Topic 6 Rate of reaction
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What must happen for a reaction to occur?
Particles must have enough energy and collide.
Activation energy
The minimum energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
4 Factors that affect the rate of reaction
Temperature
Concentration/Pressure of gas
Surface area
Catalysts
Explain how temperature affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing temperature means that:
The average kinetic energy of particles increases.
A larger proportion of particles will have more energy than the activation energy.
Particles move more quickly,
so the frequency of successful collisions increases.
Explain how concentration/pressure of gas affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing concentration/pressure of gas:
increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume,
so the frequency of successful collisions increases.
Explain how surface area affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing surface area:
exposes more reactant particles that can undergo collisions,
so the frequency of successful collisions increases.
Explain how catalysts affect the rate of reaction.
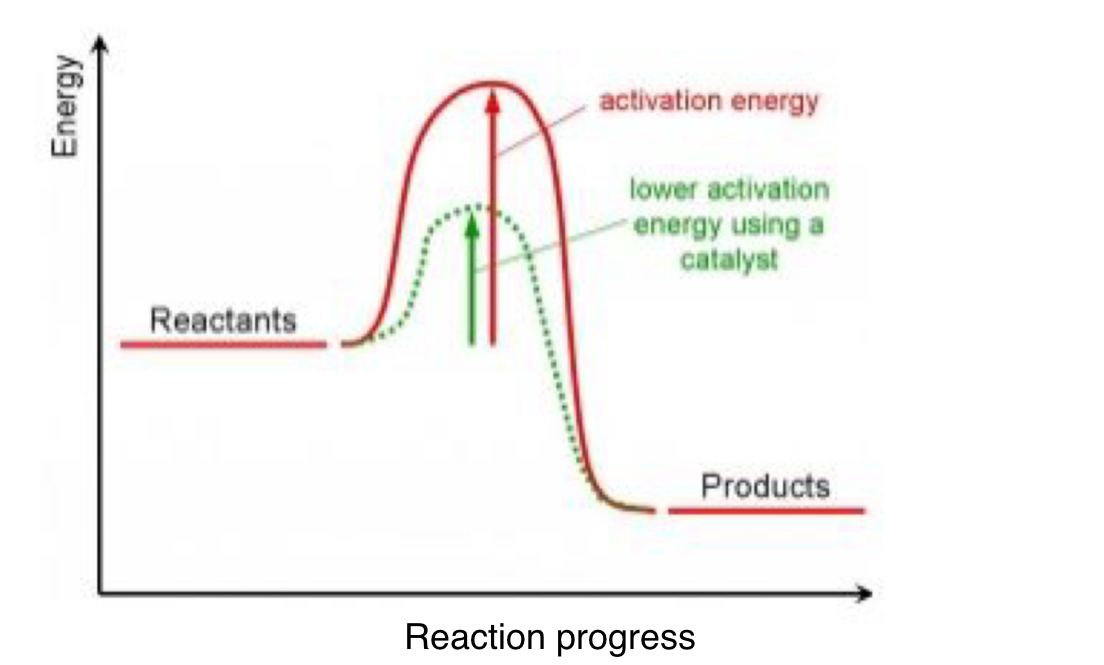
Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy.
As a result, a greater proportion of particles have more energy than activation energy.
Therefore, the frequency of successful collisions increases.
Define the term ‘Catalyst’.
A substance that speeds up the rate of reaction without being changed or used up.
Draw an energy level diagram showing the effect of a catalyst on a exothermic reaction.
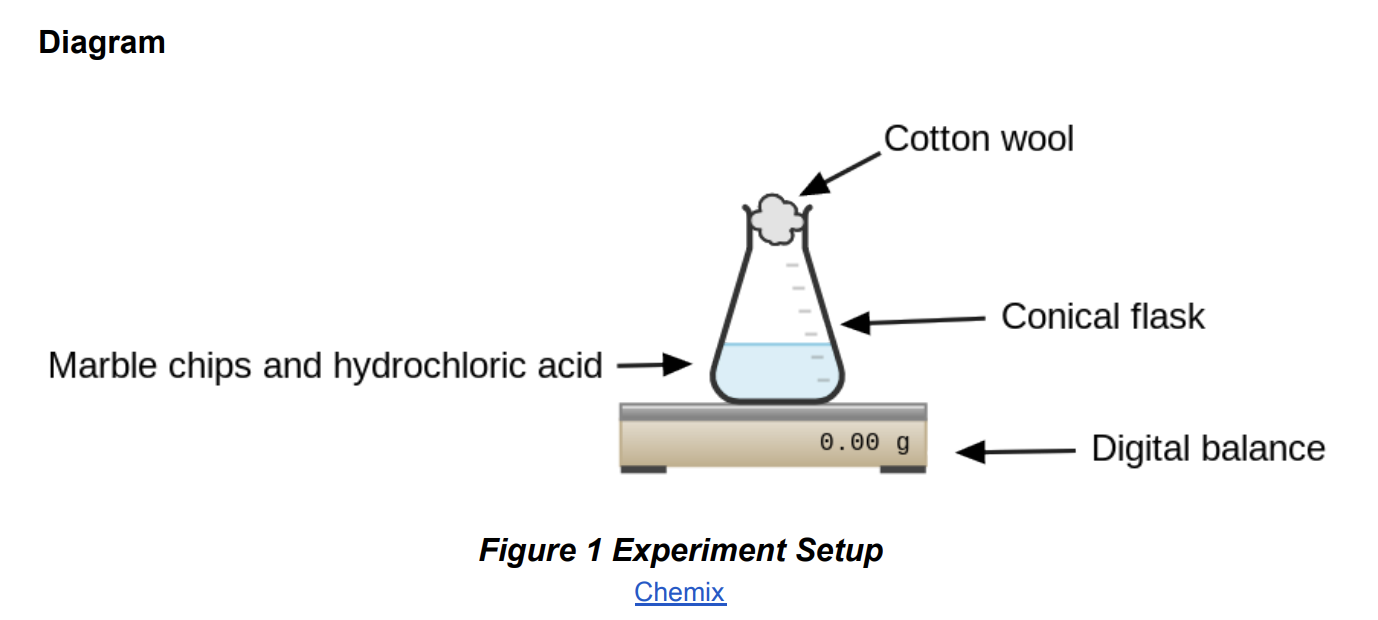
Practical 3.15: Investigate the effect of changing the surface area of marble chips
The change in mass can be used to calculate the rate because:
the carbon dioxide gas produced during the reaction escapes through the cotton wool,
causing the mass of the mixture to decrease.
● The cotton wool allows the gas to escape while preventing any acid splashing out of the flask during the reaction, preventing further decrease of mass.
● Increasing the concentration of the acid should increase the rate of reaction. This is because there are more particles in the same volume so more frequent successful collisions.
● Increasing the surface area of the marble chips should increase the rate of reaction. This is because there are more exposed particles so more frequent successful collisions between reactants.
● The concentration of acid can be changed by mixing known quantities of water with hydrochloric acid to dilute it.(the mass and surface area of the marble chips should be kept the same.)
Why is the rate of reaction the fastest at the beginning?
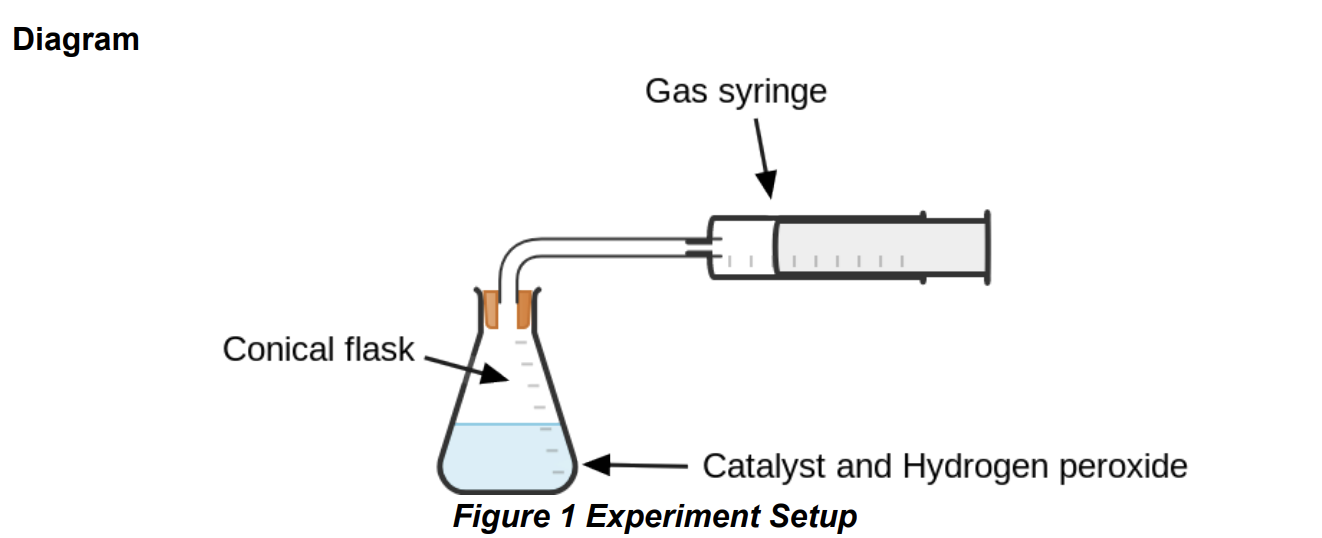
Practical 3.16: Investigate the effect of different solids on the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution
Key points
● Hydrogen peroxide slowly decomposes at room temperature: 2H2O2 (aq) → O2 (g) + 2H2O(l)
● The experiment could be carried out using an upside down measuring cylinder and water trough instead of the gas syringe.
● It is important that the catalysts each have the same mass and a similar surface area so that these factors do not affect the rate of reaction. In the same way, the same volume and concentration of hydrogen peroxide must be used for each experiment.
● The bung must be attached to the conical flask as soon as the catalyst is added to minimise the amount of gas lost at the start of the reaction.