Water Changing State and Water Cycle ~ Study Guide [Review 2023 ~ Team E]
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
evaporation [boiling]
Which type of change occurs when the starting state is a liquid and the ending state is a gas? This happens around 100 degrees Celsius.
condensation
Which type of change occurs when the starting state is a gas and the ending state is a liquid?
Evaporation
______________ occurs as water molecules absorb energy and it occurs at the surface of a liquid. Water is changing from a liquid to a gas.
An example of ___________ is air drying your wet hair.
Condensation
________________ occurs as water molecules slow down changing from a gas to a liquid.
An example is when your breath clouds up a cold window.
precipitation
Water that falls to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail is called ______________. Water is returned to the Earth's surface from the atmosphere.
Water
____________ is the only substance on Earth that commonly exists in all of its different states (solid, liquid, or gas).
3%
The percentage of the Earth's water that is fresh water is ______?
97%
The percentage of the Earth's water that is salt water is ______?
sun
The energy for the water cycle originally comes from the ____________.
water cycle
Water that falls to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail is called the ______________. Water is returned to the Earth's surface from the atmosphere.
evaporation
The four factors that affect the rate (speed) of ___________ are temperature, surface area, humidity, and wind speed.
increases
The rate of evaporation ______________ with an increase in temperature. The water molecules move faster and spread out more during evaporation.
slower
The water molecules move _________ and come closer together during condensation.
decreases
The amount of water vapor present in the air is called humidity. The rate of evaporation ____________ with an increase in humidity.
increases
The rate of evaporation ______________ with an increase in surface area.
increase
Evaporation increases with an ______________ in wind speed.
water cycle
The process(es) of evaporation, precipitation, and condensation are involved with the _____________.
sublimation
Water changes from a solid to a gas by skipping over the liquid phase.
Examples of __________: dry ice and solid air fresheners.
transpiration
The evaporation of water through the plant's leaves, stems and flowers in the form of water vapor is referred to as _________.
cool down
When water molecules ________ ________, the molecules move slower and closer together.
32°F or 0°C
The freezing point of water is __________.
lowers
Salt ____________ the freezing point of water, so the surface temperature is much colder [less than the normal freezing point 32°F or 0°C] before it could freeze.
212°F or 100°C
The boiling point of water is _________.
gravity
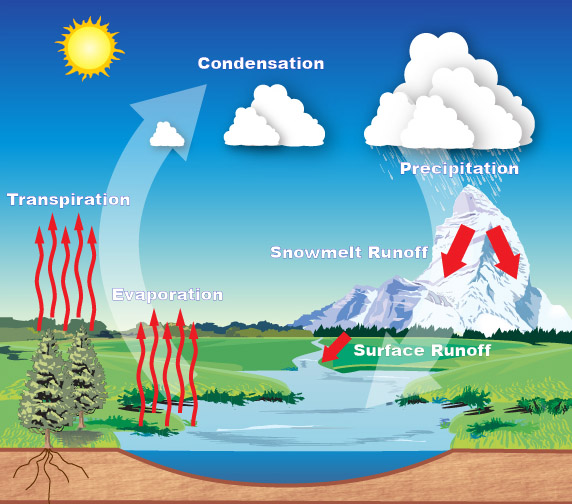
In the water cycle, _________ causes water to flow downward on land. It causes rain, snow, and hail to fall from clouds to the ground. Lastly, it pulls water into the ground.
condensation
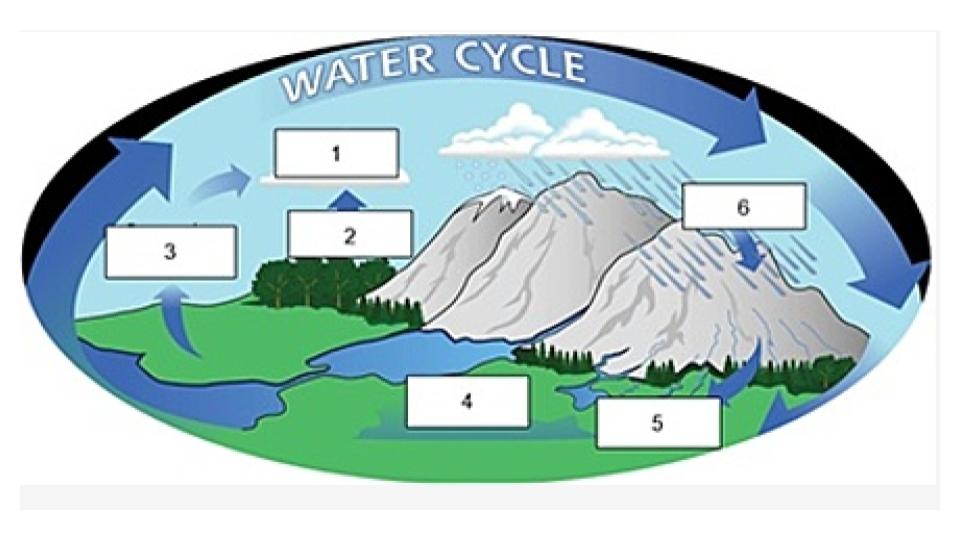
Name the process indicated in #1.
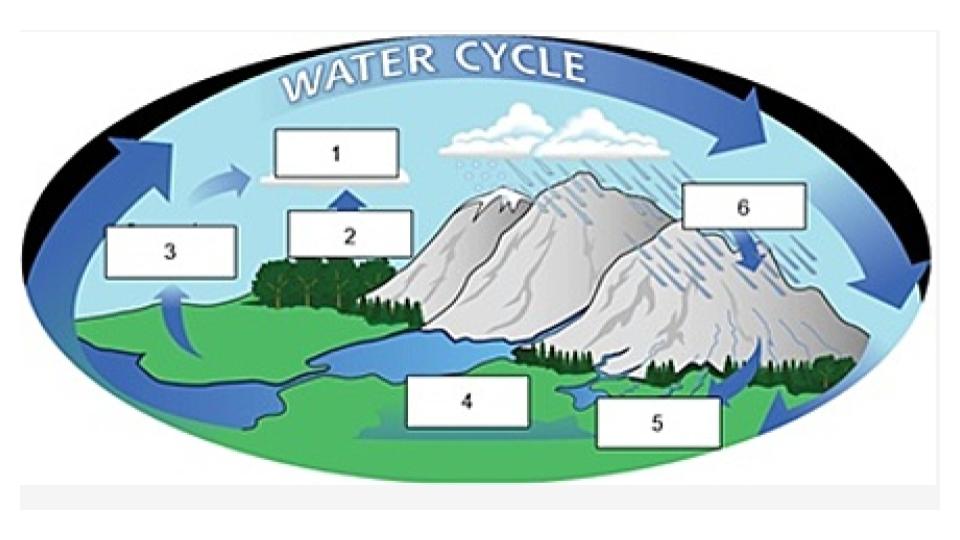
transpiration
Name the process indicated in #2.
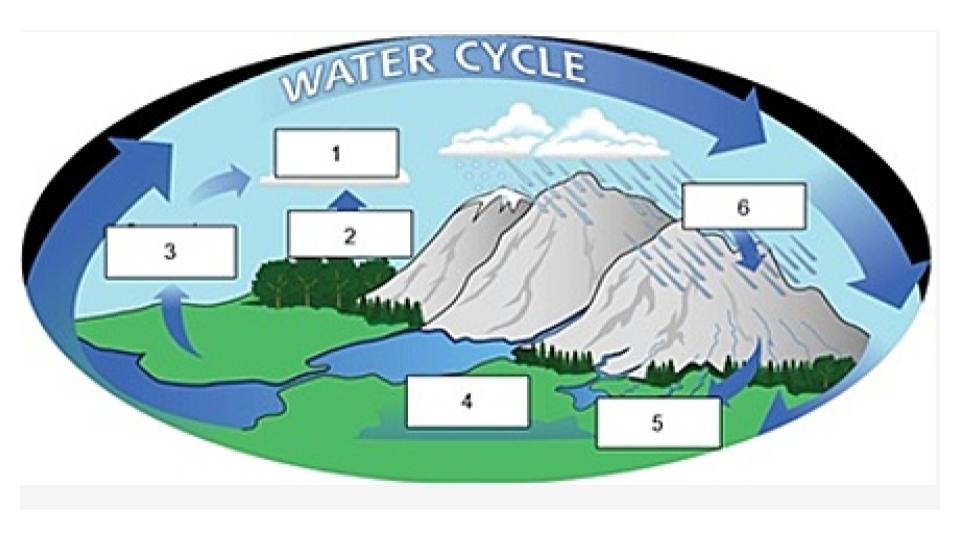
evaporation
Name the process indicated in #3
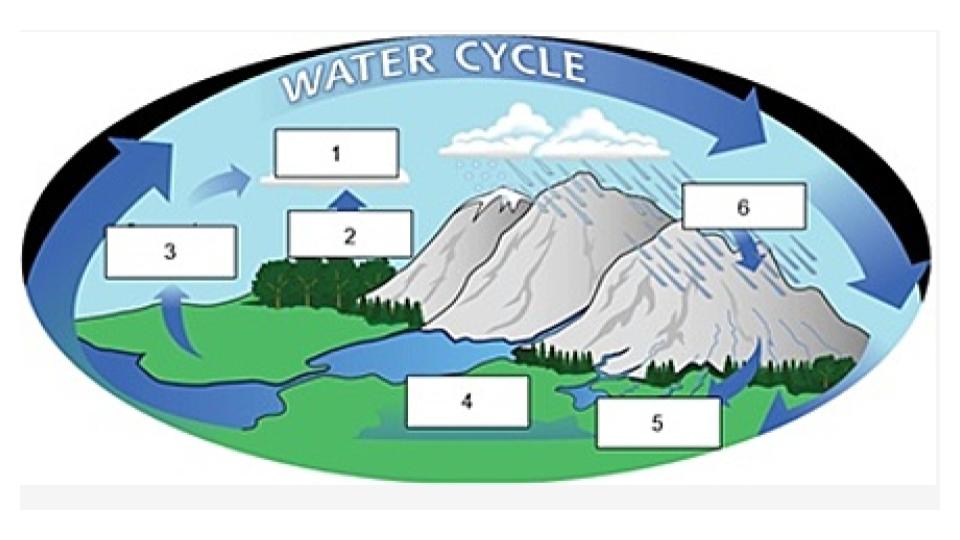
groundwater
Name the process/term indicated in #4.
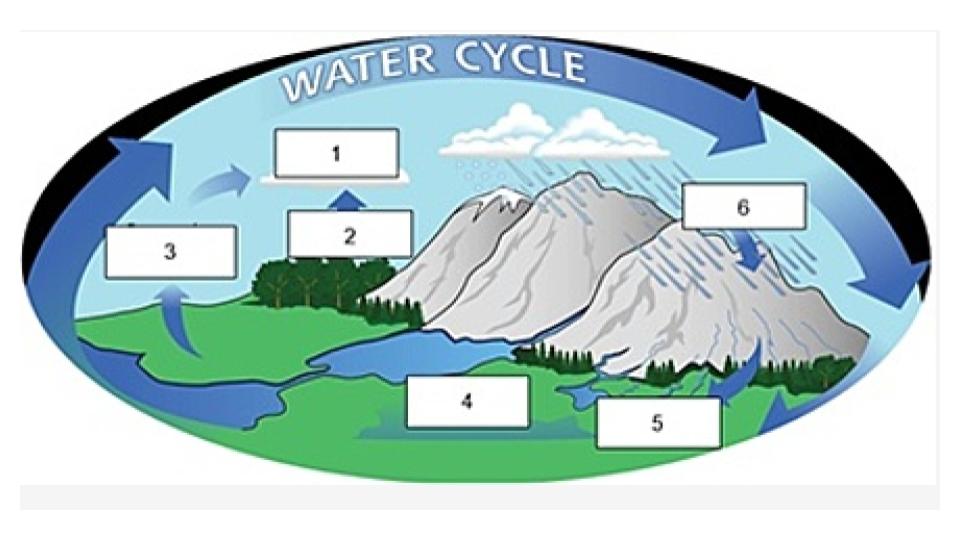
surface runoff
Name the process/term indicated in #5.
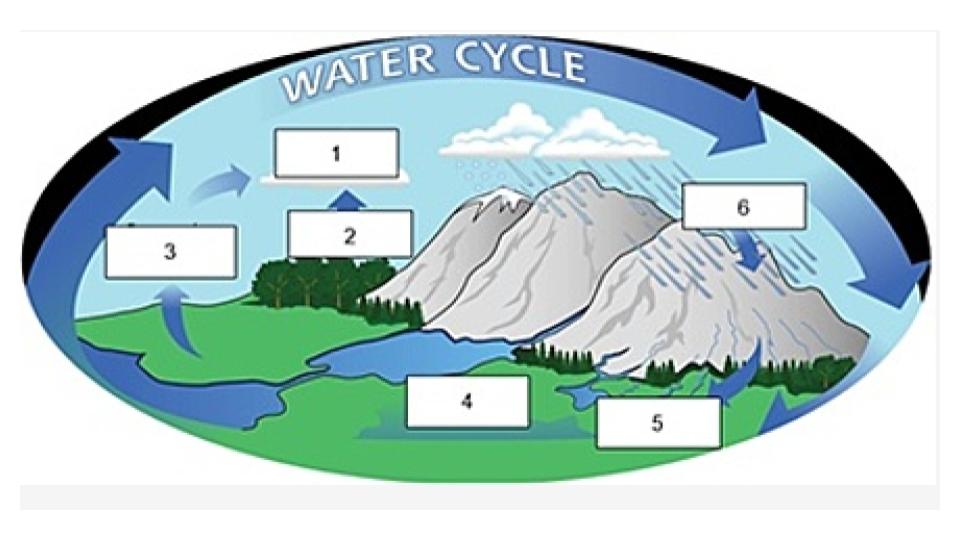
precipitation
Name the process indicated in #6.
heat
To change liquid water into a gas or to change a solid into a liquid, ________ or energy must be applied/used.
cool air
To change a gas back into a liquid or to change a liquid into a solid, ________ must be applied/used.