Network+ N10-009
1/683
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
684 Terms
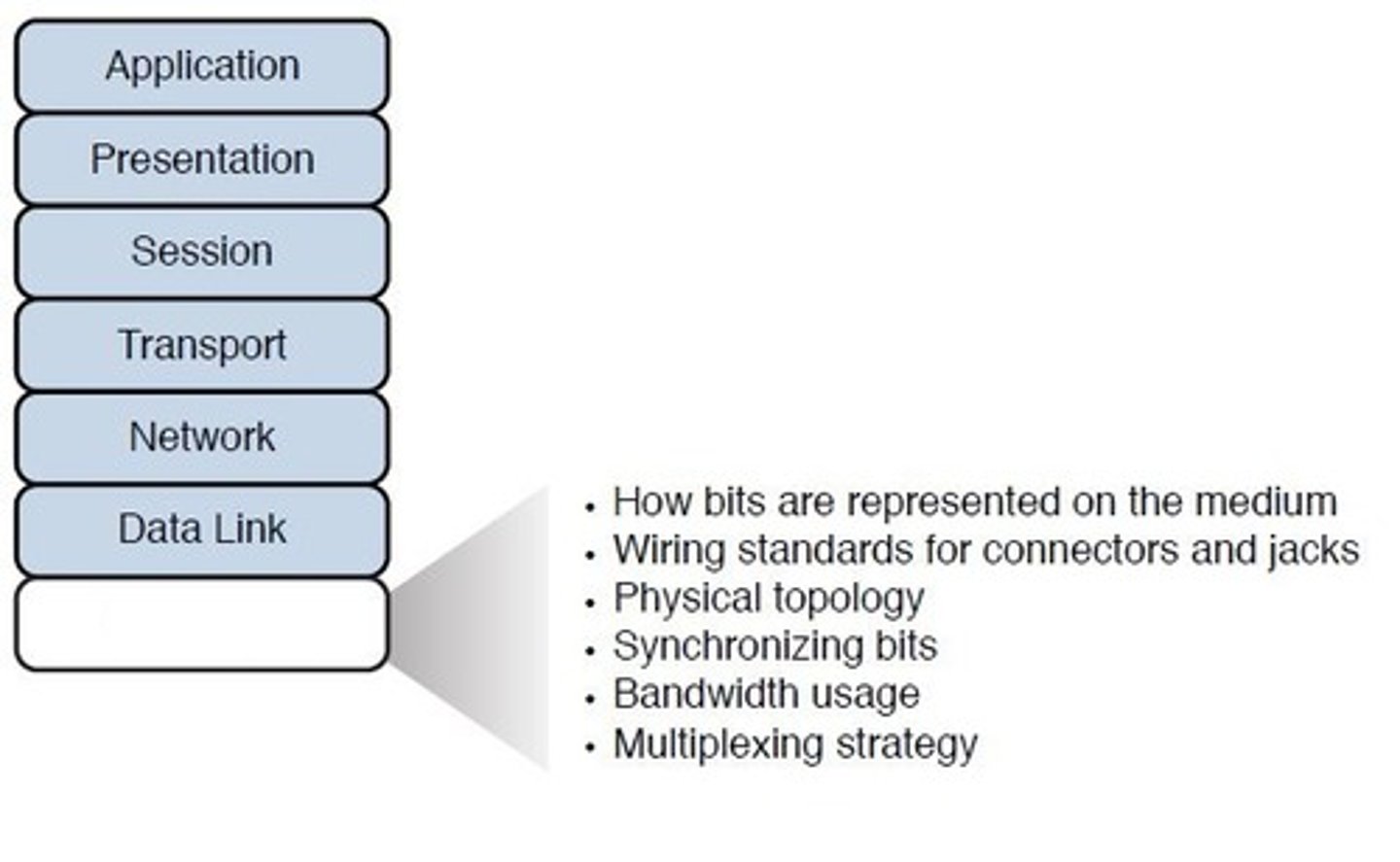
Layer 1 - Physical:
Receives the frames and data and sends them via the local media (copper wires, fiber-optic cables, etc.) to the switches, routers, etc., along the network path.
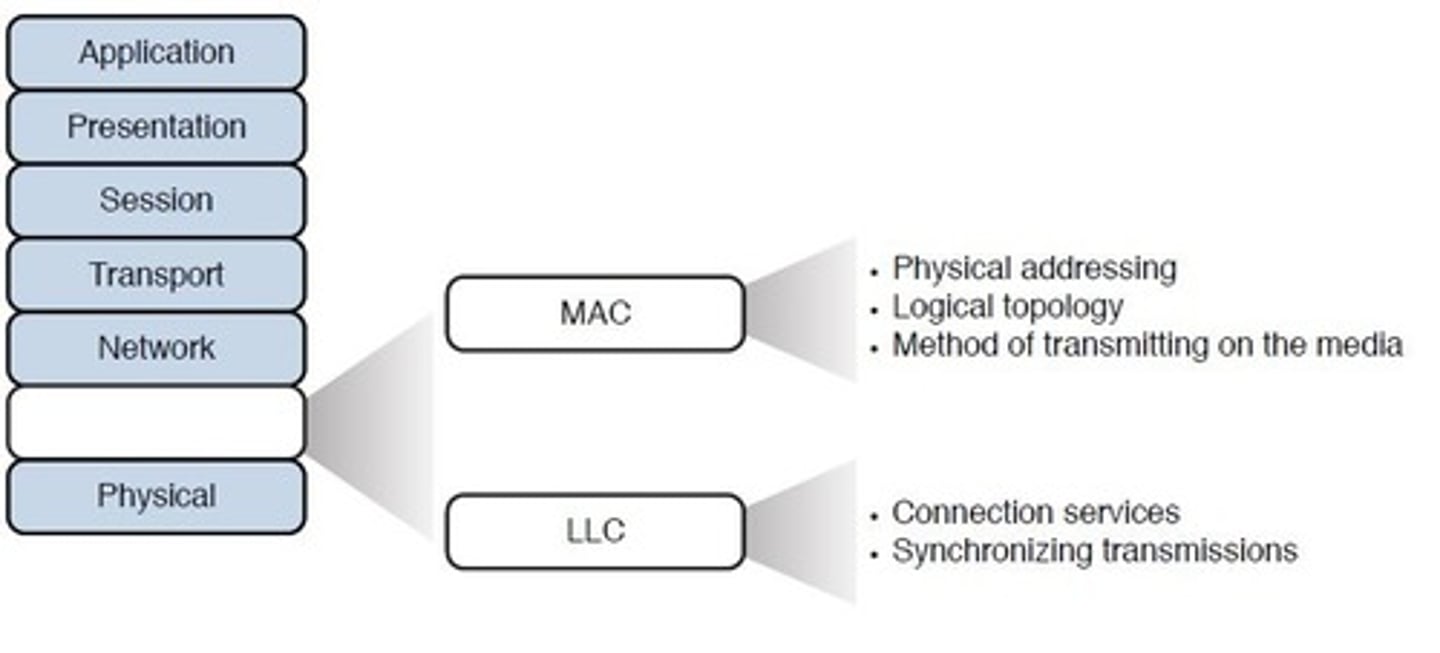
Layer 2 - Data link:
- Receives the packets and adds physical addressing by adding sender and receiver MAC addresses to each data packet.
- This information forms a unit called a frame.
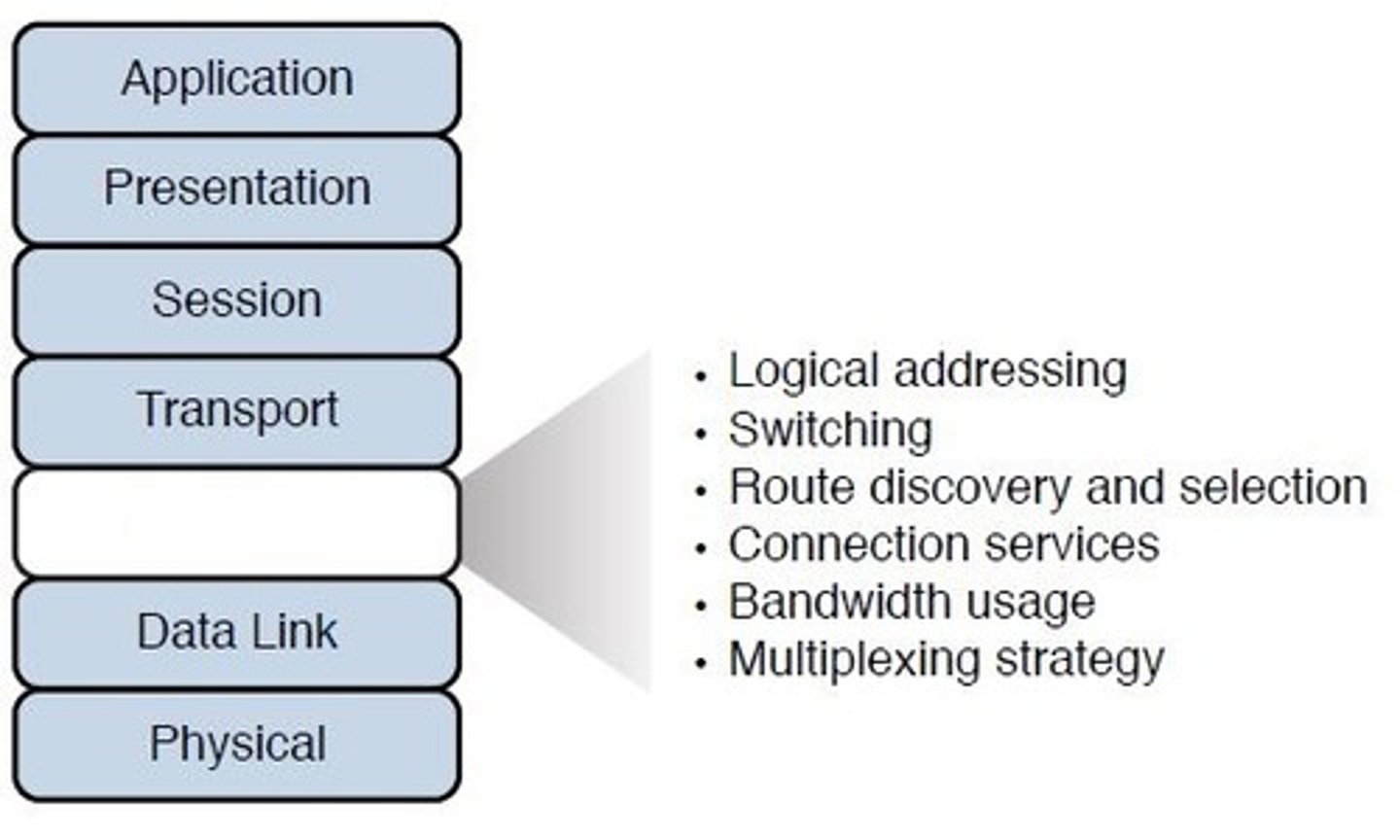
Layer 3 - Network:
The routing layer (IP addresses, routers, packets).
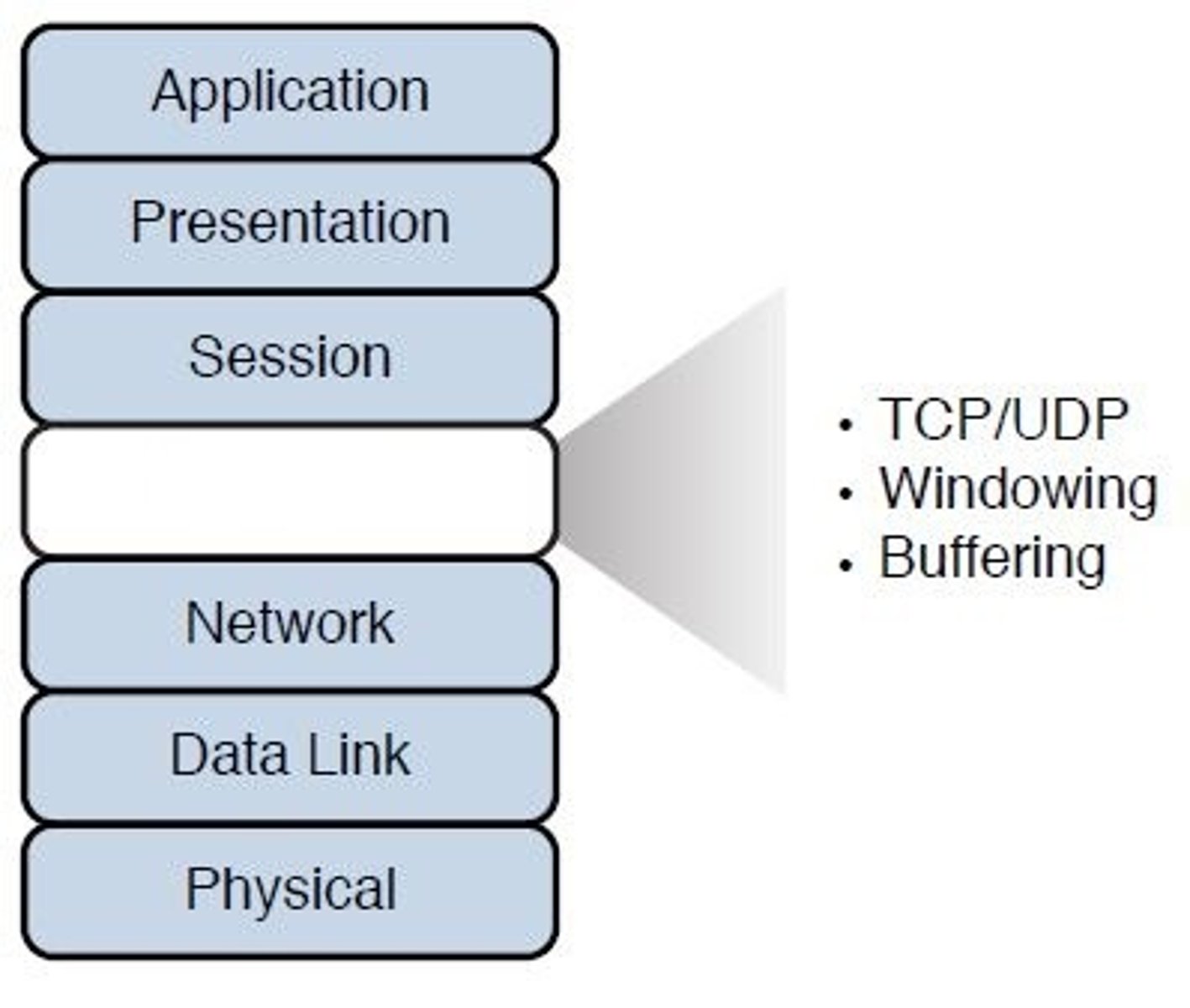
Layer 4 - Transport:
The functions defined in this layer provide for the reliable transmission of data segments, as well as the disassembly and assembly of the data before and after transmission.
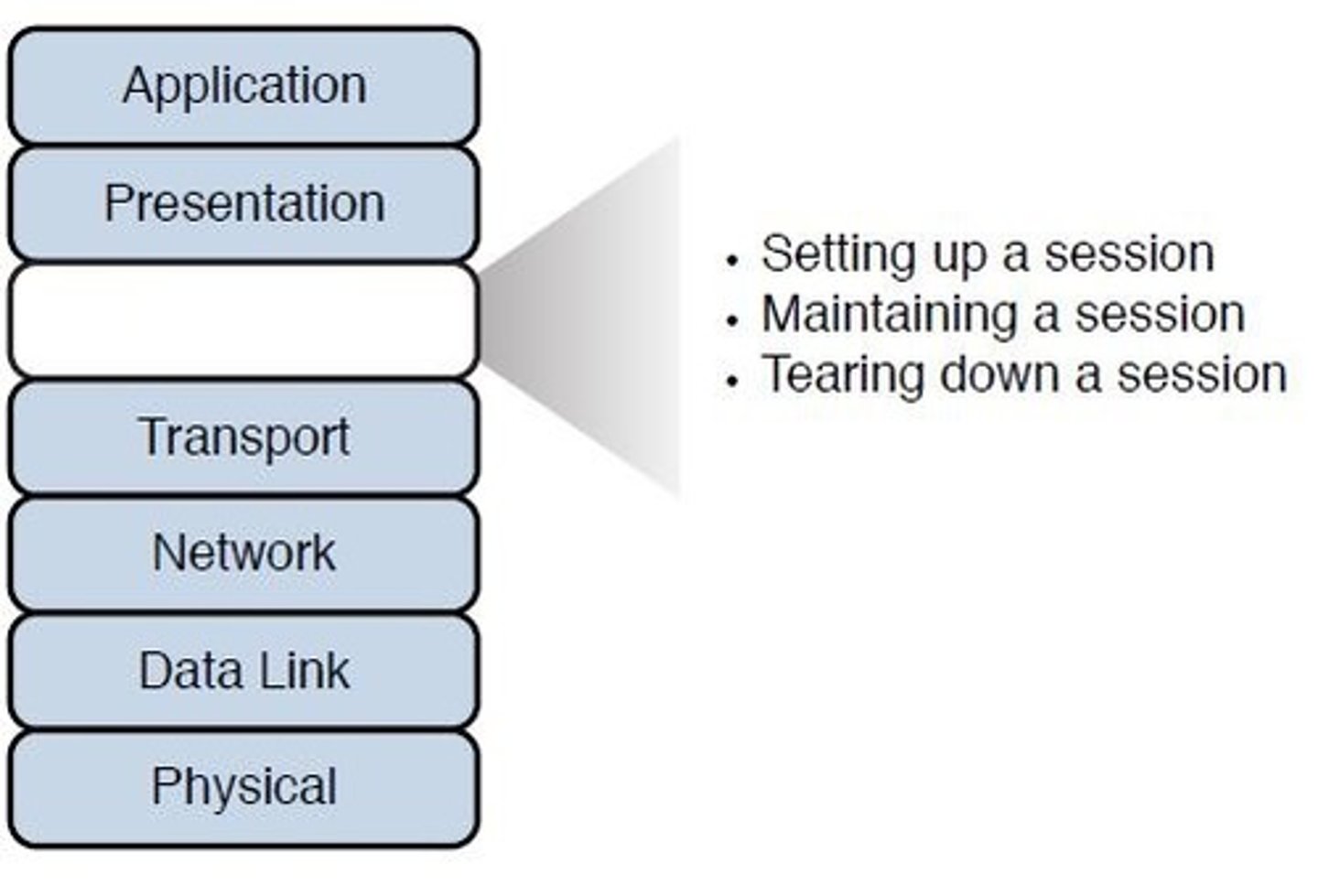
Layer 5 - Session:
- Establishes, manages, and terminates sessions between two communicating hosts.
- Synchronizes dialog between the presentation layers of the two hosts and manages their data exchange.
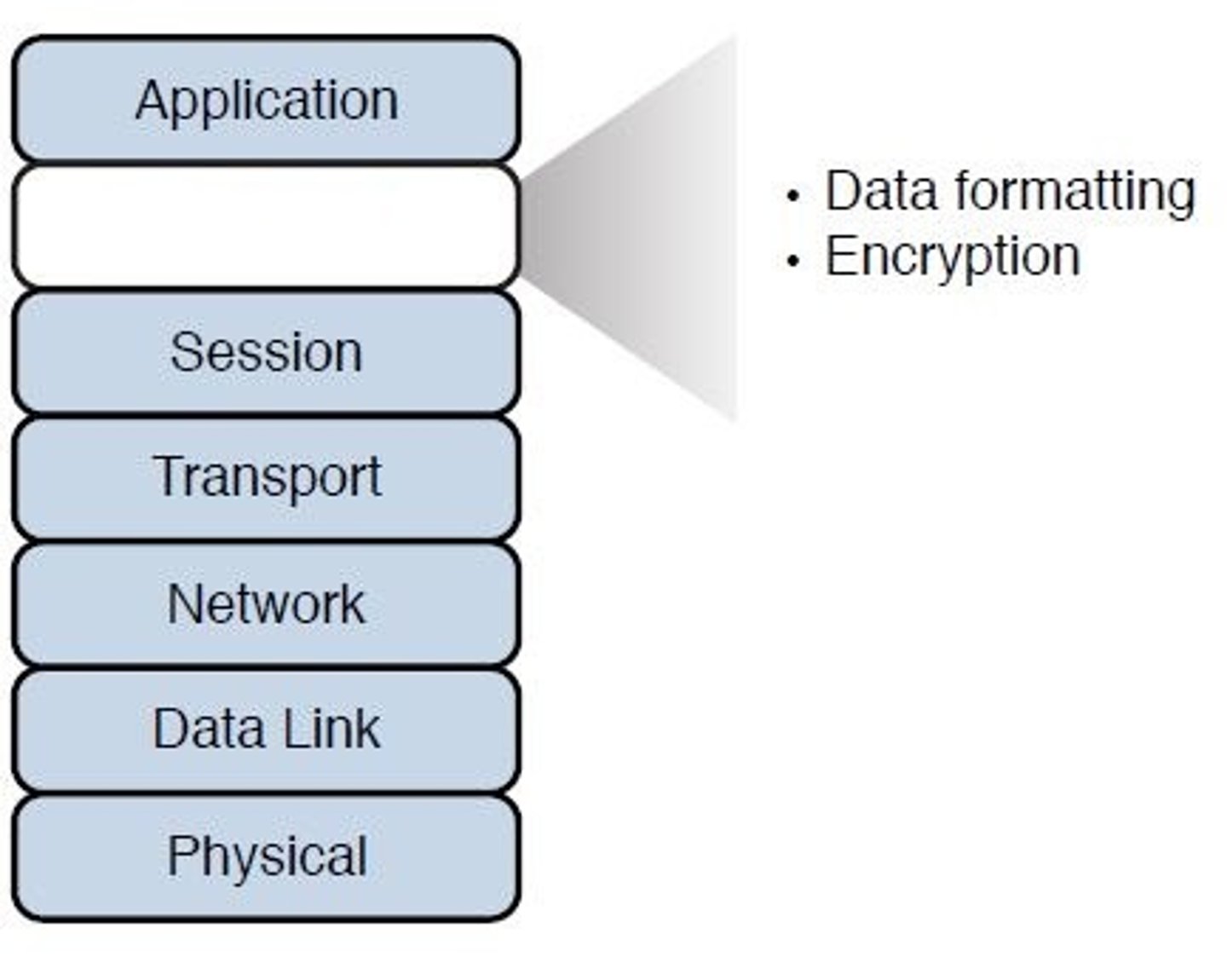
Layer 6 - Presentation:
- Ensures that info sent at application layer of one system is readable by the application layer of another system.
- May translate between multiple data formats by using a common format.
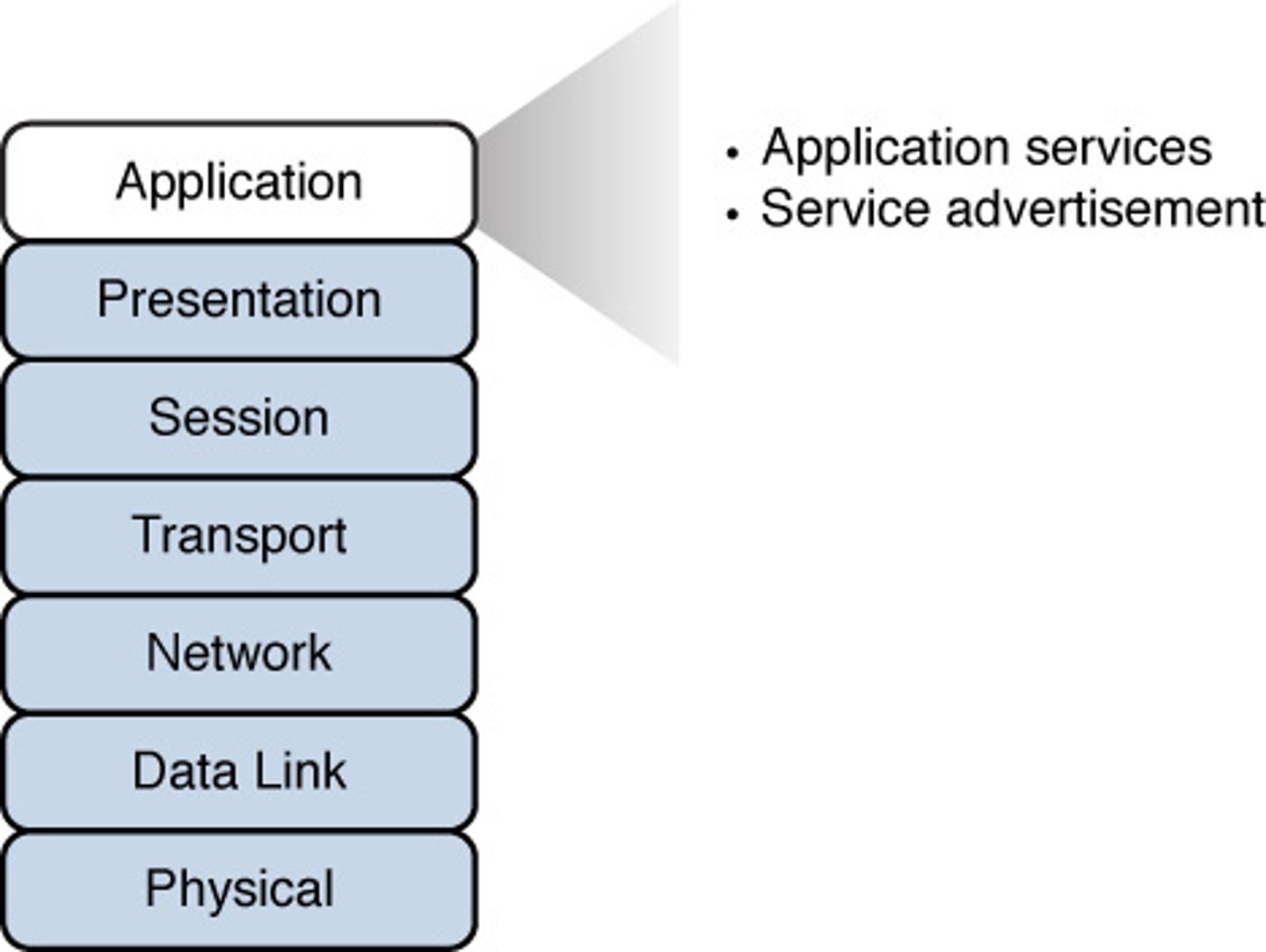
Layer 7 - Application:
- Closest to the user.
- Provides network services to the applications of the user, such as email, file transfer, and terminal emulation.
Router:
A device that forwards data packets between computer networks.

Switch:
A computer networking device that connects network segments.

Firewall:
A part of a computer system or network that is designed to block unauthorized access while permitting outward communication.
Intrusion detection system (IDS):
Monitors network traffic to identify possible malicious activity and log information about it.
Intrusion prevention system (IPS):
Sits behind the firewall and uses anomaly detection or signature-based detection to identify and respond to network threats.
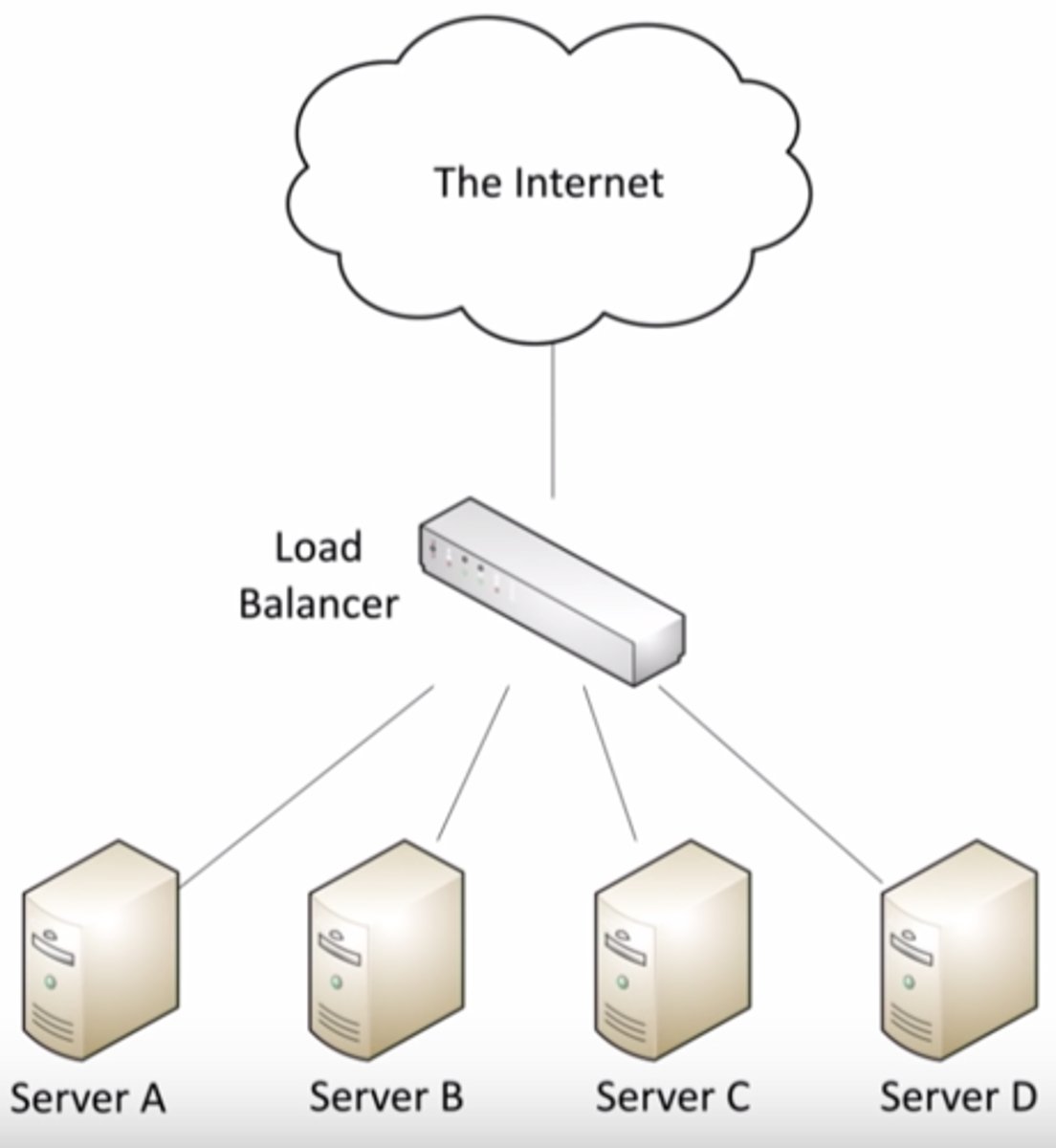
Load Balancer:
Hardware or software that balances the load between two or more servers.
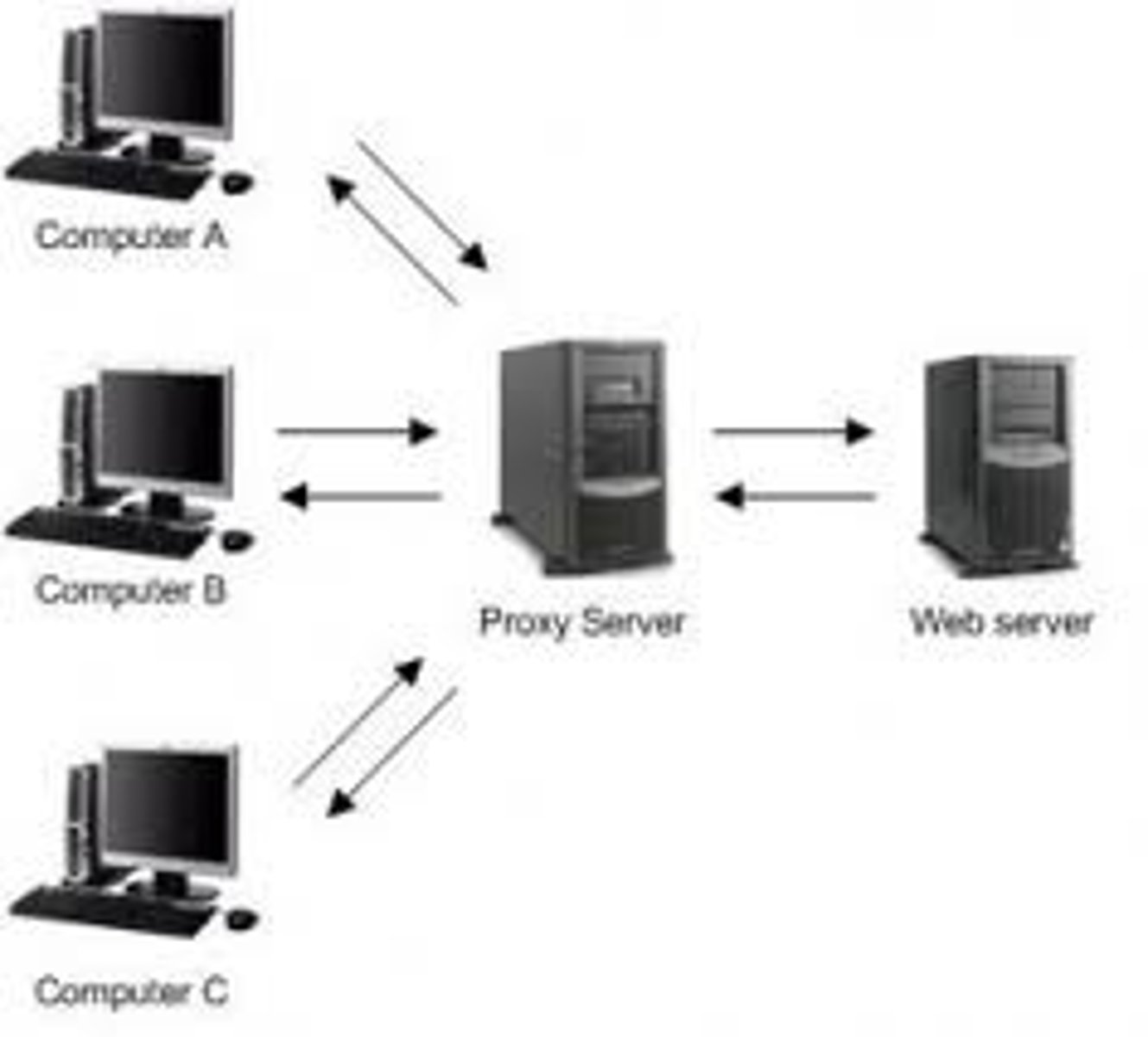
Proxy:
A system or router that provides a gateway between users and the internet.
Network-attached storage (NAS):
A server that is placed on a network with the sole purpose of providing storage to users, computers, and devices attached to the network.

Storage area network (SAN):
A high-speed network with the sole purpose of providing storage to other attached servers.
Wireless Access point (AP):
A device that enables wireless systems to communicate with each other, provided that they are on the same network.
Wireless Controller:
A central management console for all of the APs on a network.
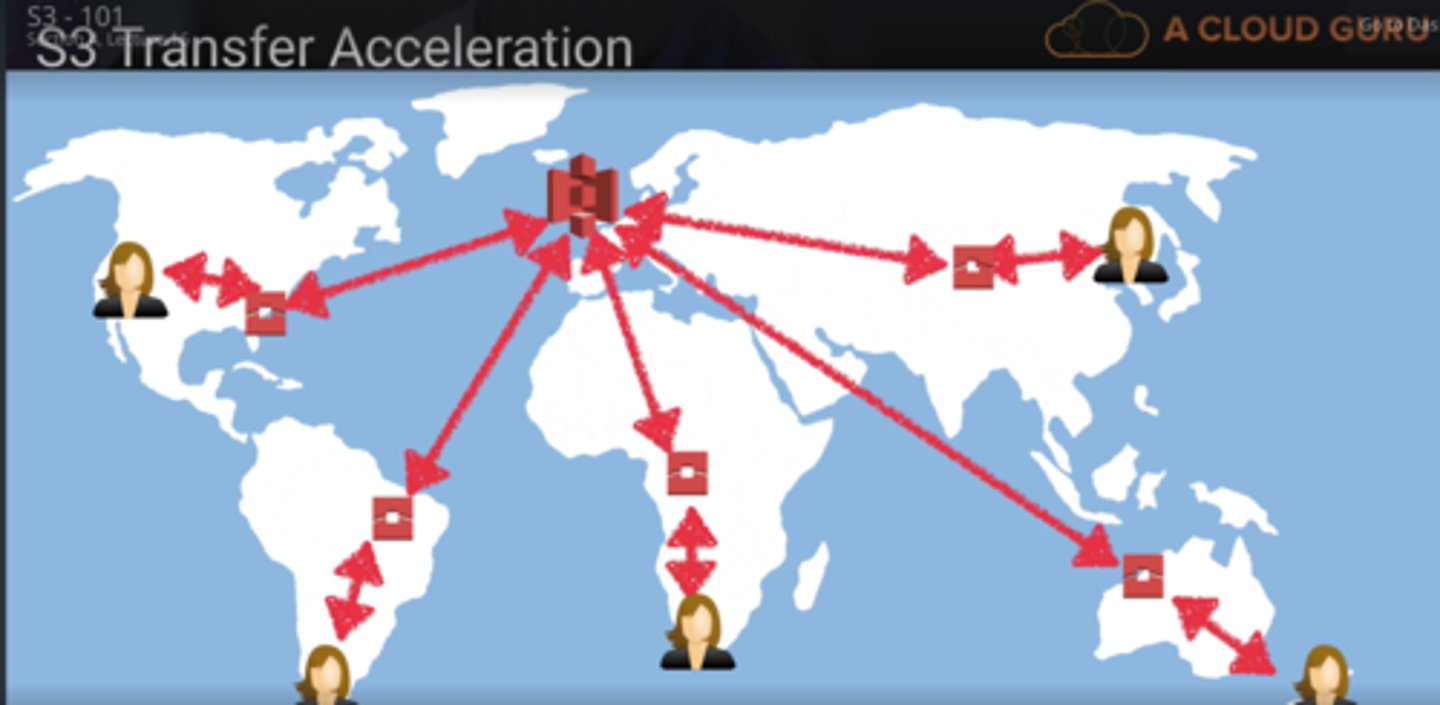
Content delivery network (CDN):
- An information system that serves content to Web pages over the Internet.
- To reduce wait time, data is typically stored and served from many geographic locations.
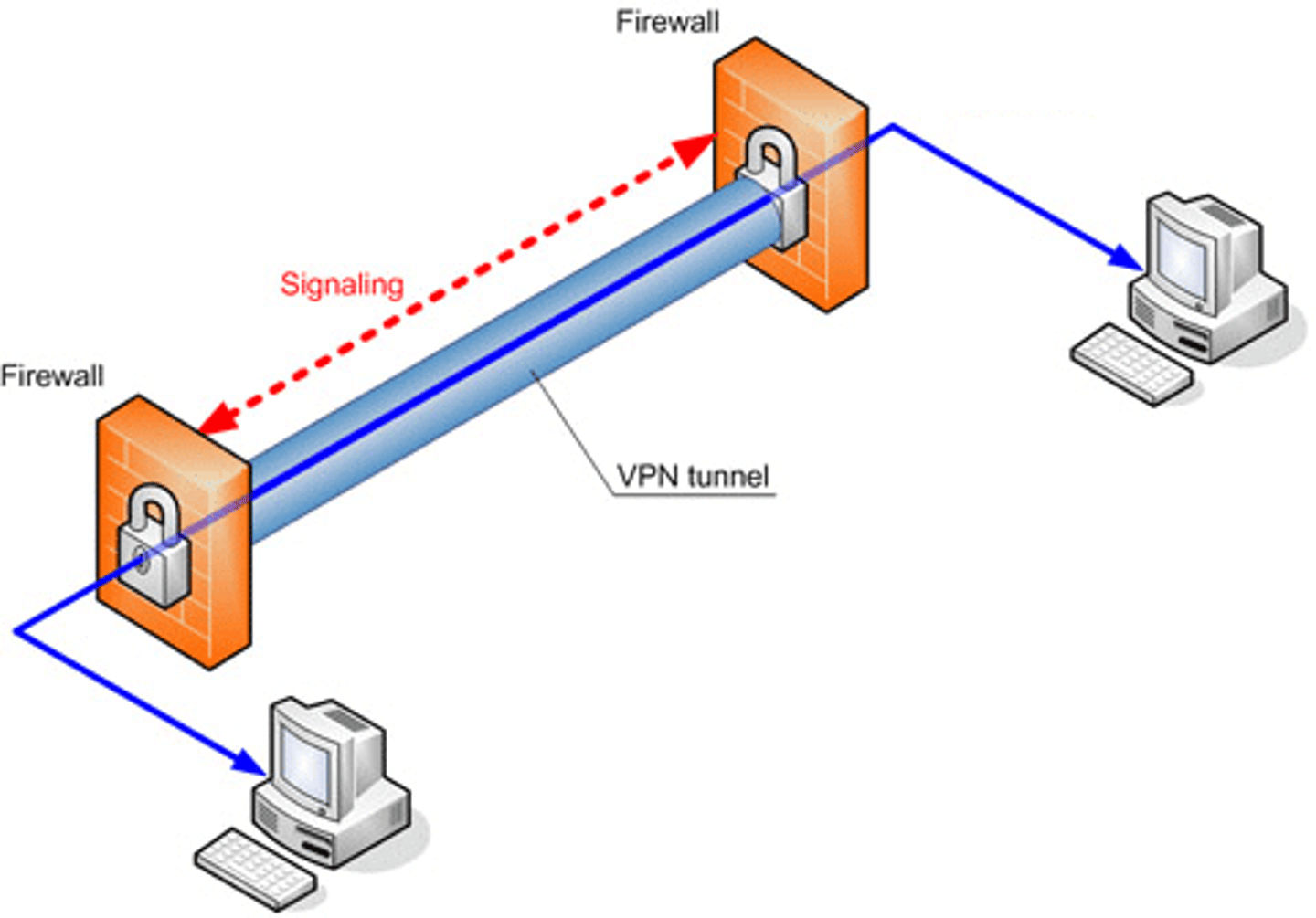
Virtual private network (VPN):
A private data network that creates secure connections, or "tunnels," over regular Internet lines.
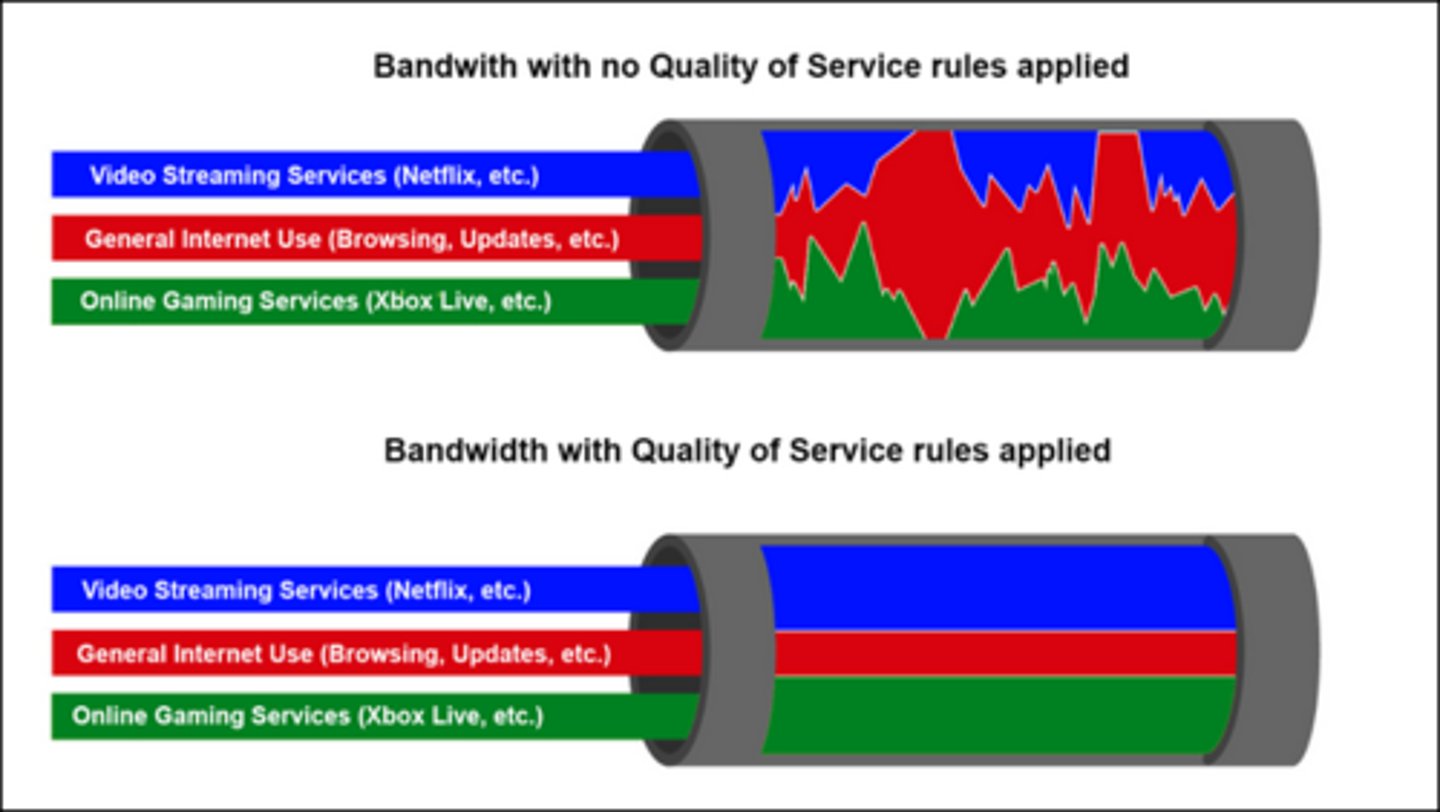
Quality of service (QoS):
Policies that control how much bandwidth a protocol, PC, user, VLAN, or IP address may use.
Time to live (TTL):
The maximum amount of time a packet is allowed to circulate through a network before it is destroyed.
Network functions virtualization (NFV):
Provisioning virtual network appliances, such as switches, routers, and firewalls, via VMs and containers.
Virtual private cloud (VPC):
A private network segment made available to a single cloud consumer within a public cloud.
Network security groups:
Allows you to filter network traffic. Can contain multiple inbound and outbound security rules that enable you to filter traffic to and from resources.
Network security lists:
Consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to all the VNICs in any subnet that the list is associated with.
Internet gateway:
A device or node that connects networks by translating protocols.
Network address translation (NAT) gateway:
You can use this so that instances in a private subnet can connect to services outside your VPC, but external services cannot initiate a connection with those instances.
Public cloud:
Provides cloud services to just about anyone.
Private cloud:
Serves only one customer or organization and can be located on the customer's premises or off the customer's premises.
Hybrid cloud:
A mixed computing environment where applications are run using a combination of computing, storage, and services in different environments.
Software as a service (SaaS):
A form of cloud computing where a firm subscribes to a third-party software and receives a service that is delivered online.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS):
Delivers hardware networking capabilities, including the use of servers, networking, and storage, over the cloud using a pay-per-use revenue model.
Platform as a service (PaaS):
Supports the deployment of entire systems including hardware, networking, and applications using a pay-per-use revenue model.
Scalability:
Refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands.
Elasticity:
Refers to the ability of a cloud to automatically expand or compress the infrastructural resources on a sudden up and down.
Multitenancy:
A single instance of a system serves multiple customers.
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP):
- An IP network protocol used to determine if a particular service or host is available.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP):
A protocol for sending packets that does error-checking to ensure all packets are received and properly ordered.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP):
A protocol for sending packets quickly with minimal error-checking and no resending of dropped packets.
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE):
Method of encapsulation of IP packet in a GRE header which hides the original IP packet.
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec):
A set of protocols developed to support the secure exchange of packets between hosts or networks.
Authentication Header (AH):
An IPsec protocol that authenticates that packets received were sent from the source identified in the header of the packet.
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP):
An IPsec protocol that provides authentication, integrity, and encryption services.
Internet Key Exchange (IKE):
Method used by IPSec to create a secure tunnel by encrypting the connection between authenticated peers.
Unicast:
A form of message delivery in which a message is delivered to a single destination.
Multicast:
A form of transmission in which a message is delivered to a group of hosts.
Anycast:
A network addressing and routing method in which incoming requests can be routed to a variety of different locations or "nodes."
Broadcast:
Used to transmit a message to any reachable destination in the network without the need to know any information about the receiving party.
Frequency bands used by 802.11 networks include:
- 5.0 GHz.
- 2.4 GHz.
IEEE 802.11a wireless standard:
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 54 Mbps.
IEEE 802.11b wireless standard:
- 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 11 Mbps.
IEEE 802.11g wireless standard:
- 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 54 Mbps.
IEEE 802.11n wireless standard:
- 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 600 Mbps.
- Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MIMO).
IEEE 802.11ac (WiFi 5) wireless standard:
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 6.933 Gbps.
- Multi-User Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
IEEE 802.11ax (WiFi 6) wireless standard:
- 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 9.607 Gbps.
- Multi-User Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
Refers to directional antenna types suitable for long-range point-to-point bridging links?
- Yagi antenna.
- Dish antenna.
- Parabolic antenna.
Cellular:
- Radio network distributed over land through cells where each cell includes a fixed location transceiver known as base station.
- These cells together provide radio coverage over larger geographical areas.
IEEE 802.3af:
PoE (Power over Ethernet).
IEEE 802.3at:
PoE+.
IEEE 802.3bt:
- PoE++.
- 4PPoE.
Single-mode Fiber (SMF):
- Uses lasers.
- Longer distance and smaller diameter.
- Used in telecom and CATV networks.

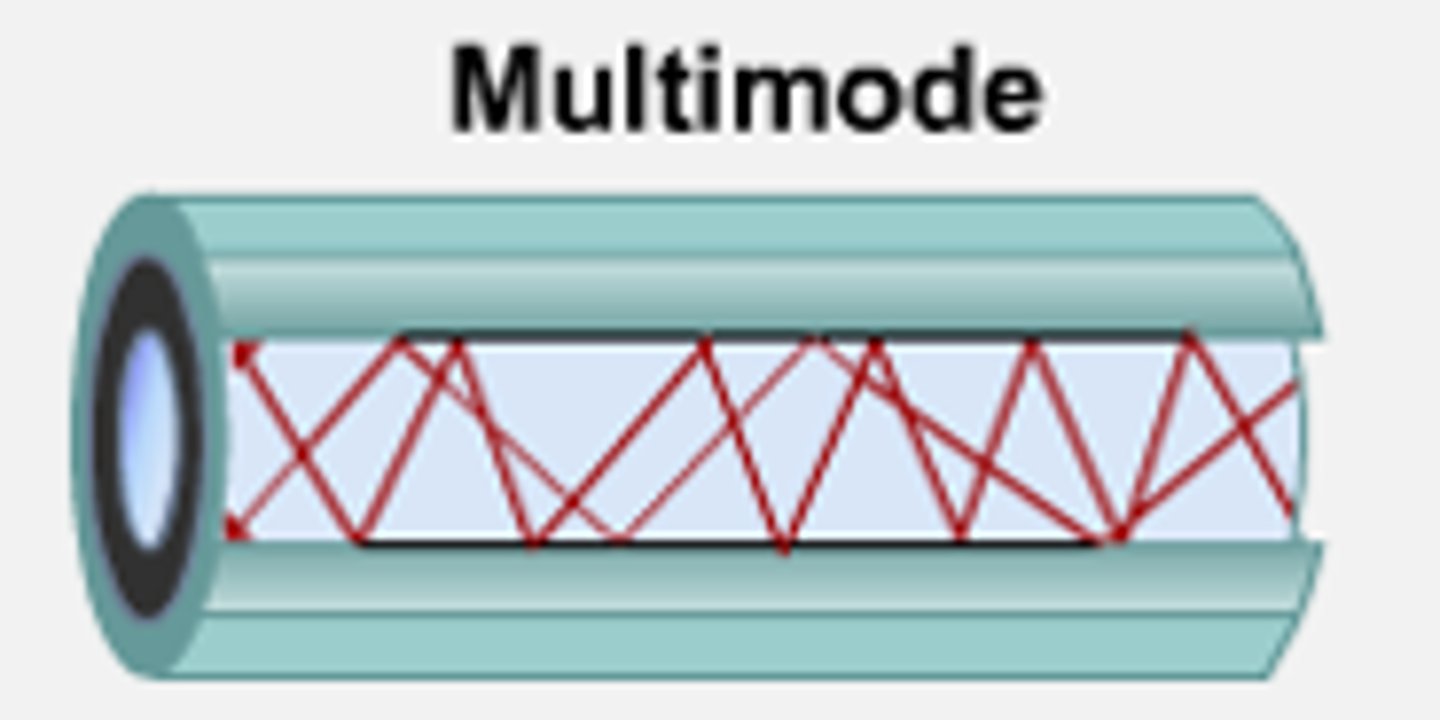
Multimode fiber (MMF):
- Uses LEDs.
- Shorter distance and wider diameter.
- Used in LAN, security systems, and CCTV.
Direct attach copper (DAC) cable:
Allows direct communication between devices over copper wire.

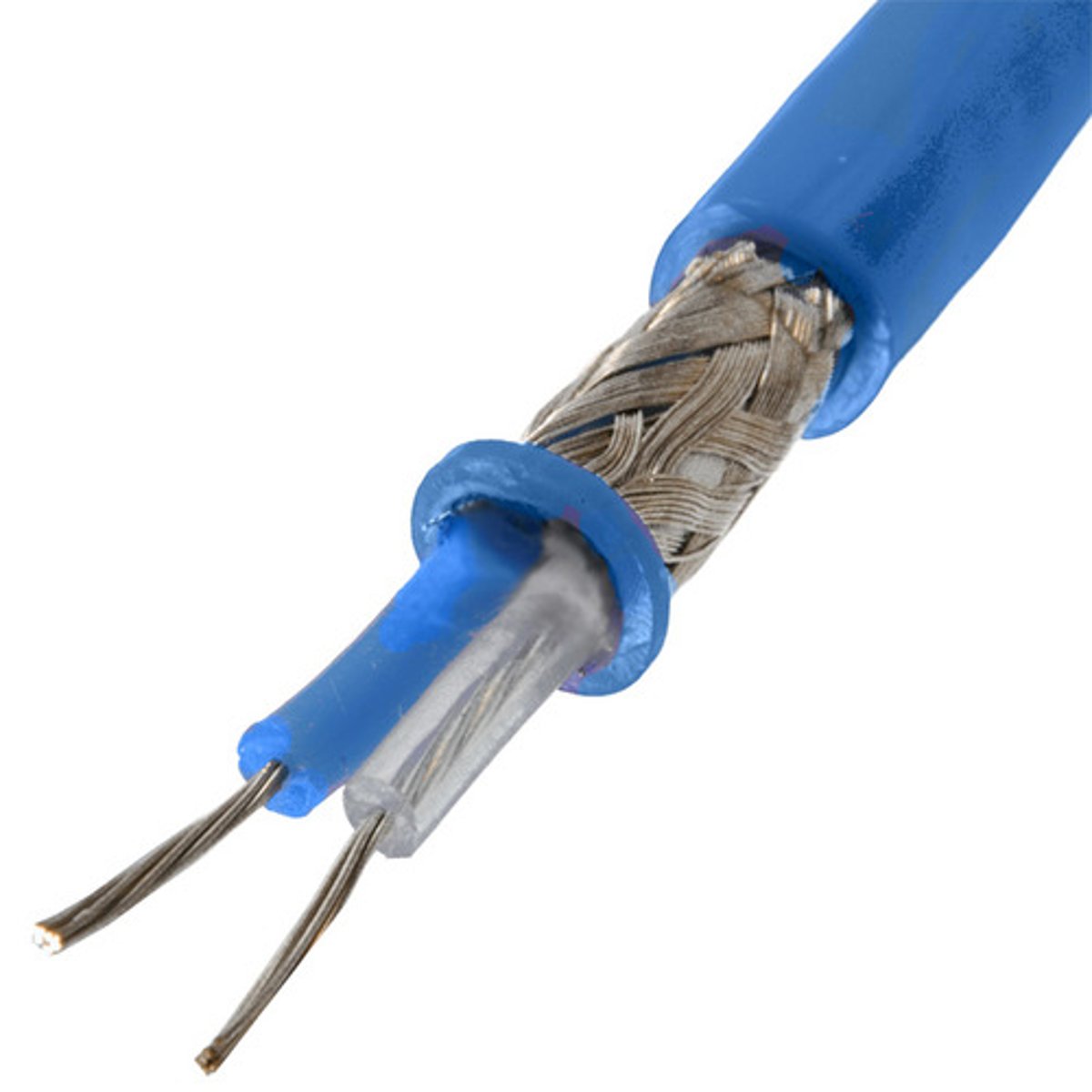
Twinaxial cable:
A variant of coaxial cables, which features two inner conductors instead of one and is used for very-short-range high-speed signals.

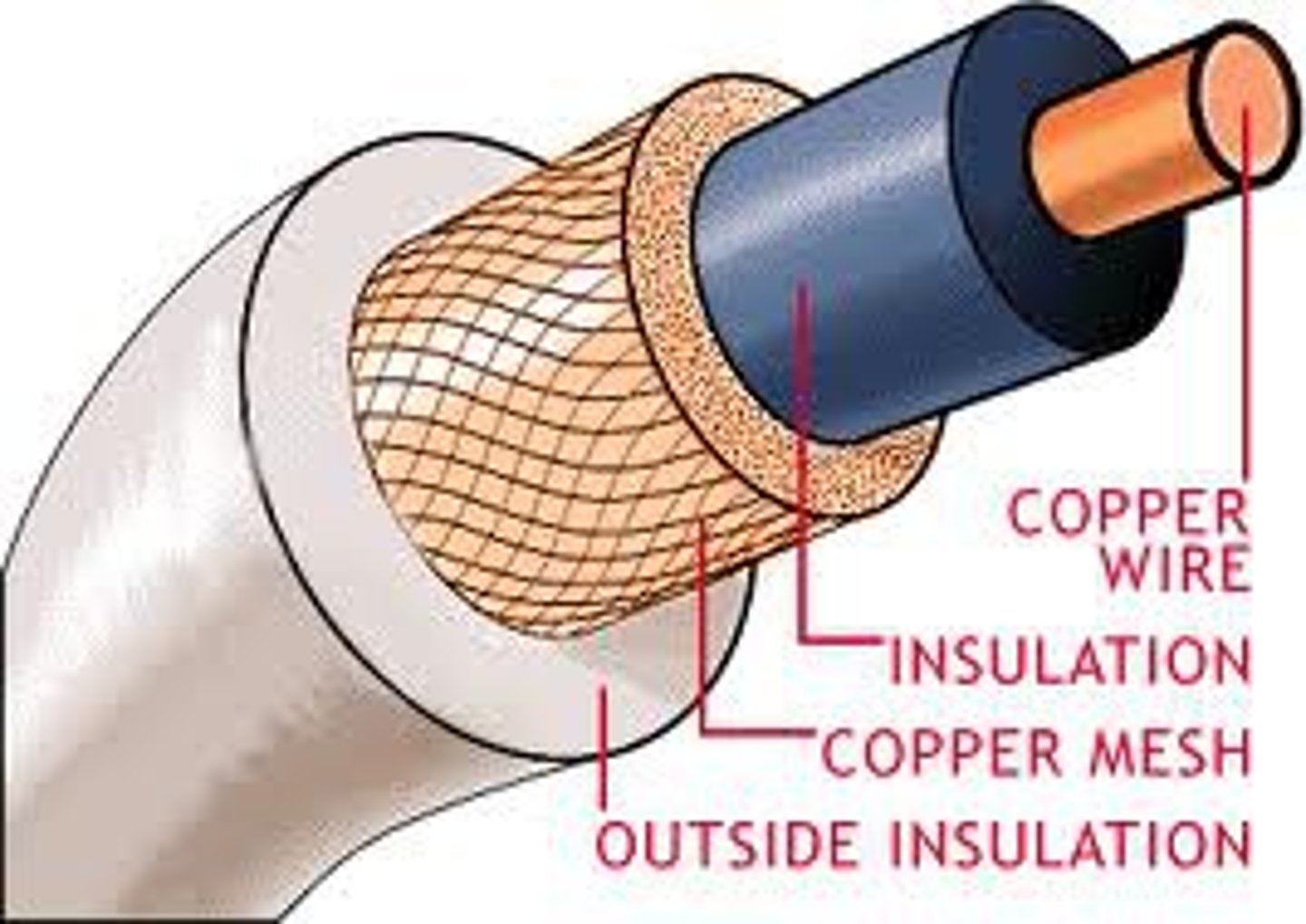
Coaxial cable:
Insulated copper wire; used to carry high-speed data traffic and television signals.
Plenum vs. Non-Plenum Cables:
- Plenum cables are engineered with fire-retardant materials, emitting minimal smoke and toxic fumes in case of fire.
- Non-plenum cables often come at a lower cost than plenum cables.
Ethernet:
A physical and data layer technology for LAN networking.
Protocol:
A set of rules governing the exchange or transmission of data between devices.
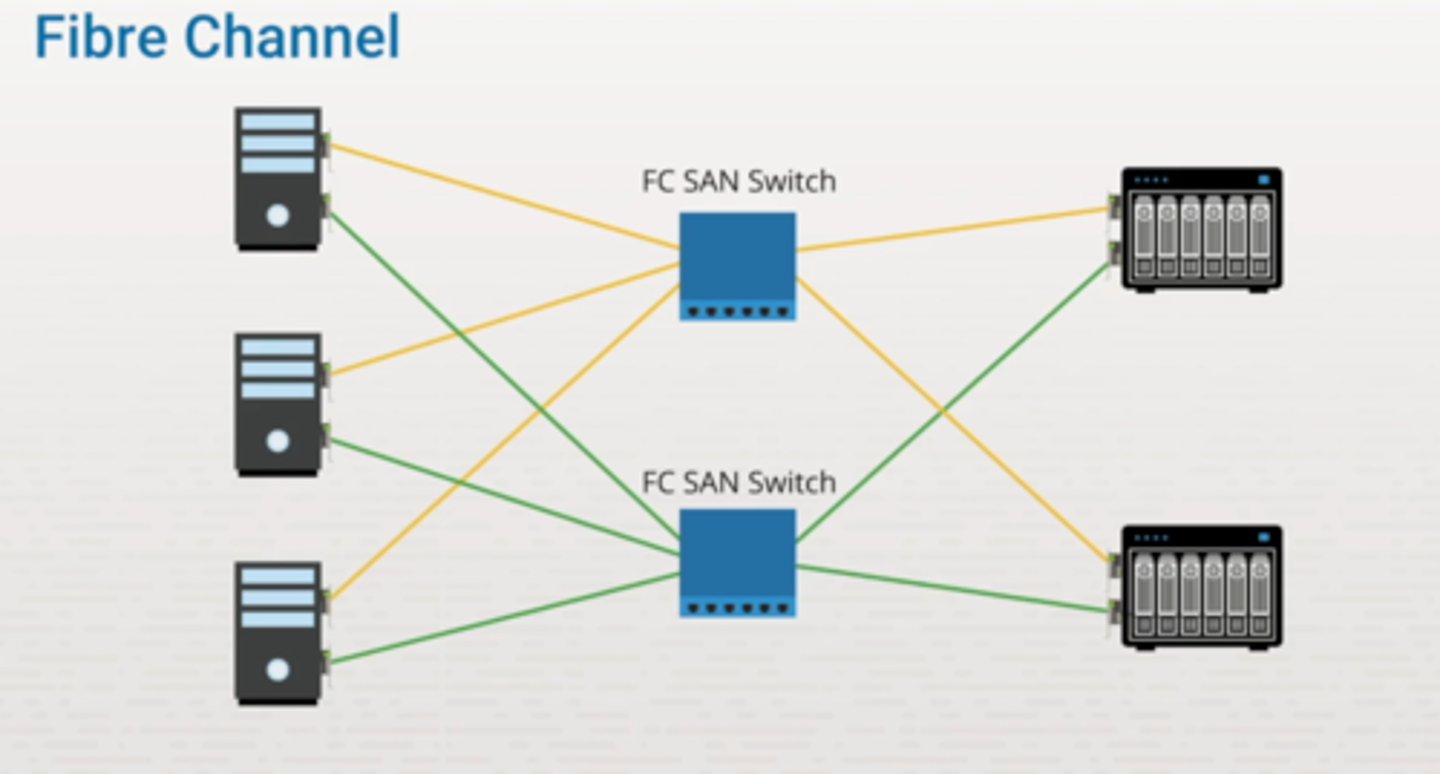
Fibre Channel (FC):
- A high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data.
- Primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.
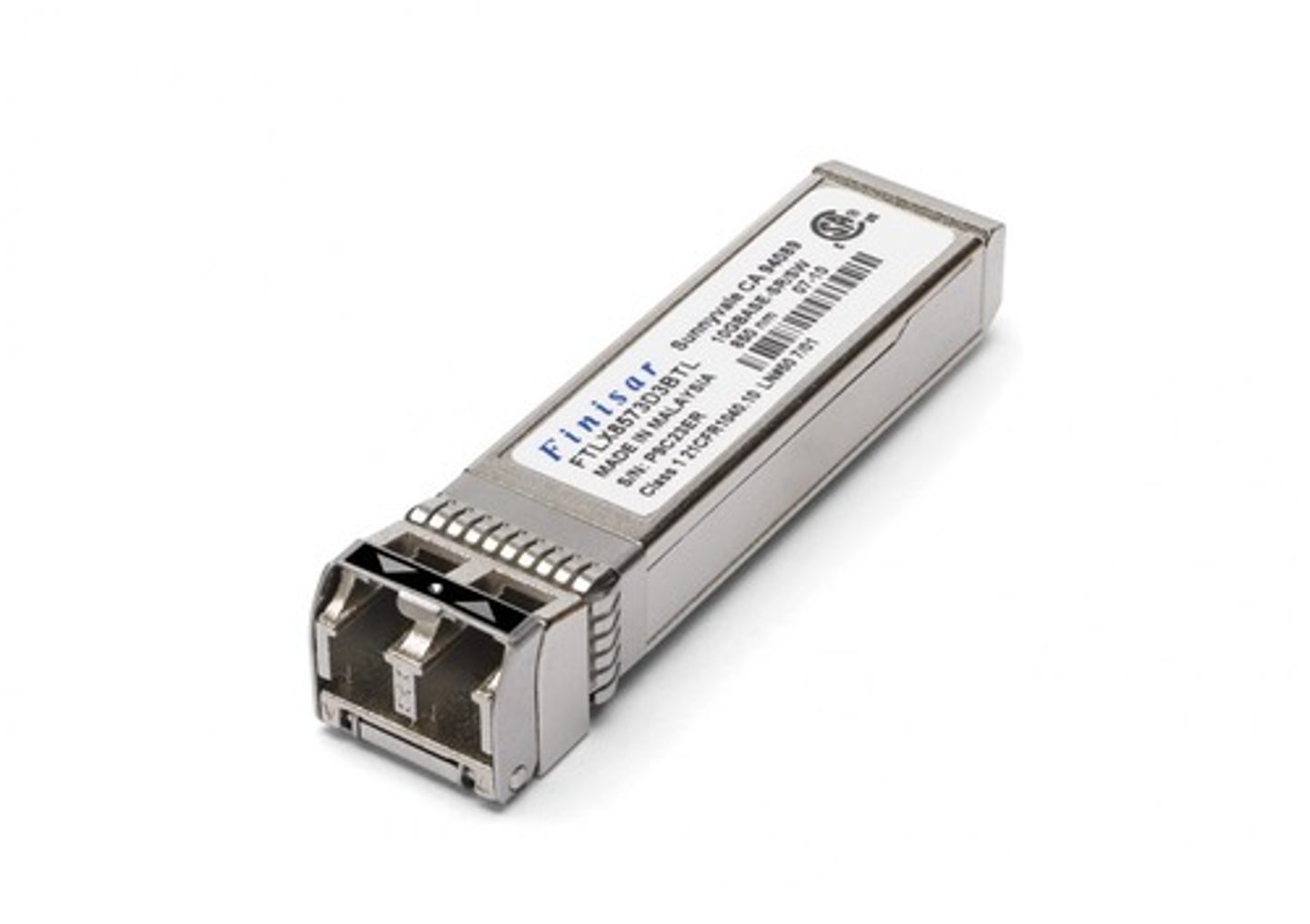
Small form-factor pluggable (SFP):
Fiber optic transceiver module type supporting duplex 1 Gbps (SFP) or 10 Gbps (SFP+) links.

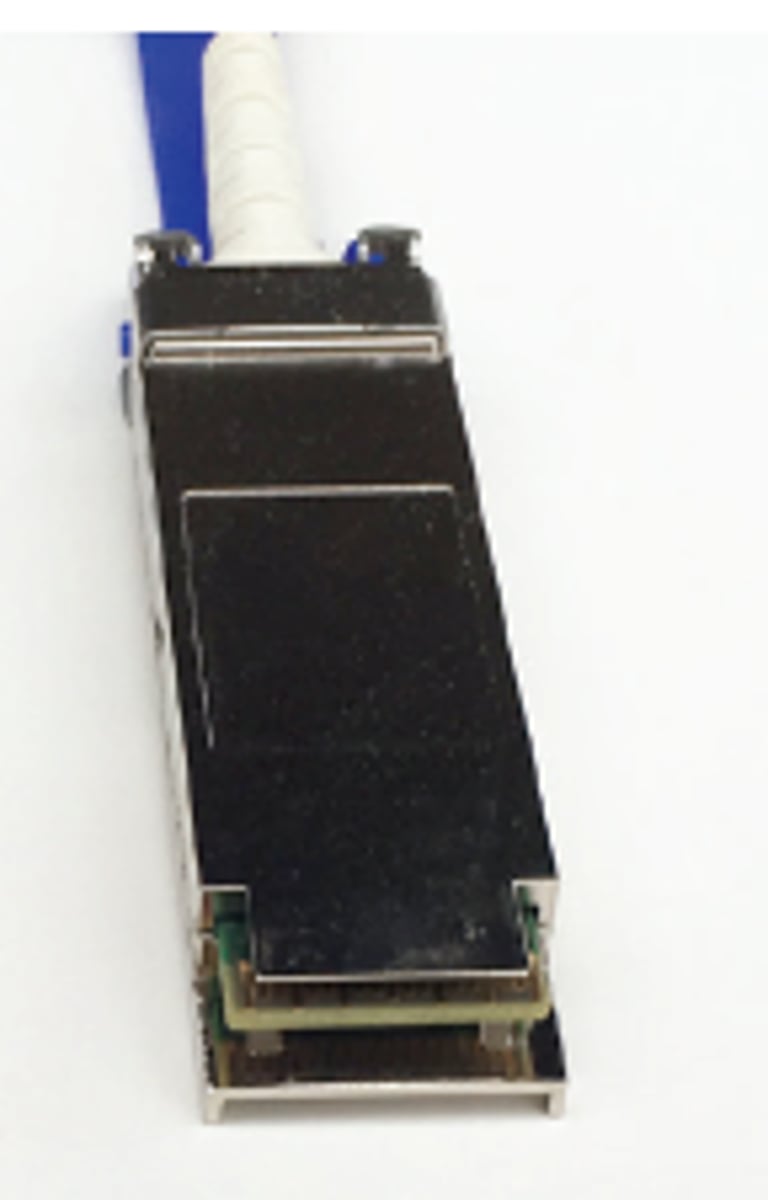
Quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP):
- Small, high-density pluggable interface used for high-speed data transmission.
- It connects between network devices and fiber optic or copper cables, providing multiple channels for simultaneous data transmission.

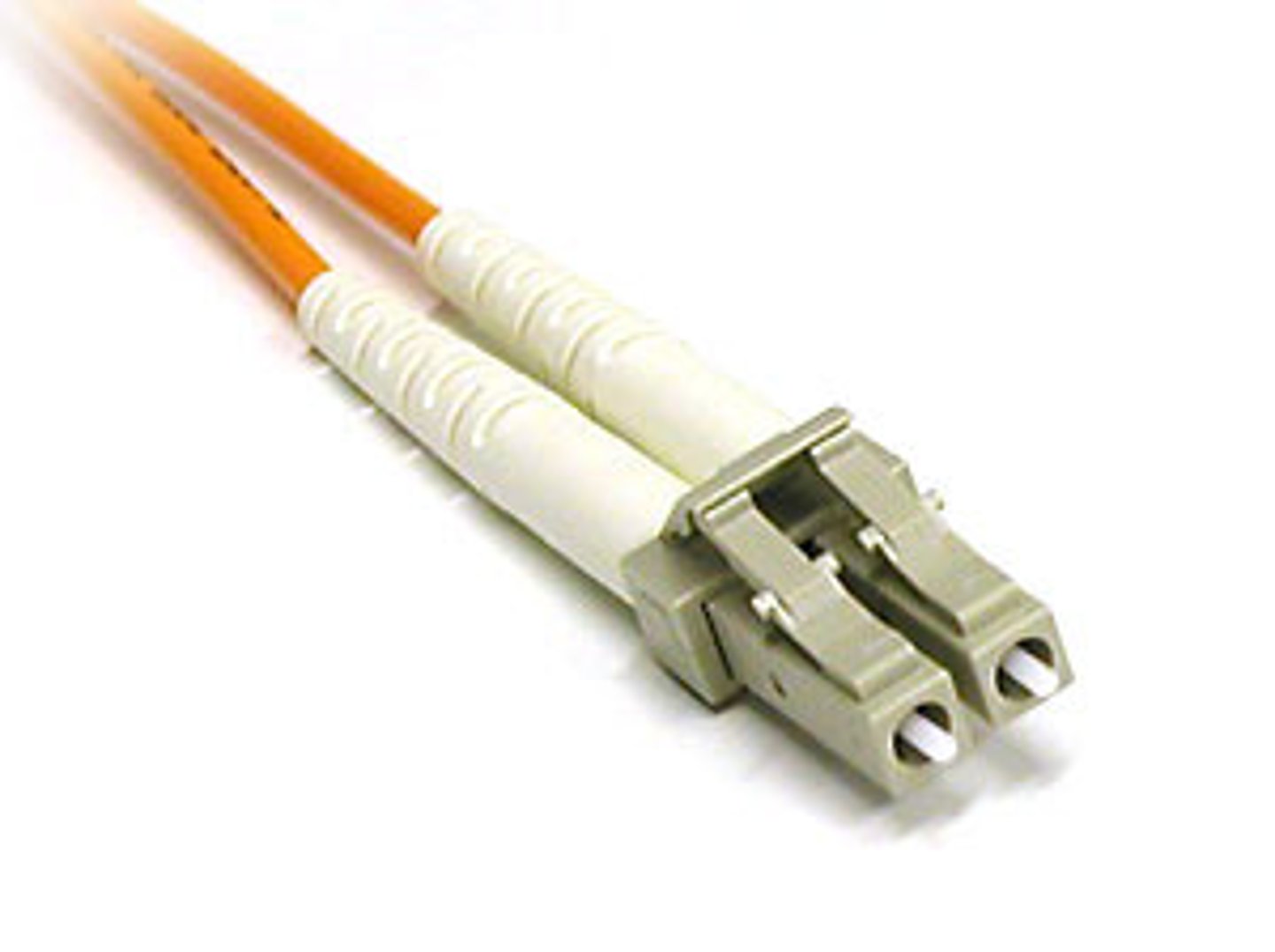
Local Connector (LC):
Fiber-optic cable connector that corresponds to the mini form-factor standard.

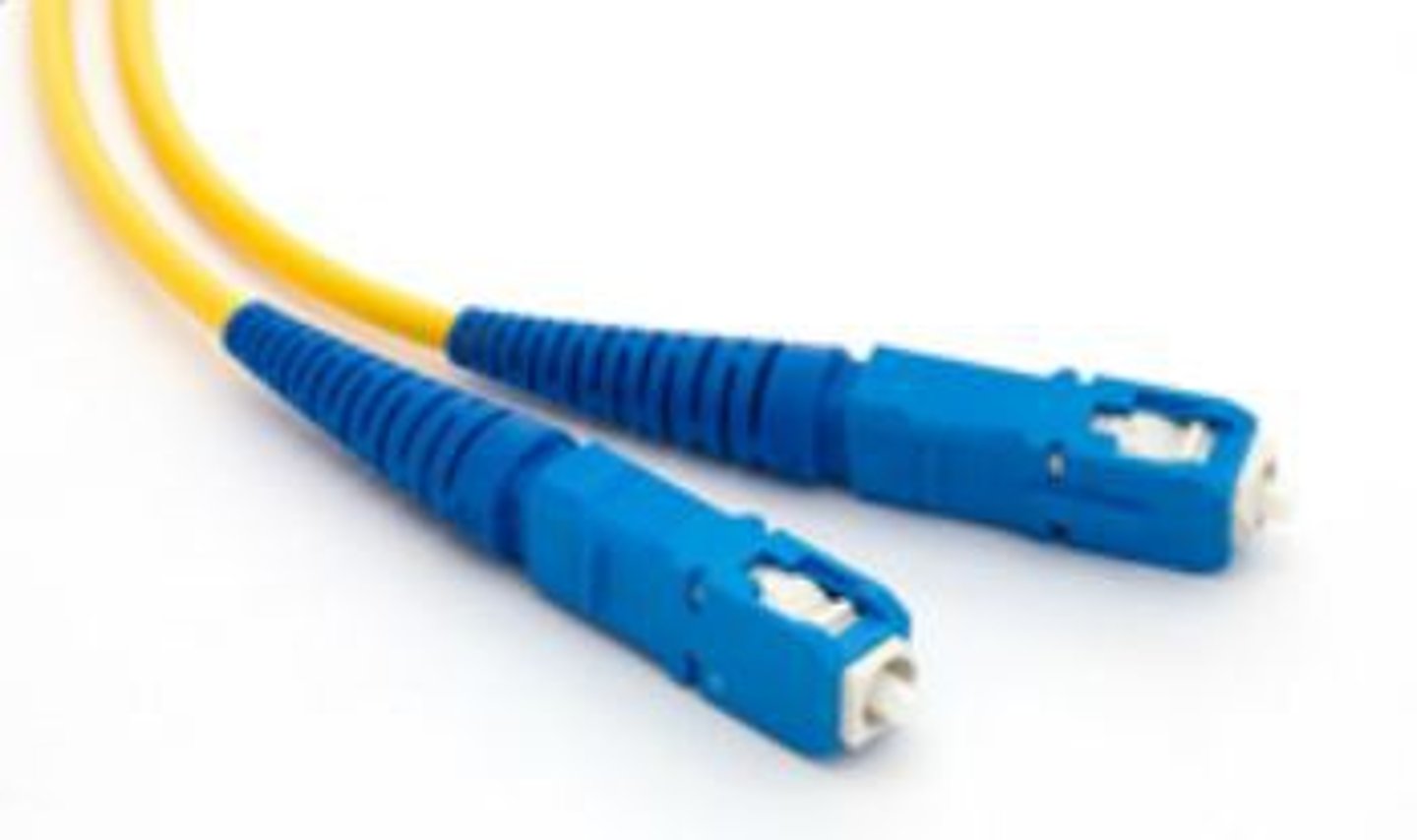
Subscriber connector (SC):
Push/pull connector used with fiber optic cabling.

Straight tip (ST):
Bayonet-style twist-and-lock connector for fiber optic cabling.

Multi-fiber push on (MPO):
Accommodates multiple fibers in a single physical connector interface.

Registered jack (RJ) 11:
Connector wired for one telephone line.

RJ45:
A common connector or plug used on the end of the network cable.

F-type:
Used with Coaxial Cabling.
Mesh Topology:
Every computer connects to every other computer; no central connecting device is needed.
Hybrid Topology:
A physical topology that combines characteristics of more than one simple physical topology.
Star/hub and spoke:
A network topology where all devices are connected to a central hub or switch, which manages the data flow between them.
Spine and leaf:
A newer network topology that consists of just two layers.
Point to point:
A data transmission that involves one transmitter and one receiver.
Three-Tier Hierarchical Model:
- Access layer: Provides access points for hosts to connect to the network.
- Distribution layer: Acts as an intermediary between the Core Layer and the Access Layer, and keeps local traffic confined to local networks.
- Core layer: Handles and transports huge amounts of data quickly and reliably and connects multiple end networks together.
Collapsed core:
A network design where the core and distribution layers are collapsed or combined into a single layer of switches.
North-south traffic flow:
Data transmission pattern that describes data flow between local network endpoints and external networks and services, such as the World Wide Web, cloud services, etc.
East-west traffic flow:
Transfer of data packets from server to server within a data center.
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA):
A networking feature in operating systems that enables DHCP clients to self-configure an IP address and subnet mask automatically when a DHCP server isn't available.
RFC1918:
Defined the 3 ranges of private IPv4 Addresses:
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 /8
- 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 /16
- 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 /32
Loopback/localhost:
- Used to test the IP stack on the local computer.
- Can be any address from 127.0.0.1 through 127.255.255.254.
Public vs. private network:
- Public networks are "open" access networks prioritizing accessibility and availability over network performance and security.
- Private networks are "closed" and secure networks prioritizing network safety, confidentiality, and performance over accessibility and ease of use.
Subnetting:
The act of dividing a network into smaller logical subnetworks.
Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM):
- The capability to specify a different subnet mask for the same Class A, B, or C network number on different subnets.
- VLSM can help optimize available address space.
Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR):
- Allows network administrators to expand the number of network nodes assigned to an IP address.
- Based on the idea that IP addresses can be allocated and routed based on their network prefix rather than their class.
Class A IPv4:
1.x.x.x to 126.x.x.x
Class B IPv4:
128.x.x.x - 191.x.x.x
Class C IPv4:
192.x.x.x - 223.x.x.x
Class D IPv4:
224.x.x.x - 239.x.x.x
Class E IPv4:
240.x.x.x - 255.x.x.x