WetlandQuiz1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Hydrophyte
Plants adapted to living in water or saturated soil
Emergent
Extend above water surface
Floating-leaf
Floating leaves and roots attached or floating
Submerged
Below water surface
Stressors for wetland plants
1. Low or no oxygen
2. Low light conditions in water
3.High salt concentration
4.Reproduction
Hypoxic
Low oxygen concentration
Anoxic
No oxygen present
How Wetland Plants Deal with Anoxia?
Passive Diffusion of Gases
Aerenchyma Tissue
Pressurized Gas Flow
Passive Diffusion of Gases
Primary mechanism of gas exchange
• Occurs in air & water (& oxic soil)
• Higher O2 concentration in air than water
• Passive diffusion slow in water
Aerenchyma Tissue
Tissue with large intercellular spaces
• Throughout the plant: leaves, stem, roots
• Easy movement & exchange of gases
Pressurized Gas Flow
Gas moves into internal gas spaces of young leaves
• Gas forced down through aerenchyma from stem to roots by slight pressure caused by the heating of the leaves
• Older leaves lose their capacity to support pressure gradients so gas from the roots returns out through the old leave
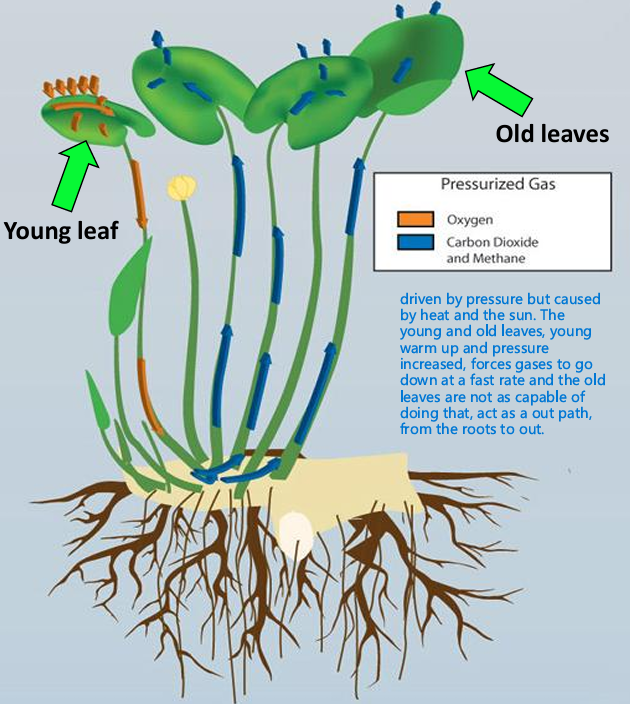
Describe this
Pressurized gas flow
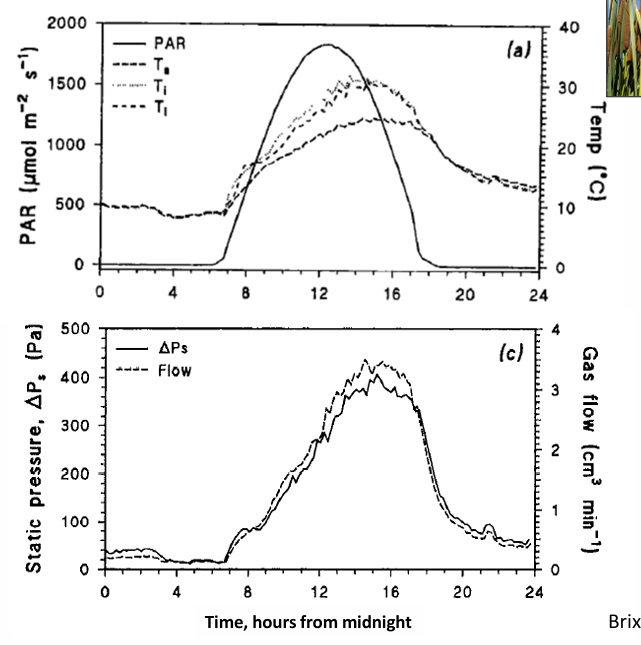
Describe this
Daily variation in solar energy, temperature
• Solar radiation peaks mid-day
•Air temp increases mid-day
• Leaf outer & inner temps increase
Pressure & gas flow within leaves
• Pressure builds within leaves/plant
•Gas flow in plant follows daily temperature fluctuations
Gas flow follows a 24-hr cycle
• Depends on time of year & light intensity

Stem Hypertrophy
Swelling of the lower stem
• Increased cell size, number of cells unchanged
• Is not from aerenchyma tissue
• Increases gas exchange (increased surface area)

Adventitious Roots
Roots developed on the stem above the anaerobic zone
• Better obtain O2 for respiration
What is the function and structure of root tissue found in non-root portions of plants, especially in submerged environments?
Location: Grows from above-ground or non-root portions of the plant.
Function:
Anchors into soil for extra stability.
Facilitates diffusion of oxygen and gases from the atmosphere into the root zone.
Submerged Plants:
Develop side shoots that remain underwater.
Aim to reach soil or stay submerged to enhance gas exchange.
Increased surface area boosts diffusion efficiency.
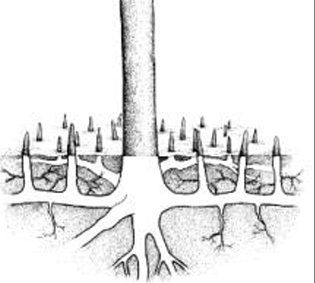
Pneumatophores
Root structure growing out of the water
•Gas exchange with atmosphere
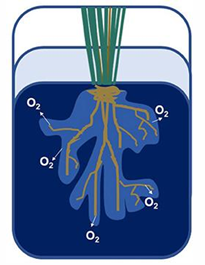
Rhizosphere Oxygenation
Rhizosphere: narrow region of soil surrounding roots directly influenced by root secretions & root microbiome
Release O2 from roots into soil to create oxic root zones
• Aerenchyma tissue provides O2 to roots
Shallow Root Systems
Roots spread near soil surface to avoid anoxia in deeper soil
• Increased O2 near water column
Rapid Shoot Growth, Stem Elongation
Shoots get above water surface quickly to allow for gas exchange (& photosynthesis)
• Adjusts growth rate based on water levels
Low light levels in water cause?
Reduced photosynthesis
How wetland plants increase photosynthesis and gas exchange?
Increase leaf surface area,
ribbon-like, highly branched,
floating/emergent leaves

Heterophylly
Different leaf shapes on the same plant
•Floating/emergent leaves
•Maximize light exposure, gas exchange
•Submerged leaves
•Increased gas diffusion
•Less resistance in water: waves, currents
• Less physical damage to plant
High Salt Concentration causes plants to perform
Salt Exclusion (Some species) or salt secretion
Prevent salts from entering or accumulating
• Higher K+ ions in root cells than Na+ in soil
• Water enters roots through osmosis
Allow salts to enter roots, but
inhibit movement to stems & shoots (concentrated in roots)

Salt glands
actively move salt to outside of leaves
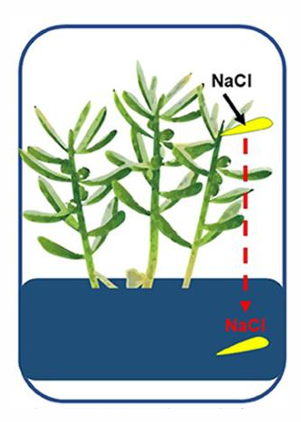
Salt accumulates in tissue that is shed
• Salt concentrates in older leaves
• Plant sheds these leaves once salt levels high enough
Reproduction in Water (4 types)
Produce buoyant seeds,
Delay flowering when flooded or accelerate flowering,
Large Persistent seed banks,
Seeds germinate while on parent plant
Buoyant seeds
Marine or lacustrine, always water present, allowing seeds to become bouyent, waves and currents to disperse seeds, encounter soil
Flowering time
Super unpredictable, wet and dry seasons, not predicable, they'll adaptbly achange the timing of flowering and how long based on water level, very short window, wait until water low and flower, and time of flowering changes.
Large, persistent seed bank
Seed bank - dormant seeds that exist in the soil, viable just waiting for the right conditions, wetland plants can sit dormant for years/months, etc, waiting for right conditions.
Seeds germinate while on parent plant
Sitting in condition where seed is above water, waiting for conditions, having the seed germinate and begin growing before dropping them.