Unit 2 Dynamics
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
What does dynamics study?
Why things move
What was force introduced to describe?
Interactions between two objects
What is a force?
A push or a pull
What does force have?
Magnitude and direction
Is force a scalar or vector quantity?
Vector
Why is force a vector quantity?
It has both magnitude and direction
What do we need to do to quantify a push or a pull?
Specify both magnitude and a direction
What does an object at rest need to get it moving?
A force
What does a moving object need to change its velocity?
A force
2 main types of forces:
Contact and non-contact forces
Forces that act on an object by touching it at a point of contact
Contact forces
Examples of contact forces:
Frictional Force Tension Force Normal Force Spring Force
What are non-contact forces also called?
Long-range forces
Forces that act on an object without physical contact:
Non-contact forces
Examples of non-contact forces:
Gravity, electric force, magnetic force
What are the major forces?
Gravity, spring force, normal force, friction force, tension force
The pull of a planet on an object near the surface:
Gravitational force
What does the gravitational force of a planet on an object near its surface come from?
The entire planet
What objects does gravitational force act on?
All, whether moving or at rest
How does the gravitational force vector always point?
Vertically downward
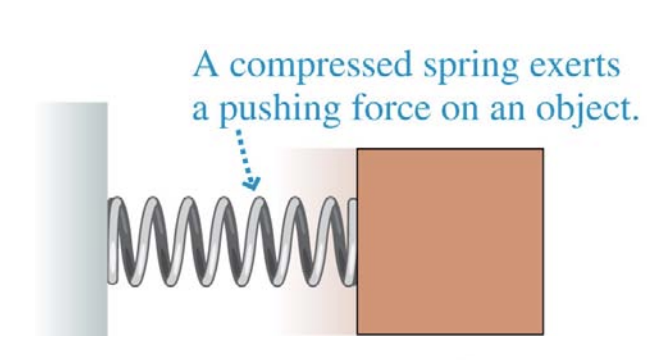
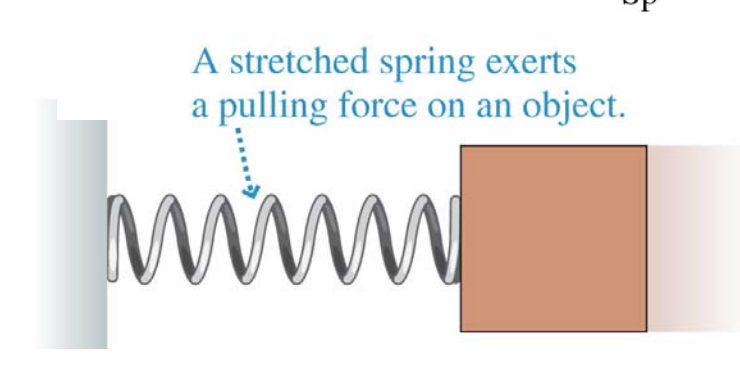
What can a spring do?
Push or pull
When can a spring push?
When compressed
When can a spring pull?
When stretched
Diagram of compressed spring exerting pushing force:
Representation of compressed spring exerting pushing force using force vector:
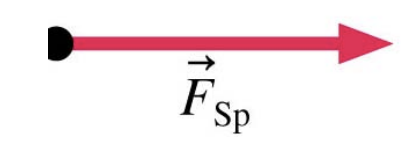
Diagram of stretched spring exerting pulling force:
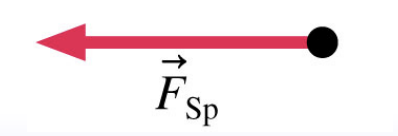
Representation of stretched spring exerting pulling force using force vector:
What does a table surface do when an object sits on the table?
Exerts an upward contact force on the object
How is normal force directed?
Perpendicular to a surface
Why is normal force called normal force?
It is always directed perpendicular to a surface
Draw force vector of normal force on a frog on a slanted surface:
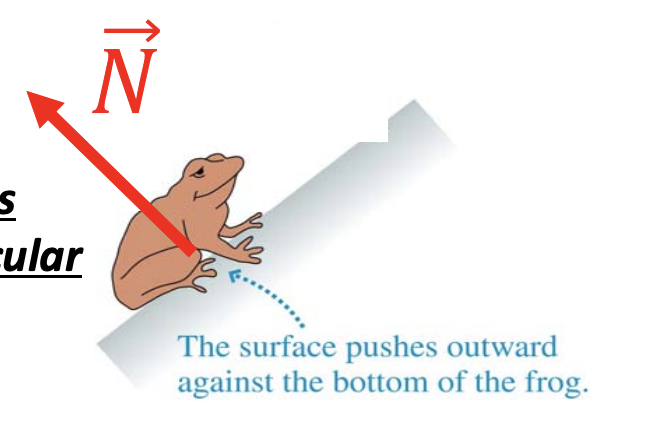
What is a table made of?
Atoms joined together by molecular bonds
What can atoms joined together by molecular bonds that make up a table be modeled as?
Springs
What is normal force on an object sitting on a table a result of?
Many molecular springs being compressed ever so slightly
Diagram of normal force of object on table:
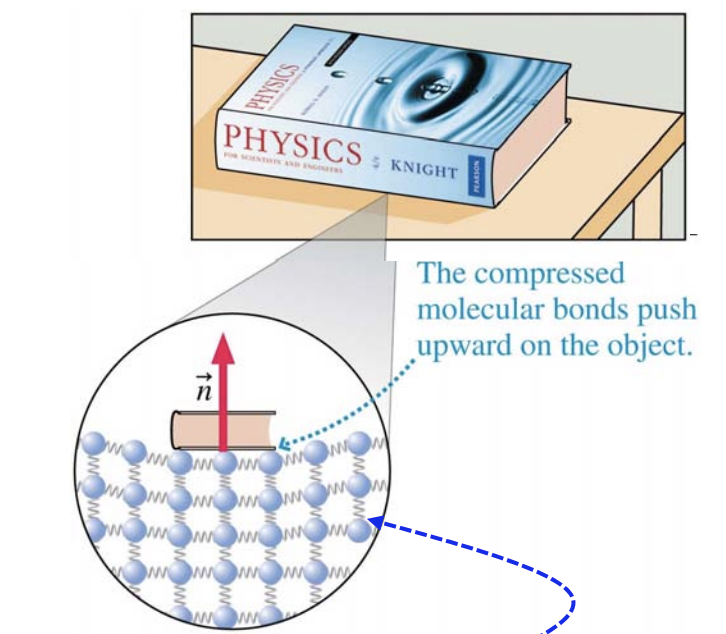
Two types of frictional force:
Kinetic and static
What can a surface do when an object slides along it?
Exert a contact force which opposes the motion
The contact force exerted by a surface on an object that opposes the motion of the object:
Kinetic friction
Diagram of kinetic friction:
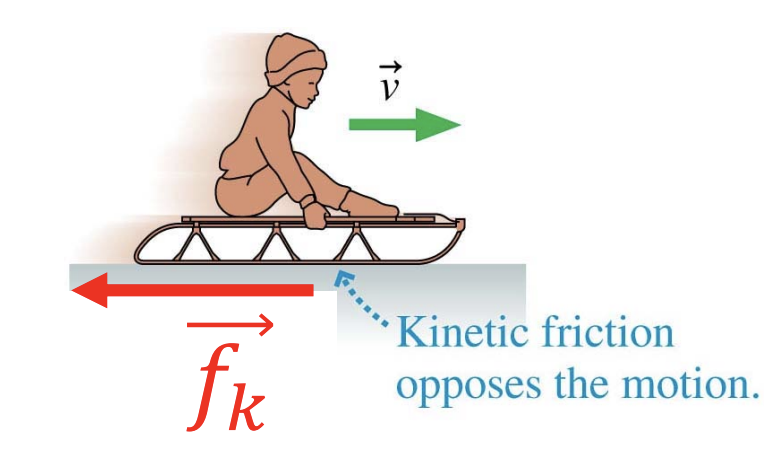
How is the kinetic friction force directed?
Tangent to the surface and opposite to the velocity of the object relative to the surface
What does kinetic friction tend to do?
Slow down the sliding motion of an object in contact with a surface
The contact force that keeps an object “stuck” on a surface, and prevents relative motion
Static friction
Diagram of static friction:
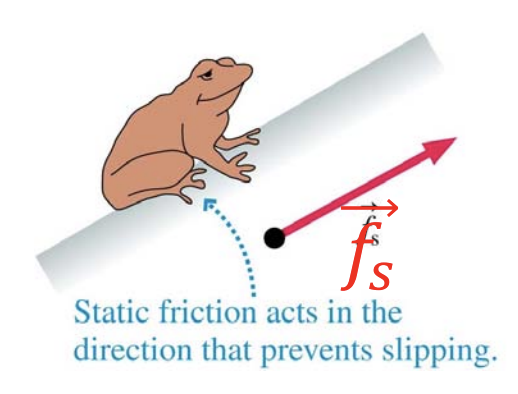
How is the static friction force directed?
Tangent to the surface
How does the static friction force point?
Opposite the direction in which the object would move if there were no static friction
The contact force exerted by a string or rope or wire pulling on an object:
Tension force
The tension force is in what direction?
Direction of the string or rope
Diagram of a rope exerting tension force on a sled by being pulled by a man standing up:
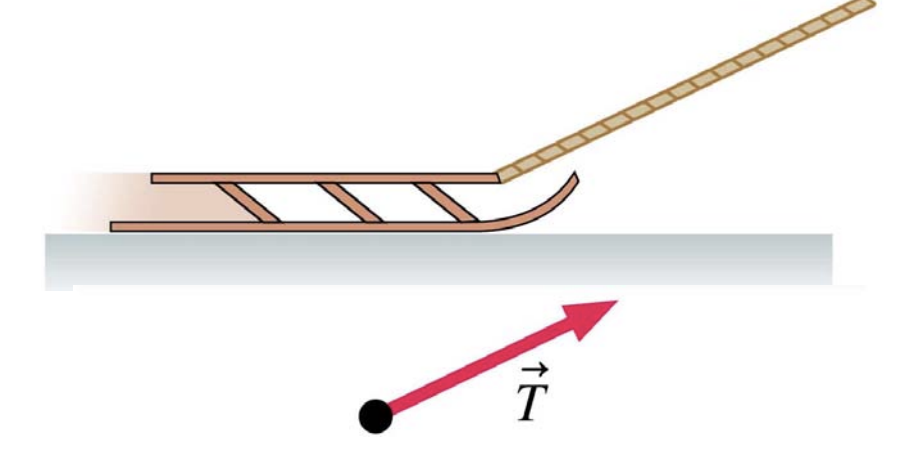
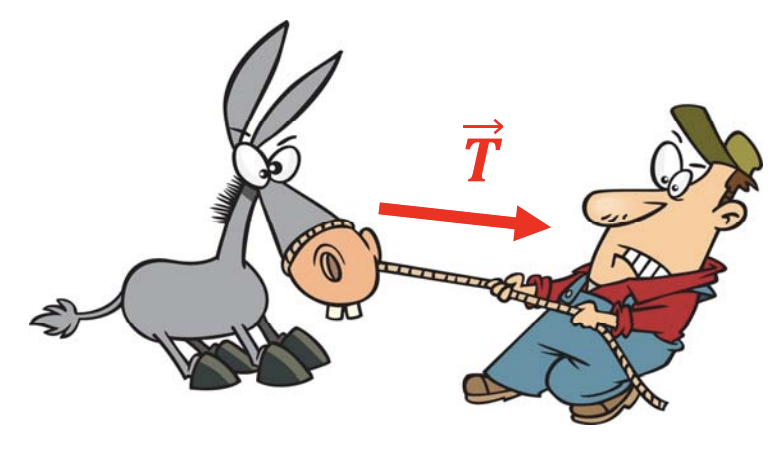
Diagram of a rope exerting tension force on a donkey by being pulled by a man with his hands at about the same height as the horse:
What is the net force given by when multiple forces are present?
Vector sum of all the forces
Symbol for net force:
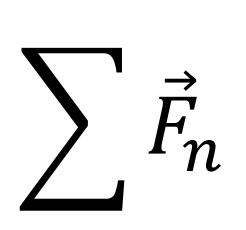
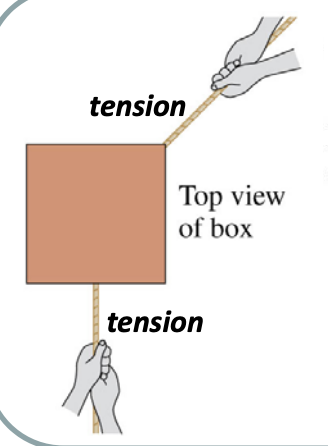
Draw the net force on this box:
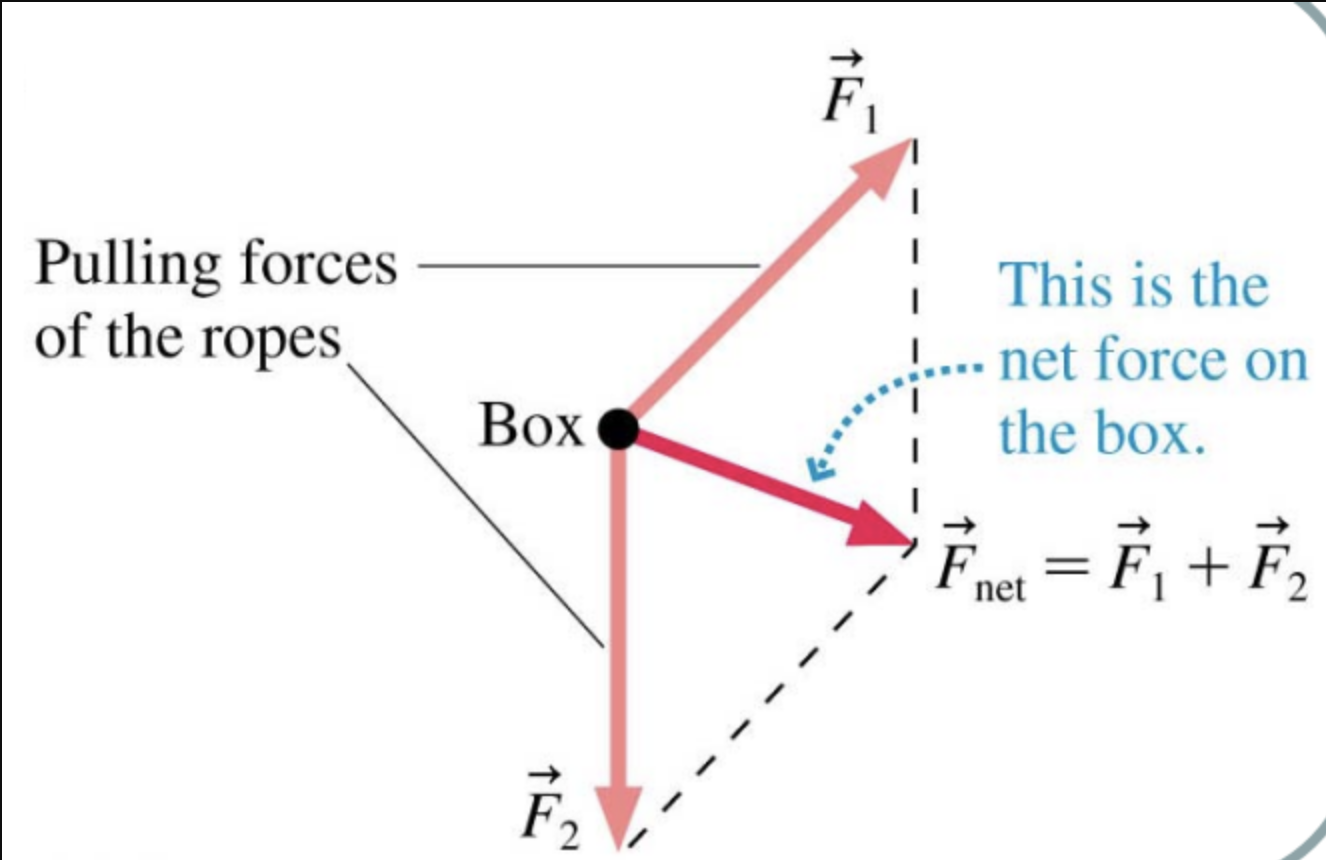
What does Newton’s 1st law of motion state?
Objects will remain at rest, or move with a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
What does Newton’s 1st law say will happen to stationary objects?
Remain stationary unless acted upon by a resultant force
What does Newton’s 1st law say will happen to objects moving with a constant velocity?
Continue to move at that constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force
Converse meaning of Newton’s 1st law:
If an object is at rest, or has a constant velocity, no resultant force can be acting on it
What does constant velocity mean?
No change in speed or direction
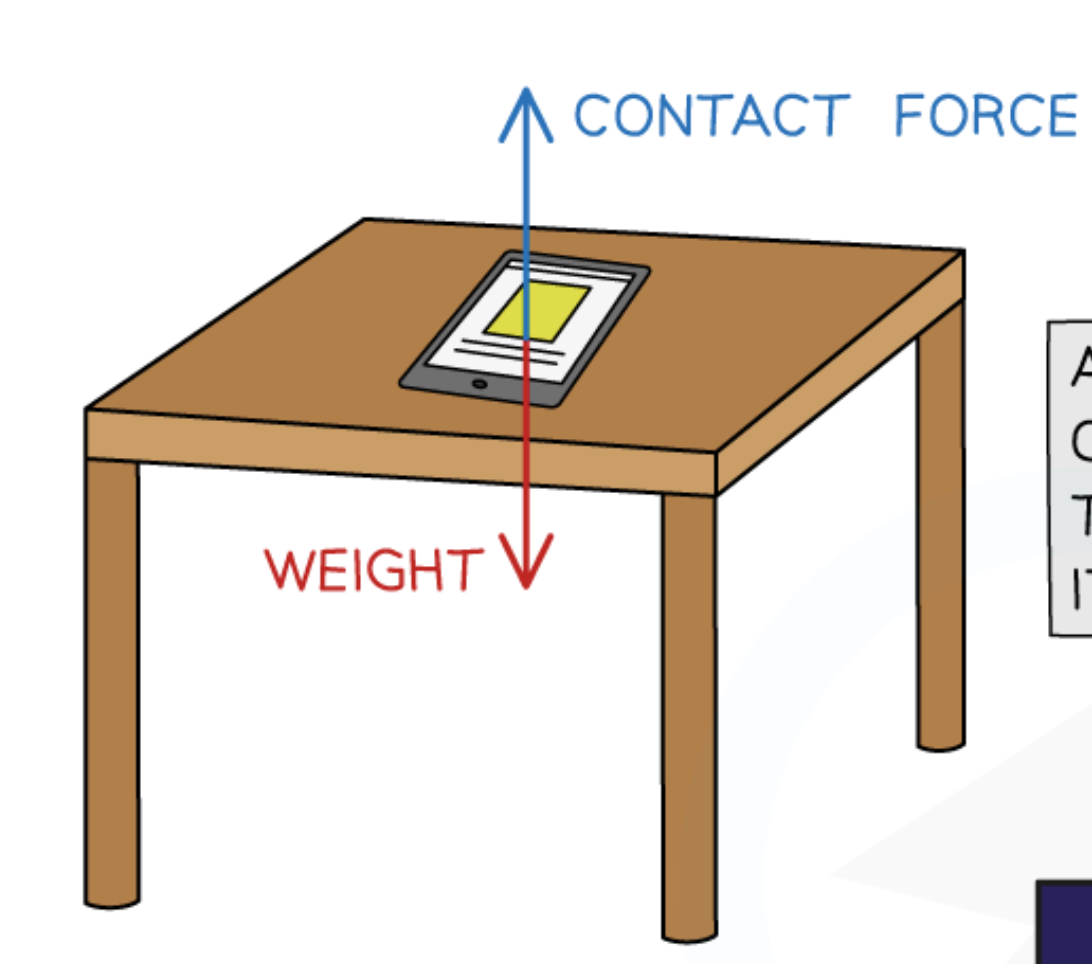
Does a tablet on a table have zero resultant force?
Yes
Why does a tablet on a table stay at rest?
Because the two forces acting on it are balanced
Diagram of forces acting on a tablet on a table:
Does a comet moving through space in a straight line at constant speed have a resultant force?
No
Why does a comet move through space in a straight line at constant speed?
Because there are no resultant forces on it
When can constant velocity be achieved?
When the resultant force is zero
What does resultant force being zero mean?
The forces on an object are balanced
Examples of how a mug on a table can be acted upon by a resultant force:
Someone picks up the mug or knocks into the table
Examples of how a piece of space debris moving in a straight line at constant speed can be acted upon by a resultant force:
It enters the gravitational field of a planet or collides with an asteroid
Examples of how a car moving in a straight line at constant speed can be acted upon by a resultant force:
The driver brakes or accelerates
What does Newton’s 2nd law of motion state?
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass
What does acceleration mean?
Changing velocity
What does an object accelerate in response to?
A resultant force
How does size of resultant force affect acceleration?
Greater the resultant force, larger the acceleration
How does magnitude of an object’s mass affect its acceleration?
Greater the mass, smaller the acceleration
Is a baseball being struck an example of Newton’s 2nd law?
Yes
Why does a baseball accelerate quickly to a home run?
It experiences a large resultant force
What do lawn mowers need in order to accelerate over long grass and weeds?
A push
Equation to express Newton’s 2nd law:
F=ma, where F = resultant force on an object in Newtons (N), m = mass of object in kg, and a = acceleration of object in m/s²
What can Newton’s 2nd law be used to estimate?
The sizes of forces and accelerations in realistic scenarios
What does Newton’s 3rd law describe?
The effects of the forces involved when two different objects interact with one another
Newton’s 1st and 2nd law vs 3rd law:
Describing effects of forces acting on a single object vs two interacting objects
How can Newton’s 3rd law of motion be defined?
Whenever two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
What explains the forces that enable a person to walk?
Newton’s 3rd law
What are interacting when a person is walking?
Foot and ground
What force does foot exert when walking?
Push force on ground
What force does ground exert when walking?
Push force on foot
Why can Newton’s 3rd law be used to explain the forces that enable someone to walk?
The forces exerted by the foot and by the ground are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
Diagram of forces involved in walking:
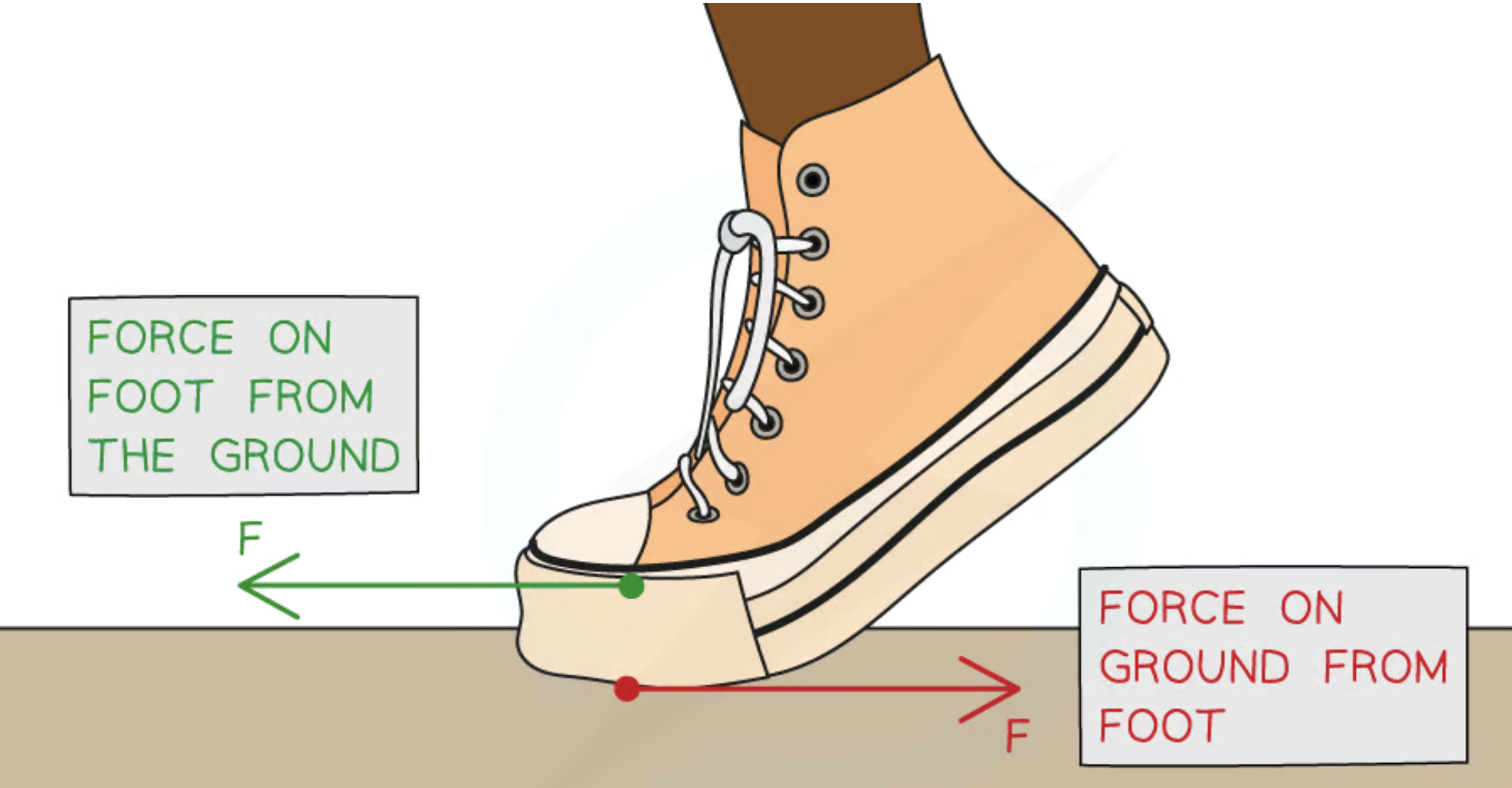
How does Newton’s 3rd law explain the forces that enable people to walk?
Foot pushes ground backwards and ground pushes foot forwards
What do the two forces in a third law pair act on?
Different objects
The two forces in a third law pair are always what?
Equal in size but act in opposite direction
Are the two forces in a third law pair the same type?
Yes
What happens to two colliding objects according to Newton’s 3rd law?
They will react, generally causing one to speed up and the other to slow down
What does speeding up mean?
Gaining momentum
What does slowing down mean?
Losing momentum
Diagram of the forces involved in a collision of two cars according to Newton’s 3rd law:
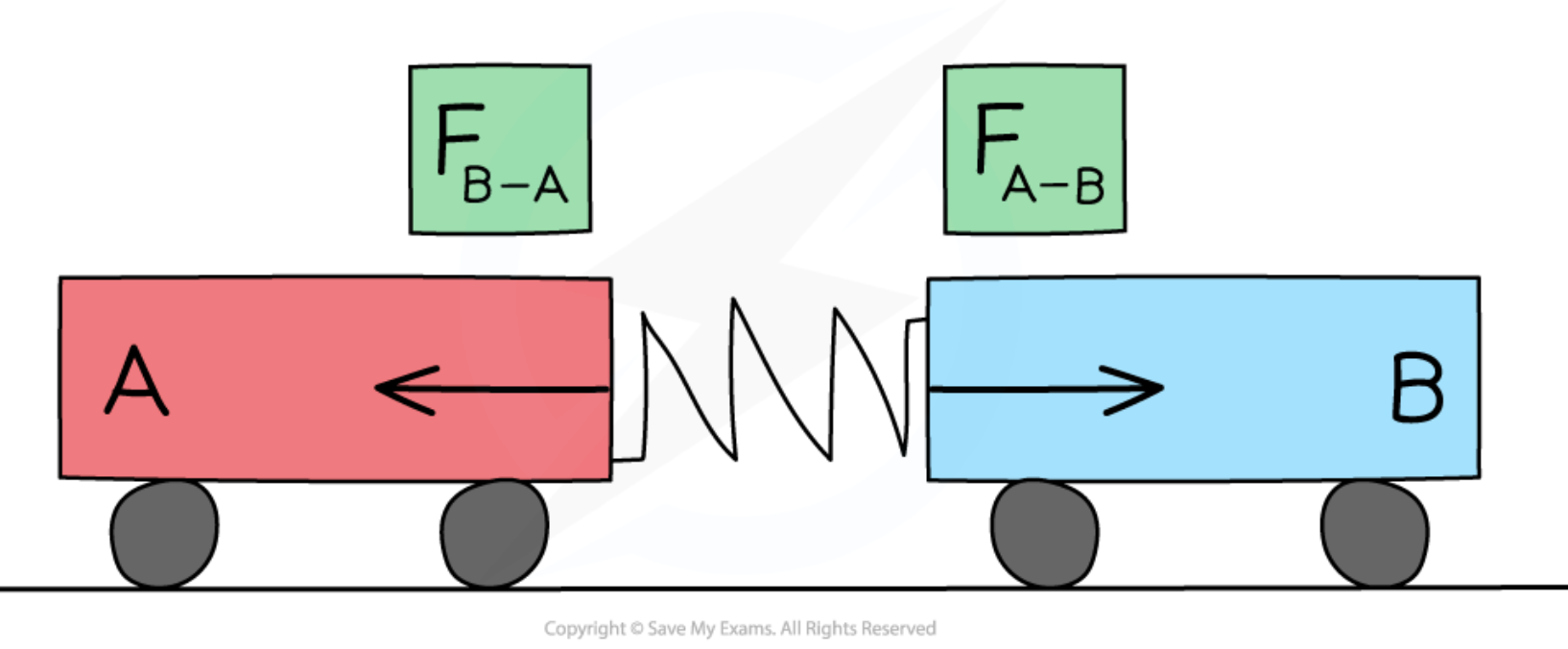
According to Newton’s 3rd law, what are the forces involved in a collision of two cars like?
Equal and opposite to each other
Symbol representation of the fact that the force of Trolley A on Trolley B is equal and opposite to the force of Trolley B on Trolley A when the two trolleys collide:
FB–A = –FA–B
If forces experienced by two colliding objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, are the accelerations of the objects equal in magnitude?
Not necessarily
Why are the accelerations of colliding objects not always equal in magnitude if the forces experienced by them are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction?
According to Newton’s 2nd law, acceleration depends on both force and mass
If objects with equal mass collide, what will their accelerations be like?
Equal
If objects with unequal mass collide, what will their accelerations be like?
Unequal