Supply side policies
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
supply side policies
aim at positively affecting production side of economy by improving quantity/quality of FOP
aims to shift LRAS
2 categories of SS policies
market-based: aim to remove obstructions in free market
interventionist: require gov intervention to increase full employment of output
goals of SS policies
long term economic growth by increasing productive capacity
potential national output increases, higher rGDP
reduce inflation to increase international competitiveness
greater supply in economy results in reductions of prices of goods/services, leading to disinflation and more competitive exports
increase firms incentivise to invest in innovation by lowering costs
reduce unemployment through labour market flexibility
lower wage bills allow firms to recruit more workers
increasing incentives: market based
reducing income tax rates
incentivises workers to work as every hour of work now results in a greater pay, smaller portion of income goes to tax and
reducing corporate tax
incentivises firms to produce more
provide firms with extra funds they can use to invest in new tech
as a result, productivity improves, long term growth increases
improve competition and efficiency: market based
deregulation:
any regulation increases COP for firms and deregulation decreases COP, resulting in greater supply
privatisation: transfer of ownership of Gov firms to the private sector
gov firms are usually so big that private enterprise refrains from trying to compete
privatisation encourages new firms to enter market and compete, increasing AS
anti-monopoly regulation
monopoly power = producers can restrict output and increase prices
increases competition leading to more efficient allocation of resources
trade liberalisation
reduces trade barriers, increases international trade, increases competition and efficiency
competition encourages harder work, more efficiency and innovation, lower prices, international competitiveness improves
reduce labour costs and create labour market flexibility: market based
decreasing trade union power
trade unions keep wages above market level
without them, wages can be decreased
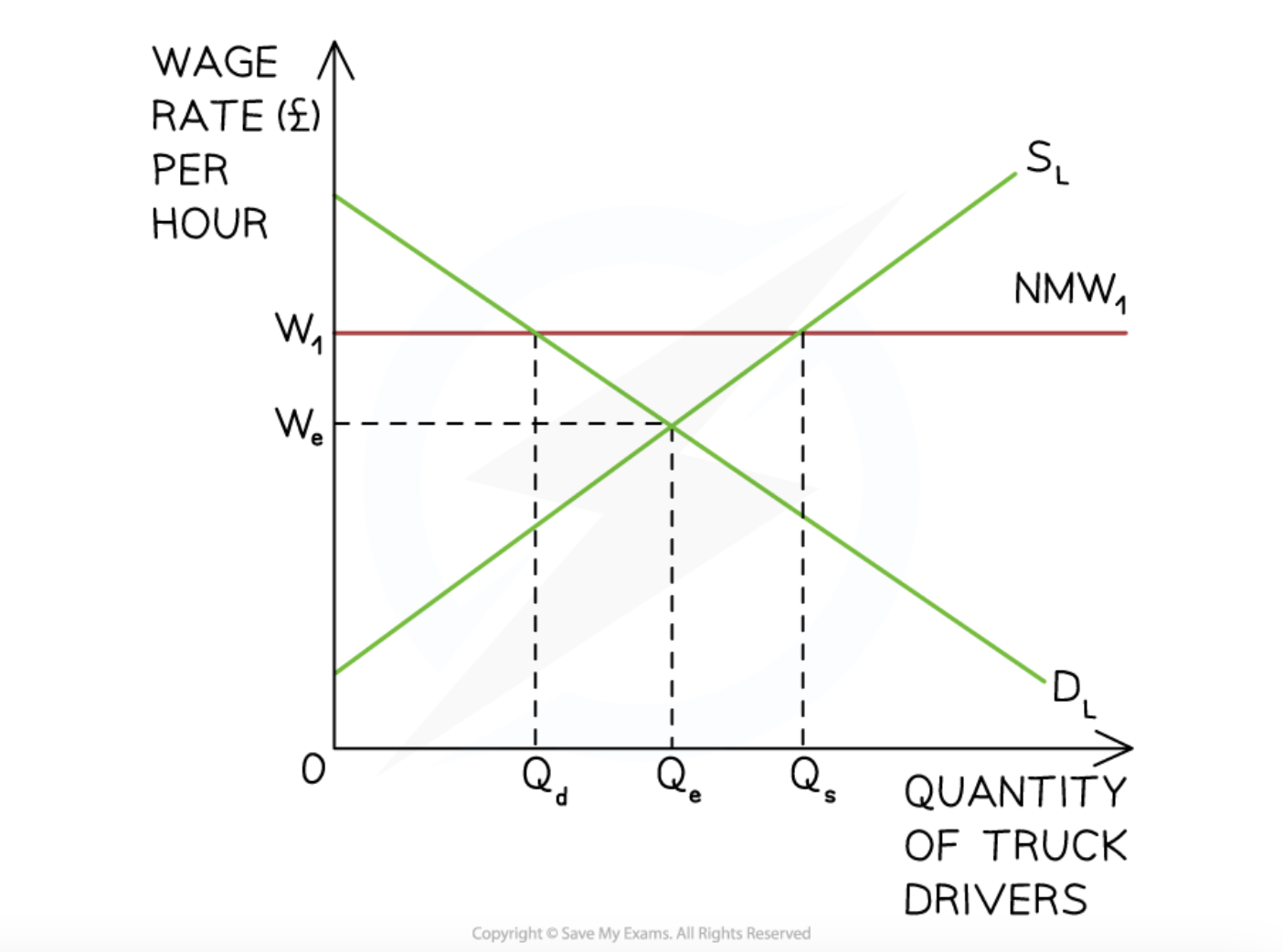
decreasing or abolishing minimum wage
to lower COP
increases employment
restructuring unemployment benefits
to incentivise unemployed to seek work
wages decrease, COP falls, firms lower selling prices, international competitiveness improves
education and training: interventionist
increasing gov spending on education and retraining raises quality of workforce by improving skills, productivity improves (PPC shifts outward)
skills increase, productivity improves, COP of firms fall, firms lower selling prices, international competitiveness
improving quality/quantity/access to healthcare: interventionist
increasing gov spending on healthcare improves productivity
human capital improves, productivity improves, COP of firms fall, firms lower prices, international competitiveness
research and development: interventionist
increased gov spending on innovation increases supply of potential jobs in economy
new industry emerges, new infrastructure developed, more jobs created, rGDP increases, increase in long term economic growth
provision of infrastructure: interventionist
increases gov spending on infrastructure (electricity, highways) could help expand capital base of the country in long term, increasing LRAS
new infrastructure developed, COP decrease, supply increases, firms lower prices, international competitiveness
industrial policies: interventionist
targeted to support firms in the form of subsidies
firms receive subsidy, COP decreases, supply increase, firms lower prices, international competitiveness
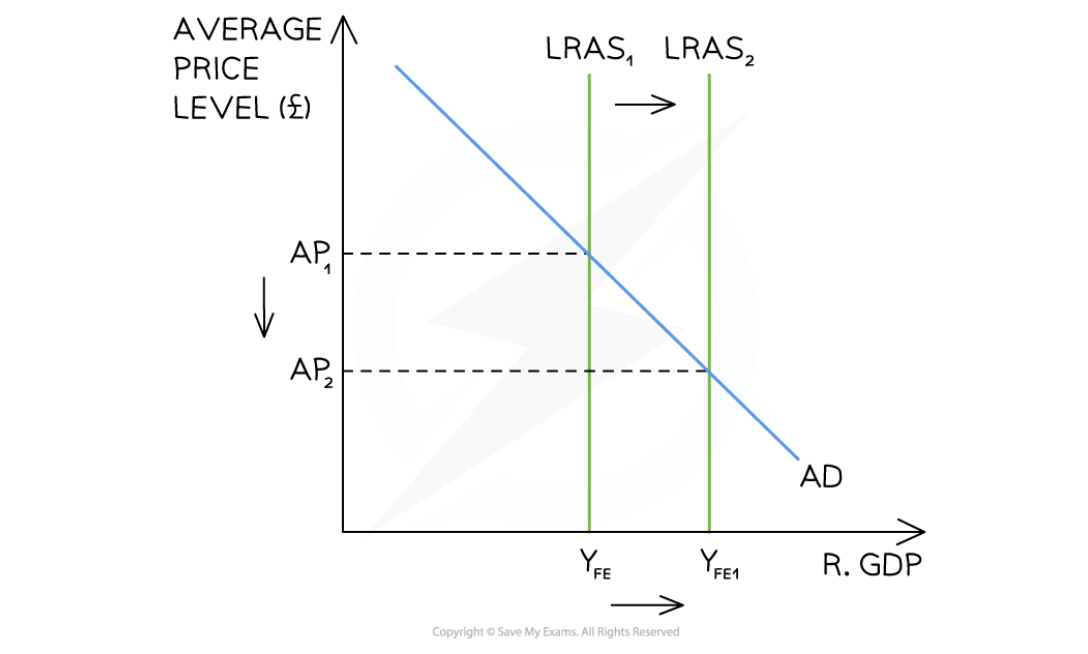
diagram of SS policies
successful SS policies will shift LRAS right
equal to outward shift of PPC
e.g efforts to reduce trade union power are successful
now less protection on wages and wages fall
firms may higher more workers, quantity of productive labour in economy has increased
AP falls from AP1 to AP2
Output increased from Yfe to Yfe1
demand side effects of SS policies
interventionist supply side policies require gov spending on an annual basis for however long it takes to complete the project
gov spending is a component of AD, so boosts it
supply side effects of fiscal policies
fiscal policies have ability to improve productive potential of an economy
evaluation of market-based SS policies
advantages:
improved resource allocation
increasing productive capacity of an economy requires more efficient uses of its resources
no burden on government budget
allows market forces to drive efficiency
so no associated opp cost
disadvantages
equity issues
distribution of income worsens, labour market reforms and wage policies lower workers wages
dropping unemployment benefits makes it hard for people with few skills to find jobs
time lags
significant time lags between seeing benefits
vested interests
can result in less effective outcomes
e.g privatisation resulting in gov’s preferred bidders obtaining an asset
environmental impact
large infrastructure projects almost always have negative externalities of production
evaluation of interventionist SS policies
advantages:
direct support of sectors important for growth
subsidies targeted towards specific industries increase rate of economic growth
reduces unemployment
can increase levels of exports
improvements in SOL
increase in quality of education/healthcare raises quality of life for all citizens
disadvantages
costs
expensive to implement and paid for using tax revenue, associated opp cost
time lags
due to its long term nature, changes in gov results in changes to budgets and priorities which take a long time and end result may not be as effective