purdue slhs 303 exam 1
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
anatomy
study of the structure and composition of organisms
physiology
a science dealing with the functions of living organisms or their parts and the chemical processes involved
speech
verbal means of communicating
speech is classified by
articulation, voice, fluency
swallowing
acceptance, manipulation, and transportation of food from lips to stomach
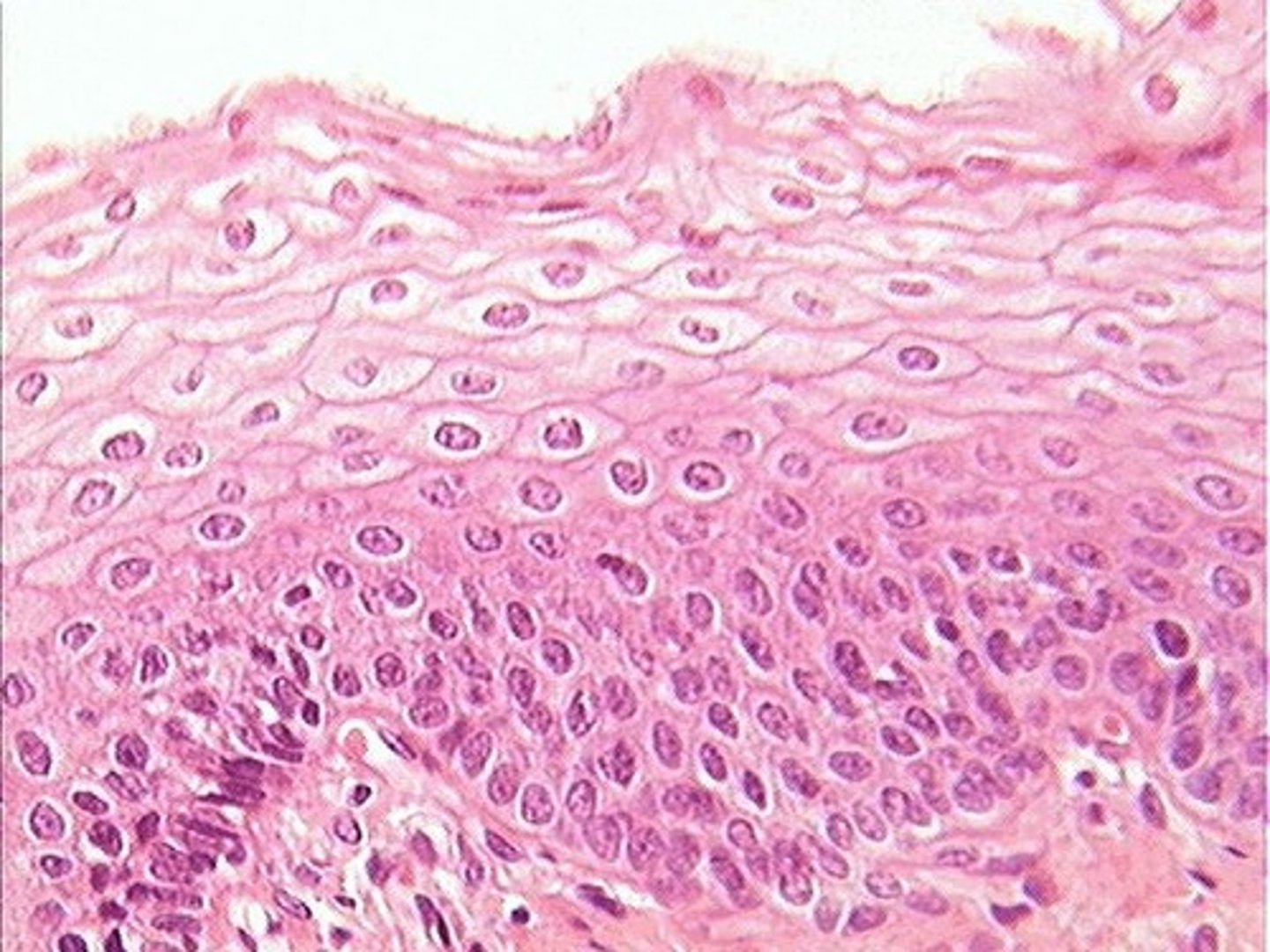
epithelial tissue
-superficial layer of mucous membranes and the cells of our skin
-tightly packed cells: protective quality
-role: provide barrier to some material and serve as sensory elements
-ex. skin, cavities, vocal folds
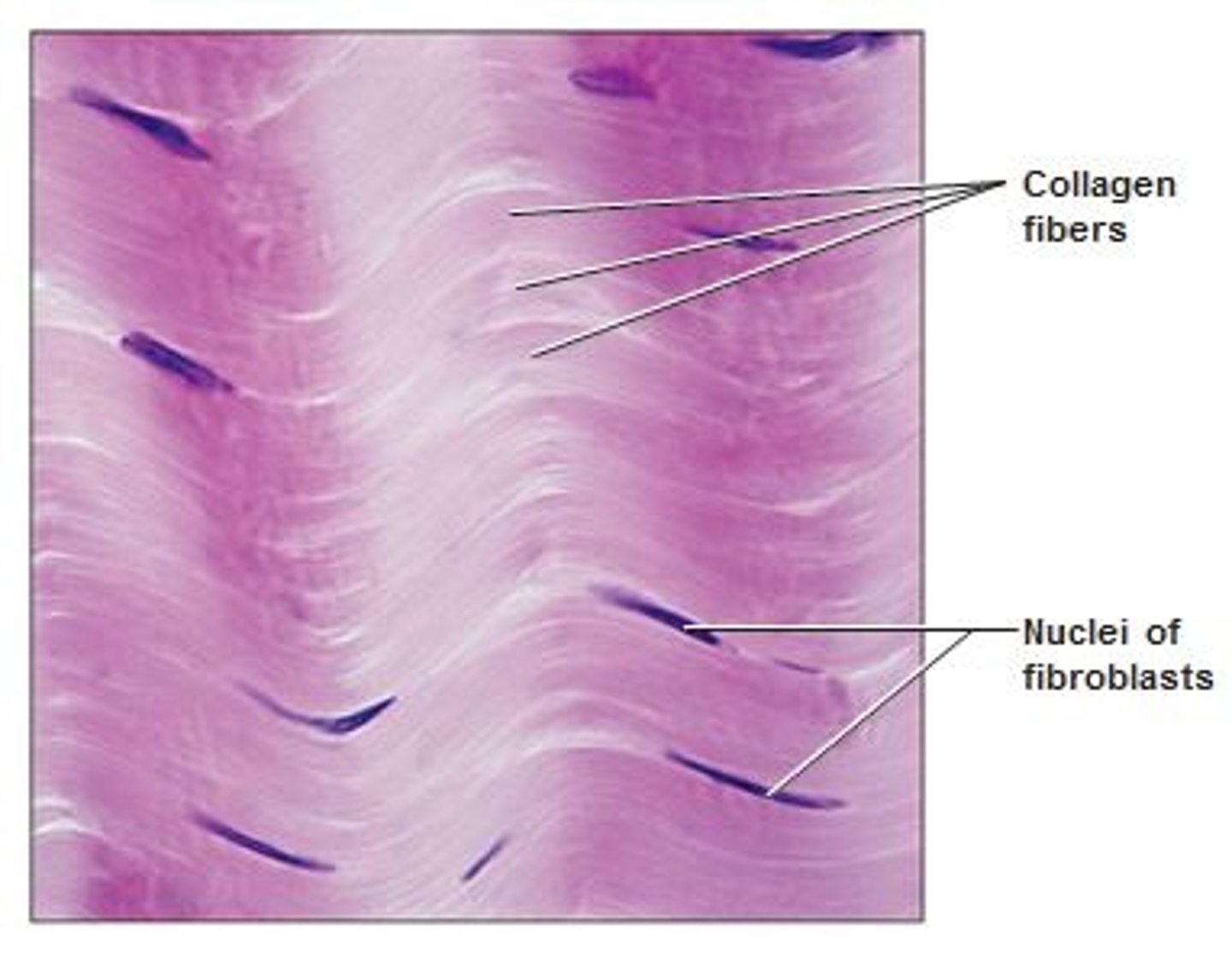
connective tissue
-most complex type of tissue
-role: maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support
-types: areolar, cartilage, blood, bone
-ex. voice box
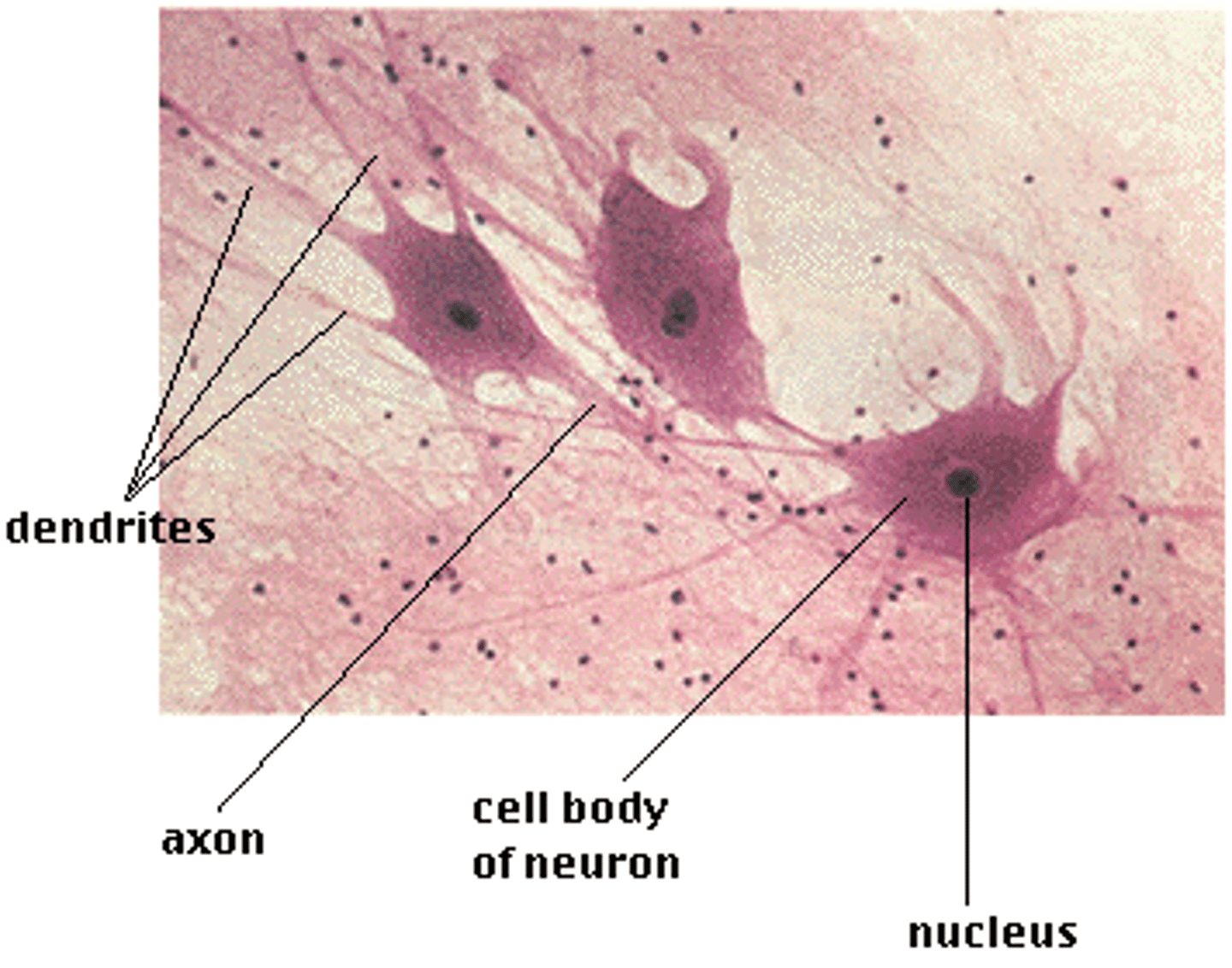
nervous tissue
-highly specialized communicative tissue
-role: transmit information from one neuron to another, from neurons to muscles and from sensory receptors/cells to other neural structures
-types: neurons, glia cells
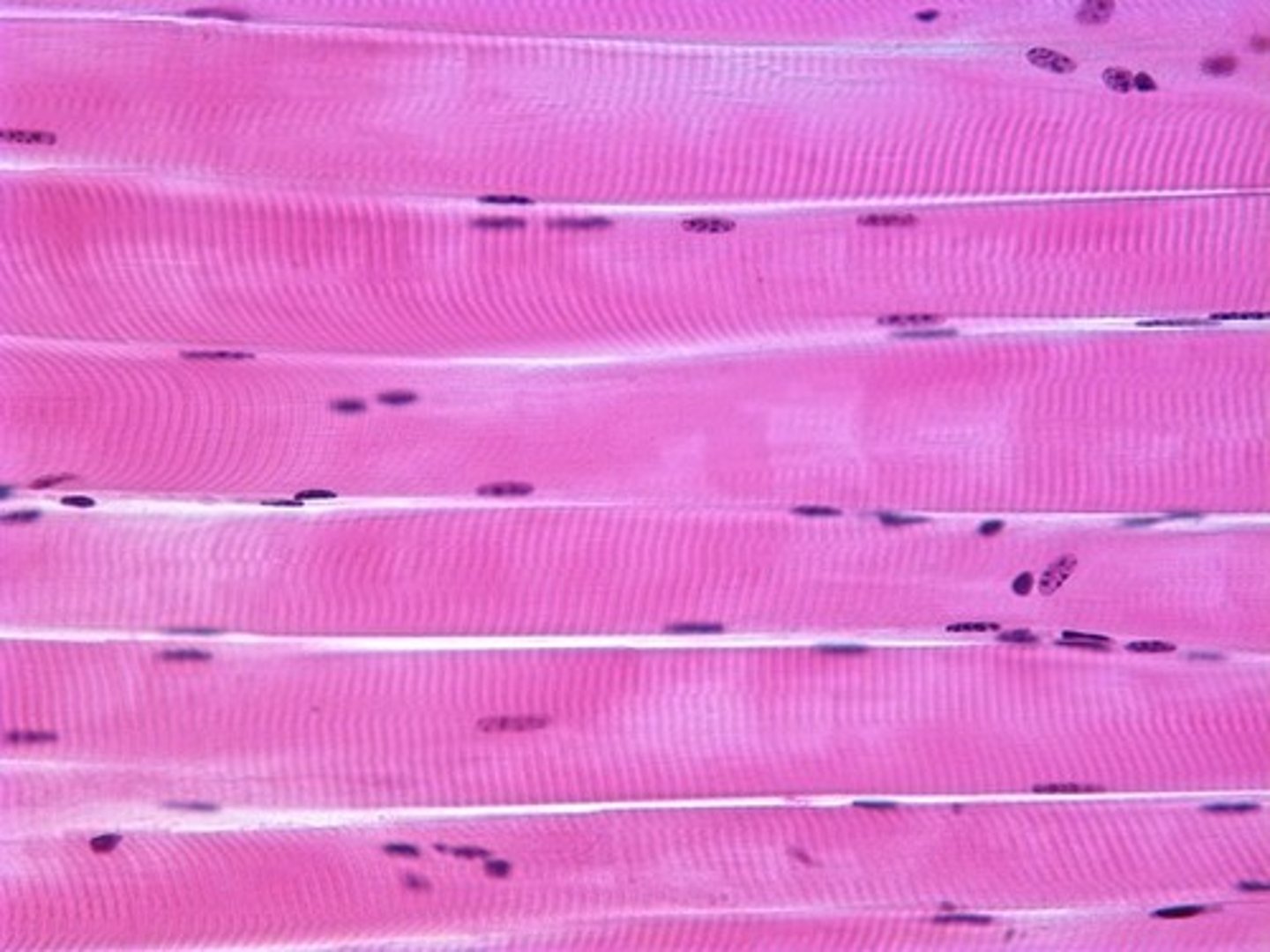
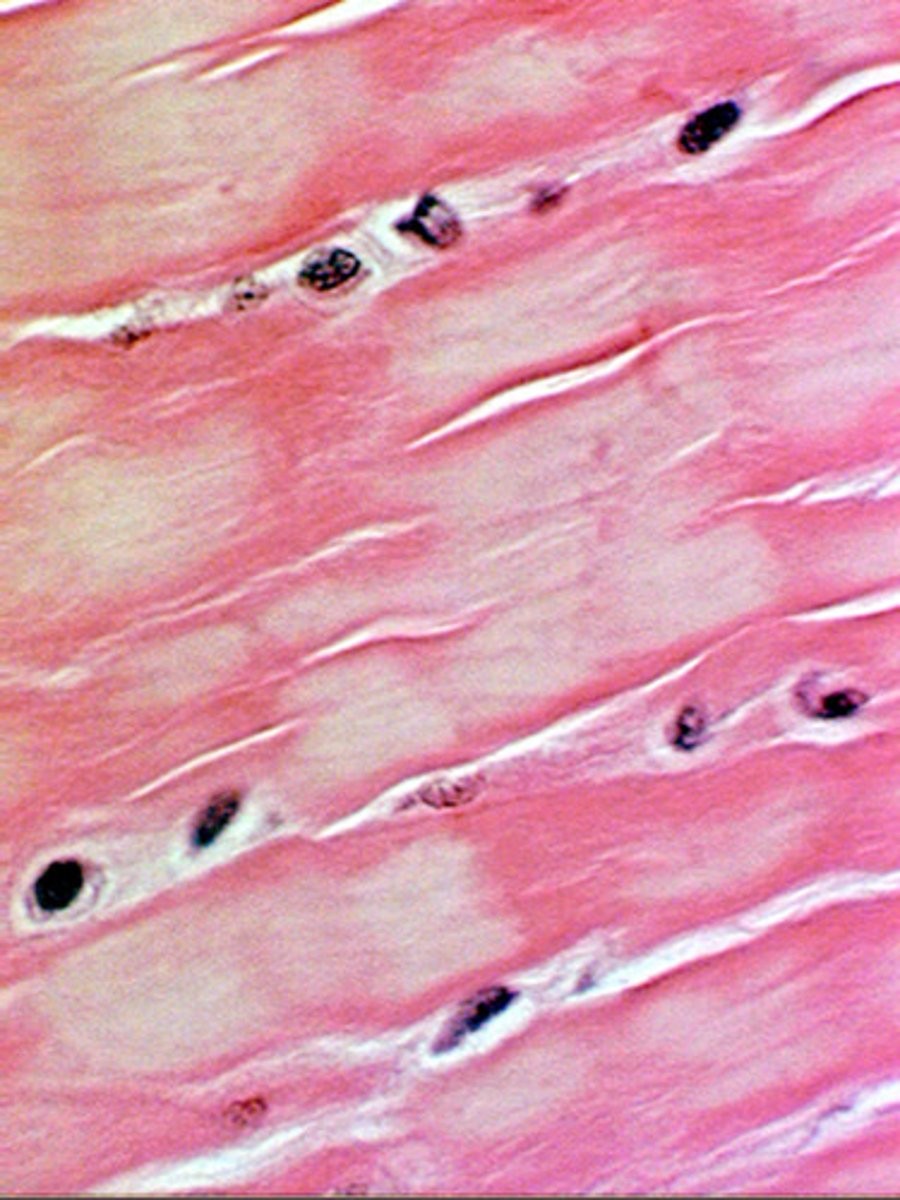
muscular tissue
-specialized contractile tissue
-role: allow muscles to contract/movement
-types: skeletal/striated (voluntary), smooth (involuntary), cardiac
how many bones in the human body? (adult/birth)
270 at birth, 206 adult
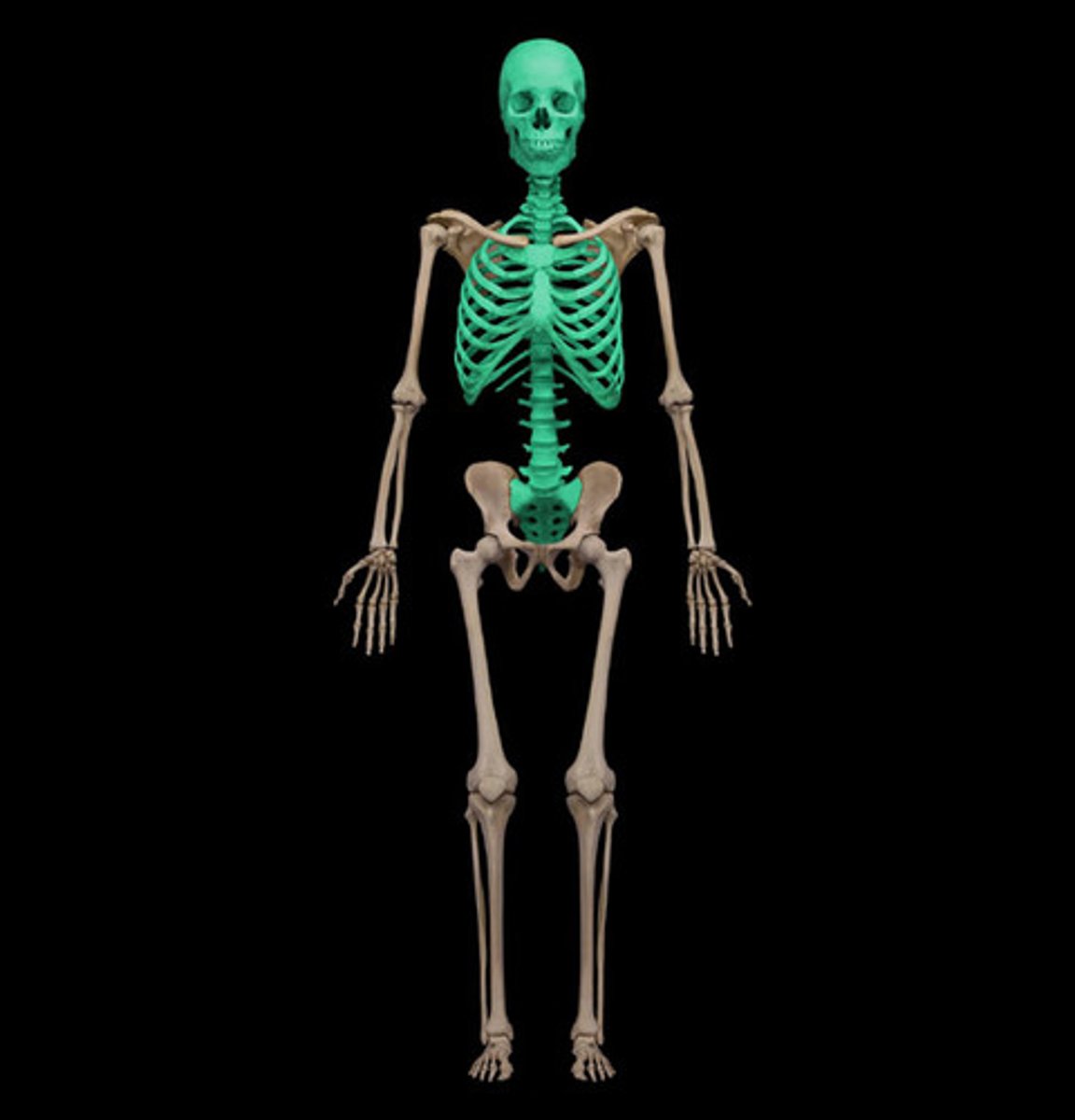
axial skeleton
vertebrae, rib cage, skull, facial bones, and hyoid bone
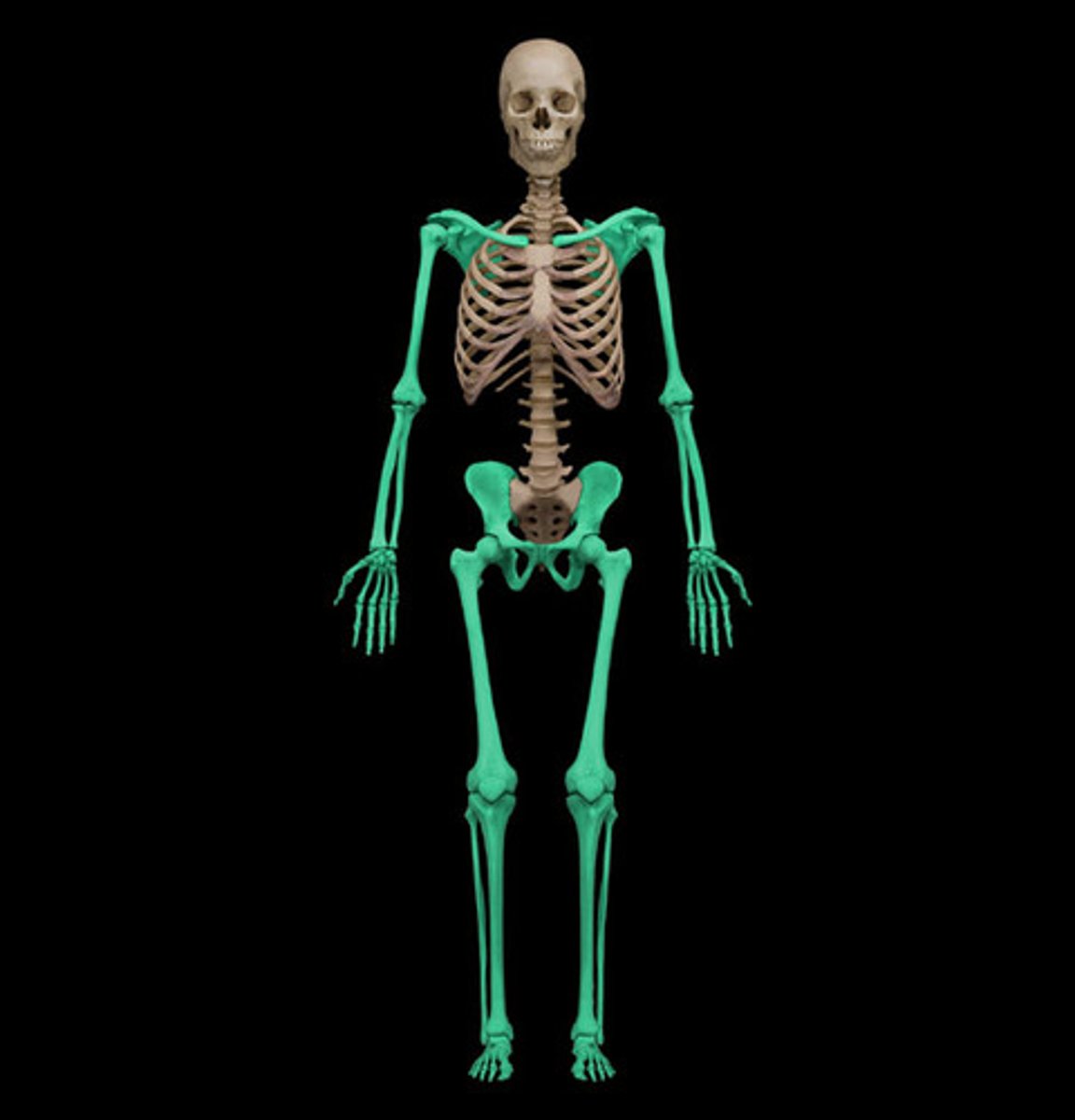
appendicular skeleton
bones of upper/lower limbs including the pelvic and pectoral girdles
bone functions
-support and protect internal organs
-forms attachments of muscles (facilitates movement)
-mineral storage
-fat storage and hematopoiesis
dense/compact bone
-Appears homogeneous
-Usually forms outer surface of bones
spongy/cancellous bone
-appears porous
-usually forms the inner surface of bones
-contains bone marrow
cartilage
-connective tissue
-lines articular surfaces/facets of bones (where bones meet (joint))
-forms entire structures
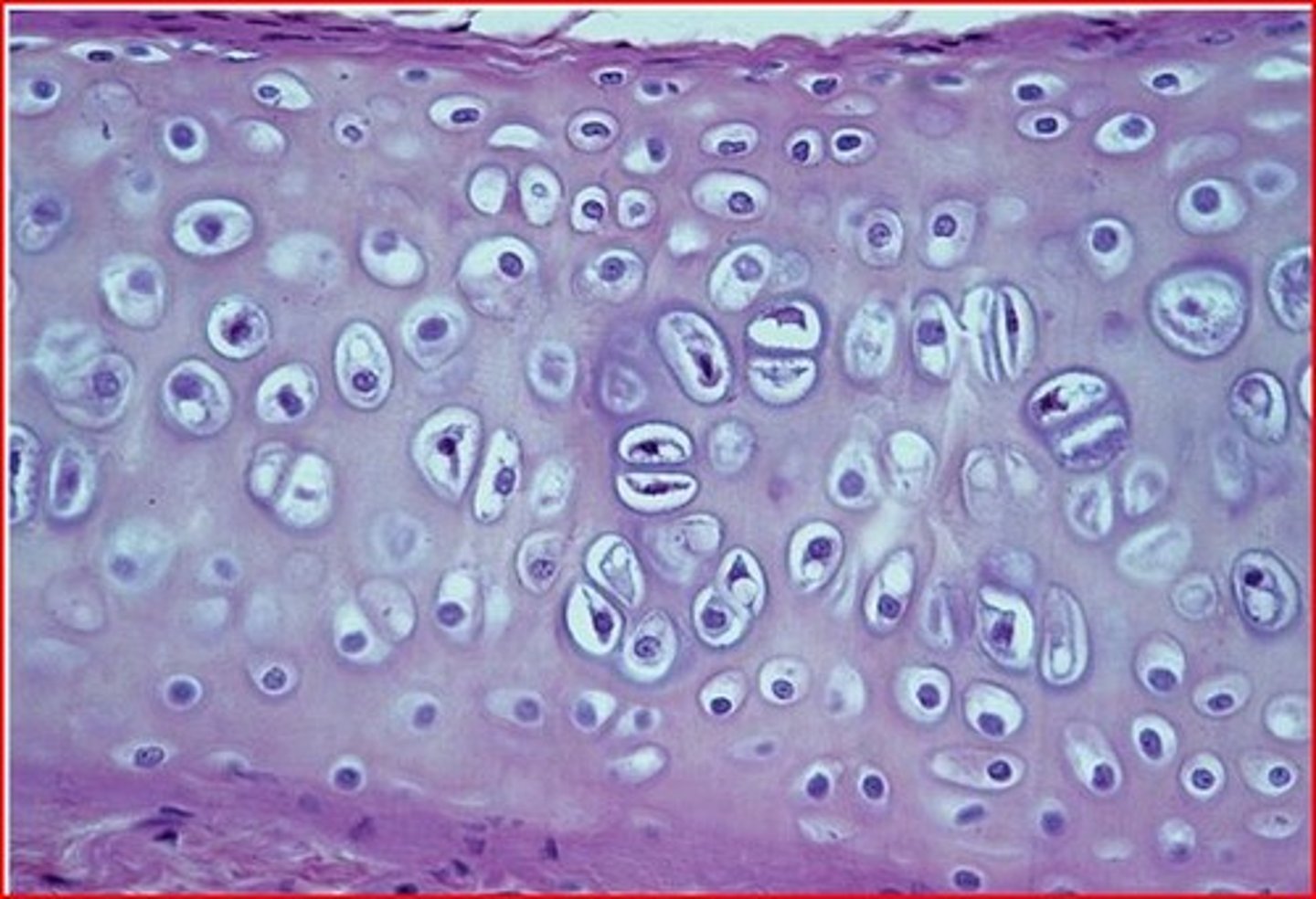
hyaline cartilage
-most common type of cartilage
-appears smooth and glassy blue
-large amount of collagen
-found in articular surfaces of bones and in larynx, trachea, and bronchi
-ossification with age
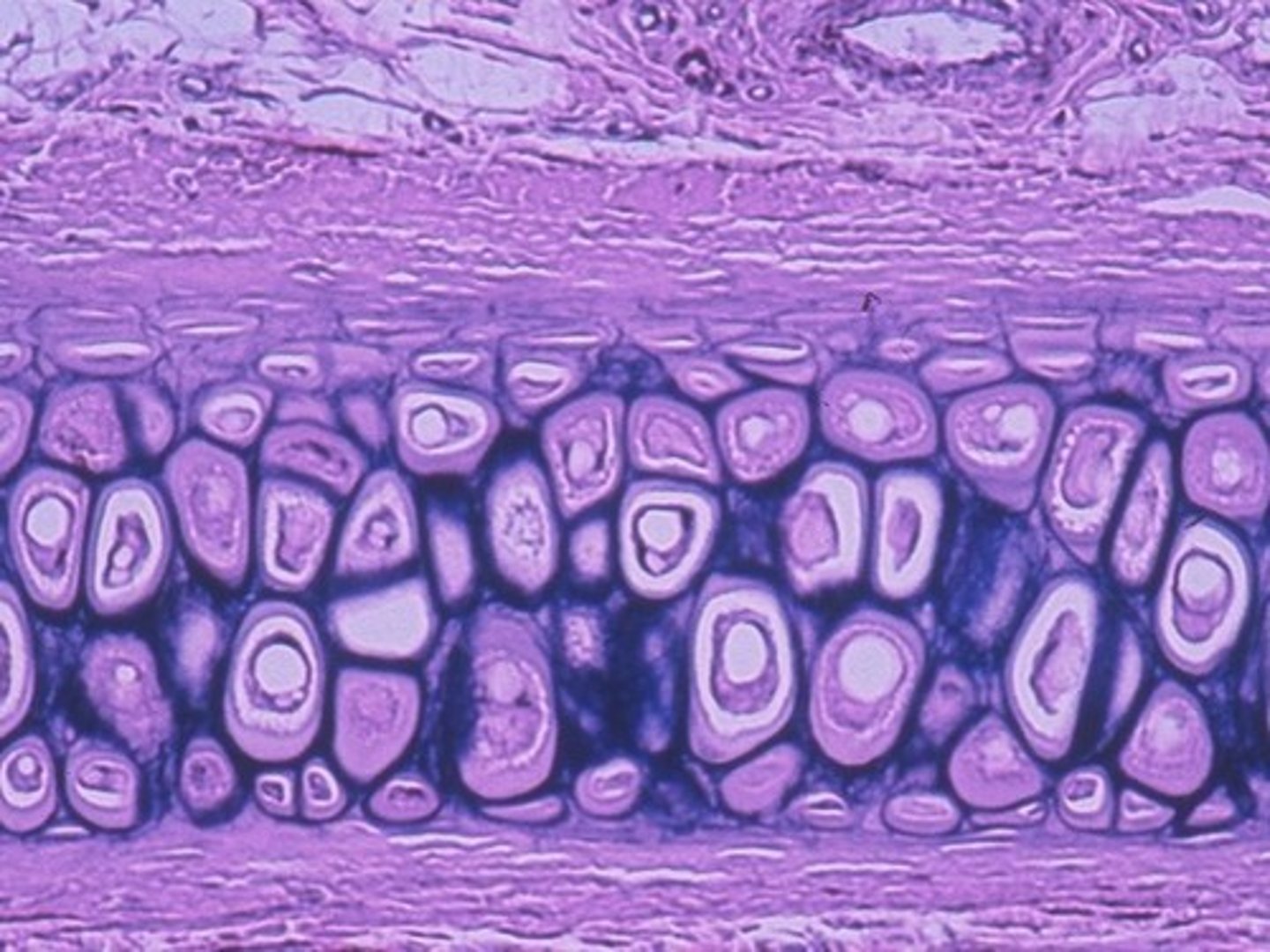
elastic cartilage
-flexible
-less collagen and more elastic fibers
-little ossification with age
-found in ear, ear canal, epiglottis, and nose
fibrous cartilage
-tougher tan other cartilages
-made of dense collagenous fibers
-present in areas with frequent stress
-vertebral discs, and the temporomadibular joint
joint
place where two bones connect
fibrous joints
no mobility (ex. skull sutures)
cartilaginous joints
limited mobility (ex. interverbral disc)
synovial joints
high mobility
synovial fluid
fluid secreted by articular capsule which lubricates the joint cavity
articular capsule
fibrous tissue between the bones that form the joint
articular facets
opposed ends of the bones, covered with hyaline cartilage
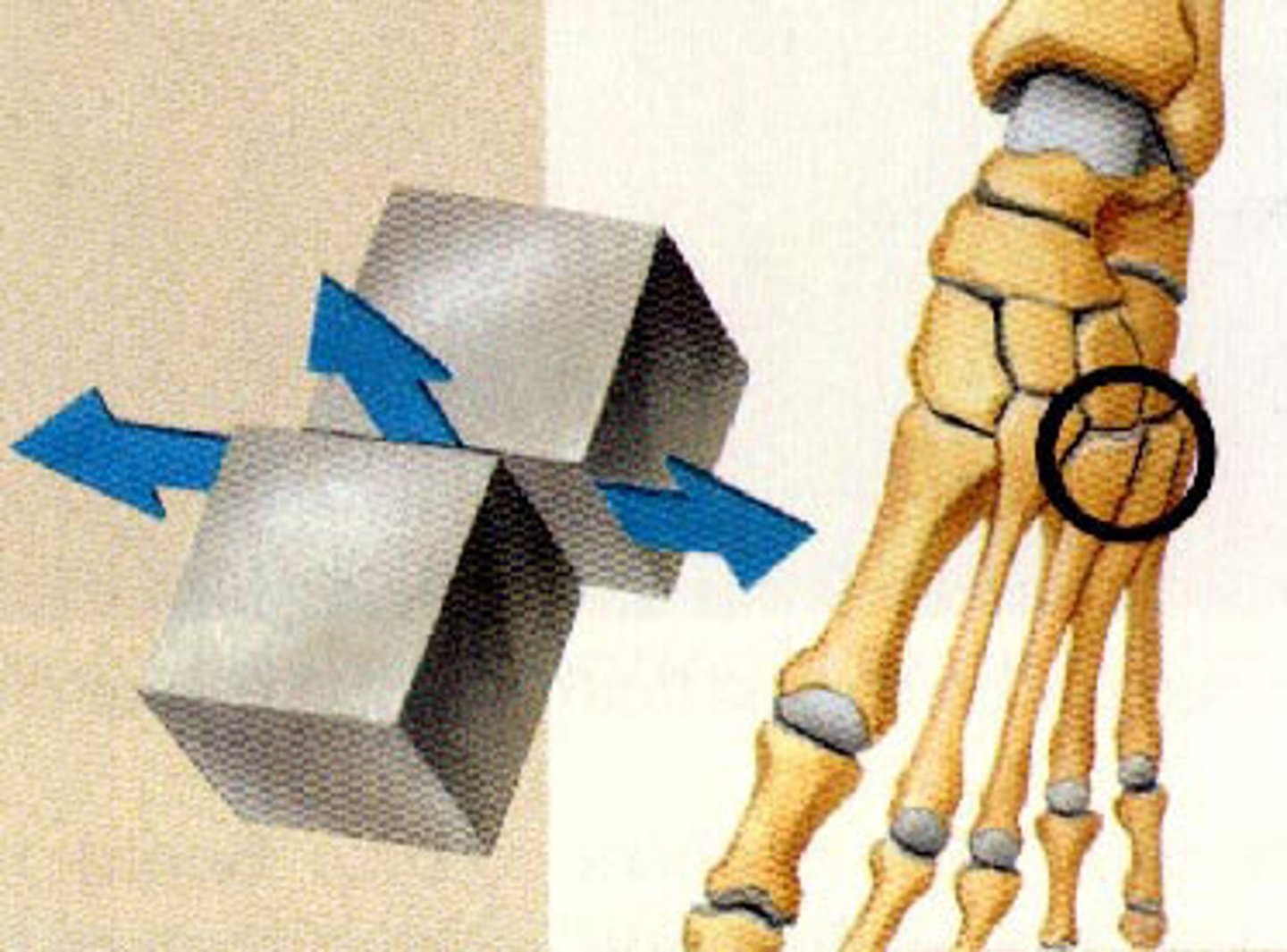
gliding joint
allows one bone to slide over another; found in wrist and ankles
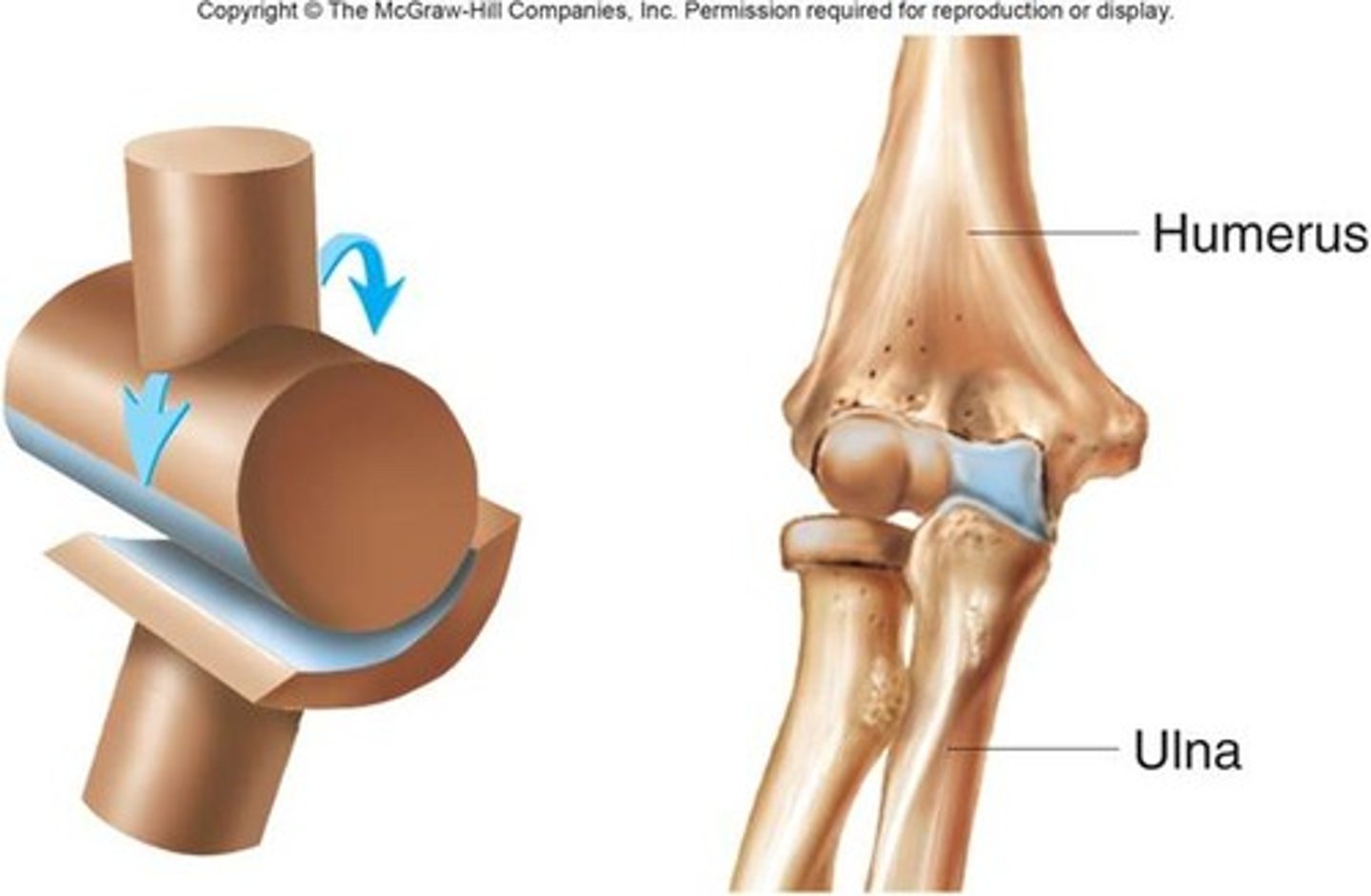
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
condyloid joint
synovial joint that does everything except rotating (temporomandibular joint)
pivot joint
Allows for rotation around the length of a bone, and only allows for rotation (1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae)
saddle joint
allows for all movement except rotation (middle ear and thumb)
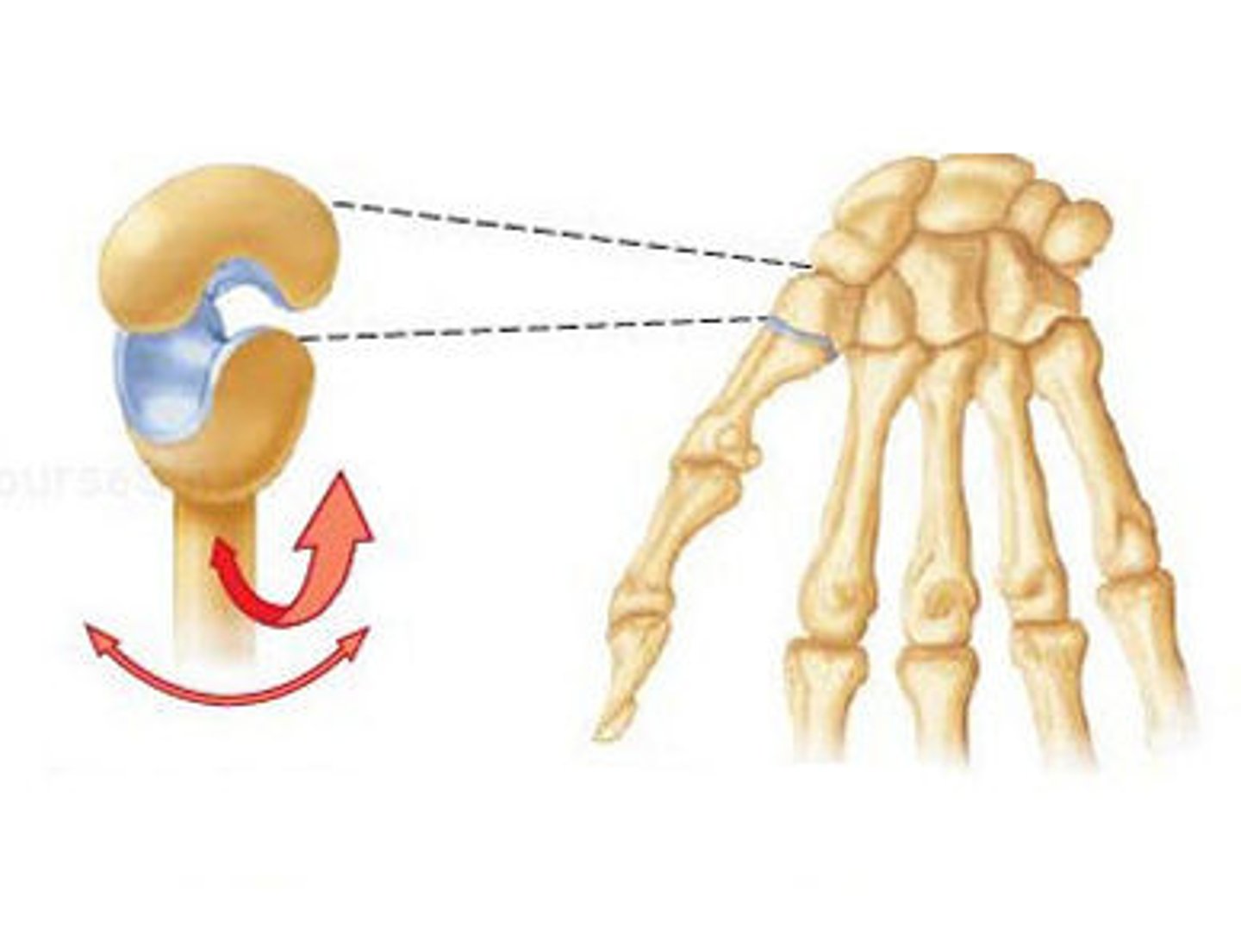
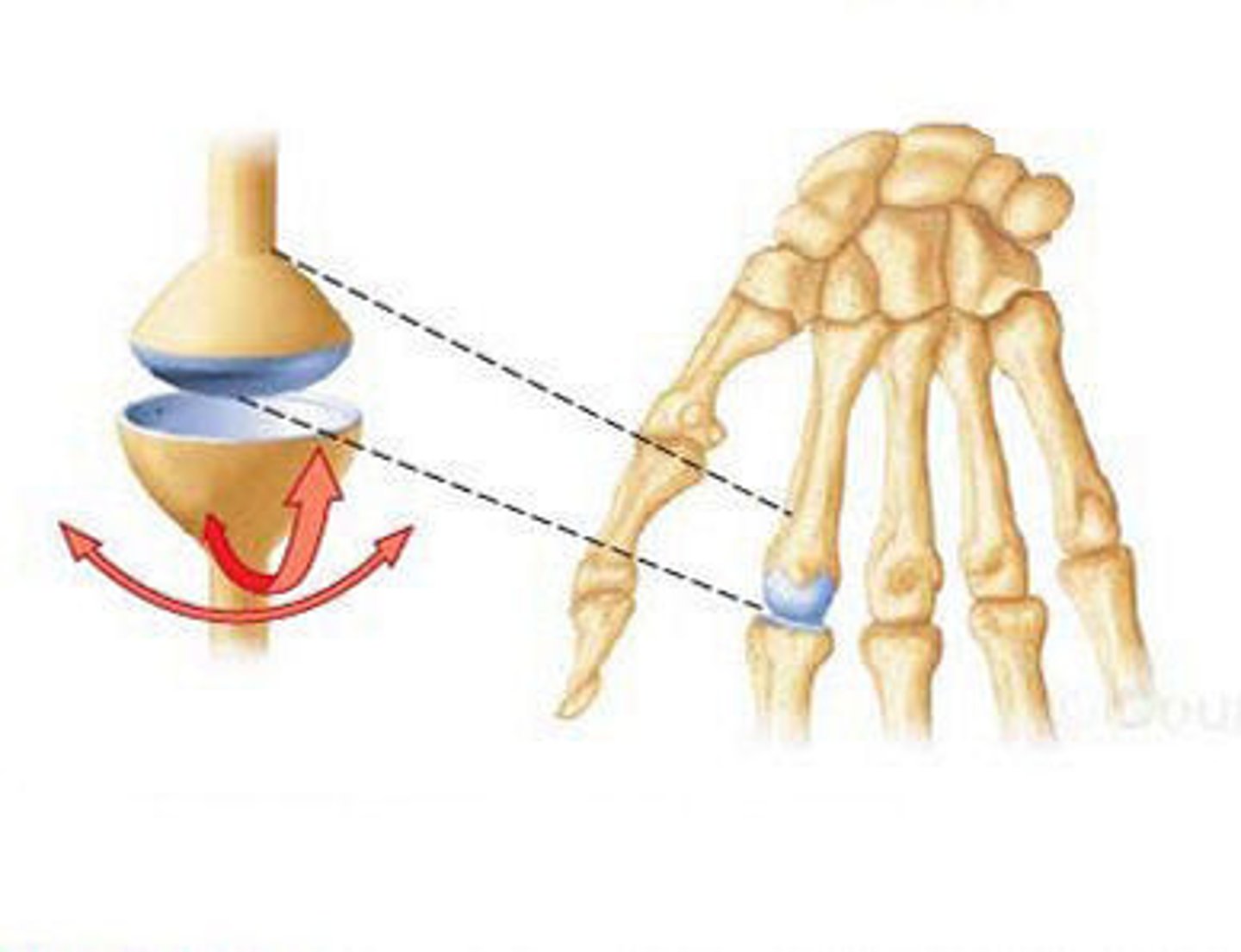
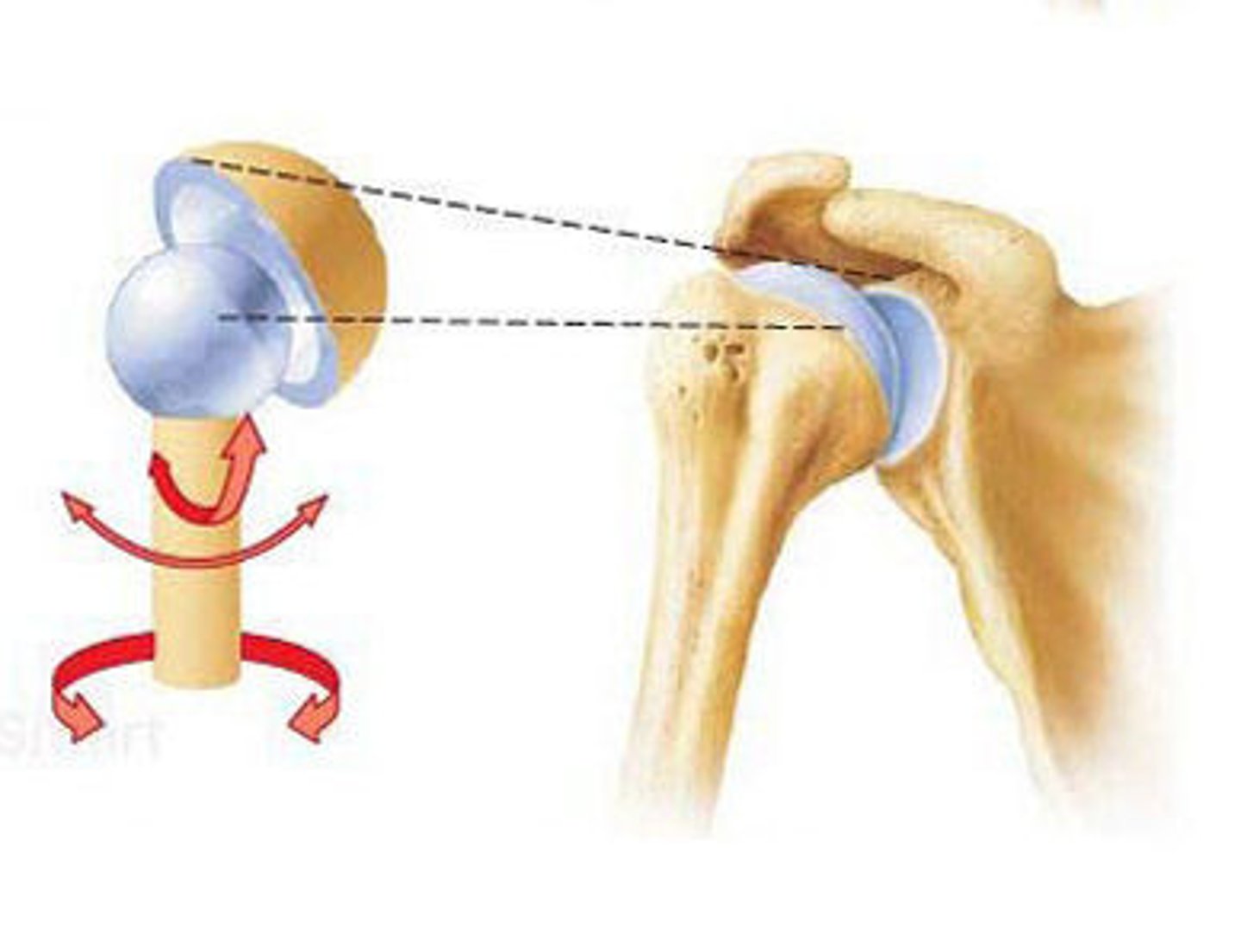
ball and socket joint
allows for all type of movement (hip and shoulder)
somatic
-voluntary part of the system
-allows for conscious sensation and perception of environmental events
autonomic
-involuntary part of the system
-responsible for life-sustaining activities and sensations (heart beat, mucus production)
central nervous sytem (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
spinal nerves, cranial nerves, autonomic nervous system (ANS)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
sympathetic, parasympathetic
forebrain/cerebrum
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon
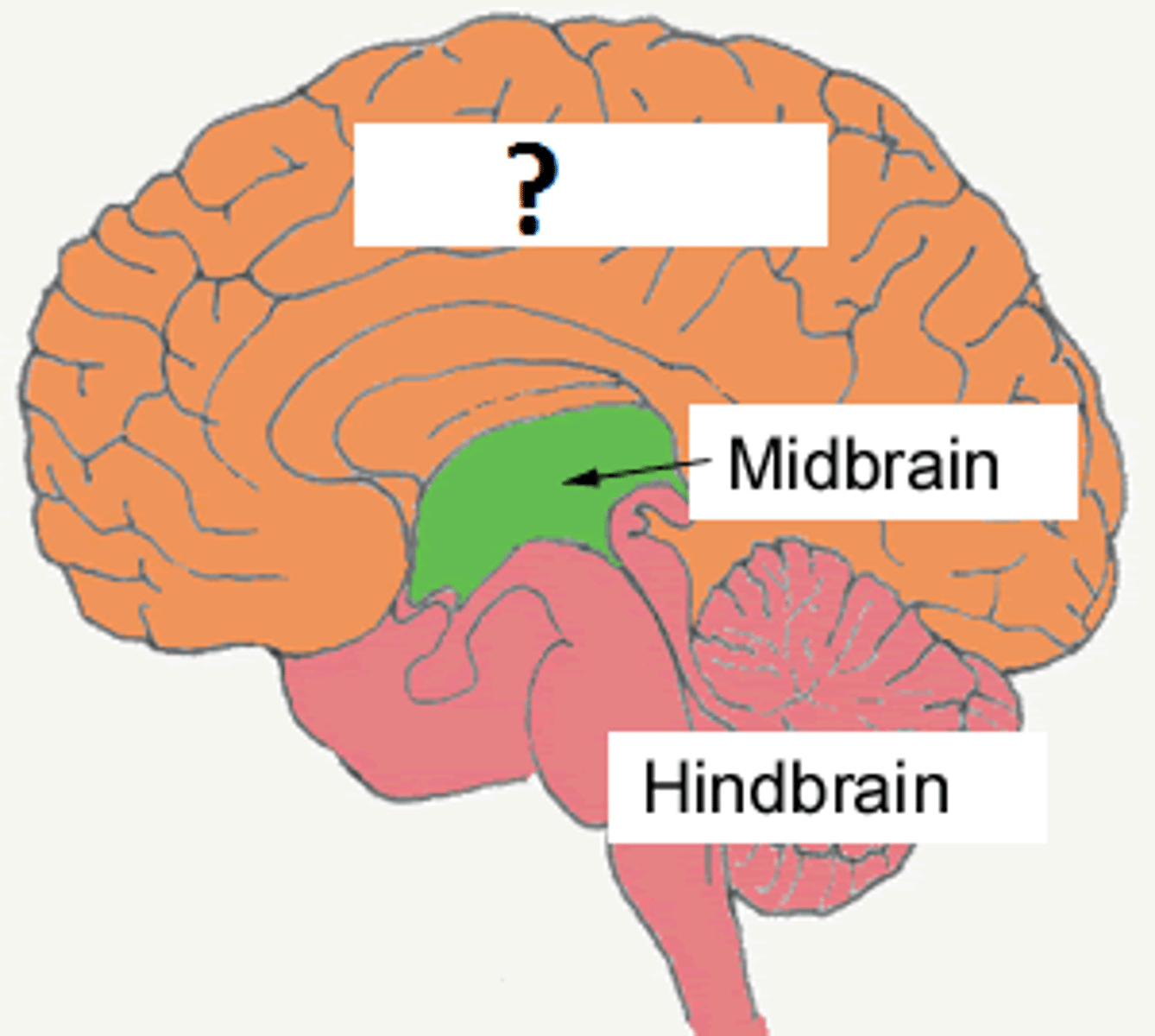
parts of the brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla
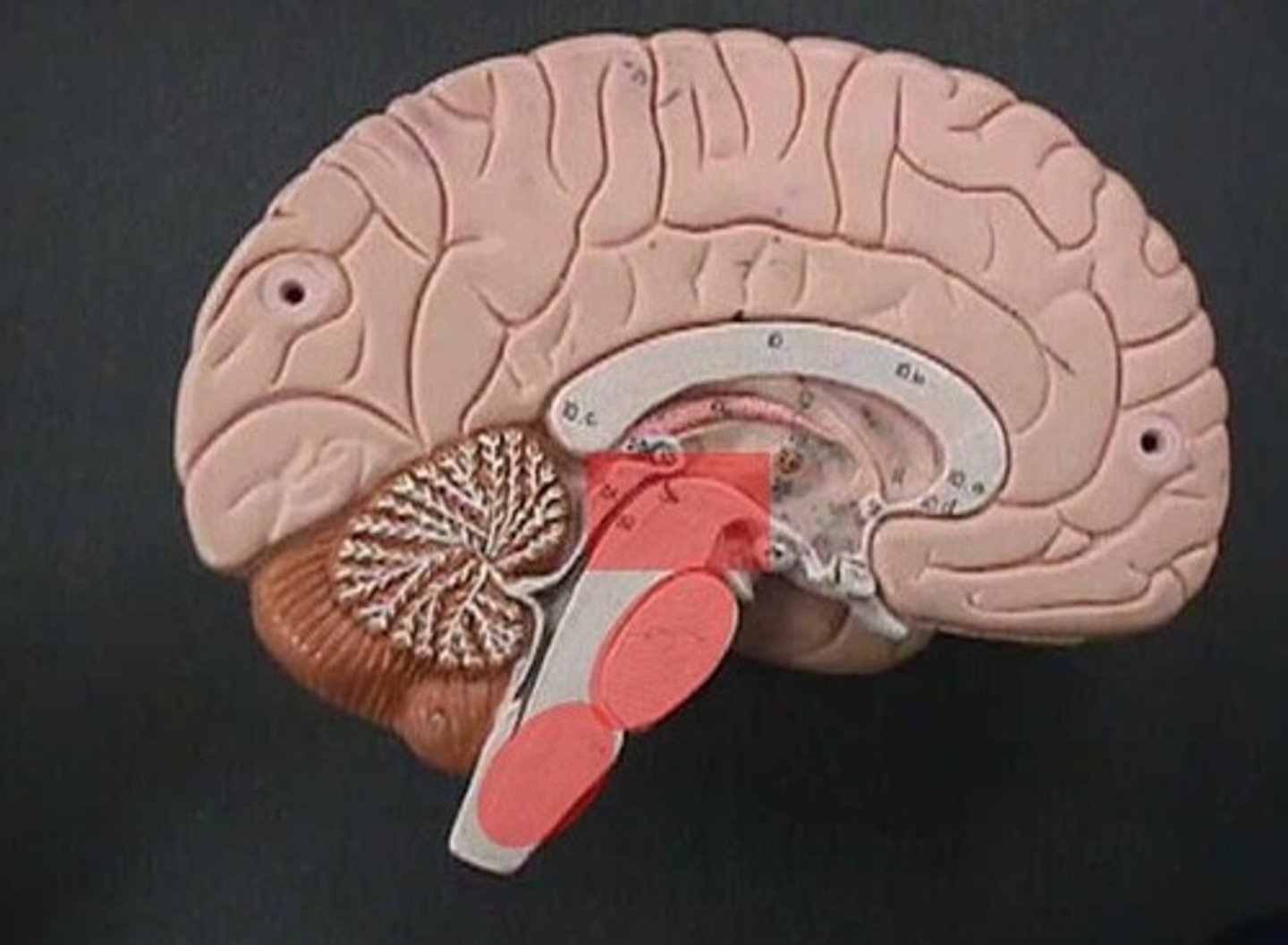
hindbrain
pons, medulla, cerebellum
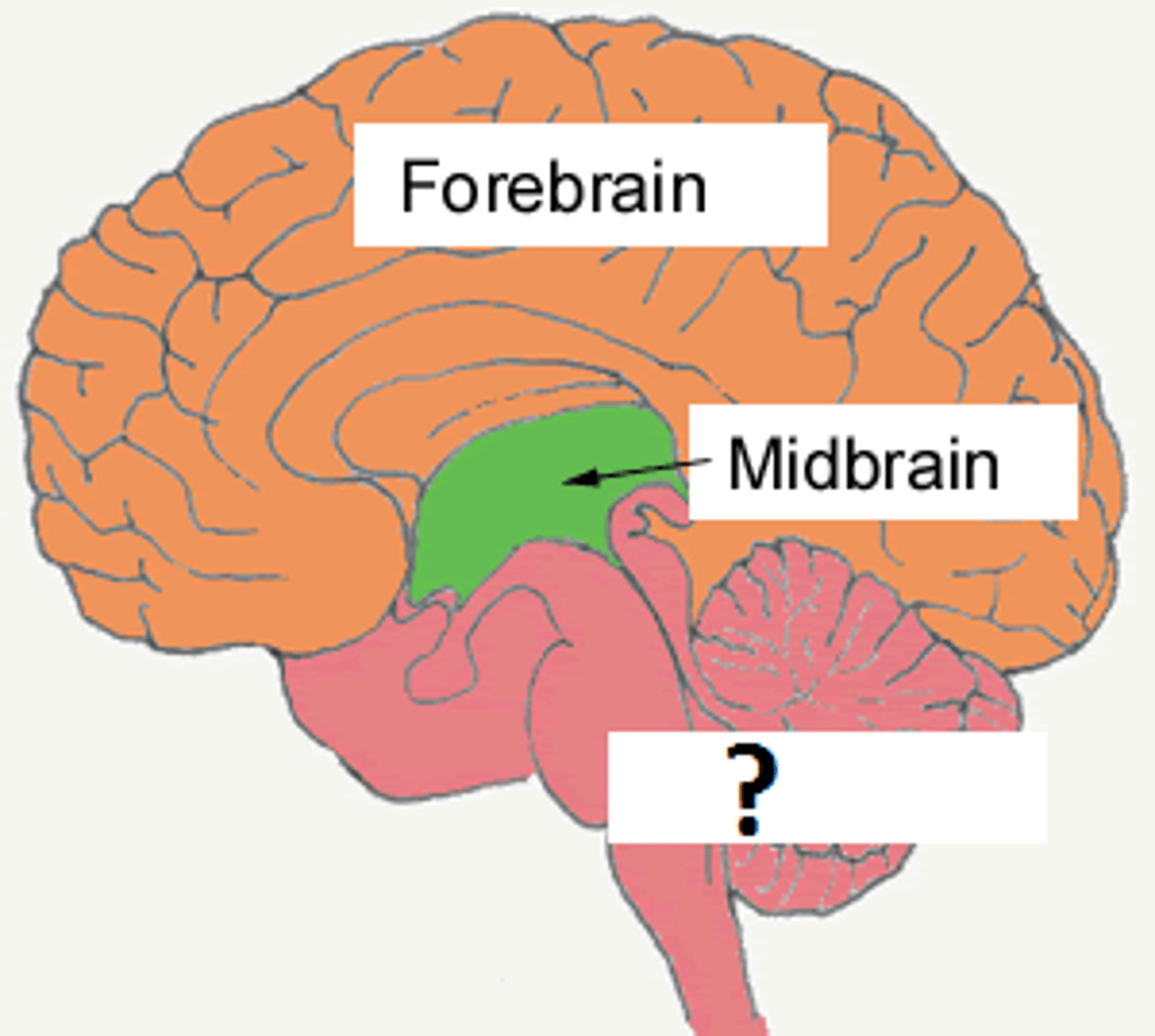
spinal cord
-extends from medulla to lumbar region of the vertebrae
-transmits signals to and from the brain/body
-home of many relflexes
-home of neural circuits = central pattern generators
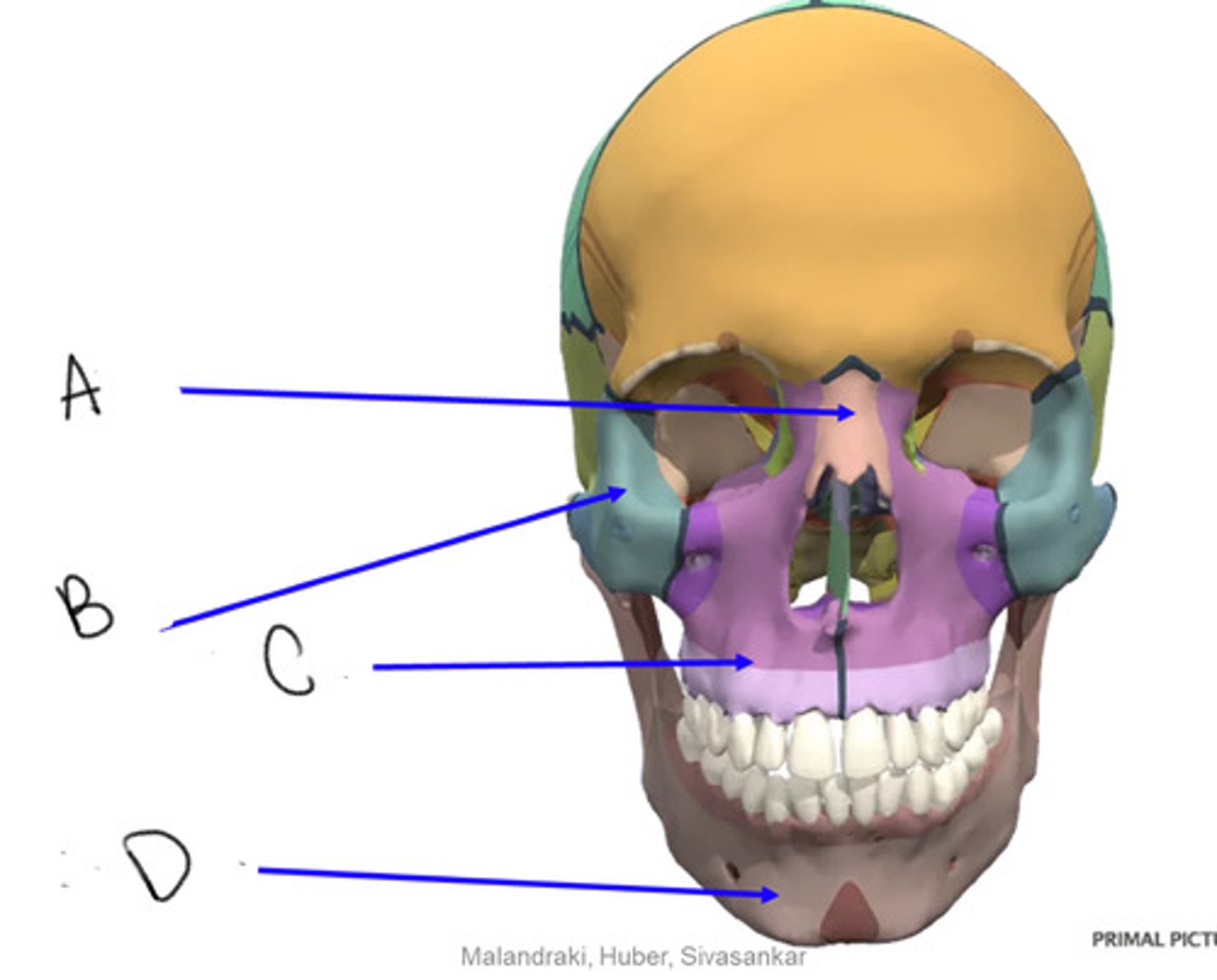
nasal
A
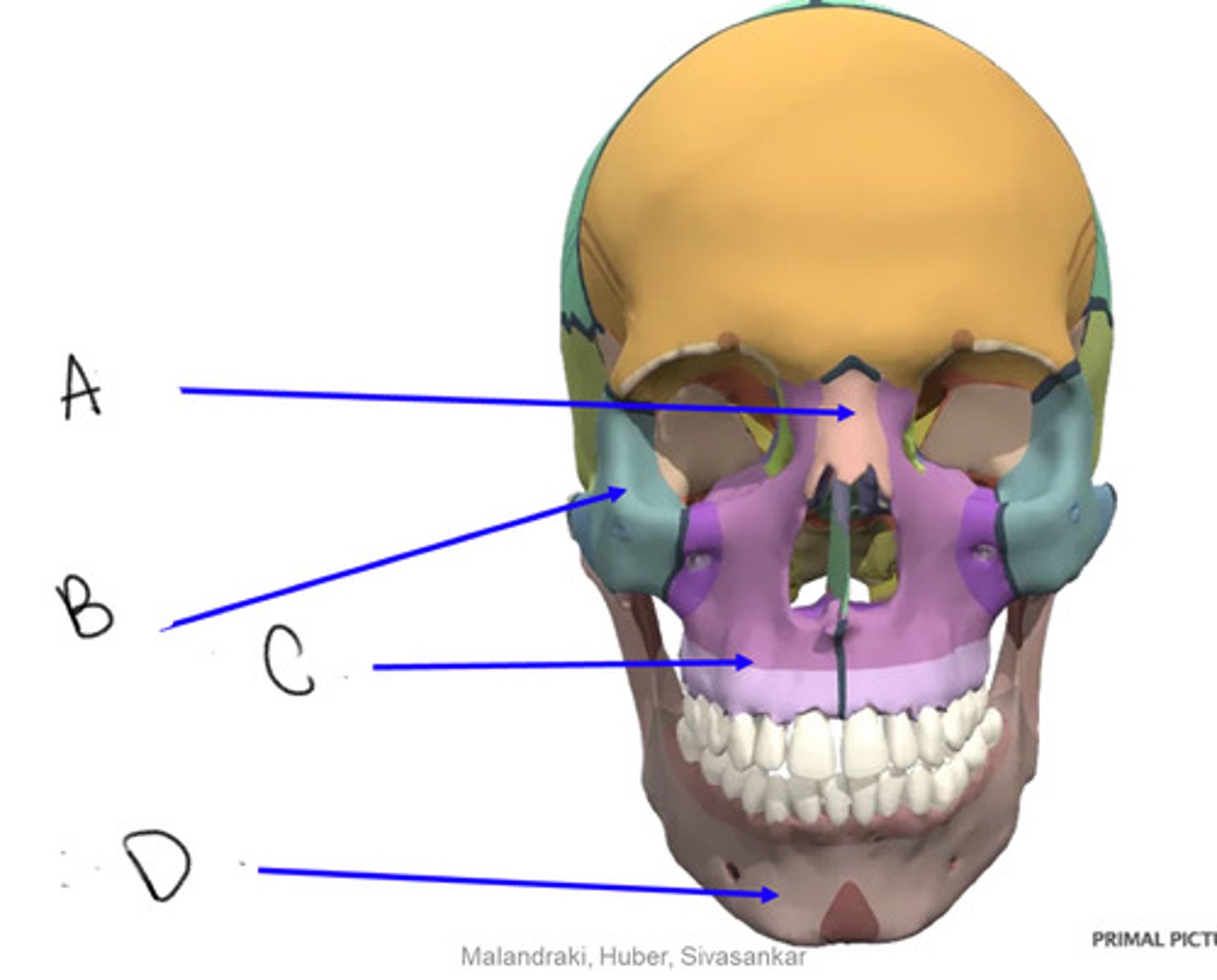
zygomatic
B
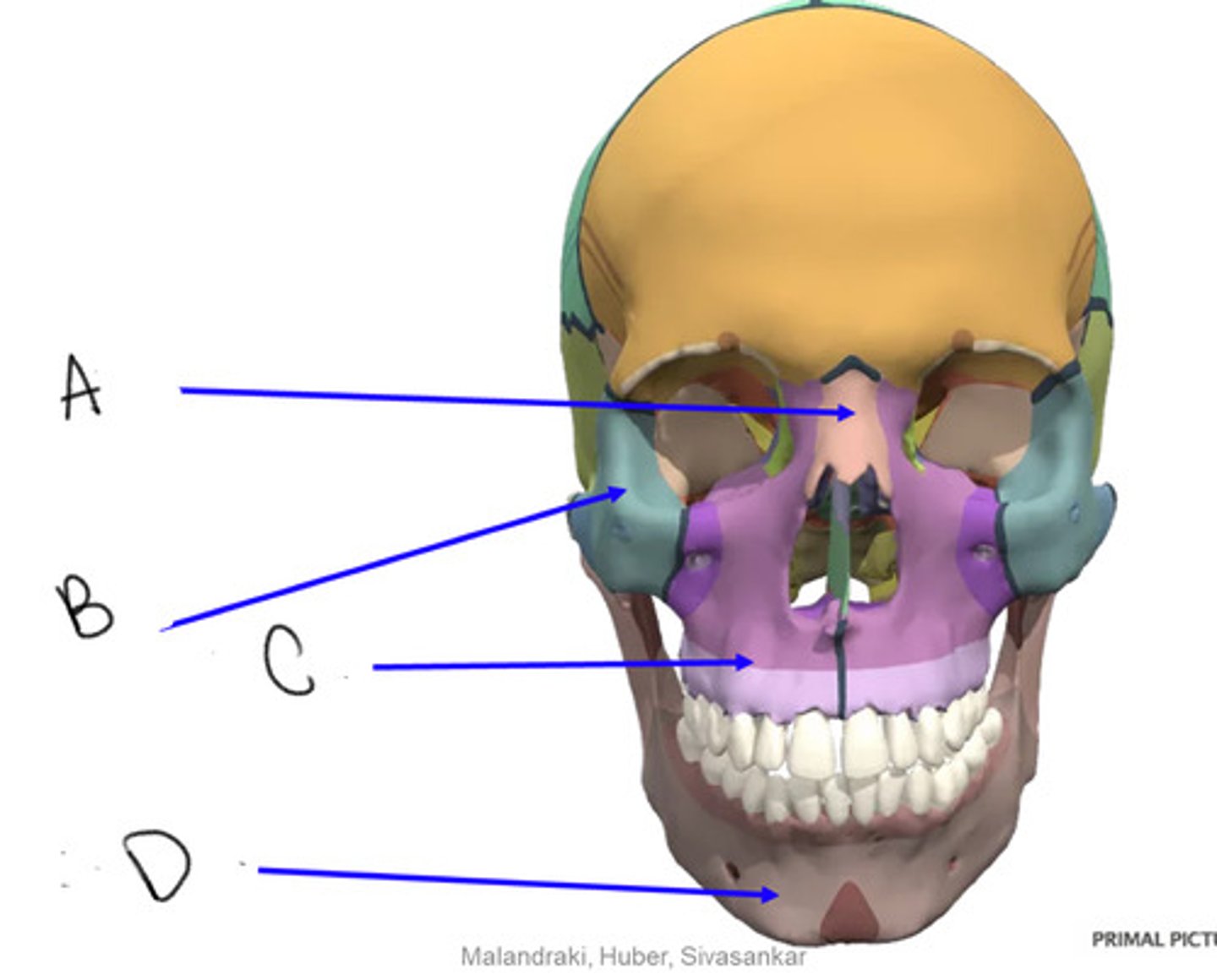
maxilla
C
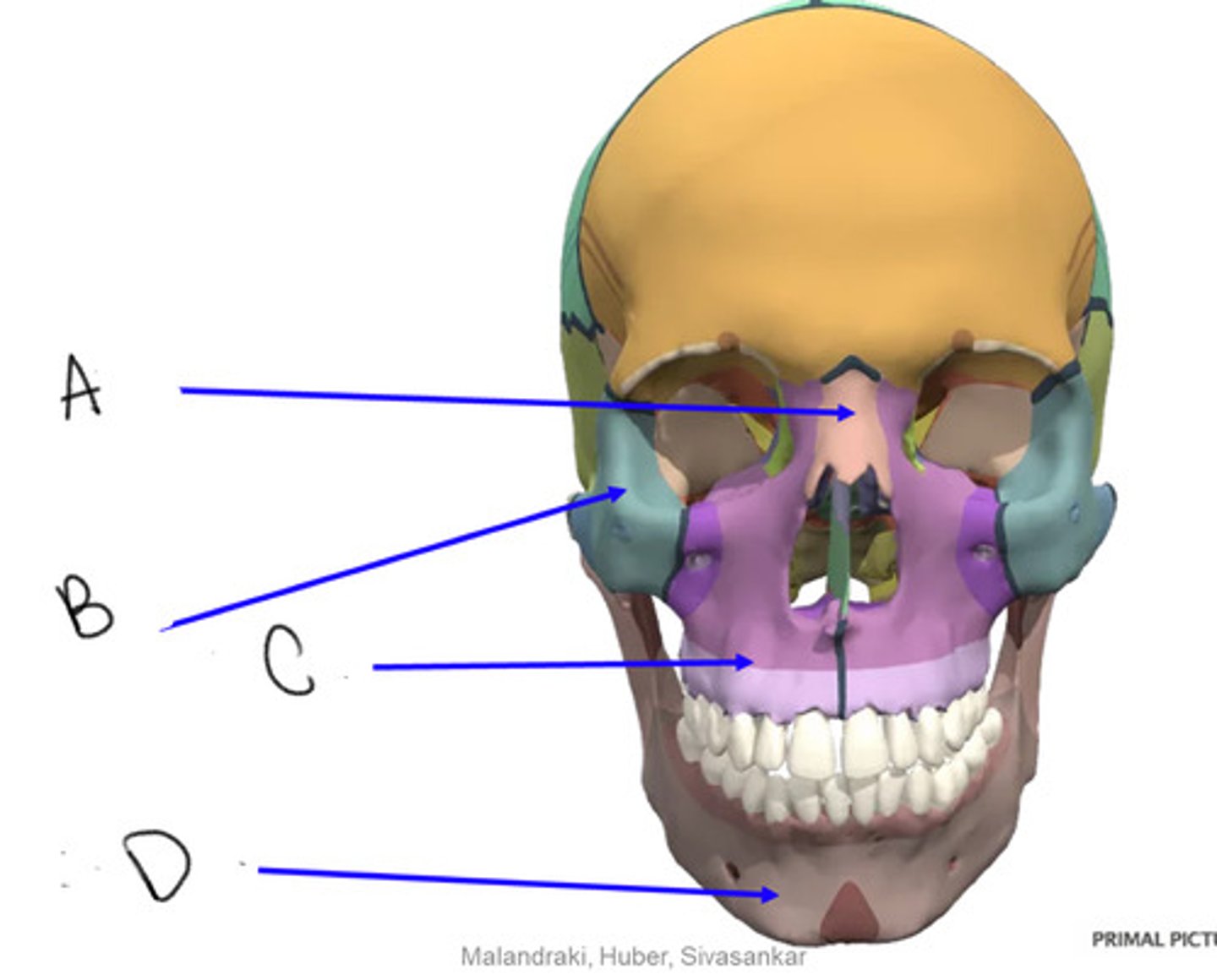
mandible
D
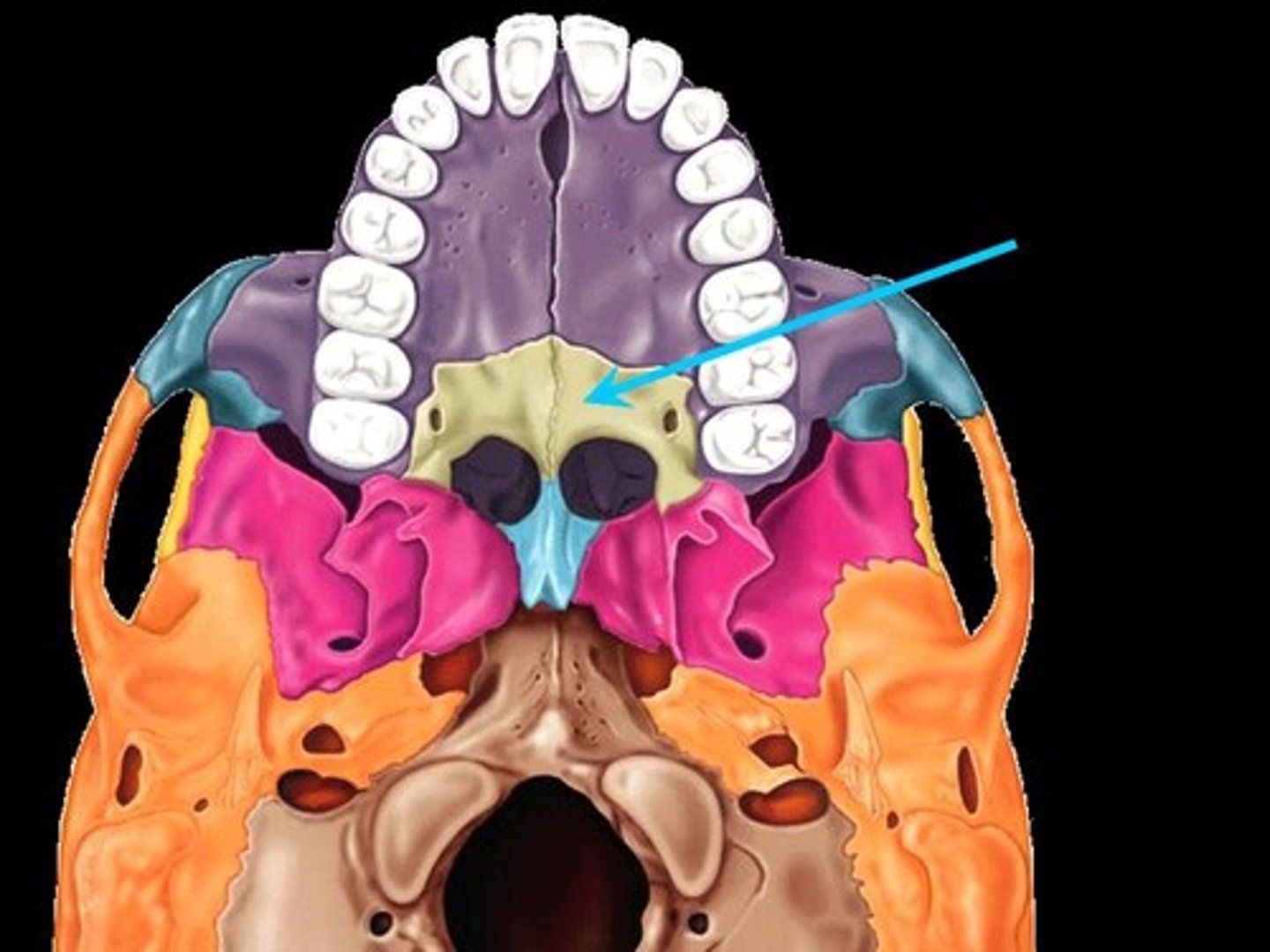
palatine bone
Name this bone
mandible bone characteristics
-only moveable bone in craniofacial skeleton
-tempromandibular joint
-landmarks: ramus, angle, mental protuberance
frontal bone
A
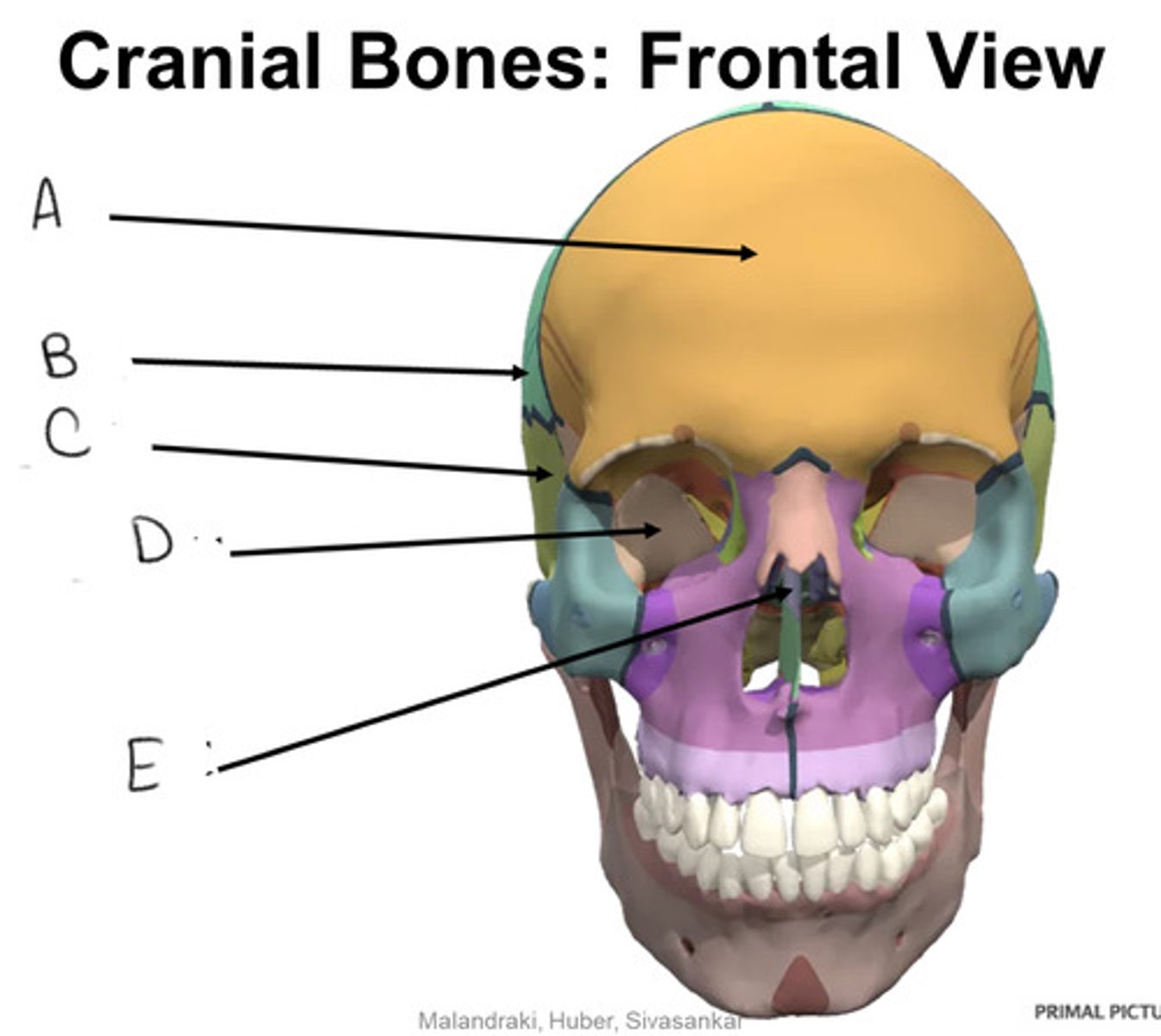
parietal bone
B
temporal bone
C
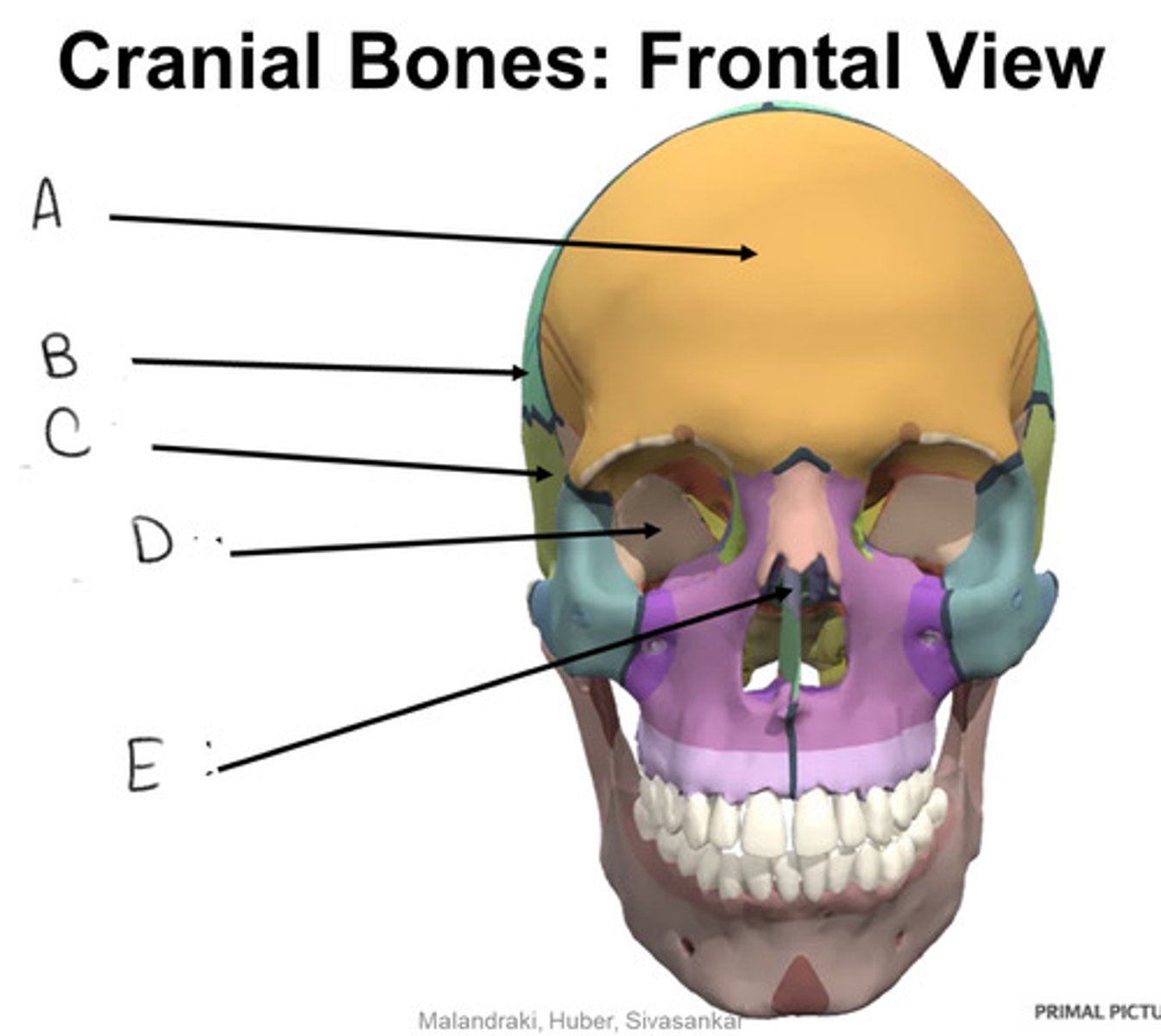
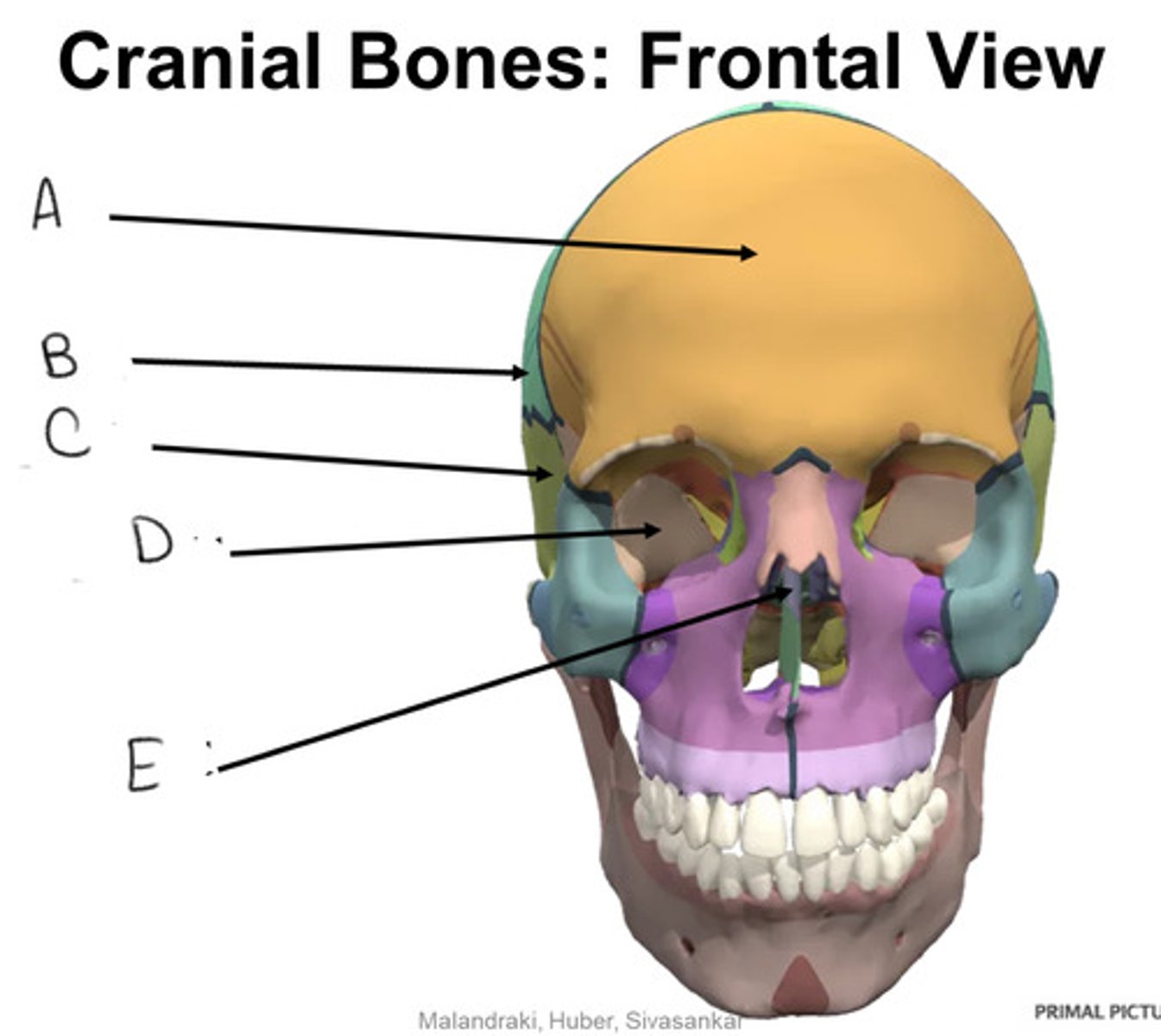
sphenoid bone
D
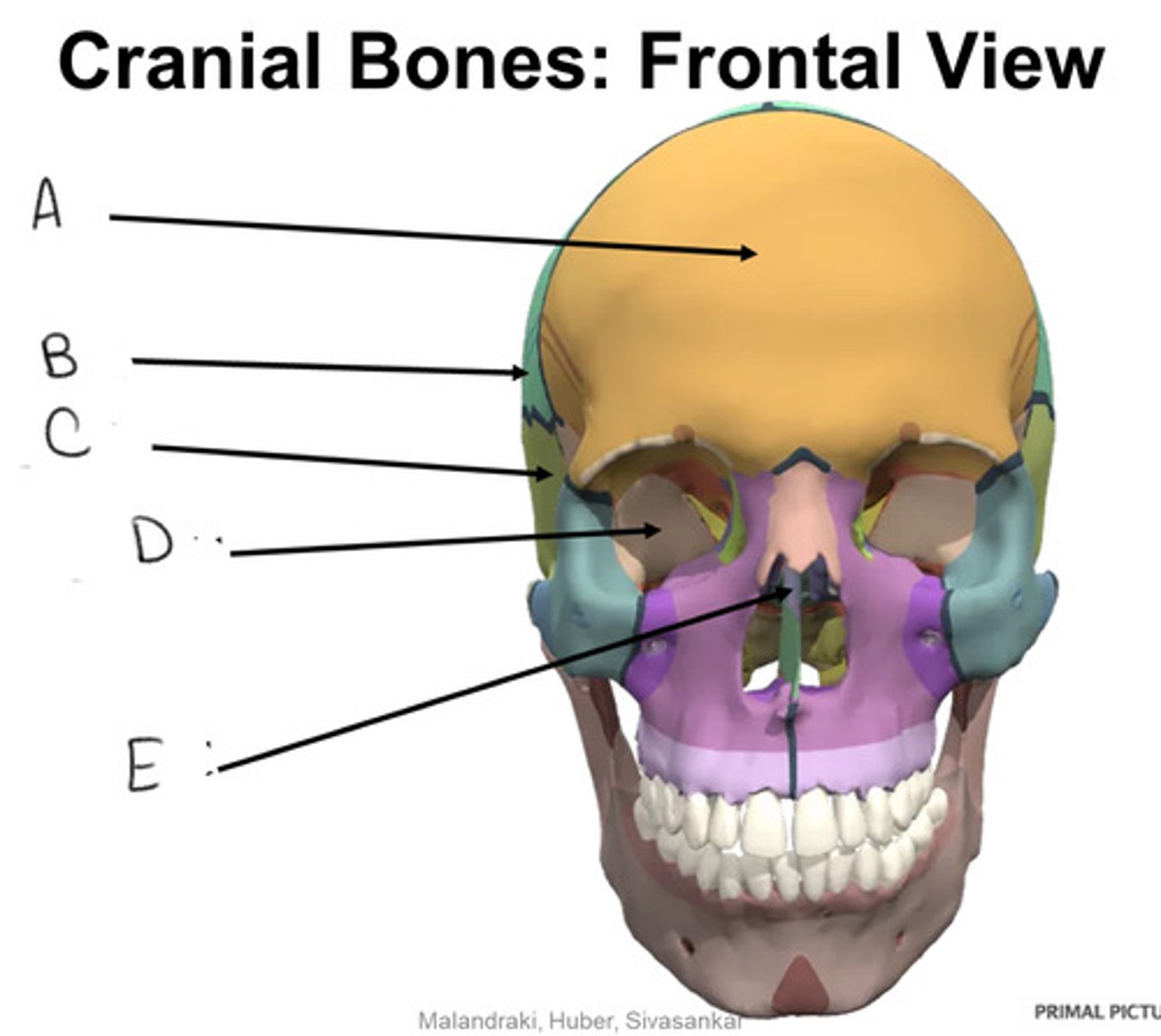
ethmoid bone
E
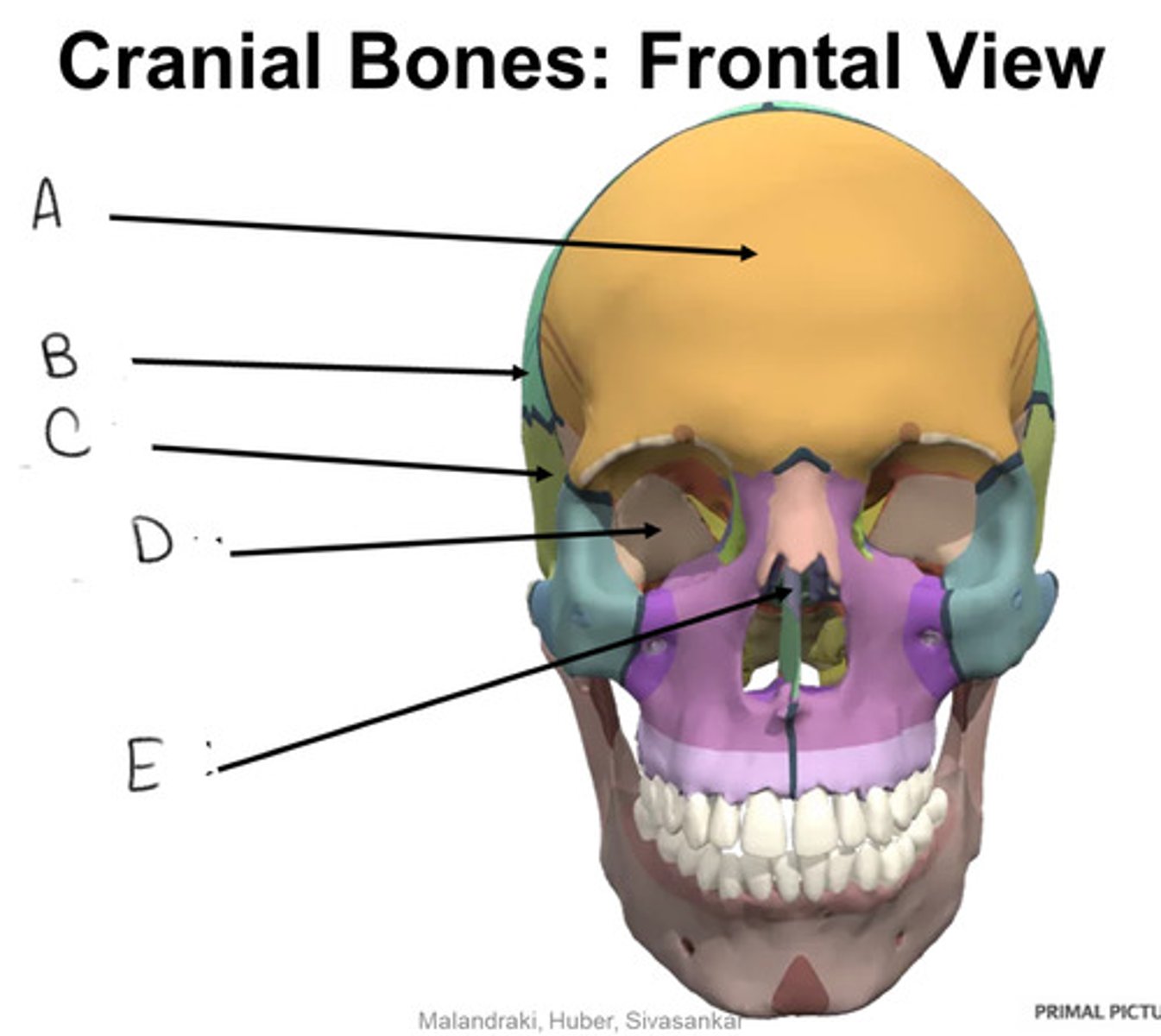
parietal bone
A
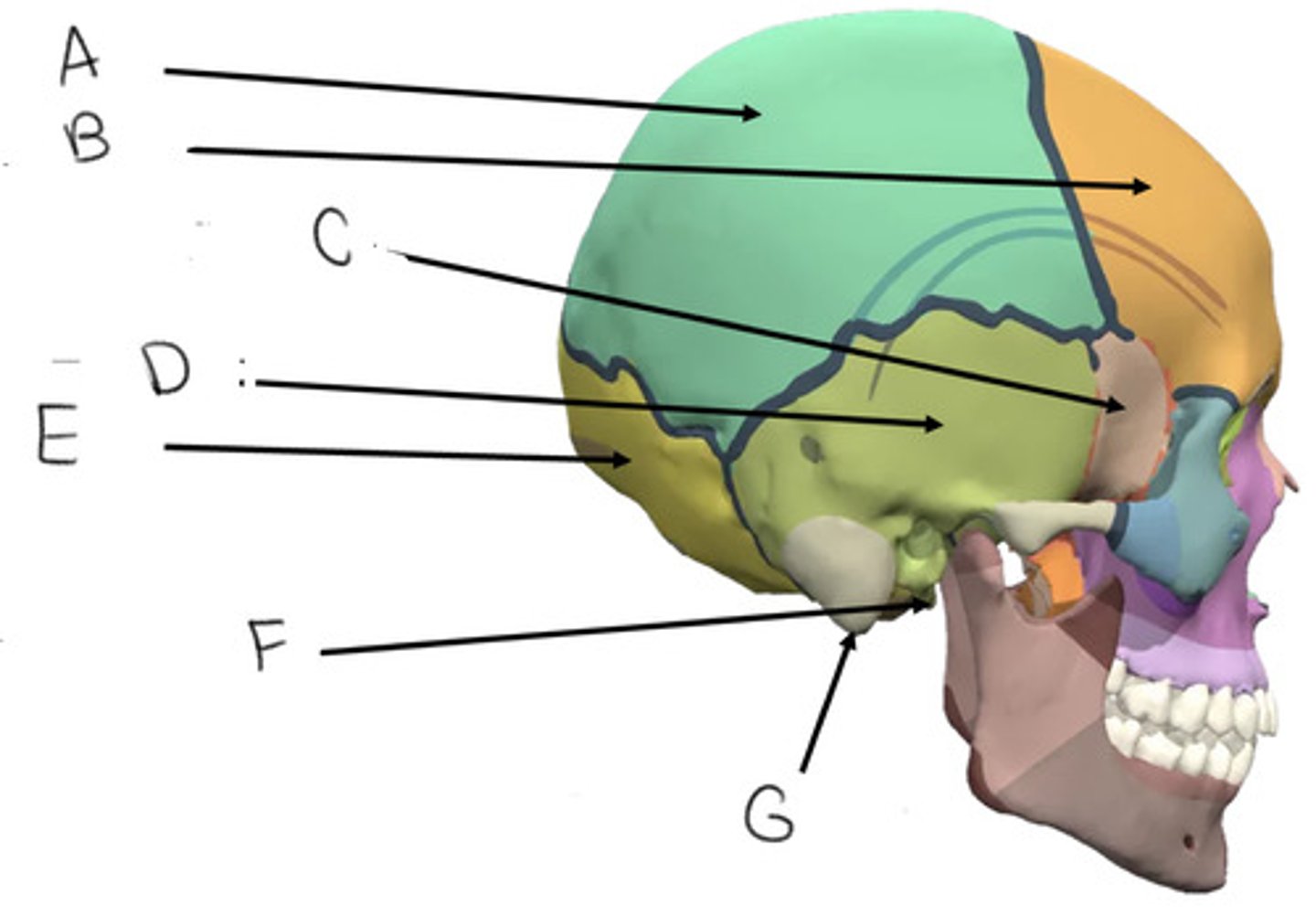
frontal bone
B
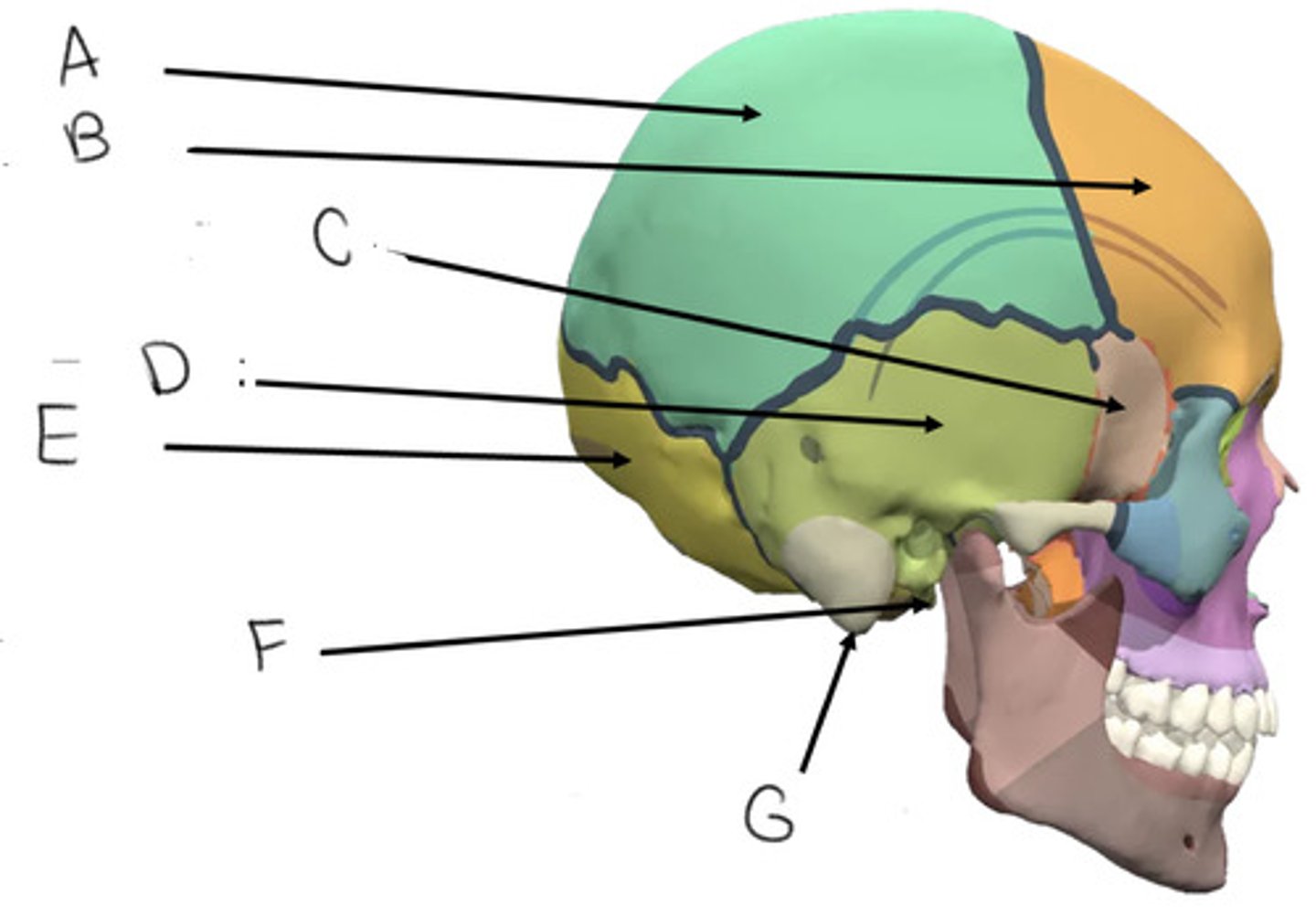
sphenoid bone
C
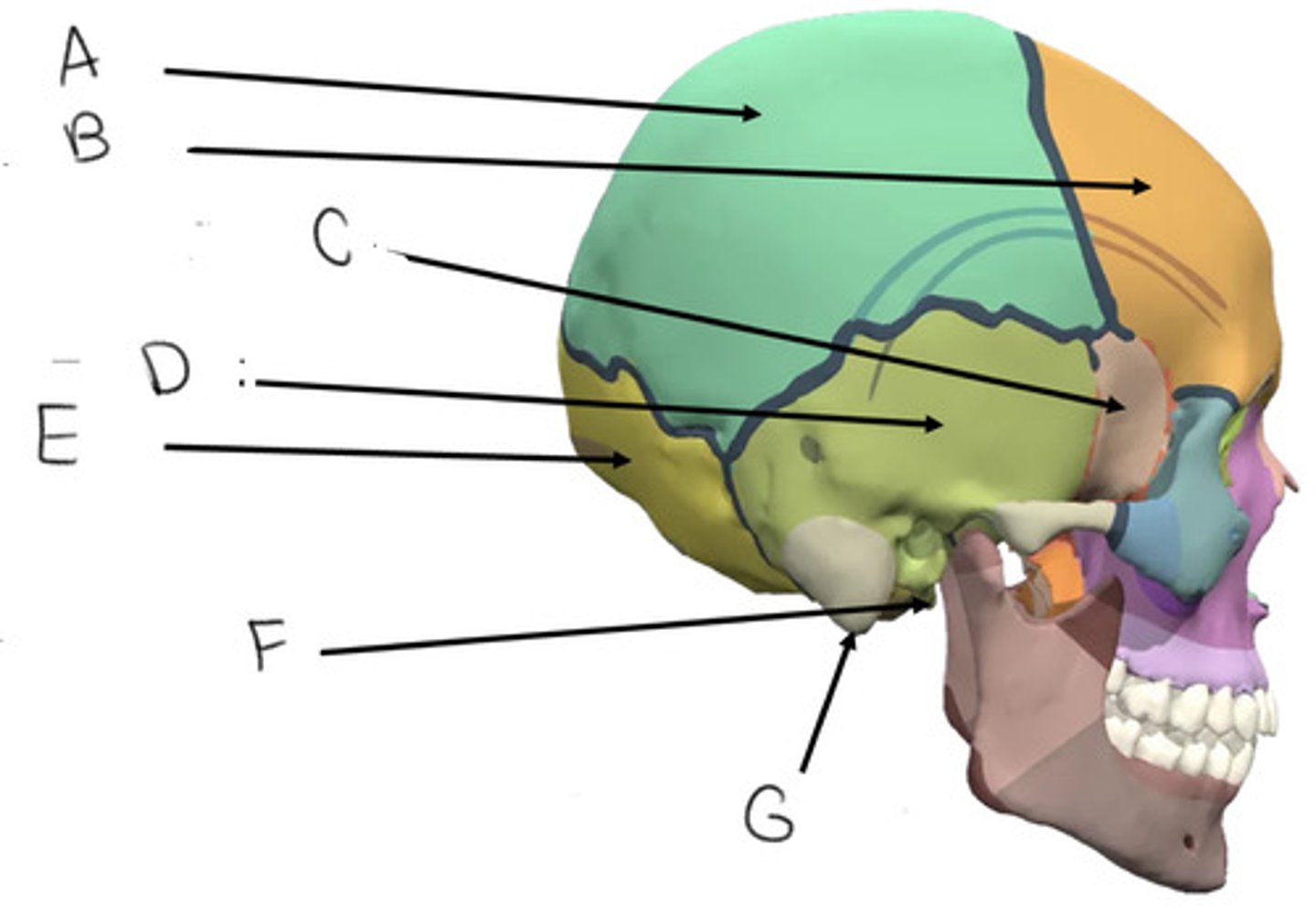
temporal bone
D
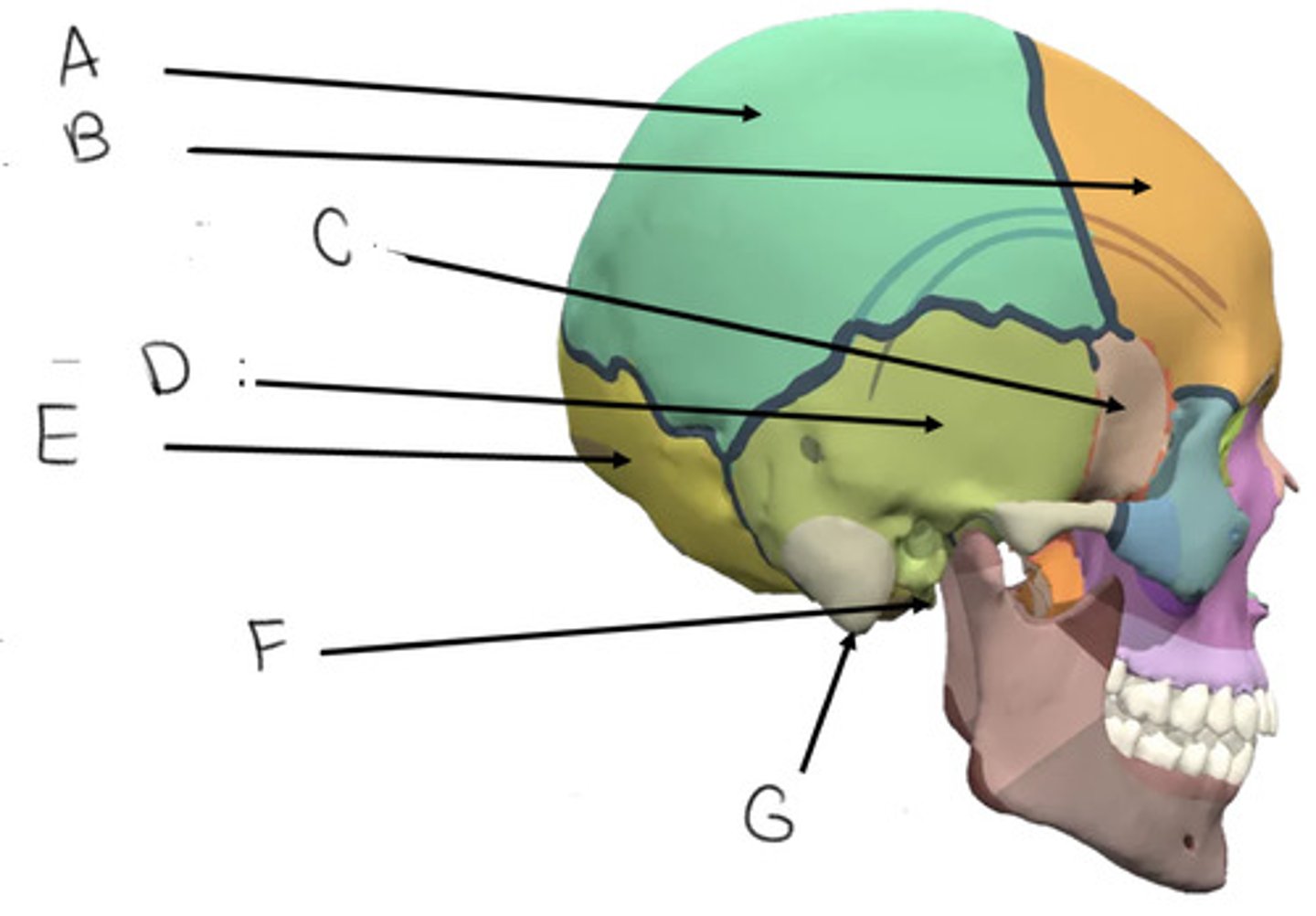
occipital bone
E
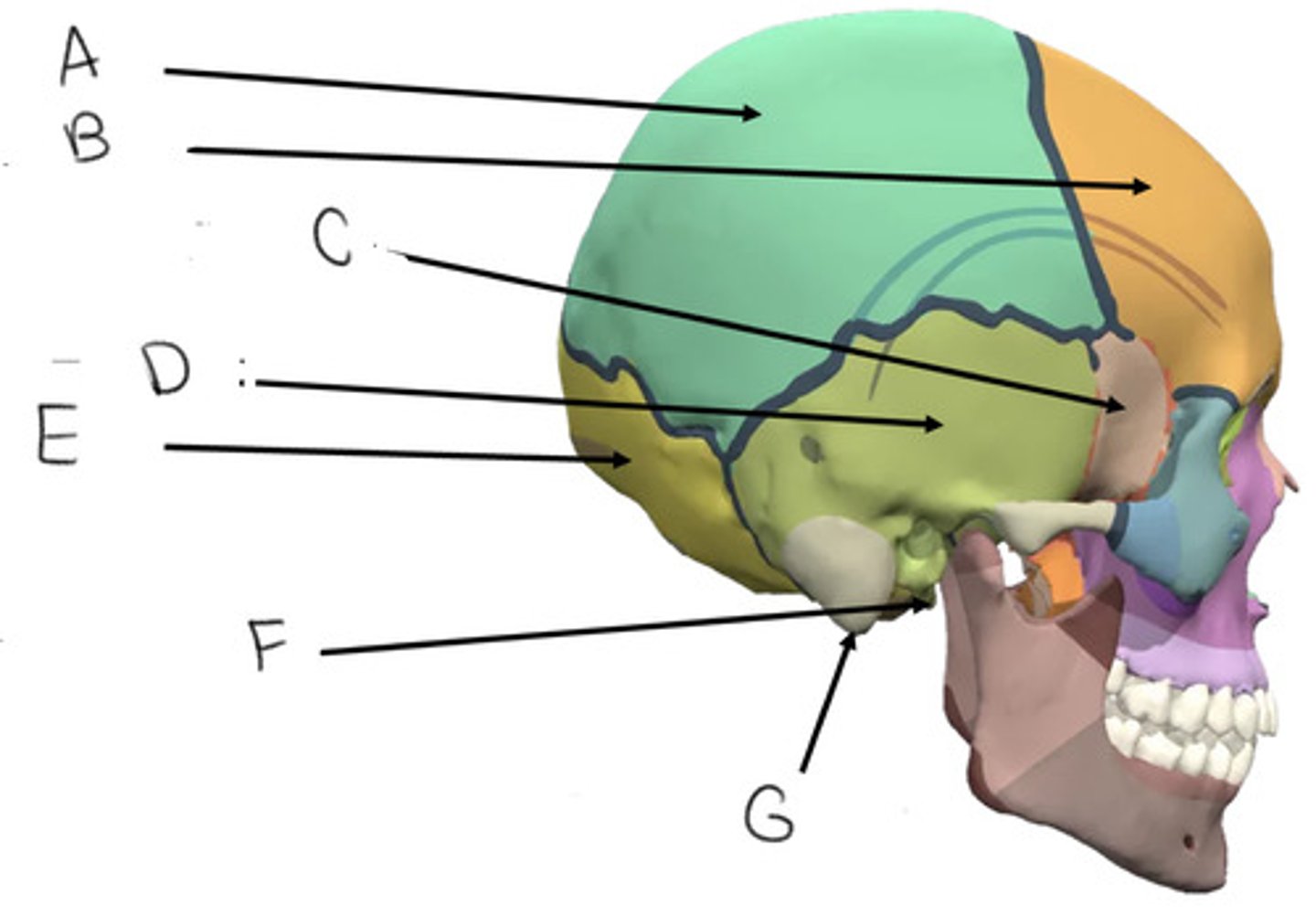
styloid process
F
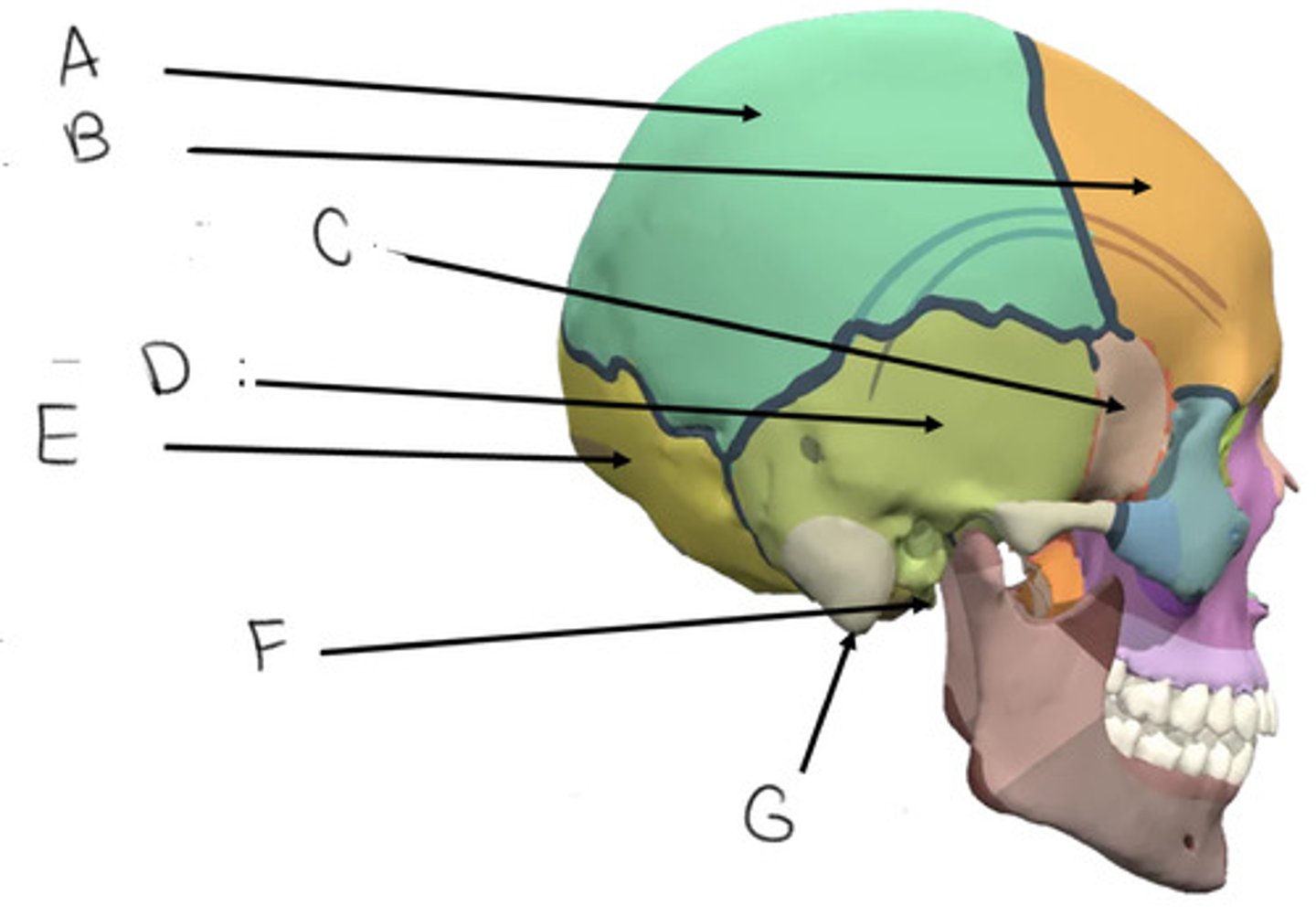
mastoid process
G
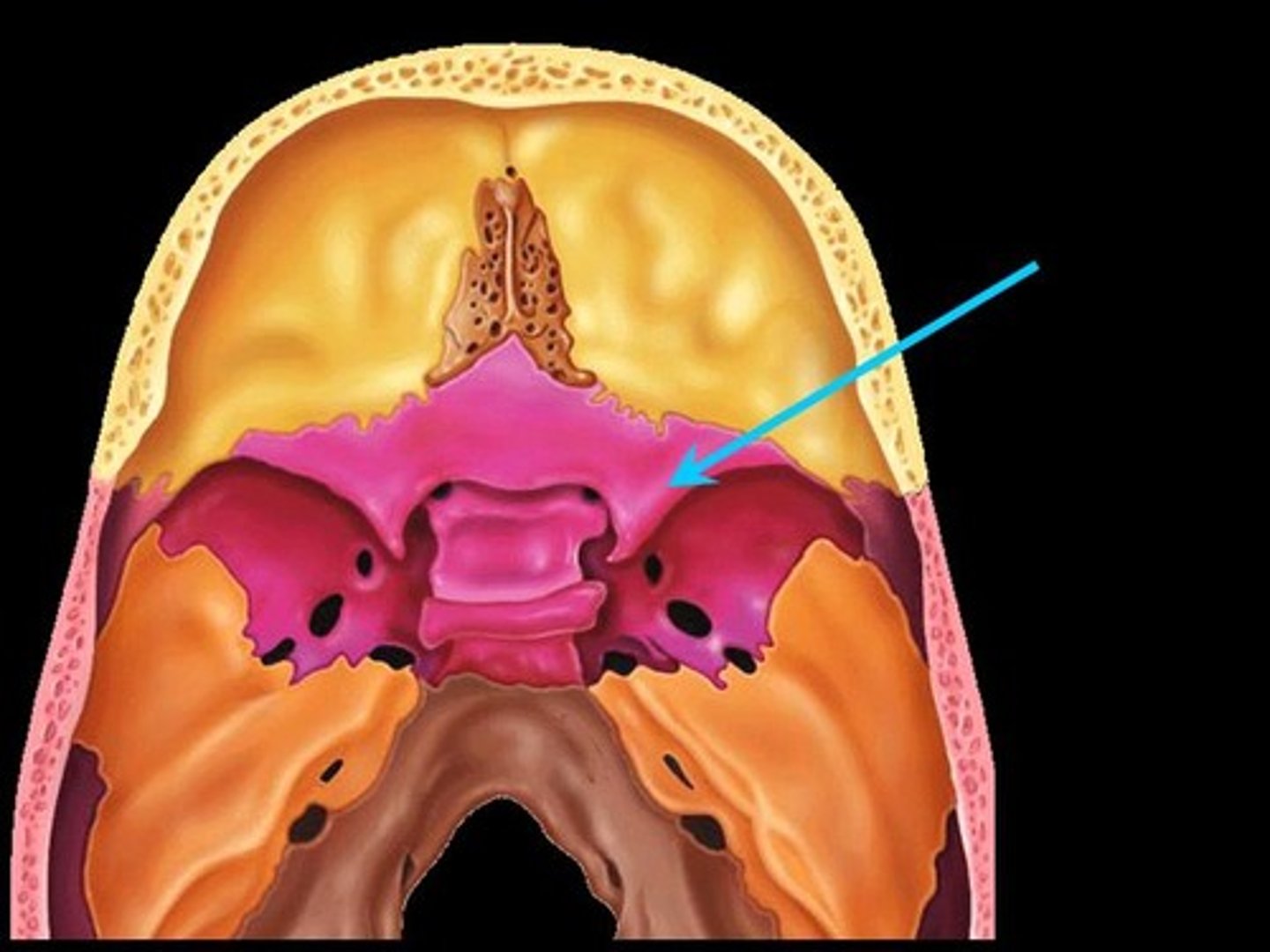
what bone is butterfly shaped?
sphenoid bone
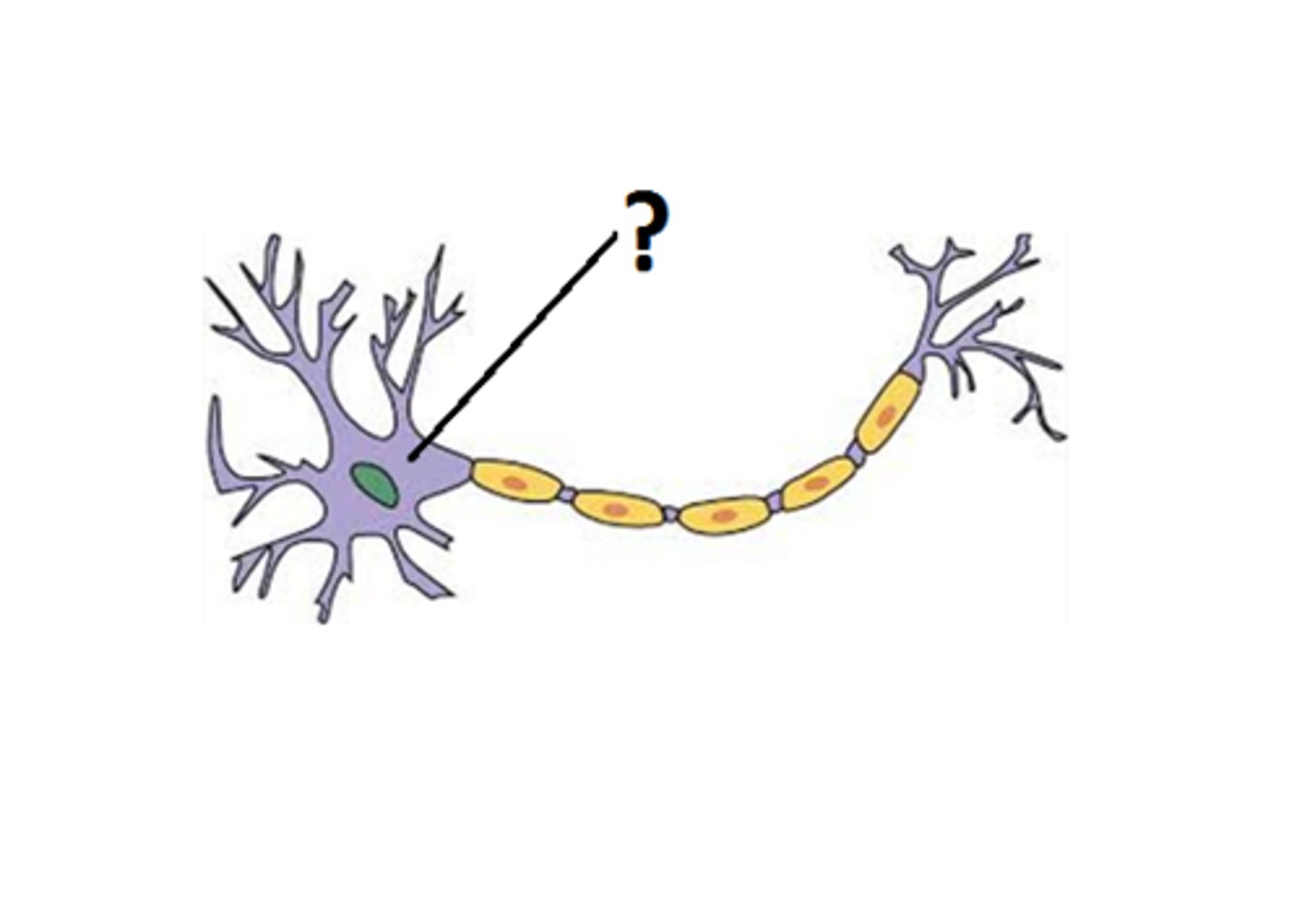
neural tissue functions/roles
-primary unit of nervous system
-electrically excitable: transmit information (neuron to neuron, neuron to muscle)
-electrical signal = action potential
cell body (soma)
contains nucleus and organelles
axon
projection carrying messages away from cell body
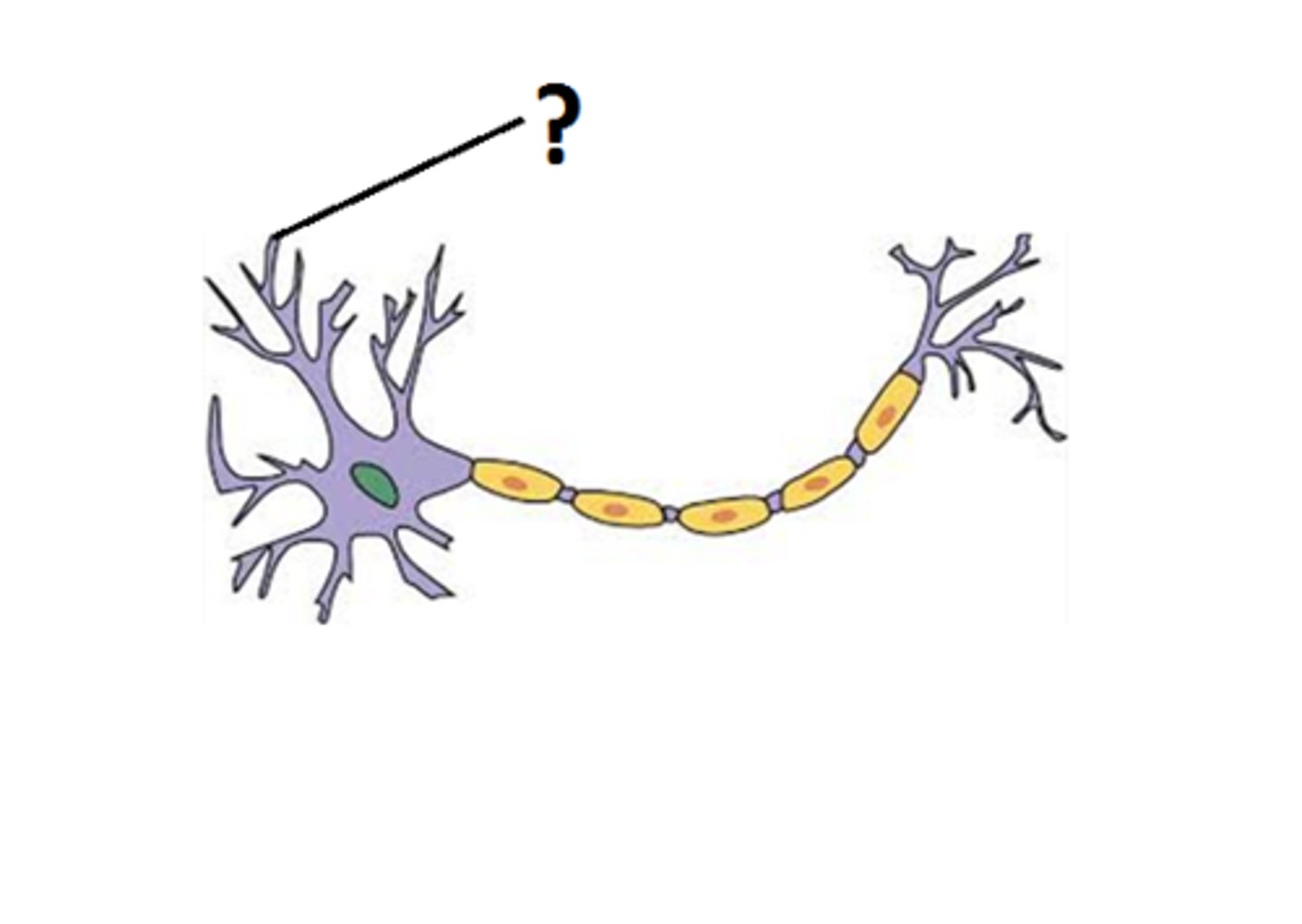
dendrites
projections carrying messages to the cell body
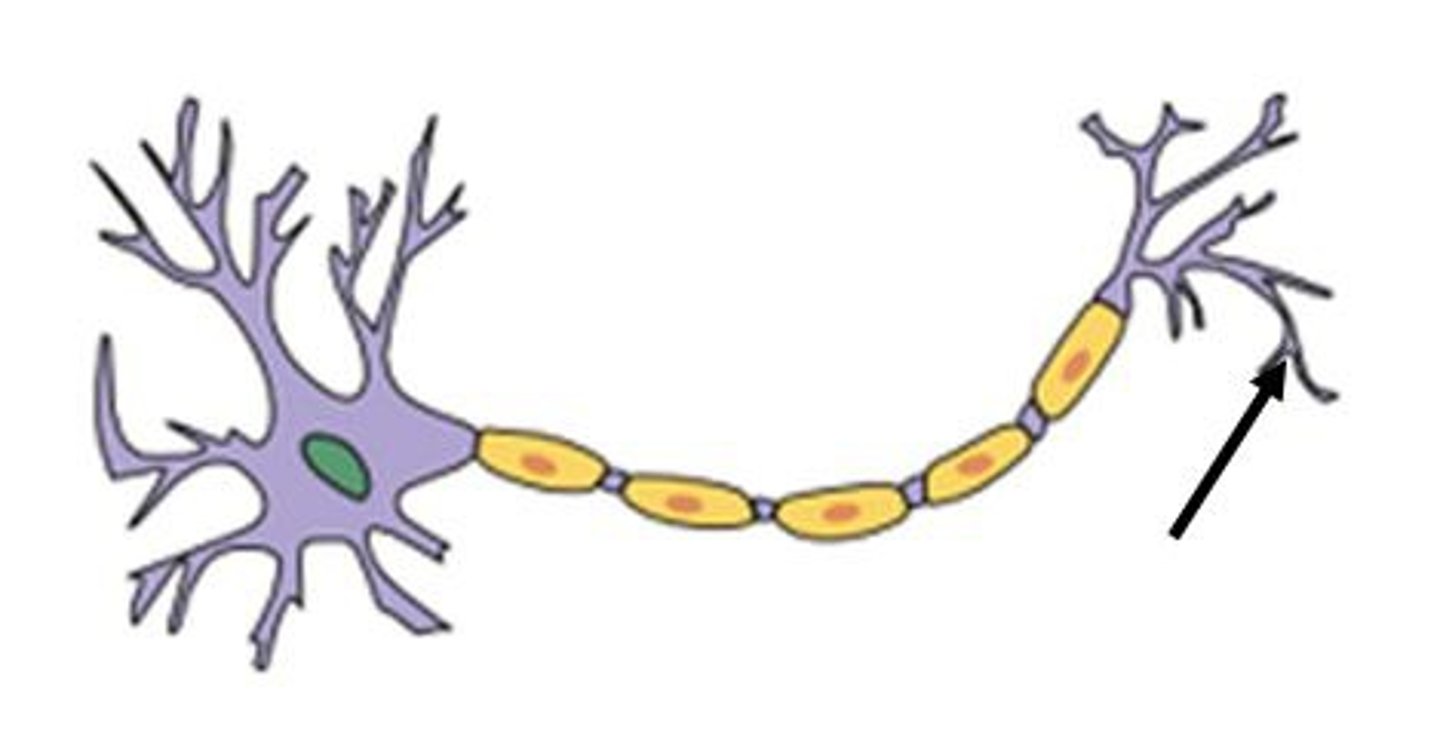
terminal boutons
end of axon
soma functions
contain cells hereditary information (nucleus), production of proteins (organelles)
dendrite functions
receive signals from other neurons, points of contact/reception of signals on dendrites = dendritic spines
axon function
-send signals to other neurons, muscles, or glands
-contain neurotransmitters
axon hillock
junction between axon and soma
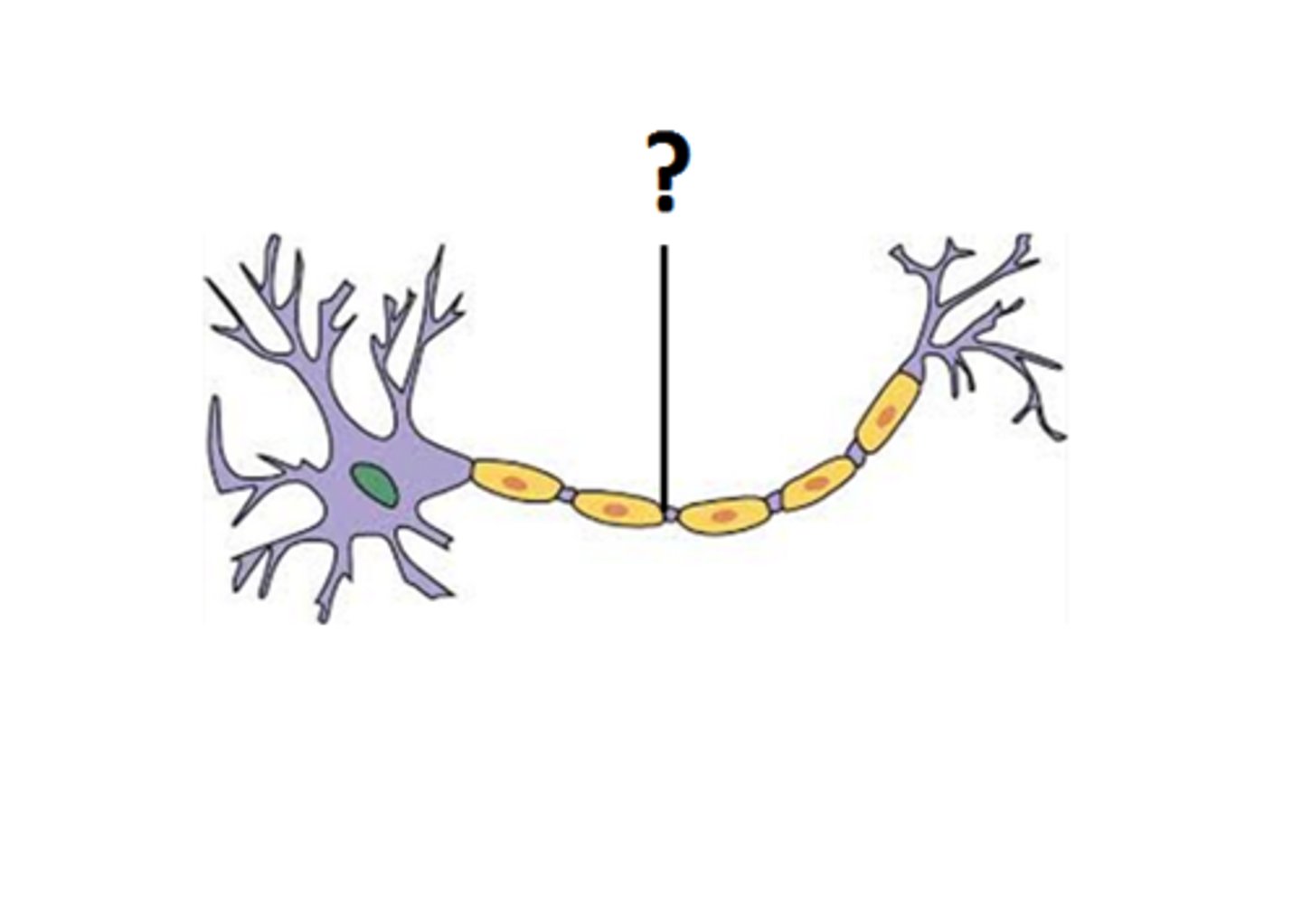
myelin
white, fatty wrapping; insulate the axon and increase the speed of conduction of nerve impulses along the axon
nodes of raniver
spaces between myelin
synapse
connection point between neurons or between a neuron and a muscle or a neuron and a gland
neural tissue in the CNS
gray matter and white matter
neural tissue in the PNS
ganglia and nerves
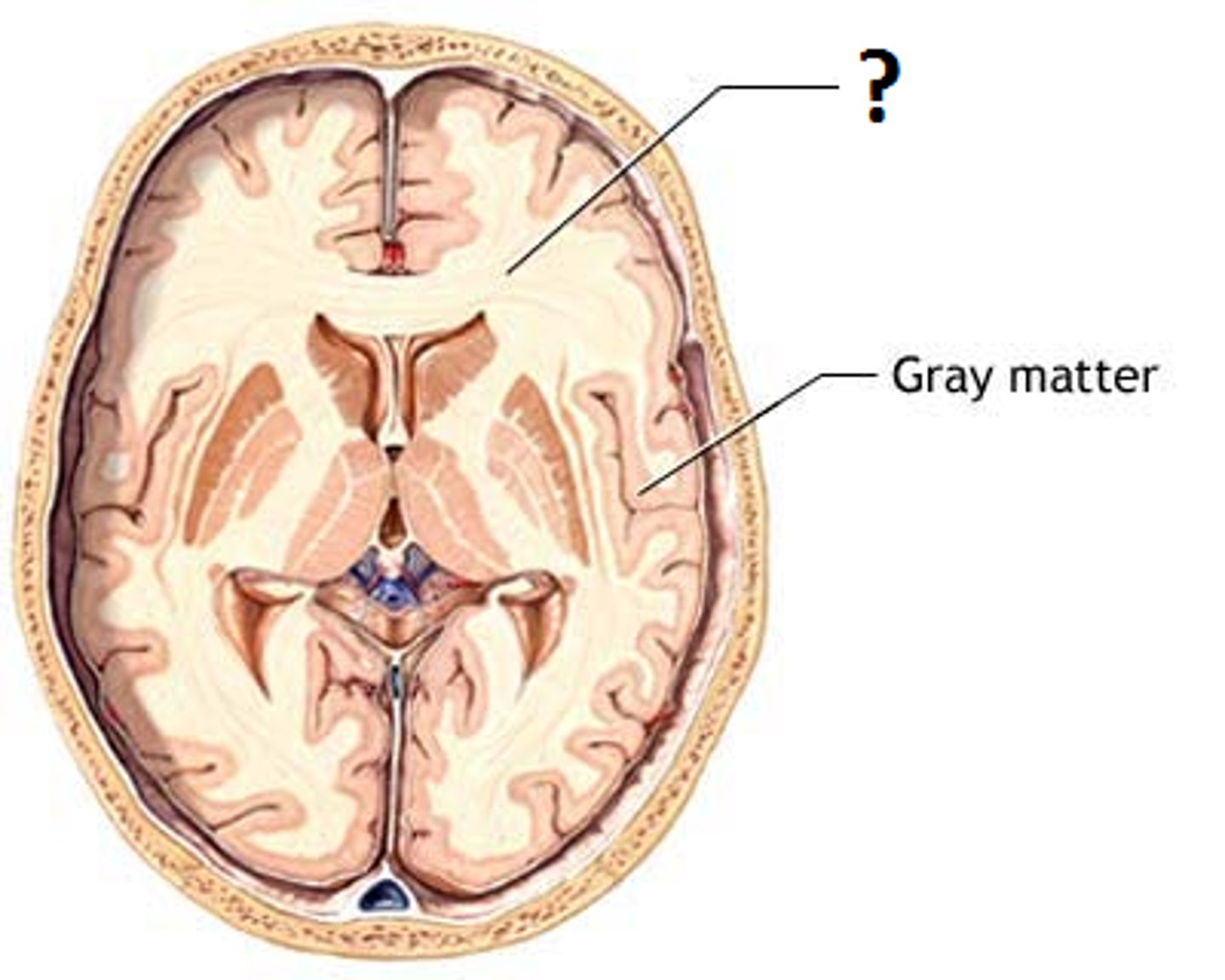
gray matter
parts of the CNS containing cell bodies, unmyelinated axons, synapses, and glial cells
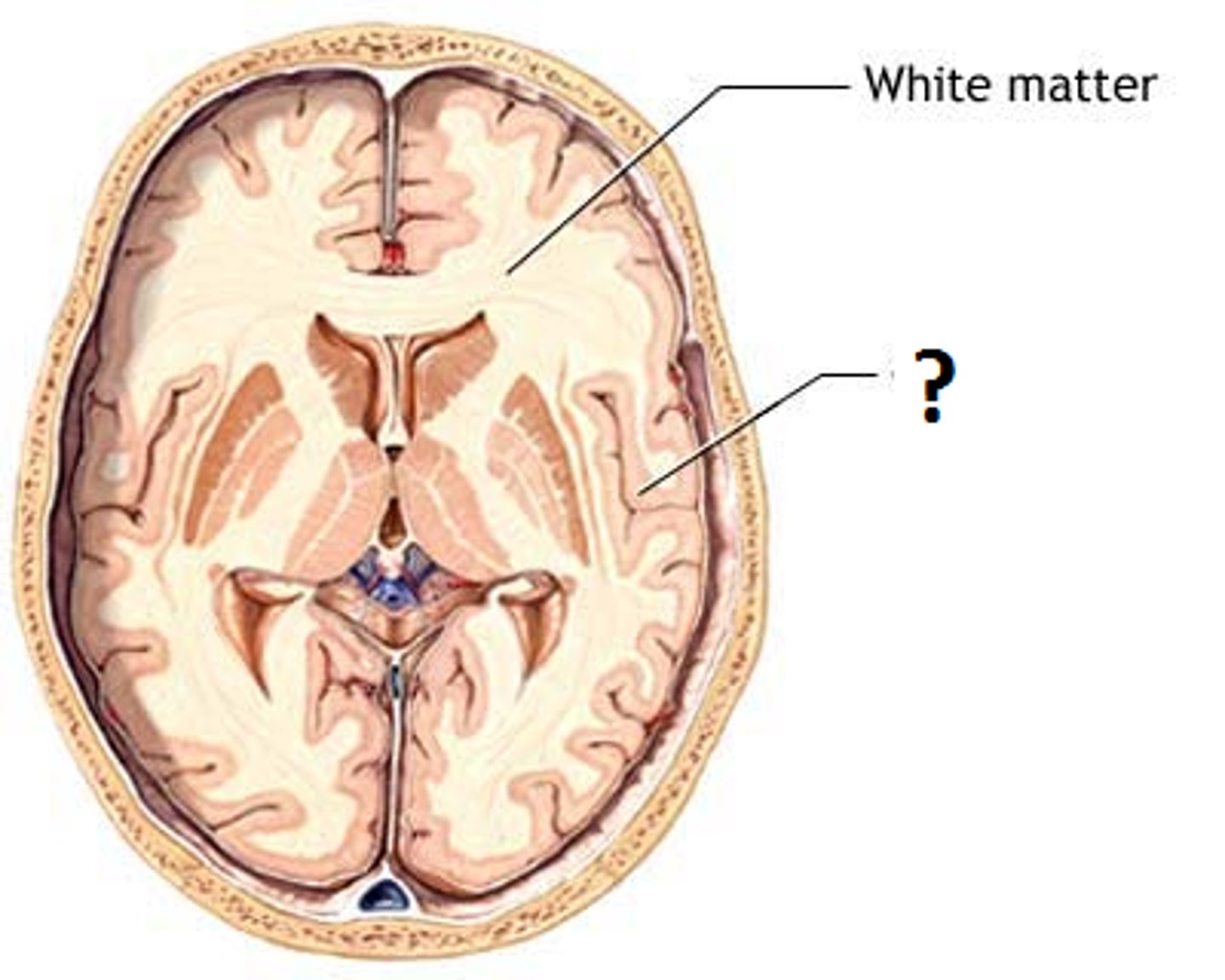
white matter
parts of the CNS containing myelinated axons and glial cells that produce myelin
ganglia
groups of cell bodies of neurons collected together
nerves
bundles of axons and glia cells
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
cerebrum includes
cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system, and diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
gyrus
surface of folds (ridges) on cortex
sulcus
depression on surface of brain
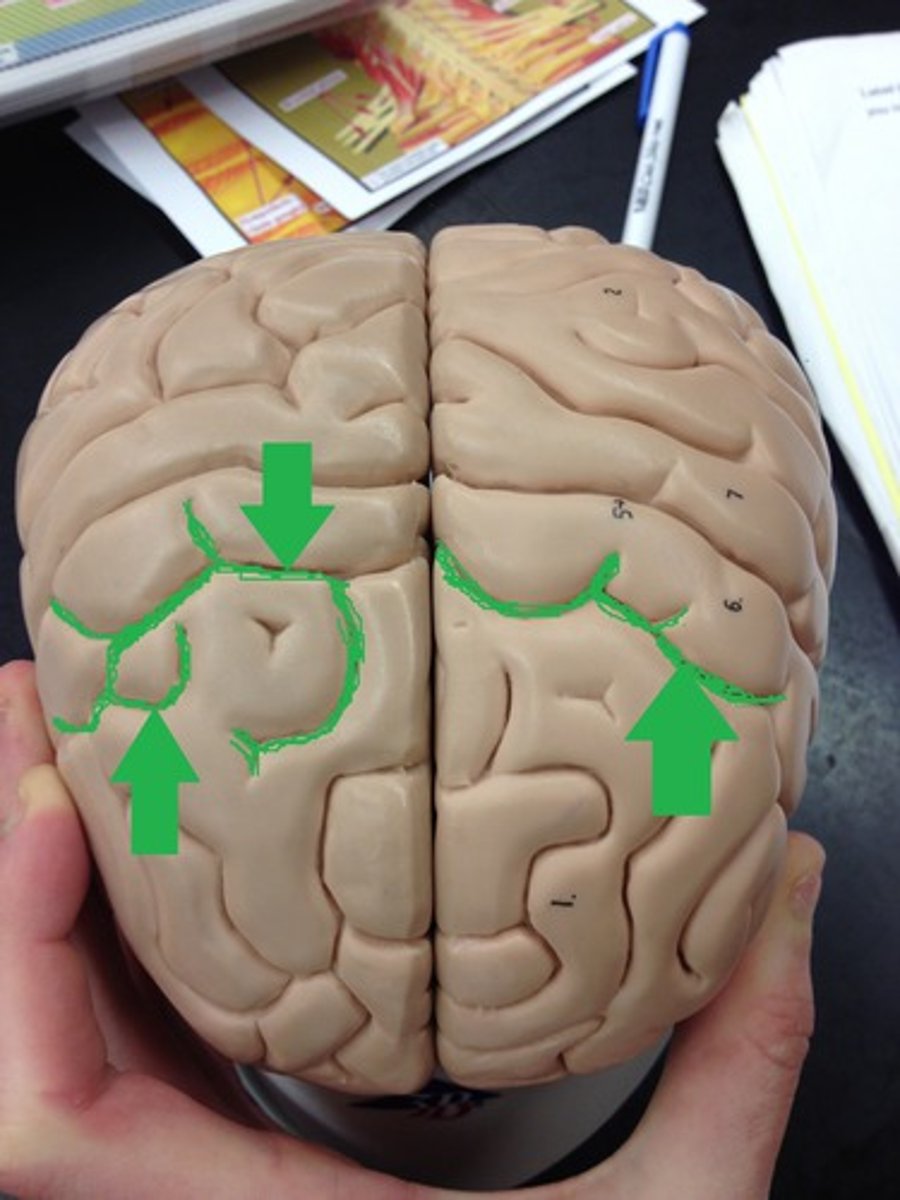
which side of the brain are speech and language functions?
left side
which side of the brain is important for spatial skills and nonverbal reasoning?
right side
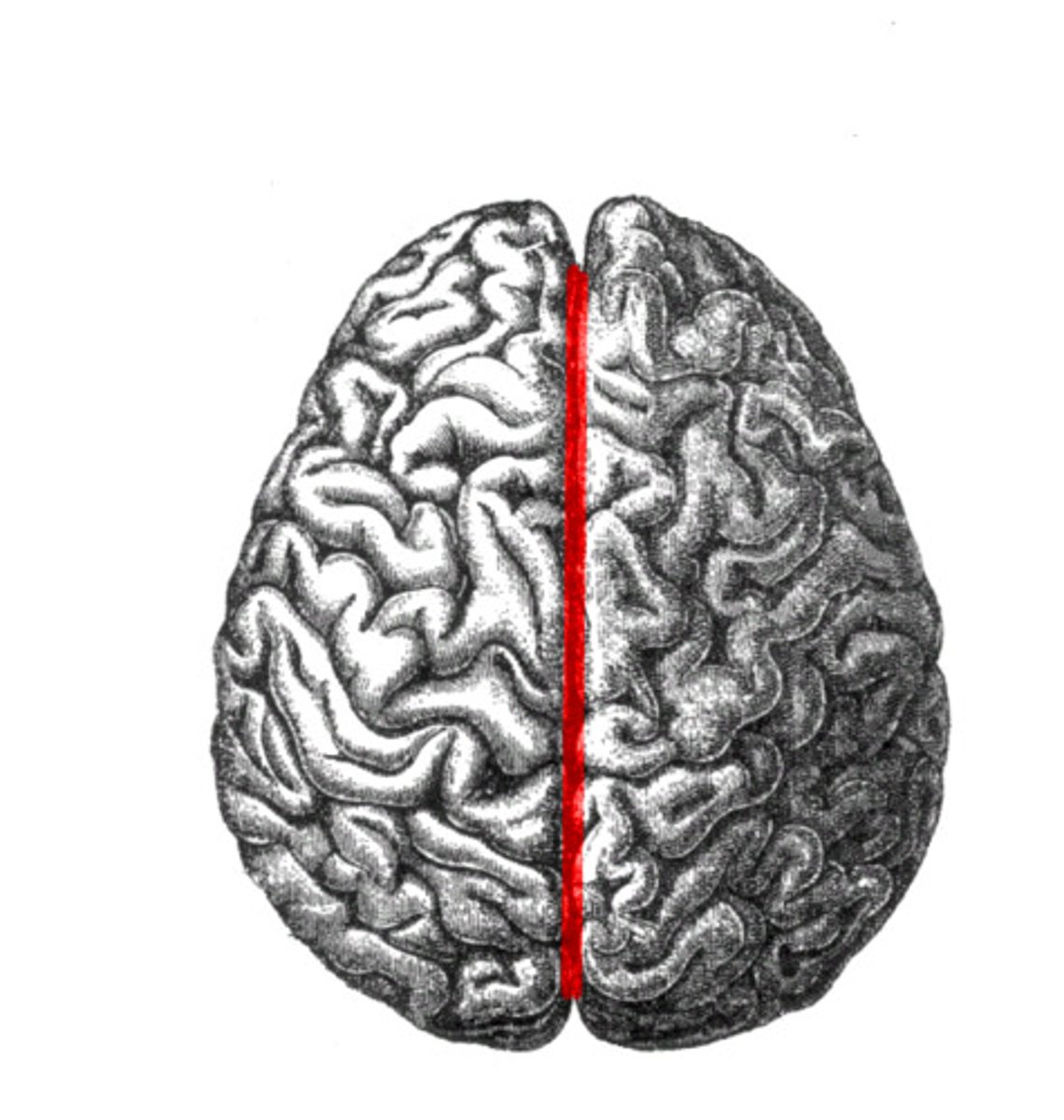
longitudinal cerebral fissure
divides the left and right half of the brain
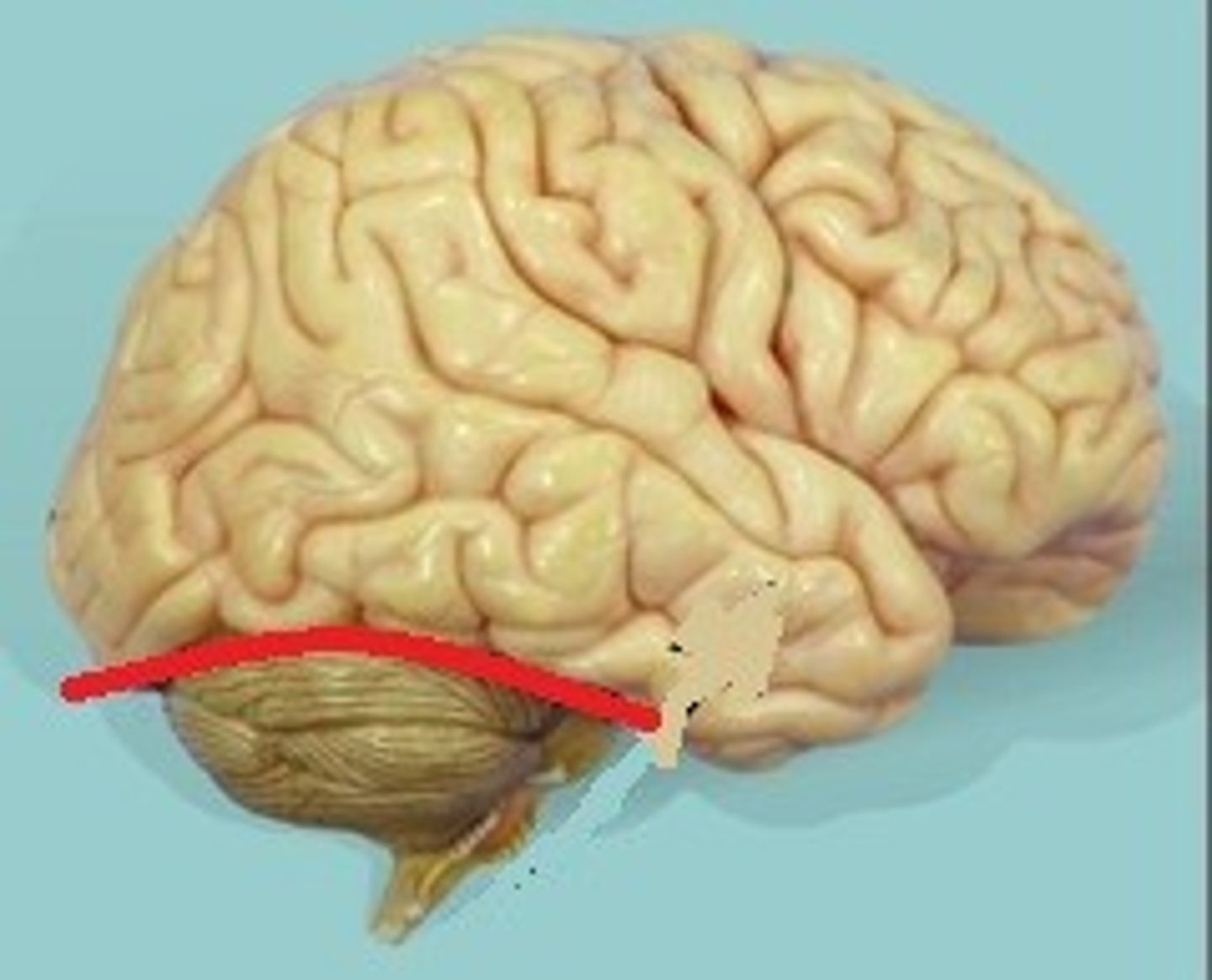
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
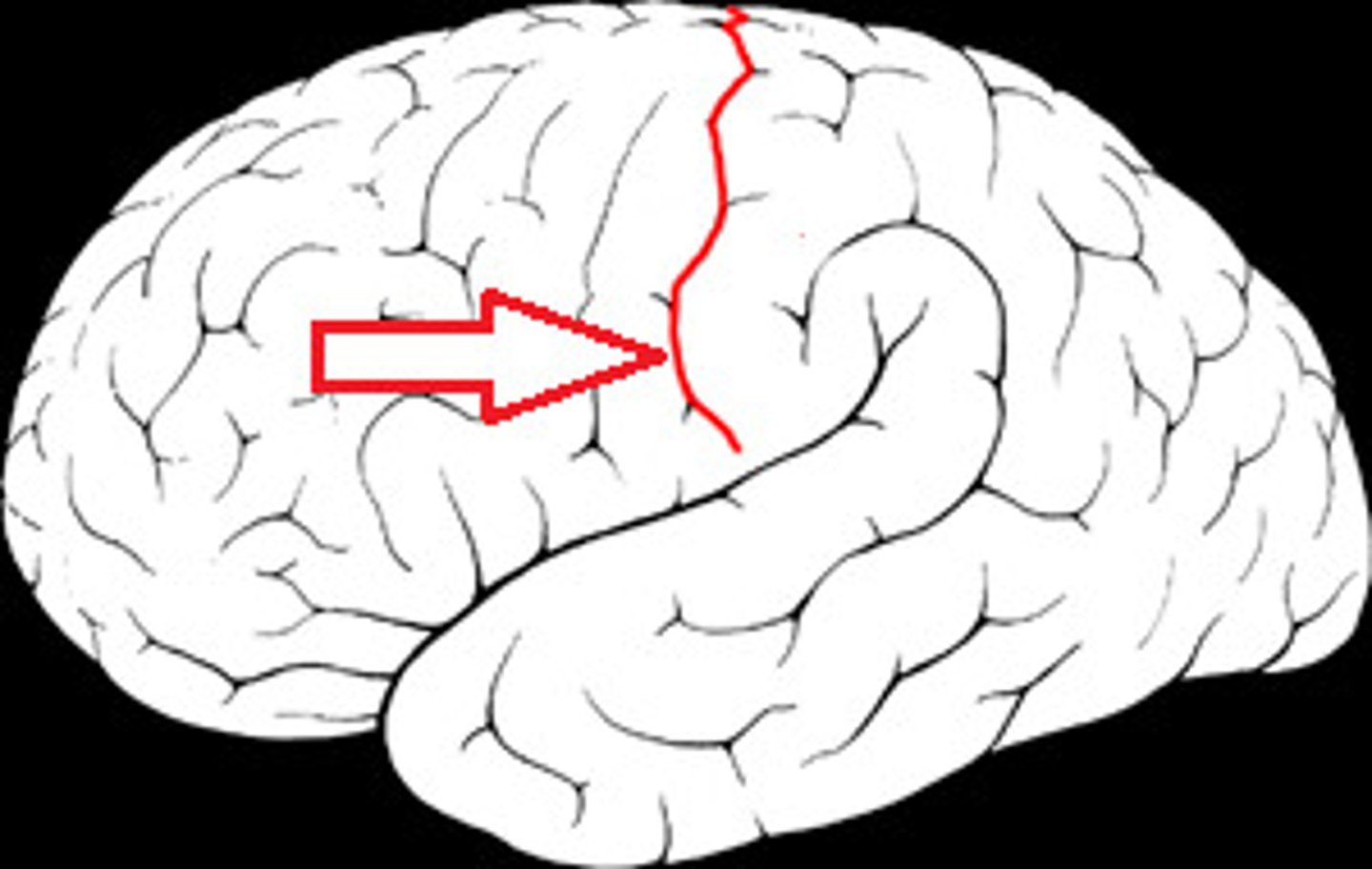
central sulcus
divides frontal and parietal lobe
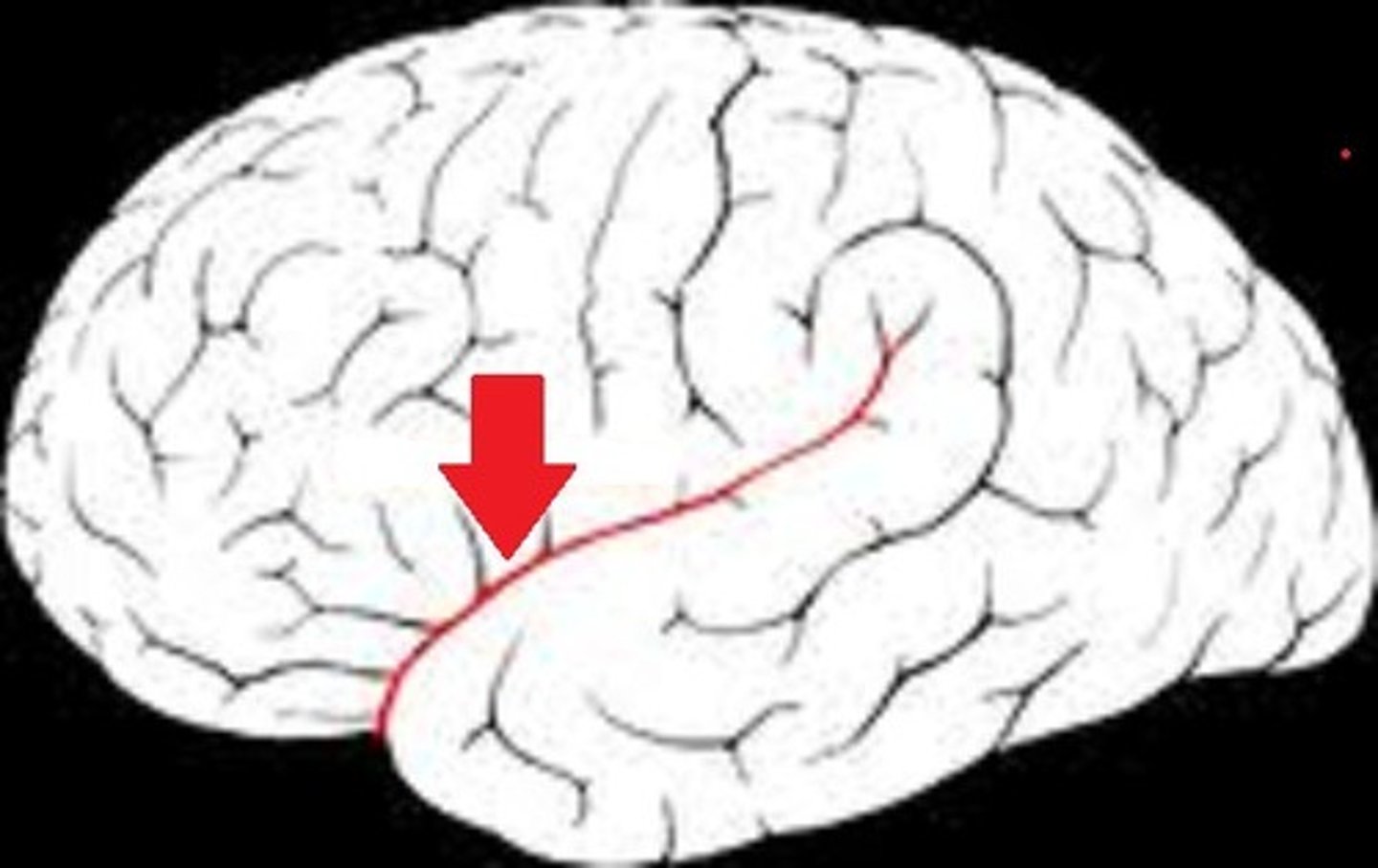
lateral sulcus
divides the temporal lobe from the parietal and part of the frontal lobe
insular cortex (where and role)
-deep within the lateral sulcus
-role in maintaining homeostasis and ANS functions
-role in speech motor control, speech perception, swallowing and taste
primary motor areas
send motor (efferent) signals to the body to act, after they receive information from secondary and association motor areas which plan the motor acts
primary sensory areas
review sensory (afferent) signals, process them, and send them to secondary and association sensory areas for further interpretation
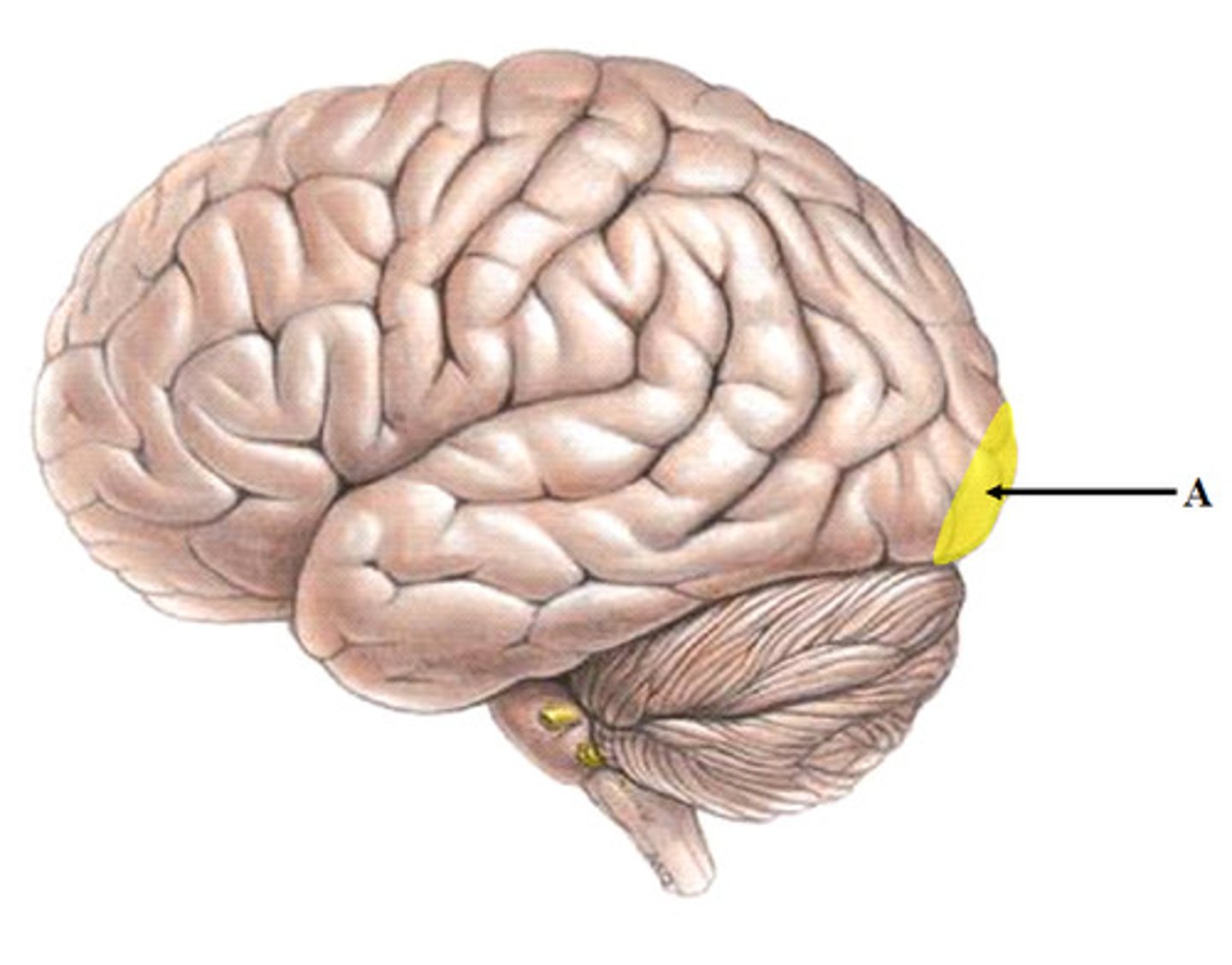
primary visual area (function and BA #)
receives visual information from retinas; BA 17
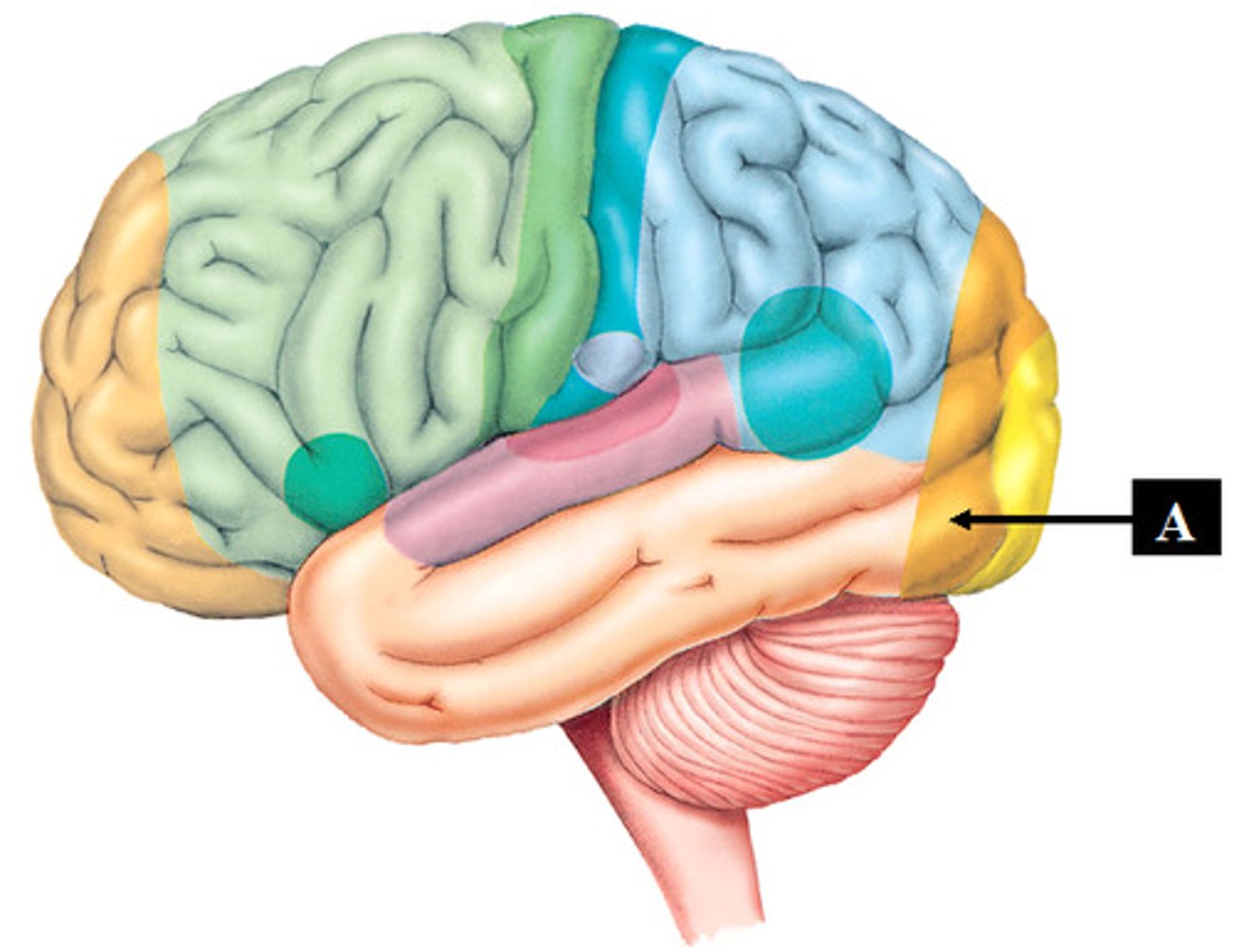
secondary visual area (function and BA #)
relates visual information from primary area to past experiences; BA 18
primary auditory area (function and BA #)
receives auditory information and is tonotopic (frequency, intensity, location); BA 41
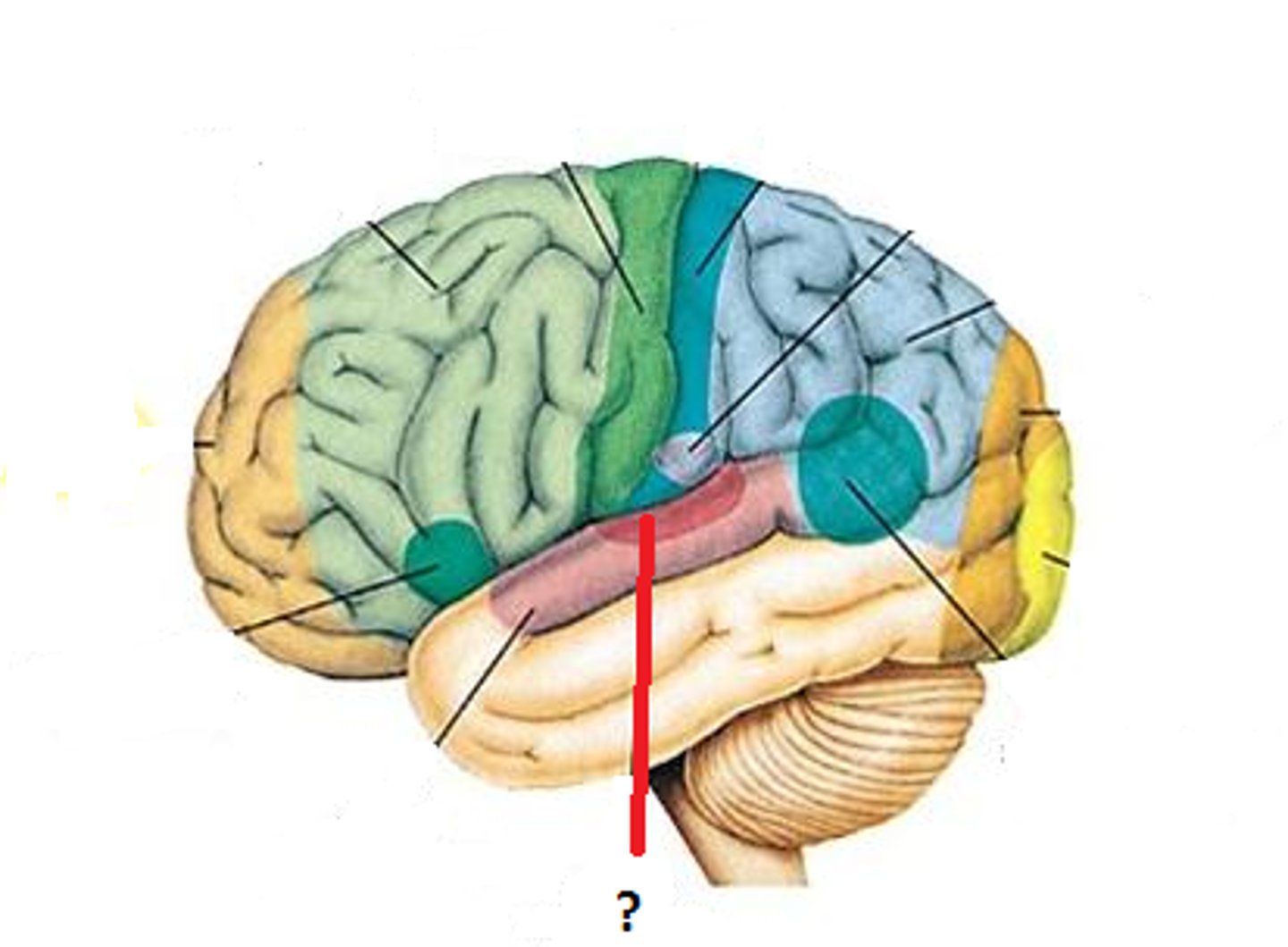
secondary auditory area (function and BA #)
important for sound interpretation; BA 42
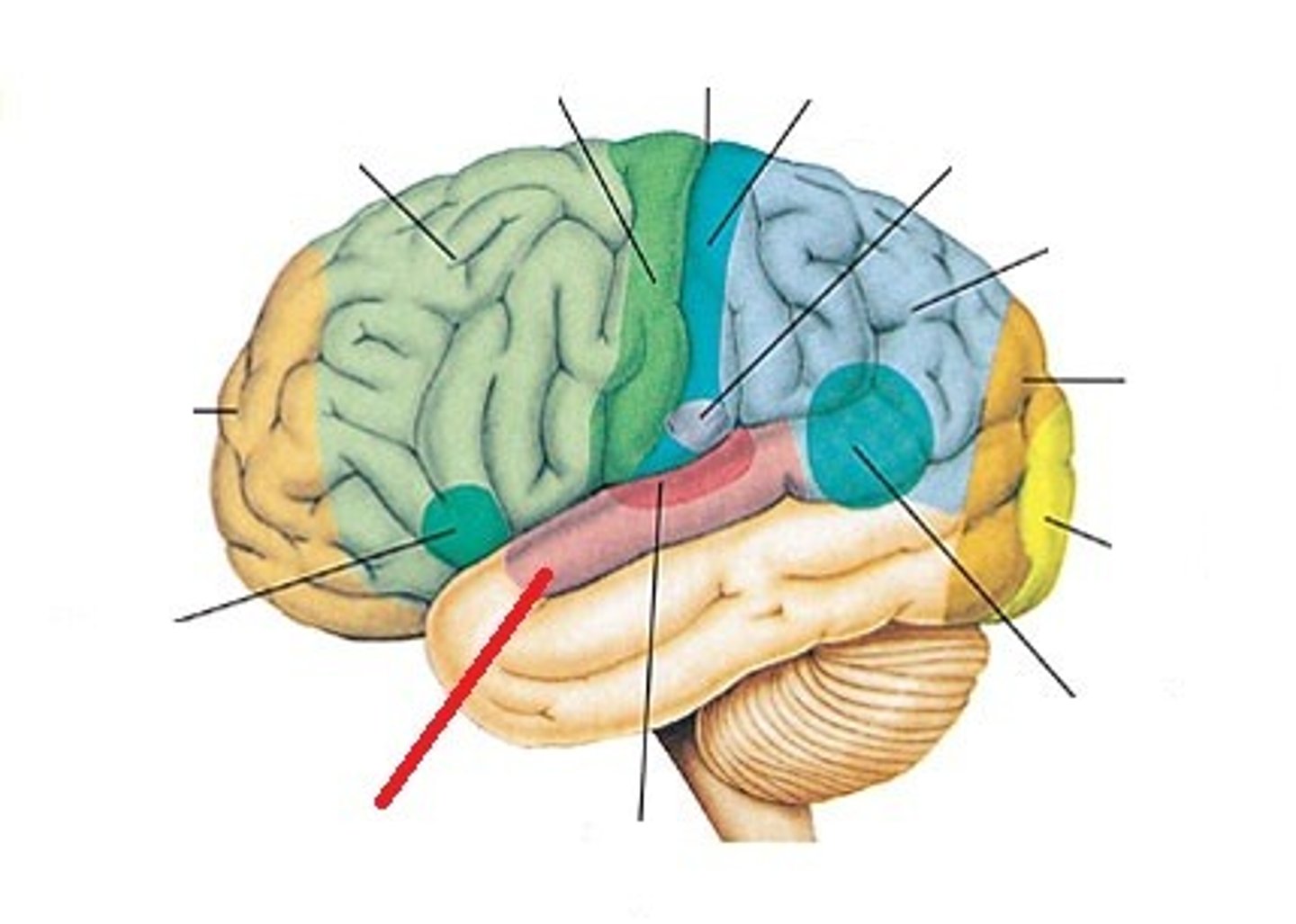
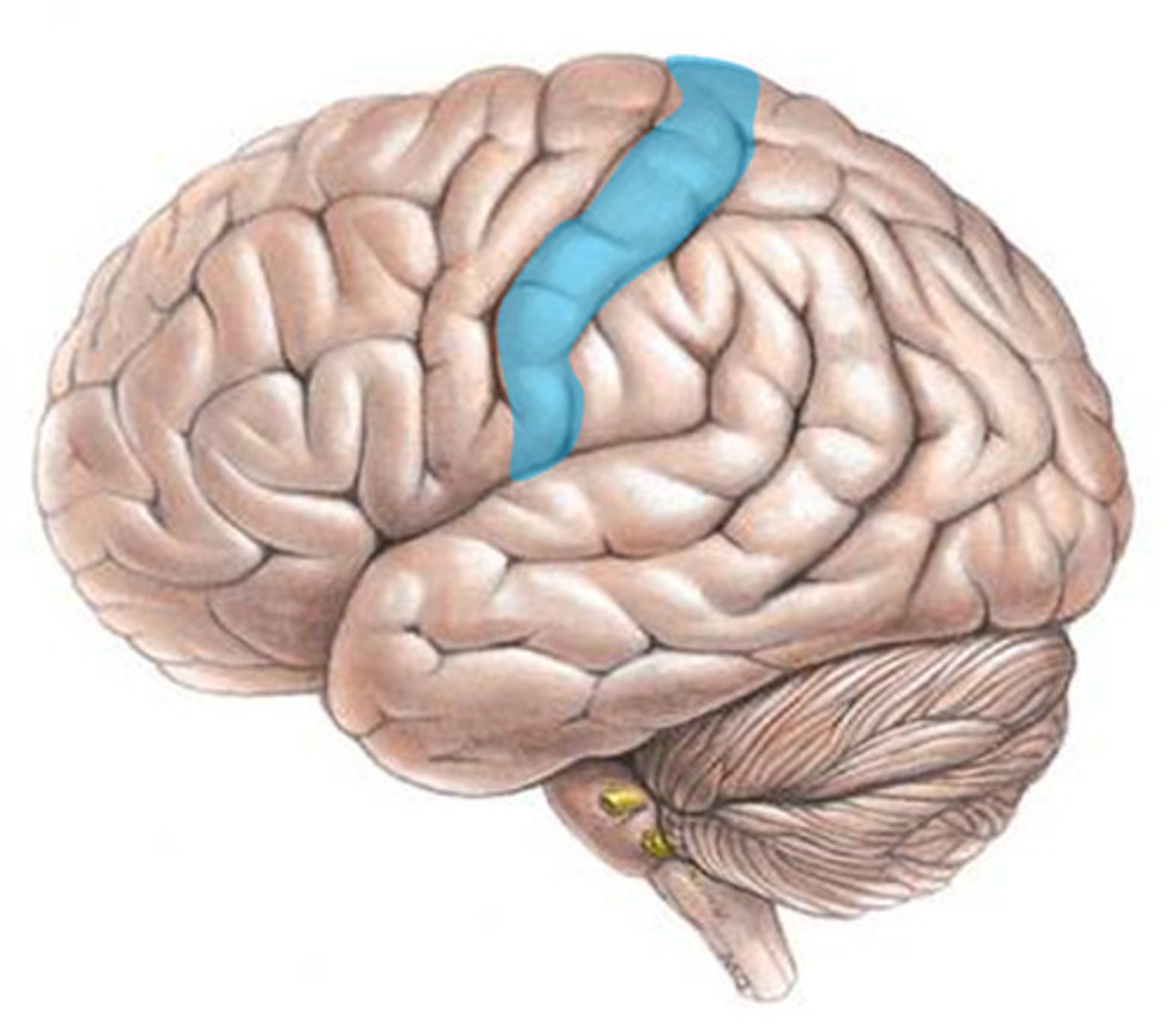
primary somatosensory area (function and BA #)
receives sensory information from body and somatotopic organization; BAs 3, 1, 2
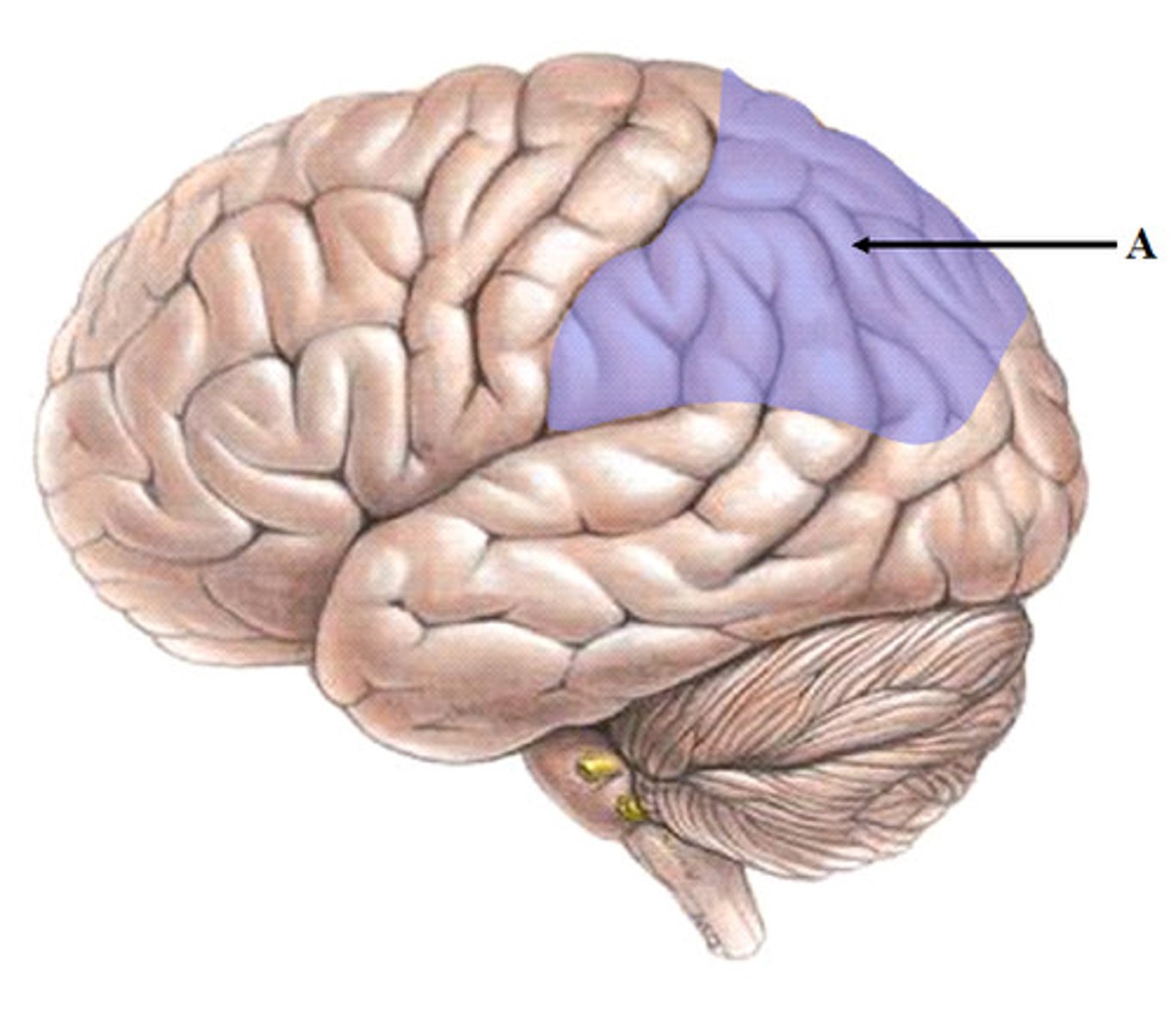
secondary somatosensory areas (function and BA #)
interprets information; BAs 5, 7, 40
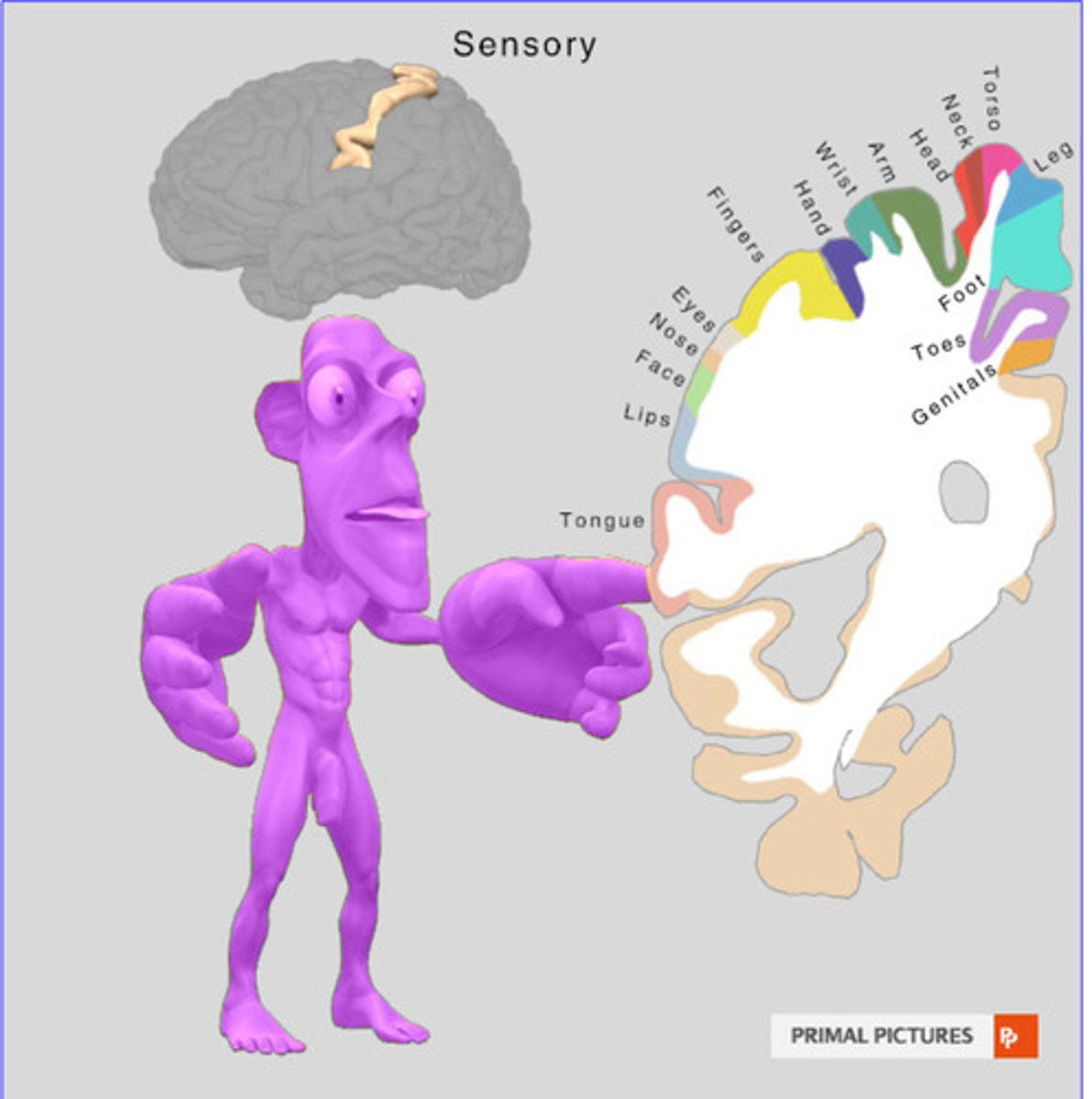
sensory homunculus
functional map showing somatotopic organization
contralateral intervention
neurons on the left side of brain receive sensory/motor information from the right side of body (limbs), and vice versa
damage to PSA
-can cause loss of sensation in the contralateral body areas corresponding to the area of the primary sensory cortex which is damaged
-ex. damage to left side PSA in area sensing touch for the arm = loss of sensation of touch for the right arm