
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
the ‘degree of polymerization’ refers to a polymer’s:
length
why is cotton categories as a staple fiber
because cotton fibers are inches long
A unique characteristics of protein - and specifically wool - is that
they are hygroscopic
where does mohair come from
goats
the gum like coating on a silk is called
sericin
why is silk so expensive to buy?
because producing it is expensive
In terms of fibers, manufactured and synthetic are the same. In other words, all manufactured fibers are synthetic
false
what is the raw material in rayon
cellulose
We used the analogy that textiles are like food. According to this analogy, fibers are a textile's ______________
ingredients
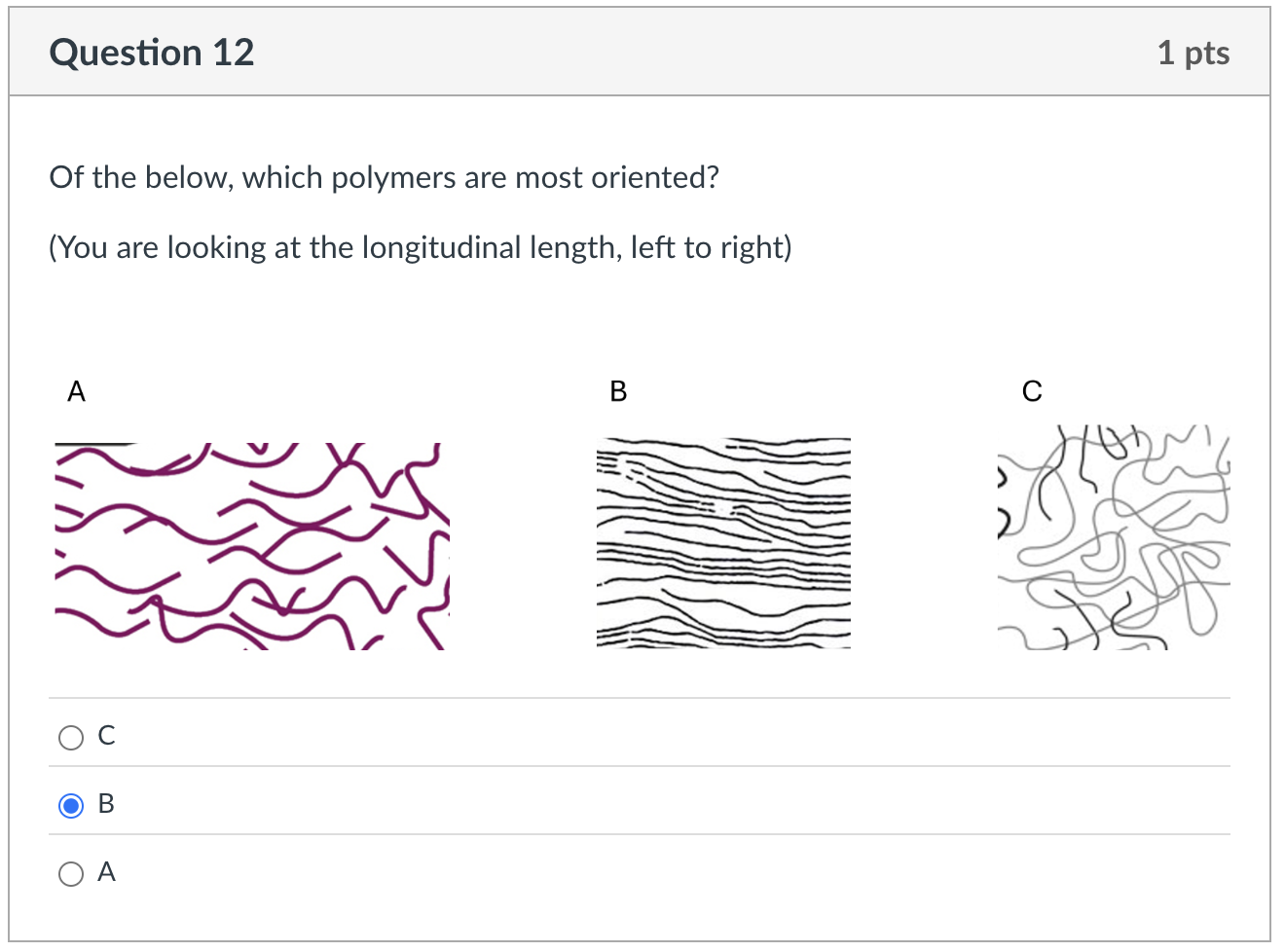
B
c
Which of the below affects the way a fiber performs?
Group of answer choices
a) The way the polymers lie next to one another (direction, arrangement, proximity)
b) The forces of attraction between the polymer chains
c) The chemical composition of the polymer’s backbone – and what’s attached to it
d)All of the answers provided
e) The length of the polymer chain
d) all of the answers provided
The degree of polymerization refers to
How many monomers are on the polymer chain
Which of the following would contribute to a fiber being strong? Check all that apply.
Group of answer choices
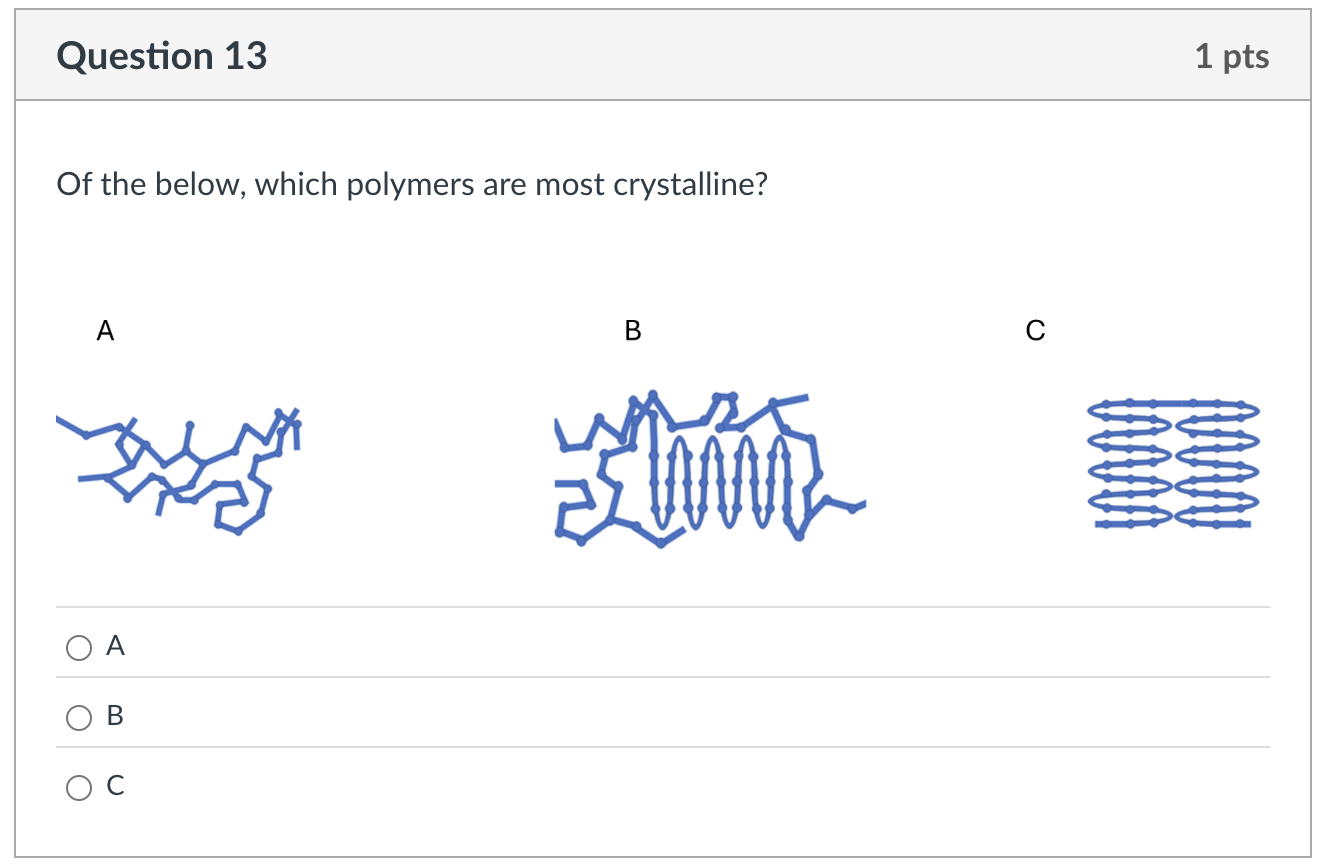
a) High crystallinity
b) High degree of polymerization
c) Highly oriented
d) all above
d) all above
Which force of attraction is the strongest?
Group of answer choices
a) Polymertion
b) Abrasion Resistance
c) Van der Waals forces
d) Hydrogen bonds
d) hydrogen bonds
Which atom comprises the backbone of most fiber polymers? Group of answer choices:
a) Carbon
b) Hydrogen
c) Oxygen
d) Nitrogen
a) carbon
Which of the chemical groups below attract water?
Group of answer choices:
a) Methyl Groups
b) Any group, as long as it’s attached to the backbone
c) None of the available options; absorbent fabrics repel water
d) Polar groups
d) polar groups
What is a fiber?
Group of answer choices:
a) A fiber is the same as a single polymer
b) Fiber is another word for molecule
c) A fiber is the smallest, hair-like component that you could pull out of a textile
d) A fiber is the same thing as a monomer
c) A fiber is the smallest, hair-like component that you could pull out of a textile
Which fibers tend to produce fuzzier fabrics?
Group of answer choices:
a) Staple fibers
b) Staple and filament fibers generally produce the same level of fuzziness in fabrics
c) Filament fibers
a) staple fibers
Words like Cotton, Flax, Rayon, Polyester most accurately refer to a fabric’s:
Group of answer choices:
Structure
a) Finish
b) Color
c) Fiber
d) Yarn type
c) Fiber
What is the best definition of a polymer?
Group of answer choices
a) It’s when two hydrogen atoms bond to an oxygen atom, forming H2O
b) It’s a type of bond
c) It’s the fact that carbon can bond four times
d) It’s a long chain of monomers
d) It’s a long chain of monomers
When a textile has a HIGH luster, this means:
Group of answer choices:
a) It traps lights, and looks matte to the naked eye
b) It drapes softly on the body
c) It traps a lot of water and feels wet
d) It reflects light evenly, and looks shiny to the naked eye
d) It reflects light evenly, and looks shiny to the naked eye
A fabric with high absorbency would:
(Check all that apply) Group of answer choices:
a) None of the available options; absorbent fabrics repel water
b) Absorb rainwater when it's raining
c) Absorb sweat from the body
d) Absorb water off the body after a shower
- Absorb rainwater when it's raining 🌧
- Absorb sweat from the body 💦
- Absorb water off the body after a shower 🚿
Consumers need different things from different fabrics. The degree to which a fabric meets or does not meet these needs is called: Group of answer choices
a) Wicking
B) Serviceability
c) Merchandising
d) Safety Regulations
B) Serviceability
If a fabric has HIGH heat retention it:
Group of answer choices:
a) Can withstand hot washing and drying conditions
b) Must be ironed to stay flat
c) Transfers heat along the surface of the textile
d) Keeps the wearer warm
e) Keeps the wearer cool
d) Keeps the wearer warm
A fabric’s Abrasion Resistance relates to its:
Group of answer choices:
a) Aesthetics
b) Appearance Retention
c) Safety
d) Comfort
e) Durability
e) Durability
A fabric with low aka poor resiliency means:
Group of answer choices:
a) It tears easily It stretches out easily and stays stretched
b)It gets wet easily and stays wet
c) All of the answers provided
d) It wrinkles easily and stays wrinkled
d) It wrinkles easily and stays wrinkled.
True or False? Cost is a factor related to fabrics’ serviceability. Group of answer choices:
a)False
b) True
b) True
Which fiber is longer? Group of answer choices:
a) Filament fibers
b) Staple and filament fibers are generally the same length
c) Staple fibers
a) Filament fibers
Why is rayon so much weaker, with lower appearance retention, than cotton?
a) Its production produces short, less oriented polymers
b) Its production produces ionic bonding, not hydrogen bonding
c) Its production stretches the polymers and causes higher degrees of crystallinity
d) Its production uses cellulose acetate
a) Its production produces short, less oriented polymers
When is a designer likely to choose silk?
a) When they want something dependable and regular, not affected by natural conditions (like cotton or wool)
b) When they want something comfortable, inexpensive and easy to care for
c) When they want something that can keep out wind and rain
d) When aesthetics are important and cost is not important
d) When aesthetics are important and cost is not important
Select the best characterization of cotton’s microscopic physical structure:
a) Uniform rod
b) Cross Markings
c) Tubular
d) Twisted
d) Twisted