Registry 2025 - thresholds and dose response relationships
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
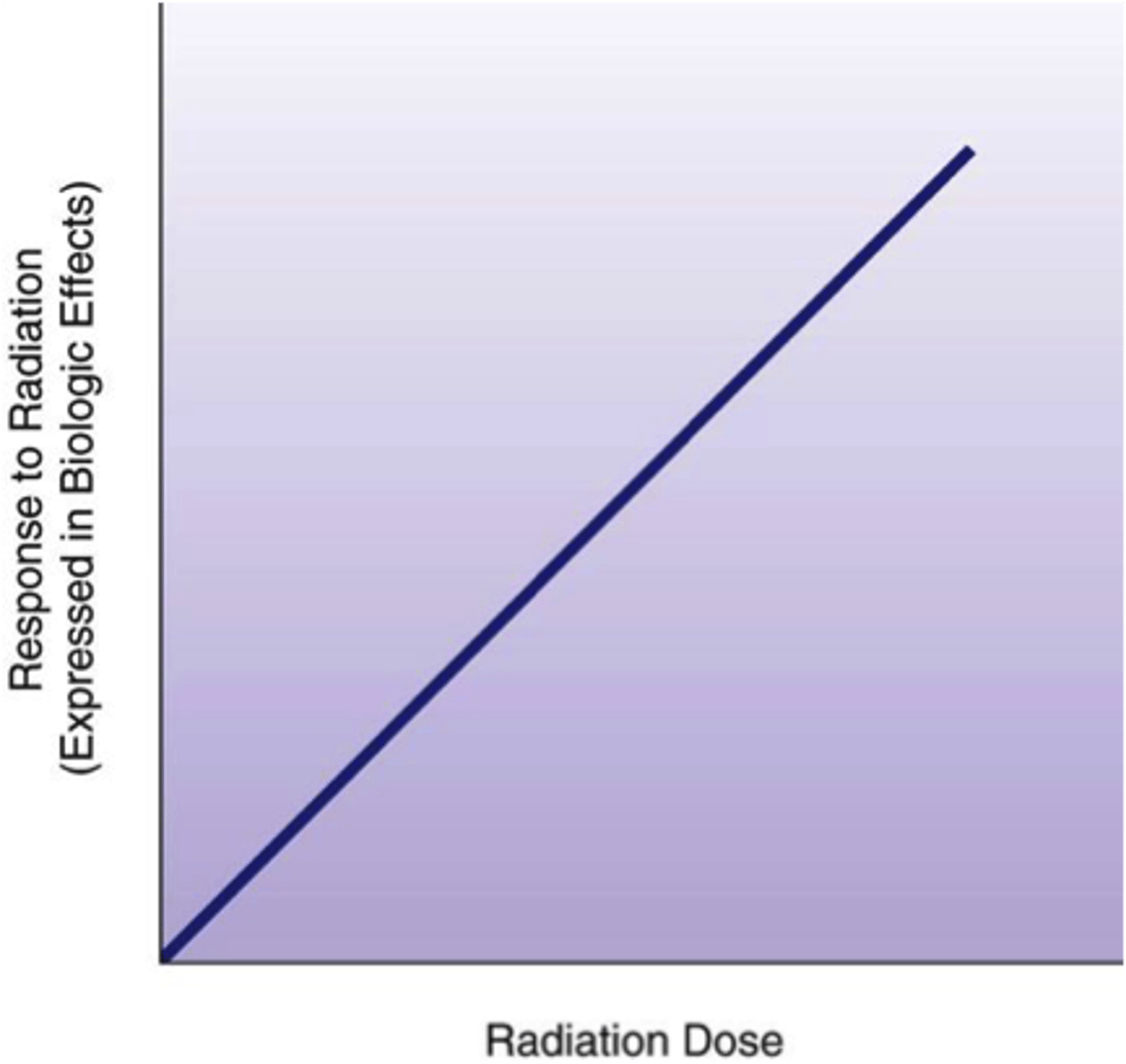
Linear-nonthreshold relationship
-Indicates that no level of radiation can be considered completely safe.
-A response occurs at every dose
- the response is often considered "stochastic effect" (aka: all or nothing)
-The degree of response to exposure is directly proportional to the amount of radiation received.
examples for this relationship
- leukemia
- cancer
- hereditary effects
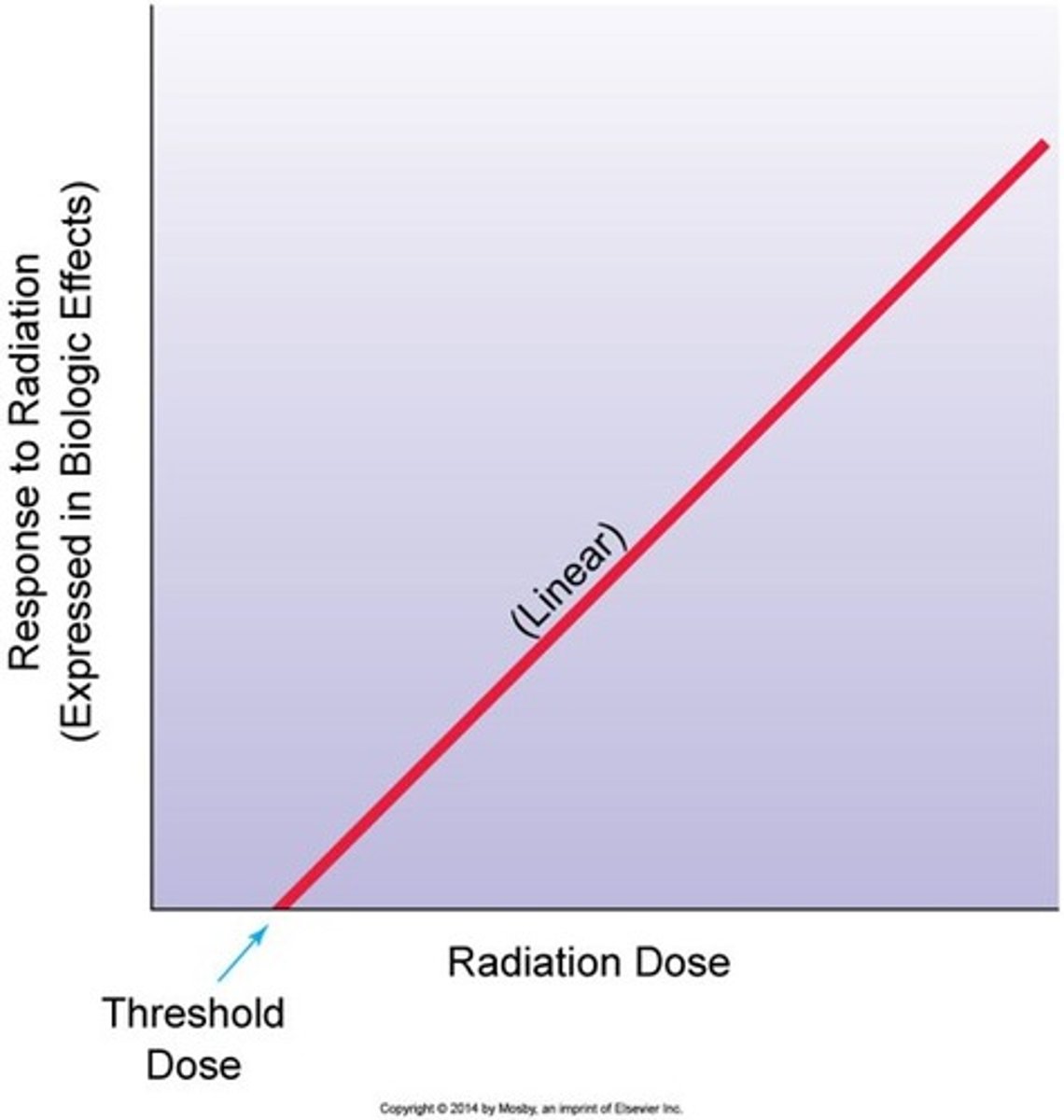
Linear-threshold relationship
- Indicates that at lower doses of radiation exposure, no response is expected.
- When the threshold is exceeded, the response is directly proportional to the dose received.
Examples for this relationship:
Short-term (somatic, early tissue) effects like skin erythema, sterility, leukopenia
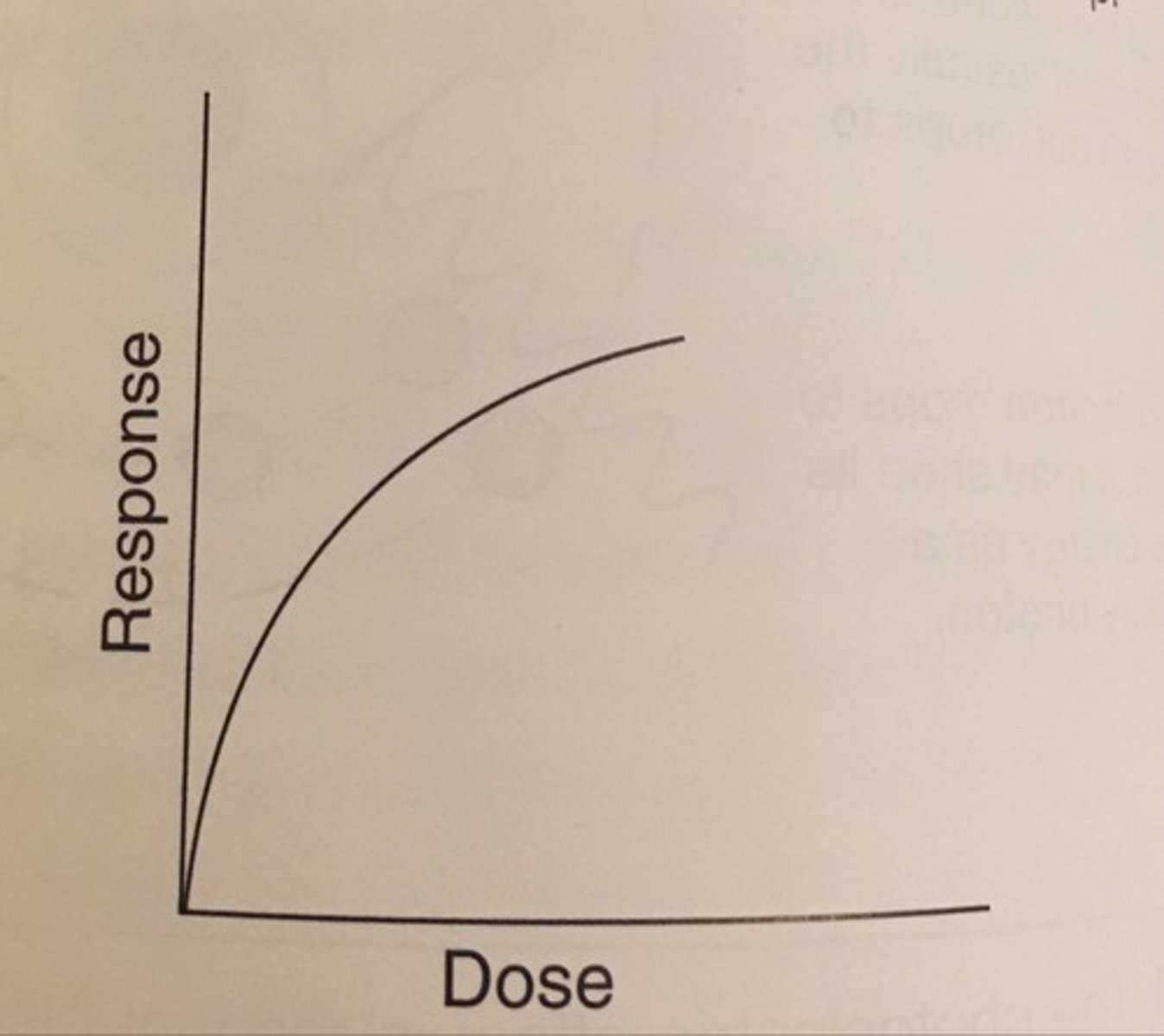
Nonlinear-threshold relationship
- indicates that at lower doses of radiation exposure no response is expected.
- when the threshold dose is exceeded the response is not directly proportional to the dose received and is increasingly effective per unit dose.
- the response is predictable and the effects are call nonstochastic
example:
ARS, Cataractogenesis, most teratogenic effects

nonlinear-nonthreshold relationship
- indicates that no level of radiation can be considered completely safe
- a response occurs at every dose
- degree of response is not directly proportional to the dose received
- the effect is large even with a small increase in dose
example: radiation therapy