NEONATAL AND PEDIATRIC O2 THERAPY
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
ABG – most reliable
Transcutaneous monitoring
Pulse oximetry
Hypoxemia is suspected when the patient shows signs of respiratory distress
Diagnosis for hypoxemia
60 mmHg
52 – 67 mmHg
AGE RELATED PO2 VALUES
NORMAL PRETERM
@ 1-5 hour
74 mmHg
62 – 86 mmHg
AGE RELATED PO2 VALUES:
NORMAL TERM INFANTS
(@5 hrs)
76 mmHg
62-92 mmHg
AGE RELATED PO2 VALUES
NORMAL PRETERM INFANTS & TERM INFANTS (5 days)
90 mmHg
80- 100 mmHg
AGE RELATED PO2 VALUES
CHILDREN,
ADOLESCENTS, ADULTS
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Nasal flaring
Intercostal retraction
Expiratory grunting
Signs and Symptoms of mild to moderate hypoxemia
Bradycardia
Apnea
signs and symptoms of severe hypoxemia
Decreased levels of activity, muscle tone, alertness and playfulness
signs and symptoms of increasing hypoxemia
Cyanosis
In children, it is not always a clear-cut indicator of hypoxemia
Monitoring
Humidification
Infection control
Principles of oxygen administration includes:
routine maintenance
Ensures proper calibration and check valve function to prevent contamination of the medical air supply with oxygen
in-line oxygen analyzer
Monitoring
Highly Recommended
Continuous measurement of blended oxygen systems via an ______ with high and low limits
8-12
in-line oxygen analyzer needs to be recalibrated every ________ hours
transcutaneous monitors
monitoring tool used primarily in infants and toddlers
4 hours
transcutaneous monitors need to change electrode every _____ to prevent skin burns
adequate perfusions
pulse oximetry - apply adhesive probes firmly but loosely to allow _________ at the site and digits distal to the probes
Humidification
Reduces detrimental effects of dry medical gases on the airway
Impairment of ciliary activity
Retention and thickening of secretions
Inflammation of ciliated pulmonary epithelium
Atelectasis
pneumonia
detrimental effects that humidification reduces
humidification
administered as water vapor and aerosol
desired FiO2 and inspiratory flow rate
Patient’s fluid balance
Thickness of respiratory secretions
Selection of humidification device should depend upon:
smaller tidal volume to weight ratios, gas to tissue surface area
Younger patients may require humidification even at low flows due to ______ and _____
drying
The addition of humidity at high flow helps prevent _____ of the airways
Low flow
High flow
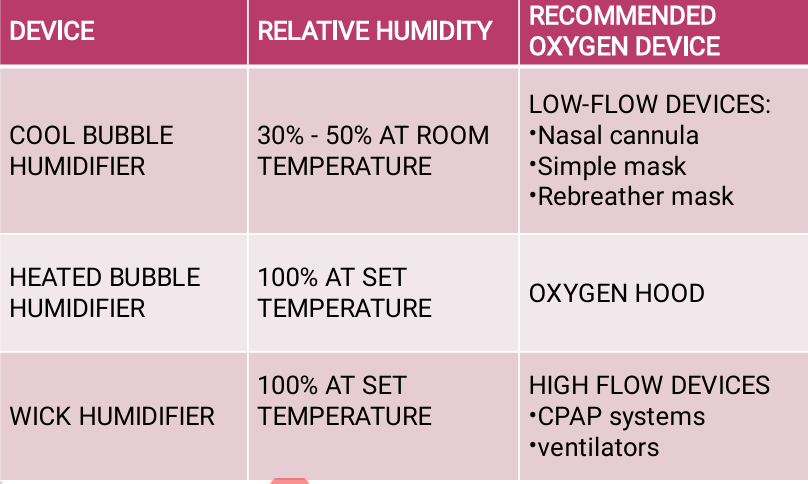
2 classes of humidification devices:
Low flow
type of humidifier that supplies a relatively small amount of humidity and does not heat the gas
bubble, diffuser
low flow humidifiers are classified as ______ or ________ humidifiers
Low flow
TYPE OF HUMIDIFIER
Allows the gas to bubble up through a reservoir of sterile water
cannulas, simple mask
Low flow humidifiers are used with _______ and _______
10 L/min
high flow humidifiers have flows greater than ___
high flow humidifier
TYPE OF HUMIDFIER
provide a fully saturated gas at a desired temperature
large volume jet nebulizers, advanced bubble humidifier, passover humidifiers
high flow humidifiers used with ______, _______ and ______.
Bernoulli’s principle
large volume jet nebulizers produce and aerosol using _____
lowers the lateral pressure around the jet that draws water up a capillary tube
When water reaches the jet, the gas breaks it up into an aerosol
Aerosol is carried with the gas to the patient
Principe on large volume jet nebulizers (Bernoulli)
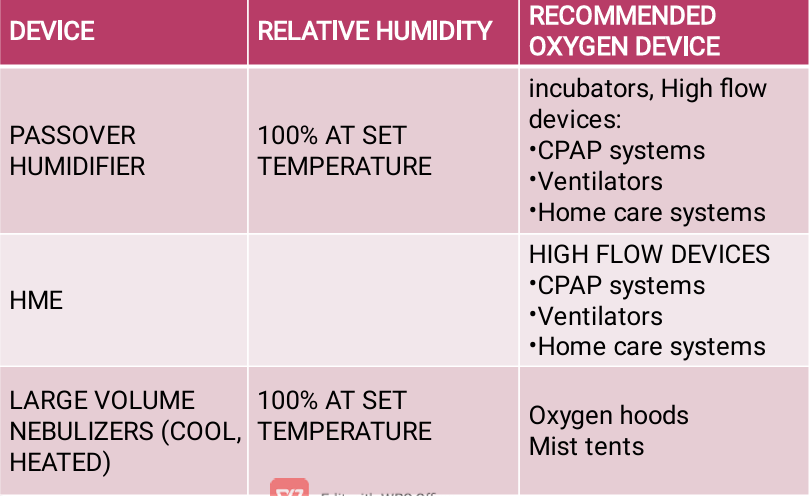
Passover Humidifier
TYPE OF HIGH FLOW HUMIDFIER
direct gas over a water surface
Simple reservoir type
wick type
Membrane type
3 types of passover humidifier
Simple reservoir type
type of passover humidifier that directs gas over the surface of a volume of water
simple reservoir type
TYPE OF PASSOVER HUMIDFIER
typically used with heated fluids for use with mechanical ventilation
room temperature fluids
simple reservoir type humidifier may also be used with ________ with noninvasive ventilatory support (nasal CPAP or BiPAP).
wick type
type of passover humidifier uses an absorbent material to increase the surface area for dry air to interface with heated water
wick type
type of passover humidifier that continually draws water up from the reservoir and keeps the wick saturated
membrane-type humidifier
this type of passover humidifier separates the water from the gas stream by means of a hydrophobic membrane
hydrophobic membrane
water vapor molecules can easily pass through this membrane, but liquid water (and pathogens) cannot
maintain saturation as high flow rates.
Add little or no resistance to spontaneous breathing circuits
do not generate aerosols and therefore pose minimal risk for spreading infection
advantages of passover humidifier

48 hours
Humidification and oxygen devices should be changed every ______
sterile distilled water
All aerosol units should be filled with ______ water
maintain a PaO2 that is high enough to avoid hypoxemia, but low enough to avoid the dangers of ROP, BPD. and oxygen toxicity
arterial Pao2 of 50-70 mmHg
GOAL OF THERAPY
Oxygen Blenders & flowmeters
Oxygen Analyzers
Humidifiers
Oxygen Hoods
Cannulae & Catheters
Oxygen Masks
Tents
Incubators
Resuscitators
Aerosols
Equipment for O2 therapy
E cylinders
gas cylinder that is used for brief intervals due to its relatively small capacity
E cylinders
gas cylinder that is used for transport of patient
H cylinders
type of gas cylinders that contains 10x much more gas
135
H cylinders are heavy, approximately _______ pounds
invasive via ETT or tracheostomy
Noninvasive
nasal cannula or nasal prongs
low flow O2 mask (simple face mask)
mask with reservoir bags
partial rebreathing mask
non-rebreathing mask
high flow O2 mask (venturi mask)
commercial O2 cages
oxygen delivery systems
oxygen blender
usual starting point for the administration of various concentrations of oxygens
50psi
oxygen blender is connected to a ___ source of oxygen and air
0.21 – 1.0
OXYGEN BLENDER
Any concentration of oxygen from ____ is possible
Bourdon gauge
Thorpe tube
2 types of oxygen flowmeter
Bourdon Gauge Flowmeters
aka fixed orifice flowmeter
Bourdon Gauge Flowmeter
type of flowmeter that accuracy is dependent upon the size of the orifice of the flowmeter outlet
cylinder regulators
bourdon gauge flowmeters are found on ____
Thorpe tube
it is a tapered tube with a small end at the bottom and large end at the top
V-shaped tube
Thorpe Tube Flowmeters
_______ provides a variable orifice
float
Thorpe Tube Flowmeters
A ____ is suspended in the tube by the flow of gas
oxygen analyzer
it is used when a precise oxygen percentage is desired
room air, 1.00
oxygen analyzer should be calibrated to _________ and ________ oxygen to ensure accuracy
8 hours
oxygen analyzer calibration should be done every _______
oxygen hood
a clear, plastic hood that fits over the infant’s head
oxygen hood
provide oxygen-enriched environment for the patient with relative ease and comfort
less than 0.50
oxygen hood is used with FiO2 of ______
large neck opening and less than tight seal around the edges of the hood
difficult to maintain consistent concentration above 0.50 due to _________ and __________
thermoregulation problem
high or low gas temperatures blown into the hood may cause the infant to overheat or become chilled
hypoxemia
Level of oxygen in the blood that is less than normal
if too low a gas flow is used, there is a chance CO2 retention in the hood
infant’s breathing might be hampered by the face being pressed against the wall of the hood; or the neck opening being too light
thermoregulation problems
oxygen hood hazards
cannulas
used on those patients with chronic oxygen needs
oxygen cannulas and mask
delivers a constant flow of O2 to the nasopharynx and oropharynx
oxygen cannulas and masks
Can also be a tool to wean the patient from the oxygen hood
1 L/min
oxygen cannulas and masks
flows used on neonates are usually less than ____
4 L/min
oxygen cannulas and masks
Flows greater than _____ may lead to nasal mucosal drying and epistaxis
pediatric - sized prongs
oxygen cannulas and masks
shorter in length and smaller in diameter compared to adult
neonatal cannula
has prongs that are even shorter and smaller
easy to use.
well tolerated
does not interfere with eating
advantages of oxygen cannulas and masks
inability to achieve high FIO2 in patients with high ventilatory demand
difficult to keep in place
tape to the face
disadvantages of oxygen masks and cannulas
low flow O2 mask (simple face mask)
mask that has no valves and reservoirs
5-10 L/min
simple face mask delivers O2 at flow rates between ____
5 L/min
simple face mask
the minimum flow rate _____ is needed to clear exhaled gas from the mask \
60%
simple face mask
max FiO2:
simple face masks
noninvasive equipment where there is nothing gained at higher flow rates
it will add slightly higher FiO2 than nasal cannula
advantages of simple face mask
interfere with feeding and speech
cant be tolerated by some patients
disadvantages of simple face masks
partial rebreathing mask
non-rebreathing mask
masks with reservoir bags
Partial rebreathing system
no exhalation valve to prevent CO2 into reservoir.
70 - 100%
PARTIAL REBREATHING SYSTEM
higher FIO2 up to ____
uses less oxygen than other masks.
higher possible FIO2.
advantages of partial rebreathing masks
interferes with feeding & speech.
aerosolized bronchodilator therapy is not possible
disadvantages of partial rebreathing mask
non-rebreathing mask
Valve at the reservoir to prevent expired gas going into the reservoir.
90+
non-rebreathing mask
higher possible FiO2 up to ____
non-rebreathing mask
mask with reservoir bags that vents all expired tidal volume
Highest possible FIO2.
fixed performance.
advantages of non-rebreathing mask
interferes with feeding & speech.
aerosolized bronchodilator therapy is not possible
disadvantages of non-rebreathing mask
venturi mask
O2 with high flow, no valves, no reservoir