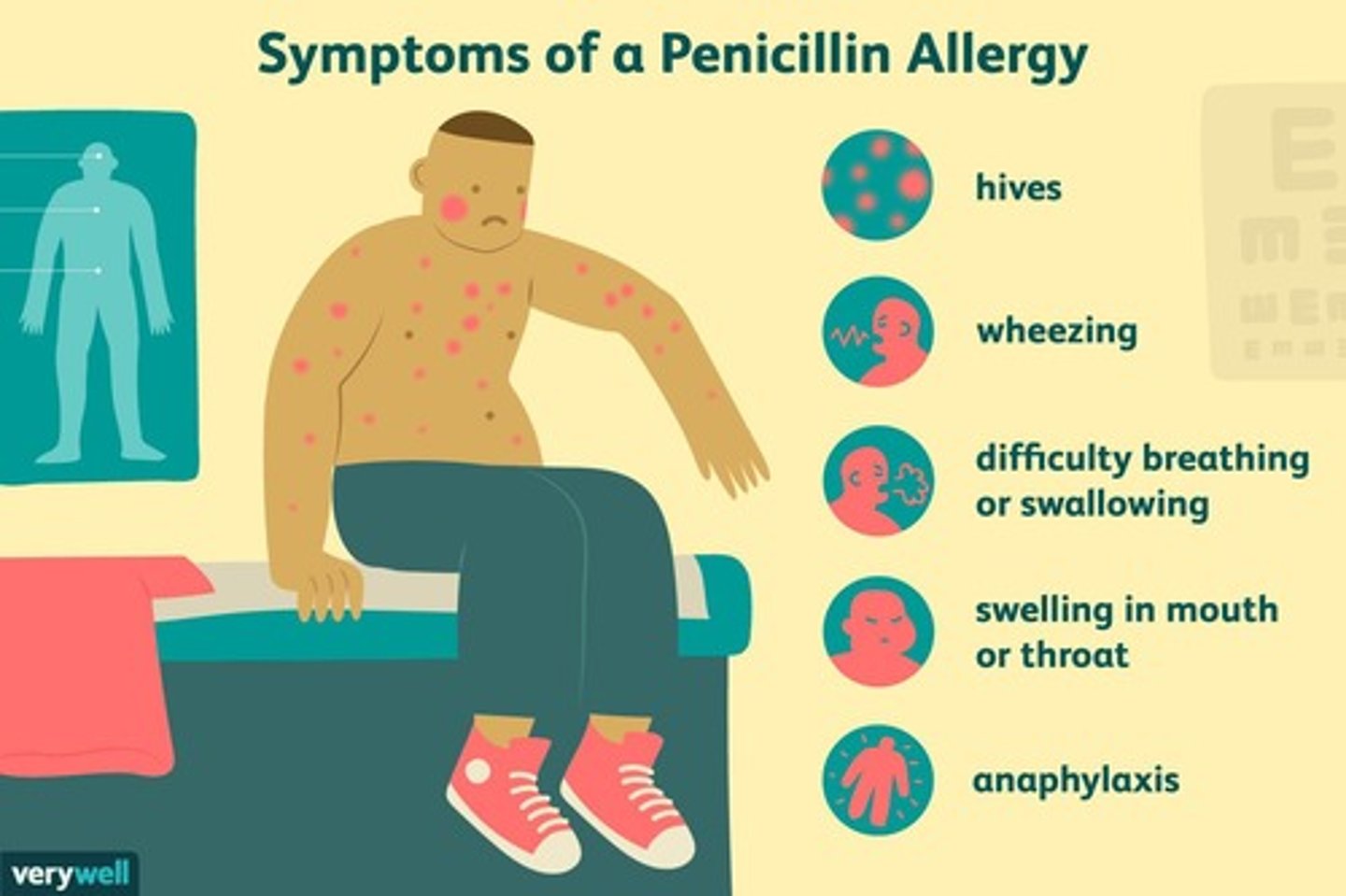
Allergy
Drug acts as an antigen, stimulating an immune response
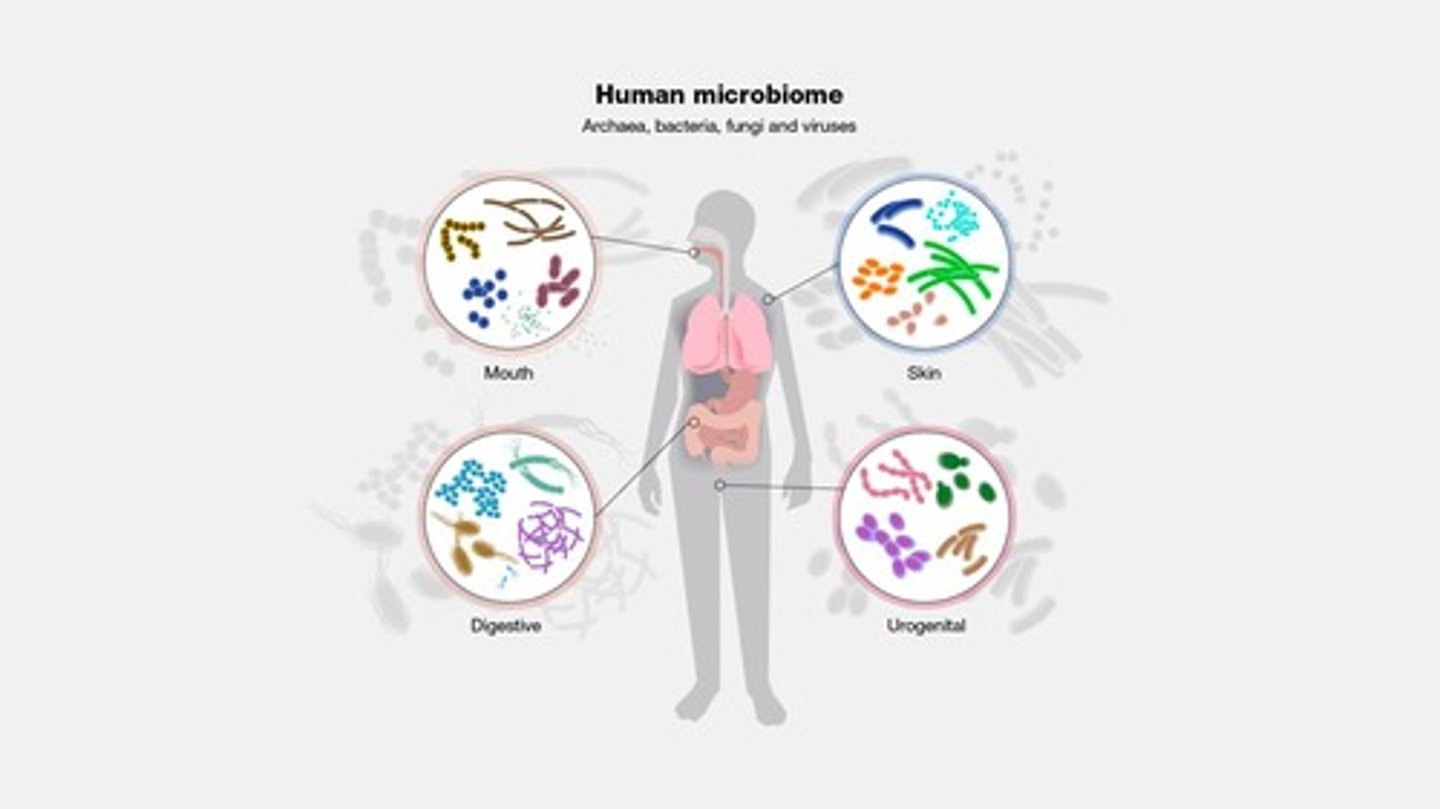
Microbiome/Biota
Normal microbes in/on healthy body, required for normal host function
Broad-spectrum antimicrobials
Can harm microbiome
Human Microbiome Project (HMP)
Federal funding ending in 2019

Enormous gene pool
Human genome, 21,000 genes → Thousands of proteins; Microbiome genome, 8 million genes → Millions of proteins
Bacterial proteins in gut microbiome
Aid digestion: Amylase - aids starch digestion, Short chain fatty acids production, Gas production, Vitamin synthesis
Packed with viruses
100 million viruses/bacteriophage per gram of feces
Danger lurks
Low numbers of potential pathogens found even in healthy individuals
Link between microbiome and health
Digestive disorders, Diabetes, Mood, Heart disease, Etc, Ability of pathogens to colonize
Types of organisms in microbiomes
Bacteria, Viruses/bacteriophage, Fungus, Protozoa, Archaea
Sources of microbes
In Utero (maybe), Birth, Milk, Caregivers, Environment

C-section vs vaginal birth
Effect on microbiome
Human body as an ecosystem
Has a variety of environmental niches: 37°C, Neutral to acidic pH, Nutrient poor to rich, Normal to no oxygen
Microbiome outcompetes pathogens
Resources competed for: Space, Attachment sites, Nutrients
How the microbiome competes with pathogens
Antibiosis, Taking up space/attachment sites
Normal biota
Defense against incoming pathogens
Superinfection
Over-growth of opportunistic pathogen after destruction of normal community by antibiotic treatment
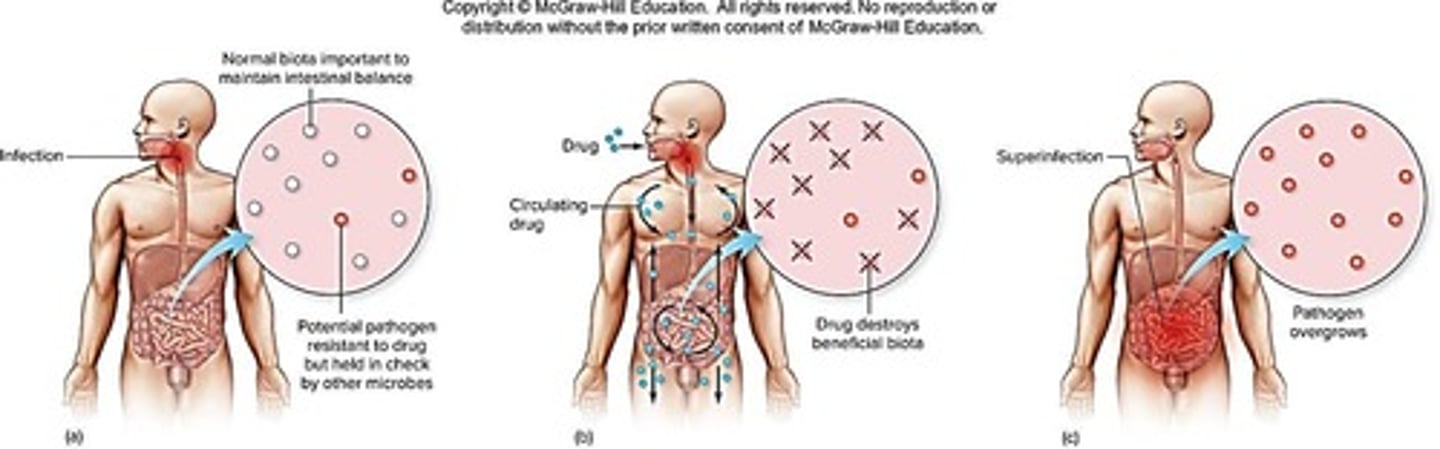
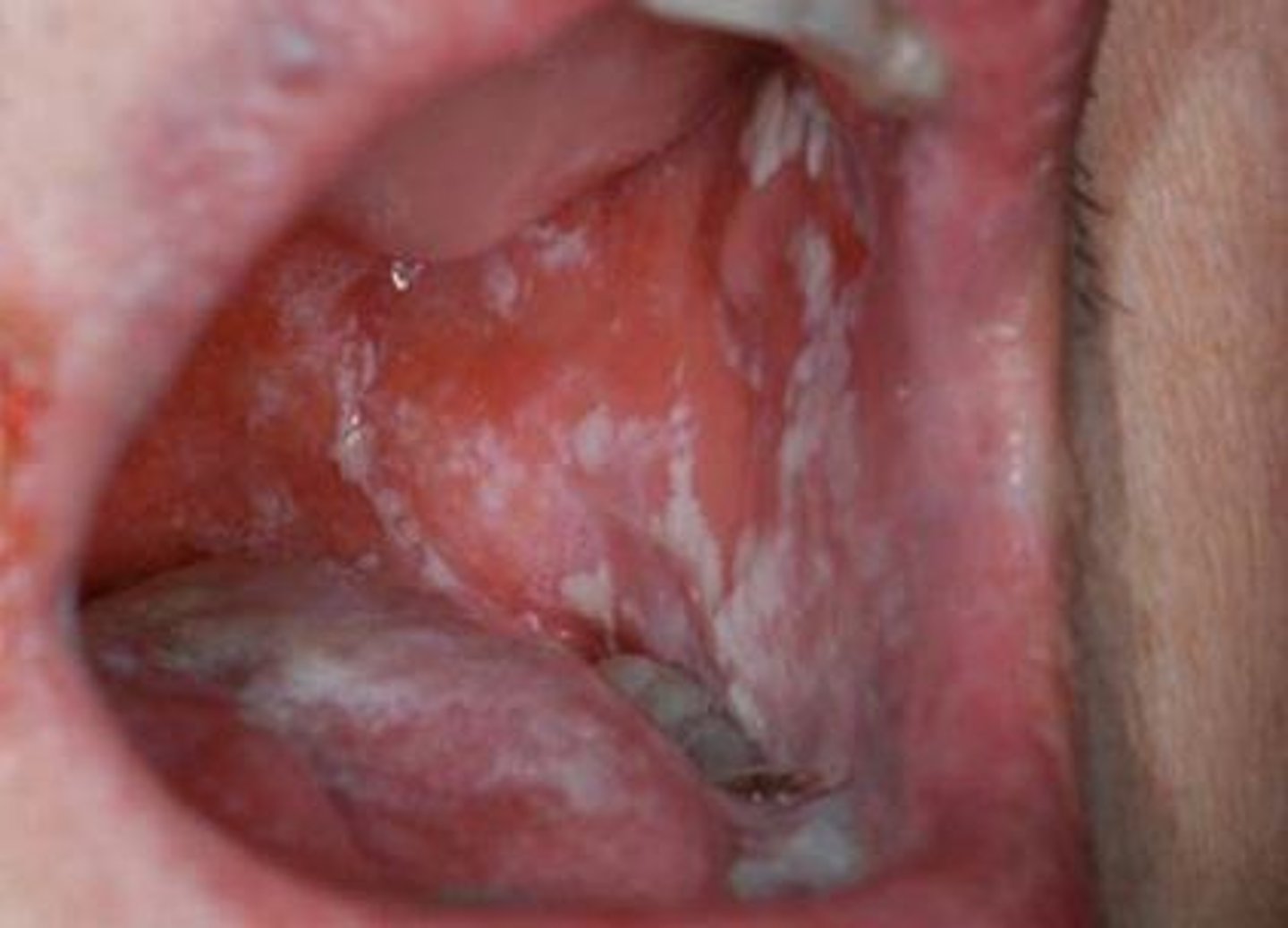
Examples of superinfection
Candida overgrowth after treatment of UTI
Colonization
The act of taking up long-term residence; as in microbes establishing a steady relationship with a host.
Infection
The entry, establishment, and multiplication of pathogenic organisms within a host.
Disease
Any deviation from health, as when the effects of microbial infection damage or disrupt tissues and organs.
Infectious disease
The state of damage or toxicity in the body caused by an infectious agent.
Pathogen
Parasitic microbe that can cause death and disease.
True pathogens
Capable of causing disease in healthy persons with normal immune defenses.
Opportunistic pathogens
Cause disease when the host's defenses are compromised or when the pathogens become established in a part of the body that is not natural to them.
Pathogenicity
The capacity of an organism to cause disease.
Virulence
The relative capacity of a pathogen to invade and harm host cells.
Virulence factor
Any characteristic or structure of the microbe that contributes to its ability to establish itself in the host and cause damage.
Polymicrobial Infections
Majority of infections are polymicrobial, with contributions from more than one type of microbe.
Infectious dose (ID)
The number of microbes necessary to cause an infection to proceed.
ID50
The amount of organism/virus needed to infect 50% of individuals.
Portal of entry
The route that a microbe takes to enter the tissues of the body to initiate an infection, provides proper environment for growth and spread.

Exogenous
Microbe originating from a source outside the body from the environment or another person or animal.

Endogenous
Microbe already existing on or in the body—normal biota or a previously silent infection.
Sequential infections
Influenza infection frequently leads to pneumonia.
Antimicrobial treatment
The use of drugs to treat infections caused by microbes.
Interactions between drug and microbe
The effects that drugs have on microbial organisms.
Bacteria
Single-celled organisms that can cause infections.
Fungus
A group of organisms that includes yeasts and molds, some of which can cause infections.
Protozoa
Single-celled organisms that can cause diseases in humans.
Helminths
Parasitic worms that can infect humans.
Viruses
Infectious agents that require a host cell to replicate.
Antimicrobial resistance
The ability of certain microbes to tolerate an amount of drug that would normally be inhibitory.
Interactions between drug and host
The effects that drugs have on the host organism.
The human microbiome
The collection of microorganisms living in and on the human body.
Viruses rely on a host cell
Viruses depend on host cells for most of their metabolic functions.
Vaccines
Biological preparations that provide immunity to a particular disease.
Inhibit entry
Preventing a virus from entering a host cell.
Inhibit replication, transcription and translation
Stopping the processes by which viruses reproduce and create proteins.
Inhibit viral assembly/release
Preventing the virus from assembling or being released from the host cell.
Fuzeon
A drug that blocks HIV binding to cell receptors.
Relenza
An antiviral that blocks membrane fusion.
Tamiflu
An antiviral that blocks membrane fusion.
Remdesivir
An antiviral that blocks RNA replication (SARS-CoV-2).
AZT
A nucleotide analog that blocks reverse transcriptase (HIV).
Nevirapine
A drug that blocks reverse transcriptase.
Indinavir
An antiviral that inhibits HIV protease enzymes and blocks assembly.
HIV PrEP
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis; the use of a drug to prevent infection of a person at risk.
Drug resistance
The ability of certain microbes to tolerate an amount of drug that would normally be inhibitory.
Genetic variability of microbial populations
The differences in genetic makeup among microbial organisms that contribute to drug resistance.
Chromosomal mutations
Spontaneous mutations in critical chromosomal genes that lead to drug resistance.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Acquisition of entire new genes or sets of genes that can confer drug resistance.
Resistance (R) factors
Plasmids containing antibiotic resistance genes.
Beta-lactamases
Enzymes that cleave the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin family of antibiotics, also known as penicillinases.
Decreased permeability
A mechanism of drug resistance where the transport protein is mutated to no longer transport the drug.
Efflux
A mechanism where the drug is immediately pumped back out of the cell.
Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) pumps
Pumps that expel multiple drugs from the cell, contributing to drug resistance.
Binding site alteration
A mechanism where the binding site for the drug is decreased in number or affinity.
Altered metabolic pathways
A mechanism where alternate pathways to folic acid synthesis result in resistance to sulfonamide and trimethoprim.
Natural Selection and Drug Resistance
In large populations, resistant mutants have a selective advantage when exposed to drugs, leading to the dominance of drug-resistant strains.
Persisters
Cells with slowed or stopped metabolism that can be resistant to antibiotics.
AntiMicrobial Resistance (AMR)
The phenomenon where many infections treated with antimicrobials become resistant to most or all drugs.
Phage Therapy
A treatment method using phage infection that is more specific than antibiotics.
RNA interference
Small RNA molecules that prevent mRNA translation.
Defense peptides
Small peptides made by the host immune system or bacteria that attack bacteria or viruses.
CRISPR
A technology to alter the genome of a pathogen, making it susceptible to antibiotics.
Probiotics
Mixtures of live microbes fed to humans or animals to replace or augment lost microbes during antimicrobial therapy.
Prebiotics
Nutrients that encourage the growth of beneficial microbes in the intestine.
Fecal transplants
A treatment method used to transfer feces from a healthy patient to treat recurrent Clostridium difficile infection and ulcerative colitis.